全文HTML
--> --> --> 随着我国环境保护政策越来越严格,市区内污染较重的工业、企业需要搬迁至郊区或工业园区。但由于原址工业三废的排放以及各种人类活动,可能导致了土壤中有机物的积累[1],主要有多环芳烃、二噁英、多溴联苯醚、多氯联苯、六氯苯、艾氏剂等[2]。针对低沸点有机物污染的土壤,土壤气相提取(soil vapor extraction,SVE)是一种常见的高效修复技术。通过耦合其他技术,可扩大其适用范围。电阻加热(electrical resistance heating,ERH)基于欧姆定律,将电能转化为热能用来提升土壤温度和加热土壤中孔隙水,最终通过气相抽提将污染物转移且处理完全[3]。ERH具有温度低、操作简单、处理周期短、处理效率高等特点,尤其适用于含挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs)、半挥发性有机物(semi-volatile organic compounds,SVOCs)和VOCs-石油混合物污染的低渗透性、高电导率土壤[4]。ZUTPHEN等[5]利用二维沙箱研究ERH强化土壤气相抽提对土壤中三氯乙烯(trichloroethylene, TCE)的修复,TCE的去除率较SVE提升了19倍,最终去除率为99.87%。李鹏等[6]研究发现,相比SVE,ERH强化处理作用下砂土和壤土中苯的去除效率分别提高了13.1%和12.3%。岳昌盛等[7]采用ERH技术修复焦化场地时发现,通过增加保温时间能提高修复效率,并能加快苯和多环芳烃的解吸分离。
影响ERH去除率的因素包括土壤质地[8]、电导率[9]、水分[9]及电场强度[10]等。HAN等[11]发现,水分、盐度是土壤导电性能的主要影响因素,高电流具有较高的加热效率,能够使土壤达到更高的温度。FU等[12]发现,土壤温度与电流直接相关,不同位置土壤温升取决于土壤特性。土壤电导率与孔隙水的饱和度、矿物成分、温度和溶解离子等因素相关,温度升高会促进弱电解质电离,水分可以提供离子传输通道,提高土壤加热效率。杨康等[13]发现,在ERH较低温度时,混合有机物发生负共沸现象,不利于甲苯脱附;在ERH较高温度条件下混合有机物发生正共沸现象,可促进甲苯脱附。田垚[14]针对人工模拟污染土壤及钢铁厂区土壤的修复,发现ERH的最佳条件为:在电场强度8 V·cm?1时,添加6 mL的0.1%NaCl溶液。
