 ), 涂冬波(
), 涂冬波( )
) 江西师范大学心理学院, 南昌 330022
收稿日期:2020-11-30出版日期:2021-11-25发布日期:2021-09-23通讯作者:蔡艳,涂冬波E-mail:cy1979123@aliyun.com;tudongbo@aliyun.com基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(31760288);国家自然科学基金项目(31960186);国家自然科学基金项目(31660278)A high-efficiency and new online calibration method in CD-CAT based on information gain of entropy and EM algorithm
TAN Qingrong, WANG Daxun, LUO Fen, CAI Yan( ), TU Dongbo(
), TU Dongbo( )
) School of Psychology, Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang 330022, China
Received:2020-11-30Online:2021-11-25Published:2021-09-23Contact:CAI Yan,TU Dongbo E-mail:cy1979123@aliyun.com;tudongbo@aliyun.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 项目增补(Item Replenishing)对认知诊断计算机自适应测验(CD-CAT)题库的维护有着至关重要的作用, 而在线标定是一种重要的项目增补方式。基于数据挖掘中特征选择(Feature Selection)的思路, 提出一种高效的基于熵的信息增益的在线标定方法(记为IGEOCM), 该方法利用被试在新旧题上的作答联合估计新题的Q矩阵和项目参数。研究采用Monte Carlo模拟实验验证所开发新方法的效果, 并同时与已有的在线标定方法SIE、SIE-R-BIC和RMSEA-N进行比较。结果表明:新开发的IGEOCM在各实验条件下均具有较好的项目标定精度和项目估计效率, 且整体上优于已有的SIE等方法; 同时, IGEOCM标定新题所需的时间低于SIE等方法。总之, 研究为CD-CAT题库中项目的增补提供了一种更为高效、准确的方法。
图/表 5
表1不同q向量下E(Rj|qj)和g(Rj, qj)的计算
| q向量 | 掌握组 | 非掌握组 | E(Rj|qj) | g(Rj, qj) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qcorrect j = [100] | 属性掌握模式 | [100] [110] [101] [111] | [000] [010] [001] [011] | 0 | 0.690 |
| 被试数目 | nj/2 | nj/2 | |||
| 正确作答比 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 错误作答比 | 0 | 1 | |||
| qincorrect j = [011] | 属性掌握模式 | [011] [111] | [000] [100] [010] [001] [110] [101] | 0.690 | 0.003 |
| 被试数目 | nj/4 | 3nj/4 | |||
| 正确作答比 | 0.500 | 0.500 | |||
| 错误作答比 | 0.500 | 0.500 | |||
表1不同q向量下E(Rj|qj)和g(Rj, qj)的计算
| q向量 | 掌握组 | 非掌握组 | E(Rj|qj) | g(Rj, qj) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qcorrect j = [100] | 属性掌握模式 | [100] [110] [101] [111] | [000] [010] [001] [011] | 0 | 0.690 |
| 被试数目 | nj/2 | nj/2 | |||
| 正确作答比 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 错误作答比 | 0 | 1 | |||
| qincorrect j = [011] | 属性掌握模式 | [011] [111] | [000] [100] [010] [001] [110] [101] | 0.690 | 0.003 |
| 被试数目 | nj/4 | 3nj/4 | |||
| 正确作答比 | 0.500 | 0.500 | |||
| 错误作答比 | 0.500 | 0.500 | |||
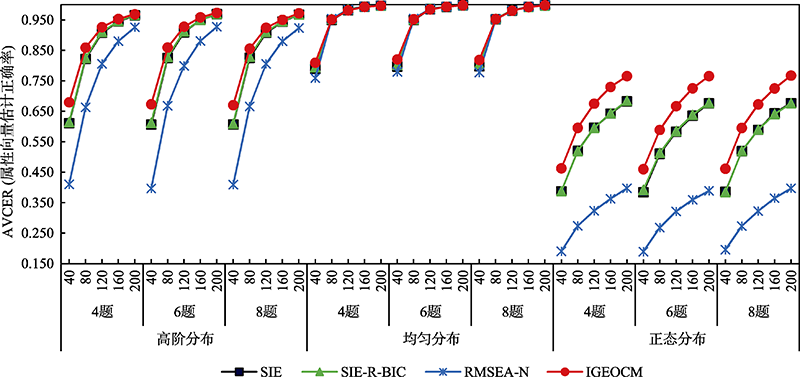
图1各在线标定方法在不同条件下的AVCER (属性向量估计正确率)结果
 图1各在线标定方法在不同条件下的AVCER (属性向量估计正确率)结果
图1各在线标定方法在不同条件下的AVCER (属性向量估计正确率)结果表2各在线标定方法在不同条件下的RMSE (均方根误差)结果
| 分布 | 项目 | 方法 | 40 | 80 | 120 | 160 | 200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高阶 | 4 | SIE | 0.090 | 0.060 | 0.048 | 0.041 | 0.036 |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.088 | 0.065 | 0.057 | 0.052 | 0.049 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.132 | 0.099 | 0.086 | 0.079 | 0.073 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.090 | 0.060 | 0.048 | 0.041 | 0.036 | ||
| 6 | SIE | 0.092 | 0.061 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.037 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.089 | 0.066 | 0.057 | 0.053 | 0.050 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.132 | 0.099 | 0.085 | 0.077 | 0.074 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.092 | 0.061 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.037 | ||
| 8 | SIE | 0.095 | 0.060 | 0.048 | 0.042 | 0.037 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.090 | 0.066 | 0.057 | 0.053 | 0.050 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.132 | 0.098 | 0.085 | 0.078 | 0.074 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.095 | 0.061 | 0.048 | 0.042 | 0.037 | ||
