 )
) 1 青少年网络心理与行为教育部重点实验室, 华中师范大学心理学院, 湖北省人的发展与心理健康重点实验室, 武汉 430079
2 北京师范大学认知神经科学与学习国家重点实验室, IDG/麦戈文脑科学研究院, 北京, 100875
3 北德克萨斯大学, 德克萨斯, 76203, 美国
4 中国科学院心理研究所, 中国科学院心理研究所心理健康重点实验室, 北京 100101
收稿日期:2018-08-10出版日期:2019-06-25发布日期:2019-04-25通讯作者:祝卓宏E-mail:zhuzh@psych.ac.cn基金资助:* 国家社科基金项目资助(16CSH051)Mechanisms of the Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: A meta-analytic structural equation model
REN Zhihong1, ZHAO Chunxiao1, BIAN Cheng2, ZHU Wenzhen3, JIANG Guangrong1, ZHU Zhuohong4( )
) 1 Key Laboratory of Adolescent Cyberpsychology and Behavior (CCNU), Ministry of Education; School of Psychology, Central China Normal University; Key Laboratory of Human Development and Mental Health of Hubei Province, Wuhan 430079, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Cognitive Neuroscience and Learning, IDG/McGovern Institution for Brain Research, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875, China
3 University of North Texas, Texas, 76203, United State
4 Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences; The Key Laboratory of Mental Health, Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
Received:2018-08-10Online:2019-06-25Published:2019-04-25Contact:ZHU Zhuohong E-mail:zhuzh@psych.ac.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 接纳承诺疗法(Acceptance and Commitment Therapy, ACT)被认为是行为治疗“第三浪潮”的重要代表。本研究使用元分析结构方程模型, 考察ACT的作用机制。通过数据库检索与筛选, 最终纳入文献50篇。结果发现: ACT所假设的心理灵活性、接纳、此时此刻、价值的中介作用都达到统计显著, 认知解离这一中介变量并不显著; 中介机制在网络化干预中仍然得到检验; 相较之传统CBT, ACT在所假设的机制上有其区别于CBT的优势。后续临床研究应更全面地测量6大核心机制, 关注对美好生活提升的影响, 采用多点瞬时评价法, 并尽可能使用更高级、更先进的统计方法检验其作用机制。
图/表 2
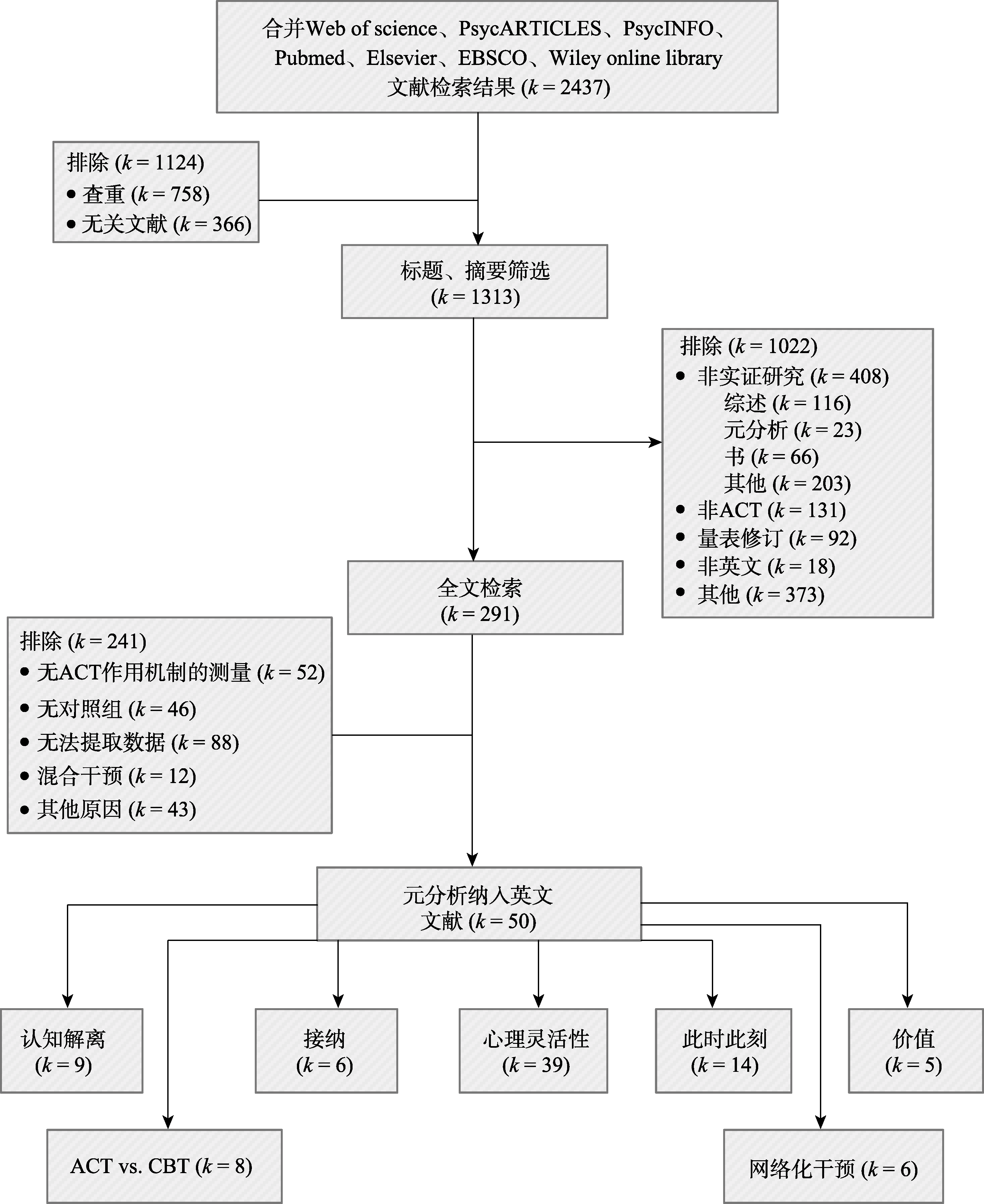
图1文献检索和筛选流程图
 图1文献检索和筛选流程图
图1文献检索和筛选流程图
图2TSSEM分析路径图, 以ACT假设机制的改变为中介变量
 图2TSSEM分析路径图, 以ACT假设机制的改变为中介变量
图2TSSEM分析路径图, 以ACT假设机制的改变为中介变量参考文献 87
| [1] | Aderka I. M., Nickerson A., Bøe H. J., & Hofmann S. G . ( 2012). Sudden gains during psychological treatments of anxiety and depression: A meta-analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 80( 1), 93-101. doi: 10.1037/a0026455URLpmid: 22122290 |
| [2] | Alonso-Fernández M., López-López A., Losada A., González J. L., & Wetherell J. L . ( 2013). Acceptance and commitment therapy and selective optimization with compensation for institutionalized older people with chronic pain: A pilot study. Pain Medicine, 17( 2), 264-277. doi: 10.1111/pme.12885URLpmid: 26304771 |
| [3] | Alsubaie M., Abbott R., Dunn B., Dickens C., Keil T. F., Henley W., & Kuyken W . ( 2017). Mechanisms of action in mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) in people with physical and/or psychological conditions: A systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 55, 74-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2017.04.008URL |
| [4] | Arch J. J., Eifert G. H., Davies C., Vilardaga J. C. P., Rose R. D., & Craske M. G . ( 2012). Randomized clinical trial of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) versus acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) for mixed anxiety disorders. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 80( 5), 750-765. doi: 10.1037/a0028310URLpmid: 22563639 |
| [5] | Assaz D. A., Roche B., Kanter J. W., & Oshiro, C. K. B .( 2018). Cognitive defusion in acceptance and commitment therapy: What are the basic processes of change. The Psychological Record, 68( 4), 405-418. doi: 10.1007/s40732-017-0254-z |
