全文HTML
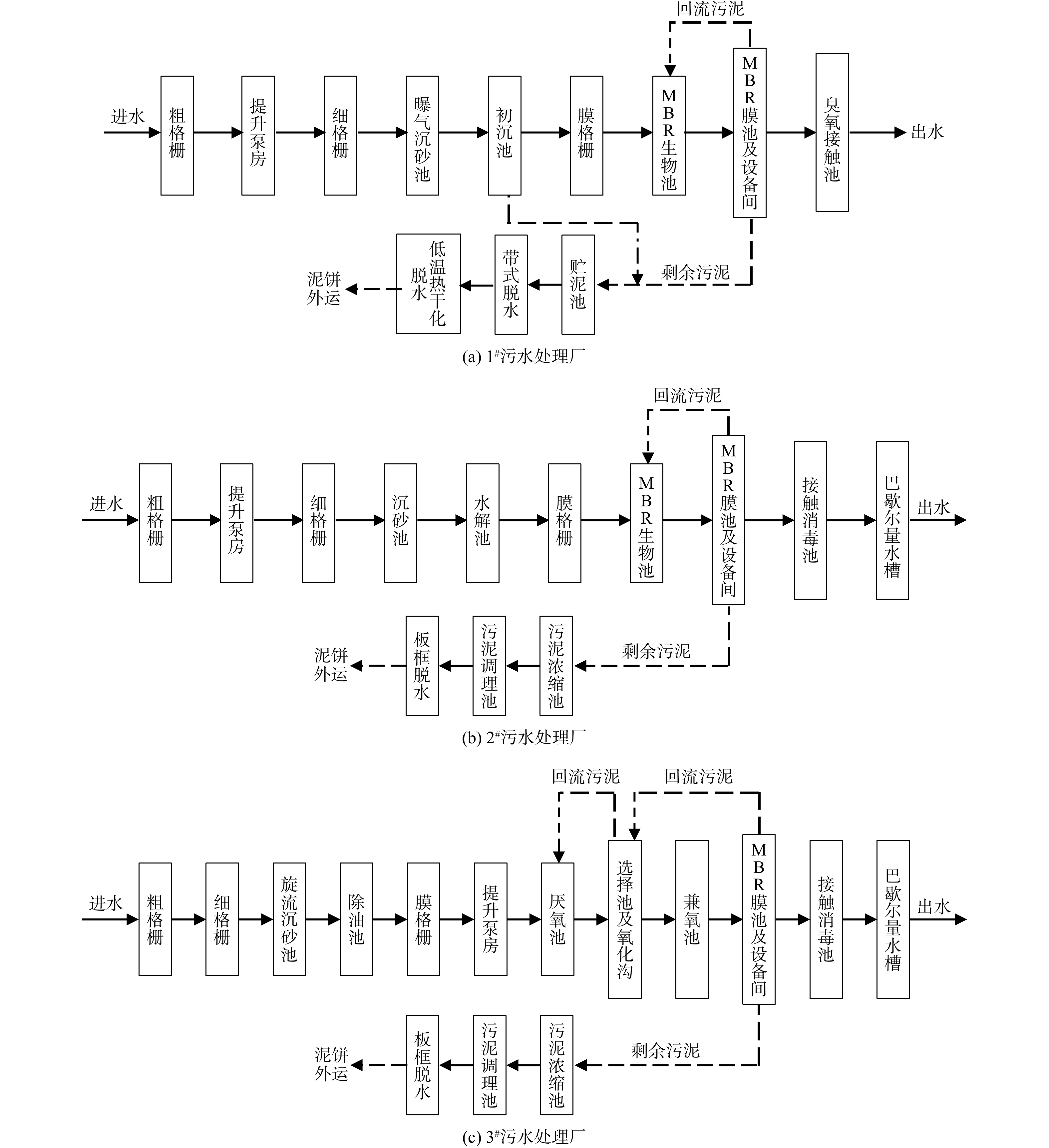
--> --> --> MBR工艺具有占地小、出水水质好、直接投资及运行费用高[1-3]等特点。目前,由于污水厂建设用地的限制,在地下污水处理厂工程[3]及污水处理厂提标改造的建设工程[4-5]中,污水处理主工艺大部分采用MBR工艺。根据常规设计经验,MBR工艺的预处理段通常会设置3道格栅,生物段通常采用A2O矩形生物池或者多段AO等矩形池,污泥处理段通常采用污泥浓缩池或贮泥池和机械脱水工艺。然而,对于预处理段3道格栅栅条间隙的设置、生物池的池形设计、污泥浓缩池和贮泥池的适应性设计,以及污泥的资源化利用工艺等尚未见系统报道。为减少污水处理厂在运行后出现格栅运行负荷失调、生物池浮泥、污水脱水困难等问题,本研究结合3个工程案例,针对新疆维吾尔自治区3个MBR工艺进行了分析,从工艺流程、进出水水质、设计参数、不同池形内浮泥现象、污泥处理段有无浓缩池、污泥处理难易程度、运行费用等方面进行了对比,以期系统总结MBR工艺的特点,为类似工程设计或工艺选择提供参考。2.1. 设计进水水质
3座污水处理厂出水水质指标均执行《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)中一级A标准,设计进出水水质见表1。2.2. 工艺主要设计参数
2.2.1. 1#污水处理厂主要设计参数
1)粗细格栅:粗格栅采用回转式格栅除污机,栅间隙15 mm,安装角度75°;细格栅采用转网式格栅除污机,栅间隙3 mm,安装角度60°。2)沉砂池:采用曝气沉砂池,1座2格,有效水深2.6 m,水平流速0.06 m·s?1,停留时间6.08 min。
3)初沉池:采用中进周出辐流式沉淀池,2座,直径25 m,有效水深3.9 m,表面负荷2.39 m3·(m2·h)?1,沉淀时间1.63 h;剩余污泥量300 m3·d?1,污泥含水率97%。
4)膜格栅:采用内进流网板格栅除污机,栅间隙1 mm,安装角度90°。
5) MBR生物池:2座,单座尺寸64.6 m×32.9 m,有效水深6.0~6.2 m。生物池分为厌氧、缺氧、好氧段,厌氧停留时间2 h,缺氧停留时间5.5 h,好氧停留时间6.5 h;污泥负荷(以每天单位质量的MLSS去除BOD5的质量计)0.067 kg·(kg·d)?1,MLSS的质量浓度为6.0 g·L?1;缺氧池至厌氧池的混合液回流比为200%,膜池至缺氧池的为800%,膜池至好氧池的为200%;好氧池曝气采用微孔管式曝气器;在好氧池末端投加PAC药剂进行化学辅助除磷,投加量为20~30 mg·L?1(药剂的商品量,即药剂中有效成分为28%)。
