 ,1,2,*
,1,2,*A new species of Pteronisculus from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Luoping, Yunnan, China, and phylogenetic relationships of early actinopterygian fishes
REN Yi1,2,3, XU Guang-Hui ,1,2,*
,1,2,*通讯作者: *xuguanghui@ivpp.ac.cn
收稿日期:2021-01-28
| 基金资助: |
Corresponding authors: *xuguanghui@ivpp.ac.cn
Received:2021-01-28

摘要
辐鳍鱼亚纲是现存脊椎动物中最大的类群,包括腕鳍鱼次亚纲、辐鳍鱼次亚纲(包括软骨硬鳞类和新鳍鱼类)和亲缘关系密切的化石类群。已灭绝的翼鳕属(Pteronisculus)是隶属于辐鳍鱼亚纲的一个干群,包括产于马达加斯加、欧洲和北美下三叠统的11个种和中国中三叠统的一个种。根据滇东罗平中三叠世(安尼期)海相地层中发现的5块保存完好的化石,命名翼鳕属一新种,张氏翼鳕(Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.)。这是翼鳕属在中三叠世的第二个确切种,最大体长达295 mm, 代表了罗平生物群中已知体型最大的辐鳍鱼亚纲干群物种。新种具有翼鳕属的独特衍征,泪骨具有牙齿,但它又有明显区别于本属其他种的自近裔特征,如间颞骨中部有一个内突起,21根上神经骨,83列侧线鳞。分支分析结果为早期辐鳍鱼类系统发育关系提供了新的见解,认为翼鳕属是Cyranorhis的姐妹群。根据体型和口缘牙齿等特征推测张氏翼鳕是一个快速游动的捕食者,以浮游无脊椎动物和体型较小的鱼类或鱼类幼体为食。作为翼鳕属最年轻的成员之一,张氏翼鳕的发现进一步表明翼鳕的多样性比我们过去认识的要高,古特提斯洋东缘可能是该属在中三叠世早期的避难所。
关键词:
Abstract
Actinopterygii, the largest group of extant vertebrates, includes Cladistia, Actinopteri (Chondrostei plus Neopterygii) and closely related fossil taxa. The extinct genus Pteronisculus belongs to a stem lineage of actinopterygian fishes represented by 11 species from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, Europe and North America, and a single species from the early Middle Triassic of China. Here, we report the discovery of a new species of this genus, Pteronisculus changae, on the basis of five well-preserved specimens from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) marine deposits exposed in Luoping, eastern Yunnan, China. The discovery documents the second convincing species of Pteronisculus in the Middle Triassic and the largest stem actinopterygian fish in the Luoping Biota, having a maximum total length of up to 295 mm. The new species possesses a toothed lacrimal, which is characteristic ofPteronisculus, but it is easily distinguished from other species of the genus by some autapomorphies, e.g., a medial process at the middle portion of the intertemporal, 21 supraneurals, and 83 lateral line scales. The results of our cladistic analysis provide new insights into the relationships of early actinopterygians and recover Pteronisculus as a sister taxon of the Carboniferous rhadinichthyid Cyranorhis at the actinopterygian stem. Based on the body form, teeth and other features, it can be deduced that Pteronisculus changae is likely a relatively fast-swimming predator, feeding on planktonic invertebrates and smaller or younger fishes known to occur in the same biota. As one of the youngest species of the genus, the new species provides additional evidence to suggest that the diversity of Pteronisculus is higher than previously thought and that the eastern Paleotethys Ocean likely constituted a refuge for species of this genus during the early Middle Triassic.
Keywords:
PDF (11663KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
任艺, 徐光辉. 云南罗平中三叠世翼鳕属一新种及早期辐鳍鱼类系统发育关系. 古脊椎动物学报[J], 2021, 59(3): 169-199 DOI:10.19615/j.cnki.2096-9899.210518
REN Yi, XU Guang-Hui.
1 Introduction
Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) is the most diverse clade of living vertebrates comprising Cladistia, Actinopteri (Chondrostei plus Neopterygii) and their closely related fossil taxa (Patterson, 1982; Gardiner, 1984; Coates, 1999; Hurley et al., 2007; Sallan, 2014; Friedman, 2015; Giles et al., 2017; Argyriou et al., 2018). The oldest proposed actinopterygian is the Early Devonian (~415 Ma) Meemannia on the basis of a few detached skull roofs and an isolated lower jaw (Lu et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2006); even earlier candidates are represented by fragments subject to differing phylogenetic interpretations (Wang and Dong, 1989; Basden and Young, 2001; Schultze, 2015). The earliest widely accepted actinopterygian based on relatively complete specimens is the Middle Devonian (Eifelian, ~390 Ma) Cheirolepis spp. (Pearson and Westoll, 1979; Pearson, 1982; Arratia and Cloutier, 1996; Lu et al., 2016; Giles et al., 2017). There are so far 22 actinopterygian species (in 16 genera) recovered from the Devonian, according to our preliminary statistics. A greater diversification of actinopterygians occurred in the Carboniferous and Permian, with about 100 genera known from those periods (Gardiner, 1993; Lund and Poplin, 1997; Lund, 2000; Poplin and Lund, 2000, 2002; Bender, 2002, 2005; Figueiredo and Carvalho, 2004; Hamel, 2005; Mickle et al., 2009; Mickle, 2018; Wilson et al., 2018 and others). In the aftermath of the end-Permian mass extinction, neopterygians underwent a rapid radiation and basal actinopterygians (traditionally referred to the paraphyletic ‘Palaeonisciformes’) greatly declined and died out at the end of the Cretaceous ( Friedman, 2015).Pteronisculus is a basal actinopterygian genus with a geological range confined to Early to Middle Triassic. Until recently, 12 species were referred to the genus (Fig. 1A; Online Supplementary Material); among which there are four well-studied species based on relatively complete specimens: the Early Triassic P. cicatrosus (type species, Madagascar), P. stensioi (modified from P. stensiöi, according to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature 32.5.2.1) andP. magnus (Greenland), and the Middle Triassic (Anisian) P. nielseni (South China). Although possible species of Pteronisculus were also reported from the late Permian (Lopingian) continental deposits of South Africa (Gardiner, 1966; Bender, 2004) and Early Triassic marine deposits of Alberta and British Columbia in Canada (Schaeffer and Mangus, 1976), they are based on poorly-preserved specimens and their reference to this genus is questionable (Romano et al., 2019). The relationships between Pteronisculus and other early actinopterygians are controversial; the genus has been recovered as either a stem actinopteran ( Gardiner and Schaeffer, 1989; Xu and Gao, 2011; Xu et al., 2014a) or a stem actinopterygian (Giles et al., 2017; Argyriou et al., 2018). Additionally, the interrelationships between species of Pteronisculus have never been explored in a phylogenetic analysis.
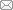
Fig. 1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 1Fossil localities of Pteronisculus
A. Map showing the global distribution of fossil localities of Pteronisculus: ① Yunnan, China, ② Spitsbergen (Svalbard, Norway), ③ East Greenland, ④ Nevada, USA, ⑤ Madagascar; B. Geographic locality yielding Pteronisculus changae sp. nov. in Luoping, Yunnan, China; C. Map of eastern Yunnan showing the fossil locality (World map: GS(2016)No. 1611; China map: GS(2016)No. 1549)
Here, we report the discovery of a new species of Pteronisculus on the basis of five specimens from the Second Member of the Guanling Formation exposed near Dawazi village, Luoping Country in Yunnan Province (Fig. 1C). The specimens are nearly complete and well-preserved in thinly laminated micritic limestone, permitting a detailed description of the morphology of the new species. The discovery documents the second species of Pteronisculus in South China (or more generally in Asia), and represents one of the youngest members of this genus, along with P. nielseni from the same fossil beds. A phylogenetic analysis was performed to resolve the interrelationships between Pteronisculus and other early actinopterygians.
In addition to the new species of Pteronisculus reported here, other macrofossils have been reported from the same fossiliferous horizons at the Luoping localities, including plants, invertebrates, diverse marine reptiles and other taxa of ray-finned fishes (Tintori et al., 2007, 2010; Sun et al., 2009, 2015, 2016; López-Arbarello et al., 2011; Wu et al., 2011; Xu and Wu, 2012; Feldmann et al., 2012; Wen et al., 2012, 2013, 2019; Xu and Ma, 2016; Xu and Zhao, 2016; Xu et al., 2014a, b; Ma and Xu, 2017; Xu, 2020a). The whole of the fossil assemblage, known as the Luoping Biota, was suggested to have inhabited a semi-enclosed intraplatform basin (Hu et al., 2011; Benton et al., 2013). The age of this biota (Pelsonian, Anisian, ~244.2 Ma) is well constrained by conodont biozonation and zircon dating (Zhang et. al., 2009, 2015).
