全文HTML
--> --> --> 2019年,国内196个大、中城市生活垃圾产量为23 560.2×104 t[1],较2018年所公布的数值上升了11.41%[2]。我国不同地区处理生活垃圾的主要方式有填埋、堆肥、焚烧[3]。其中,焚烧具有减容率高、处理时间短、无害化程度高等优点[4],故在世界范围内已被广泛应用[5]。焚烧主要采用炉排炉和流化床2种焚烧炉型[6],广泛应用于我国大中型城市的生活垃圾焚烧发电厂中[7]。然而,焚烧过程中会产生副产物飞灰[8],即由静电除尘器或织物过滤器所捕获的烟气中的细颗粒物[9]。由于飞灰中所含的重金属和二恶英会对人体及环境造成严重危害,故垃圾焚烧飞灰已被列入《国家危险废物名录》[10]。2014年,我国飞灰产量占危险废物产生总量的比例达11%,高效处置飞灰的意义重大。熔融玻璃化技术是处理飞灰最具重要的技术之一,可去除飞灰中的二恶英、固化重金属元素于玻璃态渣中[11],且产生的玻璃渣可进一步资源化利用。热等离子体可产生高温[12],具有极高的能量密度,可在极短时间内将飞灰中有机物彻底分解。由于其处理废物范围广,已成为当前研究的热点[13]。国外的相关研究已进入工业应用阶段。美国西屋公司已建成规模220 t·d?1的等离子体处理城市生活垃圾气化工厂;英国APP公司在2008年建成了规模2.4 t·d?1的实验示范装置[14];以色列EER公司建成了规模12 t·d?1的等离子示范项目[15]。在国内,WANG等[16]在浙江大学研发了一套实验室规模的热等离子体玻璃化系统,采用直流双阳极等离子体火炬,用来处理飞灰;TU等[17]以浙江大学火电工程所为研究对象,研制了基于等离子弧技术的实验室玻璃化系统;潘新潮等[18]利用直流等离子体搭建的实验平台对飞灰进行熔融处理,测试飞灰熔融重金属浓度的浸出效果;李润东等[19]对在自行设计的实验台上研究了运行条件对重金属固化特性的影响;卢欢亮等[20]开发了一套等离子体高温熔融技术处理工艺和中试处理设备;高飞等[21]采用了与其他研究者不同的实验设备,其使用的等离子体火炬具有二路进气双阳极的特殊结构。
国内目前开展的热等离子体熔融技术研究大部分处于实验室阶段,已进入到中试阶段进行大批量飞灰熔融实验的研究较少;而且,有关热等离子体熔融飞灰过程中的重金属浸出毒性的研究多集中在少数元素,对微量重金属元素的研究则相对较少。
本研究以自主设计建造的热等离子体熔融炉中试系统为依托进行实验,旨在探究中试过程中飞灰熔融前后9种重金属元素浸出毒性浓度变化特性及飞灰中二恶英的分布特性,以期为后续的热等离子体处理垃圾飞灰技术的工业应用提供参考。
1.1. 实验原料
