 )
) 1 中南财经政法大学公共管理学院, 武汉 430073
2 河南大学商学院, 开封 475004
收稿日期:2018-05-08出版日期:2019-05-15发布日期:2019-03-20通讯作者:张永军E-mail:zhangyj0505@126.com基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(71832004);国家自然科学基金项目(71402190);国家自然科学基金项目(71602050);湖北省高等学校优秀中青年科技创新团队计划资助(T201722)The mutual relationship of organizational citizenship behaviors and counterproductive work behaviors: An integrated process of emotion and cognition
ZHAO Jun1, YAN Miao1, XIAO Sufang1, ZHANG Yongjun2( )
) 1 School of Public Administration, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, Wuhan 430073, China
2 School of Business Administration, Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, China
Received:2018-05-08Online:2019-05-15Published:2019-03-20Contact:ZHANG Yongjun E-mail:zhangyj0505@126.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 传统观点认为, 组织公民行为和反生产行为是同一连续体的对立两级或者负相关的独立二维结构。但近期研究表明, 这二者关系并非那样简单, 在特定情境下它们也许存在一种适度的正相关性。首先, 回顾组织公民行为与反生产行为的影响因素, 以及这二者关系的认知演变; 然后, 基于情绪与认知整合框架, 采用资源守恒理论和道德平衡理论探讨组织公民行为与反生产行为的互动关系; 最后, 对未来研究方向进行了展望, 如通过实证研究探索二者互动关系的边界机制、采用多种研究方法验证这二者之间互动关系、基于潜增长模型探讨这二者关系的动态变化、以及深入探讨这二者互动关系的管理实践策略。
图/表 4
表1组织公民行为与反生产行为的影响因素
| 分类 | 影响因素 | 组织公民行为 | 反生产行为 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 个人因素 | 人口统计学变量( | 不相关 | 相关 |
| 宜人性、责任心( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 自尊( | — | 负相关 | |
| 积极(消极)情绪( | 正相关 (负相关) | 负相关 (正相关) | |
| 满意度( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 组织公平感( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 组织支持感( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 自我控制( | — | 负相关 | |
| 印象管理( | 正相关 | — | |
| 组织/ 情境因素 | 组织伦理氛围( | 正相关 | 负相关 |
| 组织约束( | 正相关 | 正相关 | |
| 人际冲突、工作负荷( | 正相关 | 正相关 | |
| 领导-成员交换关系( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 团队心理氛围( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 精神型领导( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 辱虐型领导( | 负相关 | 正相关 |
表1组织公民行为与反生产行为的影响因素
| 分类 | 影响因素 | 组织公民行为 | 反生产行为 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 个人因素 | 人口统计学变量( | 不相关 | 相关 |
| 宜人性、责任心( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 自尊( | — | 负相关 | |
| 积极(消极)情绪( | 正相关 (负相关) | 负相关 (正相关) | |
| 满意度( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 组织公平感( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 组织支持感( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 自我控制( | — | 负相关 | |
| 印象管理( | 正相关 | — | |
| 组织/ 情境因素 | 组织伦理氛围( | 正相关 | 负相关 |
| 组织约束( | 正相关 | 正相关 | |
| 人际冲突、工作负荷( | 正相关 | 正相关 | |
| 领导-成员交换关系( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 团队心理氛围( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 精神型领导( | 正相关 | 负相关 | |
| 辱虐型领导( | 负相关 | 正相关 |

图1组织公民行为与反生产行为的互动关系框架示意图
 图1组织公民行为与反生产行为的互动关系框架示意图
图1组织公民行为与反生产行为的互动关系框架示意图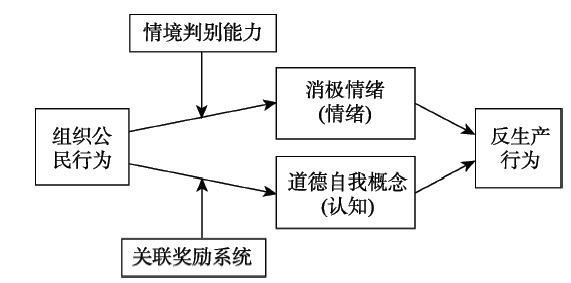
图2组织公民行为对反生产行为的影响机制概念模型
 图2组织公民行为对反生产行为的影响机制概念模型
图2组织公民行为对反生产行为的影响机制概念模型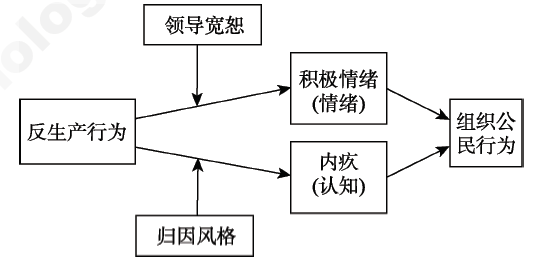
图3反生产行为对组织公民行为的影响机制概念模型
 图3反生产行为对组织公民行为的影响机制概念模型
图3反生产行为对组织公民行为的影响机制概念模型参考文献 103
| [1] | 郭文臣, 杨静, 付佳 . ( 2015). 以组织犬儒主义为中介的组织支持感、组织公平感对反生产行为影响的研究. 管理学报, 12( 4), 530-537. |
| [2] | 冷冰冰, 王香玲, 高贺明, 李富洪 . ( 2015). 内疚的认知和情绪活动及其脑区调控. 心理科学进展, 23( 12), 2064-2071. |
| [3] | 刘文彬, 井润田, 李贵卿, 唐杰 . ( 2014). 员工“大五”人格特质、组织伦理气氛与反生产行为:一项跨层次检验. 管理评论, 26( 11), 141-151. |
| [4] | 彭正龙, 梁东, 赵红丹 . ( 2011). 上下级交换关系与知识员工反生产行为——中国人传统性的调节作用. 情报杂志, 30( 4), 196-200. |
| [5] | 沈伊默, 袁登华, 张华, 杨东, 张进辅, 张庆林 . ( 2009). 两种社会交换对组织公民行为的影响:组织认同和自尊需要的不同作用. 心理学报, 41( 12), 1215-1227. |
| [6] | 孙旭, 严鸣, 储小平 . ( 2014). 坏心情与工作行为:中庸思维跨层次的调节作用. 心理学报, 46( 11), 1704-1718. |
| [7] | 唐翌 . ( 2005). 团队心理安全、组织公民行为和团队创新:一个中介传导模型的实证分析. 南开管理评论, 8( 6), 24-29. |
| [8] | 王华强, 丁志慧, 刘文兴 . ( 2018). 精神型领导对知识共享的影响:内部人身份感知的中介作用. 珞珈管理评论, 12( 3), 115-129. |
| [9] | 王震, 孙健敏, 张瑞娟 . ( 2012). 管理者核心自我评价对下属组织公民行为的影响:道德式领导和集体主义导向的作用. 心理学报, 44( 9), 1231-1243. |
| [10] | 赵君, 廖建桥, 张永军 . ( 2014). 评估式绩效考核对职场偏差行为的影响:探讨工作满意度和马基雅维利主义的作用. 经济管理, 36( 3), 63-76. |
