2.西安市市政设施管理局,西安 710016
1.Key Laboratory of Northwest Water Resources Environment and Ecology, Ministry of Education, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi'an 710055, China
2.Xi'an Municipal Facilities Administration, Xi'an 710016, China
的研究进展,并根据研究成果和目前存在的问题提出未来的研究方向。
) produced by sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) metabolism in the sewer will lead to H
S gas release and pipeline corrosion, thus it will increase the maintenance cost of the pipelines, and furthermore threaten the health of workers and residents. The addition of chemicals is main technical measure to inhibit the formation of sulfide in sewer pipelines. Among the available chemicals, nitrate was widely used and studied for the reduction of H
S production due to its high inhibition efficiency and easy-to-use. In this study, the state of art of S
controlled by nitrate was reviewed in the focus of the principle, the efficiency, influencing factors, nitrate consumption rules, as well as the effect of nitrate on the evolution of microbial community. In addition, the perspectives of this technology were also discussed here based on the current research progress and problems.
.
control with nitrate
S ratio among sulfide species
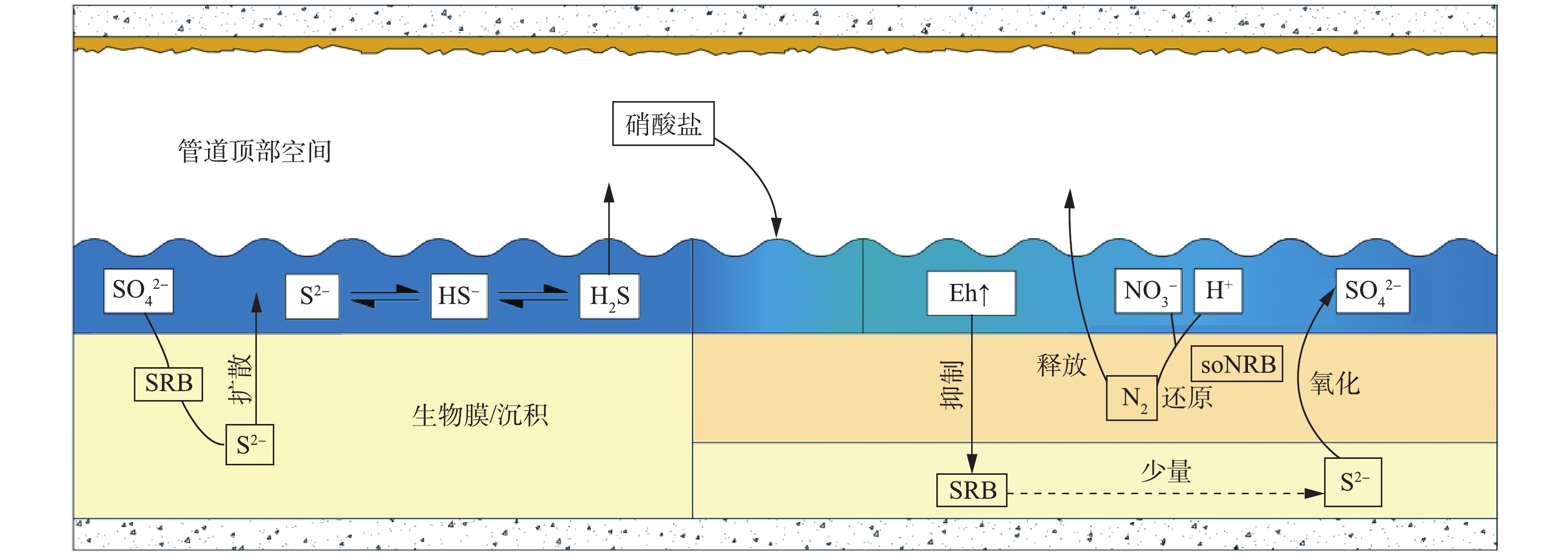
Biological phase stratification before and after nitrate addtion
| [1] | JEFF F, YUAN Z G, PAUL L. Dissolved methane in rising main sewer systems: Field measurements and simple model development for estimating greenhouse gas emissions[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2009, 60(11): 2963-2971. doi: 10.2166/wst.2009.718 |
| [2] | GUISASOLA A, HAAS D D, KELLER J, et al. Methane formation in sewer systems[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(6/7): 1421-1430. |
| [3] | SHARMA K R, YUAN Z G, HAAS D D, et al. Dynamics and dynamic modelling of H2S production in sewer systems[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(10/11): 2527-2538. |
| [4] | SUN J, HU S H, SHARMA K R, et al. Stratified microbial structure and activity in sulfide and methane-producing anaerobic sewer biofilms[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(22): 7042-7052. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02146-14 |
| [5] | SUTHERLAND-STACEY L, CORRIE S, NEETHLING A, et al. Continuous measurement of dissolved sulfide in sewer systems[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2008, 57(3): 375-381. doi: 10.2166/wst.2008.132 |
| [6] | BOON A G. Septicity in sewers: Causes, consequences and containment[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1995, 31(7): 237-253. doi: 10.2166/wst.1995.0240 |
| [7] | ROBERTS D J, NICA D, ZUO G, et al. Quantifying microbially induced deterioration of concrete: Initial studies[J]. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 2002, 49(4): 227-234. doi: 10.1016/S0964-8305(02)00049-5 |
| [8] | 许小冰, 王怡, 王社平, 等. 城市排水管道中有害气体控制的国内外研究现状[J]. 中国给水排水, 2012, 28(14): 9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4602.2012.14.003 |
| [9] | MUEZZINOGLU A. A study of volatile organic sulfur emissions causing urban odors[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 51(4): 245-252. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00821-4 |