2 Material and methods
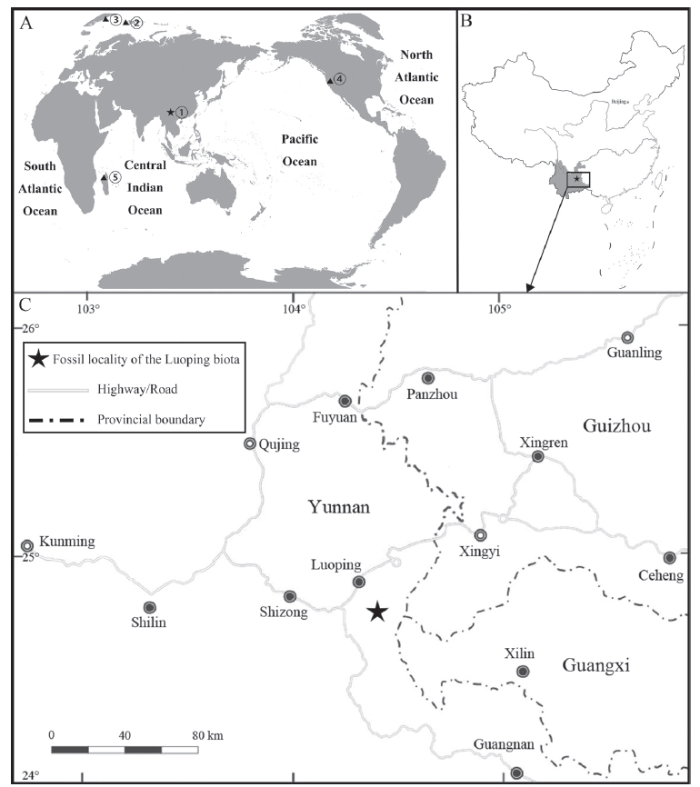
All specimens are housed in the fossil collections of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP), Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, China. They were mechanically prepared with sharp steel needles. For better contrast, some specimens were dusted with ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) or immersed in water before being photographed. The relative positions of the fins and scale row counts followWestoll (1944). The measurements of the specimens (Fig. 2) are as described in Schultze and Bardack (1987). The estimations of suspensorium angles are following Gardiner et al. (2005). The anatomical terms and bone names follow Gardiner and Schaeffer (1989), Grande and Bemis, 1998; Arratia, 2009 and Xu et al. (2014b).Fig. 2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 2Measurements adopted to describe the new species
A phylogenetic analysis was conducted by incorporating the new species of Pteronisculus into the matrix of Argyriou et al. (2018), which was in turn derived from that of Giles et al. (2017). Since the focus of this analysis is on the interrelationships of early actinopterygian clades above Cheirolepis level, we chose the basal sarcopterygian Guiyu as the outgroup, and removed other non-actinopterygians, as well as some actinopterygians based on incomplete or poorly preserved specimens (e.g., Meemannia, Lawrenciella and Tanaocrossus), and a few crown neopterygians (e.g., Macrepistius) from the data matrix. We added seven characters (Chars. 276-282), giving a total of 282 equally weighted characters coded for 67 taxa in our data matrix (Supplementary Material). Besides the new species of Pteronisculus, the additional taxa in the current data matrix include Asialepidotus shingyiensis (Su, 1959; Xu and Ma, 2018), Ionoscopus cyprinoides (Grande and Bemis, 1998; Maisey, 1999), Louwoichthys pusillus (Xu, 2021), Ophiopsiella attenuata (Wagner, 1863; Bartram, 1975; Lane and Ebert, 2015), Pteronisculus cicatrosus (Lehman, 1952), P. magnus (Nielsen 1942), P. nielseni (Xu et al., 2014b) and Teffichthys madagascariensis (Piveteau, 1934; Marramà et al., 2017). The maximum parsimony analyses were performed with a heuristic search in PAUP* v.4.0b10 using 500 random addition sequence replicates, holding five trees at each step, with the tree bisection and reconnection (TBR) strategy enabled and maxtrees set to automatically increase by 100.
Anatomical abbreviations an, anterior nostril; ang, angular; ao, antorbital; aop, antopercle; ar, articular; asp, ascending process of parasphenoid; bf, basal fulcrum; bpt, basipterygoid process; br, branchiostegal rays; cl, cleithrum; cla, clavicle; den, dentary; dhy, dermohyal; dpt, dermal palatine; dsp, dermosphenotic; ethc, ethmoid commissure canal; ff, fringing fulcra; fr, frontal; hll, horizontal longitudinal lamina; hm, hyomandibular; ih, interhyal; it, intertemporal; ju, jugal; lac, lacrimal; les, lateral extrascapular; lgu, lateral gular; lsc, lateral scute; mes, median extrascapular; mgu, medial gular; mr, median radial; msc, medial scute; mx, maxilla; na, nasal; nppn, notch on parasphenoid; op, opercle; pa, parietal; pas, parasphenoid; pcl, postcleithrum; pcr, procurrent ray; pio, postinfraorbital; pl-a, anterior pit-line; pl-m, median pit-line; pl-p, posterior pit-line; pn, posterior nostril; pop, preopercle; pq, palatoquadrate; pqn, notch of palatoquadrate; pr, principal ray; prl, proximal radial; pt, posttemporal; pv, pelvic plate; qj, quadratojugal; qu, quadrate region of palatoquadrate; r, rostral; sang, supra-angular; sbo, suborbital; sc, scute; scl, supracleithrum; slr, sclerotic ring; sn, supraneural; sop, subopercle; st, supratemporal; vo, vomer.
Measurements CD, depth at base of caudal fin; CL, caudal length; DD, body depth at origin of dorsal fin; HA, length from end of head to origin of anal fin; HD, length from hind of head to origin of dorsal fin; HL, head length; ORB, orbital length; POL, postorbital length of head; SL, standard length; TL, total length (Fig. 2).
3 Systematic paleontology
Subclass Actinopterygii Cope, 1887Family ? Rhadinichthyidae Romer, 1945
Genus PteronisculusWhite, 1933
Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.
(Figs. 3-12, 13A, 14A)
Etymology The species name honors Mee-mann Chang for her contributions to paleoichthyological studies in China.
Holotype IVPP V 18994, a nearly complete, laterally compressed skeleton.
Paratype IVPP V 20493, 24340, 25615 and 25618.
Locality and horizon Luoping, Yunnan Province; second (upper) member of Guanling Formation, Pelsonian (~244.2 Ma), Anisian, Middle Triassic (Zhang et al., 2009, 2015).
Diagnosis A large-sized species of Pteronisculus distinguished from other species of the genus by the following combination of characters: presence of intertemporal/nasal contact; presence of medial process at middle portion of intertemporal; medial extrascapular nearly as large as lateral one; postorbital length 60% of head length; suspensorium angle of 35º; opercle three times as deep as subopercle; antopercle half of depth of opercle; presence of 21 supraneurals; and pterygial formula of D53/P15, A44, C71/T83.
4 Description
General morphology and size Similar to other species of Pteronisculus, the new species has a blunt snout, an elongate fusiform body, and a heterocercal caudal fin (Figs. 3, 4). The holotype (Fig. 3A) has a total length of 221.0 mm, a standard length of 155.5 mm, and a maximum body depth of 46.5 mm. The largest known specimen has a total length of 295.3 mm, a standard length of 215.0 mm. The measurements of five specimens are presented in Table 1.Fig. 3
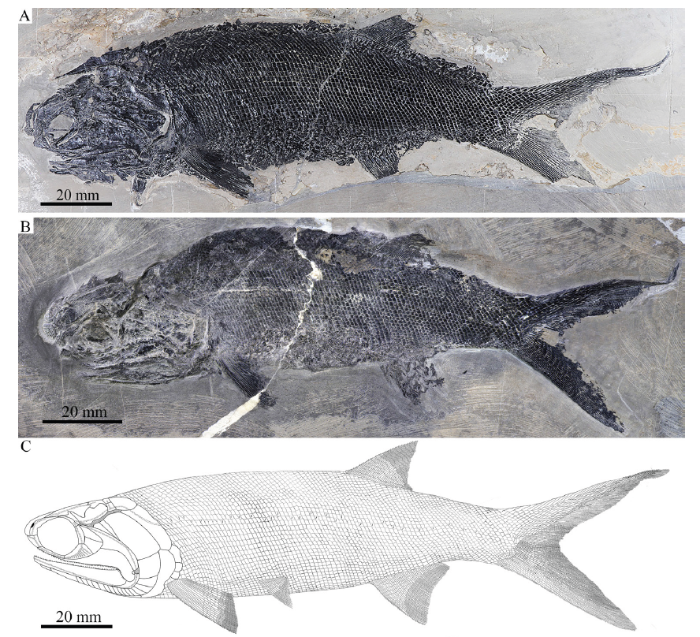 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 3Specimens and reconstruction of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.
A. IVPP V 18994, holotype; B. IVPP V 20493; C. reconstruction
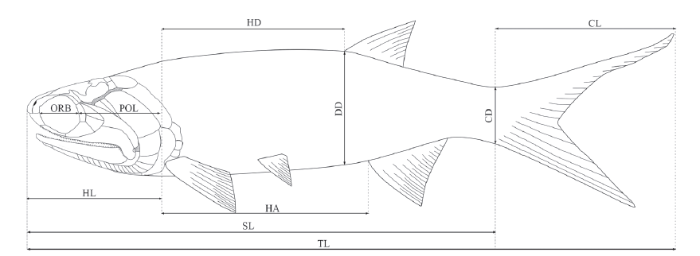
Fig. 4
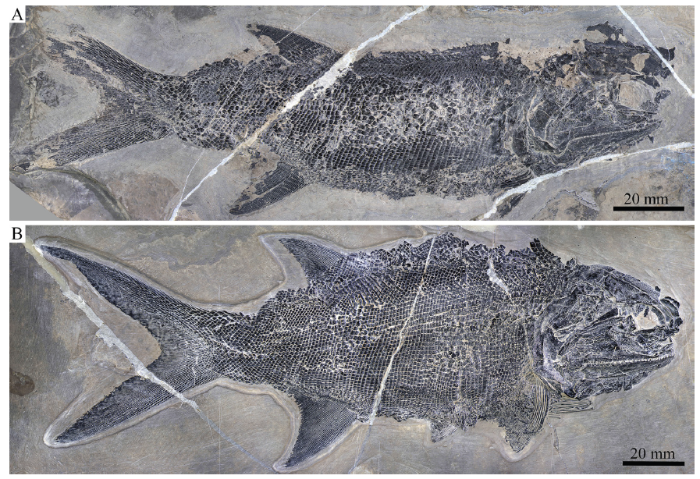 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 4Two specimens of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.
