 ), 王舒曼, 李爱梅, 李斌
), 王舒曼, 李爱梅, 李斌 暨南大学管理学院, 广州 510632
收稿日期:2018-06-21出版日期:2019-06-15发布日期:2019-04-22通讯作者:李方君E-mail:lifangjun@jnu.edu.cn基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(71602076);国家自然科学基金项目(71601084);广东省自然科学基金项目支持(2017A030308013)Team voice effectiveness and its mechanism from the perspective of group information processing: The influence of voice quantity and quality
LI Fangjun( ), WANG Shuman, LI Aimei, LI Bin
), WANG Shuman, LI Aimei, LI Bin Management School, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
Received:2018-06-21Online:2019-06-15Published:2019-04-22Contact:LI Fangjun E-mail:lifangjun@jnu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 虽然团队建言被普遍认为会为团队带来积极结果(如高的团队绩效和团队创新), 但实证研究结果却并不一致。从群体信息加工的视角, 在团队层次区分建言质量与数量两个维度, 进而构建了建言起作用的正向和负向双路径模型, 探讨团队建言的有效性及其作用机制。主要内容包括:(1)开发团队建言质量与数量量表并检验其信效度, (2)检验团队建言的双路径模型, (3)开发针对团队领导的建言管理培训项目以切实提高团队建言的有效性。这不仅可以从理论上丰富和加深现有建言研究, 也将为团队管理实践提供支持。
图/表 1
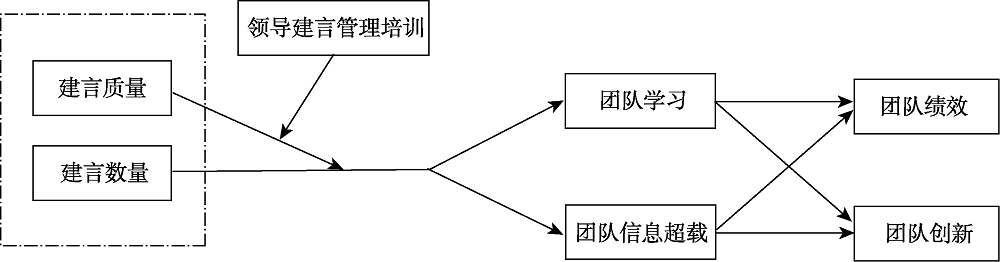
图1群体信息加工视角下的团队建言的双路径模型
 图1群体信息加工视角下的团队建言的双路径模型
图1群体信息加工视角下的团队建言的双路径模型参考文献 80
| 1 | 陈国权 . ( 2007). 团队学习和学习型团队: 概念、能力模型、 测量及对团队绩效的影响. 管理学报, 4( 5), 602-609. |
| 2 | 陈文平, 段锦云, 田晓明 . ( 2013). 员工为什么不建言: 基于中国文化视角的解析. 心理科学进展, 21( 5), 905-913. |
| 3 | 邓今朝, 黄中梅, 余绍忠 . ( 2015). 员工建言行为与团队绩效的关系——成员目标取向的作用. 软科学, 29( 6), 81-85. |
| 4 | 段锦云, 施嘉逸, 凌斌 . ( 2017). 高承诺组织与员工建言: 双过程模型检验. 心理学报, 49( 4), 539-553. |
| 5 | 段锦云, 钟建安 . ( 2012). 工作满意感与建言行为的关系探索: 组织承诺的缓冲影响. 管理工程学报, 26( 1), 170-174. |
| 6 | 李方君, 郑粉芳, 杨倩怡, 王舒曼 . ( 2018). 员工建言行为的结果及其调节机制. 心理科学进展, 26( 4), 710-718. |
| 7 | 梁建, 刘兆鹏 . ( 2016). 团队建言结构: 概念、前因及其对团队创新的影响. 中国人力资源开发, ( 5), 6-15. |
| 8 | 吕洁, 张钢 . ( 2013). 团队认知的涌现: 基于集体信息加工的视角. 心理科学进展, 21( 12), 2214-2223. |
| 9 | 莫申江, 谢小云 . ( 2009). 团队学习、交互记忆系统与团队绩效: 基于IMOI范式的纵向追踪研究. 心理学报, 41( 7), 639-648. |
| 10 | 吴梦, 白新文 . ( 2012). 动机性信息加工理论及其在工业与组织心理学中的应用. 心理科学进展, 20( 11), 1889-1898. |
| 11 | 肖君宜, 段锦云 . ( 2015). 团队层面建言行为研究: 员工建言研究的新视角. 人类工效学, 21( 2), 84-86. |
| 12 | 严瑜, 何亚男 . ( 2016). 领导对建言反应的动机感知作用机制: 基于归因理论的阐释. 心理科学进展, 24( 9), 1457-1466. |
| 13 | 于静静, 赵曙明 . ( 2013). 员工建言行为研究前沿探析与未来展望. 外国经济与管理, 35( 5), 23-30. |
| 14 | 赵祁, 李锋 . ( 2016). 团队领导与团队有效性: 基于社会认同理论的多层次研究. 心理科学进展, 24( 11), 1677-1689. |
| 15 | 周文娟 . ( 2013). 团队建言的前因与结果:变革型领导和任务互依性的作用(博士学位论文). 苏州大学. |
| 16 | Ackoff, R. L . ( 1967). Management misinformation systems. Management Science, 14( 4), 147-156. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.14.4.B147URL |
| 17 | Argote L., Gruenfeld D., & Naquin C . ( 2001). Group learning in organizations. Groups at Work: Theory and Research, 614, 369-411. |
| 18 | Bang N., Chen J., & Cremer D. D . ( 2017). When new product development fails in China: Mediating effects of voice behaviour and learning from failure. Asia Pacific Business Review, 23( 4), 559-575. doi: 10.1080/13602381.2017.1339455URL |
| 19 | Barry, M., & Wilkinson, A . ( 2016). Pro-social or pro-management? A critique of the conception of employee voice as a pro-social behaviour within organizational behaviour. British Journal of Industrial Relations, 54( 2), 261-284. doi: 10.1111/bjir.2016.54.issue-2URL |
| 20 | Bashshur, M. R., & Oc, B . ( 2015). When voice matters: A multilevel review of the impact of voice in organizations. Journal of Management, 41( 5), 1530-1554. |