| [11] | Aquino K., Grover S. L., Goldman B., & Folger R . ( 2003). When push doesn’t come to shove: Interpersonal forgiveness in workplace relationships. Journal of Management Inquiry, 12( 3), 209-216. doi: 10.1177/1056492603256337URL |
| [12] | Aquino K., & Reed A. , ( 2002). The self-importance of moral identity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 83( 6), 1423-1440. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.83.6.1423URL |
| [13] | Ashforth B. K., & Saks A. M . ( 1996). Socialization tactics: Longitudinal effects on newcomer adjustment. Academy of Management Journal, 39( 1), 149-178. |
| [14] | Bar-tal D., Raviv A., & Leiser T . ( 1980). The development of altruistic behavior: Empirical evidence. Developmental Psychology, 16( 5), 516-524. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.16.5.516URL |
| [15] | Bateman T. S., & Organ D. W . ( 1983). Job satisfaction and the good soldier: The relationship between affect and employee citizenship. Academy of Management Journal, 26( 4), 587-595. |
| [16] | Bennett R. J., & Stamper C. L . ( 2001). Corporate citizenship and deviancy: A study of discretionary work behavior. In C. Galbraith, & M. Ryan (Eds.), International research in the business disciplines: Strategies and organizations in transition( pp. 265-284). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science. |
| [17] | Bennett R. J., & Robinson S. L . ( 2000). Development of a measure of workplace deviance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 85( 3), 349-360. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.85.3.349URL |
| [18] | Bergeron D. M., Shipp A. J., Rosen B., & Furst S. A . ( 2013). Organizational citizenship behavior and career outcomes: The cost of being a good citizen. Journal of Management, 39( 4), 958-984. |
| [19] | Bolino M. C., Harvey J., & Bachrach D. G . ( 2012). A self-regulation approach to understanding citizenship behavior in organizations. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 119( 1), 126-139. doi: 10.1016/j.obhdp.2012.05.006URL |
| [20] | Bolino M. C., Hsiung H. H., Harvey J., & LePine J.A . ( 2015). “Well, I’m tired of tryin!” Organizational citizenship behavior and citizenship fatigue. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100( 1), 56-74. doi: 10.1037/a0037583URL |
| [21] | Bolino M. C., Klotz A. C., Turnley W. H., & Harvey J . ( 2013). Exploring the dark side of organizational citizenship behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 34( 4), 542-559. doi: 10.1002/job.1847URL |
| [22] | Bolino M. C., & Turnley W. H . ( 2005). The personal costs of citizenship behavior: The relationship between individual initiative and role overload, job stress, and work-family conflict. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90( 4), 740-748. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.90.4.740URL |
| [23] | Bolino M. C., Turnley W. H., Gilstrap J. B., & Suazo M. M . ( 2010). Citizenship under pressure: What’s a “good soldier” to do? Journal of Organizational Behavior, 31( 6), 835-855. |
| [24] | Borman W. C., & Motowidlo S. J . ( 1997). Task performance and contextual performance: The meaning for personnel selection research. Human Performance, 10( 2), 99-109. doi: 10.1207/s15327043hup1002_3URL |
| [25] | Bushman B. J., Baumeister R. F., & Phillips C. M . ( 2001). Do people aggress to improve their mood? Catharsis beliefs, affect regulation opportunity, and aggressive responding. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 81( 1), 17-32. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.81.1.17URL |
| [26] | Bushman B. J., Baumeister R. F., & Stack A. D . ( 1999). Catharsis, aggression, and persuasive influence: Self-fulfilling or self-defeating prophecies? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76( 3), 367-376. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.76.3.367URL |
| [27] | Cascio J., & Plant E. A . ( 2015). Prospective moral licensing: Does anticipating doing good later allow you to be bad now? Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 56( 1), 110-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2014.09.009URL |