| 均匀 | 4 | SIE | 0.123 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.046 | 0.041 |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.097 | 0.068 | 0.057 | 0.051 | 0.047 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.118 | 0.090 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.076 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.121 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.046 | 0.041 | ||
| 6 | SIE | 0.121 | 0.069 | 0.053 | 0.045 | 0.039 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.097 | 0.068 | 0.056 | 0.050 | 0.046 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.116 | 0.090 | 0.081 | 0.078 | 0.076 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.119 | 0.069 | 0.053 | 0.045 | 0.039 | ||
| 8 | SIE | 0.122 | 0.071 | 0.054 | 0.046 | 0.040 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.097 | 0.068 | 0.057 | 0.051 | 0.047 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.116 | 0.090 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.076 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.121 | 0.071 | 0.054 | 0.046 | 0.040 | ||
| 正态 | 4 | SIE | 0.126 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.044 |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.099 | 0.073 | 0.064 | 0.058 | 0.055 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.170 | 0.149 | 0.138 | 0.130 | 0.123 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.126 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.044 | ||
| 6 | SIE | 0.124 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.050 | 0.044 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.098 | 0.073 | 0.064 | 0.058 | 0.055 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.171 | 0.149 | 0.138 | 0.129 | 0.125 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.123 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.050 | 0.044 | ||
| 8 | SIE | 0.129 | 0.079 | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.044 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.100 | 0.074 | 0.063 | 0.058 | 0.055 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.170 | 0.149 | 0.136 | 0.128 | 0.121 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.130 | 0.079 | 0.060 | 0.050 | 0.044 |
表2各在线标定方法在不同条件下的RMSE (均方根误差)结果
| 分布 | 项目 | 方法 | 40 | 80 | 120 | 160 | 200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高阶 | 4 | SIE | 0.090 | 0.060 | 0.048 | 0.041 | 0.036 |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.088 | 0.065 | 0.057 | 0.052 | 0.049 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.132 | 0.099 | 0.086 | 0.079 | 0.073 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.090 | 0.060 | 0.048 | 0.041 | 0.036 | ||
| 6 | SIE | 0.092 | 0.061 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.037 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.089 | 0.066 | 0.057 | 0.053 | 0.050 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.132 | 0.099 | 0.085 | 0.077 | 0.074 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.092 | 0.061 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.037 | ||
| 8 | SIE | 0.095 | 0.060 | 0.048 | 0.042 | 0.037 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.090 | 0.066 | 0.057 | 0.053 | 0.050 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.132 | 0.098 | 0.085 | 0.078 | 0.074 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.095 | 0.061 | 0.048 | 0.042 | 0.037 | ||
| 均匀 | 4 | SIE | 0.123 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.046 | 0.041 |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.097 | 0.068 | 0.057 | 0.051 | 0.047 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.118 | 0.090 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.076 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.121 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.046 | 0.041 | ||
