全文HTML
--> --> --> 氨氮去除是污水处理系统中的重点。应用传统脱氮工艺(硝化-反硝化)处理老龄垃圾渗滤液、工业废水等低碳氮比废水时,不仅能耗高,且需外加有机碳源[1]。短程硝化是将废水中


因利用短程硝化耦合Anammox工艺处理低C/N废水时具有较大优势,所以其工艺已成为研究热点。实现短程硝化的关键在于促进氨氧化菌(ammonia oxidizing bacteria,AOB)生长的同时抑制亚硝酸盐氧化菌(nitrite oxidizing bacteria,NOB)活性,从而保持稳定的亚硝酸盐积累。有研究[7]表明,溶解氧(dissolved oxygen,DO)、pH、温度、游离氨(free ammonia,FA)和游离亚硝酸(free nitrous acid,FNA)等因素能够抑制NOB活性,从而稳定短程硝化过程。吴雪等的[8]研究表明,在pH=8.5、DO=0.8 mg·L?1、温度为30 ℃时可有效抑制NOB活性,从而使亚硝酸盐的积累量达到最大。张宇坤等[9]认为,当FA质量浓度在10 mg·L?1附近时,NOB的活性下降接近50%,而当FNA质量浓度大于0.2 mg·L?1时,NOB的活性被完全抑制,故通过控制FA和FNA有利于实现短程硝化。短程硝化过程不仅会受到NOB活性的影响,而且废水中存在的有机碳源会对短程硝化和厌氧氨氧化过程产生影响,进而可能造成整个工艺无法稳定运行。梁瑜海等[10]认为,化学需氧量(chemical oxygen demand,COD)会抑制AOB和Anammox的活性,从而使反硝化活性上升。李冬等的[11]研究表明,在氨氮质量浓度为100 mg·L?1、COD为300~400 mg·L?1的运行条件下,由于大量COD的存在会使异养好氧菌增殖,从而抑制AOB的活性,影响自养脱氮系统性能的稳定性。CAPODICI等[12]认为,通过高氨氮负荷和高COD值的综合作用也会抑制AOB活性。上述研究均表明,一定的COD值会抑制AOB活性,但未涉及有机碳源对短程硝化系统影响的机理解释,且未通过探究得到明确的调控手段以应对其性能的下降。因此,研究有机碳源对短程硝化工艺启动及稳定性的影响及恢复系统性能的调控手段具有重要意义。