COMSOL是一款高度集成的数值仿真软件,基于有限元理论,以高效的计算性能和杰出的多场耦合分析能力实现任意多物理场的数值仿真[15],可以通过建立模型快速研究在多物理场中ERH和SVE的耦合技术对去除率的影响。
梁爽[16]使用COMSOL软件对土壤冻胀过程进行模拟,分析了不同因素对土壤冻胀特性的影响。张明礼等[17]通过COMSOL软件分析了冻土水分对流与温度变化的关系,对于含水量较高的土体,水分对流传热作用不可忽略。焦会青[15]等在COMSOL多孔介质和地下水流模块模拟非饱和土壤水流的基础上,对比了不同活度系数估算方法对模拟结果的影响,发现活度系数的估算对模拟结果的准确性有重要影响,尤其是当盐分较高时。门利利[18]利用COMSOL模拟仿真技术求解土壤水热动力学方程来研究温度场与渗流场的耦合问题,构建了饱和-非饱和流-热耦合模型。
目前,关于土壤的COMSOL模拟都是围绕处理过程中土壤本身的特性而展开的,针对土壤热脱附过程中物理场变化规律的案例比较少。本研究采用ERH和SVE的耦合技术,以土壤温度为探针,采用COMSOL模拟计算不同物理场下场地温度分布规律,分析电极布置参数对土壤温度的影响机制,优化工艺参数,以期为有机物污染土壤场地修复的工程设计提供参数。
1.1. 控制方程
本研究利用COMSOL预置的传热模块,选取固体传热耦合焦耳热的多物理场进行研究,5个模拟假设条件分别为:1)传热过程符合二维、三维模型 2)土壤内部地质均匀;3)土壤的热性能稳定;4)土壤外部认为是绝热的;5)忽略大气中温度波动的影响。该模型主要包括热量守恒方程、电流守恒方程和电磁热控制方程[19]。热传导的控制方程为热量守恒方程,利用局部容积平均法计算(见式(1))。
式中:ρ为质量浓度,kg·m?3;Cp为恒压热容,J·(kg·℃)?1;T为温度,℃;t为升温时间,s;Q为热流密度,J·(m2·s)?1;q是传导热通量,W·m?2;μ是焦耳热,J·s?1。
根据傅里叶定律可得式(2)。
式中:k为固体导热系数(当有高温物体向低温物体传热时k为负值),W·(m·℃)?1。
