山东大学能源与动力工程学院,燃煤污染物减排国家工程实验室,环境热工技术教育部工程研究中心,山东省能源碳减排技术与资源化利用重点实验室,济南 250061
National Engineering Laboratory for Reducing Emissions from Coal Combustion, Engineering Research Center of Environmental Thermal Technology of Ministry of Education, Shandong Key Laboratory of Energy Carbon Reduction and Resource Utilization, School of Energy and Power Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan 250061, China
随着储能市场的快速发展,锂离子电池供求量不断攀升,废旧电池数量也随之大幅增长。废弃电池的不当处置将危及人类健康、阻碍环境和资源的可持续发展,而对其进行资源化回收再利用,尤其是回收其中具有高附加值的正极材料,有利于实现社会、经济、环境等层面的多重效益。对比总结了废旧锂电正极材料传统回收利用工艺的现状和问题,梳理了新兴微波辅助技术在材料回收及资源化利用过程中的应用和研究进展。微波技术由于其独特的加热机制在优化杂质降解、强化碳热还原、提升浸出效率、再生材料等诸多方面体现出显著优势和发展潜力。基于实际问题和数值模拟总结了微波处理技术的局限性,并提出了改进策略,以期对锂电回收体系的改良和发展提供参考。
With the rapid development of energy storage market, the supply and demand of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) as well as the discard have continued to increase in recent years. Waste LIBs, if not handled properly, will endanger human health, the environment and the sustainable development of resources. However, recycling and regeneration of LIBs, especially the positive materials with high added value, can achieve multiple benefits in social, economic and environmental aspects. In this paper, the research status and problems of the conventional methods and the new microwave-assisted technology for recycling and regeneration processes of waste cathode materials are reviewed. Owing to the unique thermal mechanism, microwave technology shows significant advantages and potentials in optimizing impurity degradation, strengthening carbothermal reduction, improve the efficiency of leaching, regenerating active materials and other aspects. Meanwhile, limitations and improved strategies are summarized based on practical problems and numerical simulations, proving guidance and reference for the improvement and development of LIB recovery system in the future.
.
Schematic representation of the displacement of electrons under microwave heating
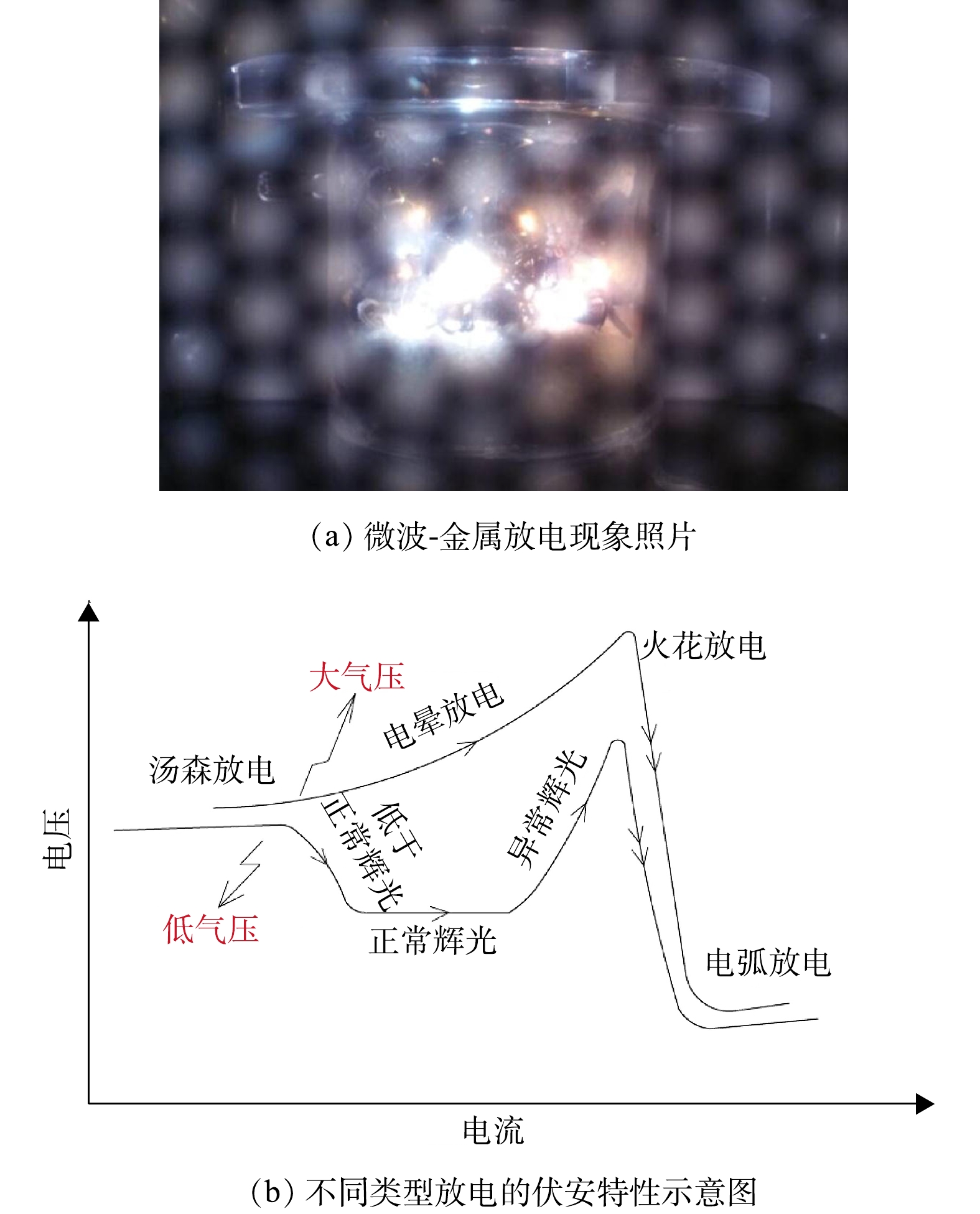
Microwave-metal discharge phenomenon and the schematic current-voltage characteristics of the different types of discharges
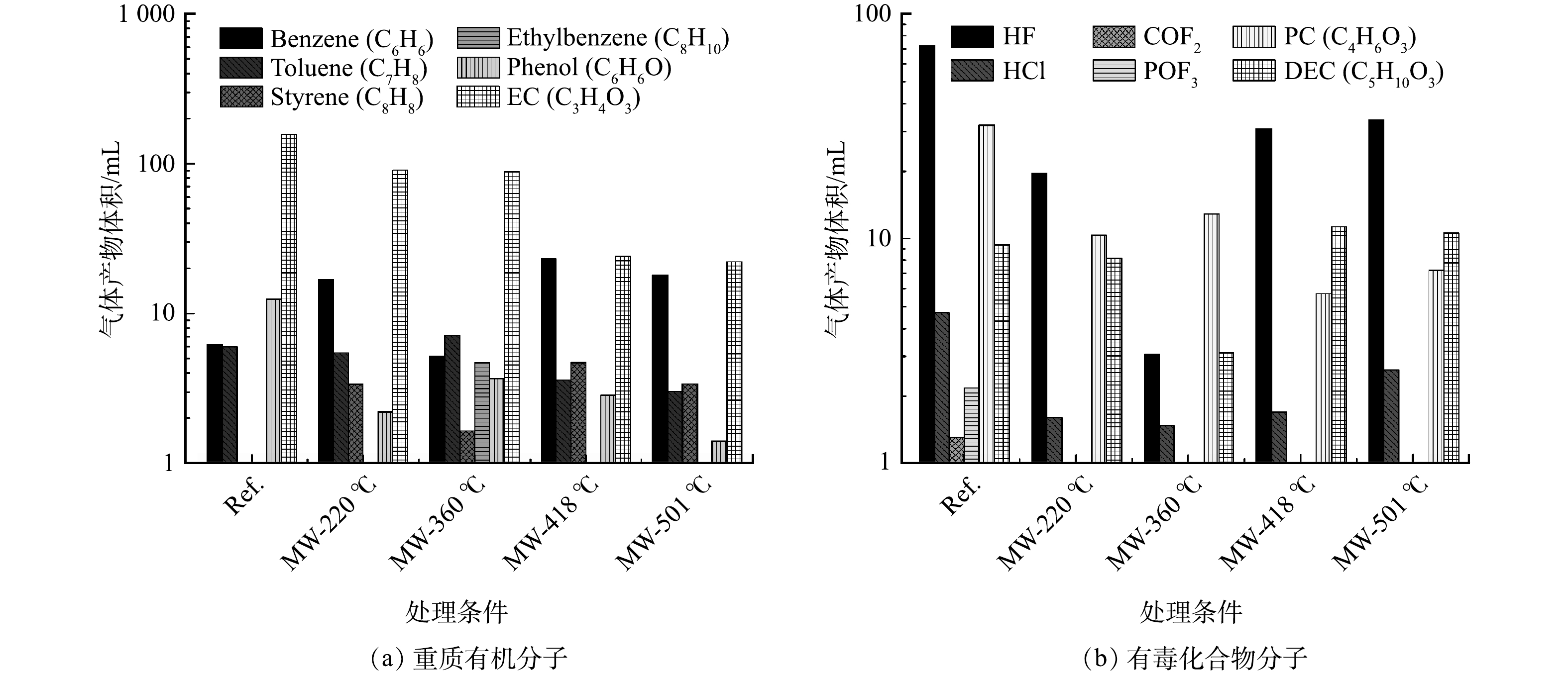
Volume of heavy molecules and toxic compounds generated at different target temperature with microwave heating
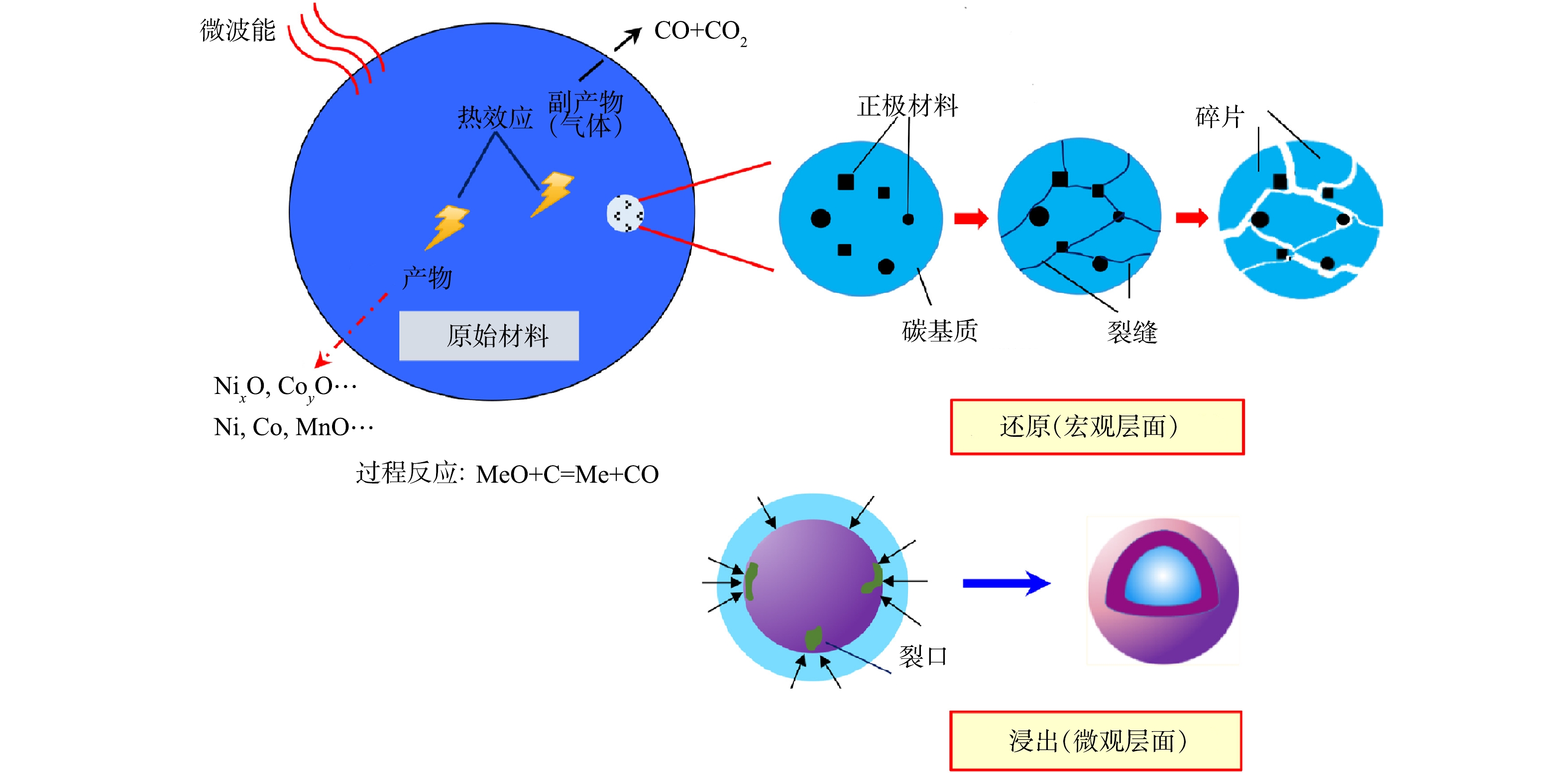
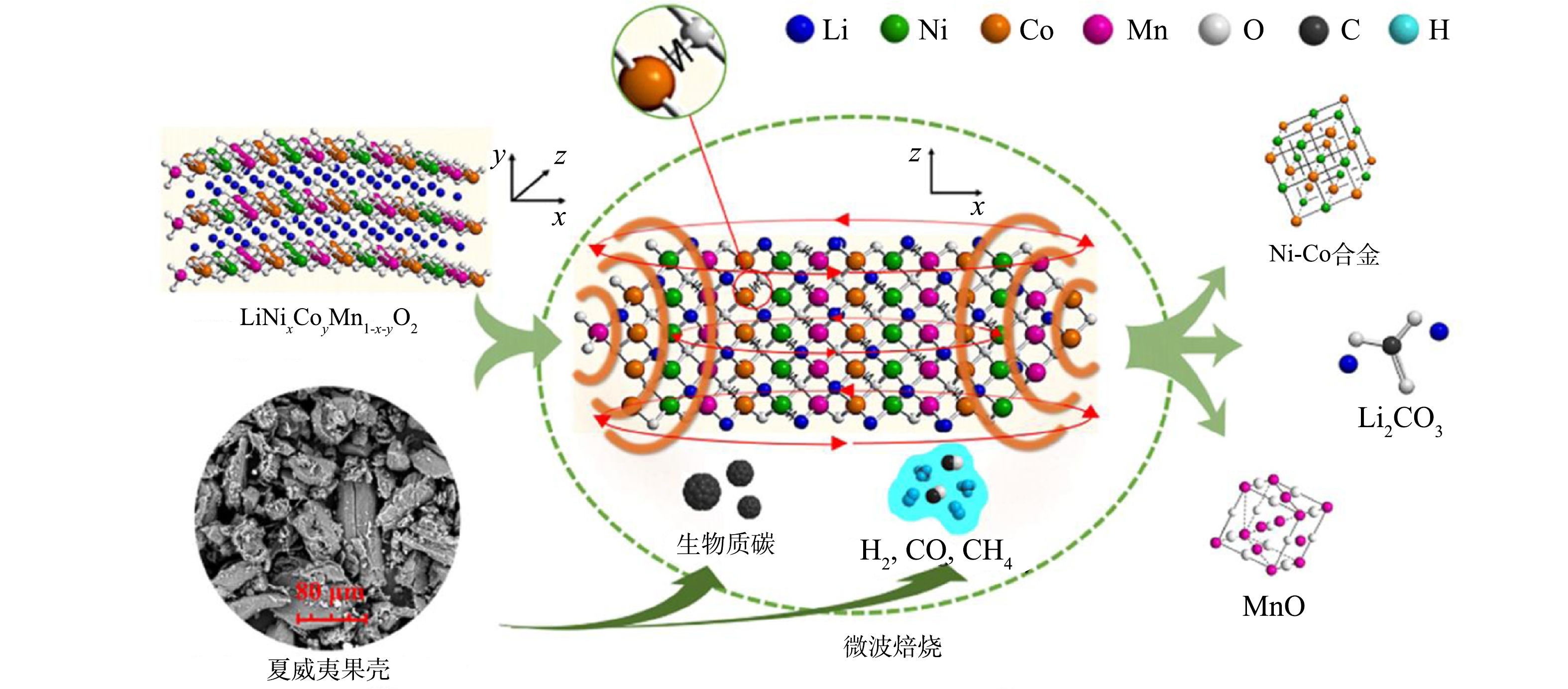
Mechanism of microwave pyrolysis of biomass for efficient recycling lithium from spent lithium-ion batteries
Polyhedral representation of the olivine crystal structure (space group Pnma) of LiCoPO
Microwave-absorbing properties of the current collector under the frequency of 2.45 GHz
Conventional laboratory methods and their advantages and disadvantages in the pretreatment of lithium-ion batteries
Conventional methods of indirect recovery of valuable substances from lithium-ion battery cathode materials and their advantages and disadvantages
Conventional and MW-assisted pyrometallurgical in the carbothermic reduction process researches
Approximate cost ($) estimation in the Indian context for the leaching processes of 20 g LiCoO
Methods of indirect regeneration of lithium-ion battery cathode materials and their advantages and disadvantages
| [1] | DENG S J, ZHU H, WANG G Z, et al. Boosting fast energy storage by synergistic engineering of carbon and deficiency[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7 |
| [2] | ZHANG L S, WANG H, WANG L Z, et al. High electrochemical performance of lithium-rich Li1.2Mn0.54NixCoyO2 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Letters, 2016, 185: 100-103. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2016.08.118 |
| [3] | BHATLU M L D, BHAUMIK M, SUKANYA K. Energy management by using lithium-ion batteries, piezo materials, sensors and renewal energy system in the daily life: A review[J]. Journal of Critical Reviews, 2020, 7(7): 798-801. doi: 10.31838/jcr.07.07.146 |
| [4] | NAKAMURA M, TAKENO K. Green base station using robust solar system and high performance lithium ion battery for next generation wireless network (5G) and against mega disaster[C]//IEEE. 2018 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Niigata 2018 -ECCE Asia). Niigata, Japan, 2018: 201-206. |
| [5] | CHOUDHARI V G, DHOBLE D A S, SATHE T M. A review on effect of heat generation and various thermal management systems for lithium ion battery used for electric vehicle[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 32: 101729. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2020.101729 |
| [6] | DEPCIK C, CASSADY T, COLLICOTT B, et al. Comparison of lithium ion batteries, hydrogen fueled combustion engines, and a hydrogen fuel cell in powering a small unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 207: 112514. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2020.112514 |
| [7] | LI P F, BASHIRULLAH R. A wireless power interface for rechargeable battery operated medical implants[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2007, 54(10): 912-916. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2007.901613 |
| [8] | CHEN T M, JIN Y, LV H, et al. Applications of lithium-ion batteries in grid-scale energy storage systems[J]. Transactions of Tianjin University, 2020, 26(3): 208-217. doi: 10.1007/s12209-020-00236-w |
| [9] | ZHENG Y, SONG W, MO W T, et al. Lithium fluoride recovery from cathode material of spent lithium-ion battery[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(16): 8990-8998. doi: 10.1039/C8RA00061A |
| [10] | 东莞市钜大电子有限公司. 2020年全球动力锂离子电池行业市场现状及发展前景分析[EB/OL]. (2020-05-02) [2020-09-20]. http://www.juda.cn/news/134330.html. |
