 )
) 中国科学院行为科学重点实验室(中国科学院心理研究所), 北京 100101; 中国科学院大学心理学系, 北京 100049
收稿日期:2019-04-17出版日期:2019-12-15发布日期:2019-10-21通讯作者:李会杰E-mail:lihj@psych.ac.cn基金资助:* 科技部国家重点研发计划课题(2015CB351702);国家自然科学基金项目资助(31871143)Measurement of spatial navigation and application research in cognitive aging
ZHANG Jiaxin, HAI Lagan, LI Huijie( )
) Key Laboratory of Behavioral Science, Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China; Department of Psychology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Received:2019-04-17Online:2019-12-15Published:2019-10-21Contact:LI Huijie E-mail:lihj@psych.ac.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 空间导航是日常生活所必需的高级认知功能, 参与空间导航的海马及内嗅皮层等脑区易受到老化的影响并导致结构萎缩或功能紊乱。早期研究多利用动物实验、纸笔测验、现实环境等实验范式考察老年人的空间导航老化特点。由于具有与现实环境相似的场景、兼容磁共振成像扫描以及导航者可以与场景交互等优点, 虚拟现实技术被越来越多地被应用到空间导航的老化研究中, 并进一步揭示了海马等内侧颞叶脑区在空间导航老化中的重要作用。
图/表 4
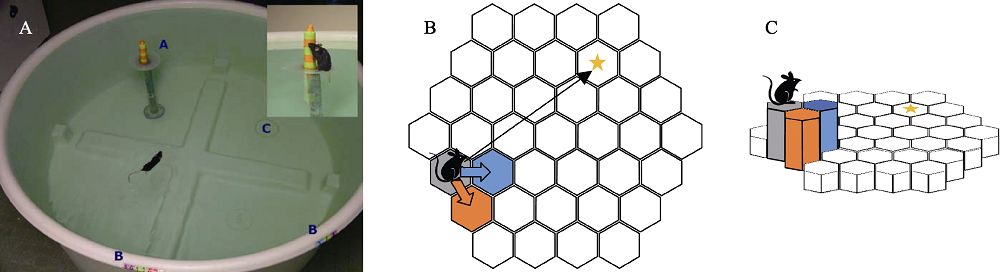
图1两类空间导航迷宫范式。A.莫里斯水迷宫范式, 不同的试次中, 导航者(小鼠)从圆形水池的不同起点出发, 通过近处、远处地标线索来定位隐藏平台, 并最终到达这一终点以避开厌恶刺激(水淹), 图片来自van Meer和Raber (2005); B.蜂巢迷宫范式, 当导航者处于任意平台时(除终点), 临近的平台中至多两块平台处于可通行状态, 导航者需要回忆终点位置, 通过反复地二择一, 最终到达终点。灰色正六边形为当前所处平台, 蓝色与橙色正六边形为抬升的紧邻平台; C.蜂巢迷宫范式的立体图。两类迷宫外围均存在远处的标志物, 以提供空间相对位置关系。黄色五角星代表正确的终点, 小鼠图标代表空间导航的起点, 蓝色平台更靠近终点, 为正确平台, 橙色平台距离终点更远, 为错误平台。
 图1两类空间导航迷宫范式。A.莫里斯水迷宫范式, 不同的试次中, 导航者(小鼠)从圆形水池的不同起点出发, 通过近处、远处地标线索来定位隐藏平台, 并最终到达这一终点以避开厌恶刺激(水淹), 图片来自van Meer和Raber (2005); B.蜂巢迷宫范式, 当导航者处于任意平台时(除终点), 临近的平台中至多两块平台处于可通行状态, 导航者需要回忆终点位置, 通过反复地二择一, 最终到达终点。灰色正六边形为当前所处平台, 蓝色与橙色正六边形为抬升的紧邻平台; C.蜂巢迷宫范式的立体图。两类迷宫外围均存在远处的标志物, 以提供空间相对位置关系。黄色五角星代表正确的终点, 小鼠图标代表空间导航的起点, 蓝色平台更靠近终点, 为正确平台, 橙色平台距离终点更远, 为错误平台。
图1两类空间导航迷宫范式。A.莫里斯水迷宫范式, 不同的试次中, 导航者(小鼠)从圆形水池的不同起点出发, 通过近处、远处地标线索来定位隐藏平台, 并最终到达这一终点以避开厌恶刺激(水淹), 图片来自van Meer和Raber (2005); B.蜂巢迷宫范式, 当导航者处于任意平台时(除终点), 临近的平台中至多两块平台处于可通行状态, 导航者需要回忆终点位置, 通过反复地二择一, 最终到达终点。灰色正六边形为当前所处平台, 蓝色与橙色正六边形为抬升的紧邻平台; C.蜂巢迷宫范式的立体图。两类迷宫外围均存在远处的标志物, 以提供空间相对位置关系。黄色五角星代表正确的终点, 小鼠图标代表空间导航的起点, 蓝色平台更靠近终点, 为正确平台, 橙色平台距离终点更远, 为错误平台。
图2不同类型的三角补全任务中的画面。A. Wolbers等(2007)研究中的三角补全任务只提供了地面的纹理信息, 画面的移动可以根据地面纹理的移动进行判断; B. Harris和Wolbers (2012)研究中的三角补全任务在地面上提供了不同大小、密度的圆点以提供视觉透视信息; C. Mahmood等(2009)的三角补全任务中采用了三种不同类型的场景。
 图2不同类型的三角补全任务中的画面。A. Wolbers等(2007)研究中的三角补全任务只提供了地面的纹理信息, 画面的移动可以根据地面纹理的移动进行判断; B. Harris和Wolbers (2012)研究中的三角补全任务在地面上提供了不同大小、密度的圆点以提供视觉透视信息; C. Mahmood等(2009)的三角补全任务中采用了三种不同类型的场景。
图2不同类型的三角补全任务中的画面。A. Wolbers等(2007)研究中的三角补全任务只提供了地面的纹理信息, 画面的移动可以根据地面纹理的移动进行判断; B. Harris和Wolbers (2012)研究中的三角补全任务在地面上提供了不同大小、密度的圆点以提供视觉透视信息; C. Mahmood等(2009)的三角补全任务中采用了三种不同类型的场景。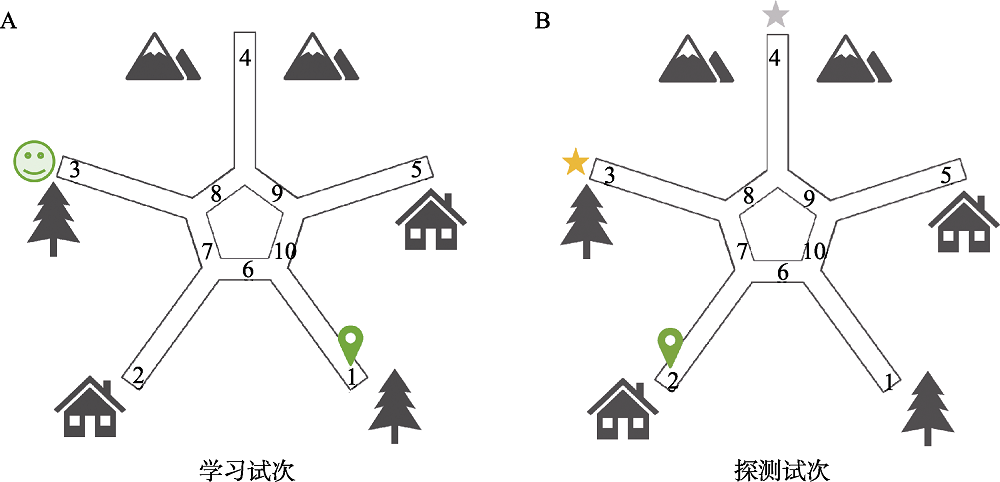
图3虚拟现实星型迷宫示意俯视图, 环境中存在各类地标以提供空间相对位置关系信息。A.学习试次中, 被试均从通道1出发, 学习并记忆位于通道3末端的终点。B.探测试次, 被试从通道2出发, 且被试提前不知道探测试次的存在。如果被试仍然移动至通道3, 则认为采用了非自我中心策略, 通过空间相对位置关系定位了终点; 反之, 如果被试移动至通道4, 则认为采用了自我中心策略, 通过记忆身体转向信息定位了终点(此处为左转-右转-左转)。绿色笑脸为学习试次中的正确终点, 到达之后, 被试会给予反馈, 黄色五角星代表非自我中心策略所对应终点, 灰色五角星代表自我中心策略所对应终点。
 图3虚拟现实星型迷宫示意俯视图, 环境中存在各类地标以提供空间相对位置关系信息。A.学习试次中, 被试均从通道1出发, 学习并记忆位于通道3末端的终点。B.探测试次, 被试从通道2出发, 且被试提前不知道探测试次的存在。如果被试仍然移动至通道3, 则认为采用了非自我中心策略, 通过空间相对位置关系定位了终点; 反之, 如果被试移动至通道4, 则认为采用了自我中心策略, 通过记忆身体转向信息定位了终点(此处为左转-右转-左转)。绿色笑脸为学习试次中的正确终点, 到达之后, 被试会给予反馈, 黄色五角星代表非自我中心策略所对应终点, 灰色五角星代表自我中心策略所对应终点。
图3虚拟现实星型迷宫示意俯视图, 环境中存在各类地标以提供空间相对位置关系信息。A.学习试次中, 被试均从通道1出发, 学习并记忆位于通道3末端的终点。B.探测试次, 被试从通道2出发, 且被试提前不知道探测试次的存在。如果被试仍然移动至通道3, 则认为采用了非自我中心策略, 通过空间相对位置关系定位了终点; 反之, 如果被试移动至通道4, 则认为采用了自我中心策略, 通过记忆身体转向信息定位了终点(此处为左转-右转-左转)。绿色笑脸为学习试次中的正确终点, 到达之后, 被试会给予反馈, 黄色五角星代表非自我中心策略所对应终点, 灰色五角星代表自我中心策略所对应终点。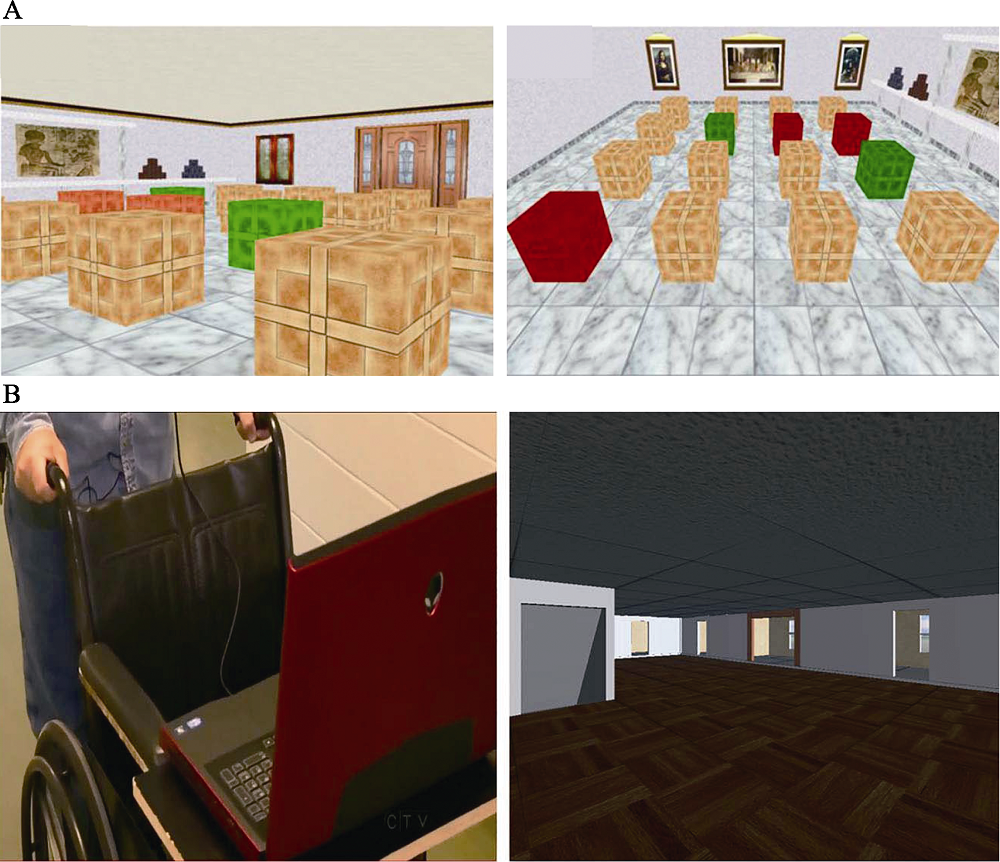
图4两类全新设计的虚拟现实空间导航老化实验。A. Tascon等(2018)采用的虚拟现实环境。左图, 被试需要使用手柄在虚拟现实环境中寻找特定木箱并进行按键反应; 右图, 被试无法进行移动, 但可以切换房间四个方向的视角, 根据固定的视角从房间中选择目标木箱; B. Ranjbar Pouya等(2017)采用的虚拟现实环境及操作方式, 老年人在开阔房间内推动轮椅, 计算机根据轮子的转动实时在虚拟现实环境中进行位移, 左图为老年被试进行实验操作, 右图为虚拟现实环境。
 图4两类全新设计的虚拟现实空间导航老化实验。A. Tascon等(2018)采用的虚拟现实环境。左图, 被试需要使用手柄在虚拟现实环境中寻找特定木箱并进行按键反应; 右图, 被试无法进行移动, 但可以切换房间四个方向的视角, 根据固定的视角从房间中选择目标木箱; B. Ranjbar Pouya等(2017)采用的虚拟现实环境及操作方式, 老年人在开阔房间内推动轮椅, 计算机根据轮子的转动实时在虚拟现实环境中进行位移, 左图为老年被试进行实验操作, 右图为虚拟现实环境。
图4两类全新设计的虚拟现实空间导航老化实验。A. Tascon等(2018)采用的虚拟现实环境。左图, 被试需要使用手柄在虚拟现实环境中寻找特定木箱并进行按键反应; 右图, 被试无法进行移动, 但可以切换房间四个方向的视角, 根据固定的视角从房间中选择目标木箱; B. Ranjbar Pouya等(2017)采用的虚拟现实环境及操作方式, 老年人在开阔房间内推动轮椅, 计算机根据轮子的转动实时在虚拟现实环境中进行位移, 左图为老年被试进行实验操作, 右图为虚拟现实环境。参考文献 115
| [1] | 胡镜清, 温泽淮, 赖世隆 . ( 2000). Morris水迷宫检测的记忆属性与方法学初探. 广州中医药大学学报, 17( 2), 117-119. |
| [2] | 胡志红, 闫君宝, 杨东伟 . ( 2016). 游泳训练次数对大鼠Morris水迷宫成绩的影响. 山西医科大学学报, 47( 1), 18-21. |
