 ), 宋伟1, 徐婧2(
), 宋伟1, 徐婧2( )
) 1. 东北师范大学心理学院, 长春 130024
2. 长春中医药大学临床医学院, 长春130117
收稿日期:2018-05-19出版日期:2018-12-15发布日期:2018-10-30通讯作者:巨兴达,徐婧E-mail:juxd513@nenu.edu.cn;xuj391@nenu.edu.cn基金资助:*全国教育科学“十二五”规划教育部青年专项课题“儿童孤独症的基因靶向教育策略研究”资助(EBA140364)CHRM3 gene and autism spectrum disorder
JU Xingda1( ), SONG Wei1, XU Jing2(
), SONG Wei1, XU Jing2( )
) 1. School of Psychology, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, China
2. School of Clinical Medicine, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130117, China
Received:2018-05-19Online:2018-12-15Published:2018-10-30Contact:JU Xingda,XU Jing E-mail:juxd513@nenu.edu.cn;xuj391@nenu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 孤独症谱系障碍是一类具有遗传基础的儿童发展障碍疾病。近些年, 研究者们从分子病理学层面发现中枢胆碱能神经系统异常与孤独症患者认知和行为异常存在相关性。尸检研究、临床案例、动物模型研究均发现毒蕈碱型(M型)乙酰胆碱受体异常和孤独症的发生有着密切的关系。在以小鼠为模型的行为学研究中, 编码毒蕈碱型乙酰胆碱受体Ⅲ亚型的CHRM3基因突变会导致小鼠出现认知障碍、刻板行为等孤独症样表现。深入了解CHRM3基因的功能将能够帮助研究者进一步解释孤独症的相关行为特征, 为孤独症儿童教育方案的制定提供新的思路和方法。
图/表 4
表1孤独症家系研究中的CHRM3突变
| 突变类型 | 等位基因改变 | 氨基酸改变 | 遗传模式 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无义突变 | c.1762C>T | p.Gln588Ter | 家系遗传 | Li et al., (2017) |
| 错义突变 | c.1504A>G | p.Ile502Val | 新生突变 | De Rubeis et al., (2014) |
| 错义突变 | c.1423A>T | p.Ile475Phe | 新生突变 | |
| 缺失 | — | — | 新生突变 | Perrone et al., (2012) |
| 缺失 | — | — | 未知 | Petersen AK et al., (2012) |
表1孤独症家系研究中的CHRM3突变
| 突变类型 | 等位基因改变 | 氨基酸改变 | 遗传模式 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无义突变 | c.1762C>T | p.Gln588Ter | 家系遗传 | Li et al., (2017) |
| 错义突变 | c.1504A>G | p.Ile502Val | 新生突变 | De Rubeis et al., (2014) |
| 错义突变 | c.1423A>T | p.Ile475Phe | 新生突变 | |
| 缺失 | — | — | 新生突变 | Perrone et al., (2012) |
| 缺失 | — | — | 未知 | Petersen AK et al., (2012) |
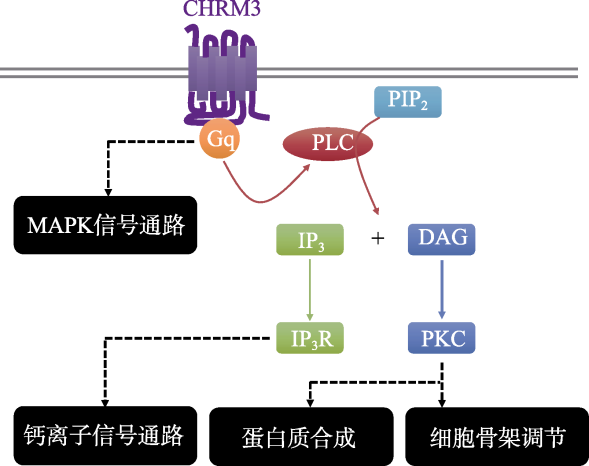
图1CHRM3信号传导模式图。CHRM3可能通过“Gq-PLC-第二信使”信号通路调控神经细胞的增殖、运动、分化、突起生长和兴奋性
 图1CHRM3信号传导模式图。CHRM3可能通过“Gq-PLC-第二信使”信号通路调控神经细胞的增殖、运动、分化、突起生长和兴奋性
图1CHRM3信号传导模式图。CHRM3可能通过“Gq-PLC-第二信使”信号通路调控神经细胞的增殖、运动、分化、突起生长和兴奋性表2两名CHRM3基因缺失的孤独症患者的临床表现对比
| 特征 | Perrone等人报道的患者 | Andrea Klunder Petersen等人报道的患者 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄、性别 | 7岁, 男 | 3岁7个月, 男 |
| 智力缺陷 | + | + |
| 发育迟缓 | + | + |
| 孤独症行为 | + | + |
| 癫痫 | - | - |
| 进食困难 | + | + |
| 身材短小 | + | - |
| 体重偏轻 | + | - |
| 曲指 | + | - |
| 斜视 | + | + |
| 自伤倾向 | + | + |
| 脑部核磁共振造影 | 正常 | 正常 |
| 社交退缩 | + | + |
| 言语发育迟缓 | + | + |
| 运动发育迟缓 | + | NA |
表2两名CHRM3基因缺失的孤独症患者的临床表现对比
| 特征 | Perrone等人报道的患者 | Andrea Klunder Petersen等人报道的患者 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄、性别 | 7岁, 男 | 3岁7个月, 男 |
| 智力缺陷 | + | + |
| 发育迟缓 | + | + |
| 孤独症行为 | + | + |
| 癫痫 | - | - |
| 进食困难 | + | + |
| 身材短小 | + | - |
| 体重偏轻 | + | - |
| 曲指 | + | - |
| 斜视 | + | + |
| 自伤倾向 | + | + |
| 脑部核磁共振造影 | 正常 | 正常 |
| 社交退缩 | + | + |
| 言语发育迟缓 | + | + |
| 运动发育迟缓 | + | NA |

图2CHRM3异常在脑与个体不同水平上的影响
 图2CHRM3异常在脑与个体不同水平上的影响
图2CHRM3异常在脑与个体不同水平上的影响参考文献 103
| 1 | Alexander G. M., Rogan S. C., Abbas A. I., Armbruster B. N., Pei Y., Allen J. A., … Roth B. L . ( 2009). Remote control of neuronal activity in transgenic mice expressing evolved g protein-coupled receptors. Neuron, 63( 1), 27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.06.014URLpmid: 19607790 |
| 2 | Amodeo D. A., Yi J., Sweeney J. A., & Ragozzino M. E . ( 2014). Oxotremorine treatment reduces repetitive behaviors in btbr t+ tf/j mice. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience, 6( 17), 1-8 doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2014.00017URLpmid: 25165445 |
| 3 | Bailey A., Le Couteur A., Gottesman I., Bolton P., Simonoff E., Yuzda E., & Rutter M . ( 1995). Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: Evidence from a British twin study. Psychological Medicine, 25( 1), 63-77. doi: 10.1017/S0033291700028099URLpmid: 7792363132 |
| 4 | Beck, C.H., &Fibiger, H.C . ( 1995). Conditioned fear-induced changes in behavior and in the expression of the immediate early gene c-fos: With and without diazepam pretreatment. Journal of Neuroscience, 15( 1), 709-720. doi: 10.1051/jphyscol:1990171URLpmid: 7823174 |
| 5 | Bentley P., Vuilleumier P., Thiel C. M., Driver J., & Dolan R. J . ( 2003). Cholinergic enhancement modulates neural correlates of selective attention and emotional processing. Neuroimage, 20( 1), 58-70. |