| [10] | ?S?Y A, ?DEGAARD H, BENTZEN G. The effect of sulphide and organic matter on the nitrification activity in a biofilm process[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1998, 37(1): 115-122. doi: 10.2166/wst.1998.0028 |
| [11] | GANIGUE R, GUTIERREZ O, ROOTSEY R, et al. Chemical dosing for sulfide control in Australia: An industry survey[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(19): 6564-6574. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.054 |
| [12] | ZHANG L H, SCHRYVER P D, GUSSEME B D, et al. Chemical and biological technologies for hydrogen sulfide emission control in sewer systems: A review[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(1/2): 1-12. |
| [13] | GANIGUé R, YUAN Z G. Impact of oxygen injection on CH4 and N2O emissions from rising main sewers[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2014, 144: 279-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.04.023 |
| [14] | GUTIERREZ O, MOHANAKRISHNAN J, SHARMA K R, et al. Evaluation of oxygen injection as a means of controlling sulfide production in a sewer system[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(17): 4549-4561. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.07.042 |
| [15] | JIANG G M, SHARMA K R, YUAN Z G. Effects of nitrate dosing on methanogenic activity in a sulfide-producing sewer biofilm reactor[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(5): 1783-1792. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.12.036 |
| [16] | JIANG G M, GUTIERREZ O, SHARMA K R, et al. Effects of nitrite concentration and exposure time on sulfide and methane production in sewer systems[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(14): 4241-4251. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.030 |
| [17] | AUGUET O, PIJUAN M, BORREGO C M, et al. Control of sulfide and methane production in anaerobic sewer systems by means of downstream nitrite dosage[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 550: 1116-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.130 |
| [18] | ZHANG L S, KELLER J, YUAN Z G. Inhibition of sulfate-reducing and methanogenic activities of anaerobic sewer biofilms by ferric iron dosing[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(17): 4123-4132. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.013 |
| [19] | FIRER D, FRIEDLER E, LAHAV O. Control of sulfide in sewer systems by dosage of iron salts: Comparison between theoretical and experimental results, and practical implications[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 392(1): 145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.11.008 |
| [20] | GUTIERREZ O, PARK D, SHARMA K R, et al. Effects of long-term pH elevation on the sulfate-reducing and methanogenic activities of anaerobic sewer biofilms[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(9): 2549-2557. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.008 |
| [21] | GUTIERREZ O, SUDARJANTO G, REN G, et al. Assessment of pH shock as a method for controlling sulfide and methane formation in pressure main sewer systems[J]. Water Research, 2014, 48: 569-578. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.021 |
| [22] | MORENO L, PREDICALA B, NEMATI M. Laboratory, semi-pilot and room scale study of nitrite and molybdate mediated control of H2S emission from swine manure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(7): 2141-2151. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.011 |
