 ), 卢宏亮4
), 卢宏亮4 1 天津商业大学会计学院, 天津 300134
2 北京航空航天大学经济管理学院, 北京 100191
3 复杂系统分析与管理决策教育部重点实验室, 北京 100191
4 东北林业大学经济管理学院, 哈尔滨 150040
收稿日期:2017-11-20出版日期:2018-11-15发布日期:2018-09-26通讯作者:姚唐E-mail:yaot@buaa.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(71602146);* 国家自然科学基金项目(71572006);* 国家自然科学基金项目(71302065);天津市哲学社会科学规划研究项目(TJGL15-042);天津市哲学社会科学规划研究项目(TJGL15-019)The mechanism of consumer impulsive buying in the context of shopping with others
WANG Yanzhi1, YAO Tang2,3( ), LU Hongliang4
), LU Hongliang4 1 School of Accounting, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin 300134, China
2 School of Economics and Management, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
3 Key Laboratory of Complex System Analysis, Management and Decision (Beihang University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China
4 College of Economics and Management, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, 150040, China;
Received:2017-11-20Online:2018-11-15Published:2018-09-26Contact:YAO Tang E-mail:yaot@buaa.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 冲动性购买是生活中的常见现象, 也是消费者行为研究的重要子领域。围绕单人购物情境下的冲动购买研究成果较多, 而对结伴购物情境下的冲动购买行为研究明显不足。聚焦结伴购物情境下消费者的冲动购买现象, 基于“欲望-意志力”模型, 在情绪感染理论、归因理论等理论基础之上, 采用焦点访谈法、实验法、问卷调查法等研究方法, 从欲望和意志力两个方面, 深入探讨结伴购物消费者冲动购买行为发生的内部决策机理。研究结论将丰富现有结伴购物情境下的冲动购买行为研究内容, 也为企业营销实践、个人冲动购买行为管理以及政府部门开展消费者教育提供理论指导。
图/表 2
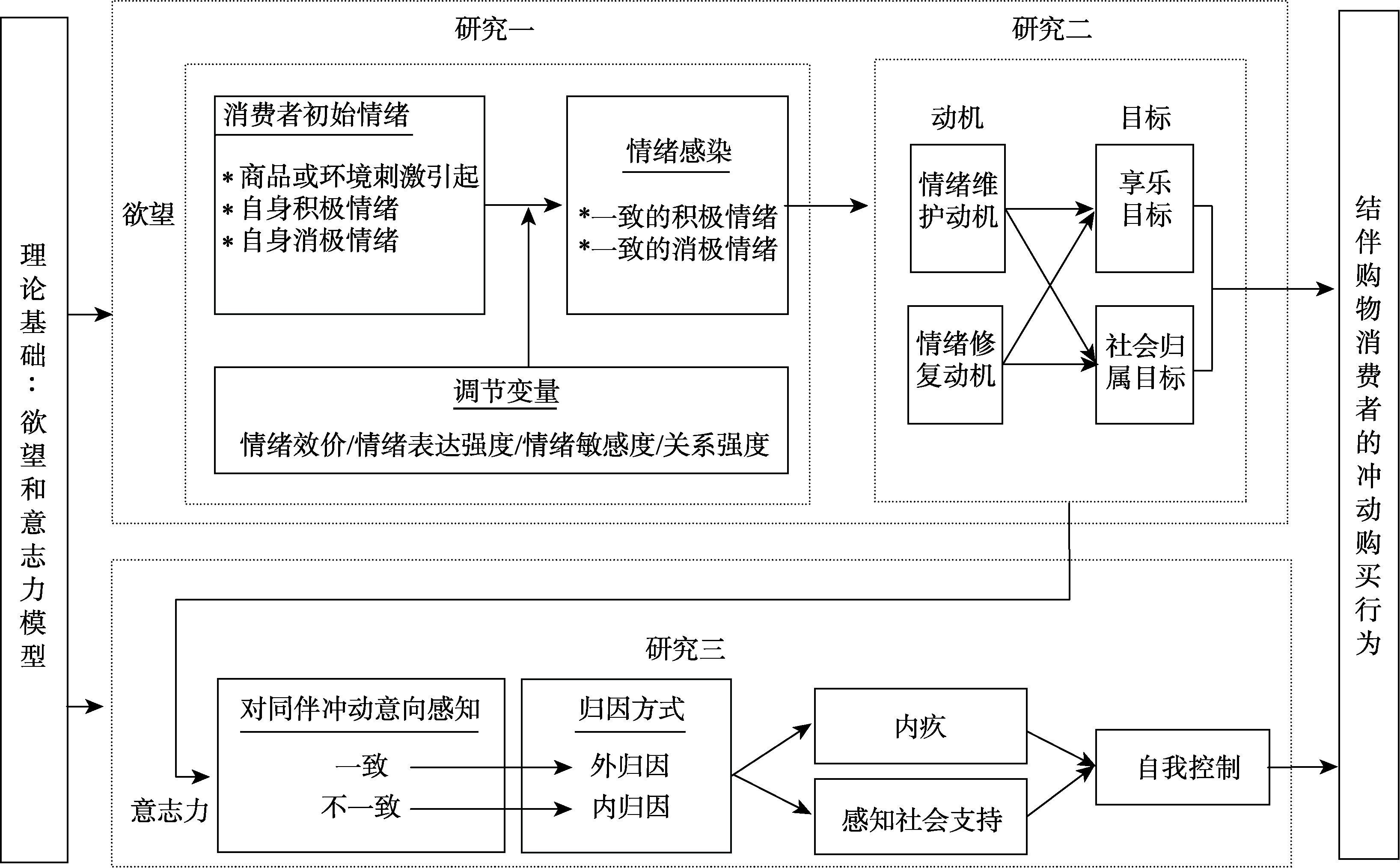
图1本研究理论框架
 图1本研究理论框架
图1本研究理论框架
图2本研究理论建构
 图2本研究理论建构
图2本研究理论建构参考文献 80
| [1] | 白建磊, 陈立平 . ( 2016). 终端陈列对顾客冲动性购买行为的诱发机制. 经济与管理研究, 37( 6), 130-136. doi: 10.13502/j.cnki.issn1000-7636.2016.06.017URL |
| [2] | 杜建刚, 范秀成 . ( 2009). 服务消费中多次情绪感染对消费者负面情绪的动态影响机制. 心理学报, 41( 4), 346-356. |
| [3] | 杜建刚, 范秀成 . ( 2011). 服务失败中群体消费者心理互动过程研究. 管理科学学报, 14( 12), 60-70. |
| [4] | 范秀成, 张运来 . ( 2006). 情感影响冲动性购买的机制研究. 社会科学家, 118( 2), 148-151. |
| [5] | 李志飞 . ( 2007). 异地性对冲动性购买行为影响的实证研究. 南开管理评论, 10( 6), 11-18. |
| [6] | 王丽丽, 吕巍, 黄静, 江麟 . ( 2008). 捆绑价格促销对冲动性购买影响研究. 管理评论, 20( 11), 17-24. |
| [7] | 汪涛, 王魁, 陈厚 . ( 2015). 时间间隔何时能够提高在线评论的有用性感知—基于归因理论的视角. 商业经济与管理, 280(2), 46-56. |
| [8] | 王振华, 柴俊武, 张倩 . ( 2014). 群体购买情境下冲动性购买影响研究: 解释水平视角. 应用心理学, 20( 2), 130-137. |
| [9] | 熊素红, 景奉杰 . ( 2009). 自我建构对群体购买环境中冲动性购买行为的影响. 情报杂志, 28( 11), 198-202. |
| [10] | 姚唐, 邱琪, 穆琳, 郑秋莹, 肖为群 . ( 2017). 社会支持视角下顾客在线互助心理和行为机制. 心理科学进展, 25( 6), 912-922. |
| [11] | 于建原, 谢丹 . ( 2008). 信用卡使用对冲动性购买行为影响研究. 营销科学学报, 4( 1), 137-149. |
| [12] | 张正林, 庄贵军 . ( 2008). 基于社会影响和面子视角的冲动购买研究. 管理科学, 21( 6), 66-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0334.2008.06.008URL |
| [13] | 张运来 . ( 2009). 基于情感视角的冲动性购买影响机制整合研究. 哈尔滨商业大学学报(社会科学版), ( 4), 3-7. |
| [14] | Barsade, S.G . ( 2002). The ripple effect: Emotional contagion and its influence on group behavior. Administrative Science Quarterly, 47( 4), 644-675. doi: 10.2307/3094912URL |
| [15] | Bartel, C.A., & Saavedra, R. ,( 2000). The collective construction of workgroup moods. Administrative Science Quarterly, 45( 2), 197-231. |
