 ), 曹照雪
), 曹照雪 武汉大学哲学学院心理学系, 武汉 430072
收稿日期:2018-12-06出版日期:2019-10-31发布日期:2019-09-23通讯作者:严瑜E-mail:yanyu@whu.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家社科基金项目“基于情绪角色模型的组织中不文明行为的螺旋效应研究”(18BGL119);教育部人文社科一般规划项目“组织不文明行为溢出效应和交叉效应的心理机制:跨层次整合研究”(17YJA190013)Workplace civility: From implicit self-promotion to explicit organizational optimization
YAN Yu( ), CAO Zhaoxue
), CAO Zhaoxue Department of Psychology, School of Philosophy, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
Received:2018-12-06Online:2019-10-31Published:2019-09-23Contact:YAN Yu E-mail:yanyu@whu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 工作场所文明行为是一种在组织文化下, 基于社会和组织角色义务的, 传达礼貌和尊重的主动性行为, 是一种向内要求自我控制, 向外主张尊重传达的行为, 它对于个体自身性格的塑造、组织中人际关系的改善以及文明氛围的培养都具有积极意义。在员工-员工、领导-下属、员工-顾客等关系中, 工作场所文明行为发挥着增进同事情谊、促进合作、增强领导力、建立信任、提升绩效等作用。未来的研究应该进一步厘清工作场所文明行为与不文明行为的关系, 运用动态视角研究它们发生、发展和被感知的机制, 以及这两种行为能否相互转化等问题。
图/表 3
表1工作场所文明行为定义总结
| 工作场所文明行为定义 | 性质 | 研究者及时间 |
|---|---|---|
| 尊重他人的尊严, 尊重他人的感情, 维护相互尊重的组织规范的行为。 | 中性 | Carter, 1998 |
| 一个在职场尊重行为规范内的对他人礼貌和关心的行为。 | 中性 | Andersson & Pearson, 1999 |
| 有助于保持工作中相互尊重的规范的行为; | ||
| 它包含的行为是与他人积极联系, 建立关系和共情的基础。 | 中性 | Pearson, Andersson, & Porath, 2000 |
| 文明假设一种超越自我的意识, 并且需要传达对他人福祉的尊重和关注。 | 积极 | Sypher, 2004 |
| 文明行为是作为一个群体公民, 以积极的方式行动, | ||
| 使个人投入有利于自身和集体的能力。 | 积极 | Marini, 2011 |
| 尊重他人, 基本礼貌, 以及营造积极学习和工作环境的行为。 | 积极 | Gilroy, 2008 |
| 文明要求人们以尊重、负责、内敛和有原则的方式说话, | ||
| 避免那些冒犯、粗鲁、贬低和威胁的方式。 | 中性 | Gill & Sypher, 2009 |
| 工作组内有礼貌和体贴的工作场所行为。 | 中性 | Osatuke et al., 2009 |
| 工作场所的文明指在人际关系中考虑他人。 | 积极 | Ferriss, 2010 |
| 工作场所文明行为是一种帮助维护工作场所相互尊重的规范的行为, | ||
| 包含了超越好的态度和礼节的其他因素。 | 积极 | Walsh et al., 2012 |
| 职业文明行为是一种交流的美德和实践智慧, 是职业精神的一部分。 | 积极 | Fritz, 2013 |
| 工作场所文明行为包含尊重、尊严、礼貌和愉快。 | 积极 | Porath, Gerbasi, & Schorch, 2015 |
| 文明包含大多数人在工作中渴望的那些尊重、礼貌的行为。 | 中性 | Cortina et al., 2017 |
表1工作场所文明行为定义总结
| 工作场所文明行为定义 | 性质 | 研究者及时间 |
|---|---|---|
| 尊重他人的尊严, 尊重他人的感情, 维护相互尊重的组织规范的行为。 | 中性 | Carter, 1998 |
| 一个在职场尊重行为规范内的对他人礼貌和关心的行为。 | 中性 | Andersson & Pearson, 1999 |
| 有助于保持工作中相互尊重的规范的行为; | ||
| 它包含的行为是与他人积极联系, 建立关系和共情的基础。 | 中性 | Pearson, Andersson, & Porath, 2000 |
| 文明假设一种超越自我的意识, 并且需要传达对他人福祉的尊重和关注。 | 积极 | Sypher, 2004 |
| 文明行为是作为一个群体公民, 以积极的方式行动, | ||
| 使个人投入有利于自身和集体的能力。 | 积极 | Marini, 2011 |
| 尊重他人, 基本礼貌, 以及营造积极学习和工作环境的行为。 | 积极 | Gilroy, 2008 |
| 文明要求人们以尊重、负责、内敛和有原则的方式说话, | ||
| 避免那些冒犯、粗鲁、贬低和威胁的方式。 | 中性 | Gill & Sypher, 2009 |
| 工作组内有礼貌和体贴的工作场所行为。 | 中性 | Osatuke et al., 2009 |
| 工作场所的文明指在人际关系中考虑他人。 | 积极 | Ferriss, 2010 |
| 工作场所文明行为是一种帮助维护工作场所相互尊重的规范的行为, | ||
| 包含了超越好的态度和礼节的其他因素。 | 积极 | Walsh et al., 2012 |
| 职业文明行为是一种交流的美德和实践智慧, 是职业精神的一部分。 | 积极 | Fritz, 2013 |
| 工作场所文明行为包含尊重、尊严、礼貌和愉快。 | 积极 | Porath, Gerbasi, & Schorch, 2015 |
| 文明包含大多数人在工作中渴望的那些尊重、礼貌的行为。 | 中性 | Cortina et al., 2017 |
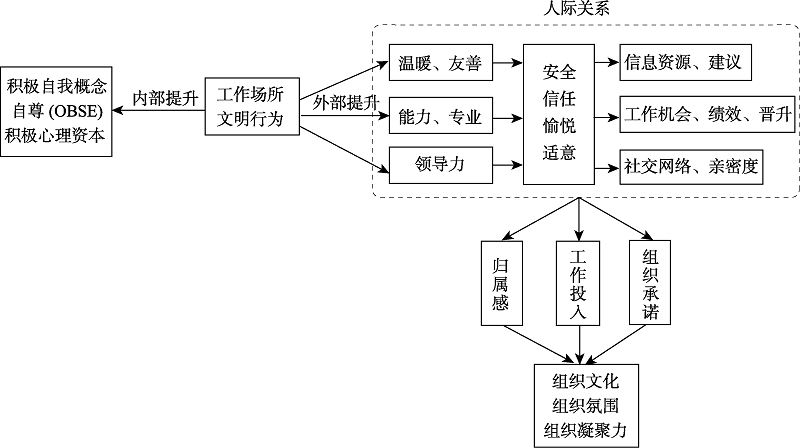
图1工作场所文明行为的作用机制
 图1工作场所文明行为的作用机制
图1工作场所文明行为的作用机制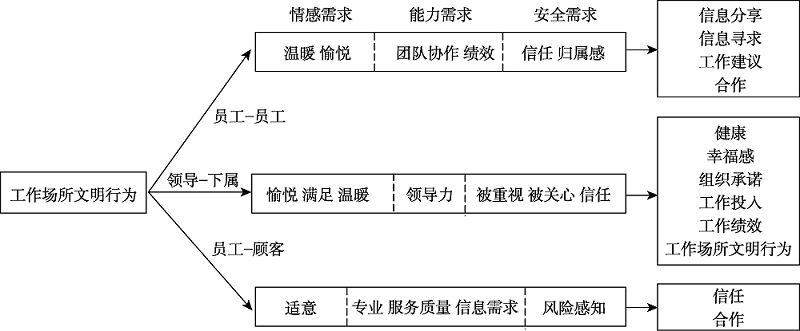
图2工作场所文明行为优化组织关系
 图2工作场所文明行为优化组织关系
图2工作场所文明行为优化组织关系参考文献 58
| 1 | 李毅红, 邱华宇 . ( 2019). 习近平关于文明的重要论述探析. 理论学刊, ( 2), 19-25. |
| 2 | 严瑜, 李佳丽 . ( 2017). 超越不文明: 从消极无礼的恶化升级到积极的文明干预. 心理科学进展, 25( 2), 319-330. |