| 6 | SIE | 0.121 | 0.069 | 0.053 | 0.045 | 0.039 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.097 | 0.068 | 0.056 | 0.050 | 0.046 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.116 | 0.090 | 0.081 | 0.078 | 0.076 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.119 | 0.069 | 0.053 | 0.045 | 0.039 | ||
| 8 | SIE | 0.122 | 0.071 | 0.054 | 0.046 | 0.040 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.097 | 0.068 | 0.057 | 0.051 | 0.047 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.116 | 0.090 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.076 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.121 | 0.071 | 0.054 | 0.046 | 0.040 | ||
| 正态 | 4 | SIE | 0.126 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.044 |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.099 | 0.073 | 0.064 | 0.058 | 0.055 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.170 | 0.149 | 0.138 | 0.130 | 0.123 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.126 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.044 | ||
| 6 | SIE | 0.124 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.050 | 0.044 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.098 | 0.073 | 0.064 | 0.058 | 0.055 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.171 | 0.149 | 0.138 | 0.129 | 0.125 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.123 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.050 | 0.044 | ||
| 8 | SIE | 0.129 | 0.079 | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.044 | |
| SIE-R-BIC | 0.100 | 0.074 | 0.063 | 0.058 | 0.055 | ||
| RMSEA-N | 0.170 | 0.149 | 0.136 | 0.128 | 0.121 | ||
| IGEOCM | 0.130 | 0.079 | 0.060 | 0.050 | 0.044 |
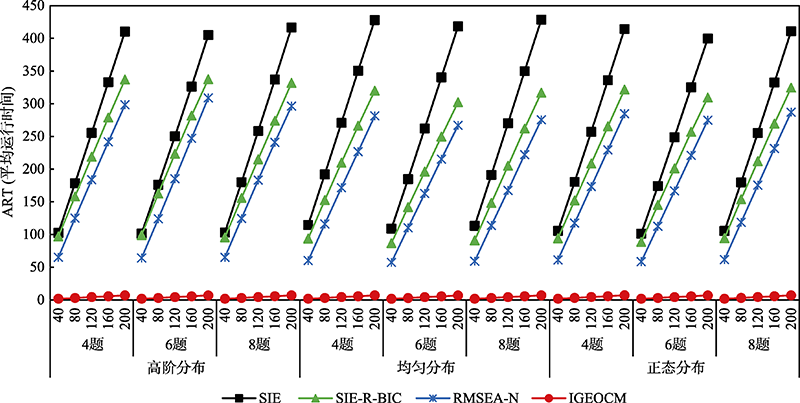
图2各在线标定方法在不同条件下的ART (平均运行时间)结果(单位:秒)
 图2各在线标定方法在不同条件下的ART (平均运行时间)结果(单位:秒)
图2各在线标定方法在不同条件下的ART (平均运行时间)结果(单位:秒)表3SIE方法和IGEOCM在不同条件下的项目标定精度与标定效率结果
| 分布 | 方法 | AVCER | RMSE | ART | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWKL | MPWKL | SHE | GDI | PWKL | MPWKL | SHE | GDI | PWKL | MPWKL | SHE | GDI | ||
| 高阶 | SIE | 0.607 | 0.617 | 0.615 | 0.614 | 0.082 | 0.083 | 0.083 | 0.083 | 78.438 | 78.083 | 78.116 | 77.818 |
| IGEOCM | 0.678 | 0.677 | 0.676 | 0.679 | 0.082 | 0.084 | 0.082 | 0.083 | 1.808 | 1.811 | 1.800 | 1.797 | |
| 均匀 | SIE | 0.809 | 0.807 | 0.814 | 0.808 | 0.089 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.089 | 90.388 | 89.742 | 90.421 | 89.702 |
| IGEOCM | 0.828 | 0.827 | 0.831 | 0.825 | 0.089 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.089 | 1.861 | 1.846 | 1.857 | 1.845 | |
| 正态 | SIE | 0.385 | 0.383 | 0.383 | 0.384 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.100 | 0.099 | 81.850 | 81.420 | 81.752 | 81.587 |
| IGEOCM | 0.454 | 0.462 | 0.457 | 0.467 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 1.884 | 1.865 | 1.873 | 1.880 | |
表3SIE方法和IGEOCM在不同条件下的项目标定精度与标定效率结果
| 分布 | 方法 | AVCER | RMSE | ART | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWKL | MPWKL | SHE | GDI | PWKL | MPWKL | SHE | GDI | PWKL | MPWKL | SHE | GDI | ||
| 高阶 | SIE | 0.607 | 0.617 | 0.615 | 0.614 | 0.082 | 0.083 | 0.083 | 0.083 | 78.438 | 78.083 | 78.116 | 77.818 |
| IGEOCM | 0.678 | 0.677 | 0.676 | 0.679 | 0.082 | 0.084 | 0.082 | 0.083 | 1.808 | 1.811 | 1.800 | 1.797 | |
| 均匀 | SIE | 0.809 | 0.807 | 0.814 | 0.808 | 0.089 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.089 | 90.388 | 89.742 | 90.421 | 89.702 |
| IGEOCM | 0.828 | 0.827 | 0.831 | 0.825 | 0.089 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.089 | 1.861 | 1.846 | 1.857 | 1.845 | |