| [16] | Bashar, A., Ahmad, I., & Wasiq, M . ( 2013). A study of influence of demographic factors on consumer impulse buying behavior. Journal of Management Research, 13( 3), 145-154. |
| [17] | Baumeister, R.F . ( 2002). Yielding to temptation: Self- control failure, impulsive purchasing, and consumer behavior. Journal of Consumer Research, 28( 4), 670-676. |
| [18] | Baumeister, R.F., & , Heatherton, T., F . ( 1996). Self- regulation failure: An overview. Psychological Inquiry, 7( 1), 1-15. |
| [19] | Baumeister, R.F., & Leary, M.R . ( 1995). The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 117(3), 497-529. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.117.3.497URL |
| [20] | Bellenger, D. N., Robertson, D. H., & Hirschman, E. C . ( 1978). Impulse buying varies by product. Journal of Advertising Research, 18( 6), 15-18. |
| [21] | Bless, H., Bohner, G., Sxhwarz, N., & Strach, F . ( 1990). Mood and persuasion: A cognitive response analysis. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 16( 2), 331-345. doi: 10.1177/0146167290162013URL |
| [22] | Botvinick, M. M., Braver, T. S., Barch, D. M., Carter, C. S., & Cohen, J. D . ( 2001). Conflict monitoring and cognitive control. Psychological Review, 108( 3), 624-652. doi: 10.1037//0033-295X.108.3.624URLpmid: 11488380 |
| [23] | >Bowlby, J .( 1988). A secure base: Clinical applications of attachment theory. London: Routledge. |
| [24] | Buss, D.M., & Schmitt, D.P, .( 1993). Sexual strategies theory: An evolutionary perspective on human mating. Psychological Review, 100( 2), 204-232. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.100.2.204URL |
| [25] | Cialdini, R. B., Levy, A., Herman, C. P., & Evenbeck, S . ( 1973). Attitudinal politics: The strategy of moderation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 25( 1), 100-108. doi: 10.1037/h0034265URL |
| [26] | Cohen, S., & Wills, T.A . ( 1985). Stress, social support, and the buffering hypothesis. Psychological Bulletin, 98( 2), 310-357. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.98.2.310URL |
| [27] | Dzhogleva, H., & Lamberton, C.P . ( 2014). Should birds of a feather flock together? Understanding self-control decisions in dyads. Journal of Consumer Research, 41( 2), 361-380. doi: 10.1086/676599URL |
| [28] | Erber, R., & Erber, M.W . ( 2000). The self-regulation of moods: Second thoughts on the importance of happiness in everyday life. Psychological Inquiry, 11( 3), 142-148. doi: 10.1207/S15327965PLI1103_02URL |
| [29] | Fedorikhin, A., & Patrick, V.M . ( 2010). Positive mood and resistance to temptation: The interfering influence of elevated arousal. Journal of Consumer Research, 37(4), 698-711. doi: 10.1086/655665URL |
| [30] | Garcia, S. M., Weaver, K., Moskowitz, G. B., & Darley, J. M . ( 2002). Crowed minds: The implicit bystander effect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 83(4), 843-853. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.83.4.843URLpmid: 12374439 |
