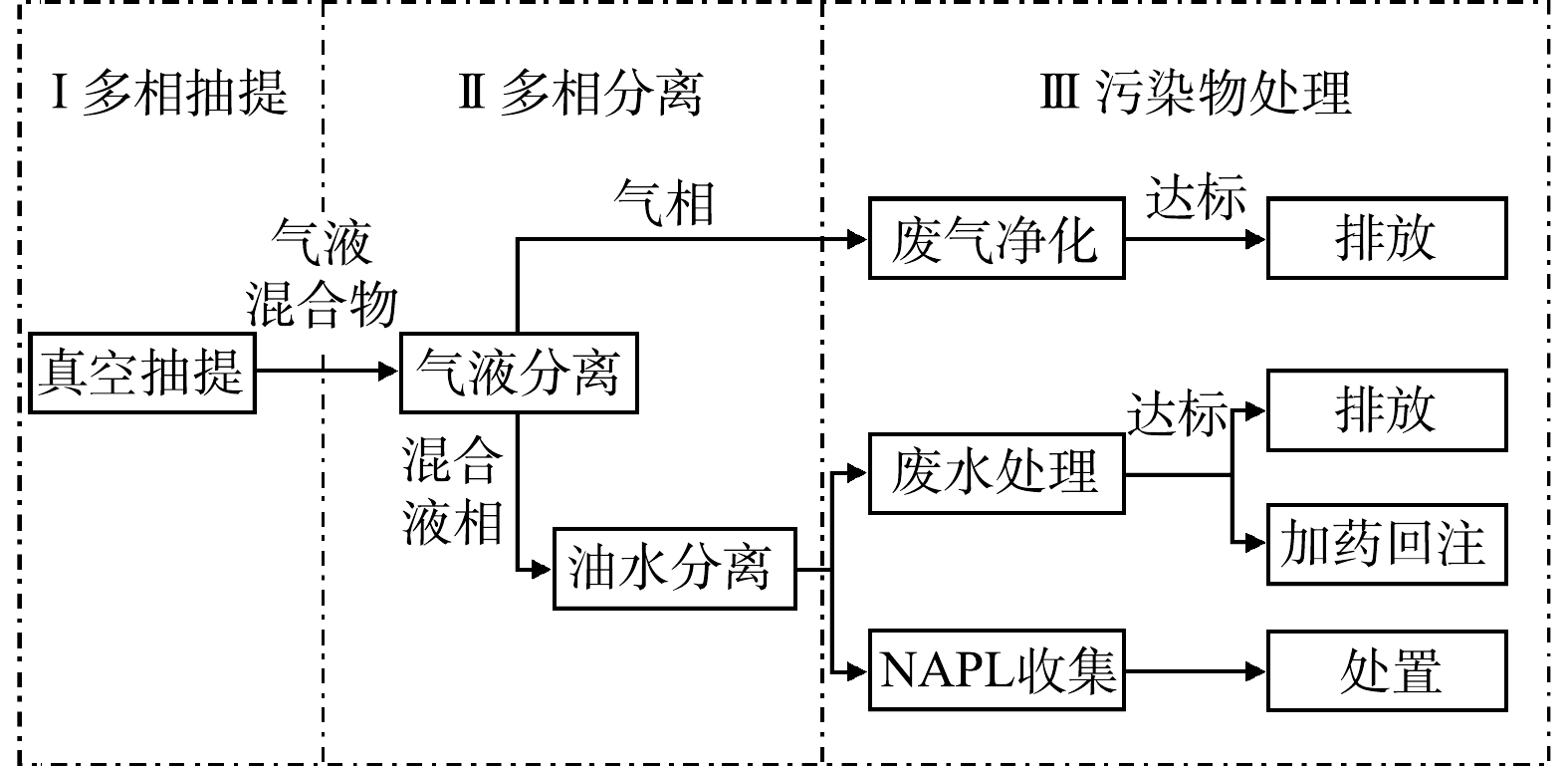
全文HTML
--> --> --> 自我国2017年发布《长江经济带生态环境保护规划》后,推动长江经济带发展的长江大保护行动就被提上了日程[1]。长江经济带自上海起,贯穿浙江、江苏、安徽、江西、湖北、湖南、重庆、贵州、四川和云南共11个省(直辖市),是我国经济发展的重点区域,在我国经济发展总格局中占据至关重要的地位。据统计,全国约37%重点化工园区位于长江经济带,长江及其主要干支流沿岸和重点湖泊附近(10 km内)聚集了约1.33×104个化工企业[2]。近年来,化工污染企业的聚集呈现自长江下游向中上游转移的趋势,且逐渐由东部传统集聚区(如江苏和浙江等)转移至中西部省份(如湖北和重庆等),给长江经济带土壤和地下水环境污染修复和风险管控带来了巨大挑战[3]。化工行业涉及广泛,基础化学原料、肥料、农药、涂料、合成材料和日用化学品等产品制造往往伴随着高毒、高持久性污染物的产生[4]。化工污染地块中典型污染物主要包括苯系物、多环芳烃和氯代烃类等,且可能出现非水相液体(non-aqueous phase liquid,NAPL)[5-7]。化工生产过程会对企业及周边土壤和地下水环境造成严重污染,因此,为保证化工企业搬迁后土地再利用安全,退役化工污染地块土壤和地下水污染修复已成为了一系列亟待解决的问题。相较于传统原位修复技术,多相抽提(multi-phase extraction,MPE)技术环境友好,对修复地块扰动小,能够同时去除包气带和含水层中的污染物,尤其对于存在NAPL的污染地块具有良好的修复效果[8-11]。目前,MPE技术在国外已被广泛用于加油站、炼油厂等石油烃污染地块修复中,并得到了良好的效果。GABR等[12]针对Rickenbacker国际机场的航空燃油污染(约85%为饱和低分子芳烃),布设了25排188口预制垂直井安装MPE系统抽提轻质非水相液体(light non-aqueous phase liquid,LNAPL)。该地块为砂质和粉质黏土、粉质砂土、黏质粉土和粉砂地层结构,LNAPL主要分布在粉质砂土层地下水位上。