A. IVPP V 24340; B. IVPP V 25615
Table 1
Table 1Measurements of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov. from Luoping, Yunnan (mm)
| Specimen | ORB | POL | DD | HD | HL | HA | CD | CL | SL | TL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V 18994 | 9.3 | 30.2 | 46.5 | 56.7 | 49.1 | 61.6 | 21.7 | 61.2 | 155.5 | 221.0 |
| V 24340 | 10.6 | 26.7 | 41.8 | 49.8 | 40.1 | 57.6 | 19.4 | - | 138.2 | - |
| V 20493 | 7.0 | 23.4 | 34.0 | 38.8 | 38.2 | 43.5 | 15.8 | 44.3 | 118.7 | 163.3 |
| V 25615 | 13.2 | 31.7 | 51.5 | 57.7 | 52.5 | 60.1 | 23.4 | 65.5 | 156.0 | 221.5 |
| V 25618 | 17.4 | 34.1 | 58.4 | 76.8 | 64.1 | 83.1 | 30.0 | 80.3 | 215.0 | 295.3 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
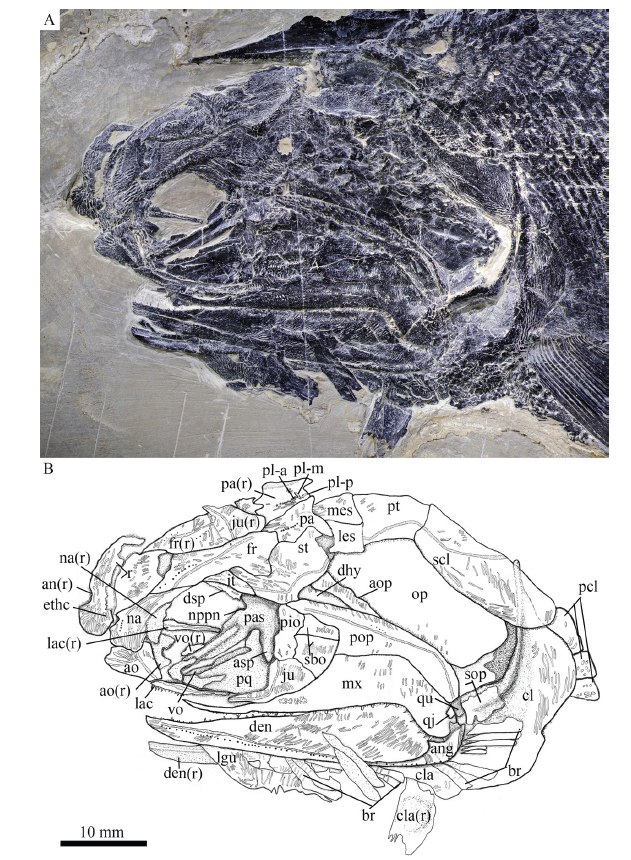
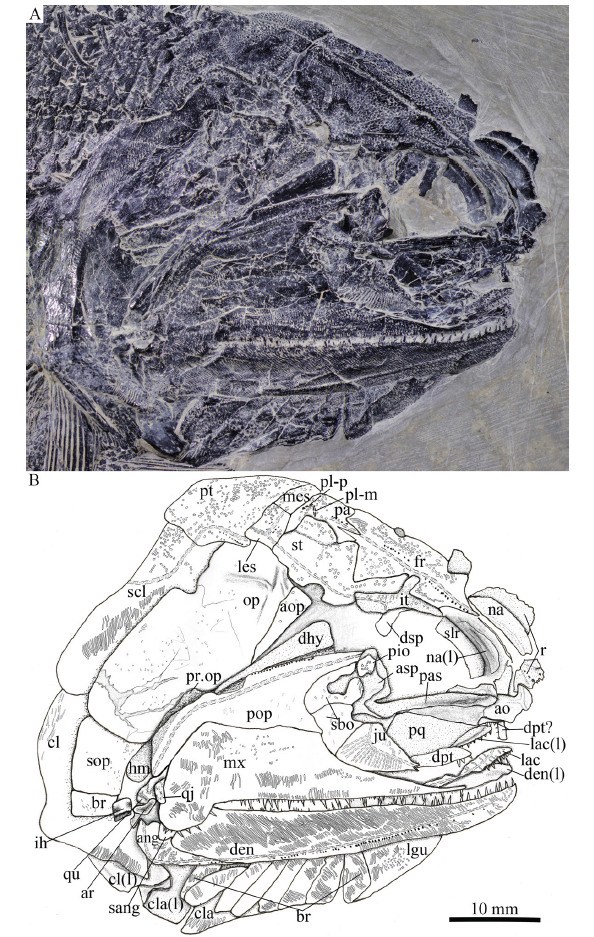
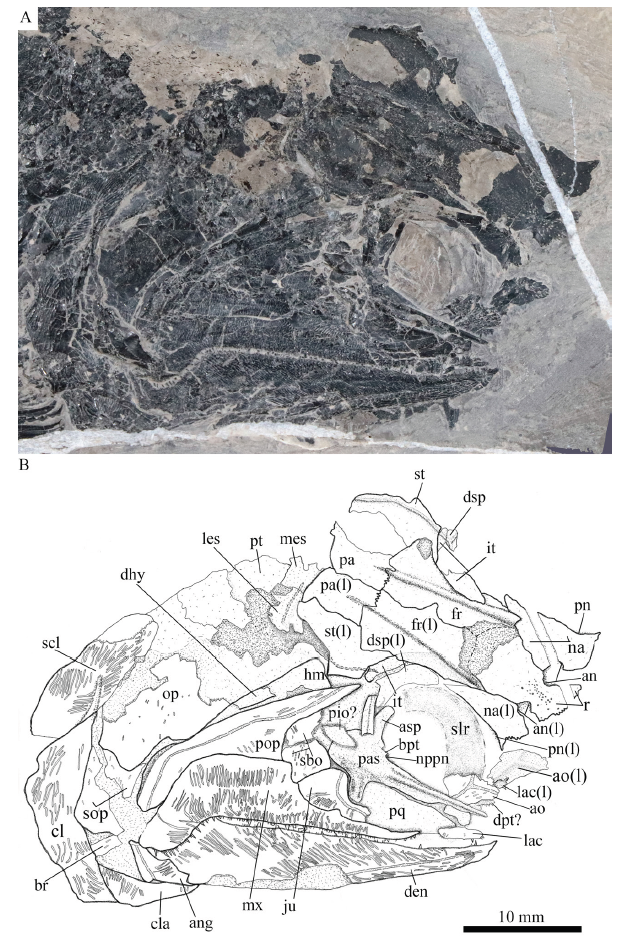
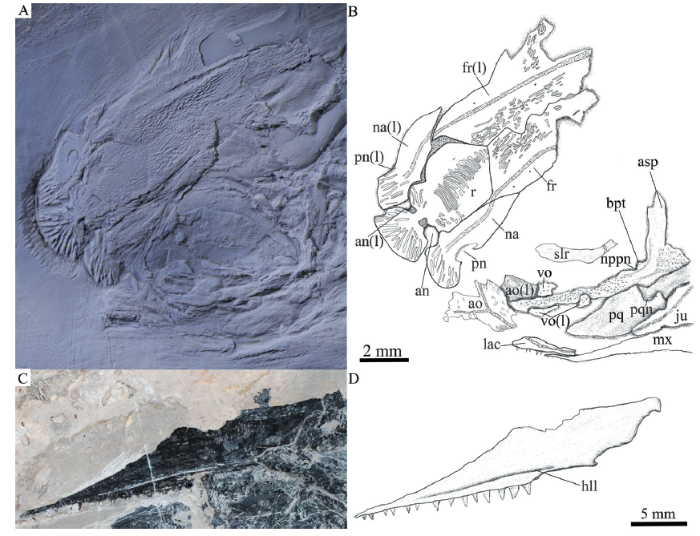
Snout The canal-bearing bones in the snout region include a median rostral and a pair of nasals and antorbitals (Figs. 5-7, 8A). The median rostral is exposed externally in IVPP V 20493 (Fig. 8A) and internally in V 24340 (Fig. 7). It is large and shield-like and twice as long as it is wide. The lateral margins of the rostral are notched for the anterior nostrils. The length from each notch to the anterior tip is a quarter of the total length of this bone. From this notch, the rostral gradually widens posteriorly, reaches its great width when it contacts the frontals, and then tapers rapidly to a pointed posterior end. The anterior portion of the rostral bends ventrally, having a rounded ventral margin. The external surface of the rostral is strongly ornamented with transverse ridges and tubercles at the posterior portion and longitudinal ridges at the anteroventral portion (Figs. 5, 8A). The ethmoid commissure in the rostral is indicated by an arc of small pores on the external surface of the anteroventral portion (just below the anterior nostril) of this bone (Fig. 5). In addition, there are some pores between both anterior nostrils in the internal surface of the rostral (Fig. 7), which might also indicate the position of the ethmoid commissure in this bone.