6) MBR膜池及设备间:膜池有效水深3.6 m,停留时间1.4 h;膜池分8个系列,每个系列设膜组器6组,预留2组空位;膜组器采用PVDF浸没式中空纤维膜,孔径<0.1 μm;MBR膜设备间配置产水泵、CIP(在线清洗)泵、剩余污泥泵、在线化学清洗加药系统以及其他辅助设备;平均名义膜通量为16.54 L·(m2·h)?1,膜吹扫总风量246 m3·min?1。
7)臭氧接触池:臭氧接触池有效水深5.5 m, 接触时间24.5 min,采用空气源臭氧发生器,臭氧最大投加量4.0 mg·L?1。
8)贮泥池:湿污泥量1 123 m3·d?1,含水率99.2%。1座2格,有效水深4.5 m,停留时间6.9 h,池内设潜水搅拌器和潜水曝气机以免污泥沉降。
9)脱水机房:采用带式脱水机,脱水至泥饼含水率≤80%后,至低温热干化,最终污泥含水率降至≤60%后运往垃圾填埋场填埋。
2.2.2. 2#污水处理厂主要设计参数
该污水处理厂为提标改造,预处理单元中新建膜格栅间,将现状生物池改造为MBR生物池,新建MBR膜池及设备间、接触消毒池和污泥浓缩脱水系统,其余建(构)筑物和设备现状利用。现状粗格栅栅条间隙为15 mm,安装角度75°,现状细格栅为内进流格栅,栅间隙为4 mm。新建和改造建(构)筑物主要设计参数如下。1)膜格栅:采用内进流网板格栅除污机,栅间隙1 mm,安装角度90°。
2) MBR生物池:现状生物池改造为厌氧、缺氧、好氧(A2O)处理工艺,根据场地和构筑物布置,将整个生物处理系统分为一期(2.2×104 m3·d?1)和二期(2.8×104 m3·d?1)处理系统。一期生物池厌氧停留时间3.18 h,缺氧停留时间7.32 h,好氧停留时间9.6 h,污泥负荷(以每天单位质量的MLSS去除BOD5的质量计)0.08 kg·(kg·d)?1,MLSS的质量浓度为6.5 g·L?1;二期生物池厌氧停留时间2.5 h,缺氧停留时间5.75 h,好氧停留时间7.54 h,污泥负荷(以每天单位质量的MLSS去除BOD5的质量计)0.085 kg·(kg·d)?1,MLSS的质量浓度为6.7 g·L?1,在生物池后增设兼氧池,停留时间3.8 h。膜池至好氧池的混合液回流比为500%,好氧池至缺氧池的为400%,缺氧池至厌氧池的为200%。好氧池和兼氧池曝气采用微孔管式曝气器。设计在膜池前段投加药剂(PAC)进行化学辅助除磷,投加量为20~30 mg·L?1(商品量28%)。
3) MBR膜池及设备间:膜池分期规模与MBR生物池一致。一期膜池有效水深3.6 m,停留时间1.49 h,膜池分6个系列,共设膜组器26组,预留10组空位;二期膜池有效水深3.6 m,停留时间1.35 h,膜池分6个系列,共设膜组器34组,预留8组空位。膜组器采用PVDF浸没式中空纤维膜,孔径<0.1 μm。平均名义膜通量为16.34 L·(m2·h)?1,膜吹扫总风量390 m3·min?1。
