全文HTML
--> --> --> 短程硝化技术较现行污水处理厂普遍应用的传统全程硝化技术具有显著的经济优势,对于活性污泥工艺处理普遍面临的低碳氮比(COD/N)污水具有可持续发展意义[1-2]。短程硝化即通过氨氧化细菌(AOB)的作用将氨氮氧化为亚硝酸盐,由亚硝酸盐氧化细菌(NOB)将亚硝酸盐进一步氧化为硝酸盐,通过以上2步过程完成全程硝化[2]。有研究表明,通过调节运行参数可以实现亚硝酸盐积累,如采用较低的溶解氧(DO)、高温、调节pH从而实现较高的游离氨(FA)或游离亚硝酸(FNA)浓度等。李培根等[3]在DO约0.3 mg·L?1,pH为8.0的条件下,采用序批式反应器(SBR)成功实现短程硝化。ZHENG等[4]将DO、温度和pH分别控制在0.4~0.6 mg·L?1、35 ℃和8~8.2,在无纺布生物转盘反应器内实现同步短程硝化、厌氧氨氧化和反硝化过程。SAUDER等[5]的研究表明,在21~33 ℃时,温度升高可提高亚硝酸盐积累的程度。此外,DURAN等[6]采用完全混合反应器(CSTR)进行了短程硝化,在pH为7.1~8.5进行调节,控制FA低于10 mg·L?1、FNA高于0.2 mg·L?1。然而实际中的低温地区或时节的大型污水处理厂若长期通过加热设备实现温度控制,或通过投加碱以提高pH所需费用较高,控制DO的实现亚硝酸盐积累具有实际可行性。虽然已证实采用低DO可以实现亚硝酸盐积累,但是氨氮氧化速率随着DO的降低也会随之下降[7-9]。活性污泥生物污水处理工艺中功能菌的比例直接影响生物降解速率[7, 10]。著名的生物添加强化技术(BABE)正是基于此原理,通过在污水处理工艺的侧流反应器培养硝化细菌,将侧流中富有硝化细菌的污泥回流于主流工艺,从而强化主流工艺的硝化能力[11-12]。