本研究所用飞灰样品取自山西省太原市某生活垃圾焚烧发电厂,该发电厂焚烧炉类型为机械炉排焚烧炉。所取飞灰呈灰色粉末状,粒径较小。经检测,飞灰浸出过程中主要有9种重金属元素:Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、Ni、Cr、Ba、As、Hg。1.2. 实验装置
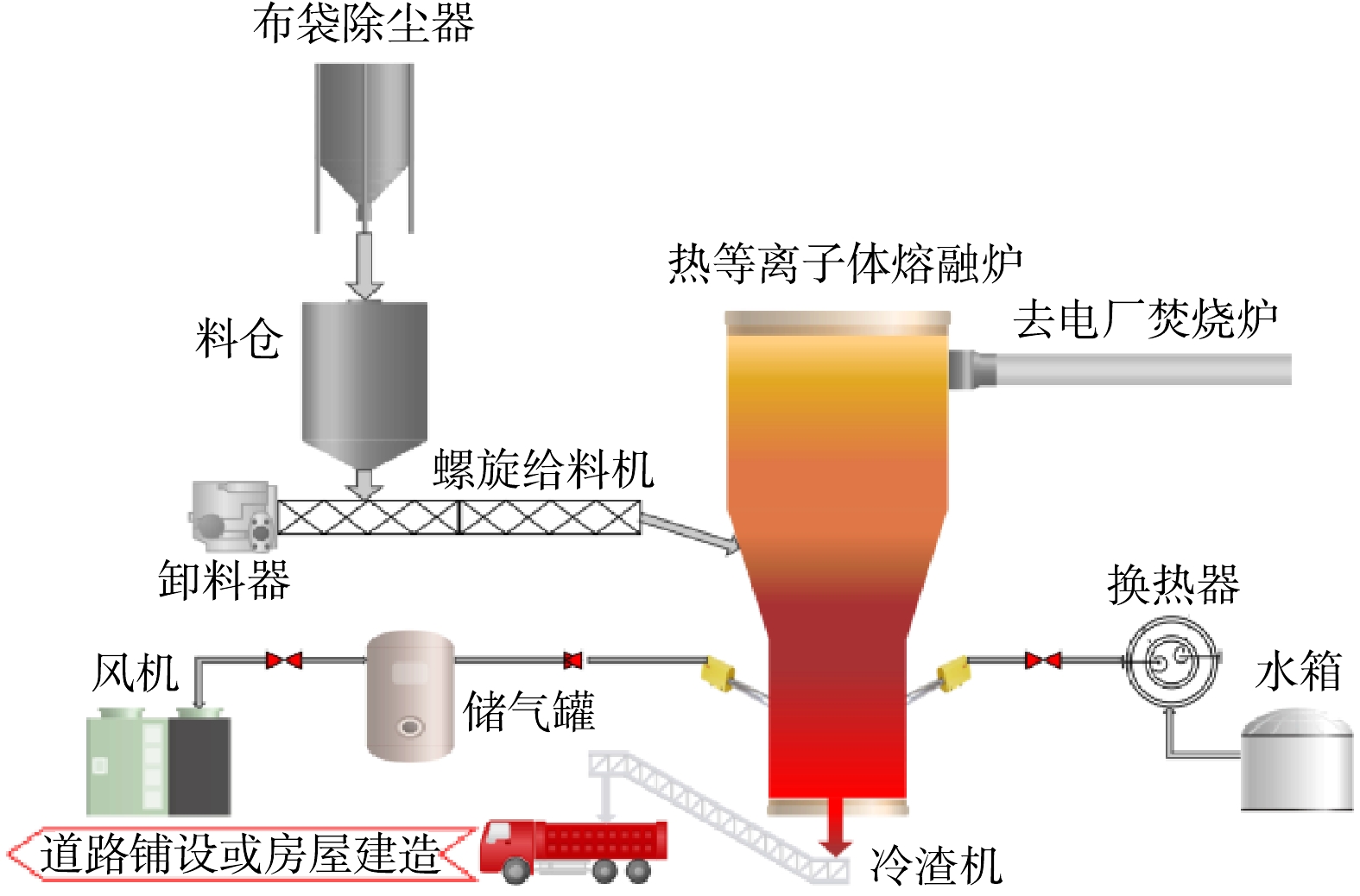
热等离子体熔融炉实验系统如图1所示,系自主设计并搭建于山西省太原市某电厂。该实验系统由布袋除尘器、料仓、螺旋给料机、热等离子体熔融炉、风机、水箱、换热器、冷渣机组成;采用功率为120 kW的3套直流非转移弧等离子火炬进行升温,设计处理量为5 t·d?1。等离子体火炬放电状态如图2所示。每套等离子火炬系统含有整流电源、等离子体点火器、冷却水系统、工质气体系统及等离子火炬。设计功率最高为150 kW,在实际使用过程中的功率为120 kW。3支等离子火炬在同一水平面呈120°分布,可长时间稳定提供1 500~2 000 ℃的高温,熔融中心区温度达2 000 ℃以上。
1.3. 实验方法
该实验共分为2部分,第1部分为升温流程,第2部分为是实验流程。1)升温流程。首先关闭热等离子体熔融炉排渣口,同时将飞灰添加至料仓;之后,使用天然气将热等离子体熔融炉升温至500 ℃,以降低能耗;升温至500 ℃后,恒温保持6 h,以保护耐材不受损耗;然后,逐步开启3支火炬升温至1 550 ℃。热等离子熔融炉中心温度比红外测量值高200 ℃;飞灰经过高温熔融炉中心区域时温度为1 750 ℃。
2)实验流程。达到实验温度后,依次打开熔融炉进料口、螺旋给料机、料仓出口,原料从料仓进入到热等离子体熔融炉内反应,3 min后全部进入熔融炉内;依次关闭料仓出口、螺旋给料机、熔融炉进料口;10 min后打开熔融炉排渣口,大量玻璃态熔渣从排渣口排出至水槽,待玻璃态熔渣冷却后进行检测。
1.4. 分析方法
1)依据GB 5085.3-2007《危险废物鉴别标准浸出毒性鉴别》[22]中火焰原子吸收光谱法对Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、Ni、Cr浸出浓度进行测定;依据石墨炉原子吸收光谱法对Ba浸出浓度进行测定;依据原子荧光法对As进行测定;使用ICP-MS对Hg进行测定。依据GB/T 15555.4-1995《固体废物六价铬的测定二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法》[23]对Cr6+浸出浓度进行测定。2)对样品含水率进行计算。重金属浸出浓度由每kg干基中的重金属浸出含量计算所得[24],含水率计算公式见式(1)。