| [28] | Chan D., . ( 2006). Interactive effects of situational judgment effectiveness and proactive personality on work perceptions and work outcomes. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91( 2), 475-481. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.91.2.475URL |
| [29] | Chan D., & Schmitt N. , ( 2002). Situational judgment and job performance. Human Performance, 15( 3), 233-254. doi: 10.1207/S15327043HUP1503_01URL |
| [30] | Chawla V., , ( 2014). The effect of workplace spirituality on salespeople’s organizational deviant behaviours: Research propositions and practical implications. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 29( 3), 199-208. |
| [31] | Chimhanzi J., ,( 2004). The impact of integration mechanisms on marketing/HR dynamics. Journal of Marketing Management, 20( 7-8), 713-740. doi: 10.1362/0267257041838782URL |
| [32] | Clark M. S., & Fiske S. T . ( 1982). Affect and cognition: The seventeenth annual Carnegie symposium on cognition. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [33] | Cohen S., & Wills T. A . ( 1985). Stress, social support, and the buffering hypothesis. Psychological Bulletin, 98( 2), 310-357. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.98.2.310URL |
| [34] | Colquitt J.A., .( 2001). On the dimensionality of organizational justice: A construct validation of a measure. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86( 3), 386-400. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.86.3.386URL |
| [35] | Dalal R. S . ( 2005). A meta-analysis of the relationship between organizational citizenship behavior and counterproductive work behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90( 6), 1241-1255. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.90.6.1241URL |
| [36] | Dalal R. S., Lam H., Weiss H. M., Welch E. R., & Hulin C. L . ( 2009). A within-person approach to work behavior and performance: Concurrent and lagged citizenship- counterproductivity associations, and dynamic relationships with affect and overall job performance. Academy of Management Journal, 52( 5), 1051-1066. doi: 10.5465/amj.2009.44636148URL |
| [37] | Duffy M. K., Ganster D. C., & Pagon M . ( 2002). Social undermining in the workplace. Academy of Management Journal, 45( 2), 331-352. |
| [38] | Dunlop P. D., & Lee K. , ( 2004). Workplace deviance, organizational citizenship behavior, and business unit performance: The bad apples do spoil the whole barrel. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 25( 1), 67-80. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1379URL |
| [39] | Felps W., Mitchell T. R., & Byington E . ( 2006). How, when, and why bad apples spoil the barrel: Negative group members and dysfunctional groups. Research in Organizational Behavior, 27( 6), 175-222. doi: 10.1016/S0191-3085(06)27005-9URL |
| [40] | Fisher M. L., & Exline J. J . ( 2006). Self-forgiveness versus excusing: The roles of remorse, effort, and acceptance of responsibility. Self & Indentity, 5( 2), 127-146. |
| [41] | Flynn F. J., & Schaumberg R. L . ( 2012). When feeling bad leads to feeling good: Guilt-proneness and affective organizational commitment. Journal of Applied Psychology, 97( 1), 124-133. doi: 10.1037/a0024166URL |
| [42] | Fox S., Spector P. E., Goh A., Bruursema K., & Kessler S. R . ( 2012). The deviant citizen: Measuring potential positive relations between counterproductive work behaviour and organizational citizenship behaviour. Journal of Occupational & Organizational Psychology, 85( 1), 199-220. |
| [43] | Gupta A. K., Raj S. P., & Wilemon D . ( 1986). A model for studying R&D. marketing interface in the product innovation process. Journal of Marketing, 50( 2), 7-17. doi: 10.1177/002224298605000101URL |
| [44] | Harper D. C . ( 1990). Spotlight abuse-save profits. Industrial Distribution, 79( 3), 47-51. |