此外,已有研究表明,载体挂膜、细胞固定化等方式也可以实现增加反应器内的目标功能菌的目标。ANTILEO等[9]采用内有纺织材料载体的生物转盘反应器,将DO控制1.0 mg·L?1以下,通过pH控制以及在氨氮氧化完成时停止曝气的运行策略,实现AOB的优势增长,长期实验结果表明亚硝酸盐积累率稳定维持在84%~88%。徐浩等[13]的研究结果表明,添加立体弹性填料的序批式生物膜反应器(SBBR)利于AOB菌种的富集,亚硝酸盐积累率达到90%以上。DANIEL等[14]证实了固定化载体利于AOB菌体附着其上,促进亚硝酸盐积累的形成。因此,为加速在低DO条件下实现亚硝酸盐积累的同时实现较高的氨氮氧化速率,向主流工艺中投加AOB,以实现其相对于NOB的菌群优势,从而强化氨氮氧化至亚硝酸盐的能力,具有重要的现实意义。
在水污染控制领域,生物反应器通常采用连续流或间歇运行方式。已有研究[15-16]采用此2种运行方式,在30 ℃左右的温度条件下,实现了AOB的富集培养,历时1个月至数月。本研究在常温(20 ℃)条件下,采用底物流加-间歇运行方式进行AOB富集培养,探讨了pH、FA、FNA、DO等因素对其的影响,并对富集过程中AOB进行了定性和定量分析,为常温快速富集高纯度的AOB提供参考。
1.1. 实验装置和原水
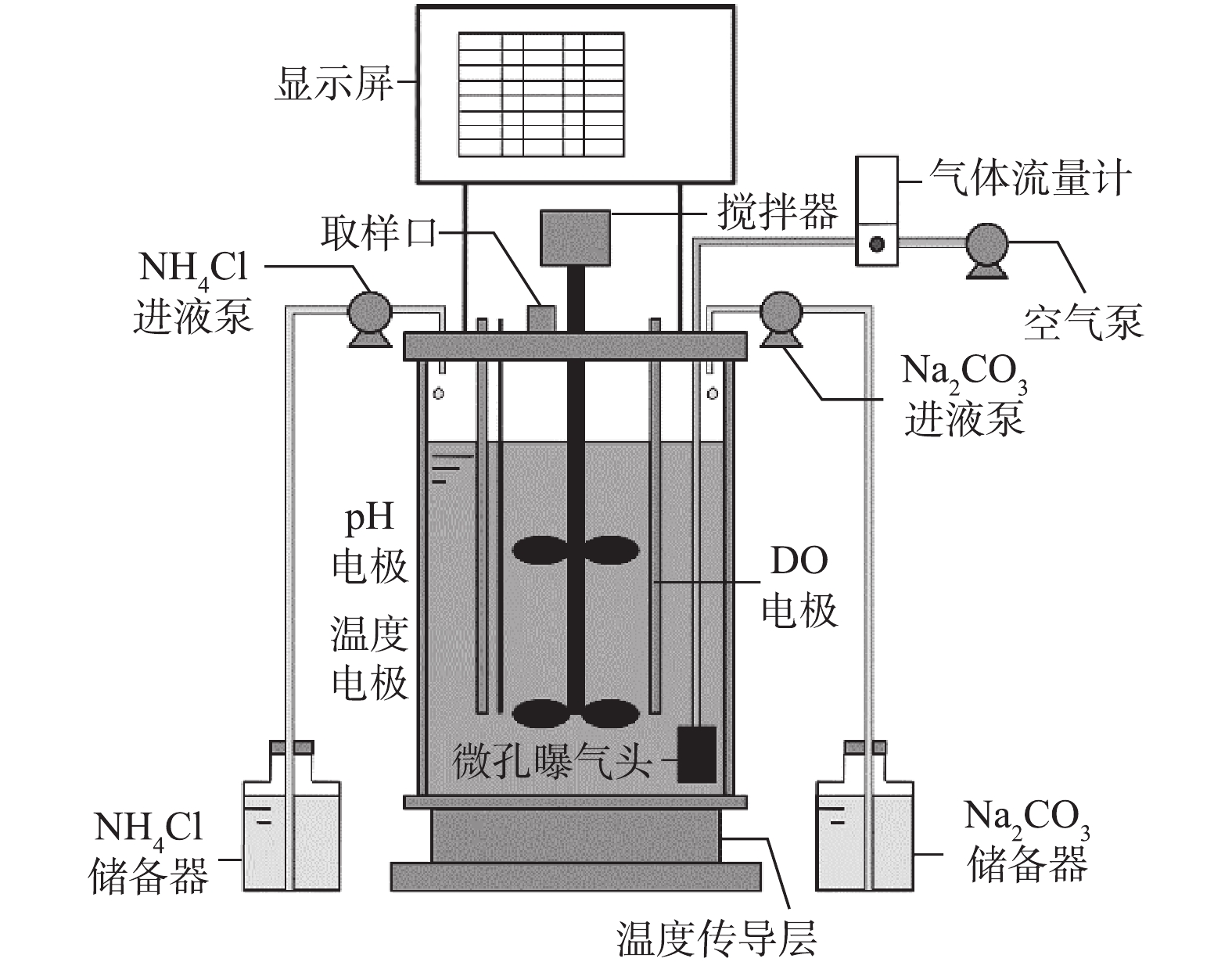
采用全自动发酵罐(BLBIO-5GJ,上海百仑生物科技有限公司,中国)为SBR,有效容积为4 L,如图1所示。