全文HTML
--> --> --> 近年来,我国垃圾产生量不断增加[1]。据《中国统计年鉴》,2019年我国城市生活垃圾清运量已经达到了2.42×108 t,焚烧处置占生活垃圾清运总量的50.7%[2]。然而,由于我国入炉垃圾组分复杂多变[3-4],粒径、组分、含碳量、含水量等特性均有所不同[5],导致入炉垃圾热值波动大,容易造成垃圾给料不均匀,这不仅影响会焚烧炉的稳定运行,而且会增加污染物的排放[6]。任超峰等[7]提出,通过双螺旋给料,可以保证垃圾松散、少量、连续入炉,从而尽可能减小对炉膛的扰动,使炉膛保持负压平稳运行;吕国钧等[8]在双螺旋给料的基础上,提出采用多级、多点给料口,以提高燃烧的稳定性。上述方法对给料设备进行改造,有效提升了给料的均匀性。但是,设备结构上的改造并不能实时定量控制给料量的均匀度,仍需要安排人工实时注视监控屏幕,观测料斗内堆料量、焚烧炉燃烧参数,如炉膛温度、炉膛出口烟气含氧量、火焰图像等,并通过不断调整控制铰刀的开关和绞龙频率,以实现相对均匀的给料。因此,给料稳定性与司炉人员的操作经验、熟练度有着极大的关系。而且,人工操作存在惰性,不可避免地会出现因反应不及时等因素引起给料波动或给料速率与炉内氧量不匹配,使得焚烧工况难以稳定[6],从而增加了CO、二噁英等污染物的排放[9-10]。通过测算垃圾料斗内垃圾体积量的变化来实时获取垃圾焚烧炉进料速率,将进料数据接入智能分散控制系统(DCS: Distributed Control System),可以实现进料量的早期预警、实时反馈和自动优化控制,能够确保垃圾焚烧炉稳定运行,以达到提高运行寿命、发电效益以及焚烧过程清洁水平的目的[11]。随着现代工业自动化的快速发展,传统的接触测距方法已无法满足垃圾焚烧系统对测量范围、精度、实时性、动态性的要求[12]。