| [3] | 李丹, 杨昭宁 . ( 2015). 空间导航:路标学习和路径整合的关系. 心理科学进展, 23( 10), 1755-1762. doi: 10.3724/ sp.j.1042.2015.01755 |
| [4] | 罗小泉, 骆利平, 陈海芳, 涂明珠, 黎艳刚, 袁金斌, 杨武亮 . ( 2010). Morris水迷宫检测大鼠记忆力方法的探讨. 时珍国医国药, 21( 10), 2667-2669. |
| [5] | 王芳芳 . ( 2017). APOE风险基因和性别差异对空间导航能力相关脑结构的影响. (硕士), 南京大学 |
| [6] | 武文博 . ( 2015). 年龄和认知状态对空间导航能力影响的行为学研究及其脑网络基础. (硕士), 南京医科大学 |
| [7] | 武文博, 张冰, 徐运 . ( 2015). 空间导航——阿尔兹海默病早期诊断的新指标. 中国实用内科杂志, 35( 02), 168-170. |
| [8] | Allard, S., Gosein, V., Cuello, A. C., & Ribeiro-da-Silva, A . ( 2011). Changes with aging in the dopaminergic and noradrenergic innervation of rat neocortex. Neurobiology of Aging, 32( 12), 2244-2253. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging. 2009.12.023 |
| [9] | Allison, S. L., Fagan, A. M., Morris, J. C., & Head, D . ( 2016). Spatial navigation in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimers Dissease, 52( 1), 77-90. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150855 |
| [10] | Antonova, E., Parslow, D., Brammer, M., Dawson, G. R., Jackson, S. H., & Morris, R. G . ( 2009). Age-related neural activity during allocentric spatial memory. Memory, 17( 2), 125-143. doi: 10.1080/09658210802077348 |
| [11] | Bai, F., Zhang, Z., Watson, D. R., Yu, H., Shi, Y., Yuan, Y., .. Qian, Y . ( 2009). Abnormal functional connectivity of hippocampus during episodic memory retrieval processing network in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Biological Psychiatry, 65( 11), 951-958. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008. 10.017 |
| [12] | Banta Lavenex, P. A., Colombo, F., Ribordy Lambert, F., & Lavenex, P . ( 2014). The human hippocampus beyond the cognitive map: Evidence from a densely amnesic patient. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 711. doi: 10.3389/ fnhum.2014.00711 |
| [13] | Barnes, C. A., Nadel, L., & Honig, W. K . ( 1980). Spatial memory deficit in senescent rats. Canadian Journal of Psychologyl, 34( 1), 29-39. |
| [14] | Barrash, J. (1994). Age-related decline in route learning ability. Developmental Neuropsychology, 10( 3), 189-201. |
| [15] | Bellassen, V., Igloi, K., de Souza, L. C., Dubois, B., & Rondi-Reig, L . ( 2012). Temporal order memory assessed during spatiotemporal navigation as a behavioral cognitive marker for differential Alzheimer's disease diagnosis. Journal of Neuroscience, 32( 6), 1942-1952. doi: 10.1523/ JNEUROSCI.4556-11.2012 |
| [16] | Besnard, S., Machado, M. L., Vignaux, G., Boulouard, M., Coquerel, A., Bouet, V., .. Lelong-Boulouard, V . ( 2012). Influence of vestibular input on spatial and nonspatial memory and on hippocampal NMDA receptors. Hippocampus, 22( 4), 814-826. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20942 |
| [17] | Boccia, M., Nemmi, F., & Guariglia, C . ( 2014). Neuropsychology of environmental navigation in humans: Review and meta-analysis of FMRI studies in healthy participants. Neuropsychology Review, 24( 2), 236-251. doi: 10.1007/s11065-014-9247-8 |
| [18] | Bohbot, V. D., Lerch, J., Thorndycraft, B., Iaria, G., & Zijdenbos, A. P . ( 2007). Gray matter differences correlate with spontaneous strategies in a human virtual navigation task. Journal of Neuroscience, 27( 38), 10078-10083. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1763-07.2007 |
| [19] | Bohil, C. J., Alicea, B., & Biocca, F. A . ( 2011). Virtual reality in neuroscience research and therapy. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12( 12), 752-762. doi: 10.1038/nrn3122 |
| [20] | Bullens, J., Igloi, K., Berthoz, A., Postma, A., & Rondi-Reig, L . ( 2010). Developmental time course of the acquisition of sequential egocentric and allocentric navigation strategies. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 107( 3), 337-350. doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2010.05.010 |
| [21] | Burgdorf, J., Zhang, X. L., Weiss, C., Matthews, E., Disterhoft, J. F., Stanton, P. K., & Moskal, J. R . ( 2011). The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulator GLYX-13 enhances learning and memory, in young adult and learning impaired aging rats. Neurobiology of Aging, 32( 4), 698-706. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.04.012 |
| [22] | Burgess, N., Maguire, E. A., & O'Keefe, J . ( 2002). The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron, 35( 4), 625-641. |