| [31] | Gardner, M.P., & , Rook, D., W . ( 1988). Effects of impulse purchases on consumers’ affective states. Advances on Consumer Research, 15( 1), 127-130. |
| [32] | Gorn, G.J . ( 1982). The effects of music in advertising on choice behavior: A classical conditioning approach. Journal of Marketing, 46( 1), 94-101. |
| [33] | Gray, J. A. ( 2003). The neuropsychology of anxiety: An enquiry into the function of the septo-hippocampal system. New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [34] | Hagtvedt, H., & Patrick, V.M . ( 2008). Art infusion: The influence of visual art on the perception and evaluation of consumer products. Journal of Marketing Research, 45( 3), 379-389. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.45.3.379URL |
| [35] | Hasford, J., Hardesty, D. M., & Kidwell, B . ( 2015). More than a feeling: Emotional contagion effects in persuasive communication. Journal of Marketing Research, 52 ( 6), 836-847. |
| [36] | Hatfield, E., Cacioppo, J. T., & Rapson, R. L . ( 1992). Primitive emotional contagion. ln M. S. Clark (Ed) Review of Personality and Social Psychology, Vol. 14. Emotion and Social Behavior ( 151-177). Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications, Inc. |
| [37] | Hatfield, E., Cacioppo, J. T., & Rapson, R. L .( 1994) . Emotional contagion. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [38] | Heider, F .( 1958). The psychology of interpersonal relations. New York: Wiley. |
| [39] | Henning-Thuar, T., Groth, M., Paul, M., & Gremler, D. D . ( 2006). Are all smiles created equal? How emotional contagion and emotional labor affect service relationships. Journal of Marketing, 70( 3), 58-73. |
| [40] | Hoch, S.J., & Loewenstein, G.F . ( 1991). Time-inconsistent preferences and consumer self-control. Journal of Consumer Research, 17( 4), 492-507. |
| [41] | Howard, D.J., & Gengler, C. .( 2001). Emotional contagion effects on product attitudes. Journal of Consumer Research, 28( 2), 189-201. |
| [42] | Hur, J. D., Koo, M., & Hofmann, W . ( 2015). When temptations come alive: How anthropomorphism undermines self-control. Journal of Consumer Research, 42( 2), 340-358. |
| [43] | Kanouse, D. E.,& Hanson, J. ( 1972). Negativity in evaluations. Morristown, NJ: General Learning Press. |
| [44] | Kelley, H.H . ( 1967). Attribution theory in social psychology. Nebraska Symposium on Motivatio n. Lincoln, 15, 192-238. |
| [45] | Khan, U. & Dhar, R .( 2010). Price framing effects on purchase of hedonic and utilitarian bundles. Journal of Marketing Research, 47(#6), 1090-1099. |
| [46] | Kivetz, R. & Simonson, I .( 2002). Earning the right to indulge: Effort as a determinant of customer preferences towards frequency program rewards. Journal of Marketing Research, 39( 2), 155-170. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.39.2.155.19084URL |