| [11] | FAN E S, LI L, WANG Z P, et al. Sustainable recycling technology for Li-ion batteries and beyond: Challenges and future prospects[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(14): 7020-7063. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00535 |
| [12] | YUAN Y, YU H X, CHENG X, et al. Preparation of TiNb6O17 nanospheres as high-performance anode candidates for lithium-ion storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 937-946. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.225 |
| [13] | DIEKMANN J, HANISCH C, FROB?SE L, et al. Ecological recycling of lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles with focus on mechanical processes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 164(1): A6184-A6191. |
| [14] | MESHRAM P, PANDEY B D, MANKHAND T R. Extraction of lithium from primary and secondary sources by pre-treatment, leaching and separation: A comprehensive review[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 150: 192-208. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.10.012 |
| [15] | TEDJAR F. Approach of “Electrodes to Electrodes”: Challenges for recycling advanced lithium-ion batteries for e-mobility[C]//IOP Publishing. 2014 ECS Meeting Abstracts. Como, Italy, 2014: 396. |
| [16] | LAROUCHE F, TEDJAR F, AMOUZEGAR K, et al. Progress and status of hydrometallurgical and direct recycling of Li-ion batteries and beyond[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(3): 801. doi: 10.3390/ma13030801 |
| [17] | KATWALA A. The spiralling environmental cost of our lithium battery addiction[EB/OL]. [2018-08-05]. https://www.wired.co.uk/article/lithium-batteries-environment-impact, 2018. |
| [18] | LARCHER D, TARASCON J M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7(1): 19-29. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2085 |
| [19] | LIANG S S, YAN W Q, WU X, et al. Gel polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries: Fabrication, characterization and performance[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2018, 318: 2-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2017.12.023 |
| [20] | LIU Y J, ZHANG Z Q, FU Y B, et al. Investigation the electrochemical performance of Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 cathode material with ZnAl2O4 coating for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 685: 523-532. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.329 |
| [21] | HARPER G, SOMMERVILLE R, KENDRICK E, et al. Recycling lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles[J]. Nature, 2019, 575(7781): 75-86. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1682-5 |
| [22] | 欧秀芹, 孙新华, 程耀丽. 废锂离子电池的综合处理方法[J]. 天津化工, 2002, 16(4): 35-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1267.2002.04.018 |
| [23] | ZHANG W, XU C, HE W, et al. A review on management of spent lithium ion batteries and strategy for resource recycling of all components from them[J]. Waste Management & Research, 2018, 36(2): 99-112. |
| [24] | ZHANG X, LI L, FAN E, et al. Toward sustainable and systematic recycling of spent rechargeable batteries[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(19): 7239-7302. doi: 10.1039/C8CS00297E |
| [25] | HUANG B, PAN Z F, SU X Y, et al. Recycling of lithium-ion batteries: Recent advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 399: 274-286. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.07.116 |
| [26] | KIM H, JANG Y C, HWANG Y, et al. End-of-life batteries management and material flow analysis in South Korea[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2018, 12(3): 1-13. |
| [27] | BOXALL N J, KING S, CHENG K Y, et al. Urban mining of lithium-ion batteries in Australia: Current state and future trends[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 128: 45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2018.08.030 |
| [28] | ZENG X L, LI J H, SINGH N. Recycling of spent lithium-ion battery: A critical review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2014, 44(10): 1129-1165. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2013.763578 |
| [29] | GUO Q S, SUN D W, CHENG J H, et al. Microwave processing techniques and their recent applications in the food industry[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2017, 67: 236-247. |
| [30] | ZHANG F, ZHOU T, LIU Y, et al. Microwave synthesis and actuation of shape memory polycaprolactone foams with high speed[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 11152. doi: 10.1038/srep11152 |
| [31] | BRODIE G. Applications of Microwave Heating in Agricultural and Forestry Related Industries[M]. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech, 2012: 45-78. |
| [32] | HUANG Y F, CHIUEH P T, LO S L. A review on microwave pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass[J]. Sustainable Environment Research, 2016, 26(3): 103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.serj.2016.04.012 |
| [33] | SUN J, JIANG Z Y, WANG K, et al. Experimental study on microwave-SiC-assisted catalytic hydrogenation of phenol[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(11): 11092-11100. |
| [34] | SUN J, WANG W L, LIU Z, et al. Recycling of waste printed circuit boards by microwave-induced pyrolysis and featured mechanical processing[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(20): 11763-11769. |
| [35] | SUN J, WANG W L, YUE Q Y. Review on microwave-matter interaction fundamentals and efficient microwave-associated heating strategies[J]. Materials, 2016, 9(4): 231. doi: 10.3390/ma9040231 |