| [23] | Byrne, P., Becker, S., & Burgess, N . ( 2007). Remembering the past and imagining the future: A neural model of spatial memory and imagery. Psychological Review, 114( 2), 340-375. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.114.2.340 |
| [24] | Cabeza, R., Anderson, N. D., Locantore, J. K., & McIntosh, A. R . ( 2002). Aging gracefully: Compensatory brain activity in high-performing older adults. NeuroImage, 17( 3), 1394-1402. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2002.1280 |
| [25] | Chersi, F., & Burgess, N. (2015). The cognitive architecture of spatial navigation: Hippocampal and striatal contributions. Neuron, 88( 1), 64-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.021 |
| [26] | Cogne, M., Taillade, M., N'Kaoua, B., Tarruella, A., Klinger, E., Larrue, F., .. Sorita, E . ( 2017). The contribution of virtual reality to the diagnosis of spatial navigation disorders and to the study of the role of navigational aids: A systematic literature review. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, 60( 3), 164-176. doi: 10.1016/ j.rehab.2015.12.004 |
| [27] | Colombo, D., Serino, S., Tuena, C., Pedroli, E., Dakanalis, A., Cipresso, P., & Riva, G . ( 2017). Egocentric and allocentric spatial reference frames in aging: A systematic review. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 80, 605-621. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.07.012 |
| [28] | Cong, S., Risacher, S. L., West, J. D., Wu, Y. C., Apostolova, L. G., Tallman, E., .. Shen, L . ( 2018). Volumetric comparison of hippocampal subfields extracted from 4- minute accelerated vs. 8-minute high-resolution T2-weighted 3T MRI scans. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 12( 6), 1583-1595. doi: 10.1007/s11682-017-9819-3 |
| [29] | Coughlan, G., Laczo, J., Hort, J., Minihane, A. M., & Hornberger, M . ( 2018). Spatial navigation deficits - overlooked cognitive marker for preclinical Alzheimer disease? Nature Reviews Neurology, 14( 8), 496-506. doi: 10.1038/s41582-018-0031-x |
| [30] | Coutureau, E., & Di Scala, G. (2009). Entorhinal cortex and cognition. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 33( 5), 753-761. doi: 10.1016/j. pnpbp.2009.03.038 |
| [31] | Cushman, L. A., Stein, K., & Duffy, C. J . ( 2008). Detecting navigational deficits in cognitive aging and Alzheimer disease using virtual reality. Neurology, 71( 12), 888-895. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000326262.67613.fe |
| [32] | Dahmani, L., & Bohbot, V. D . ( 2015). Dissociable contributions of the prefrontal cortex to hippocampus- and caudate nucleus-dependent virtual navigation strategies. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 117, 42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.07.002 |
| [33] | Daugherty, A. M., Yuan, P., Dahle, C. L., Bender, A. R., Yang, Y., & Raz, N . ( 2015). Path complexity in virtual water maze navigation: Differential associations with age, sex, and regional brain volume. Cerebral Cortex, 25( 9), 3122-3131. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhu107 |
| [34] | Davis, R. L., & Weisbeck, C. (2015). Search strategies used by older adults in a virtual reality place learning task. Gerontologist, 55 Suppl 1, S118-127. doi: 10.1093/geront/ gnv020 |
| [35] | de Bruin, J. P. C., Sànchez-Santed, F., Heinsbroek, R. P. W., Donker, A., & Postmes, P . ( 1994). A behavioural analysis of rats with damage to the medial prefrontal cortex using the morris water maze: Evidence for behavioural flexibility, but not for impaired spatial navigation. Brain Research, 652( 2), 323-333. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993 (94)90243-7 |
| [36] | Doeller, C. F., Barry, C., & Burgess, N . ( 2010). Evidence for grid cells in a human memory network. Nature, 463( 7281), 657-661. doi: 10.1038/nature08704 |
| [37] | Driscoll, I., Hamilton, D. A., Yeo, R. A., Brooks, W. M., & Sutherland, R. J . ( 2005). Virtual navigation in humans: The impact of age, sex, and hormones on place learning. Hormones and Behavior, 47( 3), 326-335. doi: 10.1016/j. yhbeh.2004.11.013 |
| [38] | Duffy, C. J . ( 2009). Visual motion processing in aging and Alzheimer's disease: neuronal mechanisms and behavior from monkeys to man. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1170( 1), 736-744. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632. 2009.04021.x |