| 21 | Bunderson, J. S., & Sutcliffe, K. M . ( 2003). Management team learning orientation and business unit performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88( 3), 552-560. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.3.552URL |
| 22 | Burris E. R., Detert J. R., & Romney A. C . ( 2013). Speaking up vs. being heard: The disagreement around and outcomes of employee voice. Organization Science, 24( 1), 22-38. doi: 10.1287/orsc.1110.0732URL |
| 23 | Burris E. R., Rockmann K. W., & Kimmons Y. S . ( 2017). The value of voice to managers: Employee identification and the content of voice. Academy of Management Journal, 60( 6), 2099-2125. doi: 10.5465/amj.2014.0320URL |
| 24 | Byyny, R. L . ( 2016). Information and cognitive overload: How much is too much?. The Pharos of Alpha Omega Alpha-Honor Medical Society, 79( 4), 2-7. |
| 25 | Cannon-Bowers, J. A., & Bowers, C . ( 2011). Team development and functioning. In S. Zedeck (Ed.), APA Handbooks in Psychology. APA handbook of industrial and organizational psychology (Vol, 1, pp. 597-650). Washington, DC, US: American Psychological Association. |
| 26 | Chatalalsingh, C., & Reeves, S . ( 2014). Leading team learning: What makes interprofessional teams learn to work well? Journal of Interprofessional Care, 28( 6), 513-518. doi: 10.3109/13561820.2014.900001URL |
| 27 | Colquitt J., Lepine J. A., Wesson M. J., & Gellatly I. R . ( 2011). Organizational behavior: Improving performance and commitment in the workplace (2th ed.). NY: McGraw-Hill Irwin. |
| 28 | de Dreu. C. K. W . ( 2007). Cooperative outcome interdependence, task reflexivity, and team effectiveness: A motivated information processing perspective. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92( 3), 628-638. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.92.3.628URL |
| 29 | Detert, J. R., & Burris, ER, . ( 2007). Leadership behavior and employee voice: Is the door really open? Academy of Management Journal, 50( 4), 869-884. doi: 10.5465/amj.2007.26279183URL |
| 30 | Detert J. R., Burris E. R., Harrison D. A., & Martin S. R . ( 2013). Voice flows to and around leaders: Understanding when units are helped or hurt by employee voice. Administrative Science Quarterly, 58( 4), 624-668. doi: 10.1177/0001839213510151URL |
| 31 | Edmondson A . ( 1999). Psychological safety and learning behavior in work teams. Administrative Science Quarterly, 44( 2), 350-383. doi: 10.2307/2666999URL |
| 32 | Edmunds, A., & Morris, A . ( 2000). The problem of information overload in business organisations: A review of the literature. International Journal of Information Management, 20( 1), 17-28. doi: 10.1016/S0268-4012(99)00051-1URL |
| 33 | Farh, C. I. C., & Chen, G . ( 2018). Leadership and member voice in action teams: Test of a dynamic phase model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 103( 1), 97-110. doi: 10.1037/apl0000256URL |
| 34 | Fast N. J., Burris E. R., & Bartel C. A . ( 2015). Managing to stay in the dark: Managerial self-efficacy, ego defensiveness, and the aversion to employee voice. Academy of Management Journal, 57( 4), 1013-1034. |
| 35 | Flanagan, J. C . ( 1954). The critical incident technique. Psychological Bulletin, 51( 4), 327-358. doi: 10.1037/h0061470URL |