| [36] | MISHRA R R, SHARMA A K. Microwave-material interaction phenomena: Heating mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in material processing[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 81: 78-97. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.10.035 |
| [37] | STUERGA D . Microwave-Material Interactions and Dielectric Properties, Key Ingredients for Mastery of Chemical Microwave Processes[M]. Weinhem: WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, 2006. |
| [38] | ZHAO Y Z, LIU B G, ZHANG L B, et al. Microwave-absorbing properties of cathode material during reduction roasting for spent lithium-ion battery recycling[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121487. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121487 |
| [39] | PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Microwave processing of spent coin cells for recycling of metallic values[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 280: 124144. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124144 |
| [40] | HE F, CHEN J, CHEN G, et al. Microwave dielectric properties and reduction behavior of low-grade pyrolusite[J]. JOM, 2019, 71(11): 3909-3914. doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03522-8 |
| [41] | LIU T, PANG Y, ZHU M, et al. Microporous Co@CoO nanoparticles with superior microwave absorption properties[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(4): 2447-2454. doi: 10.1039/c3nr05238a |
| [42] | FARAG S, SOBHY A, AKYEL C, et al. Temperature profile prediction within selected materials heated by microwaves at 2.45GHz[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 36: 360-369. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2011.10.049 |
| [43] | GUPTA M, LEONG E W W. Microwaves and Metals[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2008. |
| [44] | JILES D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials[M]. CRC Press, 2015. |
| [45] | GIERAS J F, PIECH Z J, TOMCZUK B. Linear Synchronous Motors: Transportation and Automation Systems[M]. CRC Press, 2016. |
| [46] | MENéNDEZ J A, ARENILLAS A, FIDALGO B, et al. Microwave heating processes involving carbon materials[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2010, 91(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.08.021 |
| [47] | MONSEF-MIRZAI P, RAVINDRAN M, MCWHINNIE W R, et al. Rapid microwave pyrolysis of coal: Methodology and examination of the residual and volatile phases[J]. Fuel, 1995, 74(1): 20-27. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(94)P4325-V |
| [48] | EL HARFI K, MOKHLISSE A, CHAN?A M B, et al. Pyrolysis of the Moroccan (Tarfaya) oil shales under microwave irradiation[J]. Fuel, 2000, 79(7): 733-742. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00209-4 |
| [49] | FERNáNDEZ Y, ARENILLAS A, DíEZ M A, et al. Pyrolysis of glycerol over activated carbons for syngas production[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2009, 84(2): 145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2009.01.004 |
| [50] | MENéNDEZ J A, MENéNDEZ E M, GARCíA A, et al. Thermal treatment of active carbons: A comparison between microwave and electrical hating[J]. Journal of Microwave Power and Electromagnetic Energy, 1999, 34(3): 137-143. doi: 10.1080/08327823.1999.11688398 |
| [51] | FIDALGO B, ARENILLAS A, MENéNDEZ J A. Influence of porosity and surface groups on the catalytic activity of carbon materials for the microwave-assisted CO2 reforming of CH4[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(12): 4002-4007. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.06.015 |
| [52] | SUN J, WANG W L, YUE Q Y, et al. Review on microwave-metal discharges and their applications in energy and industrial processes[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 175: 141-157. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.091 |
| [53] | DIAZ F, WANG Y, MOORTHY T, et al. Degradation mechanism of nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) cathode material from spent lithium-ion batteries in microwave-assisted pyrolysis[J]. Metals, 2018, 8(8): 565. doi: 10.3390/met8080565 |
| [54] | BAJPAI R, WAGNER H D. Fast growth of carbon nanotubes using a microwave oven[J]. Carbon, 2015, 82: 327-336. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2014.10.077 |
| [55] | DIAZ F, FLERUS B, NAGRAJ S, et al. Comparative analysis about degradation mechanisms of printed circuit boards (PCBs) in slow and fast pyrolysis: The influence of heating speed[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2018, 4(2): 205-221. doi: 10.1007/s40831-018-0163-7 |
| [56] | NIE H, XU L, SONG D, et al. LiCoO2: Recycling from spent batteries and regeneration with solid state synthesis[J]. Green Chemistry, 2015, 17(2): 1276-1280. doi: 10.1039/C4GC01951B |
| [57] | CHOUBEY P K, KIM M S, SRIVASTAVA R R, et al. Advance review on the exploitation of the prominent energy-storage element: Lithium. Part I: From mineral and brine resources[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 89: 119-137. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.01.010 |
| [58] | LI J H, SHI P X, WANG Z F, et al. A combined recovery process of metals in spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 77(8): 1132-1136. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.08.040 |
| [59] | HE L P, SUN S Y, SONG X F, et al. Recovery of cathode materials and Al from spent lithium-ion batteries by ultrasonic cleaning[J]. Waste Management, 2015, 46: 523-528. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.08.035 |
