 ,1,2,*, 袁俊霞3, 王斯人4, 胡家铭1, 陈顺港3, 姬海龙5, 侯新东1, 赖旭龙2,6
,1,2,*, 袁俊霞3, 王斯人4, 胡家铭1, 陈顺港3, 姬海龙5, 侯新东1, 赖旭龙2,6Ancient DNA molecular identification and phylogenetic analysis of Cervinae subfossils from Northeast China
XIAO Bo1, SHENG Gui-Lian ,1,2,*, YUAN Jun-Xia3, WANG Si-Ren4, HU Jia-Ming1, CHEN Shun-Gang3, JI Hai-Long5, HOU Xin-Dong1, LAI Xu-Long2,6
,1,2,*, YUAN Jun-Xia3, WANG Si-Ren4, HU Jia-Ming1, CHEN Shun-Gang3, JI Hai-Long5, HOU Xin-Dong1, LAI Xu-Long2,6通讯作者: *glsheng@cug.edu.cn;mr.shaw@outlook.com
收稿日期:2020-05-6网络出版日期:2020-10-20
| 基金资助: |
Corresponding authors: *glsheng@cug.edu.cn;mr.shaw@outlook.com
Received:2020-05-6Online:2020-10-20

摘要
我国鹿类资源丰富,鹿亚科(Cervinae)动物有7个种在中国有分布。鹿亚科的种内系统发育研究很多,但是各物种之间进化关系仍有待进一步研究,其中从分子水平对古代材料的报道更为鲜见。对采集自黑龙江的两个距今分别为3800和5100 a的古代鹿亚科动物亚化石材料开展了古DNA研究。通过古DNA提取、古DNA双链文库构建、高通量测序及数据分析,得到了两条长度分别为16475 bp (GenBank收录号:MT784751, 序列完整度:99.83%)和16167 bp (GenBank收录号:MT784752, 序列完整度:97.96%)的线粒体基因组序列,对两个样品进行了分子鉴定。结合GenBank中现生鹿亚科动物的线粒体同源序列,构建了系统发育树。结果表明:1) 二代测序DNA片段末端碱基特性分析说明序列来自古代样品;2) 两个样品代表的个体在系统发育树中均与马鹿聚类,在物种归属中被分子鉴定为马鹿(Cervus elaphus); 3) 黑龙江的两个古代样品与现生马鹿阿拉善亚种(C. elaphus alxaicus)亲缘关系最近,而与现生马鹿东北亚种(C. elaphus xanthopygus)亲缘关系较远。结合样品年代信息,说明两例样品代表的黑龙江古代马鹿种群,不是现生马鹿东北亚种的直系母系祖先。
关键词:
Abstract
The deer resources in China are abundant, with seven species in the sub-family Cervinae distributing in various areas. The intraspecific phylogeny of Cervinae has been widely explored, while the evolutionary relationship among different species requires further efforts, in which only few molecular studies on ancient materials have been performed. In this study, we carried out ancient DNA research on two Cervinae subfossils from northeastern China, dating of 3800 and 5100 aBP. Through ancient DNA extraction, double-stranded sequencing libraries construction, next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics data analysis, we reconstructed two mitochondria sequences with lengths of 16475 bp (GenBank accession number: MT784751, sequence integrity: 99.83%) and 16167 bp (GenBank accession numberh: MT784752, sequence integrity: 97.96%), respectively. Based on the mitochondrial homologous sequences of the extant Cervinae species in GenBank, we constructed a phylogenetic tree. The results show that: 1) both the average length and the C-to-T substitution frequencies at 5’- end of the NGS short reads indicate the data are from ancient specimens; 2) the two ancient individuals clustered with Cervus elaphus in the phylogenetic tree, and were molecularly identified as C. elaphus; 3) the two ancient samples from Heilongjiang are phylogenetically close to the extant C. elaphus alxaicus, but far from the extant C. elaphus xanthopygus. Combining the dates of the samples, we suggest that these two samples represent a population of ancient C. elaphus in Heilongjiang, which was not the direct maternal ancestor of the extant C. elaphus xanthopygus.