| [23] | OKABE S, ITO T, SATOH H, et al. Effect of nitrite and nitrate on biogenic sulfide production in sewer biofilms determined by the use of microelectrodes[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2003, 47(11): 281-288. doi: 10.2166/wst.2003.0616 |
| [24] | BENTZEN G, SMIT A T, BENNETT D, et al. Controlled dosing of nitrate for prevention of H2S in a sewer network and the effects on the subsequent treatment processes[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1995, 31(7): 293-302. doi: 10.2166/wst.1995.0245 |
| [25] | DAVIDOVA I, HICKS M S, FEDORAK P M, et al. The influence of nitrate on microbial processes in oil industry production waters[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2001, 27(2): 80-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.jim.7000166 |
| [26] | YANG W, VOLLERTSEN J, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T. Anoxic sulfide oxidation in wastewater of sewer networks[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2005, 52(3): 191-199. doi: 10.2166/wst.2005.0076 |
| [27] | MOHANAKRISHNAN J, GUTIERREZ O, SHARMA K R, et al. Impact of nitrate addition on biofilm properties and activities in rising main sewers[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(17): 4225-4237. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.021 |
| [28] | LIU Y W, SHARMA K R, NI B J, et al. Effects of nitrate dosing on sulfidogenic and methanogenic activities in sewer sediment[J]. Water Research, 2015, 74: 155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.017 |
| [29] | PARK K, LEE H, PHELAN S, et al. Mitigation strategies of hydrogen sulphide emission in sewer networks: A review[J]. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 2014, 95: 251-261. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.02.013 |
| [30] | NIELSEN P H, RAUNKJ?R K, NORSKER N H, et al. Transformation of wastewater in sewer systems: A review[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2015, 25(6): 17-31. |
| [31] | WIERINGA K T. The formation of acetic acid from carbon dioxide and hydrogen by anaerobic spore-forming bacteria[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 1939, 6(1): 251-262. doi: 10.1007/BF02146190 |
| [32] | PODUSKA R A, ANDERSON B D. Successful storage lagoon odor control[J]. Water Pollution Control Federation, 1981, 53(3): 299-310. |
| [33] | JIANG G M, SHARMA K R, GUISASOLA A, et al. Sulfur transformation in rising main sewers receiving nitrate dosage[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(17): 4430-4440. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.07.001 |
| [34] | LI W, ZHAO Q L, LIU H. Sulfide removal by simultaneous autotrophic and heterotrophic desulfurization-denitrification process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(2/3): 848-853. |
| [35] | MATHIOUDAKIS V L, VAIOPOULOU E, AIVASIDIS A, et al. Addition of nitrates for odor control in sewer networks: Laboratory and field experiments[J]. Global Nest, 2006, 8(1): 37-42. |
| [36] | YANG W, VOLLERTSEN J, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T. Anoxic control of odour and corrosion from sewer networks[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 50(4): 341-349. doi: 10.2166/wst.2004.0300 |