| [60] | ZENG X L, LI J H. Innovative application of ionic liquid to separate Al and cathode materials from spent high-power lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 271: 50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.02.001 |
| [61] | CHEN L, TANG X C, ZHANG Y, et al. Process for the recovery of cobalt oxalate from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108(1/2): 80-86. |
| [62] | WANG M M, TAN Q Y, LIU L L, et al. Efficient separation of aluminum foil and cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries using a low-temperature molten salt[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(9): 8287-8294. |
| [63] | SUN L, QIU K Q. Vacuum pyrolysis and hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 194: 378-384. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.114 |
| [64] | ZHANG T, HE Y Q, GE L H, et al. Characteristics of wet and dry crushing methods in the recycling process of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 240: 766-771. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.05.009 |
| [65] | 汪永威, 赵光金, 朱莉娜, 等. 一种微波热解处理废旧锂电池的方法: CN103247837A[P]. 2013-08-14. |
| [66] | 殷衡. 一种以等离子体技术回收三元电池正极材料的方法: CN108199107B[P]. 2020-02-18. |
| [67] | 刘云建, 胡启阳, 李新海, 等. 从不合格锂离子蓄电池中直接回收钴酸锂[J]. 电源技术, 2006, 30(4): 308-310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2006.04.015 |
| [68] | GEORGI-MASCHLER T, FRIEDRICH B, WEYHE R, et al. Development of a recycling process for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 207: 173-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.01.152 |
| [69] | LI J, WANG G X, XU Z M. Environmentally-friendly oxygen-free roasting/wet magnetic separation technology for in situ recycling cobalt, lithium carbonate and graphite from spent LiCoO2/graphite lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 302: 97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.050 |
| [70] | XIAO J F, LI J, XU Z M. Recycling metals from lithium ion battery by mechanical separation and vacuum metallurgy[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 338: 124-131. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.024 |
| [71] | FAN E S, LI L, LIN J, et al. Low-temperature molten-salt-assisted recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(19): 16144-16150. |
| [72] | HU J T, ZHANG J L, LI H X, et al. A promising approach for the recovery of high value-added metals from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 351: 192-199. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.03.093 |
| [73] | LIU P C, XIAO L, CHEN Y F, et al. Recovering valuable metals from LiNixCoyMn1-x-yO2 cathode materials of spent lithium ion batteries via a combination of reduction roasting and stepwise leaching[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 783: 743-752. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.226 |
| [74] | LI J H, LI X H, HU Q Y, et al. Study of extraction and purification of Ni, Co and Mn from spent battery material[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 99(1/2): 7-12. |
| [75] | JOULIé M, LAUCOURNET R, BILLY E. Hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of high value metals from spent lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide based lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 247: 551-555. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.08.128 |
| [76] | ZHANG P W, YOKOYAMA T, ITABASHI O, et al. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion secondary batteries[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1998, 47(2/3): 259-271. |
| [77] | LI L, LU J, REN Y, et al. Ascorbic-acid-assisted recovery of cobalt and lithium from spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 218: 21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.06.068 |
| [78] | LI L, GE J, CHEN R J, et al. Environmental friendly leaching reagent for cobalt and lithium recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Waste Management, 2010, 30(12): 2615-2621. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.08.008 |
| [79] | LI L, ZHAI L Y, ZHANG X X, et al. Recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries by ultrasonic-assisted leaching process[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 262: 380-385. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.04.013 |
| [80] | LI L, GE J, WU F, et al. Recovery of cobalt and lithium from spent lithium ion batteries using organic citric acid as leachant[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 176(1/2/3): 288-293. |
| [81] | MISHRA D, KIM D J, RALPH D E, et al. Bioleaching of metals from spent lithium ion secondary batteries using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Waste Management, 2008, 28(2): 333-338. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2007.01.010 |
| [82] | XIN B P, ZHANG D, ZHANG X, et al. Bioleaching mechanism of Co and Li from spent lithium-ion battery by the mixed culture of acidophilic sulfur-oxidizing and iron-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(24): 6163-6169. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.06.086 |
| [83] | ZENG G S, DENG X R, LUO S L, et al. A copper-catalyzed bioleaching process for enhancement of cobalt dissolution from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 199/200: 164-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.063 |
| [84] | ZHAO Y Z, LIU B G, ZHANG L B, et al. Microwave pyrolysis of macadamia shells for efficiently recycling lithium from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 396: 122740. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122740 |