Keywords:
PDF (1569KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
肖博, 盛桂莲, 袁俊霞, 王斯人, 胡家铭, 陈顺港, 姬海龙, 侯新东, 赖旭龙. 中国东北鹿亚科动物亚化石的古DNA分子鉴定及系统发育分析. 古脊椎动物学报[J], 2020, 58(4): 328-337 DOI:10.19615/j.cnki.1000-3118.200722
XIAO Bo, SHENG Gui-Lian, YUAN Jun-Xia, WANG Si-Ren, HU Jia-Ming, CHEN Shun-Gang, JI Hai-Long, HOU Xin-Dong, LAI Xu-Long.
鹿亚科(Cervinae)又称真鹿亚科,共分为4个属:鹿属(Cervus)、黇鹿属(Dama)、花鹿属(Axis)和麋鹿属(Elaphurus) (Sheng, 1992)。我国鹿类资源较为丰富,鹿亚科动物就包括鹿属的梅花鹿(Cervus nippon)、马鹿(C. elaphus)、坡鹿(C. eldi)、水鹿(C. unicolor)和白唇鹿(C. albirostris), 花鹿属的豚鹿(Axis porcinus)和麋鹿属的麋鹿(Elaphurus davidianus)共7个种(Tu et al., 2012)。中国现存的鹿种能表现出该亚科动物几乎全部系统发生的阶段,因此中国也被称为“鹿类动物进化的展览场”(Sheng, 1992)。
过去,人们对中国鹿类动物起源和系统进化及分类研究主要依据形态学特征,例如角的有无和形态、体型和体重、头骨和炮骨、泪窝和腺体的有无及特征、齿式和毛色特征、行为特征等,其中颅骨衍生物(牙齿、角等)是形态学系统分类的重要特征之一(Groves and Grubb, 1987; Sheng, 1992; Cai and Yin, 1992; Dong and Li, 2009; Dong et al., 2018)。基于化石的形态学研究是对古代鹿亚科动物研究的方法之一,盛和林(1992)认为鹿类动物的化石记录虽能较真实地反映其进化历史,但由于化石的分类基准大都使用角或容易变异的骨的形态,因此容易造成异议。Geist (1998)指出,偶蹄类的比较形态学在分类和进化研究中并不总是可靠的,因为这些动物的形态学特征随着环境条件变化而产生很大差异,所以结果不能被普遍接受。Emerson and Tate (1993)指出鹿类动物形态学研究所依据的角形和皮毛颜色等特征容易受到趋同或平行进化的影响。因此鹿科动物的形态学分类仍然存在较大争议。近40年来,很多****在传统分类基础上引入了细胞学(Wang and Du, 1983; Neitzel, 1987)和分子生物学以及计算机技术对鹿类动物进行分类研究,从细节上对其进行了补充和修改。然而,涉及豚鹿、麋鹿和马鹿的系统分类地位,不同****的观点尚存争议(Emerson and Tate, 1993; Grubb, 1993; Geist, 1998; Polziehn and Strobeck, 2002; Liu et al., 2003)。
古DNA是残存在古生物化石或亚化石、考古材料中的生物大分子,能从分子水平反映生物个体之间的遗传组成差异。发展利用古代鹿科动物的古DNA线粒体甚至核基因组信息,并结合现生鹿科动物的遗传信息和动物谱系地理学,综合分析研究中国鹿科动物系统发育是一个良好的发展方向(Liu et al., 2017)。本研究对采自黑龙江省肇东市和宾县的两个鹿科动物遗骨进行古DNA提取、DNA双链文库构建和高通量测序,通过生物信息学方法对序列数据进行处理,从分子水平对亚化石材料进行物种鉴定,结合现生部分鹿科动物基因序列,比较其同源序列之间的差异,通过系统发育分析探讨马鹿亚种间的进化关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
两个实验材料皆为黑龙江省大庆博物馆馆藏标本。据博物馆资料记载,CADG522于2008年发现于黑龙江省肇东市太平乡段松花江古河道;CADG527于2003年发现于黑龙江省宾县鸟河乡的泥沟。样品年代由美国BETA实验室通过放射碳同位素测定方法获得,相关信息如表1、图1所示。Table 1
表1
表1研究样品信息
Table 1
| Sample No. | Collection No. | Morphological species | Tissue type | Carbon dating (aBP) | Unearthed place |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CADG522 | H52710 | Cervus sp. | Metacarpus | 3800±30 | Zhaodong, Heilongjiang |
| CADG527 | H45190 | Cervus sp. | Radius | 5100±30 | Binxian, Heilongjiang |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图1
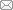
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1产自黑龙江肇东太平乡(A)和宾县鸟河乡(B)的鹿类研究样品