在真空诱导的抽提管内空气流速约为991~1 133 L·min?1条件下,MPE系统运行185 h共去除133 L LNAPL液体和467 kg气相有机污染物。BALDWIN等[13]构建了12口抽提井网络(安置于粉质黏土和砂质黏土层)MPE系统,修复受苯、甲苯、乙苯和二甲苯(BTEX)污染的加油站地下水。该系统以平均850 L·min?1蒸气流速运行2 a,共抽出污染地下水1 400 m3,去除约119 kg石油烃,其中的11口抽提井地下水中BTEX浓度低于0.5 μg·L?1。近年来,MPE技术在国内也逐渐受到关注,已有用于修复土壤和地下水中氯代烃、苯系物和石油烃等相关工程应用案例[14-18]。本研究比较了长江经济带下游地区(主要包括上海、江苏、浙江和安徽)化工污染地块水文地质条件和污染物特征与MPE技术适用条件,结合修复案例分析了该技术在长江经济带下游地区化工污染地块中的应用潜力,以期为MPE技术在该区域的推广实施提供参考。
MPE技术对污染地块中有机污染物削减存在多种机制。在真空泵作用下,抽提井附近地层中的流体响应压力梯度不断流入抽提井,地下水中溶解态污染物和浮油层LNAPL被抽离去除 [9-10]。同时,与抽提井连通的土壤孔隙中气压下降,挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs)和半挥发性有机物(semi-volatile organic compounds,SVOCs)向土壤气相加速转移,并随气流一起被抽离土壤。流通的气体使得土壤通气状况得到明显改善,土壤孔隙中氧含量增加,将有助于促进原位好氧微生物降解作用[21-22]。此外,MPE技术在抽取地下连续流体(地下水和NAPL)和土壤气体时,真空脱水作用降低了抽提井周边的地下水位,导致周围地层的空气渗透率升高,滞留在土壤中的VOCs和SVOCs将再分配至气相中,从而可提升污染物修复效率[19,23]。
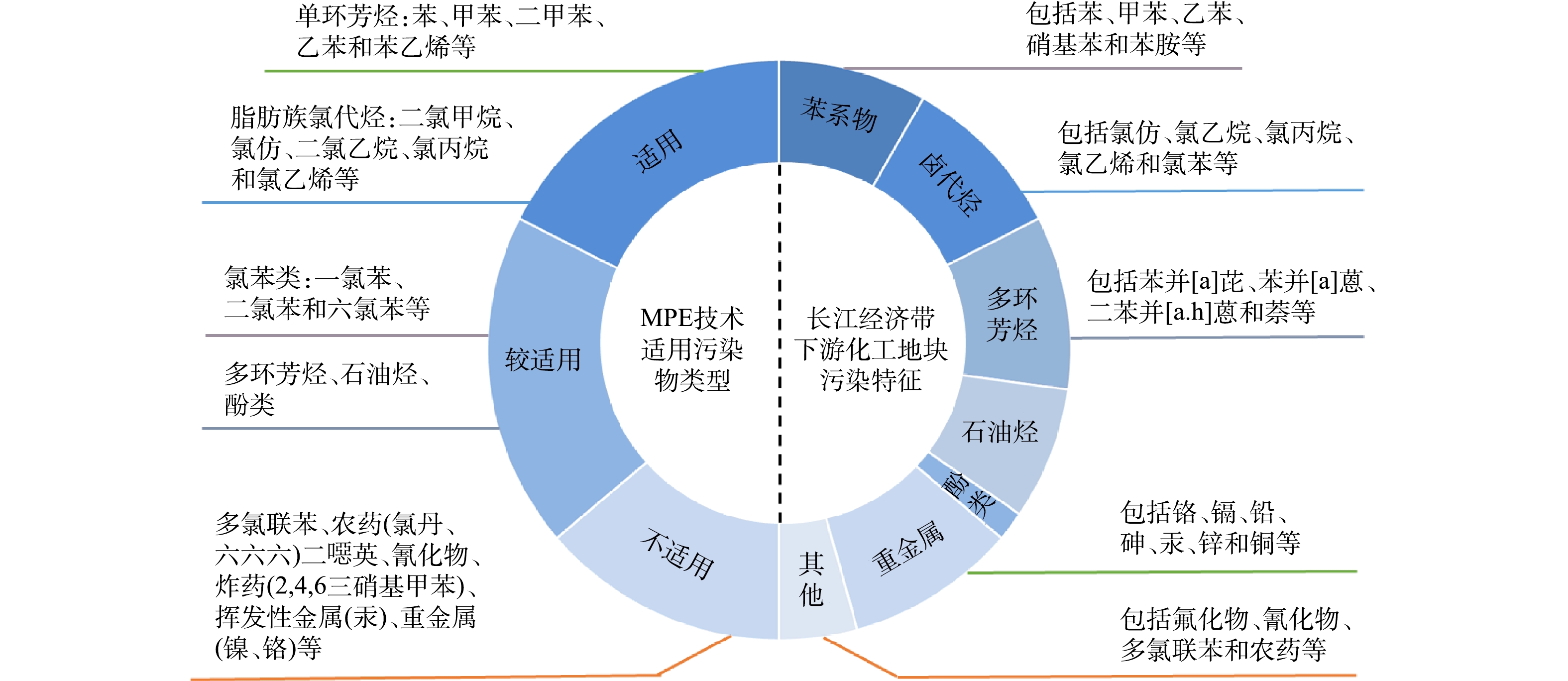