针对上述问题,本研究设置了不同质量浓度的

1.1. 实验装置及运行策略
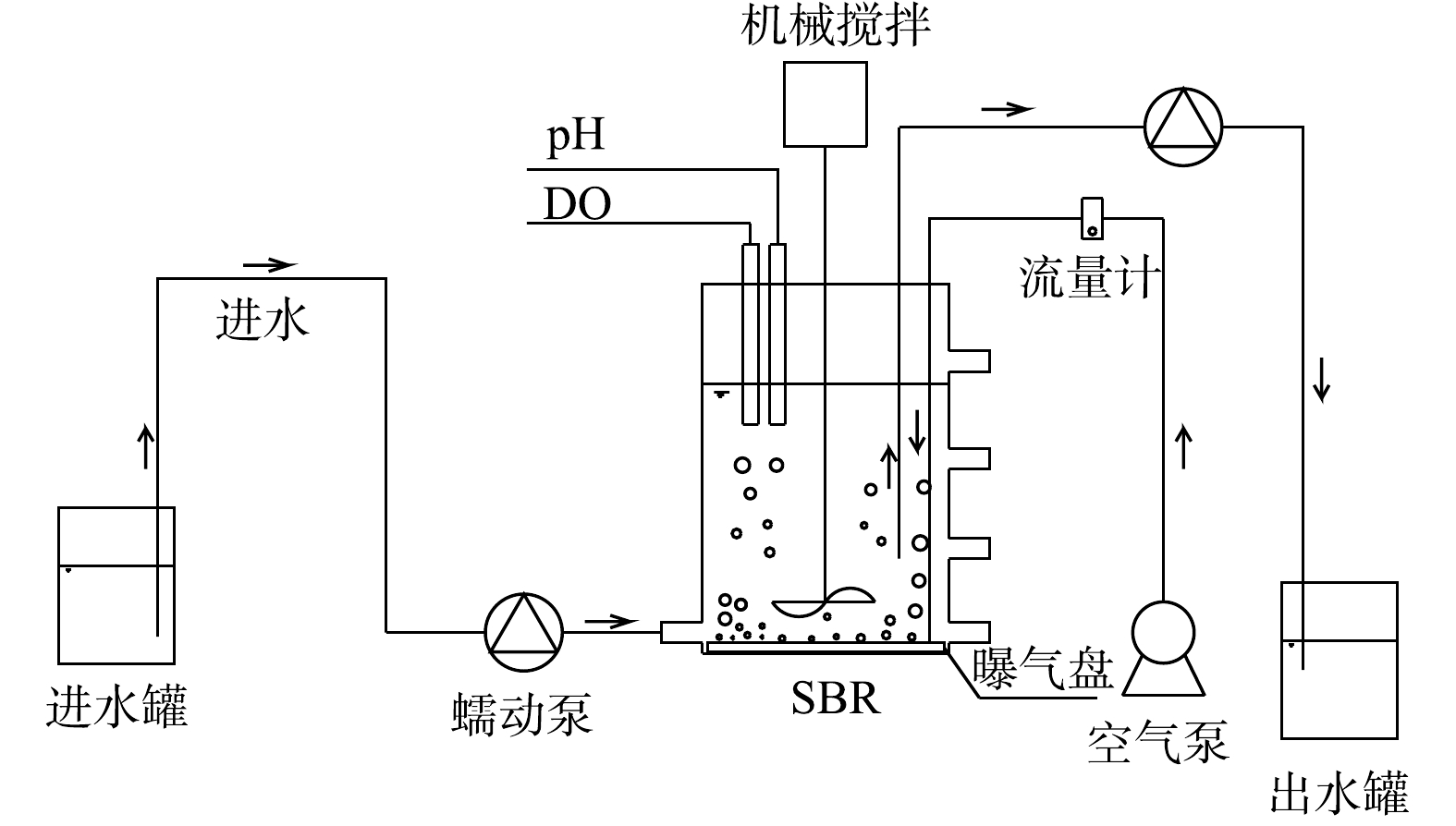
实验装置如图1所示。实验所用的序批式反应器(sequencing batch reactor,SBR)由圆柱形有机玻璃制成,内径为12 cm,高为18 cm,工作体积为1.6 L。反应器由底部进水,设有4个取样口,内部配有搅拌、曝气和控温装置,使DO为0.3~0.5 mg·L?1、温度为(26±1) ℃。反应器运行模式为每天4个周期,每个周期中包括进水15 min,曝气搅拌300 min,沉淀30 min,出水15 min。SBR体积交换比为50%,水力停留时间(hydraulic retention time,HRT)为12 h,污泥停留时间(sludge retention time,SRT)在阶段Ⅳ控制为10~15 d。实验阶段的运行参数见表1。1.2. 实验用水及接种污泥
实验中采用人工配制的模拟废水,组成[13-14]如下:1 200 mg·L?1 NaHCO3、10 mg·L?1 KH2PO4、15 mg·L?1 CaCl2·2H2O、300 mg·L?1 MgSO4·7H2O、0.05 mol·L?1 EDTA-Fe2+;1.25 mL·L?1微量元素,其组成为15 g·L?1 EDTA、0.014 g·L?1 H3BO4、0.99 g·L?1 MnCl2·4H2O、0.25 g·L?1 CuSO4·5H2O、0.43 g·L?1 ZnSO4·7H2O、0.19 g·L?1 NiCl2·6H2O、0.21 g·L?1 NaSeO4·10H2O、0.22 g·L?1 NaMoO4·2H2O、0.05 g·L?1 NaWO4·2H2O。进水
1.3. EPS提取及分析方法