式中:m0为量器质量,g;m1为量器重与样品总质量,g;m2为杯重与烘干后的样品总质量,g。
3)计算重金属浸出减少率时,ND值按照该重金属1/2检出限计算。重金属浸出减少率按式(2)计算。
式中:R为固溶率;ca为飞灰重金属浸出浓度,mg·L?1;cb为玻璃态渣中重金属浸出浓度。
依据国家标准HJ 77.3-2008《固体废物二恶英类的测定同位素稀释高分辨气相色谱-高分辨质谱法》[25]对飞灰及玻璃态渣中的二恶英毒性当量进行检测。
2.1. 熔融前后重金属浸出浓度变化分析
1)样品含水率分析。在对样品浸出毒性检测前,需对供试样品含水率进行检测,以计算固体所占比,便于称样检测重金属浸出浓度。检测结果显示,飞灰中含水率为0.56%,玻璃态渣中的含水率降至为0,与原飞灰相比熔融后玻璃态渣中含水率明显减低。这可能是因为,实验中热等离子体熔融炉温度最高为1 750 ℃,从而导致超高温的条件下检测样品中水分子作无规则运动,且运动程度剧烈,短时间内全部脱离飞灰进入到空气中,导致熔渣中含水率降为0。2)飞灰中Pb浸出浓度分析。飞灰原样中Pb的浸出浓度为GB 16889-2008《生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准》[26]中规定标准值的2倍,属于超标污染物。这是因为,垃圾经炉排炉焚烧时,PVC在200~300 ℃开始释放HCl气体,HCl又在300~400 ℃开始氯化PbO生成PbCl2,导致PbCl2在其熔点501 ℃附近开始挥发;在700~800 ℃时,NaCl结合SiO2、Al2O3直接氯化PbO,促进Pb挥发[27],在烟气中最终被除尘器捕集;同时,由于垃圾焚烧过程中Fe、Mn在高温下燃烧形成铁锰氧化物存在于飞灰中,其具有高比表面积及大量表面电荷,故大量PbO粒子吸附在其上并形成胶膜存在于烟气中,加之部分Pb在烟气处理除酸过程的碱性环境下直接形成Pb (OH)2沉淀吸附在铁锰凝结物上存在于飞灰中,最终导致飞灰中富集了大量Pb及其化合物。重金属浸出程度随飞灰的比表面积增加而增加[28],由于,飞灰粒径大多数位于0~100 μm之间,颗粒表面凹凸不平,有很多微小孔洞,间隙较大,导致Pb有较大溶解界面与溶出[29];同时,在浸出毒性检测过程中由于使用酸性浸提剂,大量铁锰氧化物结合态Pb在酸性浸提剂作用下发生反应而浸出,最终导致Pb浸出浓度超标[30]。