| 3 | Andersson,L. M., &Pearson,C. M . ( 1999). Tit for tat? The spiraling effect of incivility in the workplace. Academy of Management Review, 24( 3), 452-471. |
| 4 | Belschak,F. D., & den Hartog,D. N . ( 2010). Pro-self, prosocial, and pro-organizational foci of proactive behaviour: Differential antecedents and consequences. Journal of Occupational & Organizational Psychology, 83( 2), 475-498. |
| 5 | Boyle,K. M . ( 2017). Verification of self using a mathematical theory of identity, feeling, and behavior. Sociological Forum, 32( 2), 659-680. |
| 6 | Cater S. L. (1998). Civility:Manners, morals and the etiquette of democracy . New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| 7 | Clark,C. M., &Kenski D. 2017). Promoting civility in the OR: An ethical imperative. AORN Journal, 105( 1), 60-66. |
| 8 | Clark,O. L., &Walsh,B. M . ( 2016). Civility climate mitigates deviant reactions to organizational constraints. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 31( 1), 186-201. |
| 9 | Cortina L. M., Kabat-Farr D., Magley V. J., & Nelson K . ( 2017). Researching rudeness: The past, present, and future of the science of incivility. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 22(3),299-313. |
| 10 | Cuddy A. J., Kohut M., & Neffinger J . ( 2013). Connect, then lead. Harvard Business Review, 91( 7-8), 54-61. |
| 11 | Donia M. B. L., Johns G., & Raja U . ( 2016). Good soldier or good actor? Supervisor accuracy in distinguishing between selfless and self-serving OCB motives. Journal of Business and Psychology, 31( 1), 23-32. |
| 12 | Donnelly, B. . ( 2008). Work and integrity: The crisis and promise of professionalism in America. World Futures, 64( 3), 222-225. |
| 13 | Edyvane, D. . ( 2017). The passion for civility. Political Studies Review, 15(3) 344-354. |
| 14 | Ferriss,A. L . ( 2010). Studying and measuring civility: A framework, trends and scale. Sociological Inquiry, 72( 3), 376-392. |
| 15 | Flaherty C. The problem with civility. Retrieved September 9, 2014, from The problem with civility. Retrieved September 9, 2014, from |
| 16 | Ford M. T., Wang Y., Jin J., & Eisenberger R . ( 2018). Chronic and episodic anger and gratitude toward the organization: Relationships with organizational and supervisor supportiveness and extrarole behavior. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 23( 2), 175-187. |
| 17 | Frederickson,B. L., &Dutton,J. E . ( 2008). Unpacking positive organizing: Organizations as sites of individual and group flourishing. Journal of Positive Psychology, 3( 1), 1-3. |
| 18 | Fritz,J. H . ( 2011). Civility in the workplace. Spectra, 47( 3), 11-14. |
| 19 | Fritz J. H. (2013). Professional Civility:Communicative virtue at work. New York: Peter Lang Publishing. |
| 20 | Gill,M. J., &Sypher,B. D . ( 2009). Workplace incivility and organizational trust.In P. Lutgen-Sandvik & B. D. Sypher (Eds.), Destructive organizational communication: Processes, consequences, and constructive ways of organizing(pp. 53-73).New York: Taylor & Francis. |
| 21 | Gilroy, M. . ( 2008). Colleges grappling with incivility. Education Digest Essential Readings Condensed for Quick Review, 74( 4), 36-40. |
