 )
) 1 湖南师范大学教育科学学院心理系
2 认知与人类行为湖南省重点实验室, 长沙 410081
3 湖南农业大学教育学院应用心理系, 长沙 410081
收稿日期:2019-08-30出版日期:2020-06-25发布日期:2020-04-22通讯作者:钟毅平E-mail:ypzhong@hunnu.edu.cn基金资助:* 中国自然科学基金面上项目(31671134);国家社会科学基金重大项目(17ZDA326);湖南省社科青年项目(19YBQ080);湖南省社科青年项目(18YBQ069);湖南省研究生科研创新项目(CX2018B236)Social value orientation modulates the processing of social rewards for self: Evidence from ERPs study
LI Jin1,2, SUN Yu1,2, YANG Zilu3, ZHONG Yiping1,2( )
) 1 Department of Psychology, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China
2 Cognition and Human Behavior Key Laboratory of Hunan Province, Changsha 410081, China
3 Department of Applied Psychology, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha 410081, China
Received:2019-08-30Online:2020-06-25Published:2020-04-22Contact:ZHONG Yiping E-mail:ypzhong@hunnu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 社会价值取向(Social Value Orientation, SVO)是相互依存情境下人们对自己和他人分配结果的一种稳定的社会偏好, 按SVO不同可以将个体分为“亲社会取向”和“亲自我取向”个体。已有研究表明SVO影响个体对涉及自我金钱奖赏的结果评价加工, 而它如何影响自我社会奖赏加工过程尚不明确。本研究让亲社会取向和亲自我取向被试完成涉及自我社会奖赏(包含社会接纳和自我成就感)的猜牌建议给予任务, 同时记录其加工他人对建议的反馈(接受vs.拒绝)和他人最终结果(收益vs.损失)时诱发的脑电成分。结果发现, 在建议反馈加工阶段, 相比亲自我取向个体, 亲社会取向个体在反馈相关负波(FRN)波幅(峰-峰值)和P3平均波幅上, 建议被对方接受和被对方拒绝所诱发的波幅差异均显著; 在他人最终结果加工阶段, 建议被对方拒绝后, 对于亲社会取向个体, 对方损失诱发的反馈相关负FRN波幅比对方收益诱发的波幅更负, 而对方损失诱发的P3波幅小于对方收益诱发的波幅; 对于亲自我取向个体, 对方损失与收益诱发的FRN波幅无差异, 对方损失诱发的P3波幅显著大于对方收益诱发的波幅。这些结果表明社会价值取向调节个体对自我社会奖赏的加工。
图/表 7
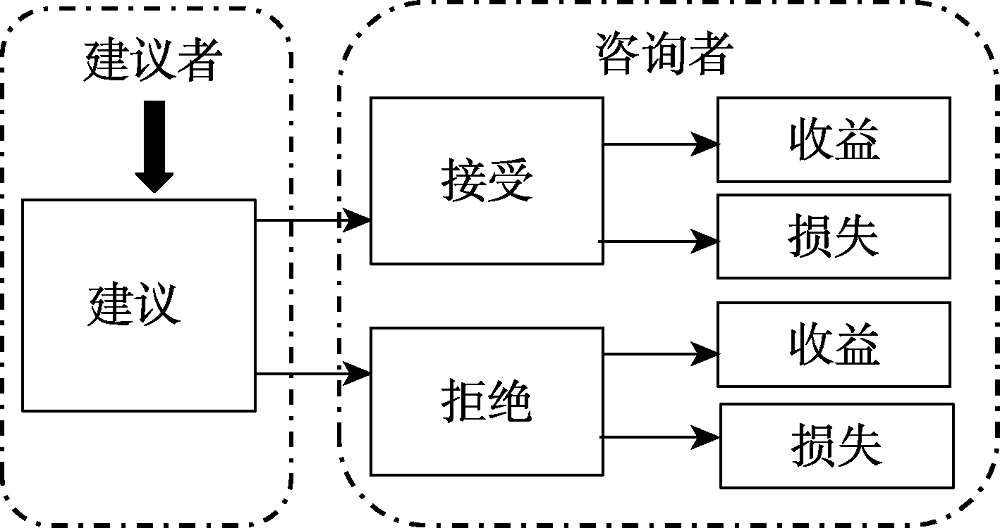
图1建议给予后建议者可能得到的不同的结果反馈
 图1建议给予后建议者可能得到的不同的结果反馈
图1建议给予后建议者可能得到的不同的结果反馈表1社会价值取向测量题目示例
| 选项 | 自己获益 | 他人获益 |
|---|---|---|
| A | 500 | 100 |
| B | 500 | 500 |
| C | 550 | 300 |
表1社会价值取向测量题目示例
| 选项 | 自己获益 | 他人获益 |
|---|---|---|
| A | 500 | 100 |
| B | 500 | 500 |
| C | 550 | 300 |
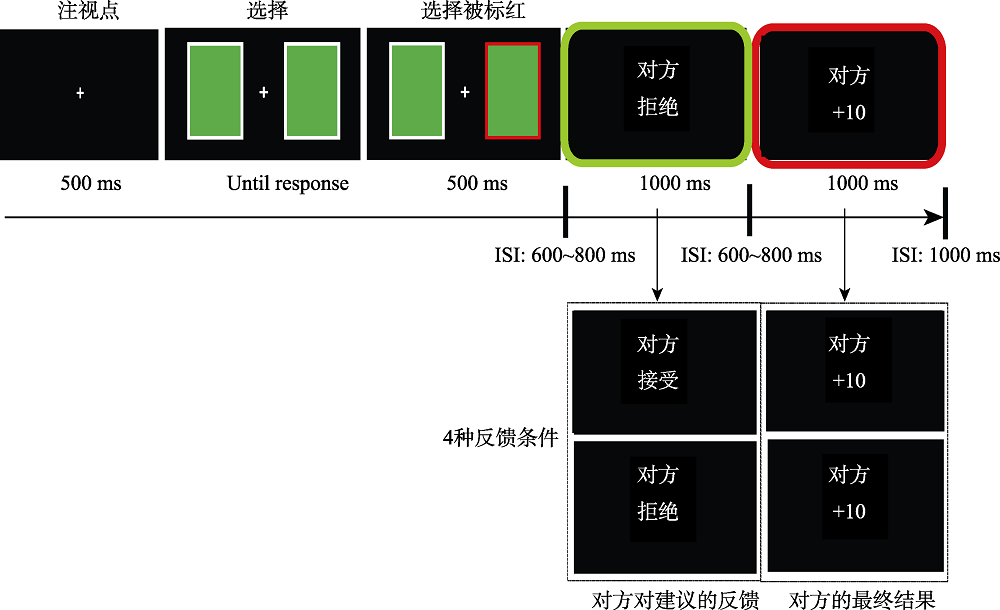
图2单个实验试次流程图示 注:绿框表示记录建议反馈加工阶段脑电成分的界面; 红框表示记录对方最终结果加工阶段脑电成分的界面
 图2单个实验试次流程图示 注:绿框表示记录建议反馈加工阶段脑电成分的界面; 红框表示记录对方最终结果加工阶段脑电成分的界面
图2单个实验试次流程图示 注:绿框表示记录建议反馈加工阶段脑电成分的界面; 红框表示记录对方最终结果加工阶段脑电成分的界面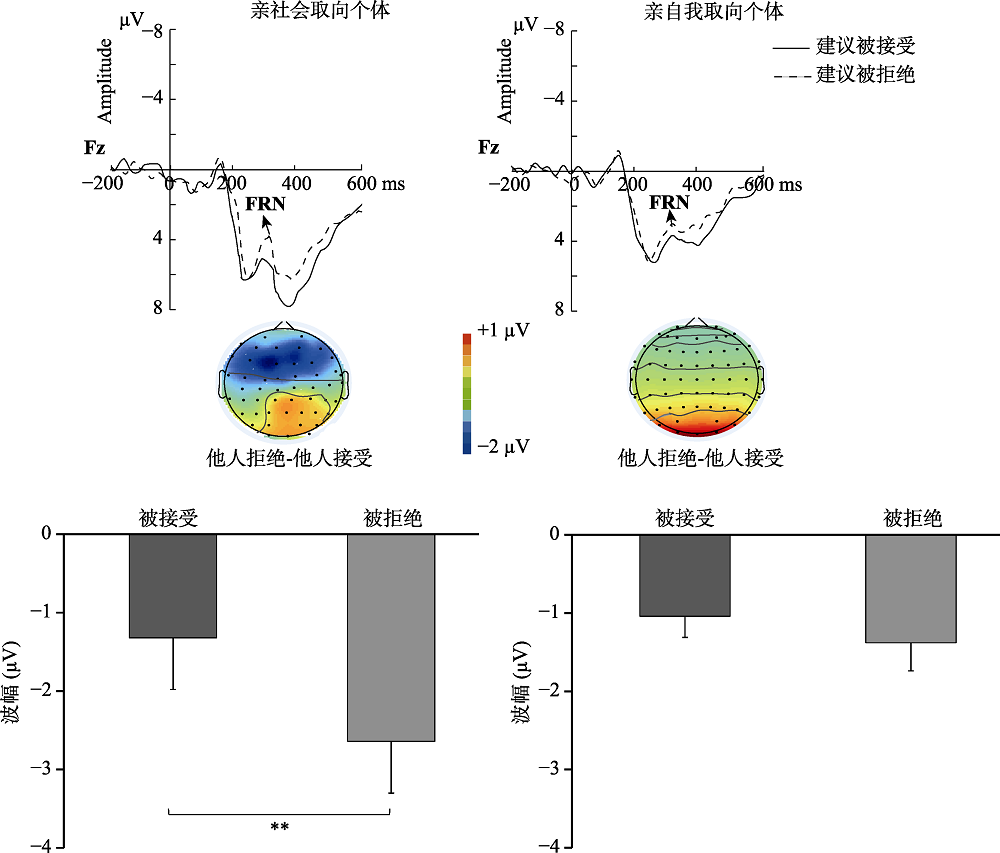
图3亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在Fz电极点上对方接受建议/拒绝建议诱发的FRN (时间窗:280~350 ms)3的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的FRN峰-峰平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05) 3根据Osinsky等(2014)研究, 采用时间窗280~350 ms的FRN脑地形图。此外, 根据以往研究, 对于两水平实验条件诱发的FRN波幅, 我们报告脑地形图为在该时间窗内的差异波地形图(王益文 等, 2015; Yang et al., 2018; Hu et al., 2017)。
 图3亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在Fz电极点上对方接受建议/拒绝建议诱发的FRN (时间窗:280~350 ms)3的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的FRN峰-峰平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05) 3根据Osinsky等(2014)研究, 采用时间窗280~350 ms的FRN脑地形图。此外, 根据以往研究, 对于两水平实验条件诱发的FRN波幅, 我们报告脑地形图为在该时间窗内的差异波地形图(王益文 等, 2015; Yang et al., 2018; Hu et al., 2017)。