通过热提取法提取EPS[15]。采用蒽酮比色法测定多糖含量,用BCA法测定蛋白质(碧云天BCA浓度测定试剂盒)[16]。利用荧光光谱仪(F-7000,Hatchi公司)测定提取的EPS样品,激发波长(Ex)为200~400 nm,发射波长(Em)为290~550 nm,其中激发和发射波长间隔分别为5 nm和1 nm。平行因子(PARAFAC)使用MATLAB进行分析[17],具体方法是:将测得的三维荧光数据转化为三维数据集,对其进行内滤校正和空白扣减,基于PARAFAC法识别三维荧光数据中通过数据校验的模型组分,通过开展平方和误比较、核心一致性和分半检验优选和验证PARAFAC模型,再通过与已知模型库中的模型进行比对,拟合文献中的模型得到各组分得分,计算各组分荧光值,从而对EPS综合分析。1.4. 其他参数的分析方法



式中:CFA为游离氨质量浓度,mg·L?1;CFNA为游离亚硝酸质量浓度,mg·L?1;


1.5. 微生物群落测定
取不同阶段泥水混合液各20 mL,10 000 r·min?1离心去上清液,用于微生物分析。根据E.Z.N.A.? soil DNA kit进行微生物群落总DNA抽提,使用1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA的提取质量,使用NanoDrop2000测定DNA浓度和纯度;使用338F(5’-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3’)和806R(5’-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3’)对16S rRNA基因V3~V4可变区进行PCR扩增,扩增程序如下:95 ℃预变性3 min,27个循环(95 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸30 s),后72 ℃稳定延伸10 min,最后在4 ℃进行保存。