 ,
, 
中国农业科学院特产研究所, 长春 130112
 ,
, 
引用本文
贡献者
基金资助
接受日期:2016-12-2接受日期:2017-01-24网络出版日期:2017-11-1
-->Copyright
2017《植物学报》编辑部
Contributors
History
Received:Accepted:Online:
摘要:
Abstract:
Key words:
山葡萄(Vitis amurensis)属于东亚种群, 为葡萄科(Vitaceae)葡萄属(Vitis)落叶藤本, 是葡萄属中最抗寒的一个种。其枝蔓可耐-45°C低温, 根系可耐-16°C低温, 原产于我国东北、华北及朝鲜北部、俄罗斯远东地区等(宋润刚等, 2009; 李晓艳等, 2014)。野生山葡萄资源在我国长白山和小兴安岭山脉极为丰富, 是我国野生果树驯化栽培最成功的树种之一。山葡萄浆果营养价值丰富, 同时是酿造高档葡萄酒的优质原料, 纯种山葡萄也对白粉病及白腐病等有较强的抵抗力, 是国内外培育抗寒、抗病、优质新品种的宝贵种质资源及砧木育种资源。目前中国农业科学院特产研究所、吉林省农业科学院果树研究所、中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所以及西北农林科技大学等单位保存部分山葡萄种质资源。农业部于1988年出资建立了国家果树种质左家山葡萄圃, 该圃挂靠于中国农业科学院特产研究所, 现保存种质资源400余份, 主要来自黑龙江、吉林、辽宁和河北等地, 其中从黑龙江收集的资源占65%以上, 包括在世界范围内首次发现的四倍体山葡萄种质4N1和两性花山葡萄种质双庆(沈育杰等, 2006)。左家山葡萄圃保存的山葡萄种质份数为世界之最, 已成为全国山葡萄生产示范和优良品种推广基地及山葡萄种质资源教学、研究及利用平台。因此, 对山葡萄种质资源进行鉴定具有重要意义。
DNA条形码(DNA barcoding)是应用一种相对较短、易扩增且有足够变异的DNA序列来进行物种分类鉴别的分子生物学技术(Hebert et al., 2003)。该技术由加拿大动物学家Hebert等(2003)首次提出, 并分析了动物界11个门13 320个物种的CO1 (cytochrome coxidase subunit 1)基因序列, 发现利用该序列种间变异能够对物种进行鉴定。自此, CO1基因成为动物界中标准的DNA条形码基因。而在植物中CO1基因进化较慢, 虽然各种DNA条形码在不同植物中都有研究, 但并没有发现能够鉴别所有物种的标准序列。CBOL Plant Working Group (2009)通过大量的研究, 提出将rbcL+matK序列组合作为植物分子鉴定的核心条形码, 中国植物条形码研究组选取1 757种植物对psbA-trnH、ITS/ITS2及rbcL+matK序列/序列组合进行鉴别能力评价, 并提出将ITS/ITS2序列作为种子植物的核心条形码(China Plant BOL Group et al., 2011)。Vinitha等(2014)对姜科7属20个种的60份样本进行分析, 发现ITS序列在测试样本中的鉴定成功率较高。目前, 已证明ITS、ITS2、psbA-trnH、rbcL、matK和rbcL+matK这几个候选序列/序列组合扩增成功率和物种识别率较高, 通用性较好, 是植物条形码研究中重点推荐的候选序列(任保青和陈之端, 2010; 王柯等, 2011)。由于目前多数研究都在某一物种的种及以上水平, 因此要确定某一植物科、属、种及品种合适的DNA条形码序列就要进行深入研究和筛选。
我国山葡萄种质资源丰富, 目前资源鉴定都以形态学标记为主, 这种方法虽然简单但易受到季节变化、栽培管理方式、环境因子和主观判断因素的影响, 致使苗木市场出现同名异物、同物异名的现象, 严重影响了山葡萄产业的发展。山葡萄种质资源的鉴别是目前研究和资源利用的难题之一。本实验采用5个DNA条形码候选序列, 并选取山葡萄种质资源11个品种33份样本进行比较, 验证各序列对山葡萄品种间的鉴别能力, 为DNA条形码技术应用于山葡萄资源鉴定提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法1.1 材料本研究选取山葡萄(Vitis amurensis Rupr.)种质11份资源品种(表1), 其中包括性状表现良好的雌能花、两性花、四倍体及雄花共33个样品。设3次重复。供试材料均采自中国农业科学院特产研究所国家果树种质左家山葡萄圃。按照山葡萄圃栽植图进行采集, 并将采集的新鲜叶片标记编号后置于变色硅胶中迅速干燥。
表1
Table 1
表1
| Number | Varieties name | Locality of origin | Parents or source | Flower type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zuoyouhong | Zuojia, Jilin | Varieties | Bisexual |
| 2 | Shuanghong | Zuojia, Jilin | Varieties | Bisexual |
| 3 | Zuoshan1 | Zuojia, Jilin | Wild resource | Male |
| 4 | Zuoshan2 | Zuojia, Jilin | Wild resource | Male |
| 5 | 4N1 | Zuojia, Jilin | Genetic material | Tetraploid |
| 6 | 4N2 | Zuojia, Jilin | Genetic material | Tetraploid |
| 7 | Shuangqing | Zuojia, Jilin | Varieties | Bisexual |
| 8 | Shuangfeng | Zuojia, Jilin | Varieties | Bisexual |
| 9 | Shuangyou | Ji’an, Jilin | Varieties | Bisexual |
| 10 | 75047 | Shangzhi, Heilongjiang | Wild resource | Female |
| 11 | 73061 | Dunhua, Jilin | Wild resource | Female |
表1
山葡萄品种信息
Table 1
Information of Vitis amurensis varieties
1.2 方法1.2.1 总DNA提取、PCR扩增和测序
称取经硅胶干燥的山葡萄叶片20 mg, 加入液氮充分碾磨, 使用植物基因组DNA提取试剂盒(Tiangen Biotech Co., China)提取总DNA, 并用1×TE洗脱。DNA提取产物经0.8%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测, OD260/ OD280比值在1.7-1.9之间。PCR反应体系总体积为25 μL, 包括DNA模板1 μL (30 ng), 正反向引物各1 μL (2.5 μmol?L-1 ), 2×PCR reagent 12.5 μL (0.1 U Taq plus polymerase?μL-1, 500 μmol?L-1 dNTP each, 20 mmol?L-1 Tris-HCl (pH8.3), 100 mmol?L-1 KCl, 3 mmol?L-1 MgCl2), 双蒸水9.5 μL。PCR扩增程序及通用引物参考Chen等(2010)的方法。为提高扩增效果, 我们对PCR反应条件进行了优化, 将退火温度设置为8个梯度, 选择对山葡萄资源扩增效果最佳的退火温度进行PCR反应(表2)。PCR产物经1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后, 用TIANGel Midi纯化试剂盒(Tiangen Biotech Co. Ltd, Beijing, China)进行纯化, 在ABI- 3730XL测序仪上直接进行测序。
表2
Table 2
表2
| Fragment | Eight annealing temperature gradient (°C) | Annealing temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| ITS2 | 54.8-55.4-56.0-56.6-57.2-57.8-58.4-59.0 | 56.0 |
| psbA-trnH | 52.2-52.8-53.4-54.0-54.6-55.2-55.8-56.4 | 55.2 |
| matK | 48.9-49.5-50.1-50.7-51.3-51.9-52.5-53.1 | 50.1 |
| rbcL | 52.1-52.7-53.3-53.9-54.5-55.1-55.7-56.3 | 54.5 |
| ITS | 49.9-50.5-51.1-51.7-52.3-52.9-53.5-54.1 | 52.9 |
表2
山葡萄DNA条形码标记引物序列及退火温度
Table 2
The primer information and annealing temperature of PCR from Vitis amurensis
1.2.2 数据处理
使用SeqMan (DNA Star package; DNA Star Inc., Madison, WI, USA)软件进行测序峰图校对拼接, 去除低质量序列及引物区。利用Clustal X-2.0.11-Win软件(Larkin et al., 2007)进行多序列比对, 并对部分
序列进行手工调整。切除ITS2序列的5.8S和26S区段(HM-Mer模型), 去除psbA-trnH序列的psbA和trnH区段, 使其获得间隔区序列。用MEGA 5.0软件对各序列进行Clustal W计算, 并计算K-2-P距离值, 比较不同序列品种间和品种内变异, 分析核苷酸含量比例。利用SPSS 18.0软件对计算结果进行Wilcoxon Sig- ned-rank检验。利用TAXON DNA软件(Slabbinck et al., 2008)作barcoding gap图。采用相似性搜索算法BLAST以及NJ (neighbor joining)树计算鉴定效率(Ross et al., 2008)。
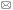
2 结果与讨论2.1 PCR扩增程序的优化为提高山葡萄资源的扩增成功率, 在进行PCR反应前先对候选序列ITS、ITS2、psbA-trnH、rbcL和matK (陈士林等, 2013)的退火温度进行优化, 分别在45- 60°C之间以0.6°C为梯度设置8个梯度(表2)。根据1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测的扩增效果(图1)进行筛选。
图1
Figure 1
下载原图ZIP
生成PPT
图1
5个候选序列PCR反应的梯度退火温度
(A) ITS2; (B) matK; (C) rbcL; (D) psbA-trnH; (E) ITS。M: DNA marker DL2000; 1-8: 45-60°C之间的温度梯度
Figure 1
Gradient annealing temperature of PCR reaction of 5 candidate sequences