MPE技术对土壤气体和地下水的抽提流量主要受污染地块水文地质条件影响。通常认为,最适合MPE技术的渗透系数(K)为10?5~10?3 cm·s?1[19-20,24],对应中低渗透性土质(砂~粉质黏土)[8,25];而黏土通常K<10?6 cm·s?1,MPE技术难以达到理想修复效果。MPE技术原位修复污染地块时,分子量较小、易挥发和易溶解的有机污染物可被有效去除;而分子量较大和挥发性较低的有机污染物则更倾向与土壤基质结合[26]。通常,有机污染物饱和蒸气压(20 ℃)>0.133 kPa、亨利系数(20 ℃)>0.01和沸点250~300 ℃是MPE技术的适用范围[24,26]。MPE技术主要用于修复受挥发性有机物污染土壤和地下水,对脂肪族氯代烃和单环芳烃污染地块适用性最高,而氯苯、石油烃、多环芳烃和酚类化合物等污染物对MPE原位修复的适用性一般,其修复效果需结合污染地块地质条件综合评估。MPE技术不适用于炸药、杀虫剂、重金属、多氯联苯和非金属无机化合物污染地块的修复[27]。
2.1. 水文地质条件
由于沉积物成因类型及地貌发育过程的差异,不同地区地层结构及岩性组合类型多样。总结长江经济带下游地区地层结构特征,可更好地了解该区域水文地质和工程地质特点,为MPE技术可行性评估及污染地块修复方案设计提供参考。王靖泰等[28]对长江三角洲全新世地质环境的研究结果表明,该地区地层可分为3层:下段(厚5~15 m)主要为粉砂质黏土;中段(厚5~15 m)主要为淤泥质亚黏土;上段(厚3~13 m)长江以南主要为亚黏土,上段长江以北则以粉细砂为主[29]。林钟扬等[30]对长江三角洲南翼第四纪地层的勘察结果表明,该地区地层自上而下岩性可大致分为杂填土(0~1 m)、淤泥质亚黏土和亚黏土中段(1~8 m)、亚砂土(8~16.6 m)、淤泥质亚黏土和黏土(18.6~22.3 m)。宗开红等[31]对长江三角洲北翼第四纪地层的研究中发现,该地区地层结构自上而下大致分为素填土(0~1.3 m)、粉砂质黏土-黏土质粉砂(1.3~2 m)、粉砂(2~9.5 m)、淤泥夹粉砂团块(9.5~11.2 m)、黏土与粉砂互层(11.2~13.6 m)和粉细砂-细砂(13.6~19.4 m)。朱辉等[32]统计我国136个有机污染地块的相关数据后发现,相较于京津冀和辽中南地区,沪宁杭地区有机污染地块土层渗透性总体偏低,土层结构以粉土、粉质黏土和黏土为主,其中21%污染地块含有粉砂,部分地区存在淤泥质黏土。潜水含水层位于填土层下部、粉质黏土层上部,地下水埋深约0.2~4 m。