| [39] | Duvernoy, H.M . ( 2005). The human hippocampus: functional anatomy, vascularization and serial sections with MRI: Springer Science & Business Media. |
| [40] | Fouquet, C., Tobin, C., & Rondi-Reig, L . ( 2010). A new approach for modeling episodic memory from rodents to humans: the temporal order memory. Behavioural Brain Research, 215( 2), 172-179. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.05.054 |
| [41] | Fu, H., Rodriguez, G. A., Herman, M., Emrani, S., Nahmani, E., Barrett, G., .. Duff, K. E . ( 2017). Tau pathology induces excitatory neuron loss, grid cell dysfunction, and spatial memory deficits reminiscent of early Alzheimer's disease. Neuron, 93( 3), 533- 541 e535. doi: 10.1016/j. neuron.2016.12.023 |
| [42] | Garcia-Betances, R. I., Arredondo Waldmeyer, M. T., Fico, G., & Cabrera-Umpierrez, M. F . ( 2015). A succinct overview of virtual reality technology use in Alzheimer's disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 7, 80. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00080 |
| [43] | Gazova, I., Laczo, J., Rubinova, E., Mokrisova, I., Hyncicova, E., Andel, R., .. Hort, J . ( 2013). Spatial navigation in young versus older adults. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 5, 94. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2013.00094 |
| [44] | Gramann, K., Muller, H. J., Eick, E. M., & Schonebeck, B . ( 2005). Evidence of separable spatial representations in a virtual navigation task. Journal of Experimental Psychology-Human Perception and Performance, 31( 6), 1199-1223. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.31.6.1199 |
| [45] | Groth-Marnat, G., & Teal, M. (2000). Block design as a measure of everyday spatial ability: A study of ecological validity. Perceptual and motor skills, 90( 2), 522-526. doi: Doi 10.2466/Pms.90.2.522-526 |
| [46] | Guzowski, J. F., Knierim, J. J., & Moser, E. I . ( 2004). Ensemble dynamics of hippocampal regions CA3 and CA1. Neuron, 44( 4), 581-584. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.11.003 |
| [47] | Harris, M. A., Wiener, J. M., & Wolbers, T . ( 2012). Aging specifically impairs switching to an allocentric navigational strategy. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 4, 29. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2012.00029 |
| [48] | Harris, M. A., & Wolbers, T. (2012). Ageing effects on path integration and landmark navigation. Hippocampus, 22( 8), 1770-1780. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22011 |
| [49] | Harris, M. A., & Wolbers, T. (2014). How age-related strategy switching deficits affect wayfinding in complex environments. Neurobiology of Aging, 35( 5), 1095-1102. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.10.086 |
| [50] | Hartley, T., Maguire, E. A., Spiers, H. J., & Burgess, N . ( 2003). The well-worn route and the path less traveled: Distinct neural bases of route following and wayfinding in humans. Neuron, 37( 5), 877-888. |
| [51] | Horner, A. J., Bisby, J. A., Zotow, E., Bush, D., & Burgess, N . ( 2016). Grid-like processing of imagined navigation. Current Biology, 26( 6), 842-847. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016. 01.042 |
| [52] | Hort, J., Laczo, J., Vyhnalek, M., Bojar, M., Bures, J., & Vlcek, K . ( 2007). Spatial navigation deficit in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104( 10), 4042-4047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611314104 |
| [53] | Howard, L. R., Javadi, A. H., Yu, Y., Mill, R. D., Morrison, L. C., Knight, R., .. Spiers, H. J . ( 2014). The hippocampus and entorhinal cortex encode the path and Euclidean distances to goals during navigation. Current Biology, 24( 12), 1331-1340. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.05.001 |
| [54] | Iaccarino, H. F., Singer, A. C., Martorell, A. J., Rudenko, A., Gao, F., Gillingham, T. Z., .. Tsai, L. H . ( 2016). Gamma frequency entrainment attenuates amyloid load and modifies microglia. Nature, 540( 7632), 230-235. doi: 10.1038/ nature20587 |
| [55] | Iaria, G., Petrides, M., Dagher, A., Pike, B., & Bohbot, V. D . ( 2003). Cognitive strategies dependent on the hippocampus and caudate nucleus in human navigation: variability and change with practice. Journal of Neuroscience, 23( 13), 5945-5952. |