(A) ITS2; (B) matK; (C) rbcL; (D) psbA-trnH; (E) ITS. M: DNA marker DL2000; 1-8: Gradient annealing temperature among 45-60°C
2.2 PCR扩增效率和测序成功率本实验统计了5个候选序列的PCR扩增效率、测序成功率及有效序列的获得率(表3)。其中, ITS2、matK和psbA-trnH的扩增效率均为100%, 测序成功率大小依次为psbA-trnH>ITS2>matK>rbcL>ITS。psbA- trnH的有效序列为100%; ITS2和matK的有效序列比例为96.9%; rbcL为88.1%。由于Chen等(2010)得出nrDNA ITS2序列在山葡萄资源33个样本中扩增成功率较高, 而ITS引物的有效序列仅成功扩增5个山葡萄品种, 故我们对ITS不作深入研究。
表3
Table 3
表3
| Marker | Amplification efficiency (%) | Sequencing success rate (%) | Effective sequence ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITS2 | 100.0 | 96.9 | 96.9 |
| matK | 100.0 | 96.9 | 96.9 |
| psbA-trnH | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| rbcL | 96.9 | 90.9 | 88.1 |
| ITS | 45.5 | 30.3 | 13.8 |
表3
不同DNA条形码序列扩增获得的有效序列比例
Table 3
The effective sequence ratio obtained by PCR am- plification of five DNA barcode sequences
2.3 不同序列的品种内及品种间差异通过测序结果分析比对序列特征, 计算平均变异位点数、品种间差异、平均品种内差异及GC含量, 并将序列组合进行比对分析。结果(表4)表明, 各序列变异位点数由大到小依次为ITS2>psbA-trnH>rbcL>matK, GC含量ITS2>matK>rbcL>psbA-trnH, psbA-trnH和ITS2序列的品种间变异最大, rbcL序列次之, matK序列最小, 与psbA-trnH或ITS2序列组合的序列组品种间变异也相应变大; 品种内变异rbcL与psbA-trnH序列最大, matK序列次之, ITS2序列最小, 与rbcL和psbA-trnH序列组合的序列组品种内差异也会相应增大; rbcL与matK序列品种间及品种内变异都不显著, 不适于区分山葡萄资源品种。
表4
Table 4
表4
| Potential barcode | Aligned length (bp) | Number of variable sites | Mean intra- distance | Mean inter- distance | Average of GC content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS2 | 483 | 397 | 0.0015 | 0.1162 | 64.50 |
| matK | 896 | 44 | 0.0032 | 0.0110 | 35.40 |
| psbA-trnH | 422 | 238 | 0.0089 | 0.0921 | 27.50 |
| rbcL | 697 | 82 | 0.0068 | 0.0180 | 44.20 |
| ITS2+matK | 1379 | 441 | 0.0024 | 0.0652 | 49.95 |
| ITS2+psbA-trnH | 905 | 635 | 0.0058 | 0.0985 | 46.00 |
| ITS2+rbcL | 1180 | 479 | 0.0045 | 0.0655 | 54.35 |
| matK+psbA-trnH | 1318 | 282 | 0.0064 | 0.0550 | 31.45 |
| matK+rbcL | 1543 | 126 | 0.0051 | 0.0220 | 41.35 |
| psbA-trnH+rbcL | 1119 | 320 | 0.0076 | 0.0560 | 39.80 |
表4
4个候选序列/序列组合的长度、GC含量及品种间和品种内差异
Table 4
Measures of inter-varieties and intra-varieties divergence locus length and average of GC content for 4 candidate barcodes/combination sequences
2.4 不同序列的品种间及品种内变异我们利用Wilcoxon检验分析两两序列品种间及品种内的变异情况。结果(表5, 表6)表明, ITS2序列的品种间变异大于其它各序列, 且差异极显著, rbcL与matK序列差异不显著, 且极显著小于psbA-trnH与ITS2序列; 品种内变异方面, psbA-trnH与ITS2序列差异不显著, 且极显著大于rbcL和matK序列。此结果与单一序列比较结论相符。
表5
Table 5
表5
| w+ | w- | Inter relative ranks | n | P value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS2 | rbcL | w+=33035.00, w-=13630.00 | 319 | 0.000 | P<0.01, ITS2>rbcL |
| ITS2 | matK | w+=1444453.00, w-=0.00 | 577 | 0.000 | P<0.01, ITS2>matK |
| ITS2 | psbA-trnH | w+=11562.00, w-=8660.00 | 500 | 0.000 | P<0.01, ITS2>psbA-trnH |
| rbcL | matK | w+=8673.00, w-=6903.00 | 319 | 0.174 | P>0.05, rbcL=matK |
| rbcL | psbA-trnH | w+=4350.00, w-=8720.00 | 620 | 0.000 | P<0.01, rbcL<psbA-trnH |
| matK | psbA-trnH | w+=12556.00, w-=25330.00 | 422 | 0.000 | P<0.01, matK<psbA-trnH |
表5
候选序列品种间差异的Wilcoxon检验
Table 5
Wilcoxon signes tests for inter-varieties divergences of candidate sequences
表6
Table 6
表6
| w+ | w- | Inter relative ranks | n | P value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS2 | rbcL | w+=39345.00, w-=18966.00 | 384 | 0.000 | P<0.01, ITS2>rbcL |
| ITS2 | matK | w+=142845.00, w-=0.00 | 577 | 0.000 | P<0.01, ITS2>matK |
| ITS2 | psbA-trnH | w+=17550.00, w-=18326.00 | 366 | 0.056 | P>0.05, ITS2=psbA-trnH |
| rbcL | matK | w+=11952.00, w-=5253.00 | 384 | 0.000 | P<0.01, rbcL>matK |
| rbcL | psbA-trnH | w+=5968.00, w-=13589.00 | 469 | 0.000 | P<0.01, rbc<psbA-trnH |
| matK | psbA-trnH | w+=3985.00, w-=12578.00 | 580 | 0.000 | P<0.01, matK<psbA-trnH |
表6
候选序列品种内差异的Wilcoxon检验
Table 6
Wilcoxon signes tests for intra-varieties divergences of candidate sequences
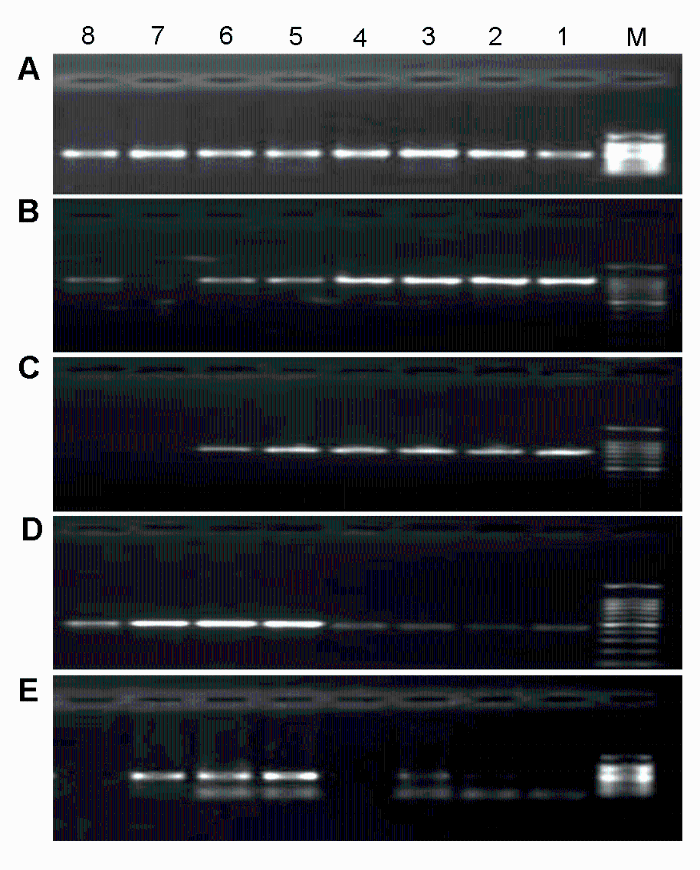
2.5 不同序列Barcoding gap检验Barcoding gap是指物种间DNA条形码序列的种间遗传变异明显大于种内变异, 并在两者之间形成一个明显的间隔区(Meyer and Paulay, 2005; Lahaye et al., 2008)。由图2 (X轴为K2P遗传距离, Y轴为在不同变异值时资源的分布情况)可知, matK序列的品种间和品种内变异重合(图2D), 不适合用于山葡萄资源的鉴定; rbcL序列正态分布图整体向品种内变异方向倾斜(图2C); psbA-trnH序列品种内变异差异和样本分布的比例明显较小, 而品种间的样本分布和变异差异明显较大, 有利于山葡萄资源的鉴定(图2B); ITS2序列品种内变异集中在barcoding gap图的左端(0.09- 0.15之间), 且品种间和品种内变异分别集中在bar- coding gap图的两端, 没有明显的变异间隔区, 但正态分布图有偏向两端的趋势, 有利于山葡萄资源的鉴别(图2A)。
图2
Figure 2
下载原图ZIP
生成PPT
图2
山葡萄品种间和品种内变异barcoding gap图
(A) ITS2序列; (B) psbA-trnH序列; (C) rbcL序列; (D) matK序列
Figure 2
Distribution for intra- and inter-varieties variation of Vitis amurensis
(A) ITS2 sequence; (B) psbA-trnH sequence; (C) rbcL sequence; (D) matK sequence
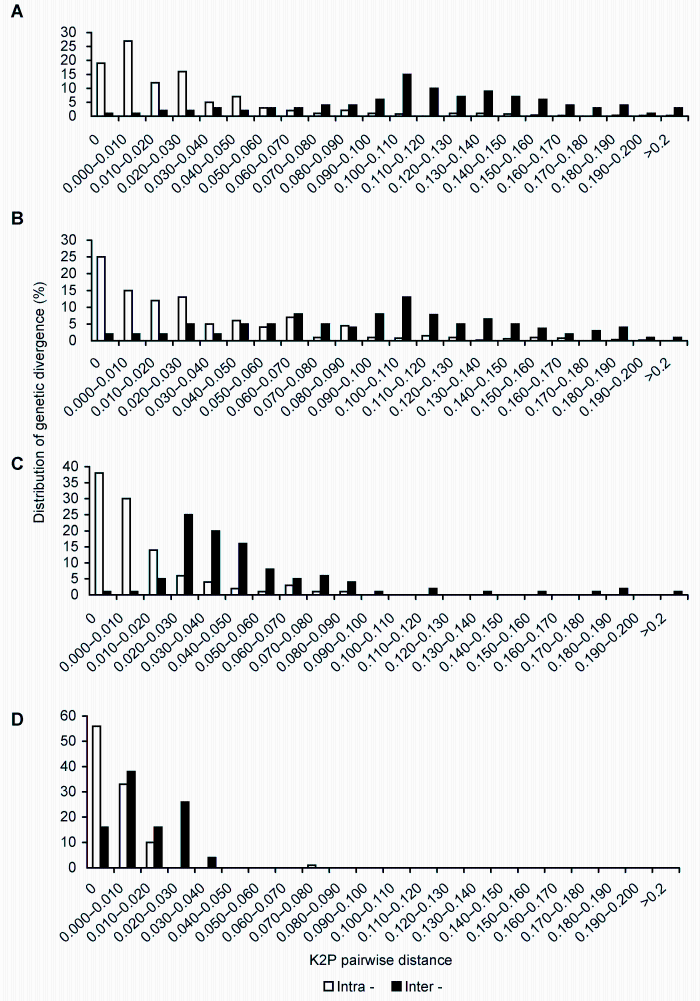
2.6 候选序列的鉴定效率评估鉴于山葡萄资源中某些品种内的变异较大, 将已编辑的序列进行相似性搜索算法(BLAST)比对, 结果表明ITS2和psbA-trnH序列在品种间的鉴定成功率较高, rbcL和matK序列难以单独完成对山葡萄资源所有品种的鉴别。NJ聚类分析结果表明, 利用ITS2序列构建的系统发育树中, 不同资源品种间存在差异, 能够鉴定花性及遗传关系差异较大的资源品种(图3A)。利用psbA-trnH序列构建的系统发育树中, 不同资源品种间无明显的分辨率, 其中4N2与Shuangyou及73061与Shuangqing存在一定的差异(图3B)。利用rbcL序列构建的系统发育树中, 不同资源品种间的分辨率相对较高, 但其遗传距离值很小(图3C)。matK序列的鉴定效果优于rbcL序列, 其分辨率较高(图3D)。综合上述2种方法可知, 虽然rbcL和matK序列的分辨率相对较高, 但其扩增成功率和测序成功率均低于ITS2与psbA-trnH序列, 且不能对部分资源品种进行鉴定, 如考虑到全部资源的鉴定, 其真正的鉴定成功率会低于ITS2和psbA-trnH序列。因此, ITS2和psbA-trnH序列更适合作为山葡萄资源鉴定的条形码序列。
图3
Figure 3
