全文HTML
--> --> --> 大气环境颗粒物中的铬(Cr)主要以三价铬(Cr(Ⅲ))和六价铬(Cr(Ⅵ)) 2种价态存在。Cr(Ⅲ)是人体进行糖类和脂类等代谢活动必不可少的微量物质;Cr(Ⅵ)则是剧毒物质,具有致癌性。1990年,美国的《清洁空气法》将Cr(Ⅵ)化合物列入188种有害空气污染物,美国环境保护局也将其列入18种核心污染物[1]。我国的《环境空气质量标准》规定其年平均浓度限值为25 pg·m?3[2]。近年来,相关****围绕Cr这种环境颗粒物中重要的有害过渡金属[3-5],展开了Cr的污染特征和来源解析、潜在生物危害和健康风险评估以及在环境中可能存在的化学作用等[6-9]方面的研究。大气颗粒物产生化学过程往往只持续较短时间(大约几个小时)。切实模拟和研究其产生、传输、消耗的动态过程,需要在该时间精度内进行分析测定[10-11]。在高时空分辨率背景下,研究大气化学过程中过渡金属的污染特征,可为探索此类气溶胶的理化特性、并控制其潜在毒性提供重要见解。建立灵敏而可靠的测量方法需要解决3个问题:1)如何提高测量的灵敏度(达到更低的检测限);2)如何降低测量过程中的潜在干扰;3)如何在处理和测量过程中降低样品中待测物质的损失。目前,多数研究者倾向于使用原子吸收光谱技术测定样品中的总Cr,包括火焰原子吸收光谱法(FAAS)、石墨炉原子吸收光谱法、电热原子吸收光谱法(ET-AAS)等[12-13]。但是,此类方法的样品前处理较为繁琐,所需仪器设备造价昂贵。紫外/可见光分光光度法(UV/Vis)灵敏度很高,通过适当的显色试剂进行络合反应可在高吸收率条件下测量水溶性金属,常被用于溶液中金属浓度的高精度测量[14-15]。以此为基础,可通过配备长光液体波导毛细管来实现UV/Vis定量测定环境样品中的水溶性金属[16-17],结合测量系统的开发,还能有序测量环境颗粒物样品中的金属浓度[18-19]。
结合采样和前处理操作,设计并评估了一种基于分光光度法连续测量大气环境细颗粒物(PM2.5)中铬浓度的系统,以便于精确了解大气颗粒物中铬的污染水平及其来源,提供一种测量环境大气中水溶性痕量金属的思路,以期为开发实际监测技术奠定基础。