| 22 | Giraldi,J. M. E., &Ikeda A. 2008). Personal values dimensions: A study on brazilian executives. Latin American Business Review, 9( 2), 169-187. |
| 23 | Jawahar,I. M., &Schreurs B. 2018). Supervisor incivility and how it affects subordinates’ performance: A matter of trust. Personnel Review, 47( 3), 709-726. |
| 24 | Jensen-Campbell L. A., Knack J. M., & Gomez H. L . ( 2010). The psychology of nice people. Social & Personality Psychology Compass, 4( 11), 1042-1056. |
| 25 | Kang B., Twigg N. W., & Hertzman J . ( 2010) An examination of social support and social identity factors and their relationship to certified chefs’ burnout. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 29( 1), 168-176. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2009.08.004 |
| 26 | Kent, S., &Muurlink O. 2014). Getting a grip on why incivility happens within the workplace: A commentary essay. Social Justice Research, 27( 1), 137-148. doi: 10.1007/s11211-014-0207-5 |
| 27 | Leiter, M. . ( 2013). Analyzing and theorizing the dynamics of the workplace incivility crisis .Dordrecht, Netherlands:Springer. |
| 28 | Leiter M. P., Day A., Oore D. G., &Spence Laschinger, H. K. . ( 2012). Getting better and staying better: Assessing civility, incivility, distress, and job attitudes one year after a civility intervention. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 17( 4), 425-434. doi: 10.1037/a0029540 |
| 29 | Leiter M. P., Spence Laschinger H. K., Day A., & Oore D. G . ( 2011). The impact of civility interventions on employee social behavior. Distress, and Attitudes, 96( 6), 1258-1274. |
| 30 | Livi S., Theodorou A., Rullo M., Cinque L., & Alessandri G . ( 2018). The rocky road to prosocial behavior at work: The role of positivity and organizational socialization in preventing interpersonal strain. PLoS ONE, 13( 3):e0193508. |
| 31 | Marini, Z. . ( 2011). The thin line between civility and incivility: fostering reflection and self-awareness to create a civil learning community. Collected Essays on Learning & Teaching, 2, 61-67. |
| 32 | Maslach, C., &Leiter,M. P . ( 2017). New insights into burnout and health care: Strategies for improving civility and alleviating burnout. Medical Teacher, 39( 2), 160-163. |
| 33 | McDonald T. W., Stockton J. D., & Landrum R. E. ( 2018. Civility and academic freedom: Who defines the former (and how) may imperil rights to the latter. College Quarterly, 21(1). Retrieved September 2, 2018, from |
| 34 | Mcgonagle A. K., Walsh B. M., Kath L. M., & Morrow S. L . ( 2014). Civility norms, safety climate, and safety outcomes: A preliminary investigation. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 19( 4), 437-452. doi: 10.1037/a0037110 |
| 35 | Meyers M. C., van Woerkom M., & Bakker A. B . ( 2013). The added value of the positive: A literature review of positive psychology interventions in organizations. European Journal of Work & Organizational Psychology, 22( 5), 618-632. |
| 36 | Montalvo, L. . (2013, September). An evidence based synthesis of civility and incivility literature: A model to explain civil and uncivil behaviors in the workplace. Paper presented at the Third International Conference on Engaged Management Scholarship, Atlanta,GA. |