Fig. 5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 5Photograph (A) and line-drawing (B) of skull and pectoral girdle of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov., IVPP V 18994 (holotype)
Fig. 6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 6Photograph (A) and line-drawing (B) of skull and pectoral girdle of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov., IVPP V 25615
Fig. 7
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 7Photograph (A) and line-drawing (B) of skull and pectoral girdle of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov., IVPP V 24340
Fig. 8
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 8Anterior portion of skull and cheek region of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.
A. anterior potion of skull, IVPP V 20493, dusted with ammonium chloride; B. line-drawing of A; C. maxilla in medial view, IVPP V 18994; D. line-drawing of C
The nasals are narrow and elongate, slightly shorter than the rostral, tapering posteriorly. Each nasal contacts the rostral and frontal medially, and the dermosphenotic and intertemporal posteriorly (Figs. 5, 7, 8A). The lateral margin of the nasal is slightly notched for the posterior nostril, and defines the anterodorsal margin of the orbit. A semicircular notch for the anterior nostril is present in the medial margin of the nasal, corresponding to the notch in the lateral margin of the rostral. Indicated by several small pores, the nasal bears an anterior portion of the supraorbital sensory canal that curves ventrally from the frontal and terminates just below the level of the anterior nostril. The external surface of the nasal is ornamented with a series of longitudinal ridges (Figs. 5, 8A).
The antorbital is nearly trapezoidal, contacting the nasal dorsally, the rostral anteromedially and the lacrimal posteriorly (Figs. 5, 7, 8A). The ventral margin of the antorbital forms a short anterior length of the oral margin, and its posterodorsal margin contributes to the composition of the anterior orbital margin. The infraorbital canal and ethmoid commissure meet on this bone and form a tripartite junction. The surface of the antorbital is ornamented with horizontal ridges.
Skull roof The skull roof is comprised of a pair of frontals, parietals, intertemporals, supratemporals and two pairs of extrascapulars. These elements are ornamented with dense ridges and tubercles.
The frontals are roughly trapezoidal, 2.5 times as long as the parietal (Fig. 6). The majority of the frontal contacts its counterpart medially in a meandrous suture, except a short anterior portion which tapers anterolaterally to a point and flanks the posterior portion of the rostral (Figs. 6, 8A). There is no pineal foramen between the frontals. The supraorbital sensory canal extends longitudinally through each frontal and enters the parietal posteriorly. The sensory pores are located lateral to the sensory canal at the anterior half portion of the frontal and medial to the canal at the posterior half portion of this bone.
The parietals are nearly rectangular, slightly longer than they are broad, with a short posterolateral extension. Each parietal contacts the frontal anteriorly along a zigzag suture and the supratemporal laterally along a curved suture (Fig. 6). The medial and posterior margins of the parietal are nearly straight. Three pit-lines are present in the parietal; the anterior pit-line is continuous with the supraorbital sensory canal, the middle one extends anterolaterally for a relatively short length, and the posterior one extends posterolaterally and terminates near the posterior margin of this bone (Figs. 5, 6).
The intertemporals are triradiate, having pointed anterior and posterior tips and a medially directed process at the middle portion of this bone (Fig. 6). Each intertemporal is about half of the frontal length, contacting the anterior portion of the frontal medially, the anterior portion of the supratemporal posteromedially, and the dermosphenotic anterolaterally. Anteriorly, the intertemporal tapers to a point and terminates slightly anterior to the junction of the frontal and the nasal.
The supratemporals are large and irregular, twice the length of the intertemporal or parietal. The anterior part of the supratemporal tapers anteromedially and inserts between the frontal and intertemporal. The medial suture with the frontal is rather concave, and the anterolateral suture with the intertemporal is convex. The later margin of the supratemporal is notched at its middle portion (Figs. 5-7), similar to other species of Pteronisculus (Nielsen, 1942; Xu et al., 2014b). The supratemporal sensory canal extends longitudinally through the lateral portions of the intertemporal and supratemporal, and posteriorly enters the lateral extrascapular.
Two trapezoidal extrascapulars are present at each side of the skull (Figs. 5, 6). The lateral extrascapular is nearly equal to the medial one in width. The median extrascapular extends medially to the midline of the skull. The supratemporal commissure runs traversely through the middle portions of both extrascapulars.
Cheek The cheek region includes three infraorbitals (lacrimal, jugal and postinfraorbital), two suborbitals, a quadratojugal, a preopercle, a dermohyal and an antopercle.
The lacrimal is elongate and one third as long as the maxilla. The anterior half of the ventral margin of the lacrimal forms a part of the oral margin and bears conical teeth (Fig. 5), characteristic of Pteronisculus (Xu et al., 2014b). The jugal is relatively large and pentagonal, defining the posteroventral margin of the orbit. The lacrimal passes the infraorbital sensory canal from the antorbital to jugal, in which the canal has about ten rami.
The postinfraorbital is small and narrow, contacting the jugal ventrally, the dermosphenotic dorsally, and the suborbitals posteriorly (Fig. 5).
The dermosphenotic is exposed laterally in IVPP V 18994 and V 25615 (Figs. 5, 6), and medially in V 24340 (Fig. 7). This bone is roughly triangular, contacting the intertemporal posterodorsally and the nasal anteriorly.
There are two suborbitals between the third infraorbital and the preopercle, including a trapezoidal ventral one and a triangular dorsal one (Fig. 5). Both are ornamented by some short striae and tubercles.
The quadratojugal, discernable in V 18994 and V 25615 (Figs. 5, 6), is small and sub-circular, contacting the quadrate portion of the palatoquadrate laterally and the maxilla anteriorly.
The preopercle is hatchet-shaped, consisted of a triangular anterodorsal limb and a narrow posteroventral stem (Figs. 5-7). It tapers to a point anterodorsally and nearly reaches the anteroventral tip of the supratemporal. The preopercular canal extends through the preopercle near the posterior margin of this bone, having a series of small pores located posterodorsal to the canal (Figs. 5, 6).
The dermohyal is small, narrow and triangular, tapering ventrally (Fig. 6). It is wedged between the preopercle and antopercle, ornamented with several striae on its external surface. Medially, it is bound to the lateral surface of the hyomandibula.
In addition, there is a narrow, deep and triangular bone inserting between the dermohyal and opercle (Fig. 5). This bone is labeled as the antopercle, following Nielsen (1942).
Operculo-gular series The opercle is large, nearly rhomboid and anteriorly inclined, and the subopercle is equilateral with half of the depth of the opercle (Fig. 5). The branchiostegal rays are slender and lamellate. Eight branchiostegal rays are preserved below the dentary in V 25615 (Fig. 6) and seven are posterior to the angular in V 18994 (Fig. 5). Thus, a complete series of 15 branchiostegal rays is reconstructed at each side of the skull (Fig. 3C).
Anterior to the first branchiostegal ray, a right lateral gular is exposed in V 25615 (Fig. 6). It is relatively broad and large, being about one-fourth of the length of the lower jaw. The median gular is not exposed.
Parasphenoid, vomers and palatoquadrate Most of the parasphenoid, vomers and palatoquadrate are discernable through the orbit. The parasphenoid is elongate, slightly longer than the frontal (Figs. 6, 7, 8A). The median keel of this bone tapers anteriorly, having a narrow anterior tip and a rounded posterior margin. Two lateral processes are present on either side of the posterior portion of the parasphenoid, including a short basipterygoid process and a deep ascending process (Fig. 7, 8A). Dense small conical teeth are present on the ventral margin of the parasphenoid anterior to the basipterygoid process (Fig. 8A). There is no buccohypophyseal opening nor are there other pores discernable in this bone, which is similar to other species of Pteronisculus (Nielsen, 1942). Anterior to the base of each basipterygoid process is the small notch for the pseudobranchial efferent artery (Figs. 7, 8A).
The paired vomers are small and slender, bearing small teeth on its ventral margin (Fig. 8A). The teeth are conical and similar in size to those on the parasphenoid.
The exposed anterodorsal portion of the palatoquadrate is nearly triangular and has a distinct notch on the dorsal margin of its metapterygoid portion for articulating with the basipterygoid process (Figs. 7, 8A). Additionally, a small quadrate portion of the palatoquadrate is exposed, articulating with the lower jaw ventrally (Fig. 6).
Hyomandibula and interhyal The hyomandibula is situated at an oblique angle of 35°, bearing a short and strong opercular process at the posterior margin of this bone (Fig. 6). Most of this bone is laterally covered by the preopercle and dermohyal, and its complete shape remains unknown.
An interhyal is preserved ventral to the hyomandibula and posterior to the quadrate portion of the palatoquadrate (Fig. 6). It is small and nearly cylindrical.
Upper jaw No premaxillae are discernable, and they are probably lost or fused with lacrimal (Xu et al., 2014b).