DO、pH和温度电极实时监测反应液的DO浓度、pH和温度;以50 r·min?1搅拌,使反应液与活性污泥完全混合;温度调节装置自动调节至预期温度(20±2) ℃;空气通过微孔曝气头均匀曝气,气体流量计控制曝气量;采用反应器自带的蠕动泵用于向反应器内补充氨氧化反应底物接种污泥取自北京高碑店污水处理厂A2/O工艺回流污泥。原水采用人工配水,由高浓度基础培养液和自来水配制成预期浓度,基础培养液具体组成成分为KH2PO4 7.02 g·L?1、MgSO4·7H2O 2.00 g·L?1、CaCl2 1.20 g·L?1、FeSO4·7H2O 2.00 g·L?1。微量元素:ZnSO4·7H2O 0.50 g·L?1、MnCl2·4H2O 0.50 g·L?1、CoCl2·6H2O 0.40 g·L?1、CuSO4·5H2O 0.40 g·L?1、NiCl2·6H2O 0.20 g·L?1。
1.2. 实验方法
采用底物流加-间歇运行方式[17-18],每个周期具体为4个阶段:加培养液、反应、污泥沉淀和排水。培养时间为18 d,其中第1~7天每天1周期(22 h),第8天开始每天2周期(8 h和12 h),共运行18天、29周期。具体步骤为:将自来水与计算好体积的基础培养液加入反应器,使得反应液初始浓度为80 mg·L?1通过调节反应液的pH,控制底物流加速率和实际反应速率的关系,以实现体系内预期氨氮和亚硝酸盐浓度范围及预期的FA和FNA浓度,考察了pH、FA、FNA对AOB富集的影响,并结合污泥浓度以及采用不同DO浓度考察生物量及DO对反应速率的影响。
1.3. 测定方法
在进行化学分析前,样品首先采用中速定性滤纸进行过滤。游离氨(FA)和游离亚硝酸(FNA)浓度[20]根据公式(1)和式(2)进行计算。
式中:CFA为游离氨浓度,mg·L?1;CFNA为游离亚硝酸浓度,mg·L?1;