图3亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在Fz电极点上对方接受建议/拒绝建议诱发的FRN (时间窗:280~350 ms)3的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的FRN峰-峰平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05) 3根据Osinsky等(2014)研究, 采用时间窗280~350 ms的FRN脑地形图。此外, 根据以往研究, 对于两水平实验条件诱发的FRN波幅, 我们报告脑地形图为在该时间窗内的差异波地形图(王益文 等, 2015; Yang et al., 2018; Hu et al., 2017)。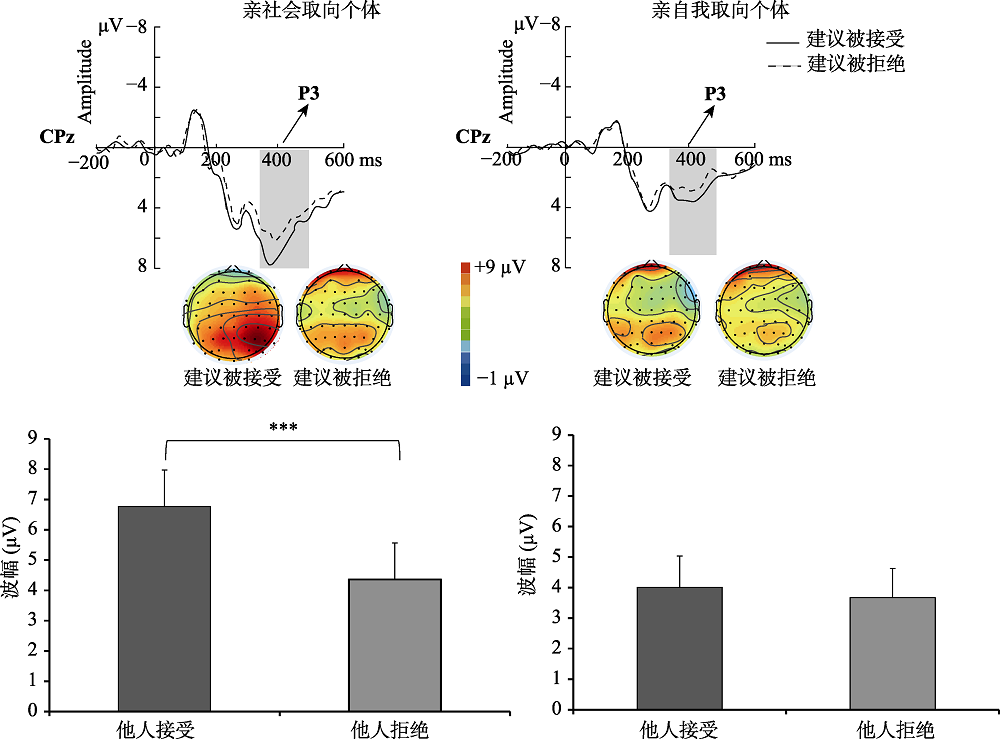
图4亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在CPz电极点上对方不同反馈的P3 (时间窗:350~500 ms)的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的P3波幅平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05)
 图4亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在CPz电极点上对方不同反馈的P3 (时间窗:350~500 ms)的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的P3波幅平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05)
图4亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在CPz电极点上对方不同反馈的P3 (时间窗:350~500 ms)的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的P3波幅平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05)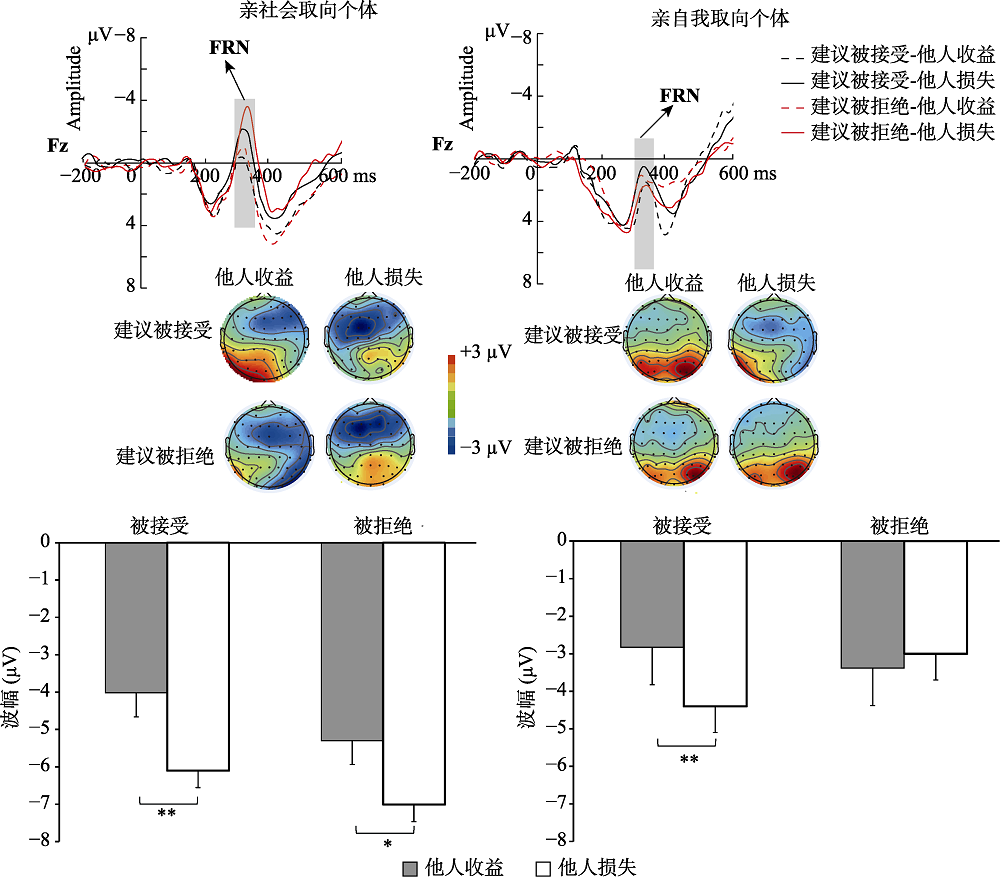
图5亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在Fz电极点上不同结果反馈的FRN (时间窗:280~350 ms)4的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的FRN峰-峰平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05) 4同图3, 根据Osinsky等(2014)研究, 采用时间窗280~350 ms的FRN脑地形图。
 图5亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在Fz电极点上不同结果反馈的FRN (时间窗:280~350 ms)4的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的FRN峰-峰平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05) 4同图3, 根据Osinsky等(2014)研究, 采用时间窗280~350 ms的FRN脑地形图。
图5亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在Fz电极点上不同结果反馈的FRN (时间窗:280~350 ms)4的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的FRN峰-峰平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05) 4同图3, 根据Osinsky等(2014)研究, 采用时间窗280~350 ms的FRN脑地形图。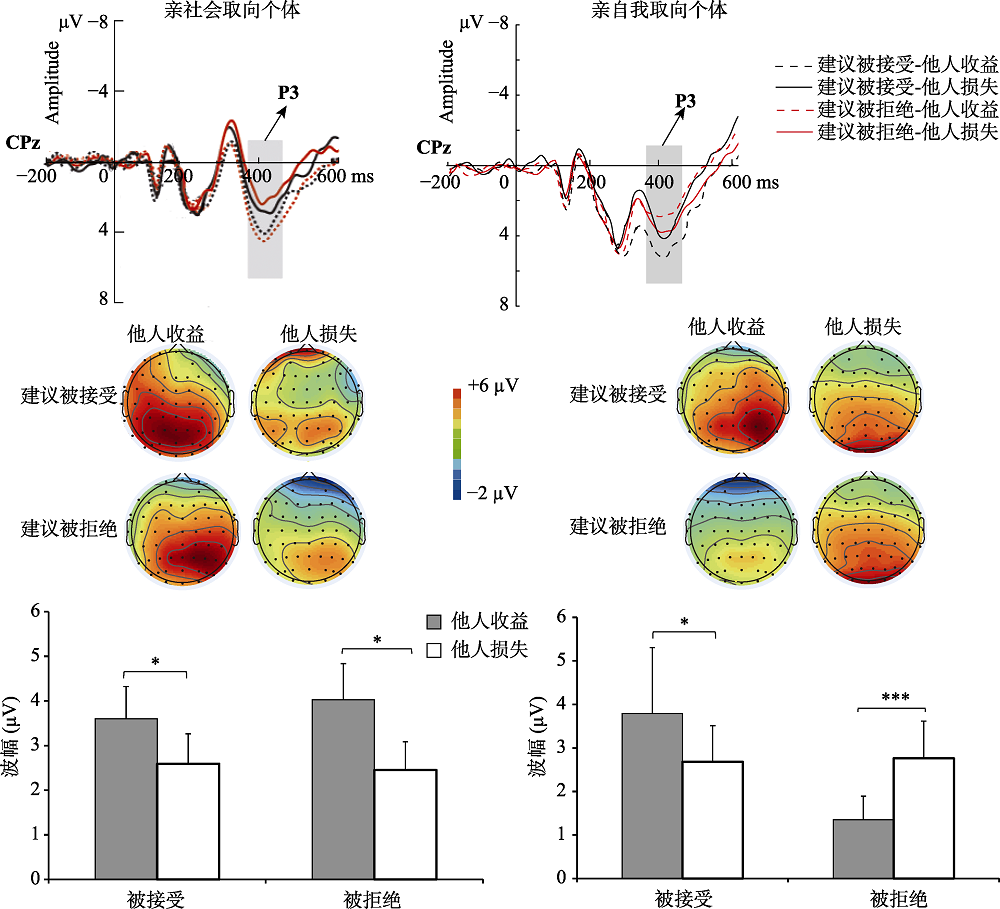
图6亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在CPz电极点上不同结果反馈的P3 (时间窗:350~480 ms)的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的P3波幅平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05)
 图6亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在CPz电极点上不同结果反馈的P3 (时间窗:350~480 ms)的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的P3波幅平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05)
图6亲社会取向和亲自我取向两组被试在CPz电极点上不同结果反馈的P3 (时间窗:350~480 ms)的ERP总平均图、脑地形图和所有分析点的P3波幅平均值柱状图, 左边是亲社会取向被试, 右边是亲自我取向被试。(*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05)参考文献 68
| [1] | Baumeister, R. F., Leary, M. R . (1995). The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 117(3), 497-529. |
| [2] | Bieleke, M., Gollwitzer, P. M., Oettingen, G., & Fischbacher, U . (2016). Social value orientation moderates the effects of intuition versus reflection on responses to unfair ultimatum offers. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 30(2), 569-581. |