PCR反应体系为:5×TransStart FastPfu缓冲液4 μL,2.5 mM dNTPs 2 μL,上游引物0.8 μL,下游引物0.8 μL,TransStart FastPfu DNA聚合酶0.4 μL,模板DNA 10 ng,补足至20 μL。每个样本3个重复。将同一样本的PCR产物混合后使用2%琼脂糖凝胶回收PCR产物利用AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit进行回收产物纯化,2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,并用Quantus? Fluorometer对回收产物进行检测定量。利用Illumina公司的Miseq PE300平台进行测序(上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司)。2.1. 反应器脱氮性能研究
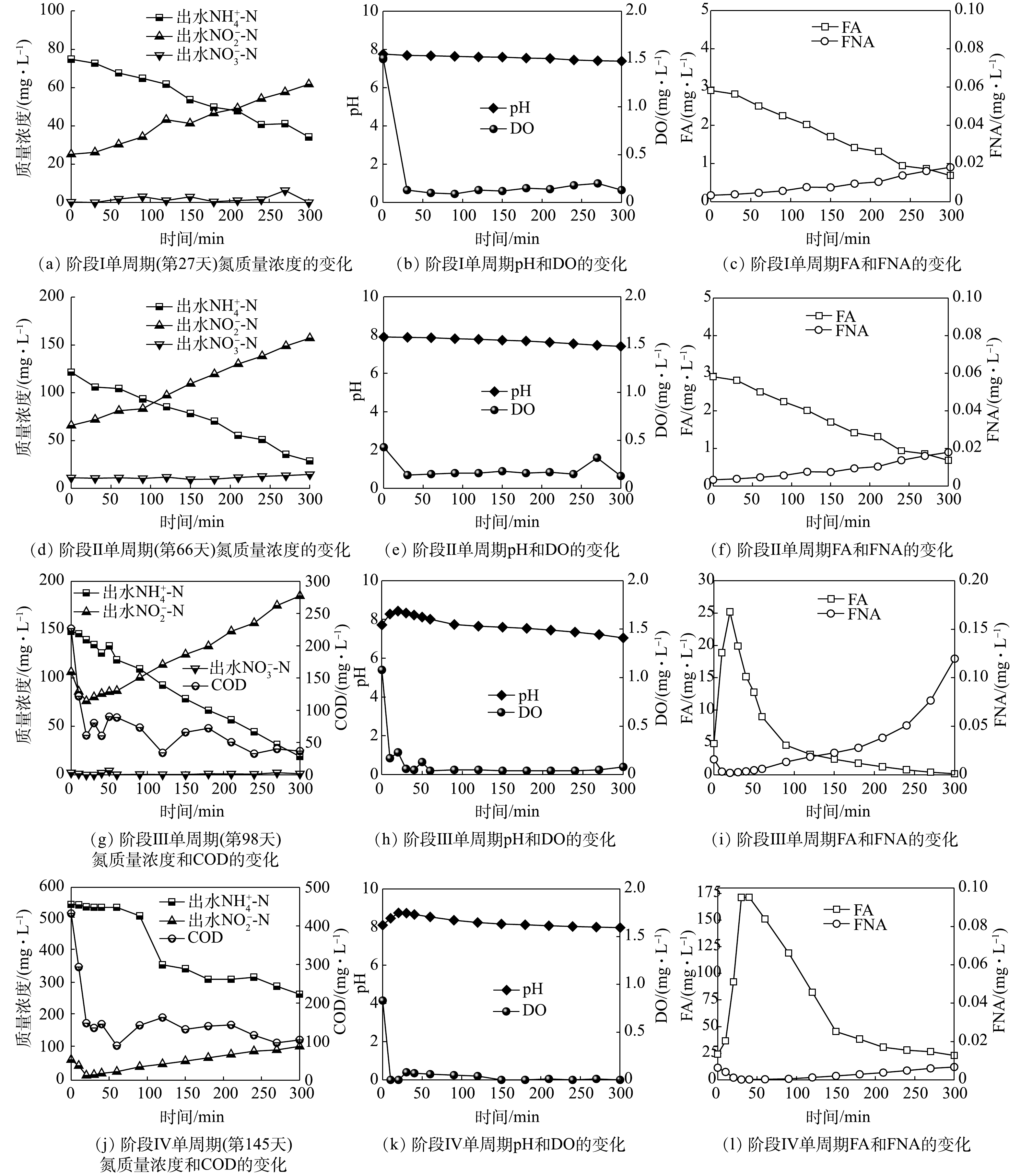
图2反映了反应器运行过程中氮质量浓度、氨氮去除率(ammonia removal rate,ARR)与亚硝酸盐积累率(nitrite accumulation rate,NAR)的变化。由于AOB和NOB的氧饱和常数分别为0.2~0.4 mg·L?1和1.2~1.5 mg·L?1,AOB对氧的亲和力大于NOB[22],因此,在阶段Ⅰ通过控制低DO(0.3~0.5 mg·L?1)可促进AOB生长活性的同时抑制NOB的生长。第3天出水


但加入有机碳源后,ARR明显下降,这是由于异养菌与AOB竞争O2导致其活性下降[23]。据此,在第16天沉降性能恢复后停止加入有机碳源,ARR在第19天回升。第24天后,ARR和NAR分别稳定至(87±2)%和(89±3)%,这表明,通过控制反应器中的曝气量能够维持AOB的生长活性并抑制NOB的生长,进而可以进行稳定的短程硝化过程。
在阶段Ⅱ(28~66 d),将进水




在阶段Ⅲ(67~98 d),将


