非接触式测量方式与传统接触测距相比,以其精度高、操作方便、节约人力物力、可在恶劣环境下工作等优势,被越来越广泛地应用于垃圾堆料、煤堆料、粮食堆料等体积测算领域。其中,机器视觉已在国内外被广泛应用于工业控制领域。目前,根据机器视觉的实现原理主要可分为3类:单目视觉、双目视觉及多目视觉[13]。双目视觉技术具有较高的测距精度和较低的硬件成本而被广泛应用[14-15]。毛佳红等[16]于2016年为克服双目立体视觉系统特征提取及匹配困难,提出采用线结构光与双目视觉技术结合,通过三维建模,积分求取规则物体的体积,相对误差可低于2%。李红卫[17]于2019年设计了基于格雷码和相位移结合的结构光的双目视觉散装堆料体积测量系统,能够将测量相对误差控制在5%以内,但该方法结构光系统复杂,抗干扰性弱。丁嗣禹等[18]于2020年提出了一种不规则堆料体积测量方法,首先采用半全局块匹配算法进行立体匹配,然后使用改进的OTSU阈值分割算法提取目标区域,最后求取堆料体积。
双目视觉测量方法的关键技术难点在于特征提取和匹配,对于利用该技术测量纹理特征不明显,表面结构不规则的物体需采用辅助光源,宜简化特征提取和匹配的难度,以提高算法执行的速度和输出结果的精度。选用合适的技术应用于垃圾料斗内垃圾量的实时测算尤为重要,这需要能够在实现垃圾堆料体积测算的同时,提高测量精准性、实时性,为垃圾焚烧炉给料端智能调节进料速率提供数据支撑,以最终实现垃圾焚烧过程智能化控制。为减少垃圾焚烧炉料斗内光线暗、垃圾表面弱纹理等复杂条件的影响,提出了一种精度高、经济性好的基于双目视觉耦合激光的入炉垃圾进料速率实时测量技术[19],并通过实验模拟了料斗内垃圾量的测算,同时对某垃圾焚烧电厂进行了经济性分析。本研究可为实现垃圾焚烧电厂给料系统的智能化提供参考。