| [3] | Crockett, M. J., Zeb, K. N., Siegel, J. Z., Peter, D., & Dolan, R. J . (2014). Harm to others outweighs harm to self in moral decision making. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(48), 17320-17325. |
| [4] | Declerck, C. H., & Bogaert, S . (2008). Social value orientation: Related to empathy and the ability to read the mind in the eyes. Journal of Social Psychology, 148(6), 711-726. |
| [5] | Delorme, A., & Makeig, S . (2004). EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 134(1), 9-21. |
| [6] | Derk, J., van Scheppingen, M. A., Lee, N. C., & Krabbendam, L . (2015). Trust and mindreading in adolescents: The moderating role of social value orientation. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 965. |
| [7] | Distefano, A., Jackson, F., Levinson, A. R., Infantolino, Z. P., Jarcho, J. M., & Nelson, B. D . (2018). A comparison of the electrocortical response to monetary and social reward. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(3), 247-255. |
| [8] | Ernst, M., & Paulus, M. P . (2005). Neurobiology of decision making: A selective review from a neurocognitive and clinical perspective. Biological Psychiatry, 58(8), 597-604. |
| [9] | Falco, A., Albinet, C., Rattat, A. C., Paul, I., & Fabre, E . (2019). Being the chosen one: Social inclusion modulates decisions in the ultimatum game. An ERP study. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 14(2), 141-149. |
| [10] | Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A . (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175-191. |
| [11] | Fu, Y. L., Luo, Y. J., & Cui, F . (2017). Consistency of choice modulates outcome evaluation: Evidence from ERP studies. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(8), 1089-1099. |
| [ 付艺蕾, 罗跃嘉, 崔芳 . (2017). 选择一致性影响结果评价的ERP研究. 心理学报, 49(8), 1089-1099.] | |
| [12] | Gangl, K., Pfabigan, D. M., Lamm, C., Kirchler, E., & Hofmann, E . (2017). Coercive and legitimate authority impact tax honesty: Evidence from behavioral and ERP experiments. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 12(7), 1108-1117. |
| [13] | Glazer, J. E., Kelley, N. J., Pornpattananangkul, N., Mittal, V. A., & Nusslock, R . (2018). Beyond the FRN: Broadening the time-course of EEG and ERP components implicated in reward processing. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 132 (B), 184-202. |
| [14] | Gu, R., Huang, W., Camilleri, J., Xu, P., Wei, P., Eickhoff, S. B., & Feng, C . (2019). Love is analogous to money in human brain: Coordinate-based and functional connectivity meta-analyses of social and monetary reward anticipation. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 100, 108-128. |
| [15] | Gu, R., Lei, Z., Broster, L., Wu, T., Jiang, Y., & Luo, Y. J . (2011). Beyond valence and magnitude: A flexible evaluative coding system in the brain. Neuropsychologia, 49(14), 3891-3897. |
| [16] | Hajcak, G., Moser, J. S., Holroyd, C. B., & Simons, R. F . (2006). The feedback-related negativity reflects the binary evaluation of good versus bad outcomes. Biological Psychology, 71(2), 148-154. |
| [17] | Haruno, M., & Frith, C. D . (2010). Activity in the amygdala elicited by unfair divisions predicts social value orientation. Nature Neuroscience, 13(2), 160-161. |
| [18] | Hauser, T. U., Iannaccone, R., St?mpfli, P., Drechsler, R., Brandeis, D., Walitza, S., & Brem, S . (2014). The feedback-related negativity (FRN) revisited: New insights into the localization, meaning and network organization. Neuroimage, 84(1), 159-168. |
| [19] | H?usler, A. N., Becker, B., Bartling, M., & Weber, B . (2015). Goal or gold: Overlapping reward processes in soccer players upon scoring and winning money. Plos One, 10(4), e0122798. |
| [20] | He, L. Z., Bian, R., & Che, H. S . (2013). The effects of the social value orientation and feedback formats on decision behavior in the Dynamic public goods dilemma. Journal of Psychological Science, 36(2), 446-452. |
| [ 何力舟, 卞冉, 车宏生 . (2013). 社会价值取向和反馈方式对公共物品困境中决策行为的影响. 心理科学, 36(2), 446-452.] | |
| [21] | Hilbig, B. E., Gl?ckner, A., & Zettler, I . (2014). Personality and prosocial behavior: Linking basic traits and social value orientations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 107(3), 529-539. |
| [22] | Holroyd, C. B., Hajcak, G., & Larsen, J. T . (2006). The good, the bad and the neutral: Electrophysiological responses to feedback stimuli. Brain Research, 1105(1), 93-101. |
| [23] | Hu, X., Xu, Z., & Mai, X . (2017). Social value orientation modulates the processing of outcome evaluation involving others. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 12(11), 1730-1739. |
| [24] | Izuma, K . (2012). The social neuroscience of reputation. Neuroscience Research, 72(4), 283-288. |
| [25] | Izuma, K., Matsumoto, K., Camerer, C. F., & Adolphs, R . (2011). Insensitivity to social reputation in autism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 71(42), 17302-17307. |
| [26] | Izuma, K., Saito, D. N., & Sadato, N . (2008). Processing of social and monetary rewards in the human striatum. Neuron, 58(2), 284-294. |
| [27] | Izuma, K., Saito, D. N., & Sadato, N . (2010). The roles of the medial prefrontal cortex and striatum in reputation processing. Social Neuroscience, 5(2), 133-147. |
| [28] | Izuma, K., Saito, D. N., & Sadato, N . (2010). Processing of the incentive for social approval in the ventral striatum during charitable donation. Journal Cognitive Neurosciece, 22(4), 621-631. |
| [29] | Kwak, Y., Chen, X. J., McDonald, K., & Boutin, B . (2019). Money for me and money for friend: An ERP study of social reward processing in adolescents and adults. Social Neuroscience, 15(1), 83-97. |