| [47] | >Kivetz, R., & Zheng, Y.H . ( 2017). The effects of promotions on hedonic versus utilitarian purchases. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 27( 1), 59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jcps.2016.05.005URL |
| [48] | Lowe, M.L.,& Haws, K.L . ( 2014). ( Im)Moral support: The social outcomes of parallel self-control decisions. Journal of Consumer Research, 41( 2), 489-505. |
| [49] | Luo, X.M . ( 2005). How does shopping with others influence impulsive purchasing? Journal of Consumer Psychology, 15( 4), 288-294. doi: 10.1207/s15327663jcp1504_3URL |
| [50] | >MacDonald, G., &Leary, M.R . ( 2005). Why does social exclusion hurt? The relationship between social and physical pain. Psychological Bulletin, 131 ( 2), 202-223. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.131.2.202URLpmid: 15740417 |
| [51] | Mano, H .( 1992). Judgments under distress: Assessing the role of unpleasantness and arousal in judgment formation. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 52( 2), 216-245. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(92)90036-7URL |
| [52] | Mead, N. L., Baumeister, R. F., Stillman, T. F., Rawn, C. D., & Vohs, K. D . ( 2011). Social exclusion causes people to spend and consume strategically in the service of affiliation. Journal of Consumer Research, 37( 5), 902-919. doi: 10.1086/656667URL |
| [53] | Mick,D.G., & DeMoss, M.( 1990). Self-gifts: Phenomenological insights from four contexts. Journal of Consumer Research, 17( 3), 322-332. |
| [54] | Mikulincer, M., Florian, V., & Hirschberger, G . ( 2003). The existential function of close relationships: Introducing death into the science of love. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 7( 1), 20-40. doi: 10.1207/S15327957PSPR0701_2URL |
| [55] | Puri, R .( 1996). Measuring and modifying consumer impulsiveness: A cost-benefit accessibility framework. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 5( 2), 87-113. doi: 10.1207/s15327663jcp0502_01URL |
| [56] | Push, S.D . ( 2001). Service with a smile: Emotional contagion in the service encounter. Academy of Management Journal, 44( 5), 1018-1027. |
| [57] | Raghunathan, R., &Corfman, K.( 2006). Is happiness shared doubled and sadness shared halved? Social influence on enjoyment of hedonic experiences. Journal of Marketing Research, 43(3), 386-394. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.43.3.386URL |
| [58] | Ramanathan, S., &Menon, G.( 2006). Time-varying effect of chronic hedonic goals on impulsive behavior. Journal of Marketing Research, 43( 4), 628-641. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.778944URL |
| [59] | Rook, D.W . ( 1987). The buying impulse. Journal of Consumer Research, 14( 2), 189-199. |
| [60] | Rook, D.W., & Gardner, M.P . ( 1993). In the mood: Impulse buying’s affective antecedents. Research in Consumer Behavior, 6( 7), 1-28. |