1.1. 试剂标准
实验所需化学药品纯度至少为光谱纯,配制的试剂和溶液使用由纯水机(Smart-DUV(F) SAIDE)生产(电阻率不低于18.2 MΩ)的超纯水和去离子水。用于试剂配制的实验器材和试剂保存的聚丙烯瓶在使用前均先用浓度为4 mol·L?1的HCl进行清洗,然后用超纯水反复冲洗干净后烘干置于干净环境中备用。用于标定和校准的Cr(Ⅵ)标准溶液通过用重铬酸钾(K2Cr2O7,纯度为99.9%)和去离子水制备的100 μg·m?3母液稀释获得,在使用前取母液用去离子水稀释到需要的浓度梯度(0.5~8 ng·mL?1)。制备4 mol·L?1的HNO3和3 mol·L?1的NaOH用于酸化和调整溶液pH。用于前处理过程的0.1%的H2O2试剂通过用0.1 mol·L?1的NaOH溶液将0.044 mL 30%的H2O2水溶液定容稀释至1 L制备。将167 mg的二苯碳酰二肼(diphenylcarbazide,DPC)溶解于100 mL的丙酮(C3H6O,纯度为99.9%)中,再与1.67%的H2SO4溶液按照1∶1的体积比混合,制备用于光度法检测前络合反应的DPC试剂[16]。除Cr(Ⅵ)标准溶液,所有的试剂均不含铬。
1.2. 样品采集与预处理
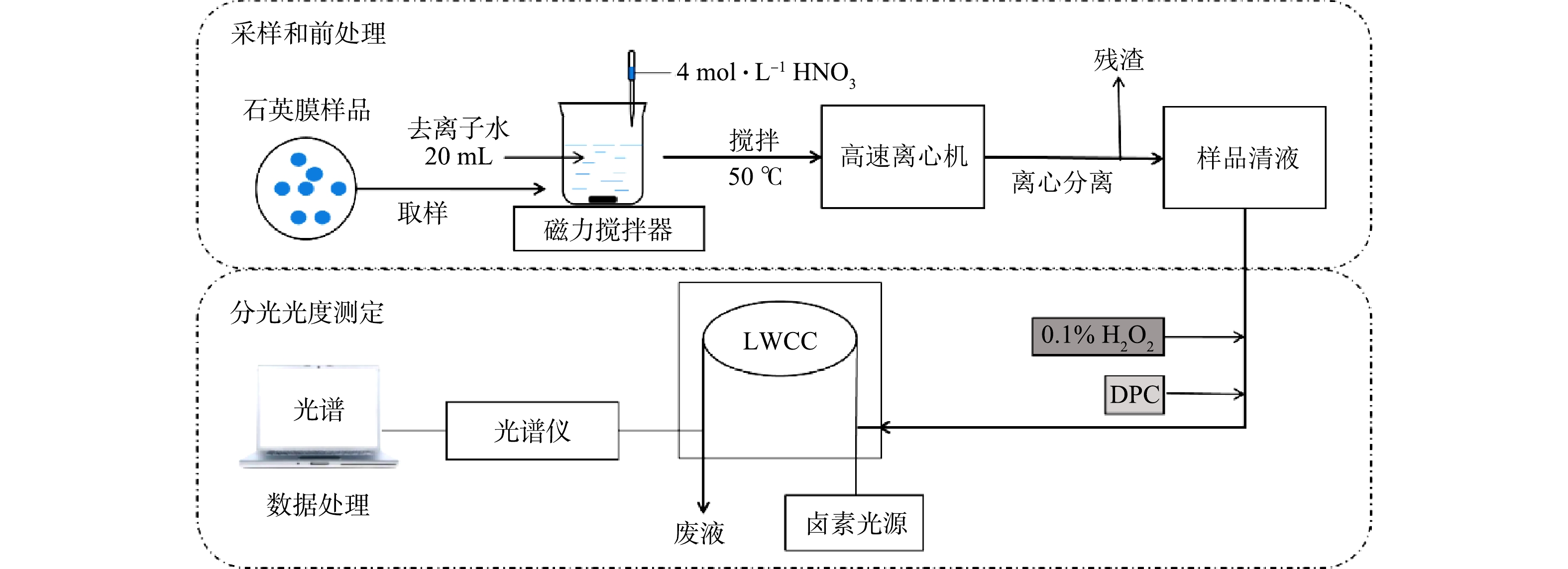
用中流量颗粒物采样器(XY-2200,青岛旭宇)通过石英膜(QMA-Whatman,20.3 cm1.3. 分光光度法检测系统及误差避免方法
分光光度检测系统由容量为112 μL、光程为50 cm的长光程流通池(liquid waveguide capillary cell,LWCC,LWCC-3050, World Precision Instruments, Inc., Sarasota, FL),钨灯光源(HL-2000-FHSA-LL,Ocean Optics, Inc., Dunedin, FL),光缆(QP450-1-XSR, Ocean Optics, Inc., Dunedin, FL)和光谱范围为200~900 nm的小型光谱仪(USB4000-UV-VIS,Ocean Optics, Inc., Dunedin, FL)组成。