 ), 孙鹏, 谢瑞波, 冯杰
), 孙鹏, 谢瑞波, 冯杰 北京师范大学心理学部, 应用实验心理北京市重点实验室, 儿童阅读与学习研究中心, 北京 100875
收稿日期:2018-11-16出版日期:2019-08-25发布日期:2019-06-24通讯作者:伍新春E-mail:xcwu@bnu.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家社会科学基金重大项目(13&ZD188)The relation between vocabulary knowledge and reading comprehension in Chinese elementary children: A cross-lagged study
CHEN Hongjun, ZHAO Ying, WU Xinchun( ), SUN Peng, XIE Ruibo, FENG Jie
), SUN Peng, XIE Ruibo, FENG Jie Faculty of Psychology, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China
Received:2018-11-16Online:2019-08-25Published:2019-06-24Contact:WU Xinchun E-mail:xcwu@bnu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 对小学1、3、5年级共399名学生进行为期1年的追踪测查, 使用交叉滞后模型检验小学低、中、高年级儿童词汇知识与阅读理解的关系。在控制了语音意识、语素意识、一般认知能力和自回归效应之后, 结果发现:在小学低年级, 词汇知识与阅读理解之间未发现显著的纵向预测关系; 在中年级, 词汇知识和阅读理解存在显著的双向预测关系; 在高年级, T1的阅读理解能够显著预测T2的词汇知识, 而T1的词汇知识对T2阅读理解的预测作用不显著。研究结果表明词汇知识与阅读理解的关系在小学不同年级段存在不同的模式, 这一发现支持了阅读发展阶段论, 并对阅读三角理论进行了一定的补充。
图/表 9
表1被试人口学变量
| 年级(T1) | 总 | 男 | 女 | 月龄(M ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一 | 127 | 67 | 60 | 76.08 ± 4.20 |
| 三 | 129 | 60 | 69 | 99.60 ± 4.68 |
| 五 | 143 | 71 | 72 | 124.56 ± 4.87 |
| 总 | 399 | 198 | 201 | 101.28 ± 20.54 |
表1被试人口学变量
| 年级(T1) | 总 | 男 | 女 | 月龄(M ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一 | 127 | 67 | 60 | 76.08 ± 4.20 |
| 三 | 129 | 60 | 69 | 99.60 ± 4.68 |
| 五 | 143 | 71 | 72 | 124.56 ± 4.87 |
| 总 | 399 | 198 | 201 | 101.28 ± 20.54 |
表2三个年级两个时间点(T1、T2)测验结果(M ± SD)及重复测量方差分析结果
| 年级 | 变量(满分) | T1 | T2 | F | ηp2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低年级 | 词汇知识(64) | 8.35 ± 5.02 | 13.51 ± 6.34 | 135.09*** | 0.52 |
| 阅读理解(20) | 10.90 ± 5.11 | 17.65 ± 2.27 | 266.03*** | 0.68 | |
| 语音意识(12) | 6.22 ± 3.75 | ||||
| 语素意识(60) | 9.08 ± 8.90 | ||||
| 一般认知能力(60) | 27.76 ± 9.30 | ||||
| 中年级 | 词汇知识(64) | 17.00 ± 7.19 | 23.13 ± 7.21 | 143.82*** | 0.53 |
| 阅读理解(16) | 6.75 ± 2.71 | 9.24 ± 3.41 | 94.13*** | 0.42 | |
| 语音意识(12) | 9.16 ± 2.45 | ||||
| 语素意识(60) | 22.07 ± 12.22 | ||||
| 一般认知能力(60) | 40.55 ± 7.64 | ||||
| 高年级 | 词汇知识(64) | 27.07 ± 6.30 | 30.76 ± 6.57 | 49.57*** | 0.26 |
| 阅读理解(17) | 9.46 ± 2.73 | 10.97 ± 2.60 | 45.71*** | 0.25 | |
| 语音意识(12) | 10.32 ± 1.77 | ||||
| 语素意识(60) | 32.37 ± 10.50 | ||||
| 一般认知能力(60) | 44.68 ± 6.52 |
表2三个年级两个时间点(T1、T2)测验结果(M ± SD)及重复测量方差分析结果
| 年级 | 变量(满分) | T1 | T2 | F | ηp2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低年级 | 词汇知识(64) | 8.35 ± 5.02 | 13.51 ± 6.34 | 135.09*** | 0.52 |
| 阅读理解(20) | 10.90 ± 5.11 | 17.65 ± 2.27 | 266.03*** | 0.68 | |