下载原图ZIP
生成PPT
图3
利用不同序列构建的11份山葡萄资源品种系统进化树
(A) ITS2序列; (B) psbA-trnH序列; (C) rbcL序列; (D) matK序列
Figure 3
Neighbor-joining (NJ) tree for 11 varieties of Vitis amurensis by using different sequences
(A) ITS2 sequence; (B) psbA-trnH sequence; (C) rbcL sequence; (D) matK sequence
2.7 讨论2.7.1 DNA条形码候选序列的筛选
理想的DNA条形码序列应具备种间变异大、种内变异小且扩增和测序成功率高等特点(Song et al., 2009; Yao et al., 2009)。本研究从5个DNA条形码序列(ITS、ITS2、psbA-trnH、rbcL和matK)中筛选出比较适合山葡萄种质资源鉴定的候选序列, 即ITS2和psbA-trnH。其中ITS2序列较短, 易扩增, 且其能够与保守的5.8S和26S区段形成特定的颈环二级结构(Selig et al., 2008; Dassanayake et al., 2008; Keller et al., 2009), 使利用ITS2序列进行处理分析更加准确。辛天怡等(2012)选取羌活(Notopterygium incisum) 31份样品进行研究, 得出ITS/ITS2序列作为DNA条形码能稳定、准确鉴别羌活药材。刘震等(2010)对忍冬科(Caprifoliaceae) DNA条形码通用序列进行筛选, 发现ITS2序列能够准确鉴别忍冬(Lonicera japonica)、接骨草(Sambucus chinensis)、濒危植物猥实(Kolkwitzia amabilis)以及七子花(Heptaco- dium miconioides)等。任阳阳等(2016)在鉴定虾脊兰属(Calanthe)植物时指出, ITS2和matK序列可以作为虾脊兰属部分植物的鉴定序列。东秀珠等(2000)在分析细菌的系统发育关系时, 提出GC含量也是判断亲缘关系远近的一项重要指标。本研究结果表明, 核基因ITS2序列在鉴定山葡萄资源中扩增效果和测序成功率均较高, GC含量最高, 表现出较大的品种间变异和较小的品种内变异, 物种鉴定成功率较高, 尤其在变异较大的资源中, 可以检测系统发生和亲缘关系的远近, 但对于差异较小的资源鉴定有一定的局限性。故在5个候选序列中, 推荐ITS2序列作为山葡萄资源鉴定的DNA条形码序列。
在本研究中, ITS序列PCR扩增成功率和测序成功率都很低, 出现多带情况, 无法用其进行山葡萄资源的鉴定。然而psbA-trnH序列在山葡萄资源中具有较高的扩增效率、测序成功率和鉴定成功率, 品种间的变异大于ITS2序列, 能够对山葡萄遗传差异较近的资源进行鉴定。Yao等(2009)的实验结果表明, psbA- trnH序列通用性较好, 扩增成功率较高, 其两端存在的75 bp保守序列是叶绿体间隔区进化速率最快的序列(Kress et al., 2005; Fazekas et al., 2008; Yao et al., 2009)。王柯等(2011)对锦葵科14个种26份样品进行分析, 发现psbA-trnH序列在属级水平上鉴定成功率为96.4%。石志刚等(2016)对宁夏枸杞(Lycium chinense)主要品种psbA-trnH序列的DNA条形码作了初步研究。高健等(2015)对鸡爪槭(Acer palmatum)的8个分类群共32个个体进行DNA条形码分析, 认为rpl16+psbA-trnH+trnL-trnF片段组合较适合作为鸡爪槭种下分类群鉴定的DNA条形码序列。我们初步认为psbA-trnH序列能够鉴定变异较小的山葡萄资源, 同时弥补了ITS2序列在山葡萄资源鉴定中的不足。目前, 在植物界还未筛选出一个能够鉴定所有物种的理想引物序列。ITS2和psbA-trnH序列在山葡萄资源鉴定中各有优势。因此, 我们建议将ITS2和psbA-trnH序列联合作为山葡萄种质资源鉴定的候选序列。
rbcL序列易扩增且容易比对, 但其在研究中多集中在种级以上的水平, 物种鉴定表现不明显(Kress and Erickson, 2007; Lahaye et al., 2008; Newmaster et al., 2008)。在山葡萄资源鉴定中, 我们发现rbcL序列在品种间和品种内差异均较小, 不适合作为山葡萄资源鉴定的DNA条形码序列。
matK序列较其它编码区序列进化速率快, 但其在不同植物的鉴定中表现不一致(Chase et al., 2007; Hollingsworth, 2008)。在对山葡萄资源鉴定中, matK序列的品种间变异较小, 但其鉴定成功率较高, 综合比较发现其对山葡萄种质的鉴定成功率仅次于ITS2和psbA-trnH序列。
2.7.2 DNA条形码技术在山葡萄种质资源鉴定中的应用
DNA条形码技术的优势是序列短、易扩增、变异明显且操作简便, 提高了物种鉴定的效率和准确性。自DNA条形码技术应用于植物界以来, 通用序列的筛选就成为难点之一。山葡萄性状变异大、类型多、生命周期长、遗传背景复杂, 属于多基因杂合体, 培育优质、丰产且抗逆性强的山葡萄新品种是目前国际上葡萄育种的重要方向。山葡萄资源中自然杂交种多, 已审定的品种是通过种内杂交后代选育出来或是利用授粉方式杂交选育的。在实际生产中, 很难对一些品种或亲本进行准确判断。本研究对DNA条形码技术在山葡萄资源中的应用作了初步探索, 选取山葡萄资源中具有代表性的11份资源33个样本, 从5个候选序列筛选得出ITS2和psbA-trnH较适合作为山葡萄资源鉴定的序列, 能够为山葡萄资源的分类鉴定、亲缘关系分析、体细胞杂种鉴定、遗传图谱构建、基因定位以及育种材料的早期选择等提供科学依据。我们相信DNA条形码技术将成为山葡萄资源鉴定的一项有力工具。
参考文献
文献选项
原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
| [1] | DOI:10.4268/cjcmm20130201URL随着中药材DNA条形码分子鉴定方法研究的深入与普及,国家药典委员会讨 论通过在《中国药典》增补本中列入中药材DNA条形码分子鉴定指导原则,该指导原则通过对大样本量中药材进行DNA条形码分子鉴定研究,建立以ITS2为 核心,psbA-trnH为辅的植物类药材DNA条形码鉴定体系和以COI为主、ITS2为辅的动物类药材DNA条形码鉴定体系.该文介绍了中药材DNA 条形码分子鉴定指导原则及其起草说明,并对该原则在中药材鉴定方面的应用前景进行展望. [本文引用: 1] |
| [2] | DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2000.02.002URL本研究测定了低GC含量的双歧杆菌(Bifidobacterium inopinatum)和新种B。thermoci.dophilum的16SrDNA全序列,在同另外19个双歧杆菌及8个相关细菌的16SrNA同源笥分析的基础上构建了系统发育树。结果表明:除低GC含蜈的B.inopinatum外,所有双杆菌的种在16SrDNA序列相似性≥82%的水平上聚类为一个簇群。尽管B.inopinaium与其它 |
| [3] | DOI:10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2015.60734URL槭属鸡爪槭(Acer palmatum Thunb.)是北温带广泛分布的一类园艺观赏树种,由于频繁的种内杂交渐渗导致其种下分类群的形态性状特征趋同,致使传统的形态学分类难以准确鉴定,新 兴的DNA条形码技术为快速、准确的鉴定鸡爪槭种下分类群提供了新的思路.本研究采用5个叶绿体DNA片段(rpl16、psbA-trnH、trnL- trnF、rbcL、matK)和核基因组ITS片段,运用PWG-distance和Tree-Building两种方法对鸡爪槭的8个分类群共32个 个体进行DNA条形码分析.结果显示,单个叶绿体基因组片段(分辨率为0%~25%)或核rDNAITS片段(12.5%)的分辨率较低,不同组合的叶绿 体DNA片段(0%~62 5%)、叶绿体片段与核rDNA ITS片段(12.5%~50%)的分辨率则相对较高.其中,rpl16+psbA-trnH+tmL-trnF片段组合的分辨率最高(62.5%),较 为符合DNA条形码快速、准确鉴定的要求,因此建议将其作为鸡爪槭种下分类群鉴定的DNA条形码. |
| [4] | DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-3356.2014.05.035URL山葡萄(V .amurensis Rupr.)是葡萄抗寒、抗病育种的珍贵种质资源,也是酿造山葡萄酒和生产天然色素的重要原料。我国自20世纪50年代开始野生山葡萄种质资源驯化与栽培 技术研究,取得了丰硕的研究成果。该文着重从山葡萄种质资源收集、保存、深度评价与高效利用等几方面取得的成果进行综述,并提出山葡萄种质资源未来的研究 方向。 [本文引用: 1] |
| [5] | DOI:10.4268/cjcmm20101906URL目的:从4条DNA片段(psbA-trnH,matK,rbcL,和ITS2)中筛选可用于忍冬科药用植物鉴定的DNA条形码通用序列。方法:通过比较各序列的PCR扩增成功率、测序效率、种内和种间变异、barcoding gap和鉴定成功率等指标评价不同序列在忍冬科植物中的鉴定能力。结果:对忍冬科13个属,33个物种,58个样本进行分析,ITS2序列在属水平上的鉴定成功率为100.0%,物种水平上的鉴定成功率为96.6%。结论:ITS2序列可以作为忍冬科植物的DNA条形码候选序列,同时推荐psbA-trnH序列作为ITS2序列的补充序列。 |
| [6] | [本文引用: 1] |
| [7] | DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2016.11.058URL目的:结合ITS2、psb A-trn H和matk序列对兰科虾脊兰属植物进行物种区分鉴定研究,并确立能准确鉴别虾脊兰属植物的序列或者序列组合。方法:采用试剂盒法对已收集的6种虾脊兰属植物进行总DNA的提取,通过扩增及测序,运用codencode V4.2软件对所得序列进行拼接与剪切,使用MEGA5.0对ITS2、psb A-trn H和matk序列3种序列分别进行比对分析,计算种内及种间Kimura 2-parameter(K2P)遗传距离,构建Neighbor-joining(NJ)系统聚类树。结果:实验共得到序列56条(包含Gen Bank序列17条),ITS2序列和mat K序列其种内最大遗传距离小于种间最小遗传距离,而该属psb Atrn H序列种内遗传距离范围和种间遗传距离范围有重合。结论:ITS2序列和mat K序列可以作为虾脊兰属部分植物的鉴定序列,而psb A-trn H序列不能用于虾脊兰属植物的鉴定。 |
| [8] | DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-4721.2006.03.020URL山葡萄是抗寒育种的珍贵资源,我国自20世纪50年代开始收集、保存、研究山葡萄种质资源,于1988年建成国家山葡萄种质资源圃,保存山葡萄种质资源380份,是世界上保存山葡萄种质份数最多的种质资源圃。利用山葡萄种质,国内多家单位先后培育出双红、双优、左优红、公酿一号等一批优良山葡萄品种和抗寒杂交品种。国内栽培面积达到5000余公顷。 [本文引用: 1] |