| [6] | A-Tjak J. G. L., Davis M. L., Morina N., Powers M. B., Smits J. A. J .,& Emmelkamp, P. M. G. ( 2015). A meta-analysis of the efficacy of acceptance and commitment therapy for clinically relevant mental and physical health problems. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 84( 1), 30-36. doi: 10.1159/000365764URLpmid: 25547522 |
| [7] | Avdagic E., Morrissey S. A., & Boschen M. J . ( 2014). A randomised controlled trial of acceptance and commitment therapy and cognitive-behaviour therapy for generalised anxiety disorder. Behaviour Change, 31( 2), 110-130. doi: 10.1017/bec.2014.5URL |
| [8] | Baron R. M., & Kenny D. A . ( 1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51( 6), 1173-1182. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173URL |
| [9] | Beck A. T . ( 1993). Cognitive therapy: Past, present, and future. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 61( 2), 194-198. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.61.2.194URLpmid: 8473571 |
| [10] | Black J. J., & Chung T. , ( 2014). Mechanisms of change in adolescent substance use treatment: How does treatment work?. Substance Abuse, 35( 4), 344-351. doi: 10.1080/08897077.2014.925029URLpmid: 4257904 |
| [11] | Bluett E. J., Homan K. J., Morrison K. L., Levin M. E., & Twohig M. P . ( 2014). Acceptance and commitment therapy for anxiety and OCD spectrum disorders: An empirical review. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 28( 6), 612-624. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2014.06.008URLpmid: 25041735 |
| [12] | Bond F. W., Hayes S. C., Baer R. A., Carpenter K. M., Guenole N., Orcutt H. K., … Zettle R. D . ( 2011). Preliminary psychometric properties of the Acceptance and Action Questionnaire-II: A revised measure of psychological inflexibility and experiential avoidance. Behavior Therapy, 42( 4), 676-688. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2011.03.007URLpmid: 22035996 |
| [13] | Cheung M. L., & Chan W. , ( 2005). Meta-analytic structural equation modeling: A two stage approach. Psychological Methods, 10( 1), 40-64. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.10.1.40URLpmid: 15810868 |
| [14] | Cheung M. W. L . ( 2014). Fixed- and random-effects meta-analytic structural equation modeling: Examples and analyses in R. Behavior Research Methods, 46( 1), 29-40. doi: 10.3758/s13428-013-0361-yURLpmid: 23807765 |
| [15] | Cheung M. W. L . ( 2015). Meta-Analysis: A structural equation modeling approach. Chichester, West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons. |
| [16] | Clarke S., Kingston J., James K., Bolderston H., & Remington B . ( 2014). Acceptance and commitment therapy group for treatment-resistant participants: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 3( 3), 179-188. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2014.04.005URL |
| [17] | Clarke S., Taylor G., Lancaster J., & Remington B . ( 2015). Acceptance and commitment therapy-based self-management versus psychoeducation training for staff caring for clients with a personality disorder: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Personality Disorders, 29( 2), 163-176. doi: 10.1521/pedi_2014_28_149URLpmid: 24963830 |
| [18] | Cohen J. Jr . ( 1988): Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences.(2nd Edition.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [19] | Dimidjian S., Arch J. J., Schneider R. L., Desormeau P., Felder J. N., & Segal Z. V . ( 2016). Considering meta-analysis, meaning, and metaphor: A systematic review and critical examination of “Third Wave” cognitive and behavioral therapies. Behavior Therapy, 47( 6), 886-905. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2016.07.002URLpmid: 27993339 |
