 ,1,2,3, 崔艺馨3,4, 梅家琴3,4, 汤青林1,2, 李加纳3,4, 钱伟
,1,2,3, 崔艺馨3,4, 梅家琴3,4, 汤青林1,2, 李加纳3,4, 钱伟 ,3,4,*
,3,4,*Genome-wide Association Study on Seed Oil Content in Rapeseed and Construction of Integration System for Oil Content Loci
WEI Da-Yong ,1,2,3, CUI Yi-Xin3,4, MEI Jia-Qin3,4, TANG Qing-Lin1,2, LI Jia-Na3,4, QIAN Wei
,1,2,3, CUI Yi-Xin3,4, MEI Jia-Qin3,4, TANG Qing-Lin1,2, LI Jia-Na3,4, QIAN Wei ,3,4,*
,3,4,*通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2018-01-30接受日期:2018-06-9网络出版日期:2018-06-11
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-01-30Accepted:2018-06-9Online:2018-06-11
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (6158KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
魏大勇, 崔艺馨, 梅家琴, 汤青林, 李加纳, 钱伟. 油菜种子含油量GWAS分析及位点整合系统构建[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(9): 1311-1319. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01311
WEI Da-Yong, CUI Yi-Xin, MEI Jia-Qin, TANG Qing-Lin, LI Jia-Na, QIAN Wei.
我国目前食用植物油自给率不足40%, 60%以上依赖进口, 严重威胁着国家食用油供给安全[1]。菜籽油是健康的食用植物油, 是发展生物柴油最具潜力的原料。甘蓝型油菜(Brassica napus L.)是我国主要的油料作物, 种植面积和总产均居世界首位[2], 美国农业部(http://apps.fas.usda.gov/ psdonline/)最新数据显示, 2016—2017年度我国油菜播种面积大约为700万公顷, 产量大约为1350万吨, 缺口依然很大, 油菜籽进口量可能达到450万吨[3]。因此, 油菜种子含油量研究对于提高油菜含油量、缓解我国油料产业和食用植物油的短缺具有重要意义。
油菜种子含油量是一个由多基因控制的复杂数量性状, 易受环境影响[4,5,6]。前人通过基于分离群体的QTL定位和基于自然群体的SNP鉴定, 将油菜种子含油量相关位点锚定在19条染色体上[7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]。分离群体QTL定位中, Delourme等[7]利用DY和RNSL 2个双单倍体(doubled haploid, DH)群体, 发现一个位点在两群体A03连锁群上能同时被检测到; Yan等[8]以黄籽高油GH06和黑籽低油P174构建重组自交系(recombinant inbred lines, RIL)群体GP-RIL, 检测到11个QTL, 单个位点可解释5.19%~13.57%的表型变异; Shi等[9]利用一个重新构建的F2 (reconstructed, RC-F2)群体, 在3个环境下检测到43个QTL; Zhao等[11]利用欧洲春性品种Sollux和中国半冬性品种Gaoyou两个种子高含油量油菜品种构建SG-DH群体, 检测到9个显著的QTL, 共解释57.79%的表型变异; Sun等[10]以中国半冬性高油材料Zy036和低油材料51070为亲本构建Z5-DH群体, 结合3年3点表型数据, 共检测到12个QTL, 其中位于A02和A09染色体的QTL能被重复检测到; Wang等[12]利用种子含油量差异大于10%的2个中国油菜品种构建KN-DH群体, 在11条染色体上共检测到24个整合的QTL; Jiang等[13]以欧洲冬性品种Tapidor和中国半冬性品种宁油7号为亲本构建TH-DH群体, 共识别46个QTL, 分布在16条染色体上, 其中18个QTL在早前报道的多个群体中得到验证; Javed等[14]利用加拿大2个春性材料构建PT-DH群体, 检测到14个QTL, 其中A10染色体上的1个QTL解释26.99%的表型变异; Fu等[16]以欧洲冬性品种Express和中国半冬性品种SWU07为亲本构建ES-DH群体, 在中国和德国2个环境下共鉴定到19个QTL。