分析过程中,Cr浓度由Cr(Ⅵ)与DPC反应产生的络合物在540 nm的吸光度进行测算。尽管DPC与大气环境中部分金属离子(Fe3+、Hg2+、Mo6+、Cu2+和V5+)会发生类似络合反应,但这些金属络合物的最大光吸收波长范围均不含540 nm,且相差较大[6]。因此,检测前加入DPC可保证结果基本不受其他金属离子干扰。设定光谱的积分时间为8 ms,每个样品平均次数为20次,光吸收谱图上800 nm处吸光度信号用于设定基线(即设定系统背景信号)。为去除检测仪器自身产生的背景吸光度,通过断开光源测得仪器的暗光谱,并在光谱分析软件中设定扣除暗光谱得到实测光谱数据,以便对系统进行自吸收校正。
1.4. 系统运行流程
系统分为2个部分(图1):石英膜采样和前处理操作的样品采集模块;以分光光度检测为基础的浓度分析模块。将采样后的石英膜用清洁陶瓷剪刀取样、剪碎,放入烧杯后加入20 mL的去离子水和1 mL浓度为4 mol·L?1的HNO3溶液。为尽可能溶解石英膜上采集的环境颗粒物,用磁力搅拌机将石英膜制成的酸化浆液加热(温度为50 ℃)搅拌40 min,分离出10 mL样品清液,装入棕色聚丙烯瓶中避光储存。每次测量后,用4 mol·L?1的HCl溶液清洗所有样品管路,再用超纯水洗净。采用分光光度方法检测样品中Cr的浓度,分以下3个步骤。1)络合反应。向样品溶液中加入0.1 mL 0.1%的H2O2试剂将样品溶液中的Cr(Ⅲ)转化为Cr(Ⅵ),同时加入0.1 mL的DPC试剂,静置10 min,待Cr络合物形成并稳定。2)样品注入。用带0.22 μm微孔滤膜(聚四氟乙烯,PTFE)的聚丙烯注射器将1 mL样品注入LWCC中。3)测定浓度。通入样品2~3 min后,待光谱稳定,得到光吸收谱图上540 nm处Cr络合物的最大吸收峰值,将该值扣减设定的800 nm基线值得出净峰高,并通过与标定结果的对比计算得出总Cr浓度。
1.5. 采样点