| 37 | Nicholson,R. M., &Leiter,M. P . ( 2014). Predicting cynicism as a function of trust and civility: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Nursing Management, 22( 8), 974-983. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12073 |
| 38 | Osatuke K., Moore S. C., Ward C., Dyrenforth S. R., & Belton L . ( 2009). Civility, respect, engagement in the workforce (CREW): Nationwide organization development intervention at Veterans Health Administration. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 45( 3), 384-410. |
| 39 | Panagopoulos,N. G., &Ogilvie J. 2015). Can salespeople lead themselves? Thought self-leadership strategies and their influence on sales performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 47, 190-203. |
| 40 | Pearson C. M., Andersson L. M., & Porath C. L . ( 2000). Assessing and attacking workplace incivility. Organizational Dynamics, 29( 2), 123-137. |
| 41 | Periard D. A., Yanchus N. J., Morris M. B., Barnes T., Yanovsky B., & Osatuke K . ( 2018). LGB and heterosexual federal civilian employee differences in the workplace. Psychology of Sexual Orientation and Gender Diversity, 5( 1), 57-71. |
| 42 | Porath C. L. (2011). Civility. In K. S. Cameron & G. M. Spreitzer (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of positive organizational scholarship (pp. 439-448). New York,NY: Oxford University Press. |
| 43 | Porath,C. L., &Gerbasi A. 2015). Does civility pay? Organizational Dynamics, 44( 4), 281-286. |
| 44 | Porath C. L., Gerbasi A., & Schorch S. L . ( 2015). The effects of civility on advice, leadership, and performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100( 5), 1527-1541. |
| 45 | Potterton, D. . ( 2018). Managing conflict through workplace civility. Industrial Management, 1, 21-24. |
| 46 | Schaefer, L. . ( 2015). History and civility . NAMTA Journal, 40( 1), 103-110. |
| 47 | Schilpzand, P., &Huang L. 2018). When and how experienced incivility dissuades proactive performance an integration of sociometer and self-identity orientation perspectives. Journal of Applied Psychology, 103( 8), 828-841. |
| 48 | Scott,J. W . ( 2015). The new thought police: Why are campus administrators invoking civility to silence critical speech? Nation, 300( 18), 12-18. |
| 49 | Spence Laschinger H. K., Finegan J., & Wilk P . ( 2009). New graduate burnout: The impact of professional practice environment, workplace civility, and empowerment. Nursing Economic, 27( 6), 377-383. |
| 50 | Spence Laschinger H. K., Leiter M. P., Day A., Gilin-Oore D., & Mackinnon S. P . ( 2012). Building empowering work environments that foster civility and organizational trust: Testing an intervention. Nursing Research, 61( 5), 316-325. doi: 10.1097/NNR.0b013e318265a58d |
| 51 | Sypher,B. D . ( 2004). Reclaiming civil discourse in the workplace. Southern Communication Journal, 69( 3), 257-269. |
| 52 | van Genugten L., Dusseldorp E., Massey E. K., & van Empelen P . ( 2017). Effective self-regulation change techniques to promote mental wellbeing among adolescents: A meta-analysis. Health Psychology Review, 11( 1), 53-71. |