4)接触消毒池:尾水采用次氯酸钠消毒,接触池形式为矩形隔板式,有效水深4.0 m, 接触时间35.04 min。
5)污泥浓缩池:湿污泥量1 763 m3·d?1,含水率99.2%。2座,直径16 m,池边水深4.0 m,浓缩时间21.9 h,固体通量43.84 kg·(m2·d)?1,浓缩后污泥含水率98%。
6)污泥脱水机房:采用板框压滤机,脱水后泥饼含水率≤60%;选用板框压滤机3台,单台过滤面积560 m2,日运行时间12 h,配套污泥调理、进泥、压榨、洗布、调理剂投加等设备。
2.2.3. 3#污水处理厂主要设计参数
该污水厂为提标改造,预处理中新建除油池和膜格栅间,现状氧化沟选择池前新建厌氧池,氧化沟后新建兼氧池,新建MBR膜池及设备间、接触消毒池和污泥浓缩脱水系统,其余建(构)筑物和设备现状利用。现状粗格栅栅条间隙为15 mm,安装角度75°,现状细格栅为回转式格栅,栅间隙为6 mm。新建和改造建(构)筑物主要设计参数如下。1)膜格栅:采用内进流网板格栅除污机,栅间隙1 mm,安装角度90°。
2)氧化沟(改造):现状选择池前端增加厌氧池,停留时间1.3 h,与现状选择池联合作为厌氧区,总厌氧区停留时间1.65 h;氧化沟停留时间14.3 h,污泥负荷(以每天单位质量的MLSS去除BOD5的质量计)0.102 kg·(kg·d)?1,MLSS的质量浓度为6.5 g·L?1;膜池至氧化沟的混合液回流比为800%,氧化沟缺氧区至厌氧区的为200%;设计在膜池前段投加PAC进行化学辅助除磷,投加量为20~30 mg·L?1(商品量28%)。
3)兼氧池:1座2格,有效水深6.0 m,停留时间3.4 h,MLSS的质量浓度为6.5 g·L?1。
4) MBR膜池及设备间:膜池有效水深3.6 m,停留时间1.4 h。膜池分10个系列,每个系列设膜组器9组,预留1组空位;膜组器采用PVDF浸没式中空纤维膜,孔径<0.1 μm;平均名义膜通量为16.53 L·(m2·h)?1,膜吹扫总风量480 m3·min?1。
5)接触消毒池:尾水采用次氯酸钠消毒,接触池形式为矩形隔板式,有效水深4.5 m, 接触时间31.1 min。
6)污泥浓缩池:湿污泥量2 206.8 m3·d?1,含水率99.2%。2座,直径16 m,池边水深4.0 m,浓缩时间17.49 h,固体通量54.88 kg·(m2·d)?1,浓缩后污泥含水率98%。