| [56] | Igloi, K., Doeller, C. F., Paradis, A. L., Benchenane, K., Berthoz, A., Burgess, N., & Rondi-Reig, L . ( 2015). Interaction between hippocampus and cerebellum Crus I in sequence-based but not place-based navigation. Cerebral Cortex, 25( 11), 4146-4154. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhu132 |
| [57] | Igloi, K., Zaoui, M., Berthoz, A., & Rondi-Reig, L . ( 2009). Sequential egocentric strategy is acquired as early as allocentric strategy: Parallel acquisition of these two navigation strategies. Hippocampus, 19( 12), 1199-1211. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20595 |
| [58] | Joy, S., Fein, D., Kaplan, E., & Freedman, M . ( 2001). Quantifying qualitative features of Block Design performance among healthy older adults. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 16( 2), 157-170. |
| [59] | Julian, J. B., Ryan, J., Hamilton, R. H., & Epstein, R. A . ( 2016). The occipital place area is causally involved in representing environmental boundaries during navigation. Current Biology, 26( 8), 1104-1109. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016. 02.066 |
| [60] | Kirasic, K. C . ( 1991). Spatial cognition and behavior in young and elderly adults: Implications for learning new environments. Psychology and Aging, 6( 1), 10-18. |
| [61] | Klencklen, G., Despres, O., & Dufour, A . ( 2012). What do we know about aging and spatial cognition? Reviews and perspectives. Ageing Research Reviews, 11( 1), 123-135. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2011.10.001 |
| [62] | Knierim, J. J., & Neunuebel, J. P . ( 2016). Tracking the flow of hippocampal computation: Pattern separation, pattern completion, and attractor dynamics. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 129, 38-49. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm. 2015.10.008 |
| [63] | Konishi, K., Bhat, V., Banner, H., Poirier, J., Joober, R., & Bohbot, V. D . ( 2016). APOE2 Is Associated with spatial navigational strategies and increased gray matter in the hippocampus. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 349. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00349 |
| [64] | Konishi, K., & Bohbot, V. D . ( 2013). Spatial navigational strategies correlate with gray matter in the hippocampus of healthy older adults tested in a virtual maze. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 5, 1. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2013.00001 |
| [65] | Kunz, L., Schroder, T. N., Lee, H., Montag, C., Lachmann, B., Sariyska, R., .. Axmacher, N . ( 2015). Reduced grid-cell-like representations in adults at genetic risk for Alzheimer's disease. Science, 350( 6259), 430-433. doi: 10.1126/science.aac8128 |
| [66] | Lavenex, P. B., Amaral, D. G., & Lavenex, P . ( 2006). Hippocampal lesion prevents spatial relational learning in adult macaque monkeys. Journal of Neuroscience, 26( 17), 4546-4558. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5412-05.2006 |
| [67] | Leal, S.L., & Yassa, M. A . ( 2015). Neurocognitive aging and the hippocampus across species. Trends in Neurosciences, 38( 12), 800-812. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2015.10.003 |
| [68] | Lemay, M., Bertram, C. P., & Stelmach, G. E . ( 2004). Pointing to an allocentric and egocentric remembered target in younger and older adults. Experimental Aging Research, 30( 4), 391-406. doi: 10.1080/03610730490484443 |
| [69] | Lester, A. W., Moffat, S. D., Wiener, J. M., Barnes, C. A., & Wolbers, T . ( 2017). The aging navigational system. Neuron, 95( 5), 1019-1035. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.06.037 |
| [70] | Liang, Z., Yang, Y., Li, G., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Zhou, Y., & Leventhal, A. G . ( 2010). Aging affects the direction selectivity of MT cells in rhesus monkeys. Neurobiology of Aging, 31( 5), 863-873. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging. 2008.06.013 |
| [71] | Lithfous, S., Dufour, A., Blanc, F., & Despres, O . ( 2014). Allocentric but not egocentric orientation is impaired during normal aging: An ERP study. Neuropsychology, 28( 5), 761-771. doi: 10.1037/neu0000084 |
| [72] | Lovden, M., Schaefer, S., Noack, H., Bodammer, N. C., Kuhn, S., Heinze, H. J., .. Lindenberger, U . ( 2012). Spatial navigation training protects the hippocampus against age-related changes during early and late adulthood. Neurobiology of Aging, 33( 3), 620 e629-620 e622. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.02.013 |