其他研究中关于长江经济带下游地区的地层结构总结如表1所示。总体而言,长江经济带下游地区多为中低渗透性地层结构,普遍分布的地层结构包括:填土层、粉质砂土层、粉土层、黏土或粉质黏土层。虽然不同地区之间的地层厚度存在一定差异(如图2所示),但长江经济带下游地区的地层结构很大程度上与MPE技术适用条件(砂-粉质黏土)相符。
2.2. 长江经济带下游地区化工污染地块污染特征
我国污染地块修复项目主要分布于京津冀和江浙沪等东部沿海区域[32]。近几年,50%以上的工业污染地块修复项目涉及多环芳烃、苯系物、石油烃和氯代烃等有机污染(单一或复合有机污染物)[40]。朱辉等[32]发现,我国有机污染地块中,检出频次最高的污染物为卤代有机溶剂,其次为苯系物、多环芳烃和石油烃,且有机污染物在地下水中的检出率普遍高于土壤。依托国家重点研发计划项目“长江经济带化工园区场地污染防治技术集成与工程示范”,项目组调研了长江经济带下游地区128处污染地块相关资料。污染地块涉及精细化工、氯碱化工、纺织化工、石油化工、钢铁化工和农药医药化工等多种类型,主要污染物为苯及苯系物、卤代烃、酚类、多环芳烃、石油烃、重金属和其他(包括氟化物、氰化物、二噁英和农药等)等7大类。调研数据显示,长江经济带下游化工污染地块中有83.6%涉及有机污染,单一有机污染地块占45.3%,重金属-有机复合污染地块占38.3%。多环芳烃和卤代有机化合物的污染地块最多,分别占总有机污染地块的43.9%和42.1%;苯系物和石油烃污染地块次之,分别占37.4%和33.6%;酚类化合物的污染地块最少,仅占7.5%。氯仿、1,2-二氯乙烷、氯乙烯、氯苯等氯代溶剂是长江经济带下游化工地块常见的卤代有机污染物,苯并[a]芘、苯并[a]蒽和萘等是长江经济带下游化工地块常见的多环芳烃类污染物,苯、甲苯、乙苯、硝基苯和苯胺是是长江经济带下游地区化工地块常见的苯系物类污染物[32]。将长江经济带下游地区化工地块主要污染物类型与MPE技术适用污染物类别进行对比(如图3所示)可知,MPE技术适用于该区域大部分化工污染地块土壤和地下水修复。对存在重金属或氟化物、氰化物、农药和多氯联苯等复合污染地块,则需选择合适的联用技术以强化MPE技术对土壤和地下水修复效果。