| 6 | Bernier R., Golzio C., Xiong B., Stessman H. A., Coe B. P., Penn O., .. Eichler E. E . ( 2014). Disruptive CHD8 mutations define a subtype of autism early in development. Cell, 158( 2), 263-276. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.017URLpmid: 24998929 |
| 7 | Bolivar V. J., Walters S. R., & Phoenix J. L . ( 2007). Assessing autism-like behavior in mice: Variations in social interactions among inbred strains. Behavoural Brain Research, 176( 1), 21-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.09.007URLpmid: 1831820 |
| 8 | Bowen D. M., Smith C. B., White P., & Davison A. N . ( 1976). Neurotransmitter-related enzymes and indices of hypoxia in senile dementia and other abiotrophies. Brain, 99( 3), 459-496. |
| 9 | Butler M. G., Rafi S. K., & Manzardo A. M . ( 2015). High-resolution chromosome ideogram representation of currently recognized genes for autism spectrum disorders. International Journal of Molecular Science, 16( 3), 6464-6495. doi: 10.3390/ijms16036464URLpmid: 25803107 |
| 10 | Buxbaum J. D., Silverman J. M., Smith C. J., Kilifarski M., Reichert J., Hollander E., .. Davis K. L . ( 2001). Evidence for a susceptibility gene for autism on chromosome 2 and for genetic heterogeneity. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 68( 6), 1514-1520. doi: 10.1086/320588URLpmid: 11353400 |
| 11 | Bymaster F. P., Carter P. A., Yamada M., Gomeza J., Wess J., Hamilton S. E., .. Felder C. C . ( 2003). Role of specific muscarinic receptor subtypes in cholinergic parasympathomimetic responses, in vivo phosphoinositide hydrolysis, and pilocarpine- induced seizure activity. European Journal Neuroscience, 17( 7), 1403-1410. |
| 12 | Carlezon Jr W. A., Duman R. S., & Nestler E. J . ( 2005). The many faces of CREB. Trends in Neuroscience, 28( 8), 436-445. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2005.06.005URLpmid: 15982754 |
| 13 | Chan S. F., Huang X., McKercher S. R., Zaidi R., Okamoto S. I., Nakanishi N., & Lipton S. A . ( 2015). Transcriptional profiling of MEF2-regulated genes in human neural progenitor cells derived from embryonic stem cells. Genomics Data, 3(C), 24-27. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2014.10.022URLpmid: 4255278 |
| 14 | Chen M., Wan Y., Ade K., Ting J., Feng G., & Calakos N . ( 2011). Sapap3 deletion anomalously activates short-term endocannabinoid-mediated synaptic plasticity. Journal of Neuroscience, 31( 26), 9563-9573. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1701-11.2011URLpmid: 21715621 |
| 15 | Ch'ng C., Kwok W., Rogic S., & Pavlidis P . ( 2015). Meta-analysis of gene expression in autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research, 8( 5), 593-608. doi: 10.1002/aur.1475URLpmid: 25720351 |
| 16 | Christensen D. L., Baio J., Van Naarden Braun K., Bilder D., Charles J., Constantino J. N., .. Yeargin-Allsopp M . ( 2016). Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years--Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2012. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 65( 3), 1-23. |
| 17 | Crane L., Pring L., Jukes K., & Goddard L . ( 2012). Patterns of autobiographical memory in adults with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42( 10), 2100-2112. doi: 10.1007/s10803-012-1459-2URLpmid: 22322581 |
| 18 | Cuccaro M. L., Shao Y., Grubber J., Slifer M., Wolpert C. M., & Donnelly S. L ., et al. ( 2003). Factor analysis of restricted and repetitive behaviors in autism using the autism diagnostic interview-r. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 34( 1), 3-17. doi: 10.1023/A:1025321707947URLpmid: 14518620 |
| 19 | Cupolillo D., Hoxha E., & Faralli A., De Luca A., Rossi F., Tempia F., & Carulli D ., ( 2015). Autistic-like traits and cerebellar dysfunction in Purkinje cell PTEN knock- out mice. . Neuropsychopharmacology, 41(6), 1457-1466. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.339URLpmid: 4832032 |
| 20 | Dani, J.A., &Bertrand, D . ( 2007). Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotinic cholinergic mechanisms of the central nervous system. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 47(1), 699-729. |
| 21 | De Rubeis S., He X., Goldberg A. P., Poultney C. S., Samocha K., Cicek A. E., .. Buxbaum J. D . ( 2014). Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature, 515( 7526), 209-215. doi: 10.1038/nature13772URLpmid: 25363760 |