| [73] | Mahmood, O., Adamo, D., Briceno, E., & Moffat, S. D . ( 2009). Age differences in visual path integration. Behavioural Brain Research, 205( 1), 88-95. doi: 10.1016/j. bbr.2009.08.001 |
| [74] | Marquez, D. X., Hunter, R. H., Griffith, M. H., Bryant, L. L., Janicek, S. J., & Atherly, A. J . ( 2017). Older adult strategies for community wayfinding. Journal of Applied Gerontology, 36( 2), 213-233. doi: 10.1177/ 0733464815581481 |
| [75] | McHail, D. G., Valibeigi, N., & Dumas, T. C . ( 2018). A Barnes maze for juvenile rats delineates the emergence of spatial navigation ability. Learn Mem, 25( 3), 138-146. doi: 10.1101/lm.046300.117 |
| [76] | Migo, E. M., O'Daly, O., Mitterschiffthaler, M., Antonova, E., Dawson, G. R., Dourish, C. T., .. Morris, R. G . ( 2016). Investigating virtual reality navigation in amnestic mild cognitive impairment using fMRI. Neuropsychol, Development, and Cognition. Section B, Aging, Neuropsychology and Cognition, 23( 2), 196-217. doi: 10.1080/13825585.2015.1073218 |
| [77] | Moffat, S. D . ( 2009). Aging and spatial navigation: What do we know and where do we go? Neuropsychology Review, 19( 4), 478-489. doi: 10.1007/s11065-009-9120-3 |
| [78] | Moffat, S. D., Kennedy, K. M., Rodrigue, K. M., & Raz, N . ( 2007). Extrahippocampal contributions to age differences in human spatial navigation. Cerebral Cortex, 17( 6), 1274-1282. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhl036 |
| [79] | Monahan, J. B., Handelmann, G. E., Hood, W. F., & Cordi, A. A . ( 1989). D-cycloserine, a positive modulator of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, enhances performance of learning tasks in rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 34( 3), 649-653. |
| [80] | Morganti, F., Stefanini, S., & Riva, G . ( 2013). From allo- to egocentric spatial ability in early Alzheimer's disease: A study with virtual reality spatial tasks. Cognitive Neuroscience, 4( 3-4), 171-180. doi: 10.1080/17588928. 2013.854762 |
| [81] | Morris, R. (1984). Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 11( 1), 47-60. |
| [82] | Mueller, S. G., Yushkevich, P. A., Das, S., Wang, L., van Leemput, K., Iglesias, J. E., .. Weiner, M. W . ( 2018). Systematic comparison of different techniques to measure hippocampal subfield volumes in ADNI2. NeuroImage: Clinical, 17, 1006-1018. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.12.036 |
| [83] | Muffato, V., Meneghetti, C., & de Beni, R . ( 2016). Not all is lost in older adults' route learning: The role of visuo-spatial abilities and type of task. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 47, 230-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvp. 2016.07.003 |
| [84] | Nemmi, F., Boccia, M., & Guariglia, C . ( 2017). Does aging affect the formation of new topographical memories? Evidence from an extensive spatial training. Neuropsychol, Development, and Cognition. Section B, Aging, Neuropsychology and Cognition, 24( 1), 29-44. doi: 10.1080/ 13825585.2016.1167162 |
| [85] | Nori, R., Grandicelli, S., & Giusberti, F . ( 2006). Visuo- spatial ability and wayfinding performance in real-world. Cognitive Processing, 7( S1), 135-137. doi: 10.1007/ s10339-006-0104-4 |
| [86] | O'Keefe, J., & Burgess, N. (2005). Dual phase and rate coding in hippocampal place cells: Theoretical significance and relationship to entorhinal grid cells. Hippocampus, 15( 7), 853-866. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20115 |
| [87] | O'Keefe, J., & Dostrovsky, J. (1971). The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Research, 34( 1), 171-175. |
| [88] | Packard, M. G., & McGaugh, J.L . ( 1996). Inactivation of hippocampus or caudate nucleus with lidocaine differentially affects expression of place and response learning. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 65( 1), 65-72. doi: 10.1006/nlme.1996.0007 |
| [89] | Pine, D. S., Grun, J., Maguire, E. A., Burgess, N., Zarahn, E., Koda, V., .. Bilder, R. M . ( 2002). Neurodevelopmental aspects of spatial navigation: A virtual reality fMRI study. NeuroImage, 15( 2), 396-406. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2001.0988 |