1.1. 双目视觉原理
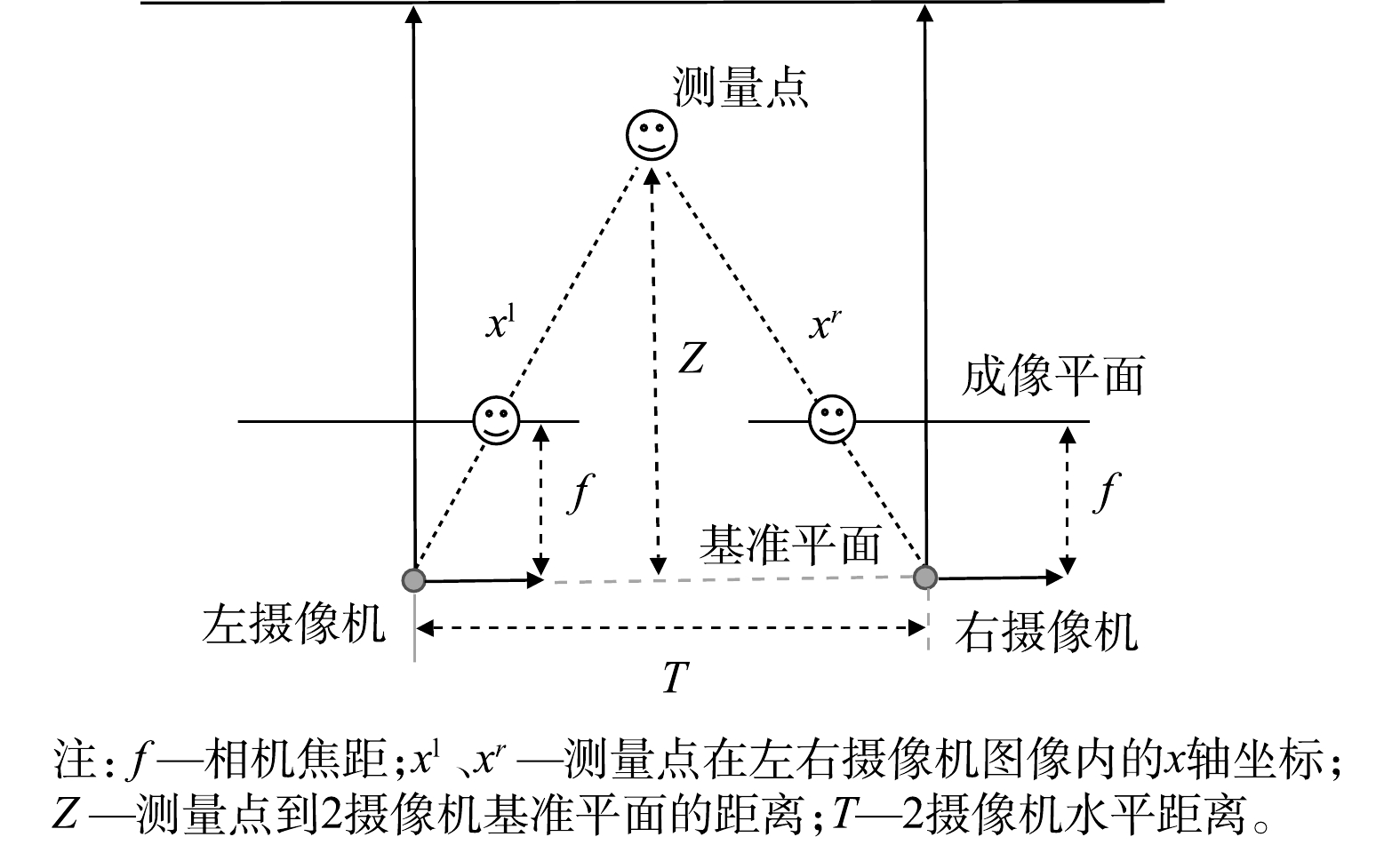
双目视觉测量方法通过2个摄像机同时拍摄同一图像信息,空间点在2个摄像机的像平面上的成像点存在视差,根据视差原理可求解图像的深度信息[20],双目视觉测距原理图如图1所示,计算公式见式(1)和式(2)。式中:Z代表测量点到2台摄像机的基准平面距离,mm;f为2个摄像机的焦距,mm;T为2摄像机水平距离,mm;


1.2. 基于双目视觉耦合激光阵列堆料体积测算实现步骤
根据目前垃圾焚烧炉料斗内的现场环境,本研究提出将激光耦合到双目视觉测距系统中[19],以克服垃圾层表面纹理弱、特征匹配困难等问题。基于双目视觉耦合激光阵列测距系统主要包含3个子系统,分别是激光阵列系统、图像采集系统和图像处理系统,其原理示意图如图2所示。激光阵列系统由若干个线激光器平行排列组成,能够将线激光均匀照射到垃圾层表面,从而为灰黑色弱纹理的垃圾图像添加明亮且区分度明显的条纹作为特征值。图像采集系统包含2个高清摄像头及其固定设备和防干扰设备,2个高清摄像头组成了双目相机,将双目相机固定在垃圾料斗上方;防干扰设备主要是镜头清洁装置,以清除镜头上的水雾和污渍,通过垃圾图像的模糊程度来判断镜头清洁装置是否工作。图像处理系统及为计算机处理系统,主要功能是对采集到的具有激光阵列特征的垃圾图像进行处理、识别、计算,并将得到的垃圾体积结果反馈给控制系统。其中,计算机处理系统消耗时长为秒级,随着建模精度的提高而增长,应根据实际现场及控制需要调节建模精度及计算时长。系统具体的工作流程分为6步。1)图像获取。在堆料上方不受投料设备遮挡处安装激光阵列,将激光阵列打在堆料表面,确保激光阵列能够均匀分布于垃圾堆料表面,通过双目相机获取堆料表面的左右图像,并通过多次测试确定激光阵列安装的最佳位置。