2.3. MPE技术与常用修复技术对比
近些年,随着《中华人民共和国土壤污染防治法》《污染地块土壤环境管理办法》和《建设用地土壤修复技术导则》等法律或规定相继颁布,我国工业污染地块修复项目逐年增多,已形成庞大的需求,土壤修复行业前景广阔。王艳伟等[40]对全国2017年之前工业地块修复项目进行了统计,发现我国工业污染地块修复主要采用异位修复技术,以固化稳定化、化学氧化、焚烧、水泥窑协同处置等技术为主,原位修复技术占全部修复技术的比例低于10%;而同期美国应用原位修复技术占的比例为近50%,其中原位气相抽提技术应用占比最高,达到29%[40-41]。通过统计我国有机污染地块已实施的修复技术发现,土壤气相抽提技术占全部修复技术的比例由2007—2017年的12.1%上升至2018年的15.8%,该技术与化学氧化、原位热脱附一起已成为有机类污染地块主流修复技术[42]。MPE技术与常用修复技术的特点对比[43-47]如表2和表3所示。在上述污染地块常用修复技术中,固化/稳定化可快速、高效地修复污染地块,应用广泛,但该技术主要用于处理重金属等无机污染物,对VOCs和石油烃适用性较差[42]。植物修复技术主要应用于重金属修复领域,投入成本较低,但该技术通常只能处理浅层污染,修复周期长,且同样不适用于修复VOCs污染土壤,不适用于化工污染地块的修复[46-47]。土壤气相抽提技术对挥发性有机污染物的处理效率高,但该技术对污染地块土壤渗透性要求较高,不适用于长江经济带下游地区污染地块中低渗透性土壤修复[45,48]。热处理和原位化学氧化技术适用范围较广,修复周期短,但面临投入成本高和二次污染等问题[46,49]。水泥窑协同处置技术是目前国内应用较广的地块修复技术,修复周期短,但该技术通常用于异位修复,需对污染土壤进行预处理,且涉及土壤挖掘和远距离运输,具有二次污染风险[44]。可渗透反应墙可修复的污染物范围较广,对VOCs、SVOCs、多环芳烃和重金属均具有很高的适用性,但该技术在修复过程中需定期更换活性材料,使用后的材料需妥善处置,且修复周期较长,需要进行长期监测[46,50]。相比上述技术,MPE技术适用于VOCs、SVOCs和石油烃等有机污染物高效去除,可用于渗透性较低的土壤。在选用MPE技术前,要考虑目标地块的地质特征和污染物类型等是否符合MPE技术适用范围。此外,该技术资金投入和运营维护成本相对较高,修复周期也较长。