在阶段Ⅳ(99~151 d),分别提升




















































2.2. EPS的变化
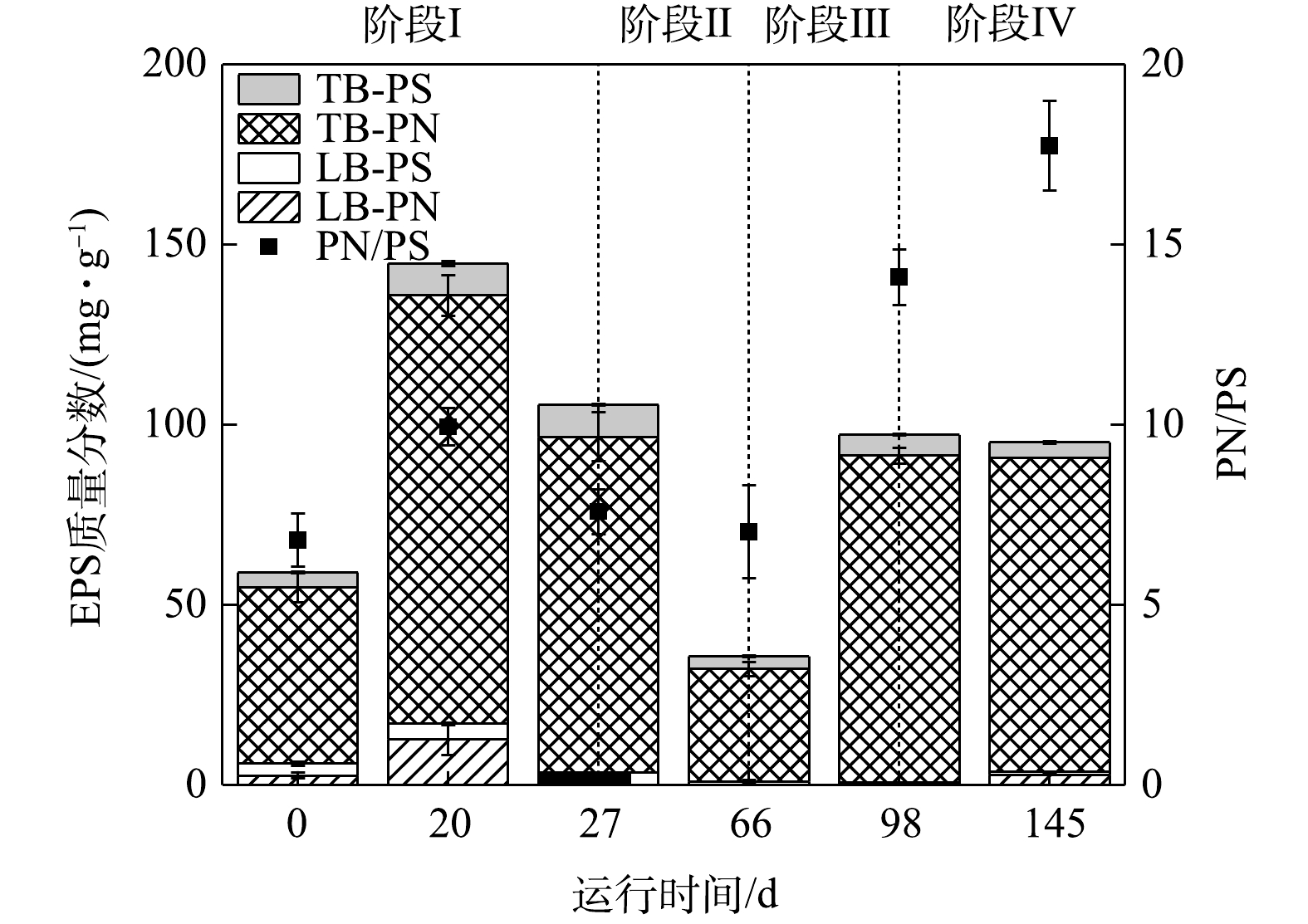
1) EPS质量分数的变化。各实验阶段EPS质量分数的变化情况如图4所示。接种污泥中EPS质量分数的平均值为(56.38±3.65) mg·g?1。第20天,由于反应环境中污泥沉降性能变差,导致MLSS和MLVSS急剧下降。在反应器中添加200 mL污水处理厂活性污泥后,其显著增加至(144.70±10.15) mg·g?1。这是由于,在添加污泥后MLSS和MLVSS上升,污泥中微生物量增加,EPS质量分数增加[28]。第27天,短程硝化过程稳定后,EPS质量分数的平均值为(105.56±6.66) mg·g?1。由于在添加活性污泥后,一定量的异养菌进入反应器内,而进水中不存在有机碳源,因此,异养菌利用了一部分EPS作为有机碳源,这导致EPS质量分数下降[29]。阶段Ⅱ提升氮负荷后,加入少量有机碳源(COD=70 mg·L?1),第66天EPS质量分数下降至(35.70±1.40) mg·g?1。这是因为,引入少量有机碳源后,激活了异养菌的内源反硝化作用,在利用反应器中有机碳源的基础上进一步利用EPS作为碳源,导致EPS明显下降[30]。阶段Ⅲ、Ⅳ增加有机碳源至400 mg·L?1和670 mg·L?1,第98天测得EPS质量分数上升并稳定至(97.16±1.93) mg·g?1和(92.16±0.32) mg·g?1。这表明反应器内有机碳源充足的情况下,异养菌不再将大量EPS作为有机碳源进行内源反硝化,EPS质量分数已趋于稳定,从而反应器内污泥的沉降性能良好。
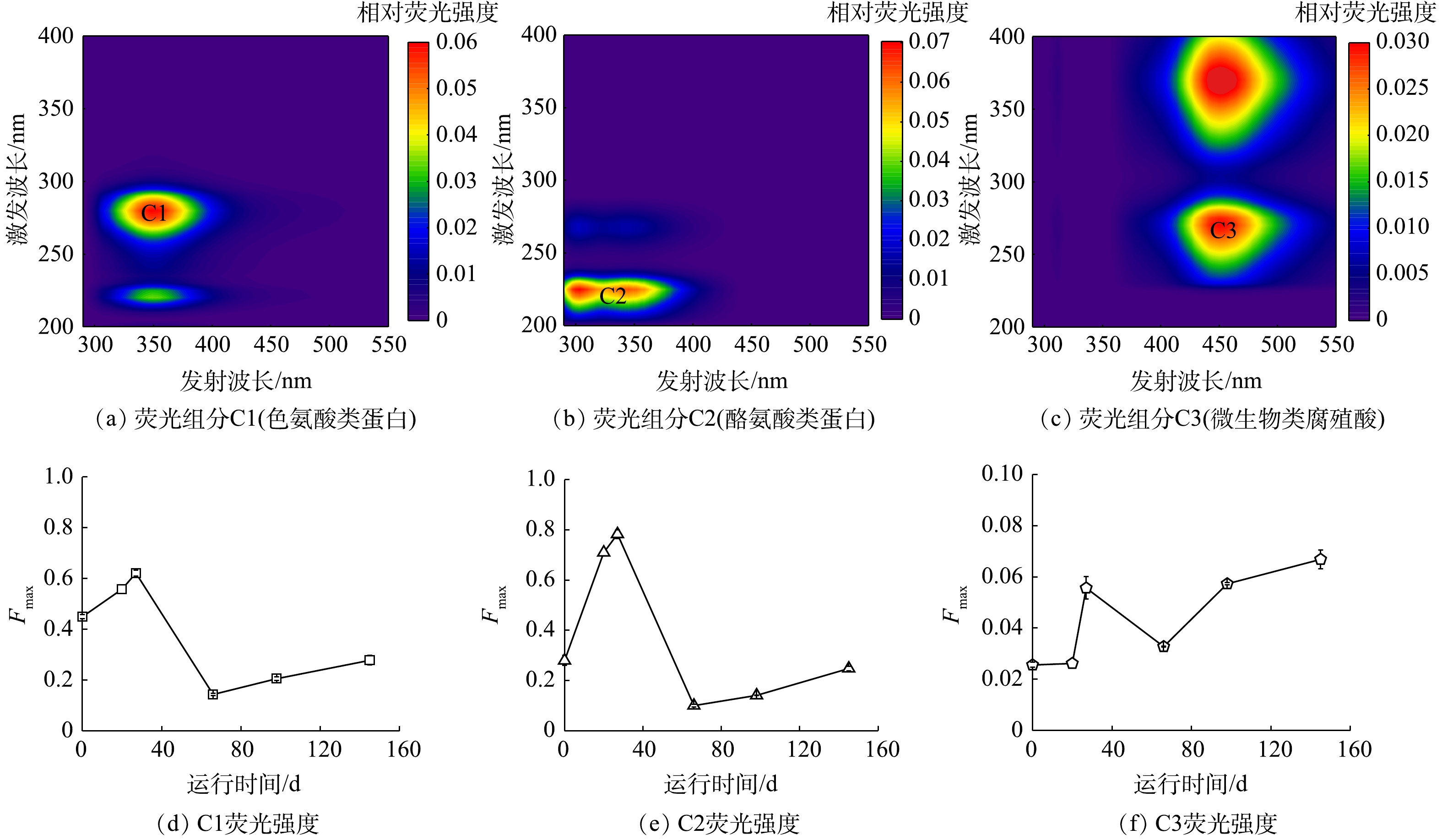