| [20] | Eilenberg T., Hoffmann D., Jensen J. S., & Frostholm L . ( 2017). Intervening variables in group-based acceptance & commitment therapy for severe health anxiety. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 92, 24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2017.01.009URL |
| [21] | Eustis E. H., Hayes-Skelton S. A., Roemer L., & Orsillo S. M . ( 2016). Reductions in experiential avoidance as a mediator of change in symptom outcome and quality of life in acceptance-based behavior therapy and applied relaxation for generalized anxiety disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 87, 188-195. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2016.09.012URLpmid: 27718414 |
| [22] | Faul F., Erdfelder E., Lang A. G., & Buchner A . ( 2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39( 2), 175-191. doi: 10.3758/BF03193146URL |
| [23] | Forman E. M., Chapman J. E., Herbert J. D., Goetter E. M., Yuen E. K., & Moitra E . ( 2012). Using session-by-session measurement to compare mechanisms of action for acceptance and commitment therapy and cognitive therapy. Behavior Therapy, 43( 2), 341-354. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2011.07.004URLpmid: 22440070 |
| [24] | Forman E. M., Herbert J. D., Moitra E., Yeomans P. D., & Geller P. A . ( 2007). A randomized controlled effectiveness trial of acceptance and commitment therapy and cognitive therapy for anxiety and depression. Behavior Modification, 31( 6), 772-799. doi: 10.1177/0145445507302202URLpmid: 17932235 |
| [25] | Francis A. W., Dawson D. L., & Golijani-Moghaddam N . ( 2016). The development and validation of the comprehensive assessment of acceptance and commitment therapy processes (CompACT). Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 5( 3), 134-145. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2016.05.003URL |
| [26] | Grimm K. J., Ram N. ,& Estabrook, R.( 2017). Growth modeling: Structural equation and multilevel modeling approaches. New York, NY: The Guilford Press Structural equation and multilevel modeling approaches. |
| [27] | Gu J., Strauss C., Bond R., & Cavanagh K . ( 2015). How do mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction improve mental health and wellbeing? A systematic review and meta-analysis of mediation studies. Clinical Psychology Review, 37, 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2015.01.006URL |
| [28] | Gumley A., White R., Briggs A., Ford I., Barry S., Stewart C., … McLeod H . ( 2017). A parallel group randomised open blinded evaluation of acceptance and commitment therapy for depression after psychosis: Pilot trial outcomes (ADAPT). Schizophrenia Research, 183, 143-150. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2016.11.026URL |
| [29] | Hacker T., Stone P., & MacBeth A . ( 2016). Acceptance and commitment therapy-Do we know enough? Cumulative and sequential meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Affective Disorders, 190, 551-565. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.10.053URL |
| [30] | Hancock K., & Swain J. , ( 2016). Long term follow up in children with anxiety disorders treated with acceptance and commitment therapy or cognitive behavioral therapy: Outcomes and predictors. Journal of Child and Adolescent Behavior, 4( 5), 317-329. |