Fig. 1Samples of Cervus sp. from Taiping, Zhaodong (A) and Niaohe, Binxian (B), Heilongjiang
A. CADG522, metacarpus; B. CADG527, radius
1.2 古DNA提取
首先用4.5%的次氯酸溶液擦拭骨骼样品表面,再用无水乙醇擦拭两次并风干。使用切割机切取约300 mg骨骼样本,用已灭菌研钵研磨成粉末。按Rohland and Hofreiter (2007a, b)的方法,使用含EDTA (0.465 mol/L)和蛋白酶K (0.4 g/L)的裂解液充分裂解样品,再使用DNA纯化试剂盒(QIAquick PCR Purification Kit)结合超滤管(Millipore)完成样品古DNA的提取。1.3 古DNA双链文库构建与测序
古DNA双链文库构建包括4个步骤(Matthias and Martin, 2010): 1) 末端修复(blunt-end repair), 使用T4多聚核苷酸激酶(T4 polynucleotide kinase)和T4 DNA聚合酶(T4 polymerase)将DNA分子片段末端修复平齐;2) 接头连接(adapter ligation), 用快速连接酶(quick ligase)将接头(adapter)片段连接至修复平齐的双链DNA分子末端;3) 接头补齐(adapter fill-in), 使用Bst DNA聚合酶将连接接头的黏性末端补齐为平末端;4) 文库分子标记(indexing), 通过添加不同的小片段序列对DNA分子进行特异性标记,以在混合文库测序时对单个文库进行区分,该过程主要使用的酶为Q5高保真DNA聚合酶(high-fidelity DNA polymerase)。最后对构建的文库进行一次磁珠纯化即可得到用于测序的古DNA双链文库。构建完成的文库送北京泛生子基因测序公司进行双向测序。本研究对两个样品分两个批次各构建两个文库(522-1, 522-2及527-1, 527-2), 对第一批次两个文库进行预测序得到测序数据522-1Y和527-1Y, 深度测序得到测序数据522-1S和527-1S。第二批次文库直接进行深度测序得到测序数据522-2S和527-2S。1.4 测序数据处理与分析
测序公司提供的测序序列文件为FASTQ格式,对每一样品的每一文库,分别使用“cutadapt-1.12” (Martin, 2011)切除接头序列并过滤掉低于30 bp的短片段,然后用软件“BWA-0.7.15” (Burrows-Wheeler Alignment) (Li and Durbin, 2010)中的“aln”和“samse”将片段与参考基因组比对,舍弃比对质量得分低于30的序列;运用SAMtools v1.3.1软件(Li et al., 2009)中的“view”和“sort”算法将剩余序列按5’端位置在参考基因组上进行排序,用“rmdup”去除可能存在的PCR重复序列,用“merge”算法得到每一文库的单一bam格式文件。将同一样品的不同文库bam文件合并,再运行“rmdup”去除可能存在的重复序列,得到同一样品的合并bam文件,最终用angsd-0.916软件(Korneliussen et al., 2014) “-doFasta”导出匹配得到的各样品基因序列FASTA格式文件。对古DNA分子碱基损伤的评估,使用各样品不同文库处理合并、并去掉重复后的bam文件作为输入文件,使用“mapDamage”软件包(Aurelien et al., 2001)统计片段末端5’端和3’端碱基损伤。
序列匹配时,先以麋鹿线粒体基因组序列(GenBank收录号:NC018358)作为参考序列对测序数据进行初步比对,将所得线粒体序列数据导出,使用BLAST (
1.5 系统发育分析
利用Bioedit 7.0.9.0 (Hall, 1999)对测得的序列进行排列对比并辅以人工校对,以所得两个样品的古DNA序列与36个鹿亚科动物和一个外类群驼鹿(Alces alces)的同源序列(15109 bp, 不包含D-loop区)在CIPRES网站(Table 2
表2
表2系统发育分析所使用序列信息
Table 2
| Subfamily | Genus | Species | Accession No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鹿亚科 Cervinae | 花鹿属 Axis | 花鹿 Axis axis | JN632599 NC020680 | |
| 豚鹿 Axis porcinus | NC020681 MF435989 | |||
| 黇鹿属 Dama | 黇鹿 Dama dama | NC024819 JN632630 JN632619 NC020700 | ||
| 麋鹿属 Elaphurus | 麋鹿 Elaphurus davidianus | JN399997 JN632632 NC018358 | ||
| 鹿属 Cervus | 白唇鹿 Cervus albirostris | HM049636 NC016707 | ||
| 坡鹿 Cervus eldi | KU133959 | |||
| 水鹿 Cervus unicolor | DQ989636 NC008414 EF035448 NC031835 KY946815 | |||
| 梅花鹿 Cervus nippon | NC006993 NC013834 NC016178 NC018595 NC008462 NC007179 NC006973 | |||