| 22 | Deng, Y.P., &Reiner, A . ( 2016). Cholinergic interneurons in the Q140 knockin mouse model of Huntington's disease: Reductions in dendritic branching and thalamostriatal input. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 524( 17), 3518-3529. |
| 23 | Deutsch S. I., Urbano M. R., Neumann S. A., Burket J. A., & Katz E . ( 2010). Cholinergic abnormalities in autism: Is there a rationale for selective nicotinic agonist interventions? Clinical Neuropharmacology, 33( 3), 114-120. doi: 10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181d6f7adURLpmid: 20190638 |
| 24 | Devor A., Andreassen O. A., Wang Y., Mäki-Marttunen T., Smeland O. B., Fan C. C., .. Dale A. M . ( 2017). Genetic evidence for role of integration of fast and slow neurotransmission in schizophrenia. Molecular Psychiatry, 22( 6), 792-801. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.33URLpmid: 28348379 |
| 25 | Dineley K. T., Pandya A. A., & Yakel J. L . ( 2015). Nicotinic ACh receptors as therapeutic targets in CNS disorders. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 36( 2), 96-108. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2014.12.002URLpmid: 4324614 |
| 26 | Donato F., Chowdhury A., Lahr M., & Caroni P . ( 2015). Early- and late-born parvalbumin basket cell subpopulations exhibiting distinct regulation and roles in learning. Neuron, 85( 4), 770-786. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.01.011URLpmid: 25695271 |
| 27 | Durand C. M., Betancur C., Boeckers T. M., Bockmann J., Chaste P., Fauchereau F., .. Bourgeron T . ( 2007). Mutations in the gene encoding the synaptic scaffolding protein SHANK3 are associated with autism spectrum disorders. Nature Genetic, 39( 1), 25-27. doi: 10.1038/ng1933URLpmid: 2017173049 |
| 28 | Forrest M. P., Waite A. J., Martin-Rendon E., & Blake D. J . ( 2013). Knockdown of human TCF4 affects multiple signaling pathways involved in cell survival, epithelial to mesenchymal transition and neuronal differentiation. PLoS ONE, 8( 8), e73169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073169URLpmid: 3751932 |
| 29 | Friedman S. D., Shaw D. W. W., Artru A. A., Dawson G., Petropoulos H., & Dager S. R . ( 2006). Gray and white matter brain chemistry in young children with autism. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63( 7), 786-794. |
| 30 | Gai X., Xie H. M., Perin J. C., Takahashi N., Murphy K., Wenocur A. S., .. White P. S . ( 2012). Rare structural variation of synapse and neurotransmission genes in autism. Molecular Psychiatry, 17( 4), 402-411. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.10URLpmid: 21358714 |
| 31 | Gao Z., Lee P., Stafford J. M., von Schimmelmann M., Schaefer A., & Reinberg D . ( 2014). An AUTS2-Polycomb complex activates gene expression in the CNS. Nature, 516( 7531), 349-354. doi: 10.1038/nature13921URLpmid: 25519132 |
| 32 | Gaugler T., Klei L., Sanders S. J., Bodea C. A., Goldberg A. P., Lee A. B., .. Buxbaum J. D . ( 2014). Most genetic risk for autism resides with common variation. Nature Genetics,46( 8), 881-885. doi: 10.1038/ng.3039URLpmid: 25038753 |
| 33 | Haglund, N. G.S., &Kallen, K. B.M . ( 2011). Risk factors for autism and Asperger syndrome. Perinatal factors and migration. Autism, 15( 2), 163-183. doi: 10.1177/1362361309353614URLpmid: 20923887 |
| 34 | Happe F., Ronald A., & Plomin R . ( 2006). Time to give up on a single explanation for autism. Nature Neuroscience, 9( 10), 1218-1220. doi: 10.1038/nn1770URLpmid: 17001340 |
| 35 | Hardan A. Y., Jou R. J., & Handen B. L . ( 2005). Retrospective study of quetiapine in children and adolescents with pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Devlopment Disorders, 35( 3), 387-391. doi: 10.1007/s10803-005-3306-1URLpmid: 16119479 |
| 36 | Huguet G., Ey E., & Bourgeron T . ( 2013). The genetic landscapes of autism spectrum disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Human Genetics, 14( 1), 191-213. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153431URLpmid: 23875794 |