| 语音意识(12) | 6.22 ± 3.75 | ||||
| 语素意识(60) | 9.08 ± 8.90 | ||||
| 一般认知能力(60) | 27.76 ± 9.30 | ||||
| 中年级 | 词汇知识(64) | 17.00 ± 7.19 | 23.13 ± 7.21 | 143.82*** | 0.53 |
| 阅读理解(16) | 6.75 ± 2.71 | 9.24 ± 3.41 | 94.13*** | 0.42 | |
| 语音意识(12) | 9.16 ± 2.45 | ||||
| 语素意识(60) | 22.07 ± 12.22 | ||||
| 一般认知能力(60) | 40.55 ± 7.64 | ||||
| 高年级 | 词汇知识(64) | 27.07 ± 6.30 | 30.76 ± 6.57 | 49.57*** | 0.26 |
| 阅读理解(17) | 9.46 ± 2.73 | 10.97 ± 2.60 | 45.71*** | 0.25 | |
| 语音意识(12) | 10.32 ± 1.77 | ||||
| 语素意识(60) | 32.37 ± 10.50 | ||||
| 一般认知能力(60) | 44.68 ± 6.52 |
表3低年级T1和T2词汇知识、阅读理解和控制变量相关分析结果(n = 126)
| 研究变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. T1词汇知识 | 1 | |||||
| 2. T1阅读理解 | 0.33*** | 1 | ||||
| 3. T2词汇知识 | 0.64*** | 0.26** | 1 | |||
| 4. T2阅读理解 | 0.23** | 0.41*** | 0.18* | 1 | ||
| 5. 语音意识 | 0.32*** | 0.25** | 0.20* | 0.32*** | 1 | |
| 6. 语素意识 | 0.40*** | 0.29*** | 0.47*** | 0.21* | 0.19* | 1 |
| 7. 一般认知能力 | 0.36*** | 0.28** | 0.35*** | 0.30** | 0.17 | 0.23** |
表3低年级T1和T2词汇知识、阅读理解和控制变量相关分析结果(n = 126)
| 研究变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. T1词汇知识 | 1 | |||||
| 2. T1阅读理解 | 0.33*** | 1 | ||||
| 3. T2词汇知识 | 0.64*** | 0.26** | 1 | |||
| 4. T2阅读理解 | 0.23** | 0.41*** | 0.18* | 1 | ||
| 5. 语音意识 | 0.32*** | 0.25** | 0.20* | 0.32*** | 1 | |
| 6. 语素意识 | 0.40*** | 0.29*** | 0.47*** | 0.21* | 0.19* | 1 |
| 7. 一般认知能力 | 0.36*** | 0.28** | 0.35*** | 0.30** | 0.17 | 0.23** |
表4中年级T1和T2词汇知识、阅读理解和控制变量相关分析结果(n = 128)
| 研究变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. T1词汇知识 | 1 | |||||
| 2. T1阅读理解 | 0.52*** | 1 | ||||
| 3. T2词汇知识 | 0.68*** | 0.51*** | 1 | |||
| 4. T2阅读理解 | 0.57*** | 0.57*** | 0.52*** | 1 | ||
| 5. 语音意识 | 0.40*** | 0.32*** | 0.37*** | 0.45*** | 1 | |
| 6. 语素意识 | 0.49*** | 0.29** | 0.47*** | 0.34*** | 0.24** | 1 |
| 7. 一般认知能力 | 0.37*** | 0.46*** | 0.34*** | 0.54*** | 0.27** | 0.26** |
表4中年级T1和T2词汇知识、阅读理解和控制变量相关分析结果(n = 128)
| 研究变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. T1词汇知识 | 1 | |||||
| 2. T1阅读理解 | 0.52*** | 1 | ||||
| 3. T2词汇知识 | 0.68*** | 0.51*** | 1 | |||
| 4. T2阅读理解 | 0.57*** | 0.57*** | 0.52*** | 1 | ||
| 5. 语音意识 | 0.40*** | 0.32*** | 0.37*** | 0.45*** | 1 | |
| 6. 语素意识 | 0.49*** | 0.29** | 0.47*** | 0.34*** | 0.24** | 1 |
| 7. 一般认知能力 | 0.37*** | 0.46*** | 0.34*** | 0.54*** | 0.27** | 0.26** |
表5高年级T1和T2词汇知识、阅读理解和控制变量相关分析结果(n = 141)
| 研究变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. T1词汇知识 | 1 | |||||
| 2. T1阅读理解 | 0.35*** | 1 | ||||
| 3. T2词汇知识 | 0.53*** | 0.39*** | 1 | |||
| 4. T2阅读理解 | 0.29** | 0.50*** | 0.32*** | 1 | ||