| [45] | Harris T. B., Li N., & Kirkman B. L . ( 2014). Leader-member exchange (LMX) in context: How LMX differentiation and LMX relational separation attenuate LMX’s influence on OCB and turnover intention. The Leadership Quarterly, 25( 2), 314-328. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2013.09.001URL |
| [46] | Heckert A., & Heckert D. M . ( 2002). A new typology of deviance: Integrating normative and reactivist definitions of deviance. Deviant Behavior, 23( 5), 449-479. doi: 10.1080/016396202320265319URL |
| [47] | Heider F., . ( 1958). The psychology of interpersonal relations. New York: Wiley. |
| [48] | Hershcovis M. S., & Barling J. , ( 2010). Towards a multi-foci approach to workplace aggression: A meta- analytic review of outcomes from different perpetrators. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 31( 1), 24-44. |
| [49] | Hobfoll S. E . ( 1989). Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist, 44( 3), 513-524. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.44.3.513URL |
| [50] | Hobfoll S. E . ( 2001). The influence of culture, community, and the nested-self in the stress process: Advancing conservation of resources theory. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 50( 3), 337-421. doi: 10.1111/apps.2001.50.issue-3URL |
| [51] | Ilies R., Peng A. C., Savani K., & Dimotakis N . ( 2013). Guilty and helpful: An emotion-based reparatory model of voluntary work behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology, 98( 6), 1051-1059. doi: 10.1037/a0034162URL |
| [52] | Ilies R., Scott B. A., & Judge T. A . ( 2006). The interactive effects of personal traits and experienced states on intraindividual patterns of citizenship behavior. Academy of Management Journal, 49( 3), 561-575. doi: 10.5465/amj.2006.21794672URL |
| [53] | Judge T. A., Scott B. A., & Ilies R . ( 2006). Hostility, job attitudes, and workplace deviance: Test of a multilevel model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91( 1), 126-138. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.91.1.126URL |
| [54] | Klotz A. C., & Bolino M. C . ( 2013). Citizenship and counterproductive work behavior: A moral licensing view. Academy of Management Review, 38( 2), 292-306. doi: 10.5465/amr.2011.0109URL |
| [55] | Kluger A. N., & DeNisi A. , ( 1996). The effects of feedback interventions on performance: A historical review, a meta-analysis, and a preliminary feedback intervention theory. Psychological Bulletin, 119( 2), 254-284. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.119.2.254URL |
| [56] | Kouchaki M. , ( 2011). Vicarious moral licensing: The influence of others’ past moral actions on moral behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 101( 4), 702-715. doi: 10.1037/a0024552URL |
| [57] | Krebs D. L . ( 1970). Altruism: An examination of the concept and a review of the literature. Psychological Bullentin, 73( 4), 258-302. doi: 10.1037/h0028987URL |
| [58] | Krischer M. M., Penney L. M., & Hunter E. M . ( 2010). Can counterproductive work behaviors be productive? CWB as emotion-focused coping. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 15( 2), 154-166. doi: 10.1037/a0018349URL |
| [59] | Lau V. C. S., Au W. T & Ho J. M. C ., ( 2003). A qualitative and quantitative review of antecedents of counterproductive behavior in organizations. Journal of Business and Psychology, 18( 1), 73-99. doi: 10.1023/A:1025035004930URL |
| [60] | Law R., Dollard M. F., Tuckey M. R., & Dormann C . ( 2011). Psychosocial safety climate as a lead indicator of workplace bullying and harassment, job resources, psychological health and employee engagement. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 43( 5), 1782-1793. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2011.04.010URL |
| [61] | Lee K., & Allen N. J . ( 2002). Organizational citizenship behavior and workplace deviance: The role of affect and cognitions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87( 1), 131-142. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.87.1.131URL |