| 37 | Hussman J. P., Chung R. H., Griswold A. J., Jaworski J. M., Salyakina D., Ma D., .. Pericak-Vance M. A . ( 2011). A noise-reduction GWAS analysis implicates altered regulation of neurite outgrowth and guidance in autism. Molecular Autism, 2( 1), 1-16 doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-2-1URLpmid: 21247446 |
| 38 | Karvat, G., &Kimchi, T . ( 2014). Acetylcholine elevation relieves cognitive rigidity and social deficiency in a mouse model of autism. Neuropsychopharmacology, 39( 4), 831-840. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.274URLpmid: 24096295 |
| 39 | Kim J. W., Seung H., Kwon K. J., Ko M. J., Lee E. J., Oh H. A., .. Bahn G. H . ( 2014). Subchronic treatment of donepezil rescues impaired social, hyperactive, and stereotypic behavior in valproic acid-induced animal model of autism. PLoS ONE, 9( 8), e104927. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104927URLpmid: 25133713 |
| 40 | King I. F., Yandava C. N., Mabb A. M., Hsiao J. S., Huang H. S., Pearson B. L., .. Zylka M. J . ( 2013). Topoisomerases facilitate transcription of long genes linked to autism. Nature, 501( 7465), 58-62. doi: 10.1038/nature12504URLpmid: 3767287 |
| 41 | Koeleman, B. P.C. ( 2018). What do genetic studies tell us about the heritable basis of common epilepsy? Polygenic or complex epilepsy? Neuroscience Letters, 667, 10-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.03.042URLpmid: 28347857 |
| 42 | Lee M., Martin-Ruiz C., Graham A., Court J., Jaros E., Perry R., .. Perry E . ( 2002). Nicotinic receptor abnormalities in the cerebellar cortex in autism. Brain, 125( Pt 7), 1483-1495. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf160URLpmid: 12076999 |
| 43 | Levey A. I., Edmunds S. M., Heilman C. J., Desmond T. J., & Frey K. A . ( 1994). Localization of muscarinic m3 receptor protein and M3 receptor binding in rat brain. Neuroscience, 63( 1), 207-221. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90017-5URLpmid: 7898649 |
| 44 | Levey A. I., Edmunds S. M., Koliatsos V., Wiley R. G., & Heilman C. J . ( 1995). Expression of m1-m4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor proteins in rat hippocampus and regulation by cholinergic innervation. Journal of Neurosci, 15( 5), 4077-4092. URLpmid: 7751967 |
| 45 | Li J., Wang L., Guo H., Shi L., Zhang K., Tang M., .. Xia K . ( 2017). Targeted sequencing and functional analysis reveal brain-size-related genes and their networks in autism spectrum disorders. Molecular Psychiatry,22( 9), 1282-1290. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.140URLpmid: 28831199 |
| 46 | Lonze, B.E., &Ginty, D.D . ( 2002). Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron, 35( 4), 605-623. |
| 47 | Luukkonen T. M., Mehrjouy M. M., Pöyhönen M., Anttonen A. K., Lahermo P., Ellonen P., .. Varilo T . ( 2017). Breakpoint mapping and haplotype analysis of translocation t(1;12) (q43;q21.1) in two apparently independent families with vascular phenotypes. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine, 6( 1), 56-68. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.346URLpmid: 29168350 |
| 48 | Maccarrone M., Rossi S., Bari M., De Chiara V., Rapino C., Musella A., .. Centonze D . ( 2010). Abnormal mGlu 5 receptor/endocannabinoid coupling in mice lacking FMRP and BC1 RNA. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35( 7), 1500-1509. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.19URLpmid: 20393458 |
| 49 | Martin A., Koenig K., Scahill L., & Bregman J . ( 1999). Open-label quetiapine in the treatment of children and adolescents with autistic disorder. Journal of Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol, 9( 2), 99-107. |
| 50 | Martin-Ruiz C. M., Lee M., Perry R. H., Baumann M., Court J. A., & Perry E. K . ( 2004). Molecular analysis of nicotinic receptor expression in autism. Molecular Brain Research, 123( 1-2), 81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.01.003URLpmid: 15046869 |
| 51 | Matsui M., Araki Y., Karasawa H., Matsubara N., Taketo M. M., & Seldin M. F . ( 1999). Mapping of five subtype genes for muscarinic acetylcholine receptor to mouse chromosomes. Genes & Genetic Systems, 74( 1), 15-21. doi: 10.1266/ggs.74.15URLpmid: 10549128 |