随着甘蓝型油菜参考基因组的公布[17]和基因组测序费用的持续降低, 基于自然群体的全基因组关联分析(genome-wide association study, GWAS)已被广泛用于解析复杂农艺性状的研究[15-16,18-20]。在油菜种子含油量方面, Liu等[15]基于油菜60K SNP芯片, 通过3种模型在521份油菜自然群体中鉴定到50个与种子含油量显著相关的SNP, 共解释80%的表型变异, 其中新发现29个位点; Fu等[16]通过标记-性状关联分析在142份油菜自然群体中, 鉴定到23个位点。
上述油菜种子含油量性状的定位研究彼此相对独立, 群体分类、标记名称和QTL阈值的设定等不尽相同, 更缺乏一个参考系统对不同群体定位结果比较分析。本研究一方面采用一个甘蓝型油菜自然群体, 结合60K SNP芯片和4年的表型数据进行种子含油量GWAS分析, 鉴定与种子含油量相关的SNP位点; 另一方面将本研究鉴定的显著SNP位点与185个前人报道的整合位点(来源于2006—2017年的10个分离群体和2个自然群体)锚定到法国公布的甘蓝型油菜品种“Darmor-Bzh”的基因组上, 对不同群体、不同环境和不同分析方法鉴定的位点进行全基因组水平比较分析。本研究可为通过分子标记辅助选择提高油菜种子含油量提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料和表型测定与分析
308份具有广泛变异的甘蓝型油菜(Brassica napus L.)自交系由重庆市油菜工程技术研究中心提供, 于2013—2016连续4年种植于中心试验地(重庆北碚), 3行区播种, 每行10株, 每年2次田间重复, 田间管理按照当地常规方式进行。采用福斯(FOSS)近红外光谱分析仪(NIR System, TR-3750)测定上述自然群体的自交种子含油量, 每份材料测定3株, 每袋样品重复测定2次。采用SAS软件(版本9.13)[21]对表型数据进行方差分析。1.2 SNP基因型分型和群体结构分析
魏大勇等[22]对该自然群体材料进行了基因型分型和群体结构分析。基因型分型方法是, 于苗期提取每份材料的DNA, 利用Illumina公司开发的Brassica 60K SNP芯片进行杂交, 得到的SNP探针序列与法国公布的甘蓝型油菜品种“Darmor- Bzh”的基因组V4.1 (1.3 全基因组关联分析和候选基因预测
利用R语言的GenABEL包[23]对多年多点自然群体材料的种子含油量进行GWAS分析, 采用主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA) +亲缘关系(kinship, K)的混合线性模型(mixed linear model, MLM)对性状和标记进行关联位点的检测, 阈值设定为P < 4.26×10-5 (1/所使用的标记, -lg P=4.37)。通过R语言的p.adjusted命令计算假阳性率(false discovery rate, FDR)。将与显著SNP处于同一单体型块(r2 > 0.5)的区间定义为候选关联区间, 在此区间参考以下标准预测候选基因: (1)在甘蓝型油菜或拟南芥参考基因组上与性状相关的已知功能的基因; (2) SNP直接落在基因内部; (3)参考已报道QTL定位的结果。1.4 种子含油量相关位点整合比较
收集了从2006—2017年共10个分离群体和2个自然群体的种子含油量定位结果[7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16], 对于分离群体, 将QTL区间侧翼引物序列与法国公布的油菜基因组V4.1进行本地BlastN, 记录比对到唯一染色体物理位置的标记, 若物理位置存在交集, 则对标记进行整合。对于自然群体, 直接记录与表型显著关联的SNP位置。将上述所有位点利用Perl语言, 整合在Circos图上[24], 对不同研究者定位的结果进行比较分析。2 结果与分析
2.1 表型数据分析
连续4年的表型鉴定, 油菜自然群体的种子含油量存在广泛变异, 变异范围介于24.50%~ 49.91%, 各年度变异系数介于8.79%~10.24% (表1)。频率分布显示, 4年的种子含油量均表现为连续的近正态分布(图1), 表明油菜种子含油量是一个数量性状, 受多基因控制。方差分析结果表明, 基因型、环境以及基因型与环境互作间都存在显著差异(P<0.01), 年度间的相关性达到显著水平(r = 0.31~0.57, P<0.01), 说明该性状易受环境影响, 但材料之间的比较具有一定的稳定性。Table 1
表1
表1308份自然群体中油菜种子含油量的表型变异
Table 1
| 年份 Year | 范围 Range (%) | 平均值±标准偏差 Mean±SD (%) | 变异系数CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 24.50-48.46 | 37.01±3.79 | 10.24 |