7)污泥脱水机房:采用板框压滤机,脱水后泥饼含水率≤60%;选用板框压滤机3台,单台过滤面积560 m2,日运行时间16 h,配套设备用于污泥调理、进泥、压榨、洗布、调理剂投加等。
3.1. 污水处理效果
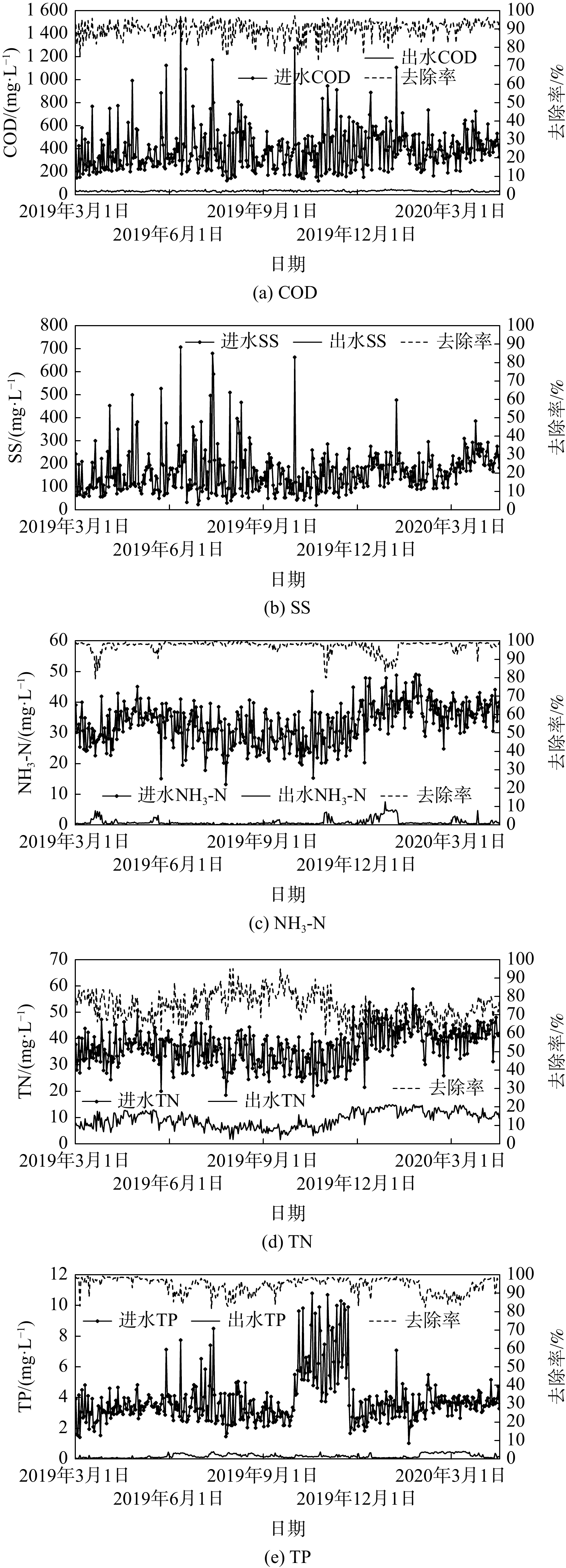
1#污水处理厂2013年8月开工建设,2014年10月通水运行。2#、3#污水处理厂2018年4月开工建设,2019年3月通水运行。尽管3座污水处理厂的主体工艺基本相同,但在进水水质、预处理单元、生物处理单元、污泥处理单元、运行等方面存在一定差别。1#污水处理厂已运行近6年,根据2019年7月至2020年6月的水质监测化验报告,绘制了图2。结果表明,该污水处理厂的处理效果稳定,且出水稳定达标。虽然进水的平均NH3-N和TN(分别为53.5 mg·L?1和55.1 mg·L?1)大于原设计进水水质的指标,偏离幅度分别达到33.75%和10.2%,但工艺对NH3-N和TN的去除率仍达到98%和83%,出水的平均NH3-N和TN分别为1.01 mg·L?1(优于地表Ⅳ类)和9.01 mg·L?1;进水的平均COD为389 mg·L?1,工艺对COD的去除率达94%,出水的平均COD为24.2 mg·L?1 (优于地表Ⅳ类)。根据2#污水处理厂2019年3月至2020年4月的水质监测数据,绘制了图3,分别为处理工艺对COD、SS、NH3-N、TN和TP的处理效果。结果表明,在近1年的调试运行中,尽管污水厂进水水质不稳定、变幅大,但该污水处理厂出水仍可达标排放。进水水质中,平均COD为389 mg·L?1,最大值为1 506 mg·L?1,最小值为120 mg·L?1;平均SS为166 mg·L?1,最大值为707 mg·L?1,最小值为20 mg·L?1;NH3-N平均值33 mg·L?1,最大值为49 mg·L?1,最小值为13 mg·L?1;平均TN为37 mg·L?1,最大值为59 mg·L?1,最小值为18 mg·L?1;平均TP为3.8 mg·L?1,最大值为10.8 mg·L?1,最小值为1 mg·L?1。受进水水质变化的影响,出水水质也相应发生变化,但仍达到一级A设计要求。其中,出水SS几乎不受进水水质变化影响,持续为未检出(优于一级A),对COD、NH3-N、TN和TP的平均去除率分别为90%、97%、75%和95%。
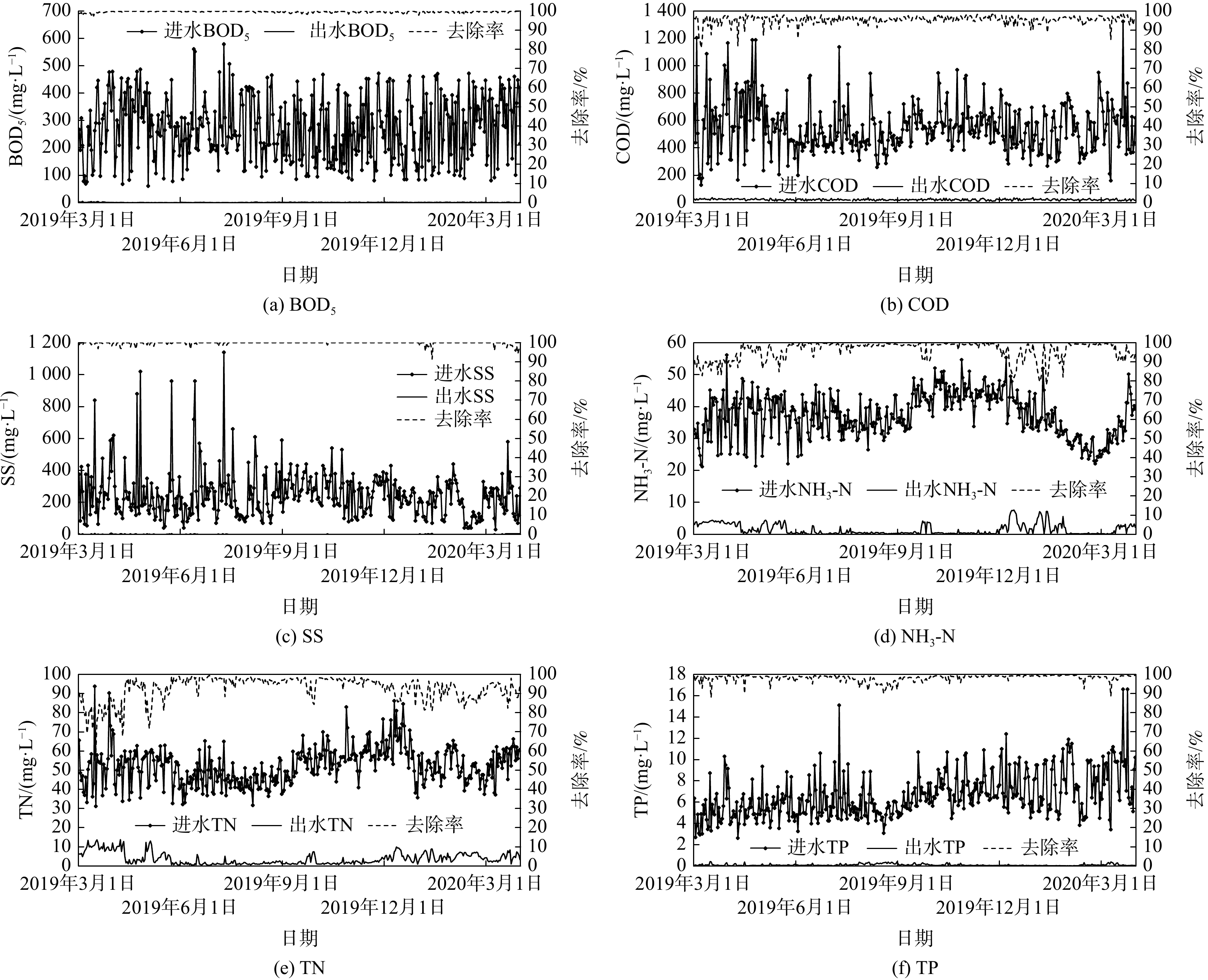