| [9] | DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-1161.2016.06.002URL对宁夏枸杞主要品种psbA-trntH的DNA条形码序列进行分析,从分子水平对枸杞做出鉴定。采用改进CTAB法提取枸杞叶片DNA,利用合成的特异引物对其叶绿体间隔序列进行扩增、克隆,对目的片段测序分析,克隆到枸杞主要品种psbA-trntH片段,并获得其碱基序列(总长为545bp)。 |
| [10] | DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-7360.2009.11.022URL本文介绍了国内外山葡萄研究现状和取得的研究成果,统计目前我国山葡萄生产栽培的面积、品种布局、产量和效益,重点总结了山葡萄生产栽培和山葡萄酒生产中存在的问题,并提出推进山葡萄产业持续发展的对策。 [本文引用: 1] |
| [11] | DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1259.2011.00276URL对锦葵科植物样品的ITS、ITS2、rbcL、matK和psbA-trnH序列进行 PCR扩增和测序,比较各序列的扩增效率、测序成功率、种内和种间变异的差异以及barcoding gap图,使用BLAST1和Nearest Distance方法评价不同序列的鉴定能力,进而从这些候选序列中筛选出较适合锦葵科植物鉴别的DNA条形码序列。结果表明,ITS序列在采集的锦葵科 植物11个种26个样品中的扩增成功率较高,其种内、种间变异差异和barcoding gap较ITS2、psbA-trnH及rbcL序列具有更明显的优势,且纳入60个属316个种共1228个样品的网上数据后,其鉴定成功率可达 89.9%。psbA-trnH序列的扩增和测序成功率最高,其鉴定成功率为63.2%,并能鉴别一些ITS序列无法鉴别的种。实验结果表明,ITS和 psbA-trnH是较适合鉴别锦葵科植物的DNA条形码序列组合。 [本文引用: 2] |
| [12] | |
| [13] | DOI:10.1073/pnas.0905845106PMID:19666622URLDNA barcoding involves sequencing a standard region of DNA as a tool for species identification. However, there has been no agreement on which region(s) should be used for barcoding land plants. To provide a community recommendation on a standard plant barcode, we have compared the performance of 7 leading candidate plastid DNA regions (atpF-atpH spacer, matK gene, rbcL gene, rpoB gene, rpoC1 gene, psbK-psbl spacer, and trnH-psbA spacer). Based on assessments of recoverability, sequence quality, and levels of species discrimination, we recommend the 2-locus combination of rbcL+ matK as the plant barcode. This core 2-locus barcode will provide a universal framework for the routine use of DNA sequence data to identify specimens and contribute toward the discovery of overlooked species of land plants. |
| [14] | DOI:10.1007/s00606-006-0507-9URLWe propose in this paper to use three regions of plastid DNA as a standard protocol for barcoding all land plants. We review the other markers that have been proposed and discuss their advantages and disadvantages. The low levels of variation in plastid DNA make three regions necessary; there are no plastid regions, coding or non-coding, that evolve as rapidly as mitochondrial DNA generally does in animals. We outline two, three-region options, (1) rpoC1, rpoB and matK or (2) rpoC1, matK and psbA-trnH as viable markers for land plant barcoding. [本文引用: 1] |
| [15] | DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0008613PMID:20062805URLBackground: The plant working group of the Consortium for the Barcode of Life recommended the two-locus combination of rbcL + matK as the plant barcode, yet the combination was shown to successfully discriminate among 907 samples from 550 species at the species level with a probability of 72%. The group admits that the two-locus barcode is far from perfect due to the low identification rate, and the search is not over. Methodology/Principal Findings: Here, we compared seven candidate DNA barcodes (psbA-trnH, matK, rbcL, rpoC1, ycf5, ITS2, and ITS) from medicinal plant species. Our ranking criteria included PCR amplification efficiency, differential intra- and inter-specific divergences, and the DNA barcoding gap. Our data suggest that the second internal transcribed spacer (ITS2) of nuclear ribosomal DNA represents the most suitable region for DNA barcoding applications. Furthermore, we tested the discrimination ability of ITS2 in more than 6600 plant samples belonging to 4800 species from 753 distinct genera and found that the rate of successful identification with the ITS2 was 92.7% at the species level. Conclusions: The ITS2 region can be potentially used as a standard DNA barcode to identify medicinal plants and their closely related species. We also propose that ITS2 can serve as a novel universal barcode for the identification of a broader range of plant taxa. |
| [16] | DOI:10.1073/pnas.1104551108PMID:22100737URLA two-marker combination of plastid rbcL and matK has previously been recommended as the core plant barcode, to be supplemented with additional markers such as plastid trnH—psbA and nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS). To assess the effectiveness and universality of these barcode markers in seed plants, we sampled 6,286 individuals representing 1,757 species in 141 genera of 75 families (42 orders) by using four, different methods of data analysis. These analyses indicate that (i) the three plastid markers showed high levels of universality (87.1—92.7%), whereas ITS performed relatively well (79%) in angiosperms but not so well in gymnosperms; (ii) in taxonomic groups for which direct sequencing of the marker is possible, ITS showed the highest discriminatory power of the four markers, and a combination of ITS and any plastid DNA marker was able to discriminate 69.9—79.1% of species, compared with only 49.7% with rbcL + matK; and (iii) where multiple individuals of a single species were tested, ascriptions based on ITS and plastid DNA barcodes were incongruent in some samples for 45.2% of the sampled genera (for genera with more than one species sampled). This finding highlights the importance of both sampling multiple individuals and using markers with different modes of inheritance. In cases where it is difficult to amplify and directly sequence ITS in its entirety, just using ITS2 is a useful backup because it is easier to amplify and sequence this subset of the marker. We therefore propose that ITS/ITS2 should be incorporated into the core barcode for seed plants. [本文引用: 1] |