电流守恒的控制方程见式(3)~式(5)。
式中:Q为电热,J;J为电功,J;E为电势差,V;D为电位移;v为电势,V。
电磁热的控制方程见式(6)~式(7)。
1.2. 模型搭建和网格划分
根据本研究的模拟污染场地条件,将模拟的边界设置为长方体,填充土壤。根据常用电极形状设置为圆柱体,半径为0.1 m,根据场地厚度设置电极高度为3 m,电极及探针排布如图1(a)所示。网格类型为三角单元网格,单元大小选择常规,图1(b)为网格划分图,网格总数为11 114个。1.3. 边界条件和参数设置
模拟过程中设置的边界条件主要包括土壤和电极棒的理化性质,土壤的物性参数设置为:初始温度为20.15 ℃、恒压热容为1 500 J·(kg·℃)?1、导热系数为2.0 W·(m·℃)?1、相对介电常数为8、密度为2 600 kg·m?3;电极棒的材质为铸铁,物性参数设置为:升温范围≤227 ℃、密度为7 000 kg·m?3、电势为380 V、频率60 Hz、导热系数为50 W·(m·℃)?1、恒压热容为420 J·(kg·℃)?1、相对介电常数为6。污染土壤中污染物浓度与时间呈线性或者指数关系,根据美国加州Santa Susana实验室研究报告[20],ERH工程案例中加热周期一般为10~50 d,考虑本研究的实际情况,选择加热周期为40 d。
在电流模块中设置电流守恒,电势的初始值为0,根据所研究的物理场,将电极棒四周的电势分别设置为0或者380 V,将电极棒的四周分别设置为接地和不接地。在固体传热模块中设置土壤和电极棒的初始温度为20.15 ℃,连续性模块中选择与电极棒有关的相同边界,电极棒的温度设置为20.15或227.00 ℃。多物理场模块中设置电磁热,选择所有的土壤和电极棒,耦合接口中的电磁选择电流,传热选择固体传热。
1.4. 电极排布方式
修复土壤的高温区域主要分布在2极间中下部,但其高温区域分布大小、温度峰值与电极布置参数直接相关[21]。本研究主要考虑电极的间距(1、2、3、4、5 m)、电极的边界距离(0.5、1、1.5、2 m)、电极个数(5、6、7)等不同条件下,模型中土壤温度随时间的分布情况。2.1. 物理场耦合的影响