| 53 | von Bergen,C. W., &Collier G. 2013). Tolerance as civility in contemporary workplace diversity initiatives. Administrative Issues Journal Education Practice & Research, 3,86-97 |
| 54 | Walker D. D., van Jaarsveld D. D., & Skarlicki D. P . ( 2017). Sticks and stones can break my bones but words can also hurt me: The relationship between customer verbal aggression and employee incivility. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102( 2), 163-179. |
| 55 | Walsh,B. M., &Magley,V. J . ( 2018). Workplace civility training: Understanding drivers of motivation to learn. International Journal of Human Resource Management , DOI: 10.1080/09585192.2018.1441164. |
| 56 | Walsh B. M., Magley V. J., Reeves D. W., Davies-Schrils, K. A. Marmet, M. D., & Gallus J. A . ( 2012). Assessing workgroup norms for civility: The development of the civility norms questionnaire-brief. Journal of Business Psychology, 27( 4):407-420. |
| 57 | Wilkins K., Caldarella P., Crook-Lyon R. E., & Young K. R . ( 2010). The civil behavior of students: A survey of school professionals. Education, 130( 5), 540-555. |
| 58 | Zhu, Y. . ( 2016). Organization-based self-esteem affects employees' exchange relationship perceptions and extrarole behavior. Social Behavior & Personality and International Journal, 44( 3), 509-518. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 何嘉梅, 金磊. 目标概念的辨析及其对决策的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1410-1419. |
| [2] | 孙国晓, 张力为. 竞赛压力、注意控制与运动表现关系的理论演进[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 1122-1130. |
| [3] | 刘毅, 王君起, 邬辛佳. 双系统模型视角下的罪犯自我控制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(8): 1379-1391. |
| [4] | 孙庆洲, 邬青渊, 张静, 江程铭, 赵雷, 胡凤培. 风险决策的概率权重偏差:心理机制与优化策略[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(5): 905-913. |
| [5] | 刘永芳, 范雯健, 侯日霞. 从理论到研究, 再到应用:塞勒及其贡献[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(3): 381-393. |
| [6] | 黄玺, 梁宏宇, 李放, 陈世民, 王巍欣, 林妙莲, 郑雪. 道德提升感:一种提升道德情操的积极道德情绪[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1253-1263. |
| [7] | 王祯, 杨丽娴. 刻板印象提升与刻板印象促进[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1264-1271. |
| [8] | 王艳芝, 姚唐, 卢宏亮. 结伴购物情境下消费者冲动购买行为发生机理[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(11): 1915-1927. |
| [9] | 利振华, 窦凯, 聂衍刚. 远离“诱惑”:预先承诺对跨期决策的调控机制及其神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(10): 1869-1877. |
| [10] | 张玥, 窦东徽, 辛自强. 解释水平对自我控制的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(10): 1878-1889. |
| [11] | 董军, 付淑英, 卢山, 杨绍峰, 齐春辉. 自我控制失败的理论模型与神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(1): 134-143. |
| [12] | 潘爱玲, 胥遥山, 李永娟. 自我损耗对工作场所安全的影响及缓解途径[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(8): 1261-1273. |
| [13] | 项明强;张力为;张阿佩;杨红英. 自我损耗对运动表现影响的元分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(4): 570-585. |
| [14] | 窦泽南;方圆;周伟;乔志宏. 自我控制的奖励模型与神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(1): 86-98. |
| [15] | 范伟; 钟毅平; 傅小兰. 自我控制对欺骗的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(7): 997-1008. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4862