| 36 | Frazier, M. L . ( 2009). Voice climate in organizations: A group-level examination of antecedents and performance outcomes (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Oklahoma State University. |
| 37 | Frazier, M. L., & Bowler, W. M . ( 2012). Voice climate, supervisor undermining, and work outcomes: A group- level examination. Journal of Management, 41( 3), 841-863. |
| 38 | Friedrich A. L., Sjöberg A., & Friedrich P . ( 2016). Leaned teamwork fattens workplace innovation: The relationship between task complexity, team learning and team proactivity. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 25( 4), 561-569. |
| 39 | Halle, Y . ( 2016). Influence of leader and follower behavior on employee voice, team task responsibility, and team effectiveness (Unpublished Master’s thesis). University of Twente. |
| 40 | Hemp, P . ( 2009). Death by information overload. Harvard Bbusiness Review, 87( 9), 82-89. |
| 41 | Hinsz V. B., Tindale R. S., & Vollrath D. A . ( 1997). The emerging conceptualization of groups as information processors. Psychological Bulletin, 121( 1), 43-64. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.121.1.43URL |
| 42 | Hong T. M. B., Baruch Y., Chau V. S., & He H-W . ( 2016). Team learning: The missing construct from a cross- cultural examination of higher education. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 33( 1), 29-51. doi: 10.1007/s10490-015-9426-zURL |
| 43 | Huang, L., & Patersonc, T. A . ( 2014). Group ethical voice: Influence of ethical leadership and impact on ethical performance. Journal of Management, 43( 4), 1157-1184. |
| 44 | Jiang, J . ( 2017). Mean leader-member exchange and team voice: Roles of team task reflexivity and perspective taking. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 45( 7), 1221-1232. doi: 10.2224/sbp.6451URL |
| 45 | Jiménez-Jiménez, D., & Sanz-Valle, R . ( 2011). Innovation, organizational learning, and performance. Journal of Business Research, 64( 4), 408-417. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2010.09.010URL |
| 46 | Kahneman, D . ( 1973). Attention and effort. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. |
| 47 | Kaufman, B. E . ( 2015). Theorising determinants of employee voice: An integrative model across disciplines and levels of analysis. Human Resource Management Journal, 25( 1), 19-40. doi: 10.1111/hrmj.2015.25.issue-1URL |
| 48 | Killumets E., D’innocenzo L., Maynard M. T., & Mathieu J. E . ( 2015). A multilevel examination of the impact of team interpersonal processes. Small Group Research, 46( 2), 227-259. doi: 10.1177/1046496415573631URL |
| 49 | Kouvonen A., Toppinen-Tanner S., Huuhtanen M. K. P., & Kalimo R . ( 2005). Job characteristics and burnout among aging professionals in information and communications technology. Psychological Reports, 97( 2), 505-514. doi: 10.2466/PR0.97.6.505-514URL |
| 50 | Kozlowski, S. W. J., & Bell, B. S . ( 2003). Work groups and teams in organizations. In W. C. Borman., D. R. Ilgen, & R. J. Klimoski (Eds.), Handbook of psychology: Industrial and organizational psychology (vol. 12, pp. 333-375). New York: Wiley. |
| 51 | Li A. N., Liao H., Tangirala S., & Firth B. M . ( 2017). The content of the message matters: The differential effects of promotive and prohibitive team voice on team productivity and safety performance gains. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102( 8), 1259-1270. |