| [31] | Hancock K. M., Swain J., Hainsworth C. J., Dixon A. L., Koo S., & Munro K . ( 2016). Acceptance and commitment therapy versus cognitive behavior therapy for children with anxiety: Outcomes of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 47( 2), 296-311. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2015.1110822URLpmid: 26998803 |
| [32] | Hayes S. C. ( 2004).Acceptance and commitment therapy and the new behavior therapies: Mindfulness, acceptance, and relationship. New York, NY: The Guilford Press. |
| [33] | Hayes S. C., Luoma J. B., Bond F. W., Masuda A., & Lillis J . ( 2006). Acceptance and commitment therapy: Model, processes and outcomes. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 44( 1), 1-25. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2005.06.006URLpmid: 16300724 |
| [34] | Hayes S. C., Villatte M., Levin M., & Hildebrandt M . ( 2011). Open, aware, and active: Contextual approaches as an emerging trend in the behavioral and cognitive therapies. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 7, 141-168. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032210-104449URLpmid: 21219193 |
| [35] | Hektner J. M., Schmidt J. A., & Csikszentmihalyi M . ( 2007). Experience sampling method: Measuring the quality of everyday life. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. |
| [36] | Higgins J. P. T., & Thompson S. G . ( 2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine, 21( 11), 1539-1558. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0258URL |
| [37] | Hofmann S. G., & Asmundson G. J. G . ( 2008). Acceptance and mindfulness-based therapy: New wave or old hat? Clinical Psychology Review, 28( 1), 1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2007.09.003URLpmid: 17904260 |
| [38] | Johnston M., Foster M., Shennan J., Starkey N. J., & Johnson A . ( 2010). The effectiveness of an acceptance and commitment therapy self-help intervention for chronic pain. Clinical Journal of Pain, 26( 5), 393-402. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181cf59ceURLpmid: 20473046 |
| [39] | Juarascio A., Shaw J., Forman E., Timko C. A., Herbert J., Butryn M., … Lowe M . ( 2013). Acceptance and commitment therapy as a novel treatment for eating disorders: An initial test of efficacy and mediation. Behavior Modification, 37( 4), 459-489. doi: 10.1177/0145445513478633URL |
| [40] | Kazdin A. E . ( 2007). Mediators and mechanisms of change in psychotherapy research. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 3( 1), 1-27. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.3.022806.091432URL |
| [41] | Kemani M. K., Hesser H., Olsson G. L., Lekander M., & Wicksell R. K . ( 2016). Processes of change in acceptance and commitment therapy and applied relaxation for long-standing pain. European Journal of Pain, 20( 4), 521-531. doi: 10.1002/ejp.754URLpmid: 26684472 |
| [42] | Keyes C. L. M., Shmotkin D., & Ryff C. D . ( 2002). Optimizing well-being: The empirical encounter of two traditions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 82( 6), 1007-1022. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.82.6.1007URLpmid: 12051575 |
| [43] | Lang A. J., Schnurr P. P., Jain S., He F., Walser R. D., Bolton E., .. Strauss J . ( 2017). Randomized controlled trial of acceptance and commitment therapy for distress and Impairment in OEF/OIF/OND veterans. Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy, 9( S1), 74-84. doi: 10.1037/tra0000127URL |
| [44] | Lappalainen P., Langrial S., Oinas-Kukkonen H., Tolvanen A., & Lappalainen R . ( 2015). Web-based acceptance and commitment therapy for depressive symptoms with minimal support: A randomized controlled trial. Behavior Modification, 39( 6), 805-834. doi: 10.1177/0145445515598142URL |