| 正态 | SIE | 0.385 | 0.383 | 0.383 | 0.384 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.100 | 0.099 | 81.850 | 81.420 | 81.752 | 81.587 |
| IGEOCM | 0.454 | 0.462 | 0.457 | 0.467 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 1.884 | 1.865 | 1.873 | 1.880 | |
参考文献 35
| [1] | Ban J. C., Hanson B. A., Wang T., Yi Q., & Harris D. J. (2001). A comparative study of on-line pretest item— Calibration/scaling methods in computerized adaptive testing. Journal of Educational Measurement, 38(3), 191-212. |
| [2] | Chandrashekar G., & Sahin F. (2014). A survey on feature selection methods. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 40(1), 16-28. |
| [3] | Chen J. (2017). A residual-based approach to validate Q-matrix specifications. Applied Psychological Measurement, 41(4), 277-293. |
| [4] | Chen, P. (2016). Two new online calibration methods for computerized adaptive testing. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(9), 1184-1198. |
| [ 陈平. (2016). 两种新的计算机化自适应测验在线标定方法. 心理学报, 48(9), 1184-1198.] | |
| [5] | Chen P. (2017). A comparative study of online item calibration methods in multidimensional computerized adaptive testing. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 42(5), 559-590. |
| [6] | Chen P., & Wang C. (2015). A new online calibration method for multidimensional computerized adaptive testing. Psychometrika, 81(3), 674-701. |
| [7] | Chen P., Wang C., Xin T., & Chang H. H. (2017). Developing new online calibration methods for multidimensional computerized adaptive testing. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 70(1), 81-117. |
| [8] | Chen P., & Xin T. (2011 a). Developing on-line calibration methods for cognitive diagnostic computerized adaptive testing. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 43(6), 710-724. |
| [ 陈平, 辛涛. (2011 a). 认知诊断计算机化自适应测验中在线标定方法的开发. 心理学报, 43(6), 710-724.] | |
| [9] | Chen P., & Xin T. (2011 b). Item replenishing in cognitive diagnostic computerized adaptive testing. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 43(7), 836-850. |
| [ 陈平, 辛涛. (2011 b). 认知诊断计算机化自适应测验中的项目增补. 心理学报, 43(7), 836-850.] | |
| [10] | Chen P., Xin T., Wang C., & Chang H. H. (2012). Online calibration methods for the DINA model with independent attributes in CD-CAT. Psychometrika, 77(2), 201-222. |
| [11] | Chen Y., Liu J., & Ying Z. (2015). Online item calibration for Q-matrix in CD-CAT. Applied Psychological Measurement, 39(1), 5-15. |
| [12] | Cheng Y. (2009). When cognitive diagnosis meets computerized adaptive testing: CD-CAT. Psychometrika, 74(4), 619-632. |
| [13] | Chiu C. Y., Sun Y., & Bian Y. (2018). Cognitive diagnosis for small educational programs: The general nonparametric classification method. Psychometrika, 83(2), 355-375. |
| [14] | de la Torre, J. (2011). The generalized DINA model framework. Psychometrika, 76(2), 179-199. |
| [15] | de la Torre, J., &Chiu C. Y. (2016). A General method of empirical Q-matrix validation. Psychometrika, 81(2), 253-273. |
| [16] | Fleuret F. (2004). Fast binary feature selection with conditional mutual information. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 5(11), 1531-1555. |
| [17] | Guyon I., & Elisseeff A. (2003). An introduction to variable and feature selection. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3(3), 1157-1182. |
| [18] | Hartz S. M. (2002). A Bayesian framework for the unified model for assessing cognitive abilities: Blending theory with practicality (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. |
| [19] | He Y., Chen P., & Li Y. (2020). New efficient and practicable adaptive designs for calibrating items online. Applied Psychological Measurement, 44 (1), 3-16. |