采样点设在南京信息工程大学气象观测场内,按12 h的时间间隔采集南京北郊大气颗粒物样品。设定样品采集的起始时间为每日06:30和18:30。采样点(红色星标)位于南京市中心以北大约15 km处,大型工业区(蓝色三角标)以西,靠近城区日常交通干道(见图2)。该地的PM2.5质量浓度数据由Met One Instruments公司的PM2.5在线监测仪进行实时在线监测,时间分辨率为1 h。2.1. 最佳样品测定条件的设定
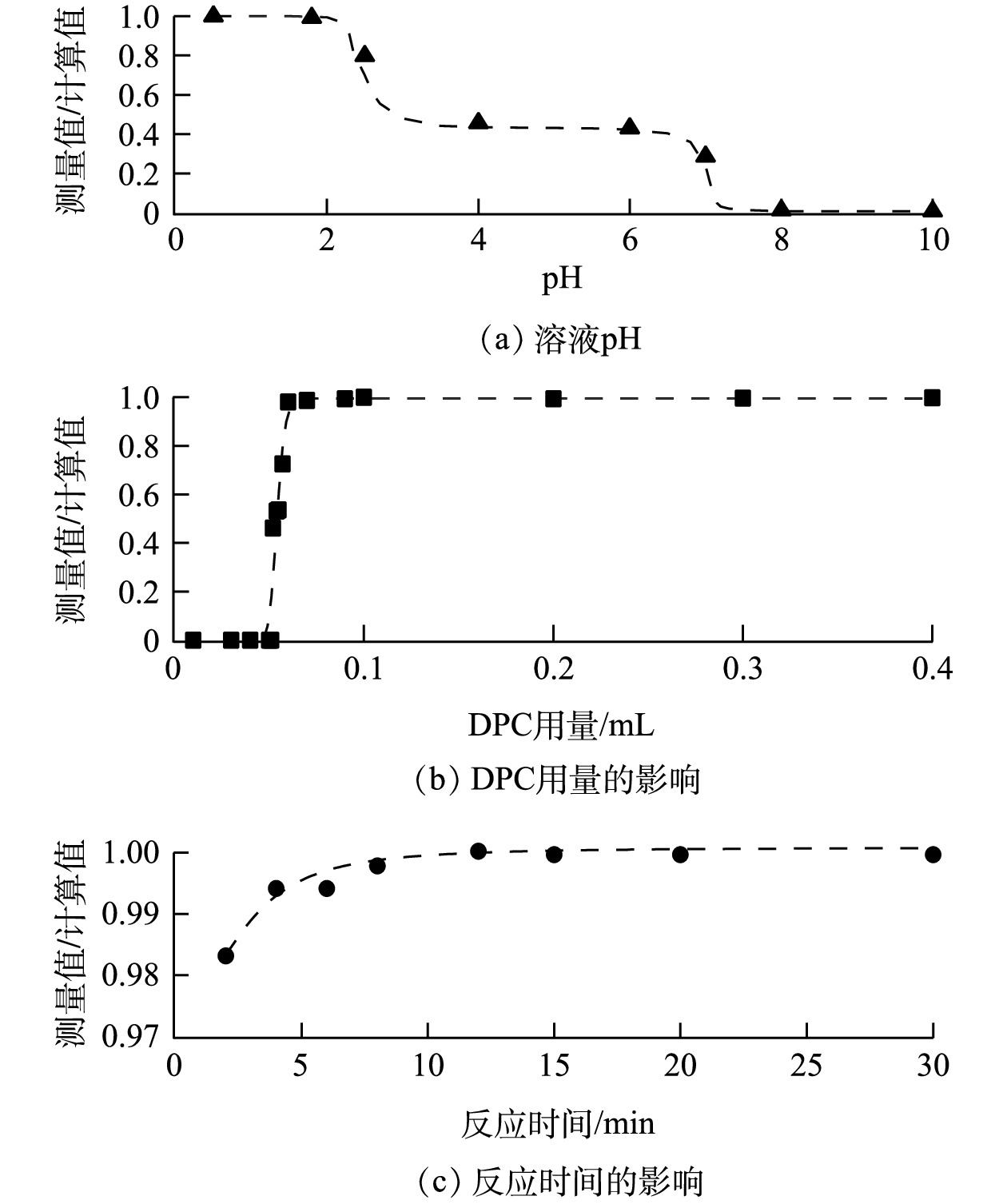
由于大气本底Cr浓度较低,每次取用10 mL浓度为5 ng·mL?1的Cr(Ⅵ)标准溶液进行条件实验。通过改变溶液的pH、DPC试剂的用量及预留的络合反应时间,根据条件实验结果来确定前述各项参数的最佳值或阈值。将仪器的测量值与标准样品浓度的计算值之比作为判别标准,比值越接近1,则结果对应的条件和参数更优。在酸性环境下,Cr(Ⅵ)与DPC络合的效率随溶液pH的升高而降低,导致测定结果偏低;在碱性环境下,Cr(Ⅵ)无法发生络合反应。因此,需要对溶液体系进行酸化。按体积比加入去离子水和HNO3溶液,得到混合溶液的pH约为0.5。用3 mol·L?1 NaOH溶液调节混合溶液pH,结果如图3(a)所示。加入DPC的Cr络合物反应后溶液的最佳pH为0.5~1,故在前处理中无需调节溶液pH。溶液中过量的氧化剂H2O2将Cr(Ⅲ)氧化成Cr(Ⅵ)后,会优先和DPC发生反应,干扰Cr络合物的生成。DPC试剂的用量为0.1 mL时,可去除过量H2O2的干扰(图3(b))。同时,所有试剂加入后静置10 min以保证溶液中的Cr络合物完全产生(图3(c))。
2.2. 标定曲线和检测限
根据实际环境大气颗粒物中总Cr浓度,选择合适浓度梯度(0.5、1、2、5、8 ng·mL?1)的Cr(Ⅵ)标准溶液确定标准曲线。每次标定使用相同Cr(Ⅵ)母液,用去离子水稀释至所需浓度。图4为14 d内不同时间进行的5次标定结果的平均值,相同浓度的多次测定值范围以error bar形式在图中标出。几次标定得到的线性方程斜率在(0.015 6±0.000 2) mL·ng?1范围变化,并且所有标定曲线的R2均能达到0.99。