| [45] | Larsson A., Hooper N., Osborne L. A., Bennett P., & McHugh L . ( 2016). Using brief cognitive restructuring and cognitive defusion techniques to cope with negative thoughts. Behavior Modification, 40( 3), 452-482. doi: 10.1177/0145445515621488URLpmid: 26685210 |
| [46] | Lemmens L. H. J. M., Müller, V. N. L. S., Arntz A & Huibers, M. J. H. .,( 2016). Mechanisms of change in psychotherapy for depression: An empirical update and evaluation of research aimed at identifying psychological mediators. Clinical Psychology Review, 50, 95-107. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2016.09.004URLpmid: 27770716 |
| [47] | Levin M. E., Haeger J., Pierce B., & Cruz R. A . ( 2017a). Evaluating an adjunctive mobile app to enhance psychological flexibility in acceptance and commitment therapy. Behavior Modification, 41( 6), 846-867. doi: 10.1177/0145445517719661URLpmid: 28689449 |
| [48] | Levin M. E., Haeger J. A., Pierce B. G., & Twohig M. P . ( 2017b). Web-based acceptance and commitment therapy for mental health problems in college students: A randomized controlled trial. Behavior Modification, 41( 1), 141-162. doi: 10.1177/0145445516659645URL |
| [49] | Levin M. E., Hayes S. C., Pistorello J., & Seeley J. R . ( 2016). Web-based self-help for preventing mental health problems in universities: Comparing acceptance and commitment training to mental health education. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 72( 3), 207-225. doi: 10.1002/jclp.22254URLpmid: 26784010 |
| [50] | Levin M. E., Pistorello J., Seeley J. R., & Hayes S. C . ( 2014). Feasibility of a prototype web-based acceptance and commitment therapy prevention program for college students. Journal of American College Health, 62( 1), 20-30. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2013.843533URLpmid: 24313693 |
| [51] | Lipsey M. W., & Wilson, D. B . ( 2001). Practical meta-analysis. Applied social research methods series. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. |
| [52] | Lloyd J., Bond F. W., & Flaxman P. E . ( 2013). The value of psychological flexibility: Examining psychological mechanisms underpinning a cognitive behavioural therapy intervention for burnout. Work and Stress, 27( 2), 181-199. doi: 10.1080/02678373.2013.782157URL |
| [53] | Longwell B. T., & Truax P. , ( 2005). The differential effects of weekly, monthly, and bimonthly administrations of the beck depression inventory-II: Psychometric properties and clinical implications. Behavior Therapy, 36( 3), 265-275. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7894(05)80075-9URL |
| [54] | Luciano J. V., Guallar J. A., Aguado J., Lopez-del-Hoyo Y., Olivan B., Magallon R., … Garcia-Campayo J . ( 2014). Effectiveness of group acceptance and commitment therapy for fibromyalgia: A 6-month randomized controlled trial (EFFIGACT study). Pain, 155( 4), 693-702. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.12.029URLpmid: 24378880 |
| [55] | MacKinnon D. P., Fairchild A. J., & Fritz M. S . ( 2007). Mediation analysis. Annual Review of Psychology, 58( 1), 593-614. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085542URL |
| [56] | Millstein D. J., Orsillo S. M., Hayes-Skelton S. A., & Roemer L . ( 2015). Interpersonal problems, mindfulness, and therapy outcome in an acceptance-based behavior therapy for generalized anxiety disorder. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy, 44( 6), 491-501. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2015.1060255URLpmid: 26228536 |