MPE技术可在较短周期内使污染物达到修复目标,在长江经济带下游地区化工污染地块修复中将发挥越来越重要的作用。MPE技术修复成功的化工污染地块的地层结构主要包括填土层、粉质砂土层、砂质粉土层和粉质黏土层,土层渗透系数多分布于10?5~10?3 cm·s?1;主要污染物为苯系物、氯代烃、多环芳烃和石油烃;污染物分布深度和地下水埋深较浅(一般≤6 m,污染位于潜水含水层),井头真空度维持在?0.02~?0.06 MPa即可实现对地下水气的快速抽提。但由于部分地块含有黏土或淤泥质黏土等微透水性地层结构,渗透系数偏低(<10?6 cm·s?1),单一MPE技术对污染物的去除效果受到限制。此时,MPE技术与其他ISCO技术联用可有效消除抽提后期出现的“拖尾”现象,充分发挥MPE技术原位、快速、高效修复污染地块的优势。
若渗透性较差的黏土层在污染地块地层结构中占比较高或污染物主要分布于黏土层,则应用单一MPE技术难以实现污染物完全抽出。戴昕等[51]针对MPE技术在低渗透性土壤中抽提效果受限的缺点,采用空气曝气AS-MPE联用修复系统,通过注气泵向含水层饱和区注入空气,向高污染且低渗透性区域提供正向气相压力梯度以促进局部空气流通,有效解决了MPE技术在不均匀低渗透性地块中抽提效率低的问题。申屠雷吉等[52]提出了一种新型气动压裂强化MPE系统,通过压裂井向污染地层中注入高温高压空气,增加地层裂隙,提升非饱和区域透气率,从而强化了MPE技术对低渗透性地层的修复效果。余湛等[53]通过电动强化MPE系统向污染介质中传输脉冲电压,使土壤中弱结合水摆脱双电层束缚成为可被抽提的自由水,以加快污染介质中的物质传质过程,从而提升了MPE技术抽提效率。谢宇等[54]提出了一种创新型MPE布井系统,以每2条气相抽提管和1条液相抽提管组成1个抽提单元,相邻抽提单元横竖交错,同时在地表加设液体喷淋装置以改变土壤低渗透性,从而最大程度地提升了MPE技术在低渗透性土壤中的抽提效果。