| [61] | Rook, D.W., & Hoch, S.J . ( 1985). Consuming impulses. Advances in Consumer Research, 12( 3), 23-27. |
| [62] | Rook, D.W., & Fisher, R.J . ( 1995). Normative influences on impulsive buying behavior. Journal of Consumer Research, 22( 3), 305-313. doi: 10.1086/jcr.1995.22.issue-3URL |
| [63] | Rucker, D. D., Galinsky, A. D., & Dubois, D . ( 2012). Power and consumer behavior: How power shapes who and what consumers value. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 22(3), 352-368. doi: 10.1016/j.jcps.2011.06.001URL |
| [64] | Sarah, M., &Arthur, K.( 2003). Negative affect: The dark side of retailing. Journal of Business Research, 56( 7), 553-559. doi: 10.1016/S0148-2963(01)00245-4URL |
| [65] | Scherer, K.R . ( 1981). Speech and emotional states. In J. K. Darby (ed.), Speech Evaluation in Psychiatry: New York: Grune and Stratton, 189-220. |
| [66] | Shiv, B., &Fedorikhin, A.( 2002). Spontaneous versus controlled influences of stimulus-based affect on choice behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 87( 2), 342-370. doi: 10.1006/obhd.2001.2977URL |
| [67] | Simpson, J. A., Griskevicius, V., & Rothman, A. J . ( 2012). Consumer decision in relationships. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 22( 3), 304-314. |
| [68] | Verplanken, B., &Herabadi, A.( 2001). Individual differences in impulsive buying tendency: feeling and no thinking. European Journal of Personality, 15( s1), 71-83. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0984URL |
| [69] | Verplanken, B., Herabadi, A. G., Perry, J. A., & Silvera, D. H . ( 2005). Consumer style and health: The role of impulsive buying in unhealthy eating. Psychology and Health, 24( 4), 429-441. |
| [70] | Vohs, K.D., & Faber, R.J . ( 2007). Spent resources: Self-regulatory resource availability affects impulse buying. Journal of Consumer Research, 33( 4), 537-547. doi: 10.1086/502810URL |
| [71] | Wallbott, H. G. , & Scherer, K. R.( 1986) . The antecedents of emotional experiences. ln K. R. Scherer, H. G. Wallbott, & A. B. Summerfield (Eds.), European monographs in social psychology. Experiencing emotion: A cross-cultural study (pp. 69-83). New York, NY, US: Cambridge University Press; Paris, France: Editions de la Maison des Sciences de l'Homme. |
| [72] | Walter, F., &Bruch, H.( 2008). The positive group affect spiral: A dynamic model of the emergence of positive affective similarity in work groups. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 29( 2), 239-261. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1379URL |
| [73] | Weiner, B.( 1986). An attributional theory of motivation and emotion. New York: Springer-Verlag. |
| [74] | Weiner, B., Frieze, I., Kukla, A., Reed, L., Rest, S. , & Rosenbaum, R. M.( 1971). Perceiving the causes of success and failure. Morristown, NJ: General Learning Publishing Group. |