| 52 | Liang J., Farh C. I., & Farh J-L . ( 2012). Psychological antecedents of promotive and prohibitive voice: A two-wave examination. Academy of Management Journal, 55( 1), 71-92. doi: 10.5465/amj.2010.0176URL |
| 53 | Liang, J., & Rui, S . ( 2017). Employee voice and team innovation: Examining the role of team voice intensity in R&D teams. Academy of Management Proceedings, 2017( 1), 11515. doi: 10.5465/AMBPP.2017.11515abstractURL |
| 54 | Lin, S-H., & Johnson, R. E . ( 2015). A suggestion to improve a day keeps your depletion away: Examining promotive and prohibitive voice behaviors within a regulatory focus and ego depletion framework. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100( 5), 1381-1397. doi: 10.1037/apl0000018URL |
| 55 | Liu W., Song Z., Li X., & Liao Z . ( 2017). Why and when leader’s affective states influence employee upward voice. Academy of Management Journal, 60( 1), 238-263. doi: 10.5465/amj.2013.1082URL |
| 56 | Luthans, F . ( 2011). Organizational behavior: An evidence- based approach. McGraw-Hill. |
| 57 | Mackenzie S. B., Podsakoff P. M., & Podsakoff N. P . ( 2011). Challenge-oriented organizational citizenship behaviors and organizational effectiveness: Do challenge- oriented behaviors really have an impact on the organization’s bottom line?. Personnel Psychology, 64( 3), 559-592. doi: 10.1111/peps.2011.64.issue-3URL |
| 58 | McClean E. J., Martin S. R., Emich K. J., & Woodruff T . ( 2017). The social consequences of voice: An examination of voice type and gender on status and subsequent leader emergence. Academy of Management Journal, 61( 5), 1869-1891. |
| 59 | Morrison, E. W . ( 2014). Employee voice and silence. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 1( 1), 173-197. doi: 10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-031413-091328URL |
| 60 | Morrison, E. W . ( 2011). Employee voice behavior: Integration and directions for future research. The Academy of Management Annals, 5( 1), 373-412. doi: 10.5465/19416520.2011.574506URL |
| 61 | Mowbray P. K., Wilkinson A., & Tse, H. H. M . ( 2015). An integrative review of employee voice: Identifying a common conceptualization and research agenda. International Journal of Management Reviews, 17( 3), 382-400. doi: 10.1111/ijmr.12045URL |
| 62 | Ng, T. W. H., & Feldman, D. C . ( 2012). Employee voice behavior: A meta-analytic test of the conservation of resources framework. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33( 2), 216-234. doi: 10.1002/job.754URL |
| 63 | Ng, T. W. H., & Feldman, D. C . ( 2015). Idiosyncratic deals and voice behavior. Journal of Management, 41( 3), 893-928. |
| 64 | Oldroyd, J. B., & Morris, S. S . ( 2012). Catching falling stars: A human resource response to social capital’s detrimental effect of information overload on star employees. Academy of Management Review, 37( 3), 396-418. |
| 65 | Rasheed M. A., Shahzad K., Conroy C., Nadeem S., & Siddique M. U . ( 2017). Exploring the role of employee voice between high-performance work system and organizational innovation in small and medium enterprises. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 24( 4), 670-688. doi: 10.1108/JSBED-11-2016-0185URL |