根据3#污水处理厂2019年3月至2020年3月水质监测数据,绘制了图4,分别为处理工艺对BOD5、COD、SS、NH3-N、TN和TP的处理效果。结果表明,在近1年的调试运行中,尽管污水厂进水水质不稳定、进水水质大于设计标准天数多,但该污水处理厂的出水仍可达标排放。进水水质中,平均BOD5为277 mg·L?1,最大值为579 mg·L?1,最小值为61 mg·L?1;平均COD为550 mg·L?1,最大值为1 324 mg·L?1,最小值为129 mg·L?1;平均SS为247 mg·L?1,最大值为1 140 mg·L?1,最小值为30 mg·L?1;平均NH3-N为37 mg·L?1,最大值为56 mg·L?1,最小值为21 mg·L?1;平均TN为52 mg·L?1,最大值为94 mg·L?1,最小值为31 mg·L?1;平均TP为6.6 mg·L?1,最大值为16.6 mg·L?1,最小值2.6 mg·L?1。受进水水质变幅影响,出水水质也相应发生变化,但仍达到一级A设计要求。其中,出水SS和BOD5几乎不受进水水质变化影响,出水平均SS仅为0.52 mg·L?1,且大多为未检出(优于一级A),出水平均BOD5仅为0.91 mg·L?1,COD、NH3-N、TN和TP的平均去除率分别为95%、96%、93%和98%。
由3座污水处理厂对污染物的去除效果可知,MBR工艺抗冲击能力强,能够适应水质、水温的变化,污染物去除率高,出水水质稳定达标。微滤膜的截留作用对固体悬浮物有很好的去除效果,出水SS低于4 mg·L?1,甚至未检出;且通过化学加药除磷,出水TP低于0.2 mg·L?1,优于地表Ⅲ类指标。由于MBR工艺系统内的活性污泥质量浓度高(6~9 g·L?1),通过膜的截留作用,大量世代周期长的硝化菌和反硝化菌得以增殖,当稳定运行时,工艺对COD和BOD5的去除率可达93%以上,出水NH3-N小于1.5 mg·L?1,优于地表Ⅳ类指标。
3.2. 预处理单元的运行状况
1#污水处理厂为新建工程,预处理单元设置了粗、细、膜格栅3道格栅,粗格栅栅条间隙为15 mm,细格栅栅条间隙为3 mm,膜格栅栅条间隙为1 mm。3道格栅负荷逐级递减,各个格栅运行正常,各自的拦渣负荷在预定设计范围内。3#污水处理厂为改造工程,现状粗格栅栅条间隙15 mm,现状细格栅栅条间隙为6 mm,项目改造时增加膜格栅,栅条间隙为1 mm。通水运行后,膜格栅负荷太重,格栅前后液位差较大,需不间断冲洗才能提高格栅的孔隙率。经查找,其原因为现状细格栅栅间隙为6 mm,且设备老化,拦渣效率降低。因此,项目运行单位提出对细格栅进行改造,将细格栅改为内进流格栅机,栅条间隙调整为4 mm后,膜格栅的运行负荷有效降低。
西北地区大多数区域属于干旱区域,排水系统中合流制、截留式合流制、不完全分流制系统较多,故污水中的悬浮物及含沙量明显要高于南方地区的污水。从3座污水处理厂的预处理单元运行情况来看,格栅的栅条间隙选择非常重要,尤其应注重细格栅间隙的选择。污水中6 mm以下的纤维类、毛发等较多。如果在细格栅这一道格栅不能有效拦截,至膜格栅前,将会增大膜格栅的运行压力,甚至会造成膜格栅渠道翻水的现象。