底物流加-间歇运行方式的每个周期氨氮氧化速率和底物原液储备器中底物质量[17-18, 21]分别采用式(3)和式(4)进行计算。
式中:
式中:m为每个周期所用NH4Cl的总质量,g;V为反应液体积,L;S为计算基准值,本研究取0.382 g,即0.382 g NH4Cl为1 L反应液提供氨氮浓度100 mg·L?1。
每个周期亚硝酸盐积累率根据每周期反应开始和结束时亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐浓度生成量[16]进行计算,计算方法见式(5)。
式中:η为每个周期亚硝酸盐积累率;
1.4. 扫描电镜
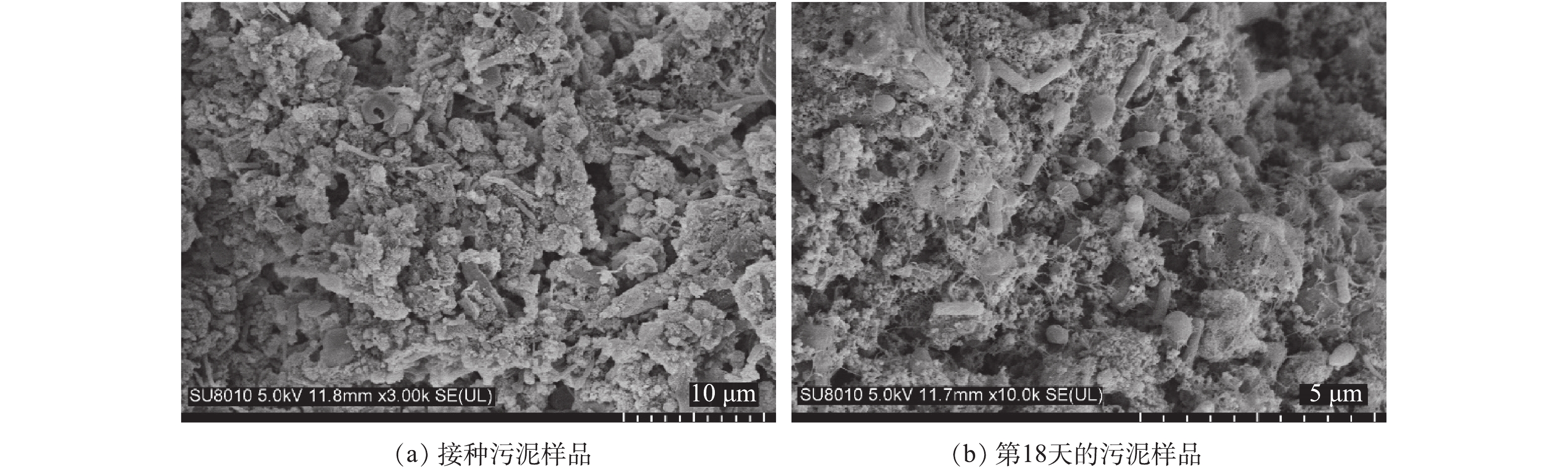
采用扫描电镜观察AOB富集培养前后的污泥中细菌的形态。制样步骤如下:在4 ℃下,使用戊二醇浸泡样品2 h以上,以固定细胞;吸出戊二醇固定液,加入去离子水浸泡样品数分钟;加入去离子水再浸泡2次;再分别加入50%、70%、85%、95%和100%乙醇浸泡;之后将样品置于纸包中进行临界点干燥,完成后取出样品并粘至金属台上,喷金处理;最后,在扫描电镜(SU8010,日立公司,日本)下进行观察。1.5. 高通量测序
取污泥样品进行DNA提取、PCR扩增(V3~V4)、琼脂糖凝胶电泳、DNA纯化,采用Illumina Miseq03测序平台进行16S rRNA高通量测序(生工生物工程股份有限公司,上海)。对结果进行过滤处理,得到优化序列。在97%相似度水平下进行操作分类单元(OTU)聚类分析,研究结果用于描述不同微生物群落在污泥中的丰度,明确了主要物种的比例。