在考虑固体传热时,2个电极棒均为火线电极棒。在考虑电磁热和耦合场时,相邻2个电极棒分别为火线和零线。为验证各物理场的单独作用以及耦合作用的效果,将两电极棒的间距定为2 m,在中点处放置探针测量土壤温度,分别模拟在仅有电极棒的固体传热和电势的电磁热,和2物理场同时耦合3种情况,如图2所示,对比不同物理场下的电势和温度分布。物理场对土壤电阻加热过程的影响如图2(d)所示。在仅有固体传热条件下,土壤最高温度为104.73 ℃,升温84.58 ℃;在单独进行电磁热条件下,温度达到117.15 ℃,升温范围提高到96.95 ℃。耦合模型兼具2个物理场的加热效果,在固体传热和电磁热耦合场辅助作用下,温度在土壤内部发生相互叠加,加热效果会有明显提升,温度升至201.20 ℃,同时比单物理场最高温度提高了85.10~96.50 ℃。但耦合场不仅仅是2个单独场的热量相加之和,中间还存在一些热量的损耗,所以耦合场升高的温度会略低于2单独场的温度之和。
有机污染物在多孔介质土壤中的迁移脱除包括脱附和扩散等过程。土壤吸附性对污染物运移有迟滞作用,因此温度越高,土壤中的有机污染物脱附效果会越好。土壤中的含水量影响土壤的导电形式,以及土壤的电阻率和导电性[22]。在ERH修复过程中,通常以土壤和土壤中的水分为天然导体,使得电流在电极之间流动,利用焦耳热加热土壤。在渗透性较高的土壤场地下,可在电极附近加入水或电极液,这一方面降低渗透性,也可以防止电极附近的土壤干化,从而影响正常的加热进程[23]。因此,当电场和热场耦合时,通过加热使土壤中水分蒸发,增加土壤电导率,提高土壤升温速率,利于有机物脱除;此外,土壤中水分有利于热量的散出从而可以使得更多的有机污染物从土壤中蒸发脱附[24]。
2.2. 电极间距的影响
钟林[25]在研究多热源加热土壤过程中发现,温度梯度是影响导热系数的重要因素,热源电极棒间距对土壤温度变化影响很大。将电极之间的水平间距分别设置为1、2、3、4、5 m,在2电极中部加入探针,以研究固体传热和电磁热耦合下,电极间距对土壤温度分布的影响。不同间距下的温度等值面如图3所示。1 m和2 m处在加热40 d后升温307.63 ℃和180.93 ℃,温度升高快,加热效果较好,超过了ERH工程的升温范围;3 m处在40 d后升温104.71 ℃,升温速度快于4 m和5 m处。根据某ERH工程案例[26]可知,电阻加热的处理时间为14~56 d,ERH工程上的升温范围需要达到100.15~120.15 ℃。从图3(f)可以看到,电极间距为1、2、3m条件下满足加热温度的要求,可在周期内完成加热任务。其中,电极间距为3 m时,处理成本适中,为最佳间距。