| [90] | Ranjbar Pouya, O., Byagowi, A., Kelly, D. M., & Moussavi, Z . ( 2017). Introducing a new age-and-cognition-sensitive measurement for assessing spatial orientation using a landmark-less virtual reality navigational task. Quarterly journal of experimental psychology (Hove), 70( 7), 1406-1419. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2016.1187181 |
| [91] | Reisberg, B., Franssen, E. H., Hasan, S. M., Monteiro, I., Boksay, I., Souren, L. E., .. Kluger, A . ( 1999). Retrogenesis: Clinical, physiologic, and pathologic mechanisms in brain aging, Alzheimer's and other dementing processes. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 249( S3), 28-36. |
| [92] | Rodgers, M. K., Sindone, J. A., 3rd, & Moffat, S. D. (2012). Effects of age on navigation strategy. Neurobiology of Aging, 33( 1), 202 e215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging. 2010.07.021 |
| [93] | Ruggiero, G., D'Errico, O., & Iachini, T . ( 2016). Development of egocentric and allocentric spatial representations from childhood to elderly age. Psychological Research, 80( 2), 259-272. doi: 10.1007/s00426-015-0658-9 |
| [94] | Salthouse, T. A . ( 1979). Adult age and the speed-accuracy trade-off. Ergonomics, 22( 7), 811-821. doi: 10.1080/ 00140137908924659 |
| [95] | Sanders, A. E., Holtzer, R., Lipton, R. B., Hall, C., & Verghese, J . ( 2008). Egocentric and exocentric navigation skills in older adults. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 63( 12), 1356-1363. |
| [96] | Spiers, H. J., & Gilbert, S. J . ( 2015). Solving the detour problem in navigation: A model of prefrontal and hippocampal interactions. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 125. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00125 |
| [97] | Stangl, M., Achtzehn, J., Huber, K., Dietrich, C., Tempelmann, C., & Wolbers, T . ( 2018). Compromised grid-cell-like representations in old age as a key mechanism to explain age-related navigational deficits. Current Biology, 28( 7), 1108- 1115 e1106. doi: 10.1016/j. cub.2018.02.038 |
| [98] | Stark, S. M., & Stark, C. E. L . ( 2017). Age-related deficits in the mnemonic similarity task for objects and scenes. Behavioural Brain Research, 333, 109-117. doi: 10.1016/ j.bbr.2017.06.049 |
| [99] | Tangen, G. G., Engedal, K., Bergland, A., Moger, T. A., Hansson, O., & Mengshoel, A. M . ( 2015). Spatial navigation measured by the Floor Maze Test in patients with subjective cognitive impairment, mild cognitive impairment, and mild Alzheimer's disease. International Psychogeriatrics, 27( 8), 1401-1409. doi: 10.1017/ S1041610215000022 |
| [100] | Tascon, L., Castillo, J., Leon, I., & Cimadevilla, J. M . ( 2018). Walking and non-walking space in an equivalent virtual reality task: Sexual dimorphism and aging decline of spatial abilities. Behavioural Brain Research, 347, 201-208. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.03.022 |
| [101] | Techentin, C., Voyer, D., & Voyer, S. D . ( 2014). Spatial abilities and aging: A meta-analysis. Experimental Aging Research, 40( 4), 395-425. doi: 10.1080/0361073X.2014.926773 |
| [102] | Topic, B., Willuhn, I., Palomero-Gallagher, N., Zilles, K., Huston, J. P., & Hasenohrl, R. U . ( 2007). Impaired maze performance in aged rats is accompanied by increased density of NMDA, 5-HT1A, and alpha-adrenoceptor binding in hippocampus. Hippocampus, 17( 1), 68-77. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20246 |
| [103] | Tu, S., Spiers, H. J., Hodges, J. R., Piguet, O., & Hornberger, M . ( 2017). Egocentric versus allocentric spatial memory in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's Disease. Journal of Alzheimers Dissease, 59( 3), 883-892. doi: 10.3233/jad-160592 |
| [104] | Tu, S., Wong, S., Hodges, J. R., Irish, M., Piguet, O., & Hornberger, M . ( 2015). Lost in spatial translation - a novel tool to objectively assess spatial disorientation in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia. Cortex, 67, 83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2015.03.016 |
| [105] | van Meer, P., & Raber, J. (2005). Mouse behavioural analysis in systems biology. Biochemical Journal, 389(Pt 3), 593-610. doi: 10.1042/BJ20042023 |
| [106] | Wang, L., Zang, Y., He, Y., Liang, M., Zhang, X., Tian, L., .. Li, K . ( 2006). Changes in hippocampal connectivity in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease: Evidence from resting state fMRI. NeuroImage, 31( 2), 496-504. doi: 10.1016/j. neuroimage.2005.12.033 |