| [37] | LIU Y C, WU C, ZHOU X H, et al. Sulfide elimination by intermittent nitrate dosing in sewer sediments[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 27(1): 259-265. |
| [38] | AUGUET O, PIJUAN M, GUASCH-BALCELLS H, et al. Implications of downstream nitrate dosage in anaerobic sewers to control sulfide and methane emissions[J]. Water Research, 2015, 68(1): 522-532. |
| [39] | RODRíGUEZ-GóMEZ L E, DELGADO S, áLVAREZ M, et al. Inhibition of sulfide generation in a reclaimed wastewater pipe by nitrate dosage and denitrification kinetics[J]. Water Environment Research, 2005, 77(2): 193-198. doi: 10.2175/106143005X41762 |
| [40] | SARACEVIC E, BERTRáN D L F, MATSCHé N. Odour and corrosion problems in pressure sewers[J]. Water Practice and Technology, 2007, 2(1): 115-123. |
| [41] | HENZE M, GUJER W, MINO T, et al. Activated sludge model No.2d, ASM2D[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1999, 39(1): 165-182. doi: 10.2166/wst.1999.0036 |
| [42] | ABDUL-TALIB S, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T, VOLLERTSEN J, et al. Half saturation constants for nitrate and nitrite by in-sewer anoxic transformations of wastewater organic matter[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 46(9): 185-192. doi: 10.2166/wst.2002.0236 |
| [43] | ABDUL-TALIB S, UJANG Z, VOLLERTSEN J, et al. Model concept for nitrate and nitrite utilization during anoxic transformation in the bulk water phase of municipal wastewater under sewer conditions[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2005, 52(3): 181-189. doi: 10.2166/wst.2005.0075 |
| [44] | VOLLERTSEN J, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T, UJANG Z, et al. Integrated design of sewers and wastewater treatment plants[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 46(9): 11-20. doi: 10.2166/wst.2002.0194 |
| [45] | EDDIE C, JAAP V R, ANDREAS S, et al. Identification of bacteria potentially responsible for oxic and anoxic sulfide oxidation in biofilters of a recirculating mariculture system[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(10): 6134-6141. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.10.6134-6141.2005 |
| [46] | BRUCE R A, ACHENBACH L A, COATES J D. Reduction of (per)chlorate by a novel organism isolated from paper mill waste[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 1(4): 319-329. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.1999.00042.x |
| [47] | BOWMAN J P, SLY L I, NICHOLS P D, et al. Revised taxonomy of the methanotrophs: Description of methylobacter gen. nov., emendation of methylococcus, validation of methylosinus and methylocystis species, and a proposal that the family methylococcaceae includes only the group I methanotrophs[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 1993, 43(4): 735-753. |
| [48] | KITS K D, KALYUZHNAYA M G, KLOTZ M G, et al. Genome sequence of the obligate gammaproteobacterial methanotroph methylomicrobium album strain BG8[J]. Genome Announcements, 2013, 1(2): 11-12. |
| [49] | OKABE S, ITOH T, SATOH H., et al Analyses of spatial distributions of sulfate-reducing bacteria and their activity in aerobic wastewater biofilms[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65: 5107-5116. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.11.5107-5116.1999 |