| [85] | YIXIN H, CHUNPENG L. Microwave-assisted carbothermic reduction of ilmenite[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2009, 9(3): 164-170. |
| [86] | RU J J, HUA Y X, WANG D. Preparation and characterisation of TiN by microwave-assisted carbothermic reduction-nitridation in air atmosphere[J]. Advances in Applied Ceramics, 2017, 116(8): 468-476. doi: 10.1080/17436753.2017.1357292 |
| [87] | CHE X K, SU X Z, CHI R A, et al. Microwave assisted atmospheric acid leaching of nickel from laterite ore[J]. Rare Metals, 2010, 29(3): 327-332. doi: 10.1007/s12598-010-0058-7 |
| [88] | SAMOUHOS M, TAXIARCHOU M, HUTCHEON R, et al. Microwave reduction of a nickeliferous laterite ore[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2012, 34: 19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2012.04.005 |
| [89] | CHANG Y F, ZHAI X J, FU Y, et al. Phase transformation in reductive roasting of laterite ore with microwave heating[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(4): 969-973. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(08)60167-3 |
| [90] | KRUESI P R, FRAHM JR V H. Process for the recovery of nickel, cobalt and manganese from their oxides and silicates: U.S. Patent No. 4, 311, 520 [P]. 1982-01-19. |
| [91] | ZHAO Y, GAO J M, YUE Y, et al. Extraction and separation of nickel and cobalt from saprolite laterite ore by microwave-assisted hydrothermal leaching and chemical deposition[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2013, 20(7): 612-619. doi: 10.1007/s12613-013-0774-8 |
| [92] | LIU X X, ZHANG Z Y, WU Y P. Absorption properties of carbon black/silicon carbide microwave absorbers[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2011, 42(2): 326-329. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2010.11.009 |
| [93] | PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Recycling of mixed discarded lithium-ion batteries via microwave processing route[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2020, 25: e00157. doi: 10.1016/j.susmat.2020.e00157 |
| [94] | SUNIL S R, DHAWAN N. Thermal processing of spent Li-ion batteries for extraction of lithium and cobalt-manganese values[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2019, 72(12): 3035-3044. doi: 10.1007/s12666-019-01769-y |
| [95] | PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Carbothermal reduction of spent mobile phones batteries for the recovery of lithium, cobalt, and manganese values[J]. JOM, 2019, 71(12): 4483-4491. doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03799-9 |
| [96] | PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Comparison of microwave and conventional indigenous carbothermal reduction for recycling of discarded lithium-ion batteries[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2020, 73(8): 2041-2051. doi: 10.1007/s12666-020-01956-2 |
| [97] | SUNIL S R, VISHVAKARMA S, BARNWAL A, et al. Processing of spent Li-ion batteries for recovery of cobalt and lithium values[J]. JOM, 2019, 71(12): 4659-4665. doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03540-6 |
| [98] | NATARAJAN S, ANANTHARAJ S, TAYADE R J, et al. Recovered spinel MnCo2O4 from spent lithium-ion batteries for enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen evolution in alkaline medium[J]. Dalton Transaction, 2017, 46(41): 14382-14392. doi: 10.1039/C7DT02613G |
| [99] | XI G X, ZHAO T T, WANG L, et al. Effect of doping rare earths on magnetostriction characteristics of CoFe2O4 prepared from spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2018, 534: 76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2018.01.036 |
| [100] | MOURA M N, BARRADA R V, ALMEIDA J R, et al. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic properties of nanostructured CoFe2O4 recycled from spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 182: 339-347. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.036 |
| [101] | FERREIRA D A, PRADOS L M Z, MAJUSTE D, et al. Hydrometallurgical separation of aluminium, cobalt, copper and lithium from spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 187(1): 238-246. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.10.077 |
| [102] | JHA M K, KUMARI A, JHA A K, et al. Recovery of lithium and cobalt from waste lithium ion batteries of mobile phone[J]. Waste Management, 2013, 33(9): 1890-1897. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2013.05.008 |
| [103] | LI L, CHEN R J, SUN F, et al. Preparation of LiCoO2 films from spent lithium-ion batteries by a combined recycling process[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108(3/4): 220-225. |
| [104] | FAN E S, LI L, ZHANG X X, et al. Selective recovery of Li and Fe from spent lithium-ion batteries by an environmentally friendly mechanochemical approach[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(8): 11029-11035. |
| [105] | WANG M M, ZHANG C C, ZHANG F S. An environmental benign process for cobalt and lithium recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries by mechanochemical approach[J]. Waste Management, 2016, 51: 239-244. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2016.03.006 |
| [106] | LI J G, ZHAO R S, HE X M, et al. Preparation of LiCoO2 cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2009, 15(1): 111-113. doi: 10.1007/s11581-008-0238-8 |
| [107] | PATIL D, CHIKKAMATH S, KENY S, et al. Rapid dissolution and recovery of Li and Co from spent LiCoO2 using mild organic acids under microwave irradiation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 256: 109935. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109935 |