相应序列的原始数据存储于NCBI数据库中(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/PRJNA563303),编号为SRR10064655、SRR10064654,SRR10064653和SRR10064652(BioProject ID:PRJNA563303;BioSample编号:SAMN12675027, SAMN12675028, SAMN12675029, SAMN12675030)。1.6. 荧光定量PCR
采用荧光定量PCR法检测污泥样品中amoA基因的绝对含量(生工生物工程股份有限公司,上海)。引物序列为amoA-1F:GGGGTTTCTACTGGTGGT和amoA-2R:CCCCTCKGSAAAGCCTTCTTC。PCR反应体系:模板DNA 0.5 μL;引物 F (10 μmol·L?1 0.5 μL;引物 R (10 μmol·L?1) 0.5 μL;dNTP (10 mmol·L?1) 0.5 μL;Taq Buffer (10×) 2.5 μL;MgCl2 (25 mmol·L?1) 2 μL;Taq 酶 (5 U·μL?1) 0.2 μL;H2O 18.3 μL。反应条件:95 ℃预变性3 min;94 ℃变性30 s;57 ℃退火30 s;72 ℃延伸30 s;72 ℃修复延伸8 min;35个循环。PCR产物回收后进行克隆测序和定量质粒信息,DNA样品稀释50倍后上机进行荧光定量PCR检测,得到平均拷贝数。2.1. FA和FNA浓度对NOB的抑制
根据式(1)和式(2),在一定温度下,反应体系的pH、本研究通过调节反应液的pH、控制底物流加速率和实际反应速率的关系,以实现体系内预期
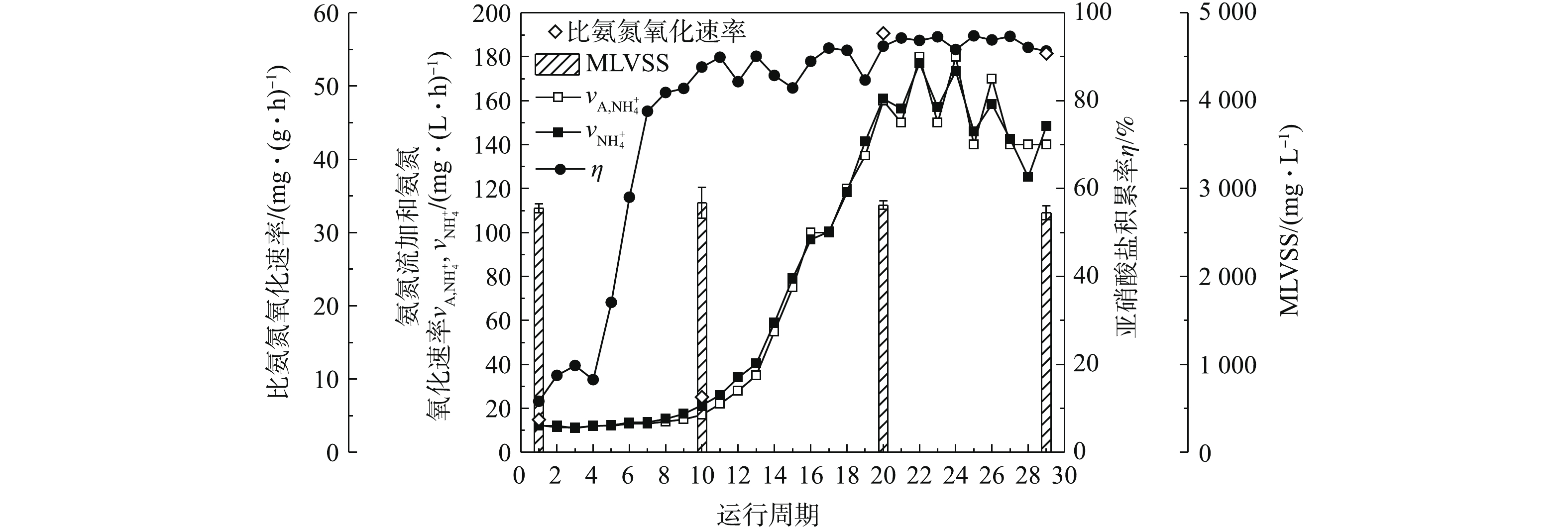