| [20] | Hoque N., Bhattacharyya D. K., & Kalita J. K. (2014). MIFS-ND: A mutual information-based feature selection method. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(14), 6371-6385. |
| [21] | Junker B. W., & Sijtsma K. (2001). Cognitive assessment models with few assumptions, and connections with nonparametric item response theory. Applied Psychological Measurement, 25(3), 258-272. |
| [22] | Kaplan M., de la Torre J., & Barrada J. R. (2015). New item selection methods for cognitive diagnosis computerized adaptive testing. Applied Psychological Measurement, 39(3), 167-188. |
| [23] | Leighton J. P., Gierl M. J., & Hunka S. M. (2004). The attribute hierarchy method for cognitive assessment: A variation on Tatsuoka's rule-space approach. Journal of Educational Measurement, 41(3), 205-237. |
| [24] | Li, H. ( 2012). Statistical learning method. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press. |
| [ 李航. ( 2012). 统计学习方法. 北京: 清华大学出版社.] | |
| [25] | Liu H. Y., You X. F., Wang W. Y., Ding S. L., & Chang H. H. (2013). The development of computerized adaptive testing with cognitive diagnosis for an English achievement test in China. Journal of Classification, 30(2), 152-172. |
| [26] | Ma, W., & de la Torre J. (2016). A sequential cognitive diagnosis model for polytomous responses. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 69(3), 253-275. |
| [27] | Pereira R. B., Plastino A., Zadrozny B., & Merschmann L. H. (2015). Information gain feature selection for multi-label classification. Journal of Information and Data Management, 6(1), 48-58. |
| [28] | Rupp A. A., & Templin J.L. (2008). The effects of Q-matrix misspecification on parameter estimates and classification accuracy in the DINA model. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 68(1), 78-96. |
| [29] | Stocking M. L. (1988). Scale drift in on-line calibration. ETS Research Report, 1988(1), 1-122. |
| [30] | Tan, Q. (2019). The development of generalized online calibration methods in CD-CAT (Unpublished master’s thesis). Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang, China. |
| [ 谭青蓉. (2019). CD-CAT广义在线标定方法开发研究 (硕士学位论文). 江西师范大学, 南昌.] | |
| [31] | Vinh L. T., Lee S., Park Y. T., & d’Auriol B. J. (2012). A novel feature selection method based on normalized mutual information. Applied Intelligence, 37(1), 100-120. |
| [32] | Wainer H., & Mislevy R. J. (1990). Item response theory, item calibration, and proficiency estimation. In H. Wainer (Ed), Computerized adaptive testing: A primer (Chap. 4, pp. 65-102). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [33] | Wang C. (2013). Mutual information item selection method in cognitive diagnostic computerized adaptive testing with short test length. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 73(6), 1017-1035. |
| [34] | Weiss D. J. (1982). Improving measurement quality and efficiency with adaptive testing. Applied Psychological Measurement, 6(4), 473-492. |
| [35] | Yu X., & Cheng Y. (2020). Data-driven Q-matrix validation using a residual-based statistic in cognitive diagnostic assessment. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 73( Suppl 1), 145-179. |
相关文章 3
| [1] | 陈平. 两种新的计算机化自适应测验在线标定方法[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(9): 1184-1198. |
| [2] | 陈平,辛涛. 认知诊断计算机化自适应测验中的项目增补[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(07): 836-850. |
| [3] | 陈平,辛涛. 认知诊断计算机化自适应测验中在线标定方法的开发[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(06): 710-724. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5094