| [62] | Marcus B. & Schuler H. , ( 2004). Antecedents of counterproductive behavior at work: A general perspective. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89( 4), 647-660. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.89.4.647URL |
| [63] | Martinko M. J., Harvey P., Brees J. R., & Mackey J . ( 2013). A review of abusive supervision research. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 34( S1), 120-137. doi: 10.1002/job.1888URL |
| [64] | Mazar N. & Zhong C-B. , ( 2010). Do green products make us better people? Psychological Science, 21( 4), 494-498. doi: 10.1177/0956797610363538URL |
| [65] | McDaniel M. A., Morgeson F. P., Finnegan E. B., Campion M. A., & Braverman E. P . ( 2001). Use of situational judgment tests to predict job performance: A clarification of the literature. Journal of Applied Psychological, 86( 4), 730-740. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.86.4.730URL |
| [66] | Meredith W. & Tisak J. , ( 1990). Latent curve analysis. Psychometrika, 55( 1), 107-122. doi: 10.1007/BF02294746URL |
| [67] | Miles D. E., Borman W. E., Spector P. E., & Fox S . ( 2002). Building an integrative model of extra role work behaviors: A comparison of counterproductive work behavior with organizational citizenship behavior. International Journal of Selection & Assessment, 10( 1-2), 51-57. |
| [68] | Moorman R. H., Blackely G. L., & Niehoff B. P . ( 1998). Does perceived organizational support mediate the relationship between procedural justice and organizational citizenship behavior? Academy of Management Journal, 41( 3), 351-357. doi: 10.5465/256913URL |
| [69] | Mosher D. L . ( 1965). Interaction of fear and guilt in inhibiting unacceptable behavior. Journal of Consulting Psychology, 29( 2), 161-167. doi: 10.1037/h0021748URL |
| [70] | Nisan M. & Horenczyk G. , ( 1990). Moral balance: The effect of prior behaviour on decision in moral conflict. British Journal of Social Psychology, 29( 1), 29-42. doi: 10.1111/bjso.1990.29.issue-1URL |
| [71] | Nordan A., & Penney L. M . ( 2013, August). Nice guys finish last: CWB and the pursuit of performance goals. In M. K. Shoss, & L. M. Penney (Chairs), Understanding motives for counterproductive work behaviors. Symposium presented at the annual meeting of the Academy of Management, Orlando, FL. |
| [72] | O’Boyle E. H., Humphrey R. H., Pollack J. M., Hawver T. H., & Story. P. A . ( 2011). The relation between emotional intelligence and job performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32( 5), 788-818. doi: 10.1002/job.v32.5URL |
| [73] | O’Brien K. E., & Allen T. D . ( 2008). The relative importance of correlates of organizational citizenship behavior and counterproductive work behavior using multiple sources of data. Human Performance, 21( 1), 62-88. |
| [74] | O’Regan N. & Ghobadian A. , ( 2005). Innovation in SMEs: The impact of strategic orientation and environmental perceptions. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 54( 2), 81-97. doi: 10.1108/17410400510576595URL |
| [75] | Organ D. W . ( 1997). Organizational citizenship behavior: It’s construct clean-up time. Human performance, 2( 10), 85-97. |
| [76] | Organ D. W., Podsakoff P. M., & Mackenzie S. B . ( 2006). Organizational citizenship behavior: Its nature, antecedents, and consequences. Personnel Psychology, 59( 2), 484-487. doi: 10.1111/peps.2006.59.issue-2URL |
| [77] | Perrewé P. L., & Zellars K. L . ( 1999). An examination of attributions and emotions in the transactional approach to the organizational stress process. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 20( 5), 739-752. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1379URL |
| [78] | Podsakoff P. M., MacKenzie S. B., Paine J. B., & Bachrach D. G . ( 2000). Organizational citizenship behaviors: A critical review of the theoretical and empirical literature and suggestions for future research. Journal of Management, 26( 3), 513-563. |