| 2014 | 27.47-47.35 | 36.82±3.45 | 9.37 |
| 2015 | 25.27-44.43 | 34.99±3.07 | 8.79 |
| 2016 | 25.21-49.91 | 38.54±3.88 | 10.06 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图1
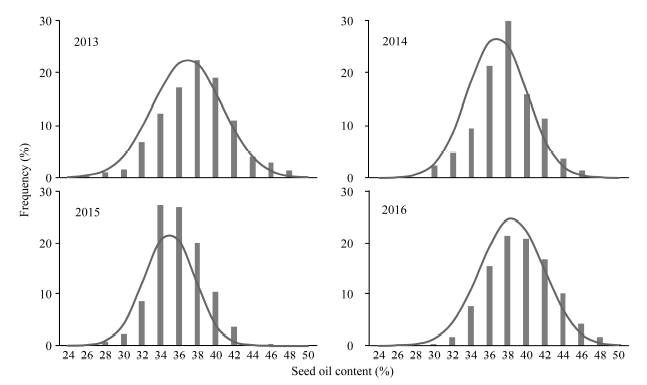 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1种子含油量的频率分布
Fig. 1Frequency distribution of seed oil content
2.2 全基因组关联分析
为了降低年际间的环境影响, 采用Merk等[25]方法对4年表型数据进行最佳线性无偏预测(best linear unbiased prediction, BLUP), 估计种子含油量的BLUP值, 同时结合自然群体的SNP基因型数据进行GWAS分析。GWAS分析共检测到8个SNP与种子含油量显著关联, 分别分布在A02、A03、A05和C02染色体上, 单个位点解释的表型变异为3.22%~ 5.13% (表2), Q-Q (quantile-quantile)图显示该模型很好地控制了假阳性概率的产生(图2)。根据位点间的连锁不平衡(r2 > 0.5), 在上述8个SNP构成的单体型块内预测到6个候选基因, 除了候选基因BnaA05g26510D, 其他5个都属于已知的油脂代谢相关基因。
Table 2
表2
表2GWAS结果和候选基因预测
Table 2
| 染色体 Chr. | 位置 Position (bp) | 贡献率 R2 (%) | 假阳性率 FDR | 候选基因 Candidate gene | 拟南芥同源基因 Arabidopsis homologue | 基因注释 Gene annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A02 | 20818388 | 3.22 | 3.85E-05 | BnaA02g28280D | AT3G26790 | B3类转录因子 B3 transcription factor |
| A03 | 6727279 | 4.56 | 3.18E-05 | BnaA03g14670D | AT2G31690 | 三酰甘油酯的降解 Involved in the degradation of triacylglycerol |
| A05 | 15959252 | 3.51 | 3.45E-05 | — | — | — |
| A05 | 18730739 | 4.29 | 2.44E-05 | BnaA05g25260D | AT3G14205 | 磷酸肌醇磷酸酯酶家族蛋白 Phosphoinositide phosphatase family protein |
| A05 | 19407850 | 3.26 | 7.52E-06 | BnaA05g26510D | AT3G12680 | C3H类转录因子 C3H transcription factor |
| A05 | 19483554 | 5.13 | 6.52E-06 | BnaA05g26900D | AT3G12120 | bZIP类转录因子 bZIP transcription factor |
| C02 | 45446662 | 3.71 | 2.46E-05 | — | — | — |
| C02 | 45458214 | 4.22 | 1.65E-05 | BnaC02g43130D | AT5G64440 | 肪酸酰胺水解酶 Fatty acid amide hydrolase |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图2
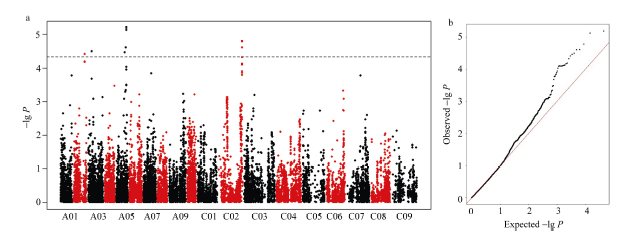 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2种子含油量的全基因组关联分析
a: 种子含油量的曼哈顿图, 水平黑色虚线表示阈值(1/23490, -lg P= 4.37); b: 估计阈值的Q-Q图。
Fig. 2GWAS of seed oil content
a: Manhattan plot of seed oil content, the horizontal dashed black line represents the significant threshold (1/23490, -lg P = 4.37); b: Q-Q plot of estimated threshold.