2)相机标定。调用MATLAB中的stereoCameraCalibrator工具箱,使用棋盘标定法[21],对双目相机进行内外参数以及畸变系数的求解,并定期根据激光阵列位置的调整或相机的偏移进行参数标定。
3)图像预处理。根据相机的标定参数,对所获取的左右图像进行校正,并对图像进行灰度化、二值化、中值滤波、形态学处理和Canny边缘检测等,降低后续步骤的误差和计算量。
4)图像匹配。对预处理后的左右图像的精准匹配,寻找左右图像中的对应点,并根据公式(2)计算出2张图像的视差值。
5)三维重建。根据视差值和公式(1)计算出图像中各特征点的深度信息,并根据各特征点的位置信息和深度信息还原三维立体图像。
6)体积计算。根据积分原理,对还原的三维立体图像进行体积求解。
1.3. 实验模型
本研究将模拟实际垃圾焚烧炉的料斗,通过沙盘模型验证上述所提双目视觉耦合激光阵列智能体积识别系统的可行性及准确性。首先,选用型号为LRC10190_1080P的USB工业变焦摄像头作为实验摄像头,并将2个摄像头并排固定形成双目相机,用游标卡尺测量2个镜头中心之间的距离;其次,选用弱纹理、表面特征难以匹配的沙土来模拟料斗内的垃圾堆料;然后,将细白色纸条模拟激光阵列照射在垃圾堆料表面的效果;最后,通过USB接口连接到计算机处理系统,编写MATLAB视频图像读取和垃圾堆料体积测算代码,开发MATLAB程序,实时获取堆料体积信息。2.1. 相机标定及图像校正
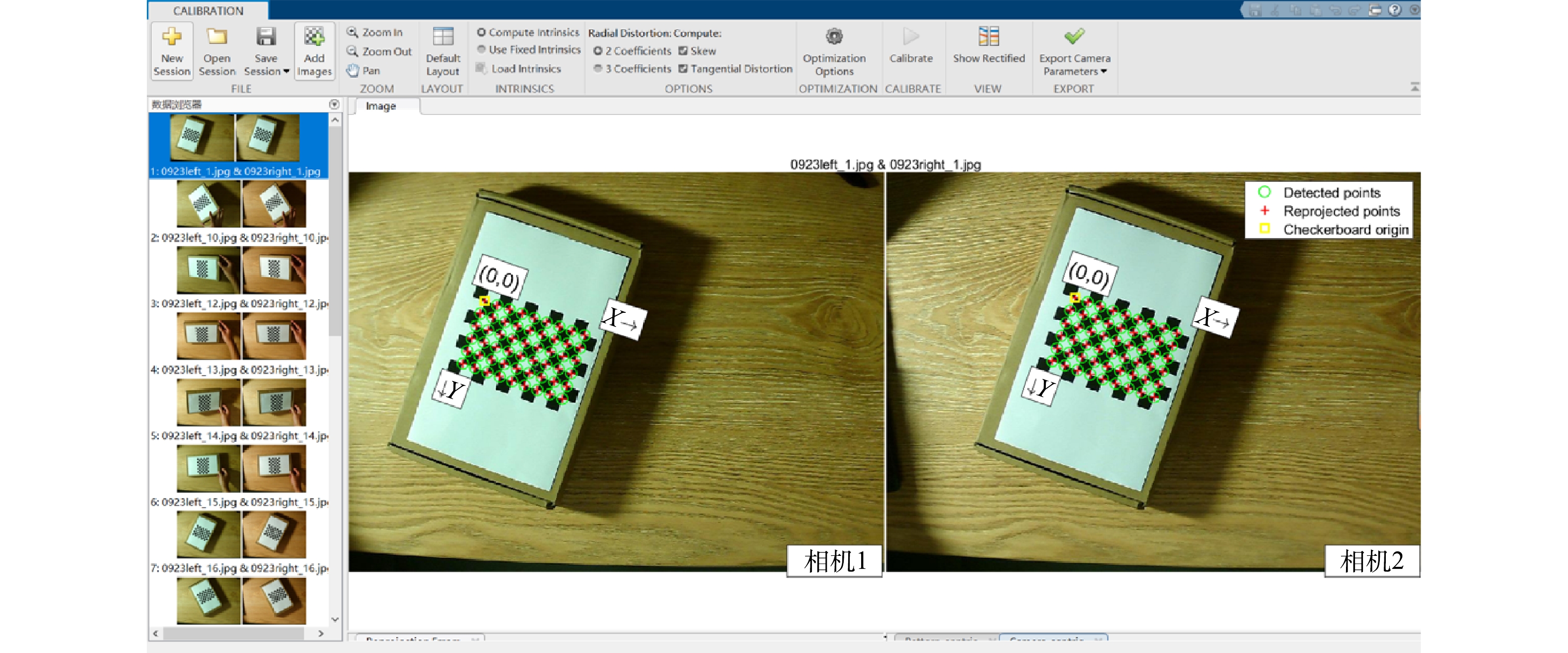
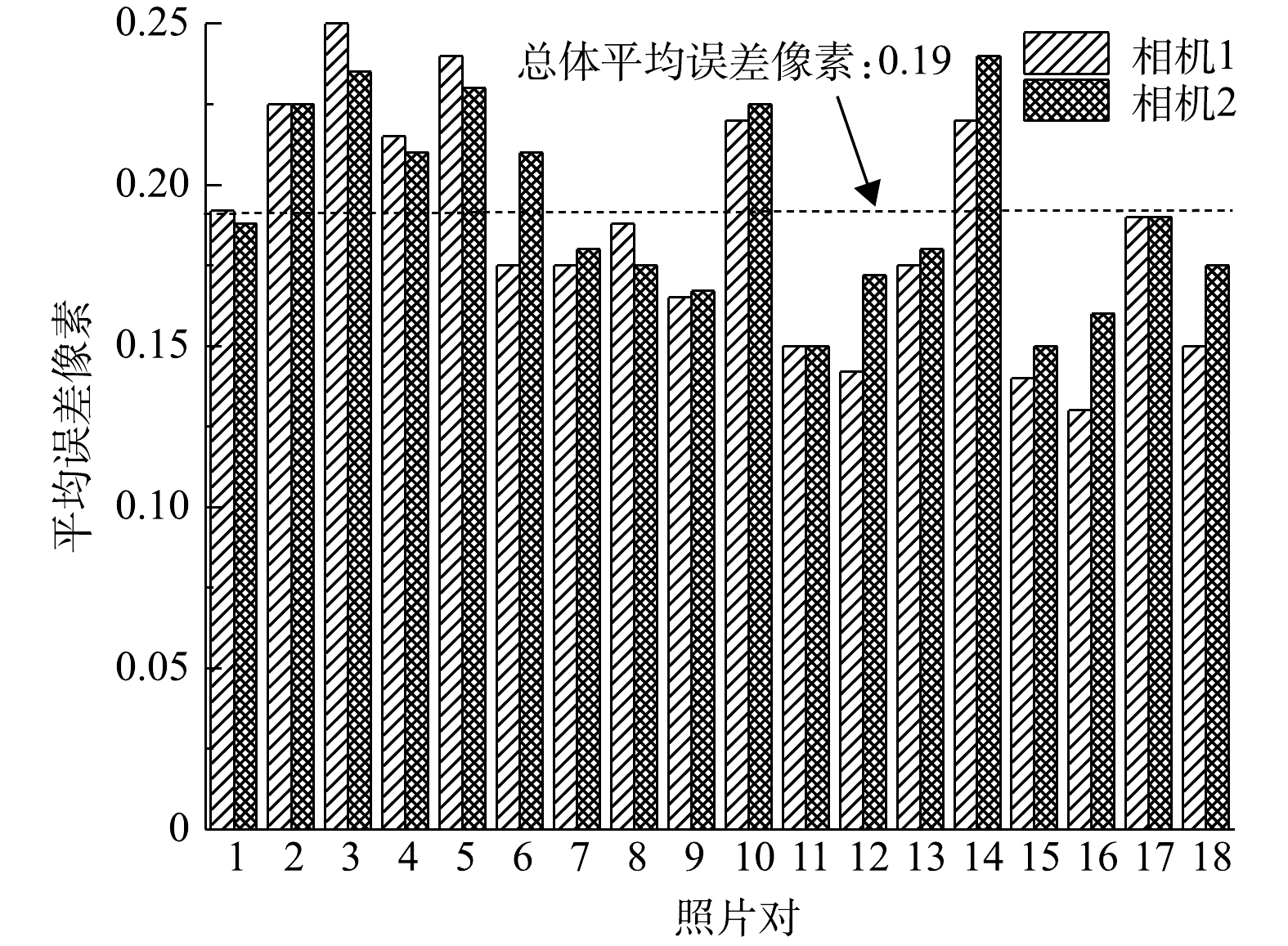
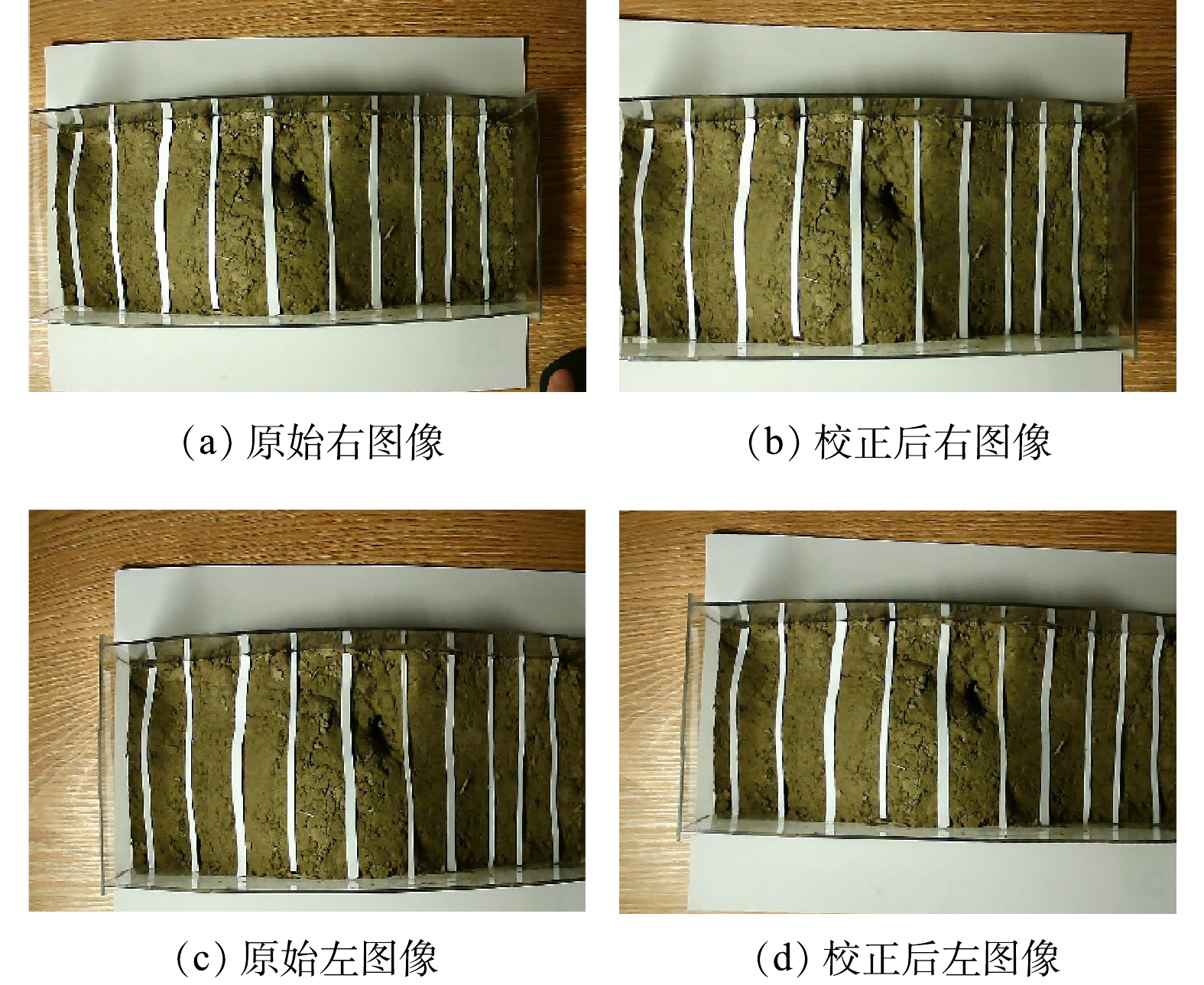