3)熔融前后重金属浸出浓度。飞灰及玻璃态渣中重金属浸出浓度检测结果见表1。由表1可知,玻璃态渣重金属浸出浓度明显低于飞灰浸出浓度,玻璃态渣中个别重金属浓度低于仪器检测限。Zn、Cd、Cr、Ba、Cr6+的浸出浓度减少率都在90%以上,除As外浸出减少率均高于60%,说明该热等离子体熔融炉系统可有效降低飞灰浸出浓度。
表2为各种重金属及其化合物熔沸点[24,31]。由表2可知,由于不同重金属在飞灰中的赋存形态不同,故其在飞灰熔融过程中的迁移转化机制不同。Cu在熔融过程中易形成不易挥发的CuO、CuO2,但因实验温度远大于Cu氧化物的熔沸点,所以飞灰中的Cu在熔融时接近完全挥发。Zn的浸出浓度减少率为96.9%。这是因为,在熔融条件下,飞灰中的SiO2、Al2O3易形成硅铝酸盐;之后,与Zn形成了Zn2SiO4、ZnSiO3、ZnAl2O4等不易挥发的化合物;而当温度达到1 750 ℃时,Zn2SiO4、ZnSiO3、ZnAl2O4等熔融在玻璃态渣中,从而造成了Zn浸出浓度的下降。Pb的在飞灰中主要以氧化物的形式存在,同时飞灰中亦含有一部分的硫酸铅。氧化铅在1 516 ℃时开始挥发,因此,Pb在熔融过程中大部分挥发。Cd在飞灰中主要以氧化镉与氯化镉的形式存在。氯化铬在1 000 ℃时已接近完全挥发,氧化镉在1 500 ℃达到熔点,最终镉大部分以气态的形式挥发。Ni、Cr在400~1 150 ℃时均不易挥发,这主要是由于Ni、Cr在1 200 ℃时形成了硅酸钙或硅铝酸盐晶体相,从而阻止2种重金属及其化合物的挥发;但是,熔融炉中心温度可达1 750 ℃,此时氧化物、硫化物、硫酸盐均已大量挥发,同时硅酸钙与硅铝酸盐已发生相变,也逐渐开始挥发。Ba在飞灰熔融过程中形成少部分难挥发的氧化物,大部分挥发到空气中。As主要以AsCl3、As2O3的形式存在,熔沸点也较低,在熔融过程中绝大多数挥发。Hg属于低沸点金属,具有较高的蒸气压,难以与矿物质结合生成稳定化合物,极易在熔融过程中变为气态,挥发性较高[32-33]。
4)熔融后As的浸出浓度。由表1可知,飞灰经熔融后,As的浸出浓度增加,这与卢欢亮等[20]、胡明等[34]的等离子体中试实验结果不同。这可能是因为,As在熔融过程中形成了易溶的钙盐,使用硫酸硝酸法浸出时,硫酸根离子夺取砷酸钙和亚砷酸钙中钙离子而释放出As,从而导致As的浸出浓度增加。其化学反应见式(3)、式(4)[35]。
2.2. 样品熔融前后二恶英浓度分布特性