| 马鹿 Cervus elaphus | 天山亚种 C. elaphus songaricus | HQ191429 NC014703 KJ025072 | ||
| 甘肃亚种 C. elaphus kansuensis | NC039923 MH513320 | |||
| 东北亚种 C. elaphus xanthopygus | GU457434 NC013836 | |||
| 塔里木亚种 C. elaphus yarkandensis | GU457435 NC013840 | |||
| 阿拉善亚种 C. elaphus alxaicus | KU942399 | |||
| 空齿鹿亚科 Odocoileinae | 驼鹿属 Alces | 驼鹿 Alces alces | NC020677 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2 结果
2.1 古代线粒体DNA片段末端碱基特性
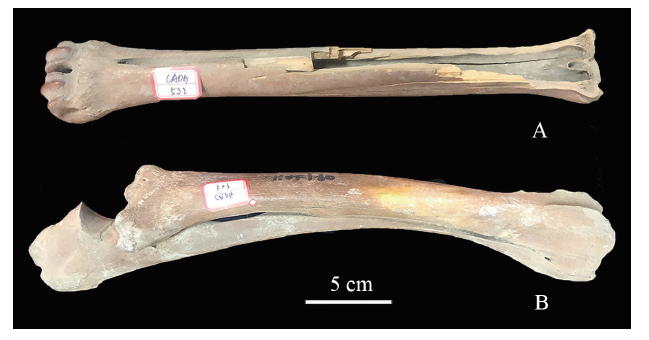
运用mapDamage软件对两个样品所得线粒体DNA二代测序序列进行分析,末端碱基替换统计结果如图2所示。CADG522和CADG527在5’端的“C→T”碱基替换频率分别为6.883%和6.897%, 3’端的“G→A”碱基替换频率分别为6.105%和9.123%。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2样品CADG522 (A)和CADG527 (B)线粒体DNA片段末端核苷酸错配统计
Fig. 2Statistical analysis of nucleotide misincorporation observed on reads of samples CADG522 and CADG527
2.2 二代测序数据及序列比对结果
先后使用麋鹿(GenBank收录号:NC018358, 全长16355 bp)和马鹿阿拉善亚种(GenBank收录号:KU942399, 全长16503 bp)的线粒体基因组作为参考基因组,对两个样品第一批次的文库(522-1和527-1)的预测序数据(522-1Y和527-1Y)进行匹配分析,结果显示两个样品均与阿拉善马鹿匹配度较高。最终以阿拉善马鹿线粒体基因组作为参考基因组对文库深度测序数据(522-1S, 522-2S和527-1S, 527-2S)进行过滤、匹配和合并处理,分别得到两个样品16475 bp (GenBank收录号:MT784751, 序列完整度:99.83%)和16167 bp (GenBank收录号:MT784752, 序列完整度:97.96%)古DNA线粒体基因序列。文库测序信息如表3所示。Table 3
表3
表3二代测序数据信息
Table 3
| Sample | CADG522 | CADG527 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Library No. | 522-1Y | 522-1Y | 522-1S | 522-2S | 527-1Y | 527-1Y | 527-1S | 527-2S | |
| Reference sequence | NC018358 | KU942399 | KU942399 | KU942399 | NC018358 | KU942399 | KU942399 | KU942399 | |
| Total reads | 6807540 | 6807540 | 30323142 | 13921352 | 11761088 | 11761088 | 41246962 | 4391446 | |
| Ratio of reads > 30 bp | 0.968 | 0.968 | 0.967 | 0.944 | 0.975 | 0.975 | 0.974 | 0.926 | |
| Mapped reads | 564 | 1372 | 6665 | 1530 | 356 | 782 | 2508 | 135 | |
| Unique mapped reads | 459 | 1117 | 4283 | 1309 | 304 | 558 | 2015 | 125 | |
| Mapped bp | 30267 | 81857 | 320240 | 61212 | 17531 | 41869 | 122203 | 5763 | |
| Mapped sequence length (bp) | 10314 | 16260 | 7437 | 14141 | |||||
| and coverage (%) | 63.06 | 98.53 | 45.47 | 85.69 | |||||
| Average reads (bp) | 73 | 74 | 46 | 75 | 60 | 46 | |||
| Depth | 26.59 | 4.63 | |||||||
| Final sequence length (bp) | 16475 | 16167 | |||||||
| and ratio (%) | 99.83 | 97.96 | |||||||
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 系统发育树
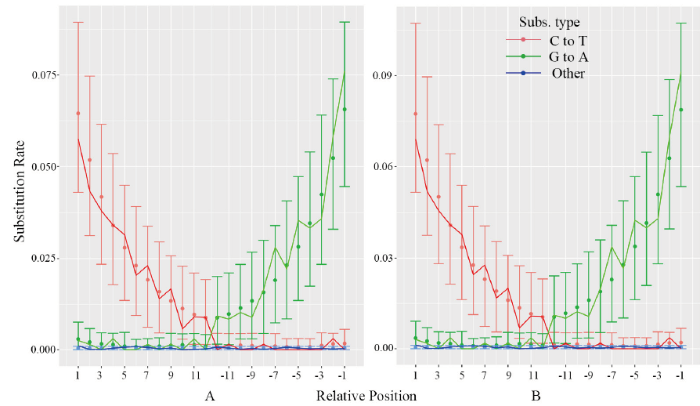