| 5. 语音意识 | 0.18* | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.18* | 1 | |
| 6. 语素意识 | 0.27** | 0.23** | 0.32*** | 0.26** | 0.23** | 1 |
| 7. 一般认知能力 | 0.19* | 0.46*** | 0.27** | 0.51*** | 0.18* | 0.18* |
表5高年级T1和T2词汇知识、阅读理解和控制变量相关分析结果(n = 141)
| 研究变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. T1词汇知识 | 1 | |||||
| 2. T1阅读理解 | 0.35*** | 1 | ||||
| 3. T2词汇知识 | 0.53*** | 0.39*** | 1 | |||
| 4. T2阅读理解 | 0.29** | 0.50*** | 0.32*** | 1 | ||
| 5. 语音意识 | 0.18* | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.18* | 1 | |
| 6. 语素意识 | 0.27** | 0.23** | 0.32*** | 0.26** | 0.23** | 1 |
| 7. 一般认知能力 | 0.19* | 0.46*** | 0.27** | 0.51*** | 0.18* | 0.18* |
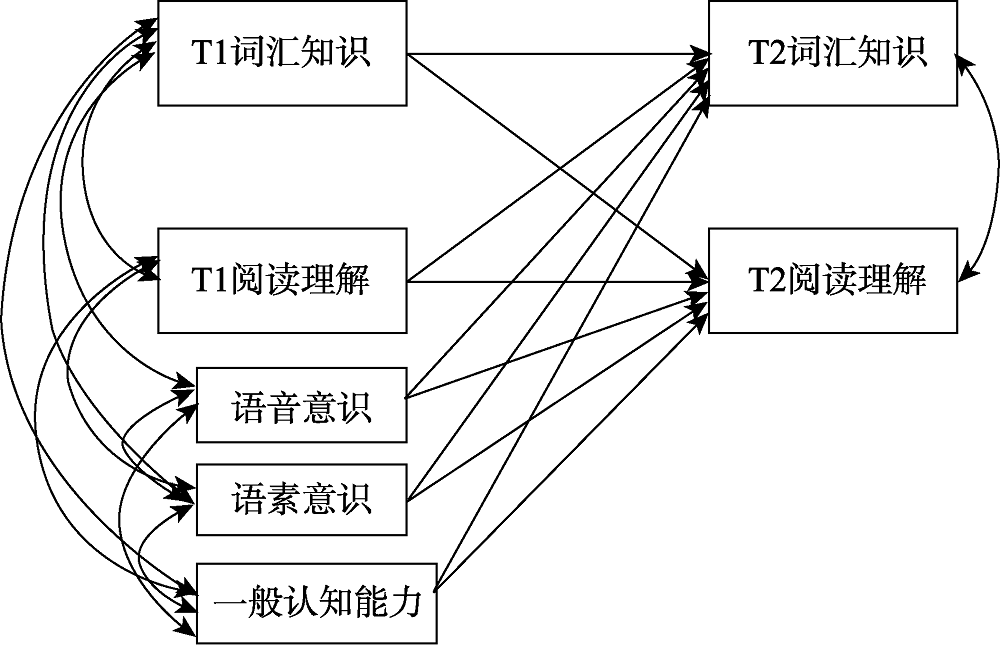
图1词汇知识与阅读理解交叉滞后检验模型 注:图中单箭头直线为预测关系, 双箭头曲线为相关关系。
 图1词汇知识与阅读理解交叉滞后检验模型 注:图中单箭头直线为预测关系, 双箭头曲线为相关关系。
图1词汇知识与阅读理解交叉滞后检验模型 注:图中单箭头直线为预测关系, 双箭头曲线为相关关系。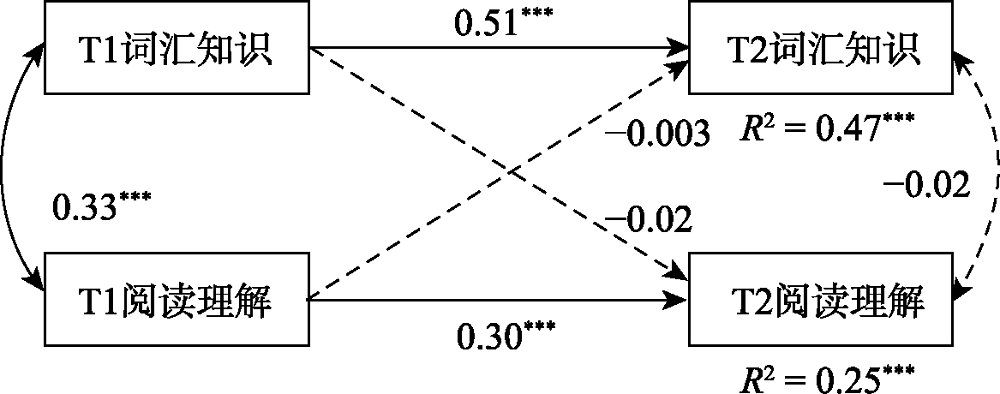
图2低年级模型结果 注:为呈现结果更加简洁, 控制变量(语音意识、语素意识和一般认知能力)及其相关路径系数未在图中显示, 下同。
 图2低年级模型结果 注:为呈现结果更加简洁, 控制变量(语音意识、语素意识和一般认知能力)及其相关路径系数未在图中显示, 下同。
图2低年级模型结果 注:为呈现结果更加简洁, 控制变量(语音意识、语素意识和一般认知能力)及其相关路径系数未在图中显示, 下同。
图3中年级模型结果
 图3中年级模型结果
图3中年级模型结果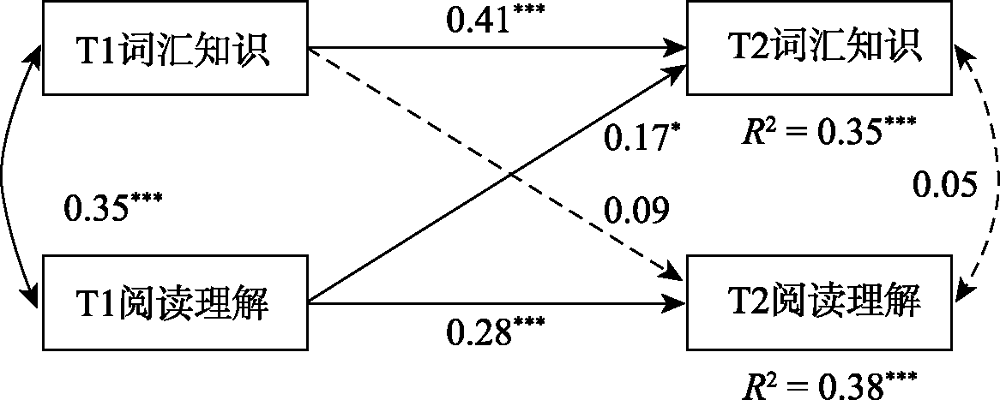
图4高年级模型结果
 图4高年级模型结果
图4高年级模型结果参考文献 46
| [1] | Cain K., Oakhill J., & Lemmon K . ( 2004). Individual differences in the inference of word meanings from context: The influence of reading comprehension, vocabulary knowledge, and memory capacity. Journal of Educational Psychology, 96(4), 671-681. |
| [2] | Chall J.S . ( 1983). Learning to read: The great debate. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. |
| [3] | Chall J.S . ( 1996). American reading achievement: Should we worry? Research in the Teaching of English, 30(3), 303-310. |
| [4] | Chen M. J., Lau L. L., & Yung Y. F . ( 1993). Development of component skills in reading Chinese. International Journal of Psychology, 28(4), 481-507. |
| [5] | Cunningham A.E., & Stanovich K.E . ( 1991). Tracking the unique effects of print exposure in children: Associations with vocabulary, general knowledge, and spelling. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83(2), 264-274. |
| [6] | Cunningham A.E., & Stanovich K.E . ( 1997). Early reading acquisition and its relation to reading experience and ability 10 years later. Developmental Psychology, 33(6), 934-945. |
| [7] | Dong Q . ( 2013). The Structure,Development of Morphological Awareness and its role in the reading development of Chinese children (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Beijing Normal University. |