3.3. 生物处理单元运行状况
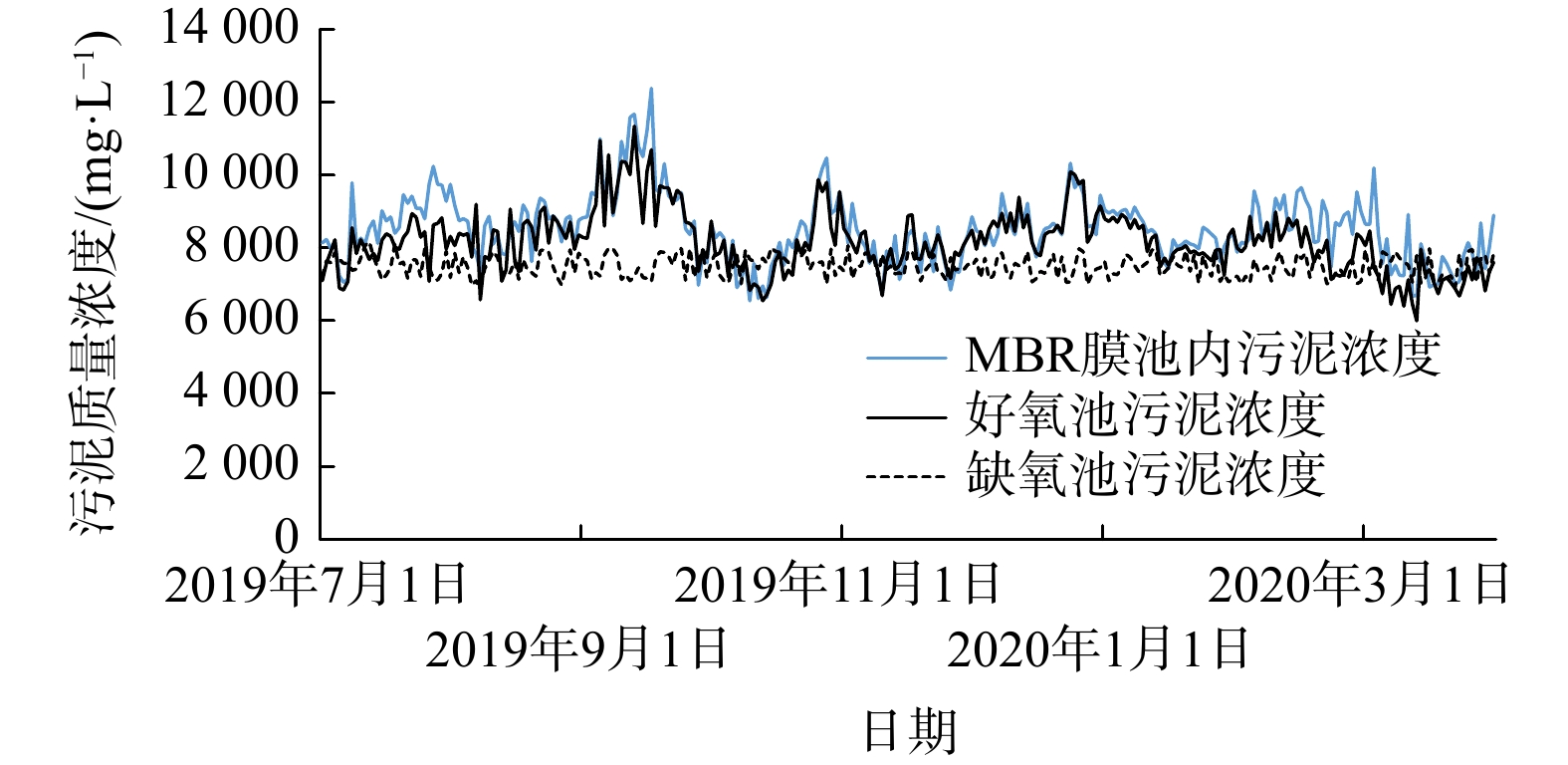
1#污水处理厂的生物处理工艺采用A2O+MBR工艺,原水分两点进水,设计厌氧池进水70%~80%,剩余20%~30%进入缺氧池。根据运行方提供资料,生物池在运行过程中,平均污泥浓度为6~7 g·L?1,膜池的污泥质量浓度为8~9 g·L?1。生物处理过程未投加碳源,但在生物处理段末端投加了除磷剂(主要成分为FeCl3)进行辅助化学除磷,除磷剂投加量为0.9 t·d?1(按质量浓度22.5 mg·L?1投加药剂,药剂商品量为28%)。生物池为矩形池型,厌氧池、缺氧池内水流转弯位置水流不畅,漂浮死泥较多。2#污水处理厂为提标改造项目。在提标改造过程中,将原CASS池改造为A2O生物池,其后端再增加MBR膜池。改造后的A2O生物池厌氧段、缺氧段、好氧段完全用隔墙分开。运行方提供MBR膜池及生物池好氧段、缺氧段污泥浓度如图5所示。
设计时,膜池至好氧池的混合液回流比为500%,好氧池至缺氧池的为400%,缺氧池至厌氧池的为200%。实际运行中,各级的回流比和设计相同。如图5所示,MBR膜池内污泥的质量浓度为6~9 g·L?1,生物池好氧段内污泥的质量浓度为6.5~9 g·L?1,生物池缺氧段内污泥的质量浓度为6.5~7 g·L?1。根据运行方提供运行台账,生物处理过程中需投加碳源、除磷药剂等。每天投加碳源(葡萄糖)为1.71 t·d?1,除磷剂投加量为1.47 t·d?1(按质量浓度29.4 mg·L?1投加药剂,药剂商品量为28%)。生物池为矩形池型,水流转弯地方死角太多,造成厌氧池、缺氧池漂浮死泥较多。
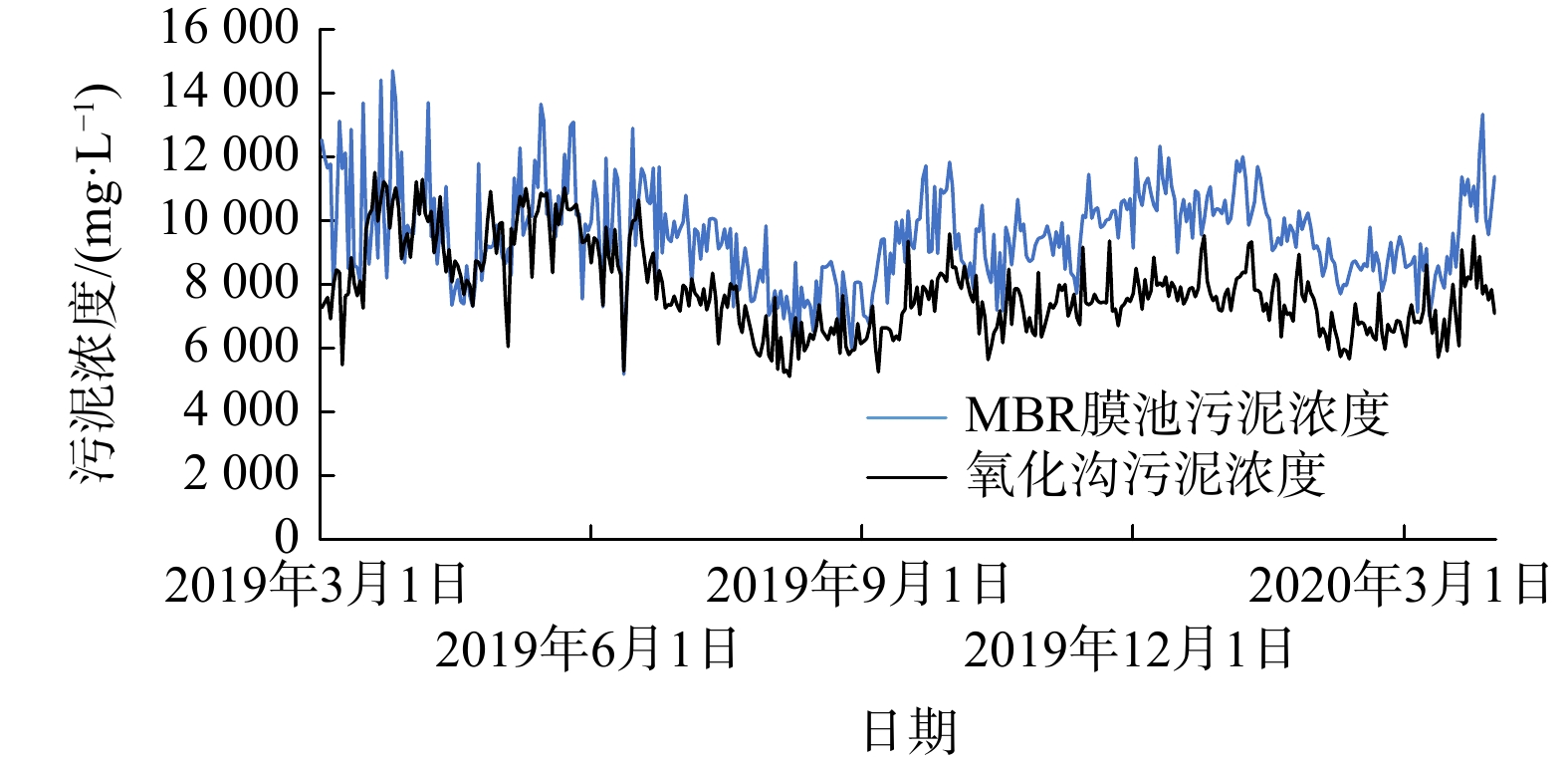
3#污水处理厂亦为提标改造项目。在提标改造过程中,在原氧化沟的选择池前端增加厌氧池,和选择池合并后作为厌氧段,强化生物除磷。氧化沟基本维持原设计。在氧化沟的后端增加兼氧池,强化脱碳脱氮。运行方提供MBR膜池及氧化沟内污泥的质量浓度如图6所示。
MBR膜池至氧化沟的混合液回流比设计为800%,氧化沟缺氧段至厌氧段回流比为200%。实际运行MBR膜池至氧化沟的混合液回流比为400%~500%,氧化沟缺氧段至厌氧段回流比200%。由图6可知,MBR膜池内污泥的质量浓度为8~10 g·L?1,氧化沟内平均污泥质量浓度为6~8 g·L?1,氧化沟内污泥质量浓度的波动趋势基本与MBR膜池内污泥质量浓度波动相似。根据运行方提供的运行台账,生物处理过程中并未投加碳源、除磷药剂等,出水水质均能稳定达标。因现状氧化沟为采用倒伞式表曝机,缺氧段设有推流器,池内水流转弯处采用圆弧倒角,水流通畅,且水流速度较快,池体表面基本无浮泥、死泥漂浮现象。