| [30] | Leong, Y. C., & Zaki, J . (2018). Unrealistic optimism in advice taking: A computational account. Journal of Experimental Psychology General, 147(2), 170-189. |
| [31] | Li, D. Y., Li, P., & Li, H . (2018). The updated theories of feedback-related negativity in the last decade. Advances in Psychological Science, 26(9), 1642-1650. |
| [ 李丹阳, 李鹏, 李红 . (2018). 反馈负波及其近10年理论解释. 心理科学进展, 26(9), 1642-1650.] | |
| [32] | Li, H., Yang, X. G., Zheng, W. Y., & Wang, C . (2019). Emotional regulation goals of young adults with depression inclination: An event-related potential study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 51(6), 637-647. |
| [ 李红, 杨小光, 郑文瑜, 王超 . (2019). 抑郁倾向对个体情绪调节目标的影响——来自事件相关电位的证据. 心理学报, 51(6), 637-647.] | |
| [33] | Li, J., Zhan, Y., Fan, W., Liu, L., Li, M., Sun, Y., & Zhong, Y . (2018). Sociality mental modes modulate the processing of advice-giving: An Event-Related Potentials study. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 42. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00042 |
| [34] | Li, P., Jia, S., Feng, T., Liu, Q., Suo, T., & Li, H . (2010). The influence of the diffusion of responsibility effect on outcome evaluations: Electrophysiological evidence from an ERP study. Neuroimage, 52(4), 1727-1733. |
| [35] | Luck, S., & Gaspelin, N . (2017). How to get statistically significant effects in any ERP experiment (and why you shouldn't). Psychophysiology, 54(1), 146-157. |
| [36] | MacKenzie, M. J., & Baumeister, R. F . (2019). Motivated gratitude and the need to belong: Social exclusion increases gratitude for people low in trait entitlement. Motivation and Emotion, 43(3), 412-433. doi: 10.1007/s11031-018-09749-3URL |
| [37] | Marco-Pallarés, J., Kr?mer, U. M., Strehl, S., Schr?der, A., & Münte, T. F . (2010). When decisions of others matter to me: An electrophysiological analysis. BMC Neuroscience, 11(1), 86. |
| [38] | Mei, S., Yi, W., Zhou, S., Liu, X., & Zheng, Y . (2018). Contextual valence modulates the effect of choice on incentive processing. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(12), 1249-1258. |
| [39] | Mobbs, D., Hagan, C. C., Yu, R., Takahashi, H., Feldmanhall, O., Calder, A. J., & Dalgleish, T . (2015). Reflected glory and failure: The role of the medial prefrontal cortex and ventral striatum in self vs other relevance during advice-giving outcomes. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(10), 1323-1328. |
| [40] | Nieuwenhuis, S., Aston-Jones, G., & Cohen, J. D . (2005). Decision making, the P3, and the locus coeruleus- norepinephrine system. Psychological Bulletin, 131(4), 510-532. |
| [41] | Olofsson, J. K., Nordin, S., Sequeira, H., & Polich, J . (2008). Affective picture processing: An integrative review of ERP findings. Biological Psychology, 77(3), 247-265. |
| [42] | Osinsky, R., Walter, H., & Hewig, J . (2014). What is and what could have been: An ERP study on counterfactual comparisons. Psychophysiology, 51(8), 773-781. |