2.2. AOB富集过程中的比氨氮氧化速率
根据图2(a)各周期初始2.3. DO浓度对氨氮氧化速率的影响
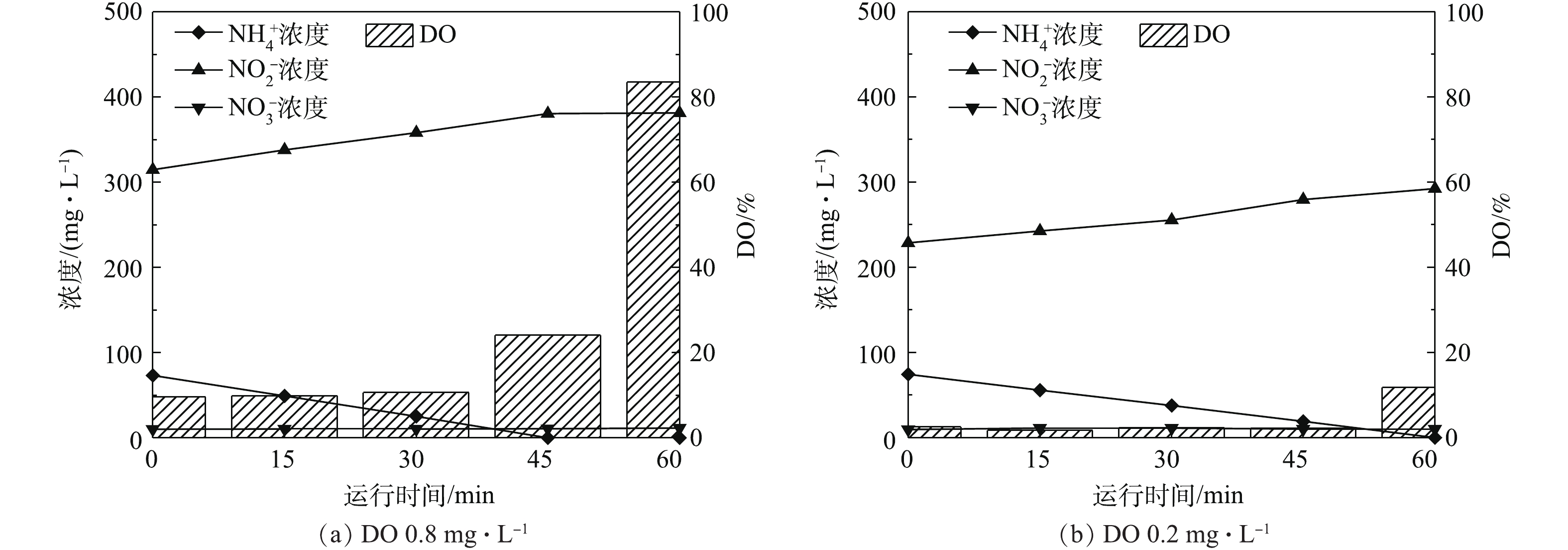
已有研究[7-9]证实,采用低DO可以实现亚硝酸盐积累,但是氨氮氧化速率随着DO降低也会随之下降。由图2(a)可知,因室内曝气机所能提供的DO有限(若需提高DO,可采用室外大型曝气机[18]),在培养后期,体系内的DO已达到了极限(波动范围为±2%),仅为0.2~0.4 mg·L?1,但仍可以实现较高的氨氮氧化速率。在AOB富集过程中,本研究采用间歇运行方式对DO的影响进行分析,结果如图4所示。由图4可知,DO浓度由0.8 mg·L?1左右降低至0.2 mg·L?1左右,对于相同的初始氨氮浓度,在低DO的条件下,氨氮氧化完全的历时较长,因此,氨氮氧化速率的确有所降低。然而在极低的DO条件下,因AOB的大量富集,仍可以实现高氨氮氧化速率。ANTILEO等[9]的实验结果表明,当DO浓度分别为1.0、0.8和0.6 mg·L?1时,氨氮氧化速率呈降低的趋势,分别为0.10、0.04、0.03 kg (m3·d)?1。WANG等[27]的研究结果同样表明,在DO分别为0.5 mg·L?1和1.5 mg·L?1时,最大氨氮氧化速率增长约为50%。
2.4. 定性分析微生物的种群分布
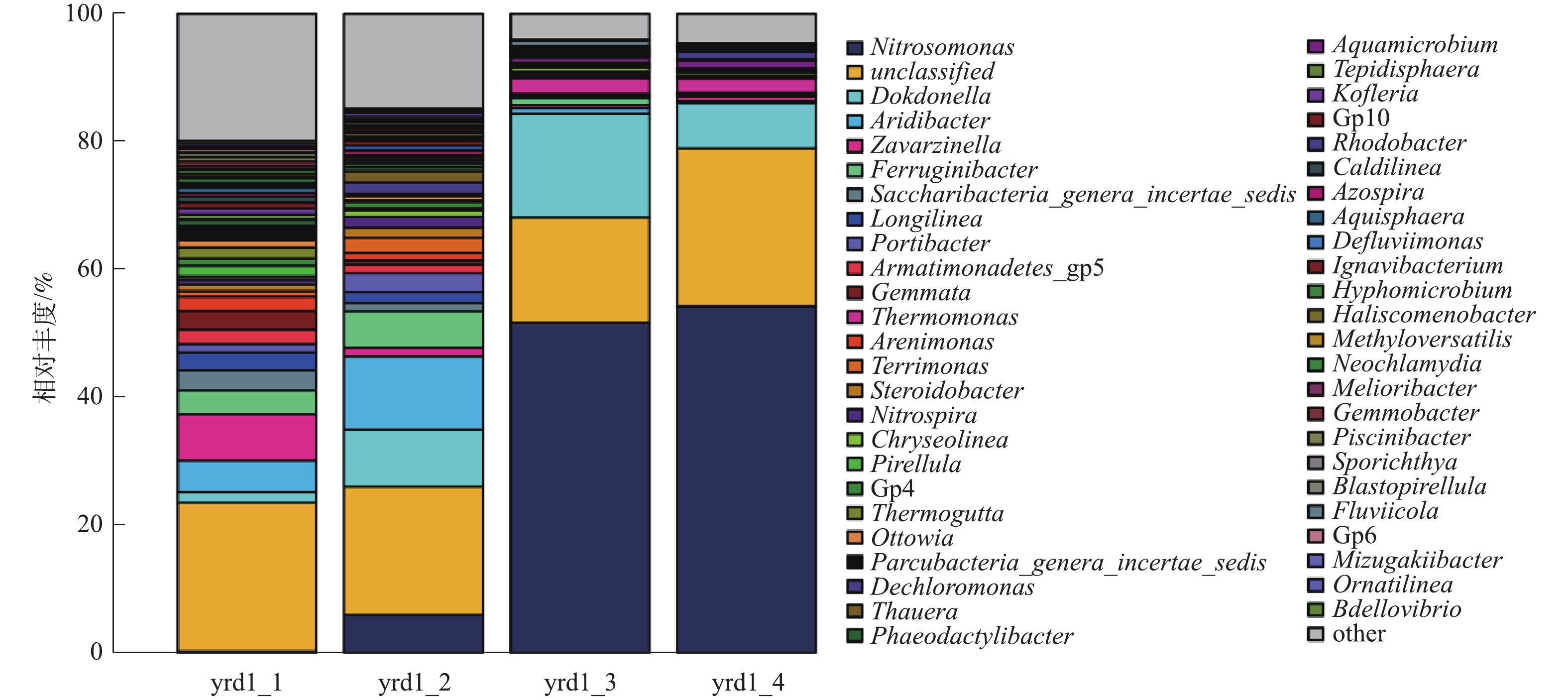
《伯杰氏细菌鉴定手册》中将AOB分为5个属,分别为亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)、亚硝化球菌属(Nitrosococcus)、亚硝化螺菌属(Nitrosospira)、亚硝化弧菌属(Nitrosovibrio)和亚硝化叶菌属(Nitrosolobus);将NOB分为4个属,分别为硝化杆菌属(Nitrobacter)、硝化球菌属(Nitrococcus)、硝化刺菌属(Nitrospina)和硝化螺菌属(Nitrospira)。有研究[28-29]表明,在污水处理厂经常出现的AOB主要是Nitrosomonas和Nitrosospira;经常出现的NOB主要是Nitrobacter和Nitrospira[30]。图5为属水平高通量测序结果,yrd1_1、yrd1_2、yrd1_3和yrd1_4分别为接种、富集培养第9、15和18天的污泥样品。接种污泥中微生物多样性较高,因AOB大量增殖,故随着AOB逐渐富集,其他细菌被淘洗出反应器,污泥中微生物多样性则随之降低。接种污泥Nitrosomonas的比例仅为0.23%,随着AOB富集的进行,在第9、15和18天,其比例逐渐上升至5.9%、51.61%和54.18%。从第9~15天增幅较大,结合图3的结果,原因为此期间AOB生长进入对数期。与Nitrosomonas属AOB相比,Nitrospira属的NOB一直处于非常低的水平,最高值仅为1.7%,最终比例仅为0.12%,并未完全淘洗出反应器。上述结果表明,AOB在富集培养期间大量生长,与反应器接近180 mg·(L·h)?1的高氨氮氧化速率相符。此外,有研究[31]已证实,采用含有机物的实际污水也可以成功培养Nitrosomonas属的AOB,因此,有机物的存在不是AOB富集的限制因素。此外,AOB形态多样,包括球状、杆状、螺旋状等,不同属的形态有所差异,已证实Nitrosomonas属的AOB为杆状或椭球状,Nitrosospira属的AOB为螺旋状[32]。本研究通过扫描电镜观察污泥样品中细菌的形态结构,如图6所示,富集培养后存在大量具有椭球状特征的细菌。