The maxilla has a dorsoventrally short and elongate suborbital ramus and a deeper posterodorsal blade with a pronounced posteroventral process laterally covering the posterior portion of the lower jaw (Figs. 5-7). It contacts the preopercle along its convex posterodorsal margin. The outer surface of the maxilla is ornamented with some short ridges. In medial view, the maxilla has a horizontal longitudinal lamina parallel to its ventral margin (Fig. 8C), as in other species of Pteronisculus (Nielsen, 1942). The dentition consists of numerous minute teeth on the outer edge and an inner row of larger conical laniary teeth (Figs. 5-7).
Lower jaw The dentary is large and elongate with a slightly concave dorsal (oral) margin, a convex ventral margin and a curved posterior margin. The dentition on the oral margin of this bone consists of longer teeth interspersed with shorter and smaller denticles.
The angular is slender and wedge-shaped, tapering anteroventrally. The supra-angular is small and not fully exposed, laterally covered by the posteroventral process of the maxilla (Fig. 6). The dentary and angular are ornamented by prominent ganoine ridges, and the supra-angular is smooth. The mandibular sensory canal extends the whole length of both the dentary and angular, with a series of small openings located ventral to the canal. (Figs. 5, 6).
The ossified articular region of the Meckelian cartilage is partly exposed laterally, having a rounded fossa that articulates with the lateral condyle of the quadrate portion of the palatoquadrate (Fig. 6).
The coronoids and prearticular are unknown because the medial surface of the lower jaw is not exposed.
Girdles and paired fins The posttemporals are fan-shaped, contacting the extrascapulars anteriorly and the supracleithrum posteroventrally (Figs. 5, 6). The supracleithrum is deep and relatively narrow with convex ventral and posterior margins. The lateral line sensory canal pierces the lateral portion of the posttemporal and extends posteroventrally into the supracleithrum.
The cleithrum is large and curved, having a concave anterior margin and a curved posterior margin. The dorsal tip is pointed, partly covered by the supracleithrum (Fig. 5). The clavicle is small and triangular, contacting the cleithrum posterodorsally. The exposed surfaces of the cleithrum and clavicle are ornamented with ganoine ridges.
The pectoral fins are large and relatively long, inserting low on the body. Each pectoral fin has about 20 distally segmented and branched rays, preceded by a basal fulcrum and a series of fringing fulcra (Fig. 9A).
Fig. 9
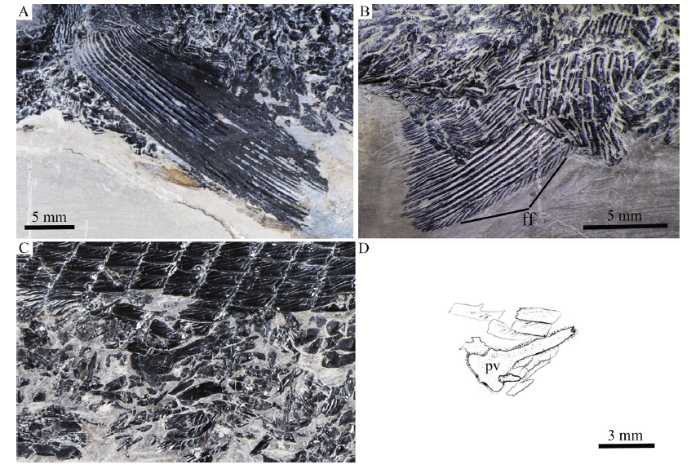 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 9Paired fins of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.
A. left pectoral fin, IVPP V 18994; B. right pelvic fin, V 25615; C. right pelvic plate, V 24340; D. line-drawing of C
The pelvic plate is elongate with a triangular posterior base and a slender anterior process (Fig. 9C).
The pelvic fins are relatively small and are located at the 15th vertical scale row. Each includes about 15 distally segmented and branched rays. Fringing fulcra are also present on the leading margin of the fin (Fig. 9B).
Median fins The triangular dorsal fin originates above the 53rd vertical scale row, and its base occupies the length of 14 vertical scale rows. It is composed of 31 principal fin rays, preceded by nine procurrent rays and two small basal fulcra (Fig. 10D). All rays are segmented through their length. The first principal ray is unbranched and five-sixths as long as the second principal ray. The latter branches once distally, being the longest ray of the dorsal fin. Other rays branch twice and gradually decrease in length posteriorly. A series of small fringing fulcra is associated with the anterior margins of all procurrent rays, and the first and second principal rays (Fig. 10D). A series of middle and proximal radials are discernable in the pterygiophores that support the dorsal fin; the distal radials, probably not ossified or unexposed, remain unknown. There are 11 middle radials present; they are rod-like or hour-glass shaped, slightly expanding at both ends (Fig. 12). Among them, the anterior two are slightly shorter than the third, which is the longest; and other radials gradually become shorter posteriorly. There are 11 proximal radials, which are 2.7-3.0 times as long as the middle radials. They are rod-like with a slightly expanded distal portion. The first radial is the longest and strongest, and the remaining gradually become shorter posteriorly.
Fig. 10
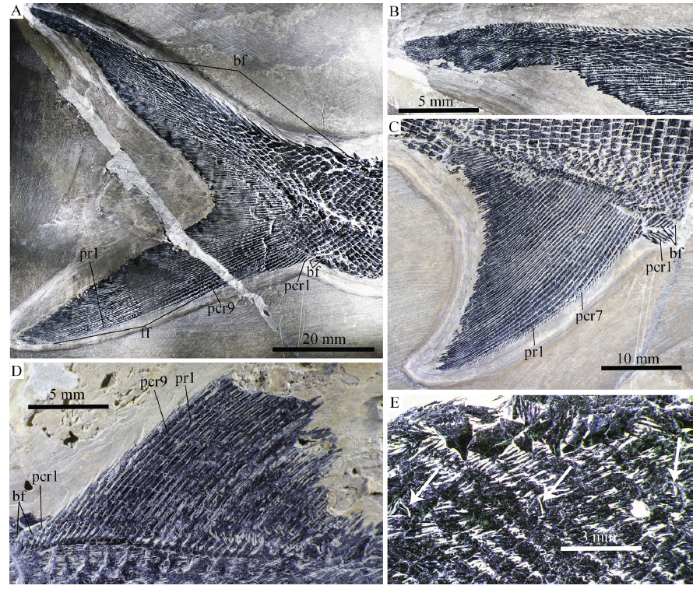 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 10Fins and scales of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.
A. caudal fin, IVPP V 25615; B. close up of epichordal lobe of caudal fin in A; C. anal fin, V 25615; D. dorsal fin, V 18994; E. pit organs in pre-dorsal region, V 18994
The anal fin originates below the 44th vertical scale row, and its base extends the length of about 20 vertical scale rows. It is also triangular and one-third larger than the dorsal fin. The anal fin is composed of 41 principal fin rays, which are preceded by nine procurrent rays and a basal fulcrum (Fig. 10C). The second and third principal rays branch once; the latter is the longest ray of the anal fin. The remaining rays branch up to three times and gradually decease in length posteriorly. Similar to those in the dorsal fin, a series of fringing fulcra are associated with the anterior margins of all procurrent rays and the first and second principal rays.
The caudal fin is heterocercal with a deeply forked profile. The dorsal lobe, which is slightly longer than the ventral one, has a small epichordal lobe at its distal tip (Fig. 10B). About 70 segmented principal rays are present with 20 in the dorsal lobe (Fig. 10A). Additionally, there are nine unbranched procurrent rays preceding the ventral most principal ray. The middle principal rays are distally branched up to five times. About 20 epaxial basal fulcra are present; they are elongate and taper posteriorly. The hypaxial basal fulcra are relatively short, two or three in number. Small leaf-like fringing fulcra are present in both lobes of the caudal fin (Fig. 10A).
Squamation The scales are rhomboid with serrated posterior margins. They are arranged in 83 transverse rows of scales between the posterior margin of the supracleithrum and the caudal inversion. The scales in the anterior flank region are slightly deeper than they are long, and they gradually become shorter and smaller dorsally and ventrally. In the middle flank region at each side of body, 15 horizontal rows of scale lie above the main lateral line, and 17 below (Figs. 3A, C). The trajectory of the main lateral line is indicated by a series of small pores in the scales of the anterior flank region. Additionally, every two to five lateral line scales have a dorsoventrally extended slit (Figs. 11D-F), which probably represents the individual pit organ that is separate and independent from the lateral line canal (Schultze, 1966). Besides those in the lateral line scales, some of anterior pit organs are also present in the adjacent row of scales above the lateral line (Fig. 11F). Moreover, an accessory dorsal lateral line lies close to the dorsal margin of the body, indicated by several slits in the predorsal region (Fig. 10E). There are a pair of enlarged lateral scutes anterior to the anal fin (Fig. 11A) and three median scutes preceding the basal fulcra at the ventral lobe of the caudal fin (Fig. 11B). Peg-and-socket articulations are exposed between some scales in the anterior flank region (Fig. 11C). The scales are ornamented with fine and diagonally directed ridges (Figs. 11C-E).