2) EPS的三维荧光光谱的平行因子分析。利用三维荧光的平行因子PARAFAC模型对EPS进行分析,有3种组分存在于EPS中(图5)。其中C1激发峰在220 nm和280 nm处,并在349 nm处有1个发射峰,为色酪氨酸蛋白质[31];组分C2激发波长在225 nm和270 nm,并在303 nm和345 nm处有2个发射峰,为类酪氨酸蛋白质[32];组分C3激发波长在270 nm和370 nm,且发射峰在451 nm,为微生物类腐殖酸[33]。
通过平行因子分析,确定了各组分的荧光强度(Fmax)。有研究[17]表明,Fmax值与各组分的浓度之间呈正相关性。由图5(d)和图5(e)中可知,组分C1和C2类色氨酸和类酪氨酸蛋白质在阶段Ⅰ的Fmax值由0.45和0.28上升至0.62和0.78,在阶段Ⅱ迅速下降至0.14和0.10,且在阶段Ⅲ、Ⅳ中继续上升,最终达到0.28和0.25。C1和C2的 Fmax值的变化趋势(图5(d)和图5(e))与EPS中蛋白质质量分数的变化趋势(图4)一致,这进一步验证了有机碳源对系统中污泥EPS质量分数的影响。对于组分C3微生物类腐殖酸的Fmax值的变化如图5(f)所示。阶段ⅠFmax由0.03上升至0.06,在阶段Ⅱ迅速下降至0.03,并于阶段Ⅲ、Ⅳ中有明显上升趋势,且最终达到0.07。这是由于,阶段Ⅰ混合了部分活性污泥,泥量增多,并且其混合的部分微生物可能无法快速适应反应环境,使得反应体系内细菌凋亡的数量增多,从而分泌更多的类腐殖酸。虽然阶段Ⅱ提升了氮负荷,但同时投加的有机碳源使体系内异养菌大量增殖,因而减少一定的内源呼吸作用,且微生物能够逐渐适应其生长环境,细菌凋亡数量减少,从而产生的类腐殖酸减少。而阶段Ⅲ、Ⅳ中继续提升氮质量浓度和COD值后,其产生的类腐殖酸有上升趋势,说明污染物浓度过高会对系统产生一定冲击,造成细菌凋亡数量增多。
2.3. 微生物群落分析
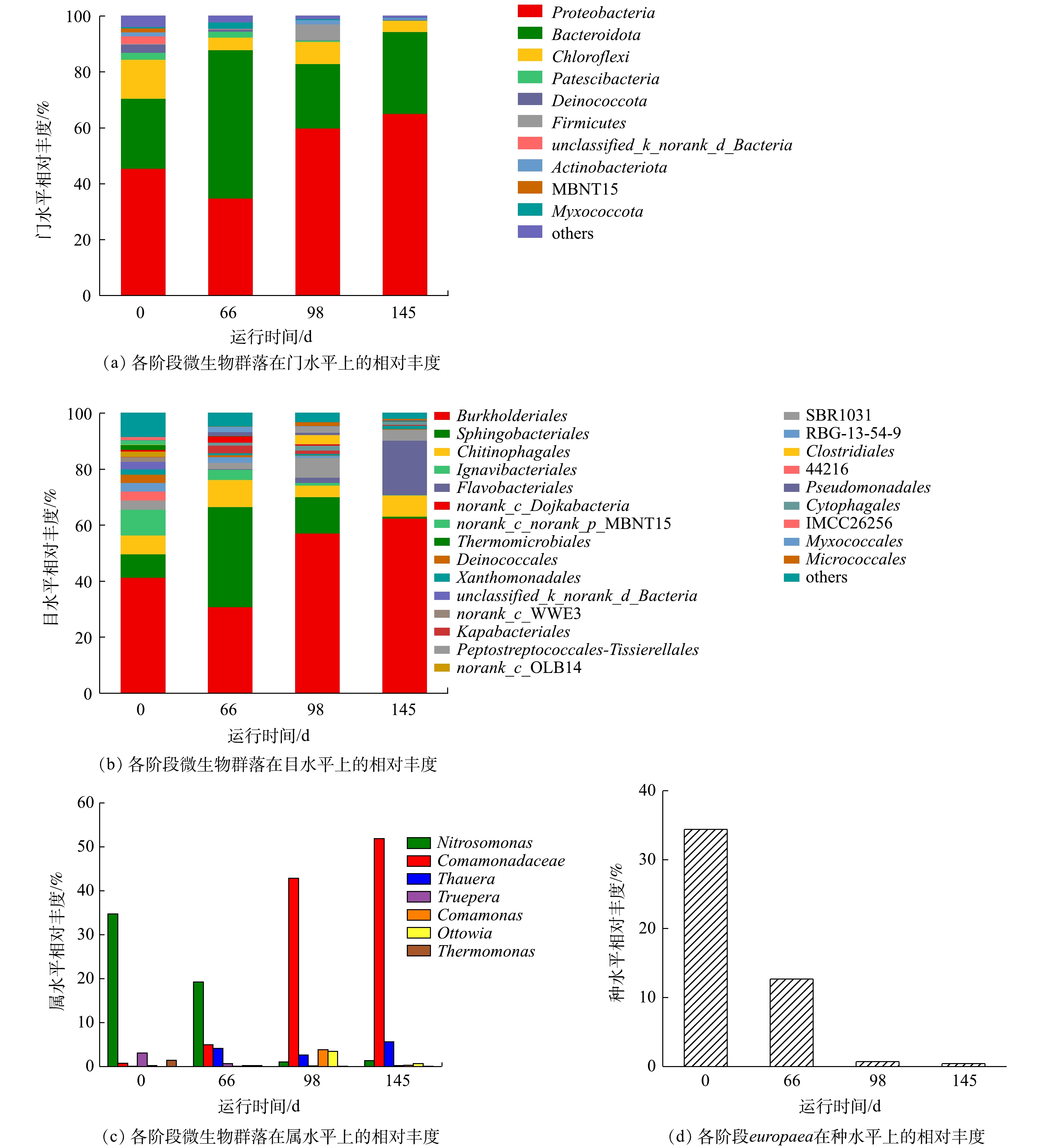