| 52 | Matsui M., Motomura D., Karasawa H., Fujikawa T., Jiang J., Komiya Y., .. Taketo M. M . ( 2000). Multiple functional defects in peripheral autonomic organs in mice lacking muscarinic acetylcholine receptor gene for the M3 subtype. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97( 17), 9579-9584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.17.9579URL |
| 53 | McTighe S. M., Neal S. J., Lin Q., Hughes Z. A., & Smith D. G . ( 2013). The BTBR mouse model of autism spectrum disorders has learning and attentional impairments and alterations in acetylcholine and kynurenic acid in prefrontal cortex. PLoS ONE, 8( 4), e62189. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062189URLpmid: 3634761 |
| 54 | Meyer L. R., Zhu V., Miller A., & Roghair R. D . ( 2014). Growth restriction, leptin, and the programming of adult behavior in mice. Behavioural Brain Research, 275, 131-135. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.08.054URLpmid: 4252372 |
| 55 | Michaelson J. J., Shi Y. J., Gujral M., Zheng H. C., Malhotra D., Jin X., .. Sebat J . ( 2012). Whole-genome sequencing in autism identifies hot spots for de novo germline mutation. Cell, 151( 7), 1431-1442. |
| 56 | Mines M. A., Yuskaitis C. J., King M. K., Beurel E., & Jope R. S . ( 2010). GSK3 influences social preference and anxiety-related behaviors during social interaction in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome and autism. PLoS ONE, 5( 3), e9706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009706URLpmid: 2838793 |
| 57 | Moretti P., Levenson J. M., Battaglia F., Atkinson R., Teague R., Antalffy B., .. Zoghbi H. Y . ( 2006). Learning and memory and synaptic plasticity are impaired in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Journal of Neuroscience, 26( 1), 319-327. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2623-05.2006URLpmid: 16399702 |
| 58 | Neale B. M., Kou Y., Liu L., Ma'ayan A., Samocha K. E., Sabo A., .. Daly M. J . ( 2012). Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders. Nature, 485( 7397), 242-245. |
| 59 | Nelson K. B., Grether J. K., Croen L. A., Dambrosia J. M., Dickens B. F., Jelliffe L. L., .. Phillips T. M . ( 2001). Neuropeptides and neurotrophins in neonatal blood of children with autism or mental retardation. Ann Neurol, 49( 5), 597-606. doi: 10.1002/ana.1024URLpmid: 11357950 |
| 60 | O'Connor E. C., Bariselli S., & Bellone C . ( 2014). Synaptic basis of social dysfunction: A focus on postsynaptic proteins linking group-I mGluRs with AMPARs and NMDARs. European Journal of Neuroscience, 39( 7), 1114-1129. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12510URLpmid: 24712991 |
| 61 | Okerlund, N.D., &Cheyette, B. N.R . ( 2011). Synaptic Wnt signaling-a contributor to major psychiatric disorders? Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 3( 2), 162-174. doi: 10.1007/s11689-011-9083-6URLpmid: 3180925 |
| 62 | O'Roak B. J., Vives L., Fu W., Egertson J. D., Stanaway I. B., Phelps I. G., .. Shendure J . ( 2012). Multiplex targeted sequencing identifies recurrently mutated genes in autism spectrum disorders. Science, 338( 6114), 1619-1622. doi: 10.1126/science.1227764URLpmid: 23160955 |
| 63 | O'Roak B. J., Vives L., Girirajan S., Karakoc E., Krumm N., Coe B. P., .. Eichler E. E . ( 2012). Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature, 485( 7397), 246-250. doi: 10.1038/nature10989URLpmid: 22495309 |
| 64 | Ozonoff S., Young G. S., Carter A., Messinger D., Yirmiya N., Zwaigenbaum L., .. Stone W. L . ( 2011). Recurrence risk for autism spectrum disorders: A baby siblings research consortium study. Pediatrics, 128( 3), e488-e495. |
| 65 | Perrone M. D., Rocca M. S., Bruno I., Faletra F., Pecile V., & Gasparini P . ( 2012). De novo 911 Kb interstitial deletion on chromosome 1q43 in a boy with mental retardation and short stature. European Journal of Medical Genetics, 55( 2), 117-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2011.11.004URLpmid: 22186213 |
| 66 | Perry E. K., Lee M. L. W., Martin-Ruiz C. M., Court J. A., Volsen S. G., Merrit J., .. Wenk G. L . ( 2001). Cholinergic activity in autism: Abnormalities in the cerebral cortex and basal forebrain. American Journal of Psychiatry, 158( 7), 1058-1066. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.158.7.1058URLpmid: 11431227 |