Fig. 11
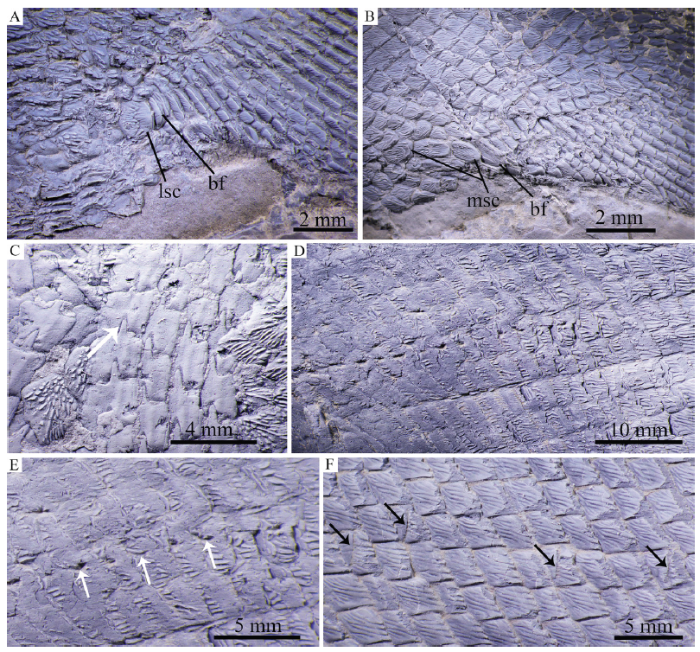 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 11Scales of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov., IVPP V 25618, dusted with ammonium chloride
A. scutes anterior to the anal fin; B. scutes anterior to the ventral lobe of the caudal fin; C. peg-socket articulation between scales; D. lateral line scales; E. scales with white arrows indicating sensory pores; F. scales with black arrows indicating pit organs
Axial skeleton Only the supraneurals are exposed; other elements of the axial skeleton remain unknown because of the coverage of the scales (Fig. 12). Twenty supraneurals are counted posterior to the supracleithrum and below the anterior four middle radials of dorsal fin. They are slender, slightly curved posteroventrally and posteriorly inclined. Additionally, there is an obvious gap posterior to the seventh supraneural, which indicates a missing supraneural. Thus, the whole series would include 21 supraneurals; 17 of those anterior to the dorsal fin and four below the dorsal fin pterygiophores.
Fig. 12
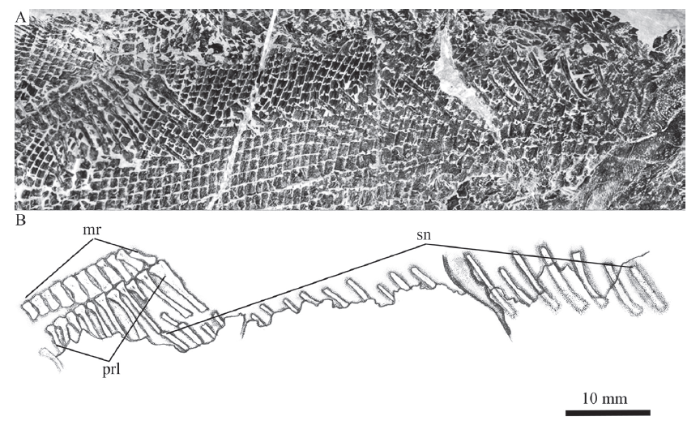 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 12Photograph (A) and line-drawing (B) of supraneural bones and pterygiophores
supporting the dorsal fin of Pteronisculus changae sp. nov., IVPP V 25615
5 Discussion
5.1 Character comparisons
Pteronisculus changae sp. nov. is easily distinguished from P. nielseni also from the Luoping Biota and other older species of this genus outside of China in the following aspects:(1) A medial process at the middle portion of the intertemporal. P. changae has a triradiate intertemporal with a medial process at the middle portion of this bone. By contrast, the intertemporal in other species of the genus is elongate or triangular and lacks a median process (Fig. 13).
Fig. 13
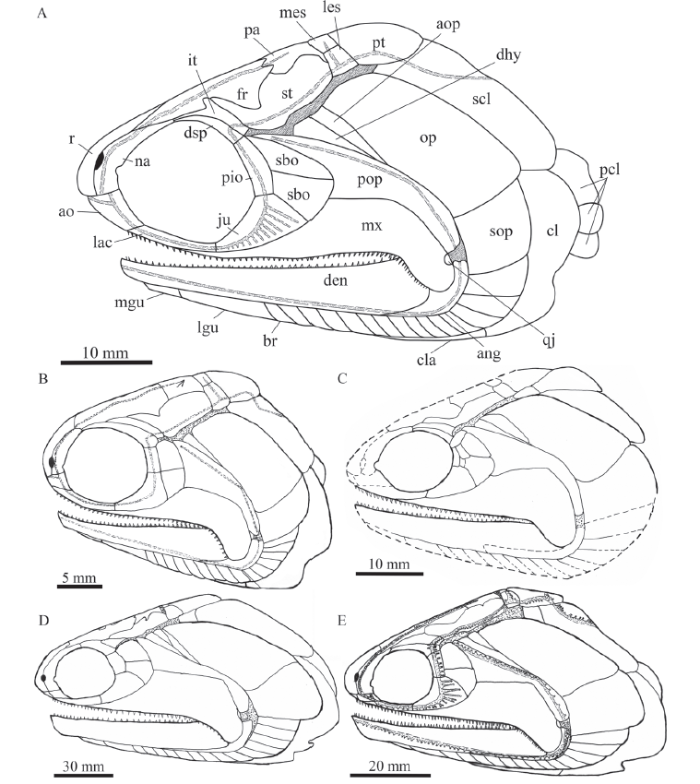 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 13Reconstructions of skulls and pectoral girdles of selected species of Pteronisculus in lateral view
A. Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.; B. P. nielseni (from Xu et al., 2014b); C. P. cicatrosus (from Lehman, 1952). D. P. magnus (from Nielsen, 1942); E. P. stensioi (from Nielsen, 1942)
(2) A postorbital skull length to skull length ratio of 60%. In this ratio, P. changae is slightly longer than P. nielseni (57%) but shorter than other species of the genus (e.g., 64% inP. cicatrosus, 70% in P. stensioi, and 72% in P. magnus).
(3) Presence of an antopercle. There is an antopercle between the dermohyal and opercle in P. changae (Fig. 13). This bone is otherwise present in P. stensioi, P. cicatrosus, P. magnus and some other early actinopterygians, but it is absent in P. nielseni.
(4) A relatively broad and large medial extrascapular. The medial extrascapular is nearly as broad as the lateral extrascapular in P. changae, but the former is generally narrower and smaller than the latter in other species of this genus (Fig. 14).
Fig. 14
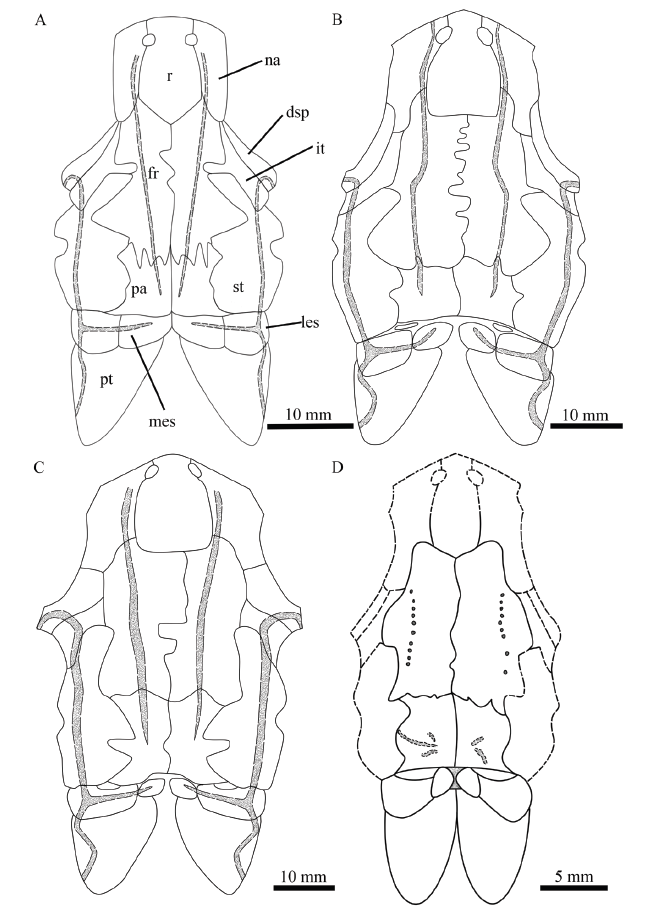 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 14Reconstructions of skulls of selected species of Pteronisculus in dorsal view
A. Pteronisculus changae sp. nov.; B. P. stensioi (from Nielsen, 1942); C. P. magnus (from Nielsen, 1942); D. P. cicatrosus (from Lehman, 1952)
(5) A suspensorium angle of 35º. In the suspensorium angle (Fig. 15), P. changae shows an intermediate state between P. nielseni (40°) and other species of the genus surveyed herein (about 30°).