分析3座污水处理厂生物段的运行情况,可得出以下2点。1)由于MBR工艺运行污泥浓度比常规工艺高很多,相应污泥龄较长,排泥不及时或者池内推流动力不足,或者池内局部区域水流不畅,很容易造成污泥上浮。因此,生物池内需提高表面水流的推力,池型设计也应尽量考虑设有弧度,避免直角池型的出现。2)1#污水处理厂生物池的缺氧段所需碳源通过原水进行了补充,故在整个生物处理过程中没有外加碳源;2#污水处理厂生物池改造后为严格的A2O生物池,总进水从厌氧段进入,依次经过缺氧段、好氧段、最终进入膜池,运行过程中在缺氧段投加碳源;3#污水处理厂运行过程中未外加碳源。分析3座污水处理厂的进水方式及各自厌氧段的停留时间,虽然生物处理过程原水中的COD、TN等指标各异,但总体来说,厌氧段会由于聚磷菌释磷、活性污泥的吸附、降解有机物等消耗较多碳源,致使进入缺氧段、好氧段的碳源含量很少,影响脱氮效果,投加碳源势必会增加运行成本。因此,可通过改变进水方式或者合理设定厌氧段的停留时间为脱碳除磷合理分配碳源,解决污水生物处理工艺中进水碳源不足的问题。
3.4. 污泥处理单元的运行状况
1#污水处理厂的污泥处理流程为:剩余污泥先排至贮泥池缓存,然后通过螺杆泵泵入帯式浓缩脱水一体机进行脱水。根据运行单位反映,从MBR膜池排出的剩余污泥,通过贮泥池暂存后直接进入帯式浓缩脱水机脱水时,脱水效果不佳,一般需要投加较多的助凝剂。2#、3#污水处理厂改造过程中,汲取1#污水处理厂的经验,设置了污泥浓缩池。污泥处理流程为:剩余污泥先排至污泥浓缩池进行浓缩,浓缩后的污泥含水率达到约98%时,通过螺杆泵泵入板框压滤机进行脱水。污泥浓缩池的设计停留时间基本都在12 h以上。根据运行单位反映,经过污泥浓缩池浓缩后的污泥脱水性能有所改善,可相应减少投加的药剂量。
为维持稳定的膜通量,需要持续不断地进行吹扫曝气。这种持续不断的曝气产生的机械剪切力会严重破坏污泥絮体,污泥的平均粒径比常规活性污泥法工艺中的污泥粒径[6]要小的多,从而造成污泥在脱水过程中较难形成大的絮体,且需要投加大量絮凝剂。3座污水处理厂污泥脱水过程中出现的现象,印证了刘吉宝等[7]A2O-MBR 脱水电耗及絮凝剂成本高于 A2O 工艺的研究结果。因此,根据工程经验,要降低污泥的处理成本,在污泥进入脱水机械设备之前需设置污泥浓缩池,使污泥通过压缩沉淀浓缩后形成较高的污泥质量浓度,提高脱水效率,减少絮凝剂投加。
3.5. 加药量、电耗分析