| [ 董琼 . ( 2013). 汉语语素意识的结构、发展及其在阅读发展中的作用(博士学位论文). 北京师范大学.] | |
| [8] | Graves M. F., Juel C., Graves B. B., & Dewitz P . ( 2011). Teaching reading in the 21st century (5th ed.). New York, NY:Pearson. |
| [9] | Henry D.L., & Maclean M.M . ( 2003). Relationships between working memory, expressive vocabulary and arithmetical reasoning in children with and without intellectual disabilities. Educational & Child Psychology, 20, 51-63. |
| [10] | Kintsch W., . ( 1998). Comprehension:A paradigm for cognition . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. |
| [11] | Koda K., .( 1989). The effects of transferred vocabulary knowledge on the development of L2 reading proficiency. Foreign Language Annals, 22(6), 529-540. |
| [12] | Ku Y.M., & Anderson R.C . ( 2001). Chinese children's incidental learning of word meanings. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 26(2), 249-266. |
| [13] | Li H., Dong Q., Zhu J., Liu J. P., & Wu X. C . ( 2009). The role of morphological awarence in kindergarteners’ linguistic skill development. Journal of Psychological Science, 32(6), 1291-1294. |
| [ 李虹, 董琼, 朱瑾, 刘俊娉, 伍新春 . ( 2009). 语素意识在学前儿童言语技能发展中的作用. 心理科学, 32(6), 1291-1294.] | |
| [14] | Li H., Rao X. S., Dong Q., Zhu J., & Wu X. C . ( 2011). The roles of phonological awareness, morphological awareness and rapid naming in linguistic skills development of kindergartener. Psychological Development and Education, 27(2), 158-163. |
| [ 李虹, 饶夏溦, 董琼, 朱瑾, 伍新春 . ( 2011). 语音意识、语素意识和快速命名在儿童言语发展中的作用. 心理发展与教育, 27(2), 158-163.] | |
| [15] | Little R. J.A., Rubin D.B . ( 2002). Statistical analysis with missing data (Second Edition). New York, NY: Wiley. |
| [16] | Liu P.D., & McBride-Chang C. , ( 2010). What is morphological awareness? Tapping lexical compounding awareness in Chinese third graders. Journal of Educational Psychology, 102(1), 62-73. |
| [17] | Mcbride-Chang C., Cho J-R., Liu H., Wagner R. K., Shu H., Zhou A., … Muse A . ( 2005). Changing models across cultures: Associations of phonological awareness and morphological structure awareness with vocabulary and word recognition in second graders from Beijing, Hong Kong, Korea, and the United States. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 92(2), 140-160. |
| [18] | McKeown M. G., Beck I. L., Omanson R. C., & Perfetti C. A . ( 1983). The effects of long-term vocabulary instruction on reading comprehension: A replication. Journal of Literacy Research, 15(1), 3-18. |
| [19] | Minskoff E., . ( 2005). Teaching Reading to Struggling Learners. Baltimore, MD:Brookes. |