| [108] | ZOU H Y, GRATZ E, APELIAN D, et al. A novel method to recycle mixed cathode materials for lithium ion batteries[J]. Green Chemistry, 2013, 15(5): 1183. doi: 10.1039/c3gc40182k |
| [109] | SA Q N, GRATZ E, HEELAN J A, et al. Synthesis of diverse LiNixMnyCozO2 cathode materials from lithium ion battery recovery stream[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2016, 2(3): 248-256. doi: 10.1007/s40831-016-0052-x |
| [110] | SHI Y, CHEN G, LIU F, et al. Resolving the compositional and structural defects of degraded LiNixCoyMnzO2 particles to directly regenerate high-performance lithium-ion battery cathodes[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(7): 1683-1692. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.8b00833 |
| [111] | ZHANG X H, CAO H B, XIE Y B, et al. A closed-loop process for recycling LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 from the cathode scraps of lithium-ion batteries: Process optimization and kinetics analysis[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 150: 186-195. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2015.07.003 |
| [112] | HE L P, SUN S Y, SONG X F, et al. Leaching process for recovering valuable metals from the LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 64: 171-181. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.02.011 |
| [113] | MESHRAM P, PANDEY B D, MANKHAND T R. Recovery of valuable metals from cathodic active material of spent lithium ion batteries: Leaching and kinetic aspects[J]. Waste Management, 2015, 45: 306-313. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.05.027 |
| [114] | GOLMOHAMMADZADEH R, RASHCHI F, VAHIDI E. Recovery of lithium and cobalt from spent lithium-ion batteries using organic acids: Process optimization and kinetic aspects[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 64: 244-254. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.03.037 |
| [115] | FU Y P, HE Y Q, YANG Y, et al. Microwave reduction enhanced leaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 832: 154920. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154920 |
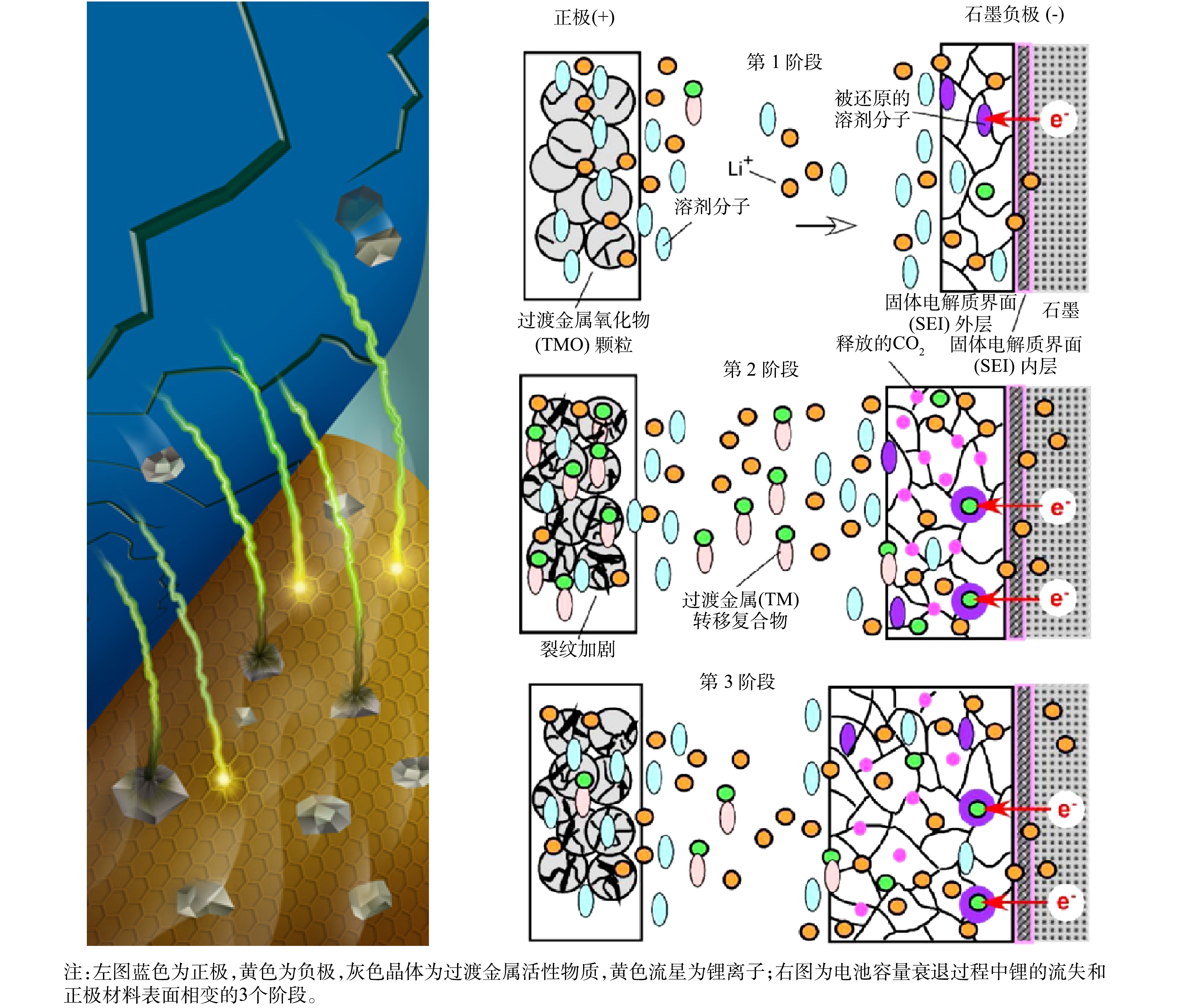
| [116] | LI L, BIAN Y F, ZHANG X X, et al. Economical recycling process for spent lithium-ion batteries and macro- and micro-scale mechanistic study[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 377: 70-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.12.006 |
| [117] | LANNOO S, VILAS-BOAS A, SADEGHI S M, et al. An environmentally friendly closed loop process to recycle raw materials from spent alkaline batteries[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 236: 117612. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117612 |
| [118] | KARIMI G R, ROWSON N A, HEWITT C J. Bioleaching of copper via iron oxidation from chalcopyrite at elevated temperatures[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 2010, 88(1): 21-25. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2009.06.005 |
| [119] | SMITH S L, GRAIL B M, JOHNSON D B. Reductive bioprocessing of cobalt-bearing limonitic laterites[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2017, 106: 86-90. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.09.009 |
| [120] | HOREH N B, MOUSAVI S M, SHOJAOSADATI S A. Bioleaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion mobile phone batteries using Aspergillus Niger[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 320: 257-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.04.104 |
| [121] | XIN Y Y, GUO X M, CHEN S, et al. Bioleaching of valuable metals Li, Co, Ni and Mn from spent electric vehicle Li-ion batteries for the purpose of recovery[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 116: 249-258. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.001 |
| [122] | POLLMANN K, RAFF J, MERROUN M, et al. Metal binding by bacteria from uranium mining waste piles and its technological applications[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2006, 24(1): 58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2005.06.002 |
| [123] | MACASKIE L E, MIKHEENKO I P, YONG P, et al. Today's wastes, tomorrow's materials for environmental protection[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104(3/4): 483-487. |
| [124] | YEMI? O, MAZZA G. Acid-catalyzed conversion of xylose, xylan and straw into furfural by microwave-assisted reaction[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(15): 7371-7378. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.050 |
| [125] | RAMASAMY S, MOGHTADERI B. Dielectric properties of typical Australian wood-based biomass materials at microwave frequency[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(8): 4534-4548. |
| [126] | SAIT H H, SALEMA A A. Microwave dielectric characterization of Saudi Arabian date palm biomass during pyrolysis and at industrial frequencies[J]. Fuel, 2015, 161: 239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.08.058 |
| [127] | TATEISHI K, DU BOULAY D, ISHIZAWA N, et al. Structural disorder along the lithium diffusion pathway in cubically stabilized lithium manganese spinel II. Molecular dynamics calculation[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2003, 174(1): 175-181. doi: 10.1016/S0022-4596(03)00207-X |
| [128] | YOON W S, IANNOPOLLO S, GREY C P, et al. Local structure and cation ordering in O3 lithium nickel manganese oxides with stoichiometry Li[NixMn(2–x)/3Li(1–2x)/3]O2[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2004, 7(7): A167. doi: 10.1149/1.1737711 |