实验各阶段的微生物群落的结构分布如图6所示。图6(a)是污泥样品在门水平上的微生物组成结构,其中的优势菌门主要包括变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)和绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)。其中Proteobacteria的相对丰度逐渐由45.6%上升至65.1%,Bacteroidetes的相对丰度波动较大,但仍然在总数中占据优势。根据文献报道,Proteobacteria和Bacteroidetes是生物脱氮过程中的优势菌门,在污水处理过程中起到重要作用[34]。如图6(b)所示,在目水平上,β-变形菌目(Burkholderiales)和鞘脂杆菌目(Sphingobacteriales)分别是Proteobacteria和Bacteroidetes的优势种群。其中Burkholderiales的相对丰度由41.4%上升至62.5%,这是由于反应器内有机碳源的增加导致异养菌的迅速增殖。Sphingobacteriales的相对丰度由8.5%先上升至35.8%再降低至7.1%。这是因为Sphingobacteriales可利用蛋白质和多糖作为有机碳源[30]。因此,当阶段Ⅱ有机碳源不足的情况下EPS消耗严重,阶段Ⅲ、Ⅳ当有机碳源充足时,Sphingobacteriales转而利用有机碳源而对EPS的消耗减少。因此,Sphingobacteriales在阶段Ⅱ相对丰度迅速上升,在阶段Ⅲ、Ⅳ迅速下降。
微生物群落分布的属水平结构分布如图6(c)所示。其优势菌属为反硝化菌属(Comamonadaceae)和亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)。其中Comamonadaceae的相对丰度由0.70%上升至51.89%,这是因为COD值的升高可为反硝化菌属(Thauera、Comamonas、Ottowia、Thermomonas)提供有利环境,进而反硝化菌迅速生长[35-37]。