2.3 不同群体定位结果的全基因组水平比较分析
对本研究及2006—2017年已报道的与油菜种子含油量相关的10篇文献进行整理(表3), 用10个分离群体(包括8个DH群体、1个RIL群体和1个RC-F2群体)共检测到105个整合的位点, 平均每个群体11个, TN-DH群体鉴定到的位点最多(27个)。用3个自然群体共鉴定到88个位点, 平均每个自然群体18个。所有193个位点在油菜的19条染色体上都有分布, 其中A03染色体分布最多(25个), C05染色体分布最少(2个), A亚基因组每条染色体平均有13个, 显著高于C亚基因组的7个。Table 3
Table 3Summary of known sites associated with seed oil content in B.napus
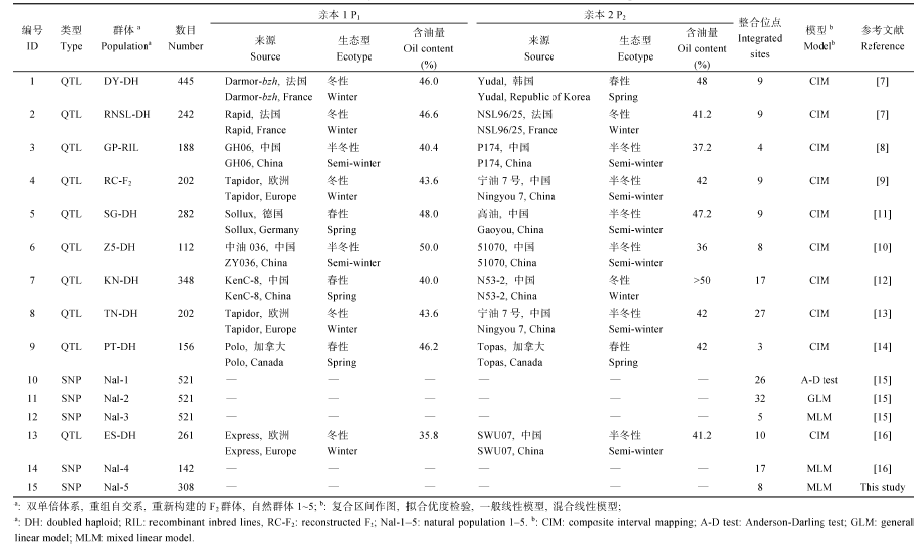 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
对A和C亚基因组上的整合区间比较发现, 2个亚基因组上存在12组部分同源的整合区间, 分别分布在A01/C01 (3组)、A02/C02 (2组)、A03/ C03 (1组)、A05/C05 (1组)、A08/C03 (1组)、A08/ C08 (2组)、A09/C08 (1组)和A10/C09 (1组)(图3)。
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3全基因组组水平展示不同油菜群体种子含油量的定位结果
(a)染色体数目; (b)参考基因组所有基因的热图(窗口大小为500 kb); (c)已知的1663个油分代谢相关基因; (1) DY-DH群体; (2) RNSL-DH群体; (3) GP-RIL群体; (4) RC-F2群体; (5) SG-DH群体; (6) Z5-DH群体; (7) KN-DH群体; (8) TN-DH群体; (9)PT-DH群体; (10) 521份自然群体1; (11) 521份自然群体2; (12) 521份自然群体3; (13) ES-DH群体; (14) 142份自然群体4; (15) 308份自然群体。中间不同颜色线条表示A和C亚基因组上存在同源关系的12组整合区间。
Fig. 3Genome-wide level display of the sites of seed oil content in different rapeseed populations
(a) chromosome number; (b) heat map of all genes in reference genome (window size is 500 kb); (c) 1663 known oil metabolic genes; (1) DY-DH population; (2) RNSL-DH population; (3) GP-RIL population; (4) RC-F2 population; (5) SG-DH population; (6) Z5-DH population; (7) KN-DH population; (8) TN-DH population; (9) PT-DH population; (10) 521 natural population 1; (11) 521 natural population 2; (12) 521 natural population 3; (13) ES-DH population; (14) 142 natural population 4; (15) 308 natural population 5. Lines in the middle indicate the homology of integrated loci between the A and the C subgenomes.