Fig. 15
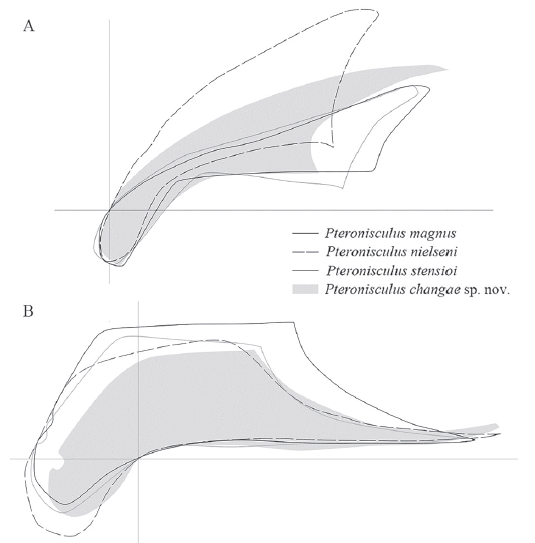 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 15Comparisons of preopercles (A) and maxillae (B) in different species ofPteronisculus
Not to scale
(6) Presence of 21 supraneurals. P. changae has the largest number of supraneurals in this genus (Fig. 12). However, P. magnus and P. gunnari generally have about 15-18 supraneurals (Nielson, 1942).
(7) A large number of lateral line scales. P. changae has 83 lateral line scales, representing the largest number known in this genus. In comparison, other species of the genus generally have 55-65 lateral line scales (55-59 in P. arctica, 63 in P. stensioi, ~65 in P. aldingeri, and 60-61 in P. nielseni; for comparisons of pterygial formula in selected species of Pteronisculus, see on-line supplementary martial).
(8) Deep and numerous pit organs in scales. The pit organs associated with the lateral line system are only slightly shorter than the scales in P. changae (Fig. 11D). However, the pit organs are dorsoventrally much shorter (i.e., no more than one third of the scale depth) in P. nielseni. In addition, P. changae has a greater number of pit organs (26 in IVPP V 18994), which are distributed not only in the lateral line scales but also in the adjacent row of scales above the lateral line. By contrast, the pit organs inP. nielseni are fewer in number (16 in V 25661), mainly confined in the lateral line scales. The pit organs were not identified in the previous description of the genus outside of China, and further studies are needed to clarify their presence in Early Triassic species.
5.2 Phylogenetic analysis
Phylogenetic analysis recovered 12 most parsimonious trees (tree length = 996 steps, consistency index = 0.3002, retention index = 0.6715). The strict consensus cladogram is shown in Fig. 16. Pteronisculus is recovered as a sister taxon of the Carboniferous rhadinichthyid Cyranorhis at the Actinopterygii stem. The Cladistia (including Scanilepiformes) forms the sister group of the Actinopteri (Chondrostei plus Neopterygii) within the Actinopterygii crown, consistent with other recent phylogenies (Giles et al., 2017; Wilson et al., 2018). The Birgeriiformes and Saurichthyiformes are nested at the Chondrostei stem, in accordance with Gardiner et al. (2005) and Xu and Gao (2011); by contrast, both clades are recovered at the Actinopterygii stem by other recent analyses (Giles et al., 2017; Argyriou et al., 2018). Additionally, some deep-bodied taxa (Discoserra, Ebenaqua and Bobasatrania) are also recovered at the Chondrostei stem rather than the Neopterygii stem (in contrast to Hurley et al., 2007; Xu et al., 2014a; Giles et al., 2017; Argyriou et al., 2018).Fig. 16
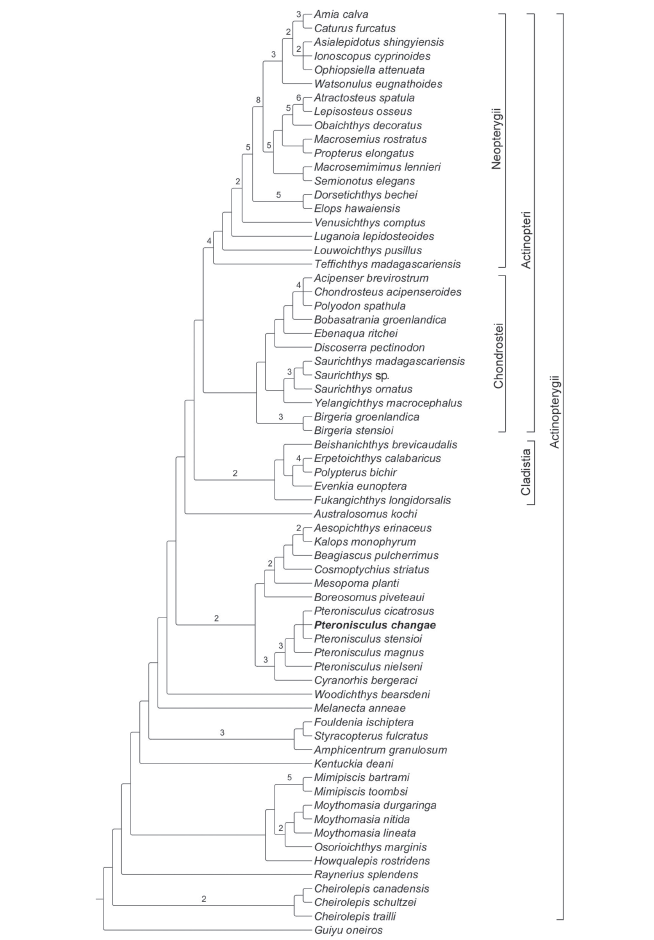 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPTFig. 16Strict consensus of 12 most parsimonious trees
Tree length = 996 steps, consistency index = 0.3002 and retention index = 0.6715
Bremer indexes larger than 1 are indicated with numbers
The genus Cheirolepis (including three species) is recovered at the base of the Actinopterygii. Raynerius is more derived than Cheirolepis due to the presence of three apomorphies shared with other actinopterygians: 1) contribution of nasals to orbital margins, 2) presence of acrodin caps on teeth, and 3) presence of a narrow interorbital septum. In Devonian actinopterygians, a monophyletic group involves Howqualepis, Mimipiscis (= Mimia), Osorioichthys and Moythomasia; the sister group relationships between Osorioichthys and Moythomasia are newly recognized, supported by four character states: 1) the presence of two pairs of extrascapulars, 2) extrascapulars not reaching the lateral edge of the skull roof (reversal in M. nitida), 3) a mandibular canal arching dorsally in the anterior half of the lower jaw (reversal in M. durgaringa), and 4) the dorsal-most branchiostegal ray deeper than the adjacent one (independently evolved in many other actinopterygians such as Boreosomus, Mesopoma, Kalops, Teffichthys, Caturus and Atractosteus). Kentuckia is the most derived of Devonian actinopterygians, as has generally been found in other phylogenies (Swartz, 2009; Choo, 2011; Xu et al., 2014a). Additionally, the Carboniferous Eurynotiformes (represented by Amphicentrum, Fouldenia and Styracopterus) is well supported as a monophyletic group that consists of the sister group of Melanecta, Woodichthys plus other more derived actinopterygians.
Further up the tree, the Cyranorhis-Pteronisculus clade is recovered sister to a monophyletic group involving Boreosomus, Mesopoma, Cosmoptychius, Beagiascus, Aesopichthys and Kalops, supported by four derived features: 1) presence of an anterior junction of supraorbital and infraorbital canals between external nares (independently acquired in Mimipiscis, Osorioichthys, Moythomasia, Kentuckia, basal chondrosteans and holosteans), 2) presence of an hourglass-shaped anterior ceratohyal (independently evolved in Ebenaqua plus more derived chondrosteans and most neopterygians), 3) presence of jointed radials supporting pectoral fins (independently evolved in Cheirolepis canadensis), and 4) presence of an epichordal lobe of the caudal fin (independently acquired in Cheirolepis, Howqualepis, Fouldenia and Styracopterus). The sister taxon relationships between Pteronisculus and Cyranorhis are supported by six derived characters states: 1) presence of a lacrimal contributing to the oral margin (probably also present in Turseodus; Schaeffer, 1967; Romano et al., 2019), 2) absence of distinct premaxillae (independently evolved inStyracopterus and most chondrosteans), 3) presence of an antorbital bone (independently acquired in Cosmoptychius, Beagiascus, Aesopichthys, Kalops, Birgeria and neopterygians), 4) presence of two suborbital bones (three in P. cicatrosus), 5) presence of an opercle significantly higher than the subopercle, and 6) presence of a presupracleithrum (last two features independently evolved multiple times in other actinopterygians).
The monophyly of Pteronisculus is supported by three synapomorphies: 1) presence of teeth on the lacrimal (uniquely derived), 2) presence of a supratemporal ending at the level of the posterior margin of the parietal (reversal in P. stensioi, absence in Mesopoma, Cosmoptychius, Beagiascus, Kalops and most crown actinopterygians), and 3) presence of three infraorbitals (independently evolved in Boreosomus and Australosomus). Within Pteronisculus, P. nielseni is located at the basal position as it possesses the above synapomorphies but lacks a uniquely derived feature shared by all other species of the genus, which is the presence of an antopercle inserting between the dermohyal and opercle. P. changae sp. nov., P. cicatrosus and P. stensioi are more derived than P. magnus in possessing the intertemporal/nasal contact and lacking the dermosphenotic/frontal contact. However, the interrelationships between these three species are unresolved, and they form a polytomy within the genus.