系统分光光度测量的标定范围涵盖了一般环境大气颗粒物中Cr浓度范围。Cr浓度与其络合物的吸光度峰值呈稳定线性关系,多次标定反映出该结果重现性好。根据空白样品吸光度峰值标准偏差的3倍来测算系统的检测限(limit of detection,LOD)。空白样品由空白石英膜按照样品的前处理过程制得。将加入DPC的空白样品通入LWCC测量吸光度峰值,LOD约为0.158 ng·mL?1,对应采样空气体积约为12 m3。经过计算对应的环境颗粒物中Cr浓度为0.133 ng·m?3,大气颗粒物中Cr浓度至少比该LOD高一个数量级,故检测系统对Cr浓度的测定灵敏度较高,可满足大气监测需求。从上述空白样品的测定结果还表明,石英膜上Cr本底浓度极低,为(0.971±0.087) ng·g?1,不会干扰实际测量。
2.3. 回收率实验
检测系统的回收率实验包括空白加标回收和样品加标回收两部分。空白样品的加标回收通过在空白石英膜上加入10 ng Cr(Ⅵ),再按照样品前处理步骤进行处理和分析测定,测定结果与理论值之比即空白加标回收率。用微升注射器(HAMILTON-7000)取用1 μL由相同Cr(Ⅵ)母液稀释所得浓度为10 μg·mL?1的Cr(Ⅵ)标液,直接加注在石英膜表面进行样品加标,以相同浓度的Cr(Ⅲ)标液(由纯度为99.99%的CrCI3·6H2O和去离子水制得)进行加标实验,通过加入0.1%的H2O2氧化Cr(Ⅲ)后,检测Cr(Ⅳ)浓度并与配置的Cr(Ⅲ)标液比较得到转化率。样品的加标回收则选用NIST商品化的城市颗粒物标准物质(NIST 1648 PM)作为样品。用清洁研钵将NIST样品磨碎,取2份(各5 mg)分别涂抹在空白石英膜上,其中1份加入10 ng Cr(Ⅵ)。将2份样品通过检测系统进行分析,2份样品测量的差值与加入标准Cr(Ⅵ)物质的理论值之比即加标回收率。上述实验均重复进行多次以减少偶然性误差。由于使用高纯度的药品且系统测量受到干扰误差很小,Cr(Ⅵ) 空白加标回收率均值可达98%,标准偏差为2.4%(样品数为10);Cr(Ⅲ)的转化率为(95±2.6)%(样品数为10)。