| 67 | Petersen A. K., Ahmad A., Shafiq M., Brown-Kipphut B., Fong C. T., & Anwar Iqbal M . ( 2013). Deletion 1q43 encompassing only CHRM3 in a patient with autistic disorder. European Journal of Medical Genetics, 56( 2), 118-122. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2012.11.003URLpmid: 23253743 |
| 68 | Pinto D., Delaby E., Merico D., Barbosa M., Merikangas A., Klei L., .. Scherer S. W . ( 2014). Convergence of genes and cellular pathways dysregulated in autism spectrum disorders. American Journal of Human Genetics, 94( 5), 677-694. |
| 69 | Pinto D., Pagnamenta A. T., Klei L., Regan R., Conroy J., Casey J., .. Ennis S . ( 2011). Functional impact of global rare copy number variation in autism spectrum disorders . American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry/ Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Joint Meeting, 466( 7304), 368-372. |
| 70 | Poulin B., Butcher A., McWilliams P., Bourgognon J. M., Pawlak R., Kong K. C., .. Tobin A. B . ( 2010). The M3-muscarinic receptor regulates learning and memory in a receptor phosphorylation/arrestin-dependent manner. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107( 20), 9440-9445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914801107URLpmid: 20439723 |
| 71 | Qu D., Ludwig D. S., Gammeltoft S., Piper M., Pelleymounter M. A., Cullen M. J., .. Maratos-Flier E . ( 1996). A role for melanin-concentrating hormone in the central regulation of feeding behaviour. Nature, 380( 6571), 243-247. |
| 72 | Ray M. A., Graham A. J., Lee M., Perry R. H., Court J. A., & Perry E. K . ( 2005). Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits in autism: An immunohistochemical investigation in the thalamus. Neurobiology of Disease, 19( 3), 366-377. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.01.017URLpmid: 16023579 |
| 73 | Riikonen, R., &Vanhala, R . ( 1999). Levels of cerebrospinal fluid nerve-growth factor differ in infantile autism and Rett syndrome. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 41( 3), 148-152. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1999.tb00573.xURLpmid: 10210246 |
| 74 | Rinaldo, L., &Hansel, C . ( 2013). Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor activation blocks long-term potentiation at cerebellar parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses via cannabinoid signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110( 27), 11181-11186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221803110URL |
| 75 | Ronald A., Happe F., & Plomin R . ( 2005). The genetic relationship between individual differences in social and nonsocial behaviours characteristic of autism. Developmental Science, 8( 5), 444-458. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2005.00433.xURLpmid: 16048517 |
| 76 | Roohi J., Tegay D. H., Pomeroy J. C., Burkett S., Stone G., Stanyon R., & Hatchwell E . ( 2008). A de novo apparently balanced translocation [46,XY,t(2;9) (p13;p24)] interrupting RAB11FIP5 identifies a potential candidate gene for autism spectrum disorder. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B Neuropsychiatr Genet, 147b(#4), 411-417. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30755URLpmid: 18384058 |
| 77 | Rosenberg R. E., Law J. K., Yenokyan G., McGready J., Kaufmann W. E., & Law P. A . ( 2009). Characteristics and concordance of autism spectrum disorders among 277 twin pairs. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 163( 10), 907-914. doi: 10.1001/archpediatrics.2009.98URLpmid: 19805709 |
| 78 | Rosethorne E. M., Nahorski S. R ., & Challiss, R. A. J. ( 2008). Regulation of cyclic AMP response-element binding-protein (CREB) by Gq/11-protein-coupled receptors in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Biochemical Pharmacology, 75( 4), 942-955. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.10.015URLpmid: 2593902 |
| 79 | Sakai Y., Shaw C. A., Dawson B. C., Dugas D. V., Al-Mohtaseb Z., Hill D. E., & Zoghbi H. Y . ( 2011). Protein interactome reveals converging molecular pathways among autism disorders. Science Translational Medicine, 3( 86), 86ra49. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002166URLpmid: 21653829 |