基于本研究所得两条古DNA线粒体序列和从GenBank检索所得36条鹿亚科动物的线粒体基因组序列,以驼鹿(A. alces)为外类群(outgroup)构建的分子系统发育树(图3)显示,两个古代样品(CADG522和CADG527)都与马鹿阿拉善亚种聚为一支,马鹿阿拉善亚种、天山亚种、甘肃亚种和东北亚种一起与梅花鹿互为姐妹群,且与后者一起共同构成马鹿塔里木亚种的姐妹群。白唇鹿两个个体聚为一支处于水鹿大分枝内部。坡鹿与3个麋鹿聚为同一分枝,往树根依次为黇鹿属的黇鹿和花鹿属的花鹿和豚鹿。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3鹿亚科线粒体基因组15109 bp同源序列ML法系统发育树
Fig. 3ML phylogenetic tree of Cervinae species based on 15109 bp mitochondrial genome homologous sequences
3 讨论
3.1 古代样品线粒体DNA真实性鉴定
本研究所得古DNA序列真实性可从如下方面论证:首先,采集样品时严格按照古DNA研究规范,样品的处理、提取及建库都在古DNA专用实验室的独立环境进行,实验者严格遵守古DNA实验防污染规则操作。其次,实验过程中,提取、建库全程设置有空白对照及正对照,对照实验组显示无异常,排除试剂、操作者及样品之间的交叉污染。再次,本研究所得序列经BLAST查询,所得推荐高可信度序列均为鹿科动物线粒体基因序列;本实验室从未进行现代鹿科动物分子生物学实验,所得序列确定来源于古代样品。最后,本研究各文库所得线粒体DNA片段平均长度较短,约45~75 bp, 符合古DNA片段特征(Hofreiter et al., 2014)。同时,经二代测序所得两个样品的DNA片段的5’端碱基“C→T”替换频率分别为6.883%和6.897%, 符合Sawyer et al. (2012)关于古代线粒体DNA片段5’端碱基“C→T”替换频率与样品年代的相关性研究结果。综上,本研究所得序列是来自古代样品的古DNA序列。3.2 鹿亚科动物的系统演化关系
近年来,关于鹿亚科各属种的系统演化关系,前人的蛋白质电泳、染色体组型、线粒体控制区序列等研究表明麋鹿和豚鹿与鹿属动物的进化关系较近,认为麋鹿和豚鹿应该并入鹿属,归并后的鹿属为单系发生(Wang and Du, 1983; Randi et al., 2001; Liu et al., 2003)。本研究加入古代鹿科动物样品序列后构建的系统发育树(图3)显示,麋鹿与鹿属的坡鹿互为姐妹支,且自展支持率为100%, 支持Randi et al. (2001)将麋鹿归为鹿属的观点;但是豚鹿在系统发育树中的位置与鹿属各种距离较远,且豚鹿与花鹿归为同一分支,因此,本研究不支持王宗仁、杜若甫(1983)和刘向华等(2003)将豚鹿划归鹿属的观点。在鹿属内部,王宗仁、杜若甫(1983)认为梅花鹿与马鹿的关系最近,现生鹿属动物中水鹿是最原始的,白唇鹿与梅花鹿几乎同时从水鹿的祖先种分化而来,马鹿则是最后分化出来的。图3中,梅花鹿并非直接从水鹿分化而来,梅花鹿分支与马鹿阿拉善亚种、天山亚种、甘肃亚种和东北亚种共同聚类形成的分支构成姊妹群,而马鹿塔里木亚种处于二者的根部。该结果显示马鹿塔里木亚种在早期从马鹿和梅花鹿的共同祖先分化而出,而后依次分化出梅花鹿和马鹿其他亚种,从线粒体基因组水平印证了王宗仁等的结论。
3.3 马鹿种群的基因交流
关于马鹿的系统进化关系,大多数观点认为马鹿分为东西两个进化种群:西部群体包括欧洲种群和我国新疆南部塔里木亚种,东部种群包括北美种群、亚洲及我国新疆北部的种群(Polziehn and Strobeck, 2002; Muhmut et al., 2002; Ludt et al., 2004)。本研究的系统进化树显示塔里木马鹿与其他生活在中国的4个马鹿亚种来源于共同祖先的两个不同分支,支持马鹿在进化中分出东西两个种群的观点。塔里木马鹿较早地分化出来,在一个封闭的地理环境下独立进化,因地理隔离而有别于其他马鹿种群。之后,东北亚种、甘肃亚种、天山亚种和阿拉善亚种相继分化,这也证明了中国马鹿是从中东和欧洲返回中国的过程中从西向东逐渐分化的(Sheng, 1992)。现分布于宁夏和内蒙古交界的贺兰山中段的阿拉善马鹿种群,是我国唯一幸存的马鹿阿拉善亚种的有效种群(Li et al., 1998; Wang et al., 1999)。受贺兰山周围被城市、沙漠、河流隔断形成孤岛的地理特征所影响,该种群已成为一个隔离种(Qiao et al., 2019)。本研究涉及的两个古代鹿科动物样品,校正年代分别为(3800±30)和(5100±30) aBP, 采集地黑龙江肇东市和宾县与贺兰山相距约1900 km。黑龙江地区的古代样品在系统发育树上与贺兰山的现生马鹿阿拉善亚种聚为一支,而与现生马鹿东北亚种亲缘关系较远,表明在历史时期两地的马鹿种群存在较密切亲缘关系,可能发生过种群消退、迁徙、引入等,也可能曾有过高于现生种群的基因交流;两例古代样品代表的古代黑龙江马鹿种群,不是现生马鹿东北亚种的母系直系祖先。本研究后续工作将对不同历史时期、不同地点的马鹿古代样品的线粒体基因组及核基因组进行研究,以期为马鹿各亚种的种群演化历史提供更为全面的分子证据。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