对不同群体鉴定的位点比较分析发现, 7个整合区间至少在3个不同群体中都能重复检测到(视为遗传较稳定的位点), 分别位于A01、A02、A03、A06、A08、A09和A10染色体(表4)。其中位于A02、A08和A10染色体上的3个区间, 分别能在C2、C8和C9染色体找到部分同源的整合区间(图4)。在7个整合的区间共发现44个已知的油脂代谢相关基因[17], 其中上述3个区间含26个。
Table 4
表4
表4甘蓝型油菜遗传稳定的种子含油量位点染色体分布及油脂代谢相关基因
Table 4
| 染色体 Chr. | 群体编号 ID | 区间 Region (Mb) | 已知的油脂代谢相关基因1) Known genes related to oil metabolism1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | 3, 4, 5, 8 | 7.23-7.49 | BnaA01g14400D, BnaA01g14480D |
| A02 | 6, 8, 11 | 8.09-10.25 | BnaA02g14460D, BnaA02g15090D, BnaA02g15290D, BnaA02g15690D, BnaA02g15770D, BnaA02g16020D, BnaA02g16070D, BnaA02g16200D, BnaA02g16260D, BnaA02g16470D, BnaA02g16520D, BnaA02g16570D, BnaA02g17050D |
| A03 | 1, 2, 8, 9 | 16.53-17.65 | BnaA03g34340D, BnaA03g34830D, BnaA03g34980D, BnaA03g35170D, |
| A06 | 1, 10, 14 | 21.5-21.7 | BnaA06g32660D |
| A08 | 2, 3, 4, 7, 8 | 10.85-12.17 | BnaA08g12720D, BnaA08g12780D, BnaA08g12850D, BnaA08g13370D, BnaA08g13410D, BnaA08g13530D, BnaA08g13870D, BnaA08g14190D |
| A09 | 8, 10, 11, 12, 13 | 30.49-31.23 | BnaA09g44630D, BnaA09g44650D, BnaA09g44980D, BnaA09g45010D, BnaA09g45250D, BnaA09g45720D |
| A10 | 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 | 14.35-16.06 | BnaA10g20920D, BnaA10g21350D, BnaA10g21780D, BnaA10g22070D, BnaA10g23290D, BnaA10g23670D, BnaA10g23790D, BnaA10g23950D, BnaA10g24440D, BnaA10g24560D |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
3.1 油菜种子含油量位点全基因组整合系统的特点
甘蓝型油菜种子含油量的定位已有很多报道[4, 6-16], 但缺乏一个共同的参考系统, 不同研究结果的比较有较大难度。Jiang等[13]将3个分离群体(DY、RNSY和SG-DH群体)的标记与TN-DH群体整合, 构建了一个包含12条染色体的QTL定位整合系统, 检测到12个整合的QTL区间。但该QTL系统使用的是遗传距离, 并不能与自然群体的定位结果有效整合。本研究利用法国公布的油菜参考基因组信息, 将自己的种子含油量定位结果与其他12个不同群体的定位结果整合, 构建了一个含193个油菜种子含油量位点的全基因组整合系统(简称为整合系统)。该整合系统的特点在于, 根据物理位置对多个研究中的含油量位点进行比较, 能准确和直观地判断位点间的位置关系。比如该系统发现12对整合区间在A和C亚基因组存在部分同源性, 除了A10/C09上的一对是在同一个群体中鉴定到的[16], 其余都是来自于不同群体的鉴定结果, 这说明该整合系统确实可以对不同研究做出充分的比较(不受群体与标记类型的限制)。3.2 整合系统对提高油菜种子含油量的指导意义
该系统可以直观体现各位点被不同研究鉴定出的概率, 从而为确定位点的重要程度(提高种子含油量的潜力)提供参考。根据该整合系统, 我们发现7个被多个群体重复鉴定到的区间, 其中3个区间在C亚基因组上能找到同源的区间, 说明这些区间可能相对普遍存在于油菜中, 它们对油菜种子含油量可能有比较重要的贡献, 因此对这些位点的精细定位和功能基因鉴定, 对于解析油菜种子含油量的调控机制有重要意义。3.3 油菜A和C亚基因组对种子含油量的贡献