| [43] | Pfabigan, D. M., Alexopoulos, J., Bauer, H., Lamm, C., & Sailer, U . (2011). All about the money -- External performance monitoring is affected by monetary, but not by socially conveyed feedback cues in more antisocial individuals. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 5(4), 100. |
| [44] | Pl?chl, M., Ossandón, J. P., & K?nig, P . (2012). Combining EEG and eye tracking: Identification, characterization, and correction of eye movement artifacts in electroencephalographic data. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6(5), 278. |
| [45] | Polich, J . (2007). Updating P300: An integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118(10), 2128-2148. |
| [46] | Pornpattananangkul, N., Nadig, A., Heidinger, S., Walden, K., & Nusslock, R . (2017). Elevated outcome-anticipation and outcome-evaluation ERPs associated with a greater preference for larger-but-delayed rewards. Cognitive Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience, 17(3), 625-641. |
| [47] | Qi, Y., Wu, H., Raiha, S., & Liu, X . (2018). Social value orientation modulates context-based social comparison preference in the outcome evaluation: An ERP study. Neuropsychologia, 112, 135-144. |
| [48] | Qi, Y. Y., Wu, H. Y., & Liu, X . (2017). The influences of social value orientation on prosocial behaviors: The evidences from behavioral and neuroimaging studies. Chinese Science Bulletin, 62(11), 52-60. |
| [ 戚艳艳, 伍海燕, 刘勋 . (2017). 社会价值取向对亲社会行为的影响:来自行为和神经影像学的证据. 科学通报, 62(11), 52-60.] | |
| [49] | Rabinovitz, S., & Nagar, M . (2017). Effects of social exclusion and losing a bet on economic decision making in social gamblers. International Conference on Behavioral Addictions. |
| [50] | Somerville, L. H., Heatherton, T. F., & Kelley, W. M . (2006). Anterior cingulate cortex responds differentially to expectancy violation and social rejection. Nature Neuroscience, 9, 1007-1008. doi: 10.1038/nn1728URL |
| [51] | van Den. B., W., van Dijk, E., Westenberg, M., Rombouts, S. A. R. B., & Crone, E. A . (2009). What motivates repayment? neural correlates of reciprocity in the trust game. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 4(3), 294-304. |
| [52] | van Lange, P. A. M., Otten, W., de Bruin, E. N. M., & Joireman, J. A . (1997). Development of prosocial, individualistic, and competitive orientations: Theory and preliminary evidence. Journal of Personality Social Psychology, 73(4), 733-746. |
| [53] | Wang, Y., Kuhlman, D. M., Roberts, K., Yuan, B., Zhang, Z., Zhang, W., & Simons, R. F . (2017). Social value orientation modulates the FRN and P300 in the Chicken Game. Biological Psychology, 127, 89-98. |