在双目视觉的测量过程中,相机标定是最重要的一环,标定结果的好坏,直接影响后续识别精度质量的高低。利用MATLAB中的stereoCameraCalibrator工具箱,使用张正友棋盘标定法[21],固定住双目摄像头组,调节2摄像头对焦环,使得成像图片的清晰度达到最高,并锁紧调焦旋钮。根据如图3所示的棋盘标定法,通过摆放不同位置拍摄18组不同的标定图像,导入MATLAB标定库,进行角点提取和相机标定,获得左右摄像头的内外参矩阵与畸变系数。通过双目相机标定,得到了相机的内外参数矩阵,其中内参矩阵是用来矫正图像的,包括5个参数,3个径向畸变参数k1、k2、k3和2个切向畸变参数p1、p2[22]。矫正之后的双目相机以及标定板的大致视图以及平均误差直方图如图4所示,最终使得平均误差小于0.2个像素点。图5为沙盘原图及相机标定之后的矫正图对比,可以看出,原始的沙盘模型边缘处存在一定程度的弯曲,呈弧形(图5(a)和图5(c)),这是由于相机镜头存在畸变导致的;经过矫正之后,可以看出,边缘线条变直(图5(b)和图5(d)),这是通过相机标定的径向畸变矫正参数实现的。
2.2. 立体匹配及视差计算
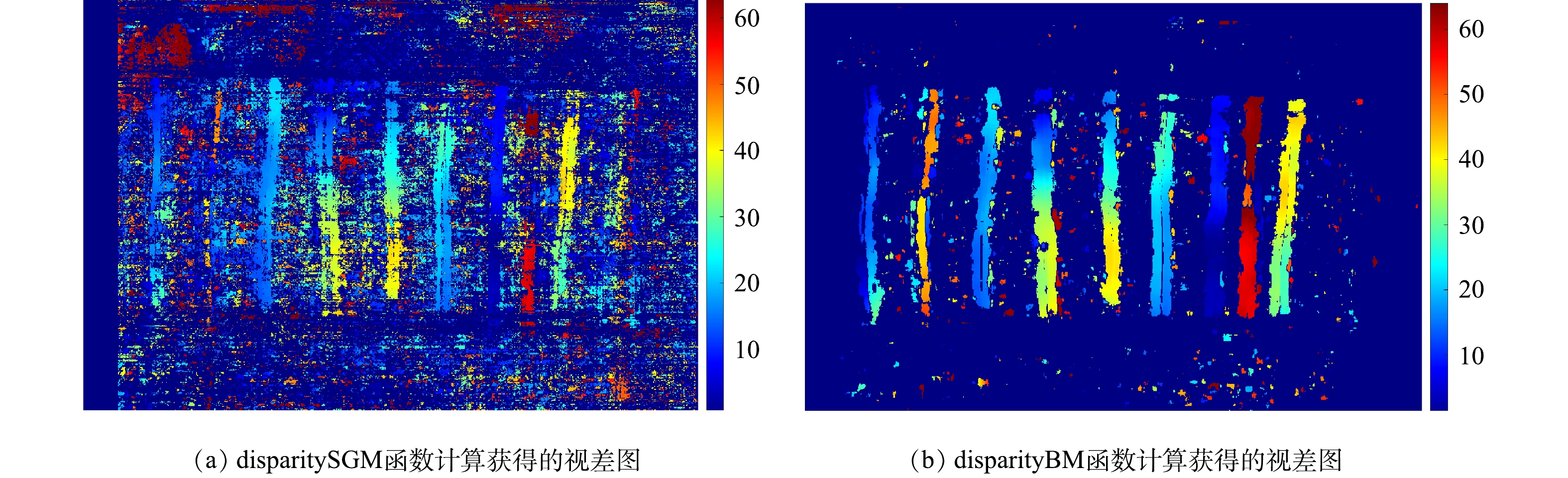
立体匹配作为双目立体视觉的关键部分,它的精度直接影响视差图及深度图的质量。因此,在双目视觉领域对立体匹配算法的精准性研究一直以来都是热点。传统的立体匹配算法主要是通过对窗口内的匹配代价进行求和或求平均值来执行[23]。随着深度学习算法的不断发展以及其应用领域的不断开拓,深度学习方法可以将匹配代价计算、代价聚合以及视差计算等步骤整合到卷积神经网络(convolutional neural networks,CNN)中,进而估算出图像的视差值[24]。