| [129] | GADJOV H, GOROVA M, KOTZEVA V, et al. LiMn2O4 prepared by different methods at identical thermal treatment conditions: structural, morphological and electrochemical characteristics[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 134(1): 110-117. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.03.027 |
| [130] | RODRíGUEZ-CARVAJAL J, ROUSSE G, MASQUELIER C, et al. Electronic crystallization in a lithium battery material: Columnar ordering of electrons and holes in the Spinel LiMn2O4[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1998, 81(21): 4660. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.4660 |
| [131] | GILBERT J A, SHKROB I A, ABRAHAM D P. Transition metal dissolution, ion migration, electrocatalytic reduction and capacity loss in lithium-ion full cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(2): A389-A399. doi: 10.1149/2.1111702jes |
| [132] | MENG X Q, HAO J, CAO H B, et al. Recycling of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries using mechanochemical activation and solid-state sintering[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 84: 54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.11.034 |
| [133] | 张维民, 张娜, 张铁柱, 等. 废弃电池回收再生制备锂电池三元正极材料的方法: CN110265659A[P]. 2019-09-20. |
| [134] | 刘静静, 仇卫华, 赵海雷, 等. 锂离子电池用层状LiMnO2基正极材料的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2005, 33(9): 1127-1132. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2005.09.016 |
| [135] | SHI Y, ZHANG M H, MENG Y S, et al. Ambient-pressure relithiation of degraded LixNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 (0<x<1) via eutectic solutions for direct regeneration of lithium-ion battery cathodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(20): 1900454. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201900454 |
| [136] | KIM D S, SOHN J S, LEE C K, et al. Simultaneous separation and renovation of lithium cobalt oxide from the cathode of spent lithium ion rechargeable batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 132(1/2): 145-149. |
| [137] | CONTESTABILE M, PANERO S, SCROSATI B. A laboratory-scale lithium-ion battery recycling process[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 92(1/2): 65-69. |
| [138] | LIU Y J, HU Q Y, LI X H, et al. Recycle and synthesis of LiCoO2 from incisors bound of Li-ion batteries[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(4): 956-959. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(06)60359-2 |
| [139] | SA Q N, GRATZ E, HE M N, et al. Synthesis of high performance LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 from lithium ion battery recovery stream[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 282: 140-145. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.02.046 |
| [140] | LEE C K, RHEE K I. Preparation of LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 109(1): 17-21. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(02)00037-X |
| [141] | LEE C K, RHEE K I. Reductive leaching of cathodic active materials from lithium ion battery wastes[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 68(1/2/3): 5-10. |
| [142] | BALAJI S, MUTHARASU D, SANKARA SUBRAMANIAN N, et al. A review on microwave synthesis of electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2009, 15(6): 765-777. doi: 10.1007/s11581-009-0350-4 |
| [143] | LI J, WANG Y, WANG L H, et al. A facile recycling and regeneration process for spent LiFePO4 batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30(15): 14580-14588. doi: 10.1007/s10854-019-01830-y |
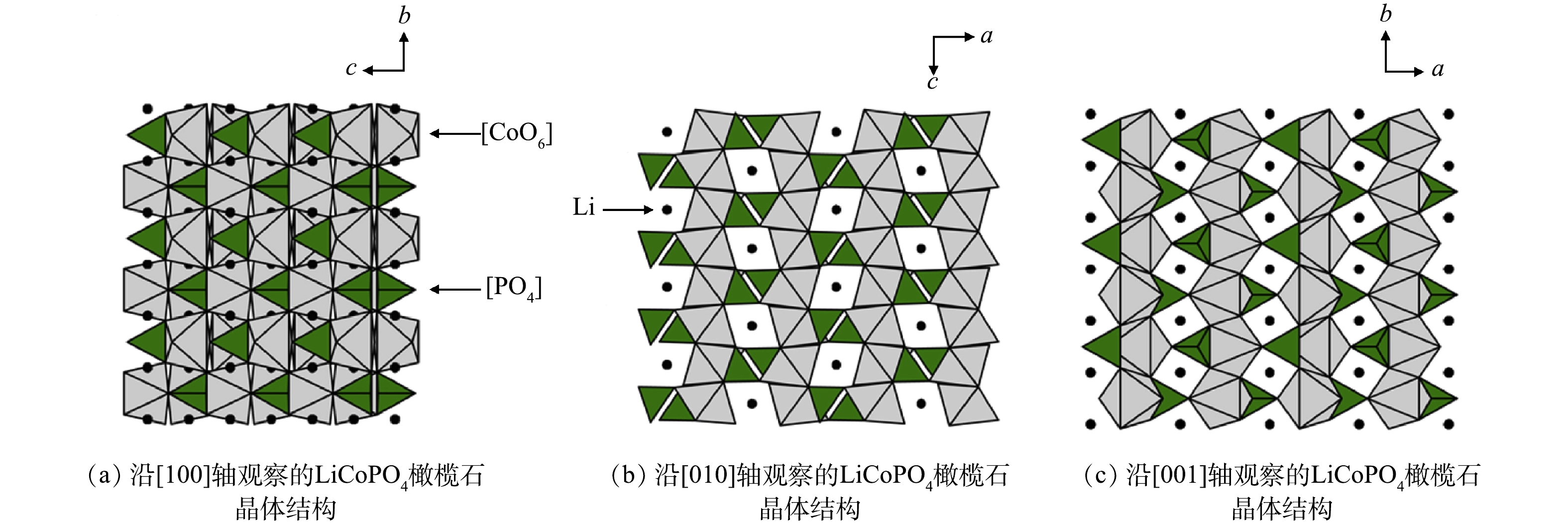
| [144] | LI X L, ZHANG J, SONG D W, et al. Direct regeneration of recycled cathode material mixture from scrapped LiFePO4 batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 345: 78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.01.118 |
| [145] | BAO S J, LIANG Y Y, LI H L. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiMn2O4 by microwave-assisted Sol-gel method[J]. Materials Letters, 2005, 59(28): 3761-3765. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2005.07.012 |
| [146] | TANG X, WANG R, REN Y F, et al. Effective regeneration of scrapped LiFePO4 material from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(27): 13036-13048. doi: 10.1007/s10853-020-04907-w |
| [147] | YAN H W, HUANG X J, LI H, et al. Electrochemical study on LiCoO2 synthesized by microwave energy[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1998, 113-115: 11-15. |
| [148] | ELUMALAI P, VASAN H N, MUNICHANDRAIAH N. Microwave synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiCo1?xMxO2 (M = Al and Mg) cathodes for Li-ion rechargeable batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 125(1): 77-84. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00815-2 |
| [149] | LIU H X, HU C, ZHU X J, et al. Solid chemical reaction in microwave and millimeter-wave fields for the syntheses of LiMn2O4 compound[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2004, 88(2/3): 290-294. |
| [150] | FU Y P, LIN C H, SU Y H, et al. Electrochemical properties of LiMn2O4 synthesized by the microwave-induced combustion method[J]. Ceramics International, 2004, 30(7): 1953-1959. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2003.12.183 |
| [151] | CUI T, HUA N, HAN Y, et al. Preparation and electrochemical properties of LiMn2O4 by a rheological-phase-assisted microwave synthesis method[J]. Inorganic Materials, 2008, 44(5): 542-548. doi: 10.1134/S002016850805021X |
| [152] | HIGUCHI M, KATAYAMA K, AZUMA Y, et al. Synthesis of LiFePO4 cathode material by microwave processing[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 119-121: 258-261. |