MOTIVATION: Phylogenies are increasingly used in all fields of medical and biological research. Moreover, because of the next-generation sequencing revolution, datasets used for conducting phylogenetic analyses grow at an unprecedented pace. RAxML (Randomized Axelerated Maximum Likelihood) is a popular program for phylogenetic analyses of large datasets under maximum likelihood. Since the last RAxML paper in 2006, it has been continuously maintained and extended to accommodate the increasingly growing input datasets and to serve the needs of the user community. RESULTS: I present some of the most notable new features and extensions of RAxML, such as a substantial extension of substitution models and supported data types, the introduction of SSE3, AVX and AVX2 vector intrinsics, techniques for reducing the memory requirements of the code and a plethora of operations for conducting post-analyses on sets of trees. In addition, an up-to-date 50-page user manual covering all new RAxML options is available.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

SUMMARY: Ancient DNA extracts consist of a mixture of contaminant DNA molecules, most often originating from environmental microbes, and endogenous fragments exhibiting substantial levels of DNA damage. The latter introduce specific nucleotide misincorporations and DNA fragmentation signatures in sequencing reads that could be advantageously used to argue for sequence validity. mapDamage is a Perl script that computes nucleotide misincorporation and fragmentation patterns using next-generation sequencing reads mapped against a reference genome. The Perl script outputs are further automatically processed in embedded R script in order to detect typical patterns of genuine ancient DNA sequences. AVAILABILITY AND IMPLEMENTATION: The Perl script mapDamage is freely available with documentation and example files at http://geogenetics.ku.dk/all_literature/mapdamage/. The script requires prior installation of the SAMtools suite and R environment and has been validated on both GNU/Linux and MacOSX operating systems.
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

The possibility of gene tree incongruence in a species-level phylogenetic analysis of the genus Ips (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) was investigated based on mitochondrial 16S rRNA (16S) and nuclear elongation factor-1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) sequences, and existing cytochrome oxidase I (COI) and nonmolecular data sets. Separate