电极间的距离过近,加热范围会发生叠加,影响加热的均匀性,无法将加热效果发挥到最大[27]。电极间距的增大会导致高温区域不断扩大,峰值升高,但也需要考虑模型的大小范围,选取适中间距,保证资源节约利用。适宜的电极间距既可以节省成本,也可以达到加热效果,使土壤中的有机污染物的脱除过程更加节能。
2.3. 电极的边界距离的影响
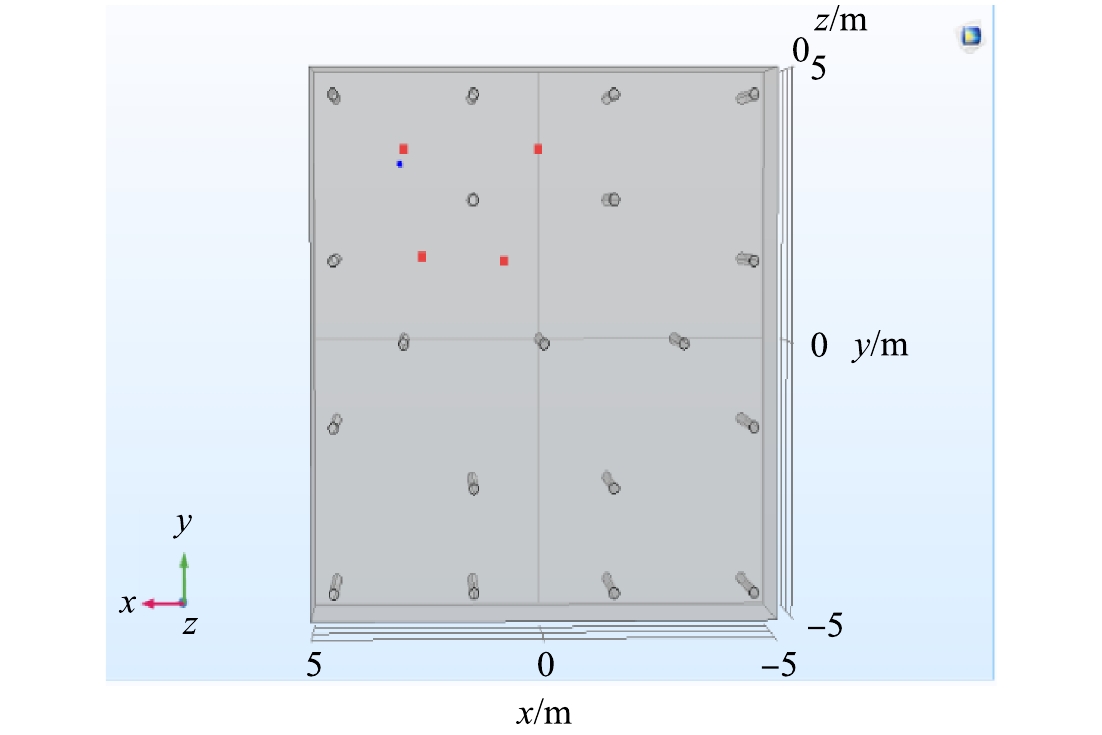
电极棒排布如图4所示。其中,选取电极棒距边界为0.5、1、1.5、2 m,在固体传热和电磁热耦合,热物理场为边界下依次进行模拟。选取了坐标为[5,5,0]、[3,5,0]、[5,0,0]、[5,3,0]的探针,依次比较各电极边界处的温度变化。如图5所示,当边界距离为1、1.5、2 m时,不能满足ERH工程的升温范围(100.15~120.15 ℃)的要求,当边界距离为0.5 m时,基本符合加热需求。可见电极距边界越远,加热效果越差,过远的距离会使电极无法对土壤加热充分,加热温度不够会导致对土壤中的有机物脱除不够充分,影响脱除效果,故采用0.5 m作为边界距离。2.4. 电极个数的影响
根据2.2节和2.3节报告的模拟结果,在4条边等距离设置12个火线电极棒,与边界间距为0.5 m,边界设置为热物理场。在剩余空间内分别布置5~7个电极,火线和零线间隔排布,间距为3 m,物理场设置为固体传热和电磁热耦合。以[0,0,0]坐标为中心,5个电极、6个电极分别采用正五边形、正六边形排布,7个电极在正六边形的中心增设1个电极。在相邻电极的中点位置分别设置4个温度探针,比较电极个数对土壤温度分布的影响。不同电极个数下温度分布如图6所示。其中,相同电极棒数量下,不同位置探针测得温度的差异是由于土壤热阻和传热滞后性所导致的[28]。根据电极的平面布置图,7电极的电极个数更多,相对于五边形和六边形分布更加均匀。通过图6(d)的对比发现7电极布置图的温度分布更加均匀,平均的温度为153 ℃,较其他布置相比,不论是加热的面积、效果以及均匀性条件,均为上述布置图样中的最佳。可见,在一定范围内,适当的电极间距,尽可能使电极排布充满整个模型,能使加热效果更佳。通常,电极排布越均匀,土壤加热的越充分,土壤的导热性也越强,均匀的升温使得土壤中的有机污染物脱附越容易[29]。