若复合污染地块中存在不适用MPE技术修去除的污染物,如重金属、多氯联苯和农药等,可选择合适的联用技术进行优势互补,以强化修复效果。王国杰[55]通过实验室模拟研究发现,表面活性剂水基泡沫强化MPE技术可有效去除模拟土壤中的有机污染物芘。修复后,土壤中芘的去除率可达85%以上。尹炳奎[56]验证了热强化MPE技术可以促进氯代烃污染地块中污染物向气相迁移,热强化可有效削减污染地块中二氯甲烷、氯乙烯和四氯乙烯的浓度。王锦淮等[17]对比了使用单一MPE技术和MPE+ISCO(过硫酸钠+氢氧化钠)联用2种方案对受氯苯和二氯苯污染地块的修复效果。该研究结果表明,采用MPE + ISCO联合可显著提高修复效率,使抽提区地下水中污染物含量降低至修复目标。王儒等[57]将土壤原位淋洗技术与MPE技术联用,通过灵活选用特定淋洗液强化了MPE技术对土壤的修复能力。同时,将淋洗液回收装置与MPE设备相连,可提高淋洗液利用效率并有效避免二次污染,使有机污染土壤原位修复更经济高效。
目前,针对低渗透性地层和难挥发有机污染物抽提的MPE联用技术研究多处于实验室研究阶段,尚缺乏在实际污染地块中开展应用的报道,需开展更多中试及以上规模的示范研究,以验证MPE技术与原位热脱附、生物修复、表面活性剂增溶、气动压裂等方法联用的可行性及实用性,进一步提升MPE技术在长江经济带下游地区化工污染地块中的应用潜力。
1)开发MPE技术模拟预测数值模型,针对目标地块工程与水文地质信息及污染物特征,优化MPE技术遴选,指导MPE技术系统设计和参数优化(如布井方式、布井深度、真空度、抽提速率和运行周期等)。
2)开展中试及以上规模试验,验证MPE技术与原位热脱附、生物修复、表面活性剂增溶、气动压裂等方法联用的可行性及实用性,解决复杂地层结构及复合污染特征的修复瓶颈。
3)设计新型MPE技术抽提系统构造,实现试剂注入系统、通风系统和地下水回注系统等多功能集成创新,减少对地下环境的影响并降低设施建造成本。
4)开发MPE自动监测与控制系统,实现运行参数实时监测与系统高效调控。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 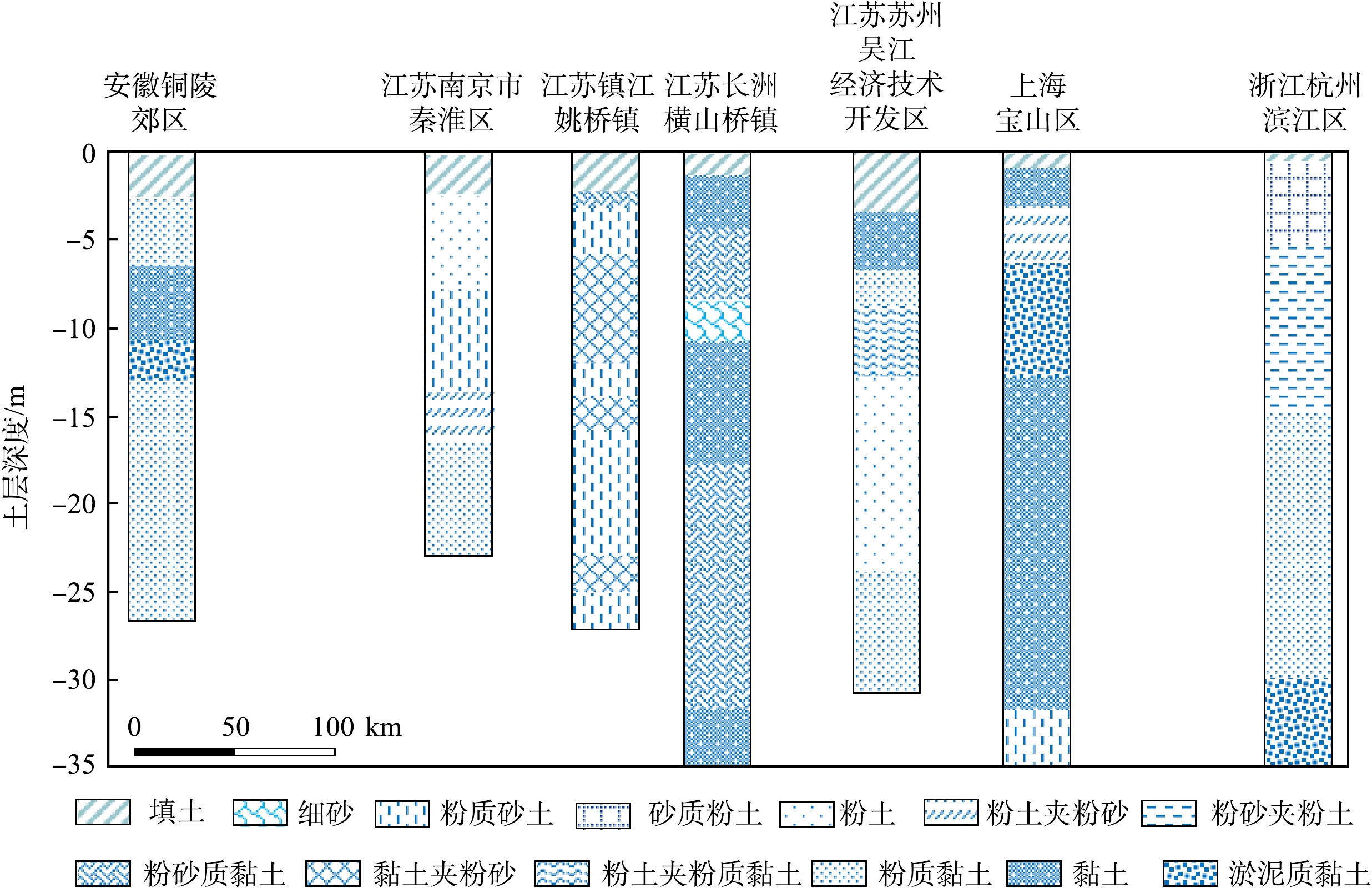
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图