| 80 | Sanders S. J., He X., Willsey A. J., Ercan-Sencicek A. G., Samocha K. E., Cicek A. E., .. State M. W . ( 2015). Insights into autism spectrum disorder genomic architecture and biology from 71 risk loci. Neuron, 87( 6), 1215-1233. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.016URLpmid: 4624267 |
| 81 | Sanders S. J., Murtha M. T., Gupta A. R., Murdoch J. D., Raubeson M. J., Willsey A. J., .. State M. W . ( 2012). De novo mutations revealed by whole-exome sequencing are strongly associated with autism. Nature, 485( 7397), 237-241. |
| 82 | Schaaf, C.P., &Zoghbi, H.Y . ( 2011). Solving the autism puzzle a few pieces at a time. Neuron, 70( 5), 806-808. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.025URLpmid: 21658575 |
| 83 | Cuccaro M. L., Shao Y., Grubber J., Slifer M., Wolpert C. M., & Donnelly S. L ., et al. ( 2003). Factor analysis of restricted and repetitive behaviors in autism using the autism diagnostic interview-r. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 34(1), 3-17. doi: 10.1023/A:1025321707947URLpmid: 14518620 |
| 84 | Shimojima K., Okamoto N., Suzuki Y., Saito M., Mori M., Yamagata T., .. Yamamoto T . ( 2012). Subtelomeric deletions of 1q43q44 and severe brain impairment associated with delayed myelination. Journal of Human Genetics, 57( 9), 593-600. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2012.77URLpmid: 22718018 |
| 85 | Silipigni R., Monfrini E., Baccarin M., Giangiobbe S., Lalatta F., Guerneri S., & Bedeschi M. F . ( 2017). Familial duplication/deletion of 1q42.13q43 as meiotic consequence of an intrachromosomal insertion in chromosome 1. Cytogenetic and Genome Research, 153( 2), 73-80. doi: 10.1159/000485226URLpmid: 29258113 |
| 86 | Silva A. J., Kogan J. H., Frankland P. W., & Kida S . ( 1998). CREB and memory. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 21( 1), 127-148. |
| 87 | Silverman J. L., Smith D. G., Rizzo S. J., Karras M. N., Turner S. M., Tolu S. S., .. Crawley J. N . ( 2012). Negative allosteric modulation of the mGluR5 receptor reduces repetitive behaviors and rescues social deficits in mouse models of autism. Science Translational Medicine, 4( 131), 131ra151. |
| 88 | Soueid J., Kourtian S., Makhoul N. J., Makoukji J., Haddad S., Ghanem S. S., .. Boustany R. M . ( 2016). RYR2, PTDSS1 and AREG genes are implicated in a Lebanese population- based study of copy number variation in autism. Scientific Reports, 6(2) 19088, 1-11 doi: 10.1038/srep19088URLpmid: 26742492 |
| 89 | Spinelli L., Black F. M., Berg J. N., Eickholt B. J., & Leslie N. R . ( 2015). Functionally distinct groups of inherited PTEN mutations in autism and tumour syndromes. Journal of Medical Genetics, 52( 2), 128-134. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102803URLpmid: 25527629 |
| 90 | State, M.W., &šestan, N . ( 2012). The emerging biology of autism spectrum disorders. Science, 337( 6100), 1301-1303. |
| 91 | Taniai H., Nishiyama T., Miyachi T., Imaeda M., & Sumi S . ( 2008). Genetic influences on the broad spectrum of autism: Study of proband-ascertained twins. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B Neuropsychiatr Genetics, 147b(#6), 844-849. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30740URLpmid: 18361421 |
| 92 | Tischmeyer W., Kaczmarek L., Strauss M., Jork R., & Matthies H . ( 1990). Accumulation of c-fos mRNA in rat hippocampus during acquisition of a brightness discrimination. Behavioral and Neural Biology, 54( 2), 165-171. doi: 10.1016/0163-1047(90)91366-JURLpmid: 2122879 |
| 93 | Tsang S. W., Francis P. T., Esiri M. M., Wong P. T., Chen C. P., & Lai M. K . ( 2008). Loss of [3h]4-damp binding to muscarinic receptors in the orbitofrontal cortex of alzheimer's disease patients with psychosis. Psychopharmacology, 198( 2), 251. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1124-9URLpmid: 18373228 |
| 94 | Vorstman J. A. S., Parr J. R., Moreno-De-Luca D., Anney R. J. L., Nurnberger J. I., Jr., & Hallmayer J. F . ( 2017). Autism genetics: Opportunities and challenges for clinical translation. Nature Reviews. Genetics, 18( 6), 362-376. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.4URLpmid: 28260791 |