甘蓝型油菜A亚基因组上存在的含油量位点数目显著高于C亚基因组, 并且被多个群体重复鉴定到的位点都分布在A亚基因组上, 这种情况的出现可能与油菜的起源与驯化有关。油菜起源于白菜(B. rapa, AA)与甘蓝(B. oleracea, CC)的杂交与染色体加倍[26], 与甘蓝相比, 白菜籽粒具有更多对含油量有利的性状, 如种皮更薄、色泽更浅等, 因此油菜从诞生之初就可能在A和C亚基因组上存在不对等的影响含油量的位点数。此外, 在自然条件下以及人类的驯化过程中, 甘蓝型油菜很容易与各类白菜杂交, 从而使更多的A基因组遗传成分渗透到甘蓝型油菜中, 并且对性状有利的位点在驯化过程中得以保留。而甘蓝型油菜与甘蓝杂交困难, 即使从C基因组上找到有利位点, 其向甘蓝型油菜中导入或渗透也存在一定难度。与此同时, 油菜群体遗传学研究发现, C亚基因组连锁不平衡衰退距离显著高于A亚基因组[27,28], 可能导致C亚基因组上含油量相关位点缺乏变异, 没有被检测到。综上所述, 从鉴定现有遗传稳定位点的功能基因、聚合多个现有的含油量位点、由亲本物种(甚至其他物种)中导入新的优异位点(基因)、打破油菜C亚基因组强选择瓶颈等入手, 油菜的种子含油量有望得到进一步提高。
4 结论
将GWAS检测到的8个与油菜种子含油量显著关联的位点与其他12个油菜群体的定位结果整合, 构建了一个包含193个油菜种子含油量位点的基因组图, 鉴定到7个遗传稳定的含油量区间, 为提高油菜种子含油量育种提供了参考。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1007/s00122-014-2271-5URLPMID:24504552 [本文引用: 4]

KEY MESSAGE : This report describes an integrative analysis of seed-oil-content quantitative trait loci (QTL) in Brassica napus , using a high-density genetic map to align QTL among different populations. Rapeseed (Brassica napus) is an important source of edible oil and sustainable energy. Given the challenge involved in using only a few genes to substantially increase the oil content of rapeseed without affecting the fatty acid composition, exploitation of a greater number of genetic loci that regulate the oil content variation among rapeseed germplasm is of fundamental importance. In this study, we investigated variation in the seed-oil content among two related genetic populations of Brassica napus, the TN double-haploid population and its derivative reconstructed-F population. Each population was grown in multiple experiments under different environmental conditions. Mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL) identified 41 QTL in the TN populations. Furthermore, of the 20 pairs of epistatic interaction loci detected, approximately one-third were located within the QTL intervals. The use of common markers on different genetic maps and the TN genetic map as a reference enabled us to project QTL from an additional three genetic populations onto the TN genetic map. In summary, we used the TN genetic map of the B. napus genome to identify 46 distinct QTL regions that control seed-oil content on 16 of the 19 linkage groups of B. napus. Of these, 18 were each detected in multiple populations. The present results are of value for ongoing efforts to breed rapeseed with high oil content, and alignment of the QTL makes an important contribution to the development of an integrative system for genetic studies of rapeseed.
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 4]
[本文引用: 7]
URL [本文引用: 4]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