| 66 | Robbins, S. P., & Coulter, M. A . ( 2018). Management (14th ed.). London, England: Pearson Education. |
| 67 | Ruck K., Welch M., & Menara B . ( 2017). Employee voice: An antecedent to organisational engagement?. Public Relations Review, 43( 5), 904-914. doi: 10.1016/j.pubrev.2017.04.008URL |
| 68 | Santos C. M., Passos A. M., & Uitdewilligen S . ( 2016). When shared cognition leads to closed minds: Temporal mental models, team learning, adaptation and performance. European Management Journal, 34( 3), 258-268. doi: 10.1016/j.emj.2015.11.006URL |
| 69 | Sparrow, P . ( 1999). Strategy and cognition: Understanding the role of management knowledge structures, organizational memory and information overload. Creativity and Innovation Management, 8( 2), 140-148. doi: 10.1111/caim.1999.8.issue-2URL |
| 70 | Speier C., Valacich J. S., & Vessey I . ( 1999). The influence of task interruption on individual decision making: An information overload perspective. Decision Sciences, 30( 2), 337-360. doi: 10.1111/deci.1999.30.issue-2URL |
| 71 | Stvilia B., Gasser L., Twidale M. B., & Smith L. C . ( 2007). A framework for information quality assessment. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 58( 12), 1720-1733. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1532-2890URL |
| 72 | van der Vegt, G. S., & Bunderson, J. S . ( 2005). Learning and performance in multidisciplinary teams: The importance of collective team identification. Academy of Management Journal, 48( 3), 532-547. doi: 10.5465/amj.2005.17407918URL |
| 73 | van Dyne, L., & Lepine, J. A . ( 1998). Helping and voice extra-role behaviors: Evidence of construct and predictive validity. Academy of Management Journal, 41( 1), 108-119. |
| 74 | Wang D., Gan C., Wu C., & Wang D . ( 2015). Ethical leadership and employee voice: Employee self-efficacy and self-impact as mediators. Psychological Reports, 116( 3), 751-767. doi: 10.2466/01.07.PR0.116k29w9URL |
| 75 | Wei X., Zhang Z-X., & Chen X-P . ( 2015). I will speak up if my voice is socially desirable: A moderated mediating process of promotive versus prohibitive voice. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100( 5), 1641-1652. doi: 10.1037/a0039046URL |
| 76 | Weiss, M., & Morrison, E. W . ( 2018). Speaking up and moving up: How voice can enhance employees’ social status. Journal of Organizational Behavior. Doi: 10.1002/job.2262 |
| 77 | West, M. A . ( 2002). Sparkling fountains or stagnant ponds: An integrative model of creativity and innovation implementation in work groups. Applied Psychology, 51( 3), 355-387. |
| 78 | Zhou, J., & Hoever I. J . ( 2014). Research on workplace creativity: A review and redirection. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 1( 1), 333-359. |
| 79 | Zhou, J., & Shalley, C. E . (Eds.). ( 2007). Handbook of organizational creativity. New York, NY: Erlbaum. |
| 80 | Zhou J., Shin S. J., Brass D. J., Choi J., & Zhang Z. X . ( 2009). Social networks, personal values, and creativity: Evidence for curvilinear and interaction effects. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94( 6), 1544-1552. |
相关文章 1
| [1] | 江静, 董雅楠, 李艳, 杨百寅. 让建言更多含金量:员工建言质量的前因机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1093-1107. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4701