| [54] | Wang, Y. W., Zhang, Z., Yuan, S., Guo, F. B., & Jing, Y. M . (2015). The decision-making and outcome evaluation during a repeated trust game. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47(8), 1028-1038. |
| [ 王益文, 张振, 原胜, 郭丰波, 何少颖, 敬一鸣 . (2015). 重复信任博弈的决策过程与结果评价. 心理学报, 47(8), 1028-1038.] | |
| [55] | Wei, P., Wang, D., & Ji, L . (2015). Reward expectation regulates brain responses to task-relevant and task-irrelevant emotional words: ERP evidence. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(2), 191-203. |
| [56] | Wischnewski, M., Bekkering, H., & Schutter, D. J. L. G . (2018). Frontal cortex electrophysiology in reward- and punishment-related feedback processing during advice-guided decision making: An interleaved EEG-DC stimulation study. Cognitive Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience, 18(2), 249-262. |
| [57] | Wu, Y., Zhang, D., Eleson, B., & Zhou, X . (2012). Brain potentials in outcome evaluation: When social comparison takes effect. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 85(2), 145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2012.06.004URL |
| [58] | Xiang, L., Wang, B. X., & Zhang, Q. L . (2012). Performance monitoring and behavioral adjustments in a time-estimation task: Evidence from ERP study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(9), 1149-1159. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01149URL |
| [ 向玲, 王宝玺, 张庆林 . (2012). 时间估计任务中的反馈加工和行为调节:来自ERP的证据. 心理学报, 44(9), 1149-1159.] | |
| [59] | Yang, Z., Sedikides, C., Gu, R., Luo, Y. L. L., Wang, Y., & Cai, H . (2018). Narcissism and risky decisions: A Neurophysiological Approach. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(8), 889-897. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsy053URL |
| [60] | Yeung, N., Holroyd, C. B., & Cohen, J. D . (2005). ERP correlates of feedback and reward processing in the presence and absence of response choice. Cerebral Cortex, 15(5), 535-544. |
| [61] | Yuan, B., Zhang, Z., Shen, Y. L., Huang, L., Li, Y., & Wang, Y. W . (2014). Value orientation and social distance influenced cooperation and aggression in decision-making: Evidences from chicken game. Journal of Psychological Science. 37(4), 962-967. |
| [ 袁博, 张振, 沈英伦, 黄亮, 李颖, 王益文 . (2014). 价值取向与社会距离影响博弈决策的合作与冲突行为: Chicken Game的证据. 心理科学, 37(4), 962-967.] | |
| [62] | Zhang, Z., Zhang, F., Huang, L., Yuan, B., & Wang, Y. W . (2014). Theories and measurement methods of social value orientation related to decision making. Advances in Psychological Science, 22(1), 48-56. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00048URL |
| [ 张振, 张帆, 黄亮, 袁博, 王益文 . (2014). 决策中社会价值取向的理论与测评方法. 心理科学进展, 22(1), 48-56.] | |
| [63] | Zhang, Z., Zhang, F., Yuan, S., Guo, F. B., & Wang, Y. W . (2015). Psychometric analysis of the SVO slider measure in Chinese cultural context. Studies of Psychology & Behavior. 13(3), 404-409. |