| [17] | [本文引用: 1] |
| [18] | DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0002802URL [本文引用: 1] |
| [19] | DOI:10.1098/rspb.2002.2218URL [本文引用: 1] |
| [20] | DOI:10.1038/hdy.2008.16PMID:18398425URLAbstract An official journal of the Genetics Society, Heredity publishes high-quality articles describing original research and theoretical insights in all areas of genetics. Research papers are complimented by News & Commentary articles and reviews, keeping researchers and students abreast of hot topics in the field. [本文引用: 1] |
| [21] | [本文引用: 1] |
| [22] | DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2008.10.012PMID:19026726URLThe internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2) of the nuclear ribosomal repeat unit is one of the most commonly applied phylogenetic markers. It is a fast evolving locus, which makes it appropriate for studies at low taxonomic levels, whereas its secondary structure is well conserved, and tree reconstructions are possible at higher taxonomic levels. However, annotation of start and end positions of the ITS2 differs markedly between studies. This is a severe shortcoming, as prediction of a correct secondary structure by standard ab initio folding programs requires accurate identification of the marker in question. Furthermore, the correct structure is essential for multiple sequence alignments based on individual structural features. The present study describes a new tool for the delimitation and identification of the ITS2. It is based on hidden Markov models (HMMs) and verifies annotations by comparison to a conserved structural motif in the 5.8S/28S rRNA regions. Our method was able to identify and delimit the ITS2 in more than 30 000 entries lacking start and end annotations in GenBank. Furthermore, 45 000 ITS2 sequences with a questionable annotation were re-annotated. Approximately 30 000 entries from the ITS2-DB, that uses a homology-based method for structure prediction, were re-annotated. We show that the method is able to correctly annotate an ITS2 as small as 58 nt from Giardia lamblia and an ITS2 as large as 1160 nt from humans. Thus, our method should be a valuable guide during the first and crucial step in any ITS2-based phylogenetic analysis: the delineation of the correct sequence. Sequences can be submitted to the following website for HMM-based ITS2 delineation: http://its2.bioapps.biozentrum.uni-wuerzburg.de. [本文引用: 1] |
| [23] | DOI:10.1073/pnas.0503123102PMID:15928076URLMethods for identifying species by using short orthologous DNA sequences, known as "DNA barcodes," have been proposed and initiated to facilitate biodiversity studies, identify juveniles, associate sexes, and enhance forensic analyses. The cytochrome c oxidase 1 sequence, which has been found to be widely applicable in animal barcoding, is not appropriate for most species of plants because of a much slower rate of cytochrome c oxidase 1 gene evolution in higher plants than in animals. We therefore propose the nuclear internal transcribed spacer region and the plastid trnH-psbA intergenic spacer as potentially usable DNA regions for applying barcoding to flowering plants. The internal transcribed spacer is the most commonly sequenced locus used in plant phylogenetic investigations at the species level and shows high levels of interspecific divergence. The trnH-psbA spacer, although short ( 450-bp), is the most variable plastid region in angiosperms and is easily amplified across a broad range of land plants. Comparison of the total plastid genomes of tobacco and deadly nightshade enhanced with trials on widely divergent angiosperm taxa, including closely related species in seven plant families and a group of species sampled from a local flora encompassing 50 plant families (for a total of 99 species, 80 genera, and 53 families), suggest that the sequences in this pair of loci have the potential to discriminate among the largest number of plant species for barcoding purposes. [本文引用: 1] |