本研究中,飞灰与玻璃态渣中的二恶英同系物浓度见表3。由表3可知,飞灰中的二恶英毒性当量远超GB 16889-2008《生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准》中规定的二恶英的排放标准限值3 ng·kg?1,故环境风险很大[35]。供试飞灰中二恶英的分布状况是,PCDFs的含量明显高于PCDDs的含量,在PCDFs中,低氯代的呋喃(4~6个氯原子)的含量明显高出高氯代的呋喃(7~8个氯原子),这与潘新潮[36]的研究结果一致。在PCDDs的同系物分布中,低氯代的呋喃(4~6个氯原子)的含量也明显高出高氯代的呋喃(7~8个氯原子),这与潘新潮[36]的研究结果不同。这可能是因为,不同地方的生活垃圾组成结构不同,表明太原地区的生活垃圾焚烧过程中偏向于生成低氯代PCDFs和PCDDs。飞灰中二恶英同系物2,3,4,7,8-P5CDF对二恶英TEQ贡献最大,达到了38.94%,其次是2,3,4,6,7,8-H6CDF与1,2,3,6,7,8-H6CDF,分别达到13.45%、10.74%,这3种二恶英同系物对二恶英TEQ的贡献值共达63.13%,这与潘新潮[36]在炉排炉收集到的FA1相似;但与严密[37]的研究结果不同,他发现,炉排炉中收集的飞灰中二恶英类同系物HpCDD、OCDD占较高比例。同时,本研究发现,PCDFs的TEQ总量远大于PCDDs的TEQ总量,其值接近于4倍,说明PCDFs是二恶英TEQ浓度大的主要原因。由表3可见,经熔融处理得到的玻璃态渣中17种二恶英同系物TEQ均在0.1 ng·kg?1以下。其中,2,3,7,8-T4CDD的贡献最大,达到18.29%;大多数二恶英同系物浓度较飞灰中的分布较为均匀;二恶英总毒性当量为0.546 6 ng·kg?1,远低于填埋标准限值3.000 0 ng·kg?1;熔渣中各种二恶英同系物浓度减少率均超过99%,计算后得二恶英总量的减排率为99.96%。上述结果表明,该中试系统能够有效去除飞灰中的二恶英,从而满足填埋要求或进行资源化利用。
2)使用硫酸硝酸法检测会导致硫酸根离子会与As在熔融过程中形成的砷酸钙和亚砷酸钙中钙离子结合,使得As的浸出浓度增加。因此,不宜使用硫酸硝酸法检测玻璃态渣中As浸出浓度。
3)太原地区PCDFs的含量高于PCDDs,玻璃态渣中二恶英同系物浓度较飞灰中的分布均匀,二恶英总毒性当量减少率为99.96%,远低于填埋时二恶英排放限值。因此,该中试系统能有效降低飞灰中的重金属浸出浓度及二恶英的毒性当量。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: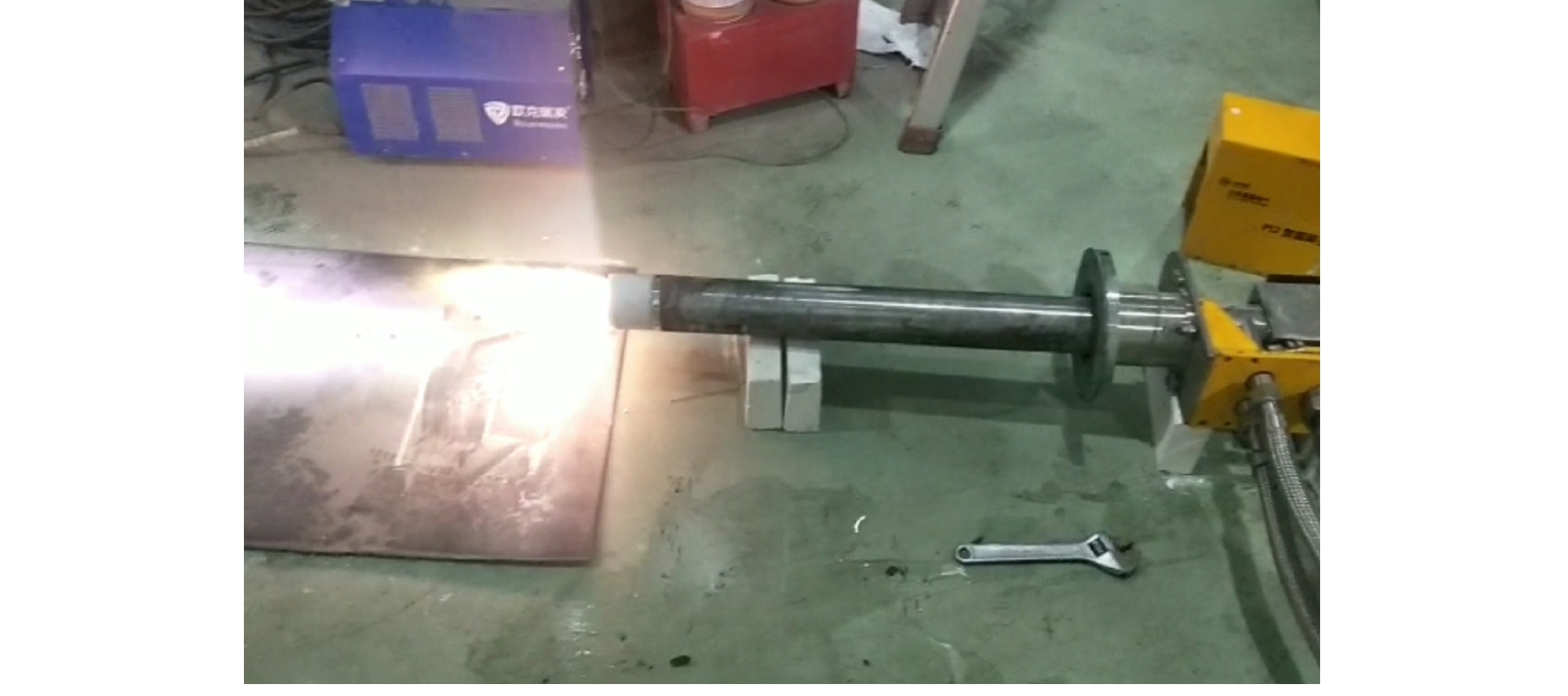 
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图