深度学习算法对数据集和计算机的算力均有较高的要求,否则会影响运算的准确性和实时性。因此,基于深度学习的立体匹配算法不适合应用于本研究所述场景。本研究首先利用MATLAB中集成的匹配算法,如Semi-Global匹配算法[25]对经过预处理的双目图像进行匹配,并利用距离公式计算出深度信息;利用MATLAB中的disparitySGM和disparityBM函数计算获取视差图,如图6所示。根据实际土堆模型可以判断使用MATLAB集成的模板匹配函数误差较大,且比较模糊,无法用于三维立体建模。因此,本研究通过自行编写特征匹配算法,进行双目图像的视差计算。具体实现步骤为:首先,对预处理后的左图像,从左到右进行像素点遍历,直到遇到第一次灰度值梯度变化,且像素点个数大于阈值,则判定为第一根特征线,并记录下x轴的位置信息xl;之后,对预处理后的右图像进行相同操作,并记录下x轴的位置信息xr;然后,依此进行后续特征线的识别及x轴位置信息的记录;最后,将左图像中特征线的x轴的位置信息减去右图像中特征线的x轴的位置信息,即视差:xl?xr。
2.3. 模型计算结果验证
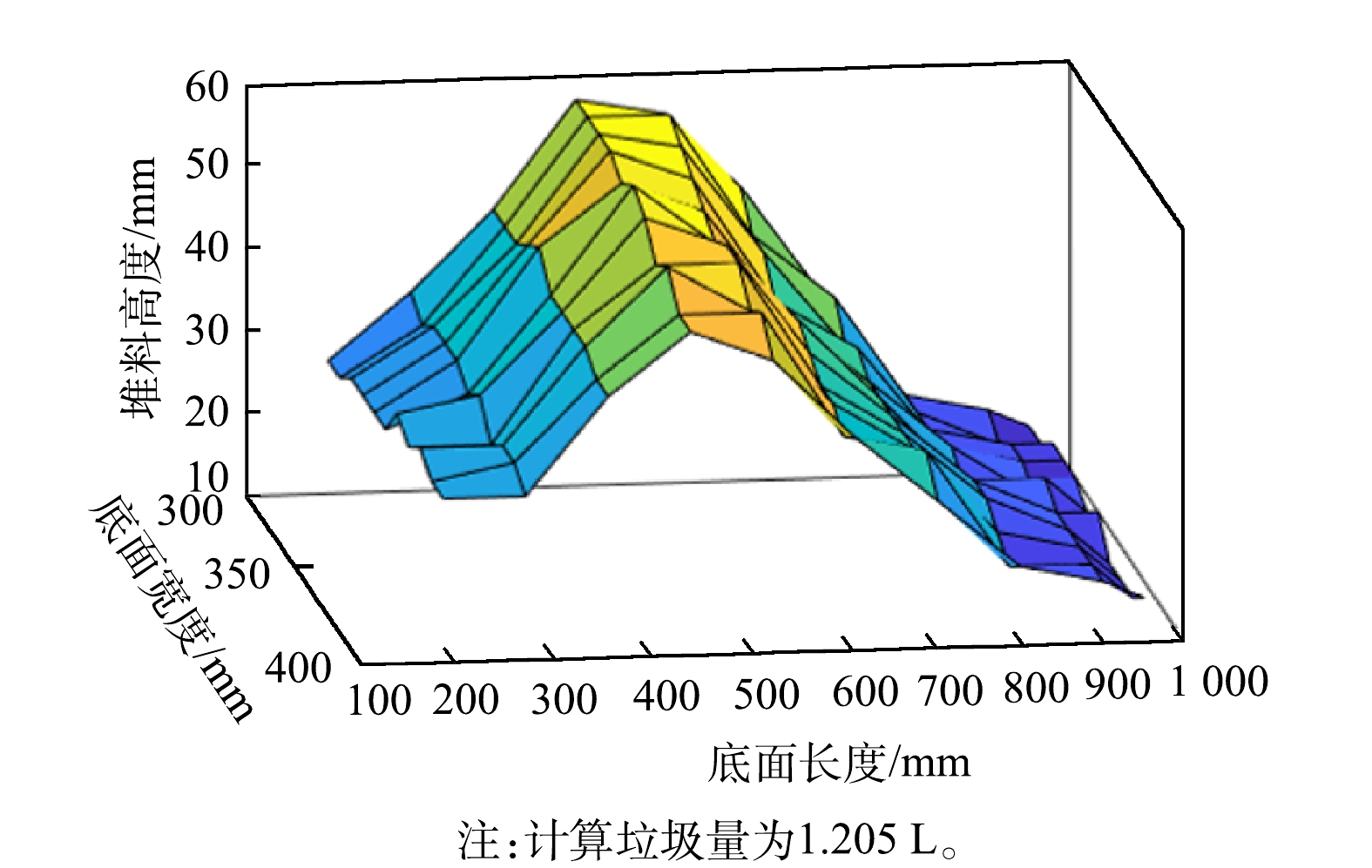
将校正后的左右图像输入到图像预处理程序,对左右图像依次进行灰度化、二值化、中值滤波、Canny边缘检测等预处理操作;随后,利用自行编写的特征匹配算法对预处理后的图像进行立体匹配并通过公式(2)计算出视差值,通过三角形相似原理即公式(1),计算出待测点到摄像头之间的距离,即料位高度;最后,通过各特征点的料位高度建立三维模型,利用积分原理计算出料堆体积。使用MATLAB中的可视化程序设计功能,将上述堆料体积计算模型设计成可视化程序,图7为利用MATLAB程序获得的三维建模图,通过三维建模图计算得到垃圾量为1.205 L。