| [24] | DOI:10.1073/pnas.0709936105PMID:18258745URLDNA barcoding is a technique in which species identification is performed by using DNA sequences from a small fragment of the genome, with the aim of contributing to a wide range of ecological and conservation studies in which traditional taxonomic identification is not practical. DNA barcoding is well established in animals, but there is not yet any universally accepted barcode for plants. Here, we undertook intensive field collections in two biodiversity hotspots (Mesoamerica and southern Africa). Using >1,600 samples, we compared eight potential barcodes. Going beyond previous plant studies, we assessed to what extent a "DNA barcoding gap" is present between intra- and interspecific variations, using multiple accessions per species. Given its adequate rate of variation, easy amplification, and alignment, we identified a portion of the plastid matK gene as a universal DNA barcode for flowering plants. Critically, we further demonstrate the applicability of DNA barcoding for biodiversity inventories. In addition, analyzing >1,000 species of Mesoamerican orchids, DNA barcoding with matK alone reveals cryptic species and proves useful in identifying species listed in Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species (CITES) appendixes. [本文引用: 2] |
| [25] | DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404PMID:17846036URLSUMMARY: The Clustal W and Clustal X multiple sequence alignment programs have been completely rewritten in C++. This will facilitate the further development of the alignment algorithms in the future and has allowed proper porting of the programs to the latest versions of Linux, Macintosh and Windows operating systems. AVAILABILITY: The programs can be run on-line from the EBI web server: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/tools/clustalw2. The source code and executables for Windows, Linux and Macintosh computers are available from the EBI ftp site ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/software/clustalw2/ [本文引用: 1] |
| [26] | DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030422URL [本文引用: 1] |
| [27] | DOI:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.02002.xPMID:21585825URLThe concept and practice of DNA barcoding have been designed as a system to facilitate species identification and recognition. The primary challenge for barcoding plants has been to identify a suitable region on which to focus the effort. The slow relative nucleotide substitution rates of plant mitochondria and the technical issues with the use of nuclear regions have focused attention on several proposed regions in the plastid genome. One of the challenges for barcoding is to discriminate closely related or recently evolved species. The Myristicaceae, or nutmeg family, is an older group within the angiosperms that contains some recently evolved species providing a challenging test for barcoding plants. The goal of this study is to determine the relative utility of six coding (Universal Plastid Amplicon UPA, rpoB , rpoc1 , accD , rbcL , matK ) and one noncoding ( trnH-psbA ) chloroplast loci for barcoding in the genus Compsoneura using both single region and multiregion approaches. Five of the regions we tested were predominantly invariant across species (UPA, rpoB , rpoC1 , accD, rbcL ). Two of the regions ( matK and trnH-psbA ) had significant variation and show promise for barcoding in nutmegs. We demonstrate that a two-gene approach utilizing a moderately variable region ( matK ) and a more variable region ( trnH-psbA ) provides resolution among all the Compsonuera species we sampled including the recently evolved C. sprucei and C. mexicana. Our classification analyses based on nonmetric multidimensional scaling ordination, suggest that the use of two regions results in a decreased range of intraspecific variation relative to the distribution of interspecific divergence with 95% of the samples correctly identified in a sequence identification analysis. [本文引用: 1] |
| [28] | DOI:10.1080/10635150802032990PMID:18398767URLAlthough genetic methods of species identification, especially DNA barcoding, are strongly debated, tests of these methods have been restricted to a few empirical cases for pragmatic reasons. Here we use simulation to test the performance of methods based on sequence comparison (BLAST and genetic distance) and tree topology over a wide range of evolutionary scenarios. Sequences were simulated on a range of gene trees spanning almost three orders of magnitude in tree depth and in coalescent depth; that is, deep or shallow trees with deep or shallow coalescences. When the query's conspecific sequences were included in the reference alignment, the rate of positive identification was related to the degree to which different species were genetically differentiated. The BLAST, distance, and liberal tree-based methods returned higher rates of correct identification than did the strict tree-based requirement that the query was within, but not sister to, a single-species clade. Under this more conservative approach, ambiguous outcomes occurred in inverse proportion to the number of reference sequences per species. When the query's conspecific sequences were not in the reference alignment, only the strict tree-based approach was relatively immune to making false-positive identifications. Thresholds affected the rates at which false-positive identifications were made when the query's species was unrepresented in the reference alignment but did not otherwise influence outcomes. A conservative approach using the strict tree-based method should be used initially in large-scale identification systems, with effort made to maximize sequence sampling within species. Once the genetic variation within a taxonomic group is well characterized and the taxonomy resolved, then the choice of method used should be dictated by considerations of computational efficiency. The requirement for extensive genetic sampling may render these techniques inappropriate in some circumstances. [本文引用: 1] |