| [79] | Rappaport J., . ( 1981). In praise of paradox: A social policy of empowerment over prevention. American Journal of Community Psychology, 9( 1), 1-25. doi: 10.1007/BF00896357URL |
| [80] | Reynolds C. A., Shoss M. K., & Jundt D. K . ( 2015). In the eye of the beholder: A multi-stakeholder perspective of organizational citizenship and counterproductive work behavior. Human Resource Management Review, 25( 1), 80-93. doi: 10.1016/j.hrmr.2014.06.002URL |
| [81] | Robinson S. L., & Bennett R. J . ( 1995). A typology of deviant work-place behaviors: A multidimensional scaling study. Academy of Management Journal, 38( 2), 555-572. |
| [82] | Rotundo M., & Sackett P. R . ( 2002). The relative importance of task, citizenship, and counterproductive performance to global ratings of job performance: A policy-capturing approach. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87( 1), 66-80. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.87.1.66URL |
| [83] | Rotundo M, & Xie J. L . ( 2008). Understanding the domain of counterproductive work behaviour in china. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 19( 5), 856-877. doi: 10.1080/09585190801991400URL |
| [84] | Sachdeva S., Iliev R., & Medin D. L . ( 2009). Sinning saints and saintly sinners the paradox of moral self-regulation. Psychological Science, 20( 4), 523-528. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2009.02326.xURL |
| [85] | Sackett P. R., Berry C. M., & Laczo R. M . ( 2006). Citizenship and counterproductive behavior: Clarifying relations between the two domains. Human Performance, 19( 4), 441-464. doi: 10.1207/s15327043hup1904_7URL |
| [86] | Shin Y., . ( 2012). CEO ethical leadership, ethical climate, climate strength, and collective organizational citizenship behavior. Journal of Business Ethics, 108( 3), 299-312. doi: 10.1007/s10551-011-1091-7URL |
| [87] | Silfver M., .( 2007). Coping with guilt and shame: A narrative approach. Journal of Moral Education, 36( 2), 169-183. doi: 10.1080/03057240701325274URL |
| [88] | Spector P. E., & Fox S. , ( 2002). An emotion-centered model of voluntary work behavior: Some parallels between counterproductive work behavior and organizational citizenship behavior. Human Resource Management Review, 12( 2), 269-292. doi: 10.1016/S1053-4822(02)00049-9URL |
| [89] | Spector P. E., & Fox S. , ( 2010a). Counterproductive work behavior and organizational citizenship behavior: Are they opposite forms of active behavior? Applied Psychology, 59( 1), 21-39. doi: 10.1111/apps.2010.59.issue-1URL |
| [90] | Spector P. E., & Fox S. , ( 2010b). Theorizing about the deviant citizen: An attributional explanation of the interplay of organizational citizenship and counterproductive work behavior. Human Resource Management Review, 20( 2), 132-143. doi: 10.1016/j.hrmr.2009.06.002URL |
| [91] | Spector P. E., Fox S., Penney L. M., Bruursema K., Goh A., & Kessler S . ( 2006). The dimensionality of counterproductivity: Are all counterproductive behaviors created equal? Journal of Vocational Behavior, 68( 3), 446-460. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2005.10.005URL |
| [92] | Tangney J. P . ( 1990). Assessing individual differences in proneness to shame and guilt: Development of the self-conscious affect and attribution inventory. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 59( 1), 102-111. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.59.1.102URL |
| [93] | Tangney J. P., Stuewig J., & Mashek D. J . ( 2007). Moral emotions and moral behavior. Annual Review of Psychology , 58: 345-372. |
| [94] | Tetlock P. E., Kristel O. V., Elson S. B., Green M. C., & Lerner J. S . ( 2000). The psychology of the unthinkable: Taboo trade-offs, forbidden base rates, and heretical counterfactuals. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78( 5), 853-870. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.78.5.853URL |