此外,土壤中有机污染物的沸点与其组分和挥发性相关[30],通过设置最优的电极个数及排布方式,使土壤温度与有机物蒸发温度接近,从而在实现有机污染土壤修复的同时,降低能耗和投资运行费用。
2.5. 耦合物理场边界的空间的影响
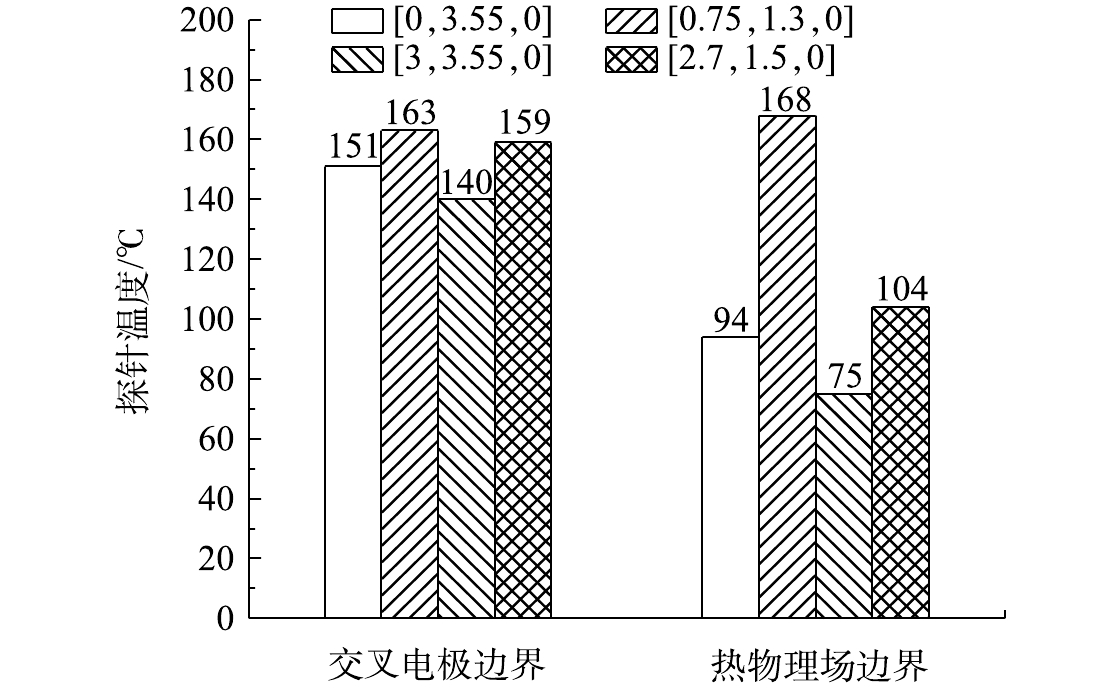
为更好地减少加热盲区,提高整体加热效果,将热物理场边界替换为耦合物理边界。在图4基础上,将火线电极棒和零线电极棒交叉排布,形成耦合电磁热的物理场。将2.4节优化所得7个电极置于模型中,探针排布如图7所示,4个探针的位置分别为[0,3.55,0]、[0.75,1.3,0]、[3,3.55,0]和[2.7,1.5,0]。由图8可知,在交叉电极边界条件下,4个探针的温度分别是151、163、140、159 ℃,最低温度为140 ℃,较热物理场边界升高65 ℃。可见交叉电极边界升温效果更明显,更能符合加热的需求,故采用交叉电极边界进行ERH的优化。电极加热效果最好的位置是2电极的中下方,对于无法充分加热的边界土壤,交叉边界耦合了电磁热边界和热物理边界,使模型内土壤整体加热更充分,有益于土壤修复。
2)在加热40 d后,电极间距为3 m处升温104.71 ℃,满足加热温度的要求,可在修复周期内完成加热任务;此加热方案处理成本低,更有利于污染物脱除。
3)当边界距离为0.5 m时,边界土层温度能够达到100.15~120.15 ℃温度修复范围。
4)不论是加热的面积、效果以及均匀性条件,7个电极排布都比其他排布方式的升温速率更高。
5)将热物理场边界替换为耦合物理边界的交叉电极边界排布使得ERH升温效果更明显,更能符合加热的需求。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: 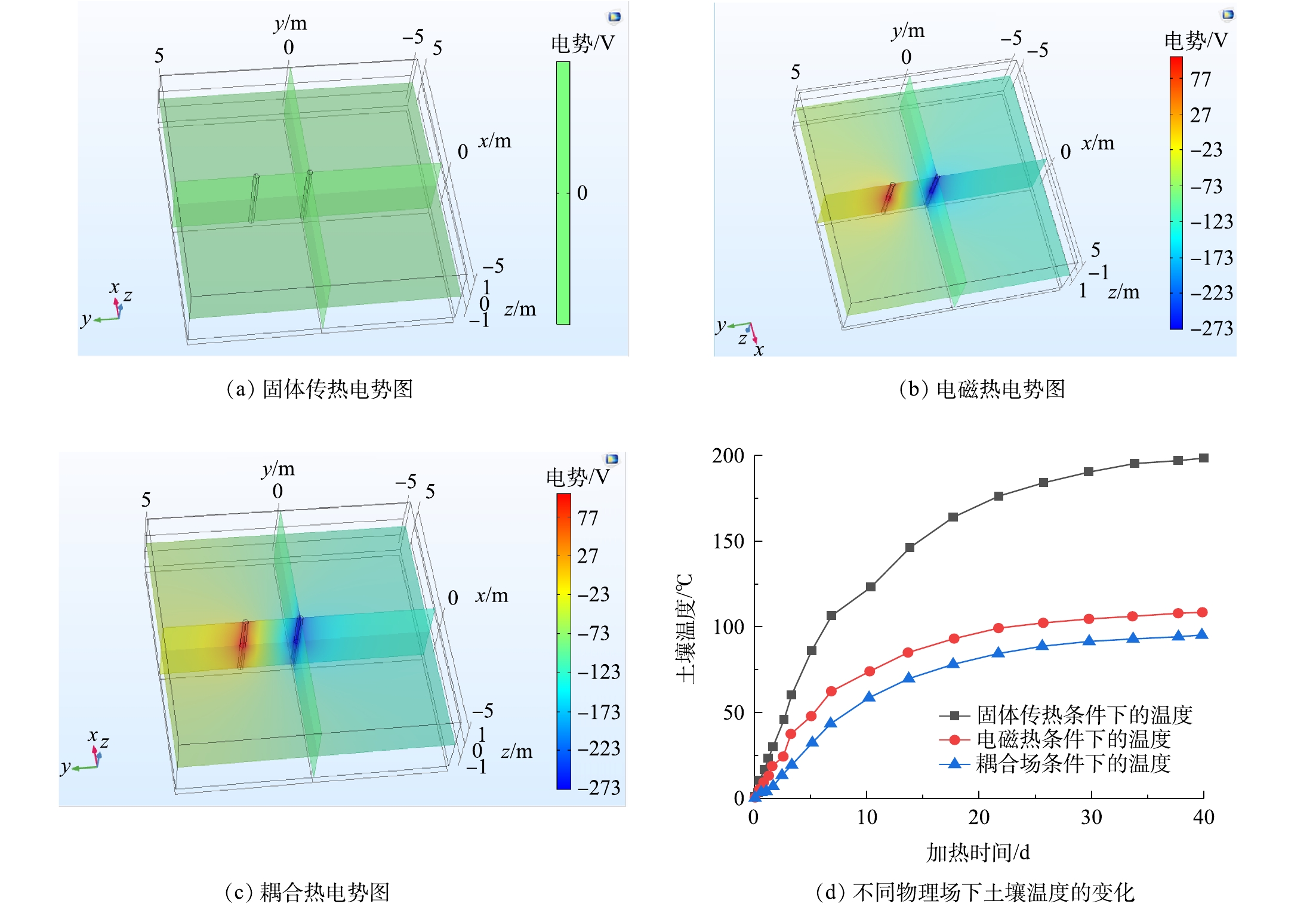



 点击查看大图
点击查看大图