| [107] | Wiener, J. M., de Condappa, O., Harris, M. A., & Wolbers, T . ( 2013). Maladaptive bias for extrahippocampal navigation strategies in aging humans. Journal of Neuroscience, 33( 14), 6012-6017. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0717-12.2013 |
| [108] | Wilson, I. A., Gallagher, M., Eichenbaum, H., & Tanila, H . ( 2006). Neurocognitive aging: Prior memories hinder new hippocampal encoding. Trends in Neurosciences, 29( 12), 662-670. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2006.10.002 |
| [109] | Wilson, K. D., Woldorff, M. G., & Mangun, G. R . ( 2005). Control networks and hemispheric asymmetries in parietal cortex during attentional orienting in different spatial reference frames. NeuroImage, 25( 3), 668-683. doi: 10. 1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.075 |
| [110] | Wolbers, T., & Hegarty, M. (2010). What determines our navigational abilities? Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14( 3), 138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.01.001 |
| [111] | Wolbers, T., Wiener, J. M., Mallot, H. A., & Buchel, C . ( 2007). Differential recruitment of the hippocampus, medial prefrontal cortex, and the human motion complex during path integration in humans. Journal of Neuroscience, 27( 35), 9408-9416. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2146-07.2007 |
| [112] | Wood, R. A., Bauza, M., Krupic, J., Burton, S., Delekate, A., Chan, D., & O'Keefe, J . ( 2018). The honeycomb maze provides a novel test to study hippocampal-dependent spatial navigation. Nature, 554( 7690), 102-105. doi: 10.1038/ nature25433 |
| [113] | Wu, Z., Gao, Y., Shi, F., Ma, G., Jewells, V., & Shen, D . ( 2018). Segmenting hippocampal subfields from 3T MRI with multi-modality images. Medical Image Analysis, 43, 10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.09.006 |
| [114] | Yassa, M. A., Lacy, J. W., Stark, S. M., Albert, M. S., Gallagher, M., & Stark, C. E . ( 2011). Pattern separation deficits associated with increased hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus activity in nondemented older adults. Hippocampus, 21( 9), 968-979. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20808 |
| [115] | Yin, S., Zhu, X., Huang, X., & Li, J . ( 2015). Visuospatial characteristics of an elderly Chinese population: Results from the WAIS-R block design test. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 7, 17. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00017 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 王琳, 王志丹, 王泓婧. 孤独症儿童动作发展障碍的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(7): 1239-1250. |
| [2] | 张照, 张力为, 龚然. 视觉工作记忆的过滤效能[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 635-651. |
| [3] | 周爱保, 胡砚冰, 周滢鑫, 李玉, 李文一, 张号博, 郭彦麟, 胡国庆. 听而不“闻”?人声失认症的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 414-424. |
| [4] | 赵小红, 童薇, 陈桃林, 吴冬梅, 张蕾, 陈正举, 方晓义, 龚启勇, 唐小蓉. 敬畏的心理模型及其认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 520-530. |
| [5] | 魏真瑜, 邓湘树, 赵治瀛. 亲社会行为中的从众效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 531-539. |
| [6] | 岳童, 黄希庭, 傅安国. 人们何以能够“舍生取义”?基于保护性价值观认知神经机制的解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 540-548. |
| [7] | 薛冰, 王雪娇, 马宁, 高军. 催产素调控心理韧性:基于对海马的作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(2): 311-322. |
| [8] | 王葛彤, 席洁, 陈霓虹, 黄昌兵. 双眼视差的神经机制与知觉学习效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 56-69. |
| [9] | 郭滢, 龚先旻, 王大华. 错误记忆产生的认知与神经机制:信息加工视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 79-92. |
| [10] | 刘启鹏, 赵小云, 王翠艳, 徐艺雅, 王淑燕. 反刍思维与注意脱离损坏的关系及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 102-111. |
| [11] | 赵鑫, 郑巧萍. 童年贫困与晚年认知老化:加速还是延缓?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 160-166. |
| [12] | 翁纯纯, 王宁. 时距知觉的动物研究范式及相关神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(9): 1478-1492. |
| [13] | 杨晓梦, 王福兴, 王燕青, 赵婷婷, 高春颍, 胡祥恩. 瞳孔是心灵的窗口吗?——瞳孔在心理学研究中的应用及测量[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1029-1041. |
| [14] | 程士静, 何文广. 语义认知的习得、发展和老化及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1156-1163. |
| [15] | 张晶晶, 梁啸岳, 陈伊笛, 陈庆荣. 音乐句法加工的认知机制与音乐结构的影响模式[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(6): 883-892. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4884