| [20] | Moats L.C., . ( 2005). How spelling supports reading. American Educator, 29(4), 4-12. |
| [21] | Nagy W.E., & Anderson R.C . ( 1984). How many words are there in printed school English? Reading Research Quarterly, 19(3), 304-330. |
| [22] | Nagy W. E., Anderson R. C., & Herman P. A . ( 1987). Learning word meanings from context during normal reading. American Educational Research Journal, 24(2), 237-270. |
| [23] | Nagy W. E., Herman P. A., & Anderson R. C . ( 1985). Learning words from context. Reading Research Quarterly, 20(2), 233-253. |
| [24] | Nagy W. E., Scott J. A ., ( 2000). Vocabulary processes., In M. L. Kamil, P. B. Mosenthal, P. D. Pearson, & R. Barr (Eds), Handbook of Reading Research (Volume III, pp. 269-284). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [25] | National reading in the “Thirteen Five” period development plan. (2016-12-28). China Press Publicitons Radio Film and Televisions Journal, 3, 1-7. |
| [ 全民阅读“十三五”时期发展规划. (2016-12-28). 国家新闻出版广电报, 3, 1-7.] | |
| [26] | Penno J. F., Wilkinson I. A., & Moore D. W . ( 2002). Vocabulary acquisition from teacher explanation and repeated listening to stories: Do they overcome the Matthew effect? Journal of Educational Psychology, 94(1), 23-33. |
| [27] | Perfetti C., . ( 2007). Reading ability: Lexical quality to comprehension. Scientific Studies of Reading, 11(4), 357-383. |
| [28] | Perfetti C., . ( 2010). Decoding, vocabulary, and comprehension.The golden triangle of reading skill. In M. G. McKeown & L. Kucan (Eds.), Bringing reading research to life (pp. 291-303). New York, NY: Guilford. |
| [29] | Quinn J. M., Wagner R. K., Petscher Y., & Lopez D . ( 2015). Developmental relations between vocabulary knowledge and reading comprehension: A latent change score modeling study. Child Development, 86(1), 159-175. |
| [30] | Raven J.C., & Court J.H . ( 1986). Raven's progressive matrices and Raven's coloured matrices . London:HK Lewis. |
| [31] | Seigneuric A., & Ehrlich M-F. , ( 2005). Contribution of working memory capacity to children’s reading comprehension: A longitudinal investigation. Reading and Writing, 18, 617-656. |
| [32] | Shu H., Anderson R. C., & Zhang H . ( 1995). Incidental learning of word meanings while reading: A Chinese and American cross-cultural study. Reading Research Quarterly, 30(1), 76-95. |
| [33] | Shu H., McBride-Chang C., Wu S., & Liu H . ( 2006). Understanding Chinese developmental dyslexia: Morphological awareness as a core cognitive construct. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98(1), 122-133. |