实验前,将沙土均匀地填充于长方体容器中,保证沙土上表面平整,测量长方体容器地面长、宽以及沙土高度,并计算获得实验所用沙土的实际体积为1.2 L。将上述测量后的沙土重新任意堆放,并通过本研究提出的双目视觉方法测量体积值,结果如图7所示,沙土体积测量值为1.2 L,与实际测量值相比,准确度高达99.5%,证实了模型实际应用于垃圾焚烧炉给料端的可行性。实验中发现,适当提高激光阵列中线激光的排列密集程度,可以增加垃圾层三维表面结构重构的准确性,从而减小体积测算的误差。将上述体积测算模型应用于垃圾焚烧炉的给料端,可以计算特定时间间隔料斗内垃圾堆料体积变化值,例如获取间隔前后1 min的体积值,将2个体积值相减便是该时间段内入炉垃圾的平均进料速率,将其反馈给控制系统,通过监控焚烧炉内的温度、火焰图像、含氧量等运行参数,提前调整进料速率。
实验证实,双目视觉耦合激光的垃圾料斗内堆料量检测技术,弥补了垃圾堆料表面纹理弱,传统双目视觉技术特征点难以匹配的缺陷,提高了垃圾焚烧炉给料的精准性和稳定性,可在垃圾焚烧电厂现有设备的基础上进行简单改造就能实现给料的智能化。上述技术可以快速准确地检测出垃圾堆料体积,通过体积检测方法能够进一步计算出单位时间的给料量。给料系统记录下单位时间进入焚烧炉的垃圾体积量后,自动控制系统通过炉内燃烧参数的反馈,通过粒子群算法、蚁群算法或遗传算法等优化算法,计算出该时刻垃圾状况下焚烧炉最优的给料速率及配风,将大量进料速率数据与炉内运行参数关联后,建立新型数据库;通过深度学习框架训练神经网络,建立故障预警[26-27]、参数预测[28]和优化控制模型;通过预测运行参数的变化以及事故判别,提前调控进料速率,实现垃圾焚烧炉进料端的智能控制,进一步推动垃圾的智慧焚烧[29]。