| 95 | Wang, J.Q., &McGinty, J.F . ( 1997). Intrastriatal injection of a muscarinic receptor agonist and antagonist regulates striatal neuropeptide mRNA expression in normal and amphetamine-treated rats. Brain Research, 748( 1-2), 62-70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(96)01244-9URLpmid: 9067445 |
| 96 | Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., & Delon M. R . ( 1982). Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: Loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science, 215( 4537), 1237-1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341URLpmid: 7058341 |
| 97 | Wing, L. ( 1981). Language, social, and cognitive impairments in autism and severe mental retardation. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 11( 1), 31-44. doi: 10.1007/BF01531339URLpmid: 6927697 |
| 98 | Wood C. L., Warnell F., Johnson M., Hames A., Pearce M. S., McConachie H., & Parr J. R . ( 2015). Evidence for ASD recurrence rates and reproductive stoppage from large UK ASD research family databases. Autism Research, 8( 1), 73-81. doi: 10.1002/aur.1414URLpmid: 25273900 |
| 99 | Yamada M., Miyakawa T., Duttaroy A., Yamanaka A., Moriguchi T., Makita R., .. Wess J . ( 2001). Mice lacking the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor are hypophagic and lean. Nature, 410( 6825), 207-212. doi: 10.1038/35065604URLpmid: 11242080 |
| 100 | Yang M., Scattoni M. L., Zhodzishsky V., Chen T., Caldwell H., Young W. S., .. Crawley J. N . ( 2007). Social approach behaviors are similar on conventional versus reverse lighting cycles, and in replications across cohorts, in BTBR T+ tf/J, C57BL/6J, and vasopressin receptor 1B mutant mice. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 1( 1). doi: 10.3389/neuro.08/001.2007URLpmid: 2525856 |
| 101 | Yun, S.H., &Trommer, B.L . ( 2011). Fragile X mice: reduced long-term potentiation and N-Methyl-D-Aspartate receptor-mediated neurotransmission in dentate gyrus. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 89( 2), 176-182. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22546URLpmid: 21162125 |
| 102 | Zhang, L., &Alger, B.E . ( 2010). Enhanced endocannabinoid signaling elevates neuronal excitability in fragile X syndrome. Journal of Neuroscience, 30( 16), 5724-5729. |
| 103 | Zhang Y., Cao S. X., Sun P., He H. Y., Yang C. H., Chen X. J., .. Li X. M . ( 2016). Loss of MeCP2 in cholinergic neurons causes part of RTT-like phenotypes via alpha7 receptor in hippocampus. Cell Research, 26( 6), 728-742. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.48URLpmid: 27103432 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 王琳, 王志丹, 王泓婧. 孤独症儿童动作发展障碍的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(7): 1239-1250. |
| [2] | 毕小彬, 范晓壮, 米文丽, 贺荟中. 高风险婴儿前瞻性纵向研究与孤独症谱系障碍早期识别[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(3): 443-455. |
| [3] | 荆伟, 王庭照. 双通路理论视角下孤独症谱系障碍者的视线加工障碍[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(3): 508-521. |
| [4] | 赵晓宁, 胡金生, 李松泽, 刘西, 刘琼阳, 吴娜. 基于眼动研究的孤独症谱系障碍早期预测[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(2): 301-311. |
| [5] | 白晓宇, TawandaS.Mutusva, 祝卓宏. PEAK关系训练系统:孤独症语言障碍康复的新方法[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(11): 1896-1905. |
| [6] | 李涛涛, 胡金生, 王琦, 李骋诗, 李松泽, 何建青, 李辰洋, 刘淑清. 孤独症谱系障碍者的视听时间整合 *[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(6): 1031-1040. |
| [7] | 王分分, 祝卓宏. 言语行为的关系框架理论视角: 孤独症谱系障碍的新探索[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(8): 1321-1326. |
| [8] | 王琦;胡金生;李骋诗;李松泽. 孤独症谱系障碍者的情绪韵律识别[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(9): 1377-1390. |
| [9] | 李松泽; 胡金生; 李骋诗; 王琦; 刘淑清; 康晓东; 崔丽 . 孤独症谱系障碍者的视觉−空间工作记忆缺陷及脑机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(7): 1050-1064. |
| [10] | 黄文强;杨沙沙;于萍. 风险决策的神经机制: 基于啮齿类动物研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(11): 1767-1779. |
| [11] | 付娟; 郑希耕; 刘正奎. 条件化恐惧复发的动物模型及相关神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(10): 1592-1599. |
| [12] | 薛晓芳;李曼;王玮文;邵枫. 母婴分离的动物模型及其神经生物学机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2013, 21(6): 990-998. |
| [13] | 程九清;李勇辉;隋南. 基于啮齿类动物的决策行为研究及其脑机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2008, 16(5): 721-725. |
| [14] | 李量;李楠欣. 建立新一代的精神分裂症动物模型[J]. 心理科学进展, 2008, 16(3): 399-403. |
| [15] | 邵枫;王玮文;刘美;金暕. 精神分裂症的潜伏抑制动物模型[J]. 心理科学进展, 2008, 16(3): 392-398. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4518