| [34] | Song S., Su M., Kang C., Liu H., Zhang Y., McBride-Chang C., … Shu H . ( 2015). Tracing children's vocabulary development from preschool through the school-age years: An 8-year longitudinal study. Developmental Science, 18(1), 119-131. |
| [35] | Sparapani N., Connor C. M., McLean L., Wood T., Toste J., & Day S . ( 2018). Direct and reciprocal effects among social skills, vocabulary, and reading comprehension in first grade. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 53, 159-167. |
| [36] | Storch S.A., & Whitehurst G.J . ( 2002). Oral language and code-related precursors to reading: Evidence from a longitudinal structural model. Developmental Psychology, 38(6), 934-947. |
| [37] | Tannenbaum K. R., Torgesen J. K., & Wagner R. K . ( 2006). Relationships between word knowledge and reading comprehension in third-grade children. Scientific Studies of Reading, 10(4), 381-398. |
| [38] | Tuinman J.J., & Brady M.E . ( 1974). How does vocabulary account for variance on reading comprehension tests? A preliminary instructional analysis. In P. Nacke (Ed), Interaction: Research and practice for college-adult reading (pp.176-184). Clemson SC: National Reading Conference. |
| [39] | van den Broek P., , ( 2010). Using texts in science education: Cognitive processes and knowledge representation. Science, 328(5977), 453-456. |
| [40] | Verhoeven L., & van Leeuwe J. ,( 2008). Prediction of the development of reading comprehension: A longitudinal study. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 22(3), 407-423. |
| [41] | Wasik B. A., Hindman A. H., & Snell E. K . ( 2016). Book reading and vocabulary development: A systematic review. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 37, 39-57. |
| [42] | Wright T.S., &Cervetti G.N . ( 2017). A systematic review of the research on vocabulary instruction that impacts text comprehension. Reading Research Quarterly, 52(2), 203-226. |
| [43] | Wu X., Anderson R. C., Li W., Wu X., Li H., Zhang J., … Gaffney J. S . ( 2009). Morphological awareness and Chinese children's literacy development: An intervention study. Scientific Studies of Reading, 13(1), 26-52. |
| [44] | Zhang H-C., & Wang X-P. , ( 1989), Standardization research on Raven’s standard progressive matrices in China. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 21, 113-121. |
| [ 张厚粲, 王晓平 . ( 1989). 瑞文标准推理测验在我国的修订. 心理学报, 21, 113-121.] | |