| [50] | KLEINJAN W E, LAMMERS J N J J, KEIZER A D, et al. Effect of biologically produced sulfur on gas absorption in a biotechnological hydrogen sulfide removal process[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 94(4): 633-644. doi: 10.1002/bit.20855 |
| [51] | ABDUL-TALIB S, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T, VOLLERTSEN J, et al. Anoxic transformations of wastewater organic matter in sewers: Process kinetics, model concept and wastewater treatment potential[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 45(3): 53-60. doi: 10.2166/wst.2002.0053 |
| [52] | 袁伟玲, 曹凑贵, 李成芳, 等. 稻鸭、稻鱼共作生态系统CH4和N2O温室效应及经济效益评估[J]. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(6): 2052-2060. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.06.022 |
| [53] | BARTACEK J, MANCONI I, SANSONE G, et al. Divalent metal addition restores sulfide-inhibited N2O reduction in pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Nitric Oxide, 2010, 23(2): 101-105. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2010.04.005 |
| [54] | PAN Y T, YE L, YUAN Z G. Effect of H2S on N2O reduction and accumulation during denitrification by methanol utilizing denitrifiers[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2013, 47(15): 8408-8415. |
| [55] | SCHONHARTING B, METZGER J W, KRAUTH K, et al. Release of nitrous oxide (N2O) from denitrifying activated sludge caused by H2S-containing wastewater: Quantification and application of a new mathematical model[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1998, 38(1): 237-246. doi: 10.2166/wst.1998.0057 |
| [56] | GU T F, TAN P Y, ZHOU Y C, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of dimethyl trisulfide formation during sulfide control in sewer by adding various oxidants[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 673: 719-725. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.131 |
| [57] | JIANG Y, CHENG B, LIU M X, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of taste and odor compounds in surface water, overlying water and sediment of the western Lake Chaohu, China[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2016, 96(2): 186-191. doi: 10.1007/s00128-015-1698-y |
| [58] | TAN W B, JIANG Z, CHEN C, et al. Thiopseudomonas denitrificans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from anaerobic activated sludge[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2015, 65(1): 225-229. |
| [59] | LIANG S, ZHANG L, JIANG F. Indirect sulfur reduction via polysulfide contributes to serious odor problem in a sewer receiving nitrate dosage[J]. Water Research, 2016, 100: 421-428. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.036 |
| [60] | HE R, YAO X Z, CHEN M, et al. Conversion of sulfur compounds and microbial community in anaerobic treatment of fish and pork waste[J]. Waste Management, 2018, 76: 383-393. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.04.006 |
| [61] | ZHOU X Y, ZHANG K J, ZHANG T Q, et al. An ignored and potential source of taste and odor (T&O) issues-biofilms in drinking water distribution system(DWDS)[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(9): 3537-3550. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8223-7 |

 下载:
下载: 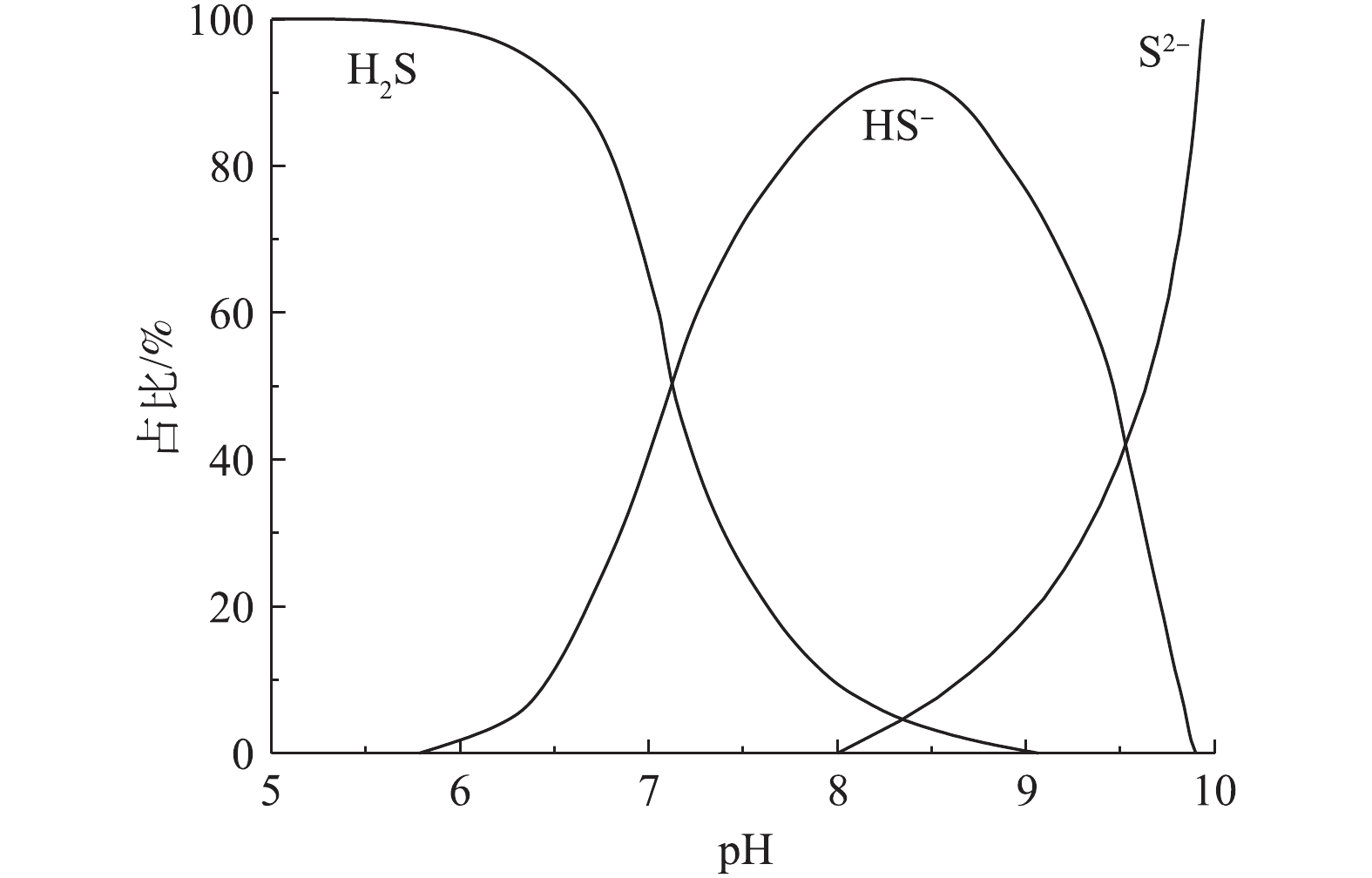










 点击查看大图
点击查看大图