1#污水处理厂设计处理规模为4.0×104 m3·d?1,而现状实际处理量为3.0~3.5 m3·d?1;2#污水处理厂设计处理规模为5.0×104 m3·d?1,现状实际处理量为3.8×104~5.0×104 m3·d?1;3#污水处理厂设计处理规模5.0×104 m3·d?1,现状实际处理量为7.5×104~8.3×104 m3·d?1。3座污水处理厂处理的污水量均已达到设计处理规模。运行过程中,污水处理生物段投加药剂种类为除磷剂、葡萄糖;膜清洗药剂为次氯酸钠、柠檬酸;尾水消毒药剂为次氯酸钠、臭氧。污泥处理段因1#污水处理厂与2#、3#污水处理厂中采用的污泥处理工艺不同,投加药剂种类也不同。1#污水处理厂污泥处理工艺采用带式脱水机+低温热干化,投加药剂为PAM;2#、3#污水处理厂污泥处理工艺采用板框压滤,投加药剂石灰、PAM、三氯化铁。各污水处理厂月平均药剂费及耗电量见表2。由表2~3可知,2#、3#污水处理厂污泥量比1#污水处理厂污泥量大。分析其原因,2#、3#污水处理厂污泥处理过程中添加的化学药剂质量约占剩余污泥(绝干)质量的30%;1#污水处理厂污泥处理工艺采用低温热干化工艺,2#、3#污水处理厂的污泥处理采用板框压滤机,1#污水处理厂的污泥处理电费远高于2#、3#污水处理厂的污泥处理单元;将污泥和污水处理费用统一折算到处理单方污水的综合成本中可知,1#污水处理厂的运行成本略低。
综上所述,MBR工艺的运行成本高,主要表现在污水处理的电耗和污泥处理的药耗上。对污泥处理工艺采用低温热干化及板框压滤2种工艺进行综合成本分析,低温热干化综合成本略低于板框压滤。因此,从污泥资源化利用的角度出发,在某些可利用峰谷电价的城市,MBR工艺的剩余污泥脱水可考虑选用低温热干化等投加药剂少的工艺。
2) MBR工艺设计时,预处理段格栅设计粗格栅栅间隙10~15 mm,细格栅间隙3~4 mm,膜格栅间隙1 mm,3道格栅逐级缩径。各级负荷相当,发挥各自优势。格栅设计可应对西北地区属于干旱区域污水中的悬浮物及含沙量明显较高的特点。
3) MBR工艺生物池需加大池内水流推力,在水流转弯位置,池型设计尽量考虑设有弧度,避免因污泥龄长出现腐化污泥上浮现象;合理设置进水方式或者设定厌氧段的停留时间,为脱氮除磷合理分配碳源,从而解决污水生物处理工艺中进水碳源不足问题。
4)在污泥处理单元,设置污泥浓缩池,提高污泥的脱水性能,以降低污泥处理过程中絮凝剂的投加量;污泥处理尽量采用投加药剂少的处理工艺,使其能够资源化利用。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 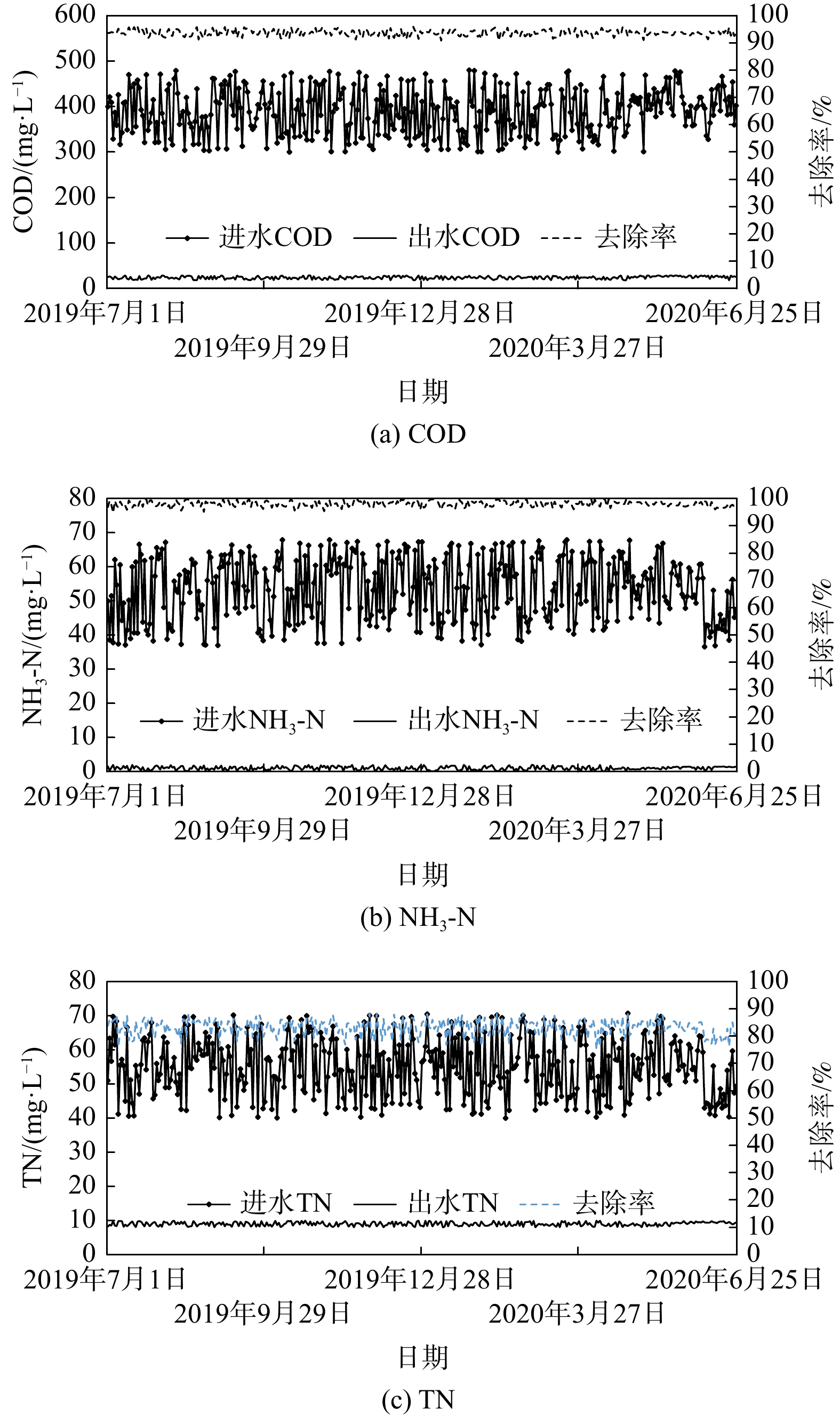
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图