随着机器视觉技术的不断发展,硬件设备的更新迭代,以及深度学习算法的不断优化,在进料端使用RGB相机拍摄垃圾图像,通过卷积神经网络预测垃圾热值[30],并结合入炉垃圾进料速率,将入炉垃圾实时热值反馈给垃圾焚烧炉的控制系统,将彻底解决垃圾给料控制滞后问题,提高垃圾焚烧炉燃烧的稳定性,实现焚烧炉高效稳定燃烧,以及一氧化碳、二噁英等常规与非常规污染物超低排放控制。
2.4. 成本分析
根据调研,某垃圾焚烧发电厂日处理垃圾量为1 300 t·d?1,国内垃圾密度约为400~700 kg·m?3[31]。购置2个高清工业远心摄像头成本约4 000 元,另外添加摄像头固定和防干扰设备约为2 000 元,该系统对计算机配置要求不高,可直接使用中控室现有计算机;人工成本按每人每月5 000 元计,垃圾焚烧电厂共有3个给料斗;不论是人工操作还是双目视觉检测均涉及摄像头的维护,于是默认维护成本均为每年1 000 元,工业摄像头一般寿命在5 a以上,按照5 a为1个周期计算成本。如表1所示,人工操作所需成本总计为90.5×104 元,而使用本研究所设计的基于双目视觉检测的智能控制系统仅需2.3×104 元,人工操作成本远远高于智能控制的成本。2)成本分析结果表明,利用双目视觉技术检测垃圾堆料体积,不仅能够提高垃圾焚烧炉给料的精准性和稳定性,而且相比现有的人工操作,大大降低了运行成本。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 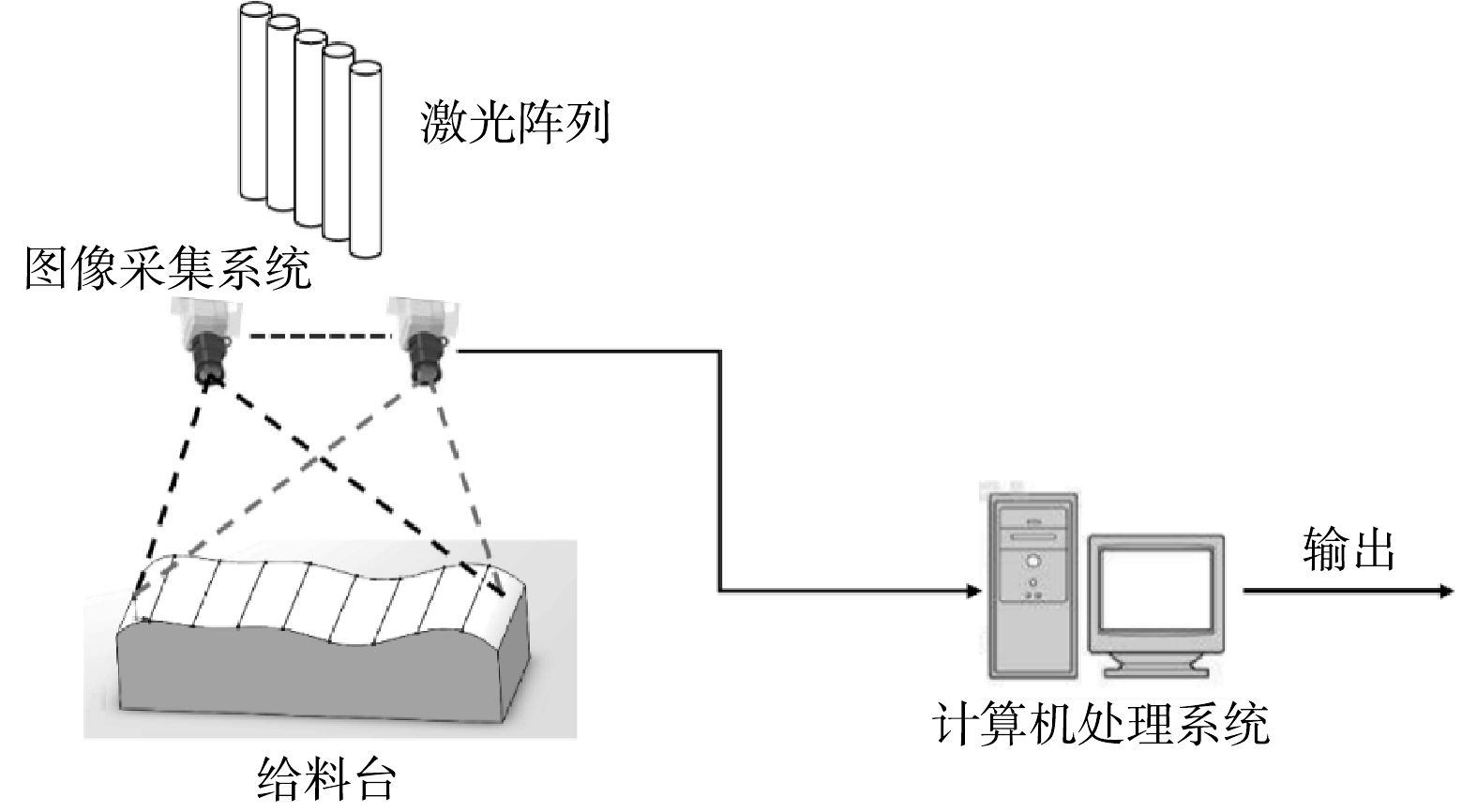
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图