| [75] | Williams, K. D., Cheung, C. K. T., & Choi, W . ( 2000). Cyberostracism: Effects of being ignored over the internet. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79( 5), 748-762. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.79.5.748URL |
| [76] | Xu, Q., Zhou, Y. J., Ye, M. L., & Zhou, X. Y . ( 2015). Perceived social support reduces the pain of spending money. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 25( 2), 219-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jcps.2014.11.004URL |
| [77] | Yamaguchi, S.( 1998). Biased risk perceptions among Japanese: Illusion of interdependence among risk companions. Asian Journal of Social Psychology, 1( 2), 117-131. doi: 10.1111/ajsp.1998.1.issue-2URL |
| [78] | Yao, T., Zheng, Q. Y., & Fan, X. C . ( 2015). The impact of online social support on patients’ quality of life and the moderating role of social exclusion. Journal of Service Research, 18( 3), 369-383. |
| [79] | Zhang, Y. L., Winterich, K. P., & Mittal, V . ( 2010). Power distance belief and impulsive buying. Journal of Marketing Research, 47( 5), 945-954. doi: 10.2307/20751555URL |
| [80] | Zhou,L.X., & Wong, A.( 2003). Consumer impulse buying and in-store stimuli in Chinese supermarkets. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 16( 2), 37-53. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 何嘉梅, 金磊. 目标概念的辨析及其对决策的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1410-1419. |
| [2] | 孙国晓, 张力为. 竞赛压力、注意控制与运动表现关系的理论演进[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 1122-1130. |
| [3] | 刘毅, 王君起, 邬辛佳. 双系统模型视角下的罪犯自我控制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(8): 1379-1391. |
| [4] | 颜爱民, 李亚丽, 谢菊兰, 李莹. 员工对企业社会责任的差异化反应:基于归因理论的阐释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(6): 1004-1014. |
| [5] | 李晓晨, 常若松, 马锦飞. 攻击性驾驶行为的综合模型[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(4): 748-760. |
| [6] | 刘永芳, 范雯健, 侯日霞. 从理论到研究, 再到应用:塞勒及其贡献[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(3): 381-393. |
| [7] | 严瑜, 曹照雪. 工作场所文明行为:从内隐的自我提升到外显的组织优化[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(11): 1906-1916. |
| [8] | 严瑜, 李彤. 工作场所不文明行为受害者向实施者反转的机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1307-1318. |
| [9] | 利振华, 窦凯, 聂衍刚. 远离“诱惑”:预先承诺对跨期决策的调控机制及其神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(10): 1869-1877. |
| [10] | 张玥, 窦东徽, 辛自强. 解释水平对自我控制的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(10): 1878-1889. |
| [11] | 董军, 付淑英, 卢山, 杨绍峰, 齐春辉. 自我控制失败的理论模型与神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(1): 134-143. |
| [12] | 潘爱玲, 胥遥山, 李永娟. 自我损耗对工作场所安全的影响及缓解途径[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(8): 1261-1273. |
| [13] | 项明强;张力为;张阿佩;杨红英. 自我损耗对运动表现影响的元分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(4): 570-585. |
| [14] | 窦泽南;方圆;周伟;乔志宏. 自我控制的奖励模型与神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(1): 86-98. |
| [15] | 严瑜;何亚男. 领导对建言反应的动机感知作用机制:基于归因理论的阐释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(9): 1457-1466. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4498