| [57] | Montazemi A. R., & Qahri-Saremi H. ,( 2015). Factors affecting adoption of online banking: A meta-analytic structural equation modeling study. Information and Management, 52( 2), 210-226. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2014.11.002URL |
| [58] | Morris S. B . ( 2008). Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organizational Research Methods, 11( 2), 364-386. doi: 10.1177/1094428106291059URL |
| [59] | Öst L. G . ( 2008). Efficacy of the third wave of behavioral therapies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 46( 3), 296-321 doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2007.12.005URLpmid: 18258216 |
| [60] | Öst L. G . ( 2014). The efficacy of acceptance and commitment therapy: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 61, 105-121. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2014.07.018URLpmid: 25193001 |
| [61] | Orwin R. G . ( 1994). Evaluating coding decisions. In H. Cooper., & L. V. Hedges (Eds.), The handbook of research synthesis(pp. 139-162). New York, NY, US: Russel Sage Foundation. |
| [62] | Powers M. B Vörding, M. B. Z. V. S., & Emmelkamp, P. M. G. ., (2009). Acceptance and commitment therapy: A meta-analytic review. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 78( 2), 73-80. doi: 10.1159/000190790URL |
| [63] | Preacher K. J., & Hayes A. F . ( 2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40( 3), 879-891. doi: 10.3758/BRM.40.3.879URL |
| [64] | Ren Z. H., Li X. Y., Zhao, L. B, Yu, X. L., Li Z. H Lai, L. Z, .. Jiang, G. R. ., (2016). Effectiveness and mechanism of internet-based self-help intervention for depression: The Chinese version of MoodGYM. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48( 7), 818-832. |
| [ 任志洪, 李献云, 赵陵波, 余香莲, 李政汉, 赖丽足 … 江光荣. , (2016). 抑郁症网络化自助干预的效果及作用机制——以汉化MoodGYM为例. 心理学报, 48( 7), 818-832.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00818URL | |
| [65] | Rost A. D., Wilson K., Buchanan E., Hildebrandt M. J., & Mutch D . ( 2012). Improving psychological adjustment among late-stage ovarian cancer patient: Examining the role of avoidance in treatment. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice, 19( 4), 508-517. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpra.2012.01.003URL |
| [66] | Rothstein H., Sutton A. J., & Borenstein M . ( 2005). Publication bias in meta-analysis: Prevention, assessment and adjustments. Chichester, West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons. |
| [67] | Ruiz F. J . ( 2012). Acceptance and commitment therapy versus traditional cognitive behavioral therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current empirical evidence. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 12( 3), 333-357. doi: 10.1007/BF02266700URL |
| [68] | Schmidt F. L., & Hunter J. E ., ( 2015). Methods of meta-analysis: Correcting error and bias in research findings (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. |
| [69] | Stafford-Brown J., & Pakenham K. I . ( 2012). The effectiveness of an act informed intervention for managing stress and improving therapist qualities in clinical psychology trainees. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 68( 6), 592-513. doi: 10.1002/jclp.2012.68.issue-6URL |