Within the actinopterygian crown, the sister group relationships between Cladistia (scanilepiforms plus polypterids) and Actinopteri (Chondrostei plus Neopterygii) are supported (Giles et al., 2017). Notably, Birgeria is recovered at the base of the Chondrostei, in accordance with some other analyses (Gardiner et al., 2005; Xu et al., 2014a; but seeGiles et al., 2017; Argyriou et al., 2018). Saurichthyiformes is more derived than Birgeria, possessing seven derived features shared with Discoserra and other chondrosteans, such as 1) the presence of an anterior junction of supraorbital and infraorbital canals between external nares (independently evolved in many early actinopterygians and holosteans), 2) presence of one or two supraorbitals, 3) absence of contribution of the maxilla to the posterior margin of the cheek, 4) presence of single dermopalatine, 5) absence of median gular, 6) presence of a complete set of dorsal ridge scales anterior to the dorsal fin, and 7) presence of ventral scutes anterior to the anal fin. Additionally, Discoserra is recovered as a sister taxon of Ebenaqua, Bobasatrania plus the remaining chondrosteans, supported by four character states: 1) presence of a dermopterotic (or supratemporal) not extending past the posterior margin of the parietal, 2) absence of the dermohyal, 3) absence of an expanded dorsal lamina of the maxilla, and 4) presence of multiple cheek bones bearing the preopercular canal.
The Triassic Teffichthys, Louwoichthys, Luganoia and Venusichthys are successively placed at the Neopterygii stem, and the sister group relationships between Holostei and Teleostei are supported within the Neopterygii crown. This topology is similar to those proposed by other recent analyses (Xu and Zhao, 2016; López-Arbarello and Sferco, 2018; Xu, 2020a, 2021; but see Giles et al., 2017).
5.3 Phylogenetic and ecological implications
Pteronisculus changae sp. nov. documents the second species of this genus from the early Middle Triassic (Anisian) Luoping Biota, and represents one of the youngest records of this genus, along with P. nielseni from the same biota. The recent finding adds new information to the morphological diversity of the genus (as listed above) and the taxonomic diversity of the Luoping Biota in the Middle Triassic Yangtze Sea, a part of the eastern Paleotethys Ocean. Outside of China, species of Pteronisculus are known only in the older (Early Triassic) marine deposits in Europe, Madagascar and North America. The successive discoveries of P. nielseni and P. changae indicate that Pteronisculus lived through the Early Triassic and survived at least until the early stage of the Middle Triassic. Based on this geological range and distribution of Pteronisculus, the Yangtze Sea in South China appears to be a refuge of this genus during the Middle Triassic.The sister taxon relationships between Pteronisculus and Cyranorhis are proposed here for the first time. The later taxon lived in the Early Carboniferous, an important period for the early radiation of actinopterygians (Sallan, 2014; Friedman, 2015). Although Pteronisculus was known only in Early to Middle Triassic, its affinities to Cyranorhis indicate that the divergence between both taxa probably occurred as early as this period. Pteronisculus and Cyranorhis were traditionally placed in the ‘paleoniscoid’ families, the Palaeoniscidae ( White, 1933) and Rhadinichthyidae (Lund and Poplin, 1997) respectively, but both families are likely paraphyletic. Recently,Romano et al. (2019) tentatively placed Pteronisculus into the Turseoidae, a family represented only by the Late Triassic Turseodus in USA before (Schaeffer, 1952, 1967), on the basis of their resemblances in the skull pattern and fins. However, Turseodus remains poorly known in some phylogenetically important features (e.g., dermal bones in the snout region), and its detailed comparisons with Pteronisculus will be the subject of future studies. Based on the sister relationships between Pteronisculus and Cyranorhis proposed here, we tentatively place Pteronisculus into the Rhadinichthyidae.
The results of our phylogenetic analysis provide new insights into the phylogenetic relationships of ‘platysomoid’ actinopterygians. The Eurynotiformes ( Amphicentrum, Fouldenia and Styracopterus) is recovered at the Actinopterygii stem, phylogenetically distant from other hypsisomatic fishes (Discoserra, Ebenaqua and Bobasatrania) that are recovered here as stem chondrosteans (rather than stem neopterygians; Giles et al., 2017; Argyriou et al., 2018). This renders to support a paraphyletic ‘Platysomoidei’; the deep body form has independently evolved multiple times in the Carboniferous to Triassic actinopterygians ( Sallan and Coates, 2013).
Results of our analysis support the historically prevalent hypothesis of the chondrostean affinities of birgeriiforms and saurichthyiforms. Argyriou et al. (2018), based on their studies of internal cranial anatomy ofSaurichthys, proposed the sister group relationships between Birgeriiformes and Saurichthyiformes at the Actinopterygii stem. These sister group relationships, however, are not supported in our analysis, although we strictly followed Argyriou et al.’s (2018) codings for Saurichthys and Birgeria here. The differences between our and Argyriou et al.’s (2018) topologies are most likely due to minor revisions on a few character codings for several early actinopterygian taxa other than Saurichthys and Birgeria in our data matrix (see Supplementary Material on line).
The discovery of P. changae provides an important addition for investigating the trophic structure of the early Middle Triassic marine ecosystems in Luoping, eastern Yunnan. The previously known P. nielseni from the Luoping Biota represents one of the smallest members of the genus with a maximum total length of 127 mm (SL=102 mm), which is largely equal to some species from the Early Triassic of Madagascar. In comparison, other Early Triassic species (mainly from Europe) are significantly larger with a total length of 190-400 mm (Nielsen, 1942). P. changae has a maximum total length of 295 mm, 2.3 times as long as the coeval P. nielseni, representing the largest stem actinopterygian in the early Middle Triassic of China. Non-saurichthyid actinopterygians with a body length exceeding 200 mm are scarce in the Luoping biota; they were known only by the ionoscopiform halecomorphRobustichthys (Xu et al., 2014c; Xu, 2019) and colobodontid neopterygian Feroxichthys (Xu, 2020b). Among them, Robustichthys is likely a voracious and opportunistic predator and Feroxichthys a durophagous predator. The large body size and numerous forwardly-inclined and sharply-pointed teeth in the jaws of P. changae indicate that it is another predator in this biota. The teeth are relatively small and slender, lacking durophagous feeding adaptations. The elongated fusiform body form, long caudal peduncle, deeply forked caudal fin and deep pit-organs in the scales indicate that P. changae is a relatively fast swimmer (Schaeffer and Rosen, 1961; Webb, 1984; Montgomery et al., 2007). P. changae probably lived in the middle to top of the water column, feeding on planktonic invertebrates and smaller or younger fishes, which are rich in the same marine ecosystems (Hu et al., 2011; Benton et al., 2013).
6 Conclusions
Studies of five well-preserved specimens recover a convincing new species of Pteronisculus from the Anisian Luoping Biota, which represents the largest stem actinopterygian fish in the early Middle Triassic of China. The new finding provides an important addition for our understanding of the taxonomic diversity and trophic structure of the early Middle Triassic marine ecosystems in the eastern Paleotethys Ocean. Phylogenetic study recovers Pteronisculus as a sister taxon of Cyranorhis at the Actinopterygii stem, and provides insights into the interrelationships ofPteronisculus and other actinopterygians. On the other hand, ‘Platysomoidei’ remains a paraphyletic group, and the historically alleged chondrostean affinities of birgeriiforms and saurichthyiforms cannot be excluded based on the current knowledge of the internal cranial anatomy for Saurichthys; further studies are still needed to reveal the evolutionary history of these specialized lineages of basal actinopterygians. The successive discoveries of Pteronisculus nielseni and P. changae sp. nov. from Luoping strongly support that Pteronisculus was not extinct at the end of the Early Triassic and the eastern Paleotethys Ocean could be a refuge for this genus during the early Middle Triassic.Acknowledegments
We thank Chang M. M. for all the constructive suggestions and discussions, Lü M. N. and Li Z. Y. for the specimen preparation, and Martha Richter and Carlo Romano for their valuable comments on an earlier version of this manuscript. We also greatly appreciate Martha Richter granting us access to comparative fossil materials in the Natural History Museum (London).Supplementary material can be found on the website of Vertebrata PalAsiatica (
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOIURL [本文引用: 10]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 3]
DOIURL [本文引用: 11]
[本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 11]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI [本文引用: 1]

Four complete platysiagid fish specimens are described from the Luoping Biota, Anisian (Middle Triassic), Yunnan Province, southwest China. They are small fishes with bones and scales covered with ganoine. All characters observed, such as nasals meeting in the midline, a keystone-like dermosphenotic, absence of post-rostral bone, two infraorbitals between dermosphenotic and jugal, large antorbital, and two postcleithra, suggest that the new materials belong to a single, new Platysiagum species, P. sinensis sp. nov. Three genera are ascribed to Platysiagidae: Platysiagum, Helmolepis and Caelatichthys. However, most specimens of the first two genera are imprints or fragmentary. The new, well-preserved specimens from the Luoping Biota provide more detailed anatomical information than before, and thus help amend the concept of the Platysiagidae. The Family Platysiagidae was previously classed in the Perleidiformes. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that the Platysiagidae is a member of basal Neopterygii, and its origin seems to predate that of Perleidiformes. Moreover, platysiagid fishes are known from the Middle Triassic of the western Tethys region. The newly found specimens of platysiagids from Luoping provide additional evidence that both eastern and western sides of the Tethys Ocean were biogeographically more connected than previously thought.
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 5]
[本文引用: 7]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