| [153] | LI J, JIN Y L, ZHANG X G, et al. Microwave solid-state synthesis of spinel Li4Ti5O12 nanocrystallites as anode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2007, 178(29/30): 1590-1594. |
| [154] | FU Y P, SU Y H, WU S H, et al. LiMn2?yMyO4 (M = Cr, Co) cathode materials synthesized by the microwave-induced combustion for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 426(1/2): 228-234. |
| [155] | FU Y P, SU Y H, LIN C H. Comparison of microwave-induced combustion and solid-state reaction for synthesis of LiMn2?xCrxO4 powders and their electrochemical properties[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2004, 166(1/2): 137-146. |
| [156] | LEE K S, MYUNG S T, PRAKASH J, et al. Optimization of microwave synthesis of Li[Ni0.4Co0.2Mn0.4]O2 as a positive electrode material for lithium batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(7): 3065-3074. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2007.11.042 |
| [157] | 赵新兵, 周斌, 曹高劭, 等. 一种从磷酸铁锂废旧电池中回收制备磷酸铁锂的方法: CN102751548A[P]. 2012-10-24. |
| [158] | LI F X, QIU W H, HU H Y, et al. Electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 synthesized by microwave processing as lithium battery cathode[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 29(6): 346. |
| [159] | AMINE K. Olivine LiCoPO4 as 4.8 V electrode material for lithium batteries[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 1999, 3(4): 178. doi: 10.1149/1.1390994 |
| [160] | OKADA S, SAWA S, EGASHIRA M, et al. Cathode properties of phospho-olivine LiMPO4 for lithium secondary batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 97-98: 430-432. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(01)00631-0 |
| [161] | LLORIS J M, PE?REZ VICENTE C, TIRADO J L. Improvement of the electrochemical performance of LiCoPO4 5 V material using a novel synthesis procedure[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2002, 5(10): A234. doi: 10.1149/1.1507941 |
| [162] | LUDWIG J, MARINO C, HAERING D, et al. Morphology-controlled microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of high-performance LiCoPO4 as a high-voltage cathode material for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 342: 214-223. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.12.059 |
| [163] | LUDWIG J, GEPR?GS S, NORDLUND D, et al. Co11Li[(OH)5O][(PO3OH)(PO4)5], a lithium-stabilized, mixed-valent cobalt(II, III) hydroxide phosphate framework[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2017, 56(18): 10950-10961. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b01152 |
| [164] | ZAINI M A A, KAMARUDDIN M J. Critical issues in microwave-assisted activated carbon preparation[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2013, 101: 238-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.02.003 |
| [165] | CHATTERJEE S, BASAK T, DAS S K. Microwave driven convection in a rotating cylindrical cavity: A numerical study[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2007, 79(4): 1269-1279. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.04.039 |
| [166] | DATTA A K, HU W. Quality optimization of dielectric heating processes[J]. Food Technology, 1992, 46(12): 53-56. |
| [167] | ROUSSY G, JASSM S, THIEBAUT J M T. Modeling of a fluidized bed irradiatel by a single or a Mult1Mode electric microwave field distribution[J]. Journal of Microwave Power and Electromagnetic Energy, 1995, 30(3): 178-187. doi: 10.1080/08327823.1995.11688274 |
| [168] | BASAK T, AYAPPA K G. Role of length scales on microwave thawing dynamics in 2D cylinders[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2002, 45(23): 4543-4559. doi: 10.1016/S0017-9310(02)00171-0 |
| [169] | CHA-UM W, RATTANADECHO P, PAKDEE W. Experimental and numerical analysis of microwave heating of water and oil using a rectangular wave guide: Influence of sample sizes, positions, and microwave power[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2011, 4(4): 544-558. doi: 10.1007/s11947-009-0187-x |
| [170] | CHA-UM W, RATTANADECHO P, PAKDEE W. Experimental analysis of microwave heating of dielectric materials using a rectangular wave guide (MODE: TE10) (Case study: Water layer and saturated porous medium)[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2009, 33(3): 472-481. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2008.11.008 |
| [171] | MORIWAKI S, MACHIDA M, TATSUMOTO H, et al. A study on thermal runaway of poly(vinyl chloride) by microwave irradiation[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2006, 76(1/2): 238-242. |
| [172] | GUPTA N, MIDHA V, BALAKOTAIAH V, et al. Bifurcation analysis of thermal runaway in microwave heating of ceramics[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1999, 146(12): 4659-4665. doi: 10.1149/1.1392690 |
| [173] | KRIEGSMANN G A. Thermal runaway in microwave heated ceramics: A one-dimensional model[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1992, 71(4): 1960-1966. doi: 10.1063/1.351191 |
| [174] | VRIEZINGA C A, SáNCHEZ-PEDRE?O S, GRASMAN J. Thermal runaway in microwave heating: A mathematical analysis[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2002, 26(11): 1029-1038. doi: 10.1016/S0307-904X(02)00058-6 |
| [175] | LIU B. The microwave heating of two-dimensional slabs with small Arrhenius absorptivity[J]. IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics, 1999, 62(2): 137-166. doi: 10.1093/imamat/62.2.137 |
| [176] | ROUSSY G, BENNANI A, THIEBAUT J M. Temperature runaway of microwave irradiated materials[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1987, 62(4): 1167-1170. doi: 10.1063/1.339666 |




















 下载:
下载: 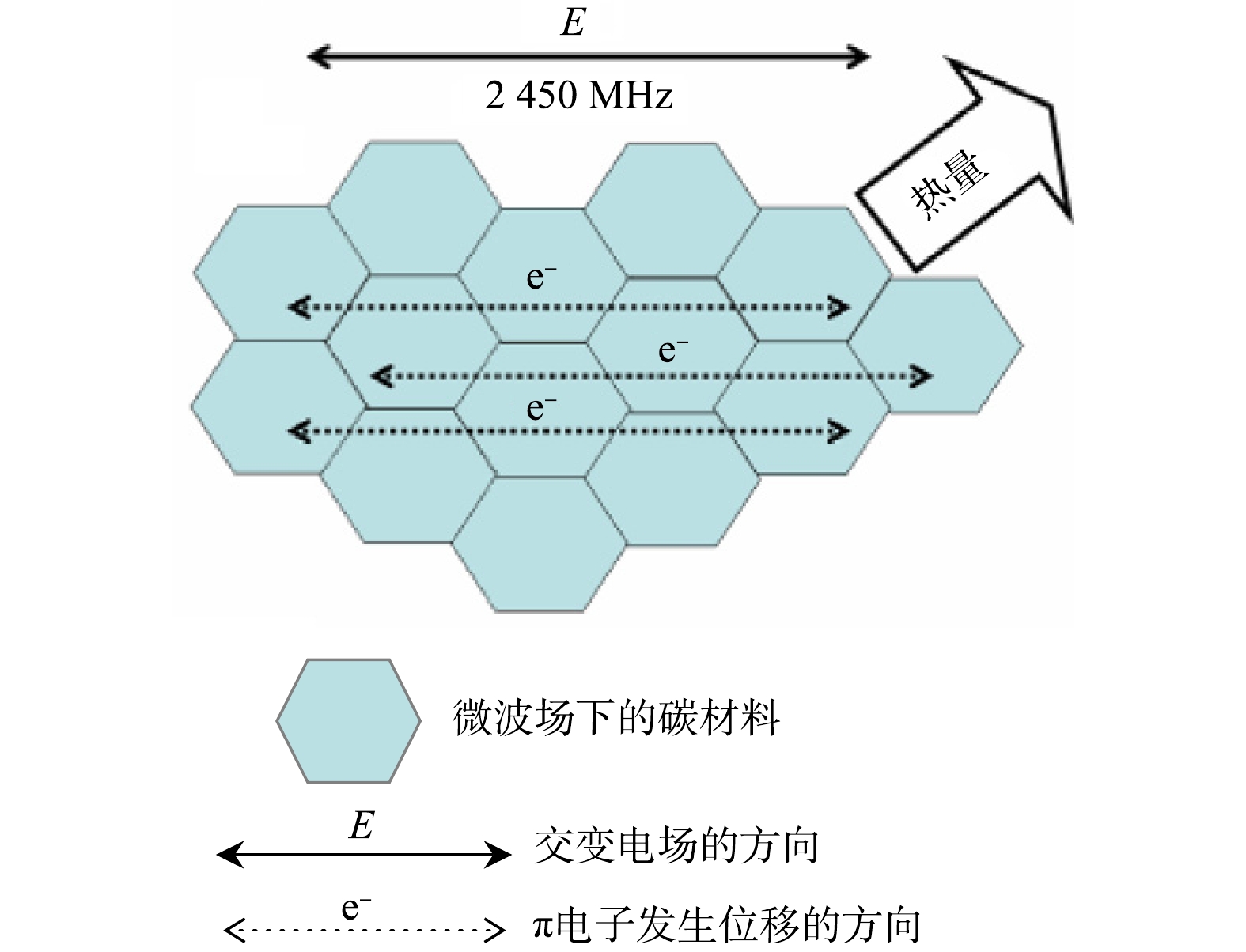









 点击查看大图
点击查看大图