| [95] | Venkataramani V., & Dalal R. S . ( 2007). Who helps and harms whom? Relational antecedents of interpersonal helping and harming in organizations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92( 4), 952-966. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.92.4.952URL |
| [96] | Wallace H. M., Exline J. J., & Baumeister R. F . ( 2008). Interpersonal consequences of forgiveness: Does forgiveness deter or encourage repeat offenses? Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 44( 2), 453-460. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2007.02.012URL |
| [97] | Williams S., & Shiaw, W. T . ( 1999). Mood and organizational citizenship behavior: The effects of positive affect on employee organizational citizenship behavior intentions. Journal of Psychology, 133( 6), 656-668. doi: 10.1080/00223989909599771URL |
| [98] | Woodyatt L. & Wenzel M. , ( 2013). Self-forgiveness and restoration of an offender following an interpersonal transgression. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 32( 2), 225-239. doi: 10.1521/jscp.2013.32.2.225URL |
| [99] | Xie J., Song M., & Stringfellow A . ( 2003). Antecedents and consequences of goal incongruity on new product development in five countries: A marketing view. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 20( 3), 233-250. doi: 10.1111/1540-5885.2003005URL |
| [100] | Xu E., Huang X., Lam C. K., & Miao Q . ( 2012). Abusive supervision and work behaviors: The mediating role of LMX. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33( 4), 531-543. doi: 10.1002/job.768URL |
| [101] | Yam K. C., Klotz A., He W., & Reynolds S. J . ( 2017). From good soldiers to psychologically entitled: Examining when and why citizenship behavior leads to deviance. Academy of Management Journal, 60( 1), 373-396. doi: 10.5465/amj.2014.0234URL |
| [102] | Zhong C-B., Ku G., Lount R. B., & Murnighan J. K . ( 2010). Compensatory ethics. Journal of Business Ethics, 92( 3), 323-339. doi: 10.1007/s10551-009-0161-6URL |
| [103] | Zhong C.B. & Liljenquist K. , ( 2006). Washing away your sins: Threatened morality and physical cleansing. Science, 313( 5792), 1451-1452. doi: 10.1126/science.1130726URL |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 张辉华. 社会网络视角的团队情绪智力[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1381-1395. |
| [2] | 李晓明, 邹是, 高友明. 失望情绪在不作为惯性产生中的作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1396-1401. |
| [3] | 张珊珊, 王婧怡, 李昱汝. 情绪自旋及其心理健康功能[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1430-1437. |
| [4] | 曾宪卿, 许冰, 孙博, 叶健彤, 傅世敏. EMMN受偏差-标准刺激对类型和情绪类型影响: 来自元分析的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(7): 1163-1178. |
| [5] | 王晓田, 王娜, 何金波. 前瞻性情绪作为社会风险的信息源假说:公共场景下风险决策的情绪及文化机制探讨[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 959-966. |
| [6] | 彭坚, 曹兵兵. 追随者主动工作行为的上行影响:内隐追随视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 967-977. |
| [7] | 隋雪, 史汉文, 李雨桐. 语言加工过程中的观点采择及其认知机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 990-999. |
| [8] | 何蔚祺, 李帅霞, 赵东方. 群体面孔情绪感知的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 761-772. |
| [9] | 肖承丽, 隋雨檠, 肖苏衡, 周仁来. 空间交互研究新视角:多重社会因素的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 796-805. |
| [10] | 尹俊婷, 王冠, 罗俊龙. 威胁对创造力的影响:认知与情绪双加工路径[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 815-826. |
| [11] | 王学思, 李静雅, 王美芳. 父母婚姻冲突对儿童发展的影响及其机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 875-884. |
| [12] | 赵宏明, 董燕萍. 口译员的认知转换优势[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 625-634. |
| [13] | 丁琳洁, 李旭, 尹述飞. 工作记忆中的积极效应:情绪效价与任务相关性的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 652-664. |
| [14] | 关旭旭, 王红波. 抑制引起的遗忘及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 665-676. |
| [15] | 徐俊怡, 李中权. 基于游戏的心理测评[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 394-403. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4683