| [ 张振, 张帆, 原胜, 郭丰波, 王益文 . (2015). 社会价值取向滑块测验中文版的测量学分析. 心理与行为研究, 13(3), 404-409.] | |
| [64] | Zheng, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Shen, H., Gao, Q., & Zhou, S . (2017). Reward processing in gain versus loss context: An ERP study. Psychophysiology, 54(7), 1040-1053. |
| [65] | Zhong, Y. P., Wu, Y., & Fan, W . (2018). The effects of reward and self processing on memory. Journal of Psychological Science, 41(2), 258-263. |
| [ 钟毅平, 吴云, 范伟 . (2018). 奖赏与自我加工对记忆的影响. 心理科学, 41(2), 258-263.] | |
| [66] | Zhou, Z., Yu, R., & Zhou, X . (2010). To do or not to do? Action enlarges the FRN and P300 effects in outcome evaluation. Neuropsychologia, 48(12), 3606-3613. |
| [67] | Zhu, R., Feng, C., Zhang, S., Mai, X., & Liu, C . (2018). Differentiating guilt and shame in an interpersonal context with univariate activation and multivariate pattern analyses. Neuroimage, 186, 476-486. |
| [68] | Zhu, R., Wu, H., Xu, Z., Tang, H., Shen, X., Mai, X., & Liu, C . (2017). Early distinction between shame and guilt processing in an interpersonal context. Social Neuroscience, 14(1), 1-14. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 张银玲, 虞祯, 买晓琴. 社会价值取向对自我-他人风险决策的影响及其机制[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(7): 895-908. |
| [2] | 王益文, 付超, 任相峰, 林羽中, 郭丰波, 张 振, 黄亮, 袁博, 郑玉玮. 自恋人格调节信任博弈的结果评价[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(8): 1080-1088. |
| [3] | 付艺蕾, 罗跃嘉, 崔芳. 选择一致性影响结果评价的ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(8): 1089-1099. |
| [4] | 崔丽莹, 何幸, 罗俊龙, 黄晓娇, 曹玮佳, 陈晓梅. 道德与关系惩罚对初中生公共物品困境中合作行为的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(10): 1322-1333. |
| [5] | 李婧; 陈安涛;陈杰;龙长权. 词语型类别属性归纳中分类与属性推理过程的时间特征[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(11): 1410-1422. |
| [6] | 王益文;张振;原胜;郭丰波;何少颖;敬一鸣. 重复信任博弈的决策过程与结果评价[J]. 心理学报, 2015, 47(8): 1028-1038. |
| [7] | 窦炜;曲璐璐;曲琛. 社会比较对合作任务结果评价的影响:来自ERP的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(3): 405-414. |
| [8] | 索涛,冯廷勇,罗俊龙,罗禹,李红. 结果的接近性对正性结果评价影响的电生理证据[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(8): 1047-1057. |
| [9] | 吴燕,罗跃嘉. 利他惩罚中的结果评价—— ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(06): 661-673. |
| [10] | 刘长江,郝芳. 不对称社会困境中社会价值取向对合作的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(04): 432-441. |
| [11] | 陈晶,索涛,袁文萍,冯廷勇. 青少年结果预期与评价的ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(02): 152-163. |
| [12] | 王沛,陈莉. 惩罚和社会价值取向对公共物品两难中人际信任与合作行为的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(01): 52-64. |
| [13] | 李月婷,李琦,郭春彦. 内隐和外显记忆测验中情绪词差异的ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2010, 42(07): 735-742. |
| [14] | 吴燕,余荣军,周晓林,罗跃嘉. 自我主观标准决定执行任务和观察任务中的结果评价[J]. 心理学报, 2010, 42(02): 279-287. |
| [15] | 张慧君,周立明,罗跃嘉. 责任对后悔强度的影响:来自ERP的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2009, 41(05): 454-463. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4722