样品加标回收实验结果显示:在15个加标的标准环境样品中Cr(Ⅵ)回收率为(90.3±8.1)%;而对不加标的NIST标准样品中Cr浓度测定的误差范围为(9.6±3.3)%。ERG使用相同样品加标,通过碳酸盐缓冲液提取与离子色谱(IC)测得的回收率为((89.8±10)%,样品数N=10)[20]。2组样品加标回收率经中位数检验并不存在统计上的显著差异,故该系统具有较好的采集和测量精度。
2.4. 与ICP-MS方法的对比测试
ICP-MS是目前颗粒物中痕量金属的热门测定方法之一[21-22]。2014年,我国环境保护部将其确定为测量环境水样中多种痕量元素的标准方法(HJ 700-2014)。近年来,ICP-MS与各种分离技术联用已常见于Cr的相关研究中[23-26]。将2016-12-17—2016-12-27在福州三中地区(PM2.5>80 μg·m?3)采集的高浓度大气颗粒物石英膜样品(膜规格:QMA-Whatman, 1851-050, Φ50 mm;采样时长3 h;采样流速16.7 L·min?1),分别通过本系统和ICP-MS测量总Cr浓度。
在进行ICP-MS测定前,将膜样品做密闭微波消解前处理。取用与本系统分析等量样品置于Teflon-TFM消解罐中,再加入10 mL HNO3和HCl的混合液(体积比为1∶1),摇匀浸湿样品膜后放入微波消解仪(XT-9900A,上海新拓)中消解8 h。待消解罐冷却至室温,将其中的混合物用0.45 μm的醋酸纤维素滤膜进行过滤。将得到滤液用去离子水稀释至50 mL,用ICP-MS(X-Series2, US Thermo fisher)进行分析。
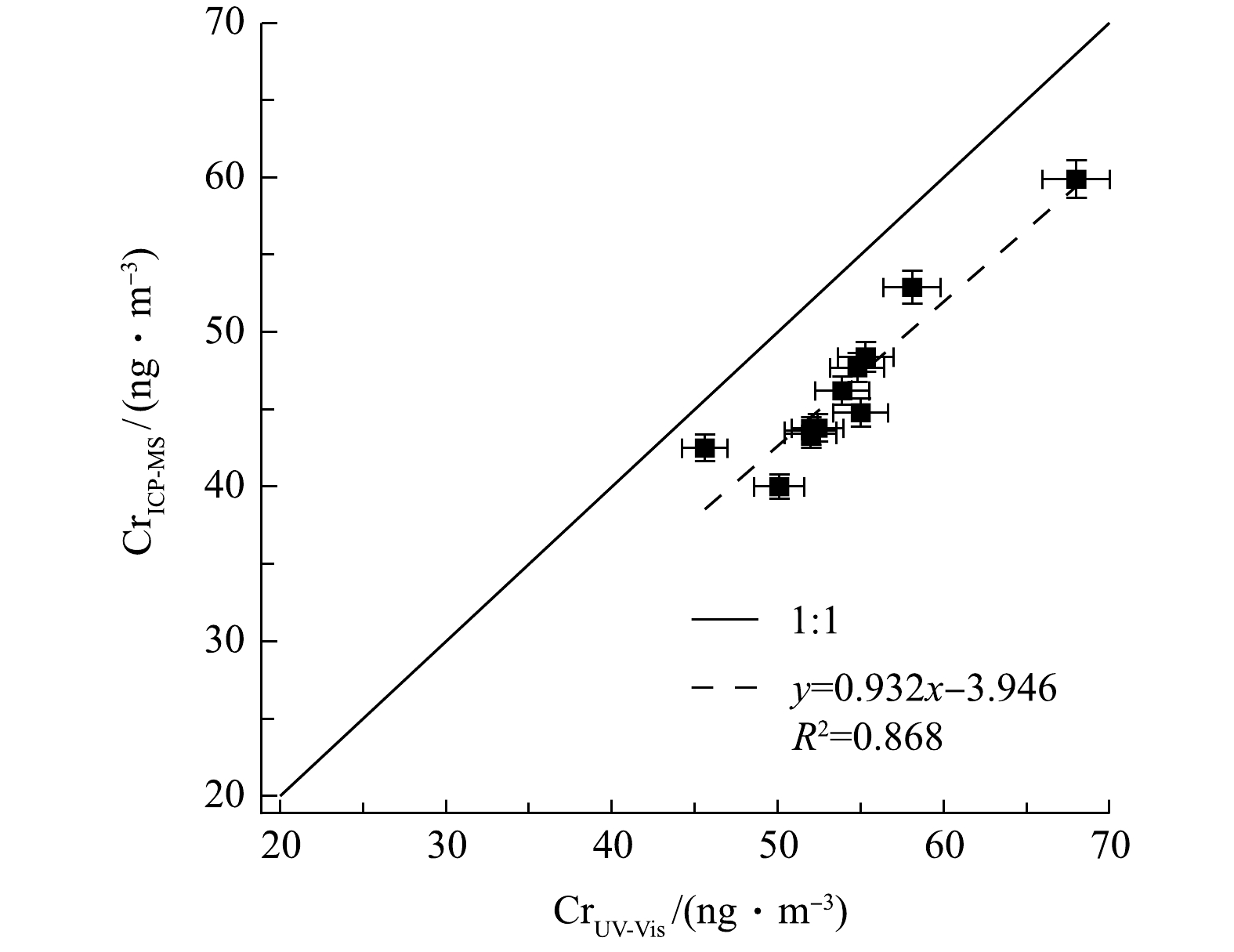
2种方法测量结果的相关性如图5所示,表明结果呈线性关系(斜率为0.932,R2为0.868)。该结果表明本系统对环境颗粒物中总Cr浓度测定的准确性与稳定性较好,也进一步证明本系统的前处理操作(包括酸化、加热搅拌等)能基本确保样品中所有含铬组分充分溶解,以得到可靠的测量结果。同时也表明若颗粒物样品含Cr组分中耐酸且难溶物质较多,会影响系统测量结果。
2.5. 大气PM2.5中Cr浓度的外场实测