| [45] | Zhang J., McBride-Chang C., Tong X., Wong A. M-Y., Shu H., & Fong C. Y-C . ( 2012). Reading with meaning: the contributions of meaning-related variables at the word and subword levels to early Chinese reading comprehension. Reading and Writing, 25(9), 2183-2203. |
| [46] | Zhao Y., Cheng Y. H., Wu X. C., & Nguyen T . ( 2016). The reciprocal relationship between morphological awareness and vocabulary knowledge among Chinese children: A longitudinal study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(11), 1434-1444. |
| [ 赵英, 程亚华, 伍新春, 阮氏芳 . ( 2016). 汉语儿童语素意识与词汇知识的双向关系: 一项追踪研究. 心理学报, 48(11), 1434-1444.] |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 张景焕, 付萌萌, 辛于雯, 陈佩佩, 沙莎. 小学高年级学生创造力的发展:性别差异及学校支持的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(9): 1057-1070. |
| [2] | 赵鑫, 李红利, 金戈, 李世峰, 周爱保, 梁文佳, 郭红霞, 蔡亚亚. 语音记忆和中央执行功能在不同年级儿童解码和语言理解中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 469-484. |
| [3] | 张明亮, 司继伟, 杨伟星, 邢淑芬, 李红霞, 张佳佳. BDNF基因rs6265多态性与父母教育卷入对小学儿童基本数学能力的交互作用 *[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(9): 1007-1017. |
| [4] | 程亚华, 王健, 伍新春. 小学低年级儿童汉语语素意识在阅读理解中的 作用:字词阅读流畅性的中介效应[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(4): 413-425. |
| [5] | 叶婉青, 李晓彤, 王大华. 老年人对夫妻间负性事件的认知性情绪调节策略及其与婚姻满意度的关系:交叉滞后分析[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(4): 426-435. |
| [6] | 程亚华, 伍新春, 刘红云, 李虹. 小学低年级儿童口语词汇知识的发展轨迹及其影响因素[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(2): 206-215. |
| [7] | 胡琼晶, 路西, 张志学. 群体背景下的自我监控:对个体地位获取和群体任务绩效的积极效应[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(10): 1169-1179. |
| [8] | 郭海英;陈丽华; 叶枝;潘瑾;林丹华. 流动儿童同伴侵害的特点及与内化问题的循环作用关系:一项追踪研究[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(3): 336-348. |
| [9] | 周宵, 伍新春, 王文超, 田雨馨. 社会支持、创伤后应激障碍与创伤后成长之间的关系:来自雅安地震后小学生的追踪研究[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(11): 1428-1438. |
| [10] | 赵英;程亚华;伍新春;阮氏芳. 汉语儿童语素意识与词汇知识的双向关系:一项追踪研究[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(11): 1434-1444. |
| [11] | 梁宗保;张光珍;邓慧华;宋媛;郑文明. 学前儿童努力控制的发展轨迹与父母养育的关系:一项多水平分析[J]. 心理学报, 2013, 45(5): 556-567. |
| [12] | 范方,耿富磊,张岚,朱清. 负性生活事件、社会支持和创伤后应激障碍症状:对汶川地震后青少年的追踪研究[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(12): 1398-1407. |
| [13] | 彭华茂,王大华,申继亮,林崇德. 老年期语义理解能力与空间定向能力的交叉滞后分析[J]. 心理学报, 2009, 41(07): 624-629. |
| [14] | 刘电芝,黄希庭. 简算策略教学提高小学四年级儿童的计算水平及延迟效应[J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(01): 47-53. |
| [15] | 周宗奎,赵冬梅,孙晓军,定险峰. 儿童的同伴交往与孤独感:一项2年纵向研究[J]. 心理学报, 2006, 38(05): 743-750. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4489