2.5. 定量分析AOB富集效果
采用荧光定量PCR技术对AOB富集各阶段的污泥样品进行检测分析,以通过数量变化考察AOB的生长状况,结果如表1所示。amoA基因是AOB的特征序列,随着AOB富集的进行,可以看出活性污泥中amoA基因平均拷贝数显著增加。DNA提取时采用200 mg污泥样品,按照60 μL进行洗脱得到DNA溶液,荧光定量PCR检测上机时DNA稀释50倍,反应体系加 1 μL DNA模板。因此,换算得出amoA基因平均拷贝数在接种、富集培养第9、15和18天分别为2.67×105、4.24×108、9.67×109、7.30×109 copies·g?1。结合比氨氮氧化速率(图3)和AOB群落占活性污泥中的比例(图5)的结果,比氨氮氧化速率、AOB在活性污泥中的比例和功能基因数量等几个方面均可证实,AOB群落得到了高度增殖,逐渐成为活性污泥中的优势菌属。
2)低DO导致氨氮氧化速率降低,体系内高纯度的AOB可以确保在极低DO条件下,氨氮氧化速率维持在较高水平。
3)综合比氨氮氧化速率指标、高通量测序定性分析活性污泥中AOB的比例以及荧光定量PCR检测其功能基因 amoA 的平均拷贝数,可以看出AOB的数量在富集期间大幅度增加。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 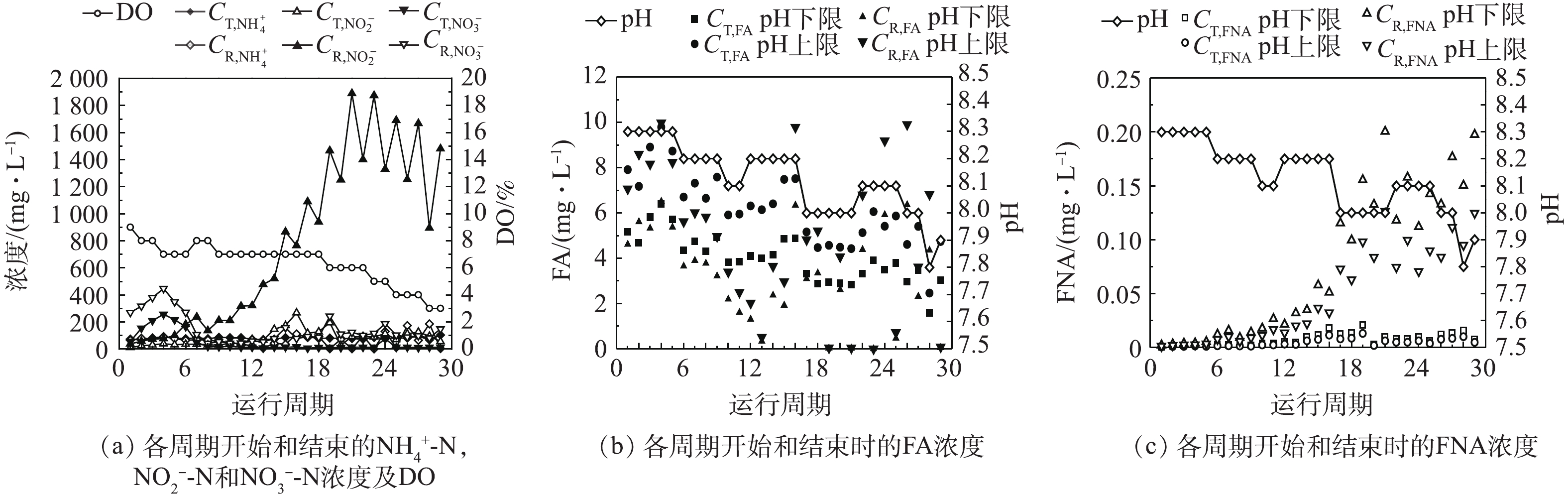
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图