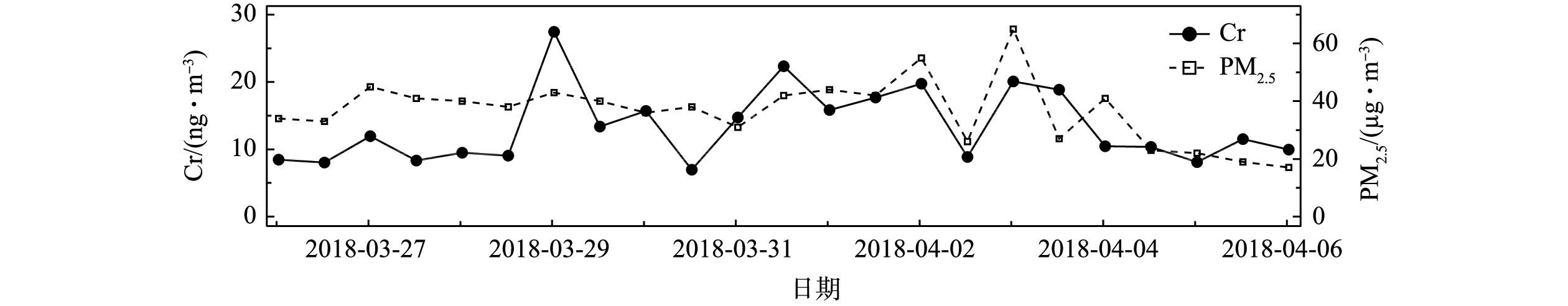
在2018-03-26—2018-04-06对环境大气PM2.5进行样品采集,每12 h采集1次,得到1周多的连续数据如图6所示。测得Cr浓度在采样期间出现了明显的变化,浓度为6.9~27.4 ng·m?3。该浓度水平与其他观测结果相似[27-28],Cr浓度的变化趋势与PM2.5的变化趋势基本一致。整个采样期间,Cr的日平均浓度为13.4 ng·m?3。而这段时间Cr浓度变化较大,这是由于春季空气污染过程频发,且受风向风速变化的影响较大。分析Cr浓度的变化可发现,2018-03-28夜间到2018-03-29凌晨、2018-03-31白天、2018-04-01夜间到2018-04-02凌晨,以及2018-04-02夜间到2018-04-03凌晨这几个时段达到观测期间的峰值,平均值比日平均浓度高50%~67%;2018-03-30全天、2018-04-02白天Cr浓度降至观测期间日平均浓度的52%~60%;2018-04-04下午到2018-04-06凌晨,Cr浓度基本与采样期间的Cr日平均浓度持平。由于Cr被广泛用于工业生产,如冶金、铬镁耐火材料制造和电镀工艺等[29-31],交通工具的尾气排放和机械磨损[32]也会使环境大气颗粒物中含有这类过渡金属,Cr是地壳中的金属物质之一,故土壤粉尘和地面扬尘也为大气颗粒物中贡献了Cr[33-34]。结合采样点的地理位置分析可推断,大气颗粒物中的Cr主要来自早晚期间强烈的交通活动导致的直接排放和扬尘排放,以及偏东风带来的工业园区排放的污染气团。上述结果表明,本系统可对PM2.5中Cr浓度进行准确连续的测量。
2)设计中用到的通过替换金属络合试剂及对前处理步骤进行优化的方法,不仅能测定Cr的价态,还能帮助测定大气环境中部分金属的浓度,为实现连续快捷地分析大气环境中水溶性金属离子的污染特征提供了参考。同时,结合大气颗粒物中Cr的来源还可以进一步判断不同季节大气中Cr的来源,并分析其日变化特征。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图