| [29] | DOI:10.1093/nar/gkn325PMID:2447805URLAbstract Endeavour (http://www.esat.kuleuven.be/endeavourweb; this web site is free and open to all users and there is no login requirement) is a web resource for the prioritization of candidate genes. Using a training set of genes known to be involved in a biological process of interest, our approach consists of (i) inferring several models (based on various genomic data sources), (ii) applying each model to the candidate genes to rank those candidates against the profile of the known genes and (iii) merging the several rankings into a global ranking of the candidate genes. In the present article, we describe the latest developments of Endeavour. First, we provide a web-based user interface, besides our Java client, to make Endeavour more universally accessible. Second, we support multiple species: in addition to Homo sapiens, we now provide gene prioritization for three major model organisms: Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus and Caenorhabditis elegans. Third, Endeavour makes use of additional data sources and is now including numerous databases: ontologies and annotations, protein-protein interactions, cis-regulatory information, gene expression data sets, sequence information and text-mining data. We tested the novel version of Endeavour on 32 recent disease gene associations from the literature. Additionally, we describe a number of recent independent studies that made use of Endeavour to prioritize candidate genes for obesity and Type II diabetes, cleft lip and cleft palate, and pulmonary fibrosis. [本文引用: 1] |
| [30] | DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btn031PMID:18227116URLAbstract Selection of optimal biomarkers for the identification of different operational taxonomic units (OTUs) may be a hard and tedious task, especially when phylogenetic trees for multiple genes need to be compared. With TaxonGap we present a novel and easy-to-handle software tool that allows visual comparison of the discriminative power of multiple biomarkers for a set of OTUs. The compact graphical output allows for easy comparison and selection of individual biomarkers. AVAILABILITY: Graphical User Interface; Executable JAVA archive file, source code, supplementary information and sample files can be downloaded from the website: http://www.kermit.ugent.be/taxongap [本文引用: 1] |
| [31] | DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2009.05.042PMID:19505556URLMedicinal plants belonging to the family Polygonaceae in Chinese pharmacopoeia possess important medicinal efficacy in traditional Chinese medicines. DNA barcodes are first used to discriminate the Polygonaceae in Chinese pharmacopoeia and their adulterants. DNA samples, extracted from thirty-eight specimens belonging to eighteen species in Polygonaceae, were used as templates. Eight candidate barcodes were amplified by polymerase chain reaction. Sequence analysis was accomplished by CodonCode Aligner V 2.06 and DNAman V 6. Species identification was performed using MEGA V 4.0. The amplification efficiency of six candidate DNA barcodes ( rbcL, trnH- psbA, ndhJ, rpoB, rpoC1, accD) was 100%, while the efficiency of YCF5 and nrITS was 56% and 44%, respectively. The interspecific divergence was highest for the trnH- psbA (20.05%), followed by the nrITS (14.01%) across all species pairs, while intraspecific variation both within populations and between populations was absent (0.0%). The trnH- psbA can not only distinguish ten species of Polygonaceae in Chinese pharmacopoeia, but also recognize eight other species of Polygonaceae including their adulterants. Our findings show that DNA barcoding is an efficient tool for identification of Polygonaceae in Chinese pharmacopoeia and their adulterants. [本文引用: 1] |