Nitrosomonas属可大致分为europaea和eutropha,通过微生物群落的种水平可分析得出(图6(d)),europaea是Nitrosomonas属的优势种,相对丰度由34.40%降低至0.41%,从而导致Nitrosomonas属的相对丰度由34.7%下降至1.35%。快速增殖的异养菌成为优势菌群,而这种下降并不意味着AOB数目的减少,而是由于作为自养菌的AOB增殖速度远远小于异养微生物,所以在反应器中引入有机碳源后,europaea在这种环境下逐渐失去优势[23]。但通过各阶段的氮质量浓度变化数据可得出其相对丰度的下降并没有严重影响短程硝化过程。
2.4. 相关酶活性分析
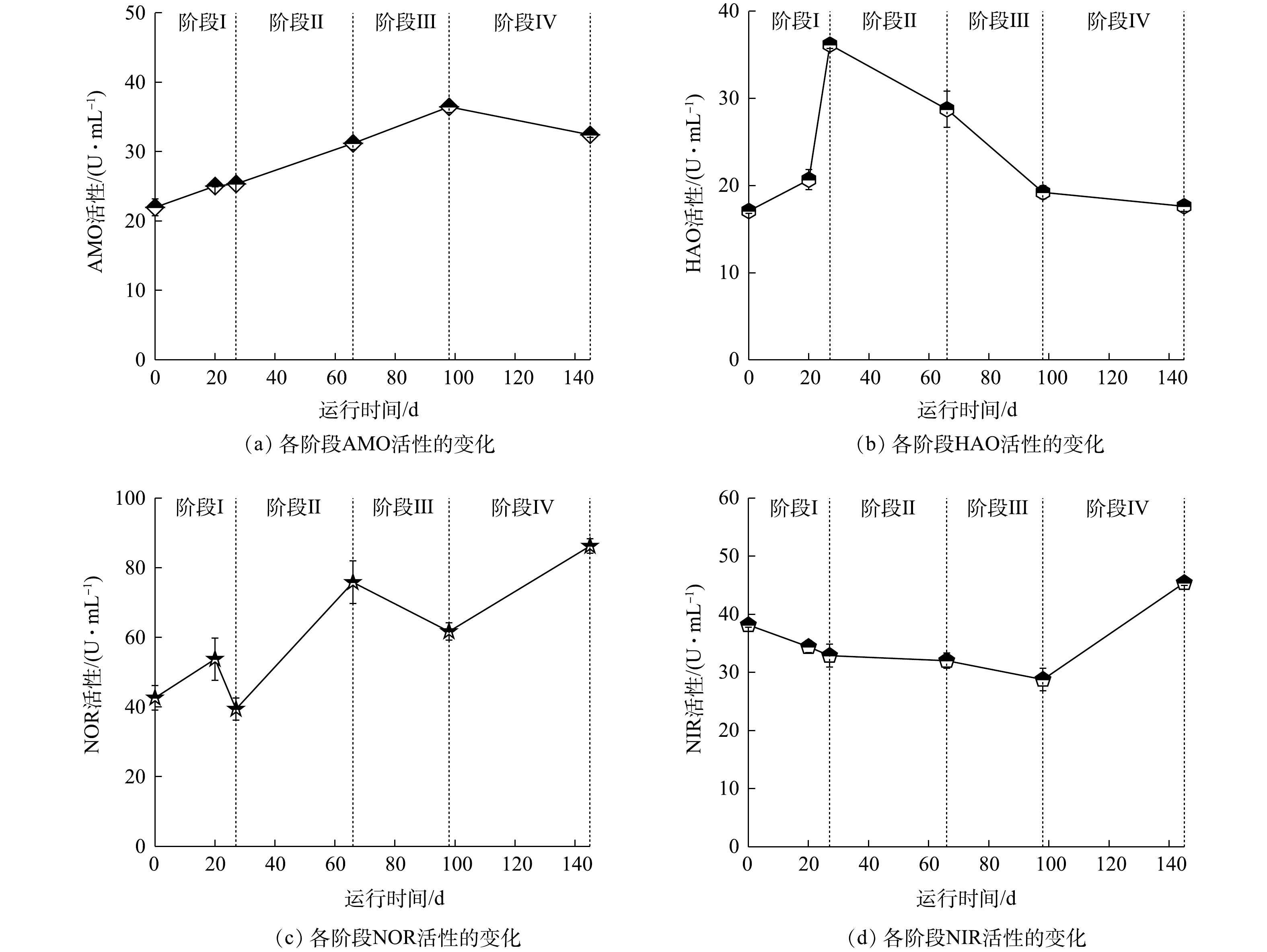
本实验研究了各阶段的AMO、HAO、NOR和NIR的活性,结果如图7所示。AMO为硝化过程中氨氮转化为羟胺过程中所参与的酶。其中AMO在第0天活性为21.97 U·L?1,在每阶段提升氮负荷后,活性均呈上升趋势,并在第145天稳定在32.42 U·L?1。根据单因素方差分析结果可知,第66天AMO活性出现显著性变化(P<0.05),并于阶段Ⅲ、Ⅳ呈极显著变化(P<0.01),说明随着进水





















由于加入有机碳源,反应器出现反硝化现象,而NIR是反硝化过程中

2)在无有机碳源的环境中仅通过调节曝气量即可成功启动短程硝化过程。在存在有机碳源的环境中,反硝化作用会随有机碳源质量浓度的提升而加剧,并会加强抑制短程硝化,通过综合控制曝气量、FA和无机碳源量可恢复稳定的短程硝化过程。
3)引入有机碳源后,反硝化菌属Comamonadaceae的相对丰度由0.70%上升至51.89%,说明在高质量浓度有机碳源的环境中更有利于反硝化菌的生长。而主要功能菌属Nitrosomonas的相对丰度由34.7%下降至1.35%,在运行过程中短程硝化性能出现下降趋势。但通过对运行参数的综合调控,最终可稳定运行短程硝化系统。
参考文献





 下载:
下载: 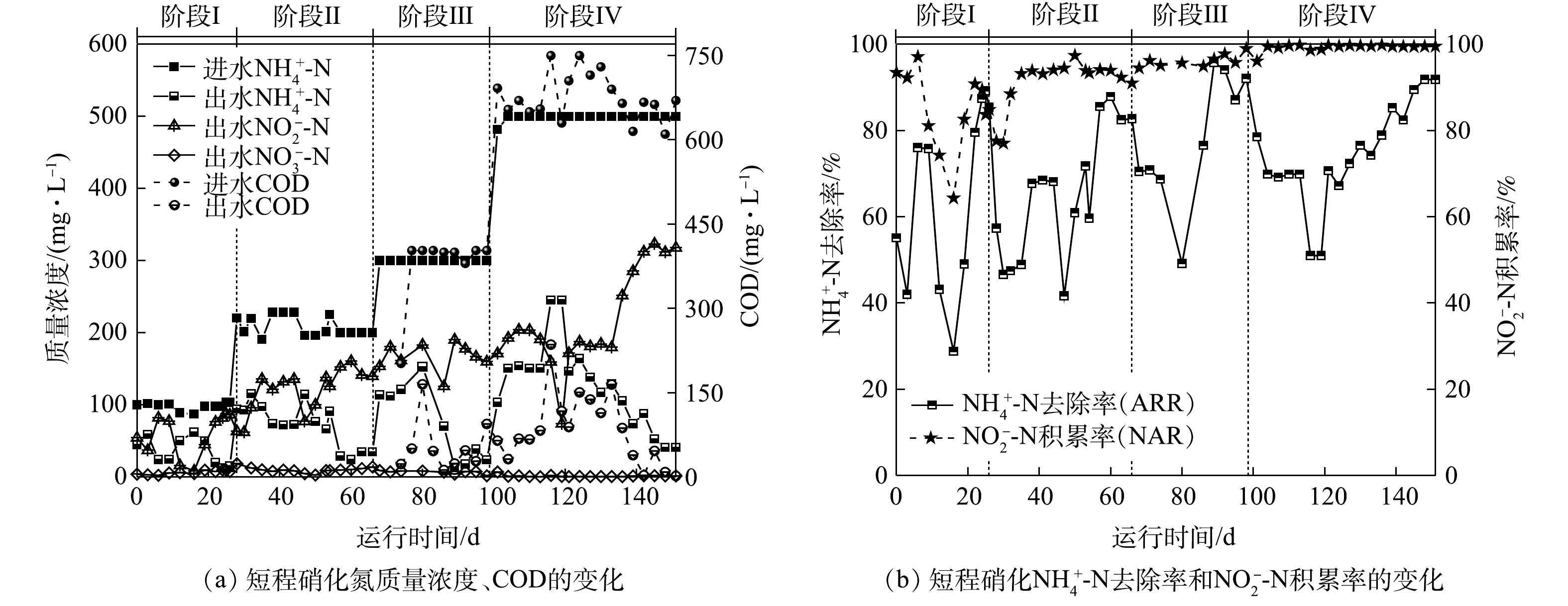







 点击查看大图
点击查看大图