| [70] | Swain J., Hancock K., Hainsworth C., & Bowman J . ( 2015). Mechanisms of change: Exploratory outcomes from a randomised controlled trial of acceptance and commitment therapy for anxious adolescents. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 4( 1), 56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2014.09.001URL |
| [71] | Takahashi M., Muto T., Tada M., & Sugiyama M . ( 2002). Acceptance rationale and increasing pain tolerance: Acceptance-based and Fear-based practice. Japanese Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 28, 35-46. |
| [72] | Trompetter H. R., Bohlmeijer E. T., Veehof M. M & Schreurs, K. M. G. .,(2015). Internet-based guided self-help intervention for chronic pain based on acceptance and commitment therapy: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 38( 1), 66-80. doi: 10.1007/s10865-014-9579-0URL |
| [73] | Villatte J. L., Vilardaga R., Villatte M., Plumb Vilardaga J. C., Atkins D. C., & Hayes S. C . ( 2016). Acceptance and commitment therapy modules: Differential impact on treatment processes and outcomes. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 77, 52-61. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2015.12.001URL |
| [74] | Viswesvaran C., & Ones D. S . ( 1995). Theory testing: Combining psychometric meta‐analysis and structural equations modeling. Personnel Psychology, 48( 4), 865-885. doi: 10.1111/peps.1995.48.issue-4URL |
| [75] | Wampold B. E . ( 2013). The great psychotherapy debate: Models, methods, and findings. New York, NY: Routledge. |
| [76] | Wampold B. E., & Imel Z. E . ( 2015). The great psychotherapy debate: The evidence for what makes psychotherapy work (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Routledge. |
| [77] | Waters C. S., Frude N., Flaxman P. E., & Boyd J . ( 2018). Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) for clinically distressed health care workers: Waitlist-controlled evaluation of an ACT workshop in a routine practice setting. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 57( 1), 82-98. doi: 10.1111/bjc.2018.57.issue-1URL |
| [78] | Westin V. Z., Schulin M., Hesser H., Karlsson M., Noe R. Z., Olofsson U., … Andersson G . ( 2011). Acceptance and commitment therapy versus tinnitus retraining therapy in the treatment of tinnitus: A randomised controlled trial. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49( 11), 737-747. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2011.08.001URL |
| [79] | Wetherell J. L., Afari N., Rutledge T., Sorrell J. T., Stoddard J. A., Petkus A. J., … Atkinson J. H . ( 2011). A randomized, controlled trial of acceptance and commitment therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy for chronic pain. Pain, 152( 9), 2098-2107. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.05.016URL |
| [80] | White R., Gumley A., McTaggart J., Rattrie L., McConville D., Cleare S., & Mitchell G . ( 2011). A feasibility study of acceptance and commitment therapy for emotional dysfunction following psychosis. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49( 12), 901-907. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2011.09.003URL |
| [81] | Wicksell R. K., Ahlqvist J., Bring A., Melin L., & Olsson G. L . ( 2008). Can exposure and acceptance strategies improve functioning and life satisfaction in people with chronic pain and whiplash-associated disorders (WAD)? A randomized controlled trial. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy, 37( 3), 169-182. doi: 10.1080/16506070802078970URL |