| [32] | DOI:10.1111/jipb.12189PMID:24612741URLAbstractWe evaluated nine plastid (matK, rbcL, rpoC1, rpoB, rpl36-rps8, ndhJ, trnL-F, trnH-psbA, accD) and two nuclear (ITS and ITS2) barcode loci in family Zingiberaceae by analyzing 60 accessions of 20 species belonging to seven genera from India. Bidirectional sequences were recovered for every plastid locus by direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplicons in all the accessions tested. However, only 35 (58%) and 40 accessions (66%) yielded ITS and ITS2 sequences, respectively, by direct sequencing. In different bioinformatics analyses, matK and rbcL consistently resolved 15 species (75%) into monophyletic groups and five species into two paraphyletic groups. The 173 ITS sequences, including 138 cloned sequences from 23 accessions, discriminated only 12 species (60%), and the remaining species were entered into three paraphyletic groups. Phylogenetic and genealogic analyses of plastid and ITS sequences imply the possible occurrence of natural hybridizations in the evolutionary past in giving rise to species paraphyly and intragenomic ITS heterogeneity in the species tested. The results support using matK and rbcL loci for barcoding Zingiberaceae members and highlight the poor utility of ITS and the highly regarded ITS2 in barcoding this family, and also caution against proposing ITS loci for barcoding taxa based on limited sampling. |
| [33] | DOI:10.1055/s-0029-1185385PMID:19235685URLDNA barcoding is a novel technology that uses a standard DNA sequence to facilitate species identification. Although a consensus has not been reached regarding which DNA sequences can be used as the best plant barcodes, the PSBA-TRNH spacer region has been tested extensively in recent years. In this study, we hypothesize that the PSBA-TRNH spacer regions are also effective barcodes for DENDROBIUM species. We have sequenced the chloroplast PSBA-TRNH intergenic spacers of 17 DENDROBIUM species to test this hypothesis. The sequences were found to be significantly different from those of other species, with percentages of variation ranging from 0.3 % to 2.3 % and an average of 1.2 %. In contrast, the intraspecific variation among the DENDROBIUM species studied ranged from 0 % to 0.1 %. The sequence difference between the PSBA-TRNH sequences of 17 DENDROBIUM species and one BULBOPHYLLUM ODORATISSIMUM ranged from 2.0 % to 3.1 %, with an average of 2.5 %. Our results support the notion that the PSBA-TRNH intergenic spacer region could be used as a barcode to distinguish various DENDROBIUM species and to differentiate DENDROBIUM species from other adulterating species. [本文引用: 2] |
中药材DNA条形码分子鉴定指导原则
1
2013
... 为提高山葡萄资源的扩增成功率, 在进行PCR反应前先对候选序列ITS、ITS2、psbA-trnH、rbcL和matK (
16S rDNA同源性所揭示的双歧杆菌与有关细菌的亲缘关系
2000
鸡爪槭种下分类群的DNA条形码筛选
2015
山葡萄种质资源收集、保存、评价与利用研究进展
1
2014
... 山葡萄(Vitis amurensis)属于东亚种群, 为葡萄科(Vitaceae)葡萄属(Vitis)落叶藤本, 是葡萄属中最抗寒的一个种.其枝蔓可耐-45°C低温, 根系可耐-16°C低温, 原产于我国东北、华北及朝鲜北部、俄罗斯远东地区等(
忍冬科药用植物DNA条形码通用序列的筛选
2010
植物DNA条形码技术
1
2010
... DNA条形码(DNA barcoding)是应用一种相对较短、易扩增且有足够变异的DNA序列来进行物种分类鉴别的分子生物学技术(
虾脊兰属植物DNA条形码的确立
2016
我国山葡萄种质资源研究与利用现状
1
2006
... 山葡萄(Vitis amurensis)属于东亚种群, 为葡萄科(Vitaceae)葡萄属(Vitis)落叶藤本, 是葡萄属中最抗寒的一个种.其枝蔓可耐-45°C低温, 根系可耐-16°C低温, 原产于我国东北、华北及朝鲜北部、俄罗斯远东地区等(
宁夏枸杞主要品种psbA-trnH的DNA条形码鉴定的初步研究
2016
中国山葡萄产业的发展及对策
1
2009
... 山葡萄(Vitis amurensis)属于东亚种群, 为葡萄科(Vitaceae)葡萄属(Vitis)落叶藤本, 是葡萄属中最抗寒的一个种.其枝蔓可耐-45°C低温, 根系可耐-16°C低温, 原产于我国东北、华北及朝鲜北部、俄罗斯远东地区等(
锦葵科植物DNA条形码通用序列的筛选
2
2011
... DNA条形码(DNA barcoding)是应用一种相对较短、易扩增且有足够变异的DNA序列来进行物种分类鉴别的分子生物学技术(
... 扩增出明显PCR条带即为成功; 测序后获得高质量的序列即为测序成功; 有效序列比例=PCR扩增效率×测序成功率(
羌活药材ITS/ITS2条形码鉴定及其稳定性与准确性研究
2012
2009
1
2007
... matK序列较其它编码区序列进化速率快, 但其在不同植物的鉴定中表现不一致(
2010
1
2011
... DNA条形码(DNA barcoding)是应用一种相对较短、易扩增且有足够变异的DNA序列来进行物种分类鉴别的分子生物学技术(
1
2008
... 理想的DNA条形码序列应具备种间变异大、种内变异小且扩增和测序成功率高等特点(
1
2008
... 在本研究中, ITS序列PCR扩增成功率和测序成功率都很低, 出现多带情况, 无法用其进行山葡萄资源的鉴定.然而psbA-trnH序列在山葡萄资源中具有较高的扩增效率、测序成功率和鉴定成功率, 品种间的变异大于ITS2序列, 能够对山葡萄遗传差异较近的资源进行鉴定.Yao等(2009)的实验结果表明, psbA- trnH序列通用性较好, 扩增成功率较高, 其两端存在的75 bp保守序列是叶绿体间隔区进化速率最快的序列(
1
2003
... DNA条形码(DNA barcoding)是应用一种相对较短、易扩增且有足够变异的DNA序列来进行物种分类鉴别的分子生物学技术(
1
2008
... matK序列较其它编码区序列进化速率快, 但其在不同植物的鉴定中表现不一致(
1
2007
... rbcL序列易扩增且容易比对, 但其在研究中多集中在种级以上的水平, 物种鉴定表现不明显(
1
2009
... 理想的DNA条形码序列应具备种间变异大、种内变异小且扩增和测序成功率高等特点(
1
2005
... 在本研究中, ITS序列PCR扩增成功率和测序成功率都很低, 出现多带情况, 无法用其进行山葡萄资源的鉴定.然而psbA-trnH序列在山葡萄资源中具有较高的扩增效率、测序成功率和鉴定成功率, 品种间的变异大于ITS2序列, 能够对山葡萄遗传差异较近的资源进行鉴定.Yao等(2009)的实验结果表明, psbA- trnH序列通用性较好, 扩增成功率较高, 其两端存在的75 bp保守序列是叶绿体间隔区进化速率最快的序列(
2
2008
... Barcoding gap是指物种间DNA条形码序列的种间遗传变异明显大于种内变异, 并在两者之间形成一个明显的间隔区(
... rbcL序列易扩增且容易比对, 但其在研究中多集中在种级以上的水平, 物种鉴定表现不明显(
1
2007
... 使用SeqMan (DNA Star package; DNA Star Inc., Madison, WI, USA)软件进行测序峰图校对拼接, 去除低质量序列及引物区.利用Clustal X-2.0.11-Win软件(
1
2005
... Barcoding gap是指物种间DNA条形码序列的种间遗传变异明显大于种内变异, 并在两者之间形成一个明显的间隔区(
1
2008
... rbcL序列易扩增且容易比对, 但其在研究中多集中在种级以上的水平, 物种鉴定表现不明显(
1
2008
... 序列进行手工调整.切除ITS2序列的5.8S和26S区段(HM-Mer模型), 去除psbA-trnH序列的psbA和trnH区段, 使其获得间隔区序列.用MEGA 5.0软件对各序列进行Clustal W计算, 并计算K-2-P距离值, 比较不同序列品种间和品种内变异, 分析核苷酸含量比例.利用SPSS 18.0软件对计算结果进行Wilcoxon Sig- ned-rank检验.利用TAXON DNA软件(
1
2008
... 理想的DNA条形码序列应具备种间变异大、种内变异小且扩增和测序成功率高等特点(
1
2008
... 序列进行手工调整.切除ITS2序列的5.8S和26S区段(HM-Mer模型), 去除psbA-trnH序列的psbA和trnH区段, 使其获得间隔区序列.用MEGA 5.0软件对各序列进行Clustal W计算, 并计算K-2-P距离值, 比较不同序列品种间和品种内变异, 分析核苷酸含量比例.利用SPSS 18.0软件对计算结果进行Wilcoxon Sig- ned-rank检验.利用TAXON DNA软件(
1
2009
... 理想的DNA条形码序列应具备种间变异大、种内变异小且扩增和测序成功率高等特点(
2014
2
2009
... 理想的DNA条形码序列应具备种间变异大、种内变异小且扩增和测序成功率高等特点(
... 在本研究中, ITS序列PCR扩增成功率和测序成功率都很低, 出现多带情况, 无法用其进行山葡萄资源的鉴定.然而psbA-trnH序列在山葡萄资源中具有较高的扩增效率、测序成功率和鉴定成功率, 品种间的变异大于ITS2序列, 能够对山葡萄遗传差异较近的资源进行鉴定.Yao等(2009)的实验结果表明, psbA- trnH序列通用性较好, 扩增成功率较高, 其两端存在的75 bp保守序列是叶绿体间隔区进化速率最快的序列(