| [82] | Wicksell R. K., Kemani M., Jensen K., Kosek E., Kadetoff D., Sorjonen K., … Olsson G. L . ( 2013). Acceptance and commitment therapy for fibromyalgia: A randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Pain, 17( 4), 599-611. doi: 10.1002/ejp.2013.17.issue-4URL |
| [83] | Yadavaia J. E., Hayes S. C., & Vilardaga R . ( 2014). Using acceptance and commitment therapy to increase self-compassion: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 3( 4), 248-257. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2014.09.002URL |
| [84] | Zarling A., Lawrence E., & Marchman J . ( 2015). A randomized controlled trial of acceptance and commitment therapy for aggressive behavior. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 83( 1), 199-212. doi: 10.1037/a0037946URL |
| [85] | Zeng X. L., Liu X. P., & Yu S . ( 2011). The theoretical background, empirical study and future development of the acceptance and commitment therapy. Advances in Psychological Science, 19( 7), 1020-1026. |
| [ 曾祥龙, 刘翔平, 于是 . ( 2011). 接纳与承诺疗法的理论背景、实证研究与未来发展. 心理科学进展, 19( 7), 1020-1026.] | |
| [86] | Zettle R. D., Rains J. C., & Hayes S. C . ( 2011). Processes of change in acceptance and commitment therapy and cognitive therapy for depression: A mediation reanalysis of Zettle and Rains. Behavior Modification, 35( 3), 265-283. doi: 10.1177/0145445511398344URL |
| [87] | Zhang Q., Wang S. J., & Zhu Z. H . ( 2012). Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT): Psychopathological model and processes of change. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 26( 5), 377-381. |
| [ 张婍, 王淑娟, 祝卓宏 ( 2012). 接纳与承诺疗法的心理病理模型和治疗模式. 中国心理卫生杂志, 26( 5), 377-381.] |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 莫李澄, 郭田友, 张岳瑶, 徐锋, 张丹丹. 激活右腹外侧前额叶提高抑郁症患者对社会疼痛的情绪调节能力:一项TMS研究[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 494-504. |
| [2] | 孙启武, 吴才智, 于丽霞, 王巍欣, 沈国成. 阅读进度反馈信息对工作同盟和咨询效果的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(4): 349-361. |
| [3] | 侯娟, 朱英格, 方晓义. 手机成瘾与抑郁:社交焦虑和负性情绪信息注意偏向的多重中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(4): 362-373. |
| [4] | 江光荣, 李丹阳, 任志洪, 闫玉朋, 伍新春, 朱旭, 于丽霞, 夏勉, 李凤兰, 韦辉, 张衍, 赵春晓, 张琳. 中国国民心理健康素养的现状与特点[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(2): 182-198. |
| [5] | 梁一鸣, 郑昊, 刘正奎. 震后儿童创伤后应激障碍的症状网络演化[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(11): 1301-1312. |
| [6] | 韩毅初, 温恒福, 程淑华, 张淳淦, 李欣. 流动儿童歧视知觉与心理健康关系的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(11): 1313-1326. |
| [7] | 罗一君, 牛更枫, 陈红. 生命早期环境不可预测性对过度进食的影响:基于生命史理论[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(10): 1224-1236. |
| [8] | 李世峰, 吴艺玲, 张福民, 许琼英, 周爱保. 自我肯定缓冲新冠疫情引发的焦虑反应:一项随机对照研究[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(7): 886-894. |
| [9] | 李垚锦, 张微, 扶蓓, 周兵平. 成人注意缺陷多动障碍在内外源冲突时的表现:眼动的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(6): 777-785. |
| [10] | 任志洪, 赵春晓, 田凡, 闫玉朋, 李丹阳, 赵子仪, 谭梦鸰, 江光荣. 中国人心理健康素养干预效果的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 497-512. |
| [11] | 王文超, 伍新春. 共情对灾后青少年亲社会行为的影响:感恩、社会支持和创伤后成长的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(3): 307-316. |
| [12] | 李雄, 李祚山, 向滨洋, 孟景. 注意线索对自闭特质个体疼痛共情的影响:来自事件相关电位的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(3): 294-306. |
| [13] | 周爱保, 谢珮, 潘超超, 田喆, 谢君伟, 刘炯. 寻找丢失的自我——精神分裂症患者的自我面孔识别[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(2): 184-196. |
| [14] | 宫火良, 杨迪, 张方屹. 提问类型对自传体记忆概括化的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(12): 1318-1329. |
| [15] | 吕小康, 付春野, 汪新建. 反驳文本对患方信任和道德判断的影响与机制 *[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(10): 1171-1186. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4454