cladistic analyses of the data partitions resulted in partially discordant most-parsimonious trees but revealed only low conflict of the phylogenetic signal. Interactions among data partitions, which differed in the extent of sequence divergence (COI > 16S > EF-1 alpha), base composition, and homoplasy, revealed that much of the branch support emerges only in the simultaneous analysis, particularly for deeper nodes in the tree, which are almost entirely supported through
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

BACKGROUND: High-throughput DNA sequencing technologies are generating vast amounts of data. Fast, flexible and memory efficient implementations are needed in order to facilitate analyses of thousands of samples simultaneously. RESULTS: We present a multithreaded program suite called ANGSD. This program can calculate various summary statistics, and perform association mapping and population genetic analyses utilizing the full information in next generation sequencing data by working directly on the raw sequencing data or by using genotype likelihoods. CONCLUSIONS: The open source c/c++ program ANGSD is available at http://www.popgen.dk/angsd . The program is tested and validated on GNU/Linux systems. The program facilitates multiple input formats including BAM and imputed beagle genotype probability files. The program allow the user to choose between combinations of existing methods and can perform analysis that is not implemented elsewhere.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

MOTIVATION: Many programs for aligning short sequencing reads to a reference genome have been developed in the last 2 years. Most of them are very efficient for short reads but inefficient or not applicable for reads >200 bp because the algorithms are heavily and specifically tuned for short queries with low sequencing error rate. However, some sequencing platforms already produce longer reads and others are expected to become available soon. For longer reads, hashing-based software such as BLAT and SSAHA2 remain the only choices. Nonetheless, these methods are substantially slower than short-read aligners in terms of aligned bases per unit time. RESULTS: We designed and implemented a new algorithm, Burrows-Wheeler Aligner's Smith-Waterman Alignment (BWA-SW), to align long sequences up to 1 Mb against a large sequence database (e.g. the human genome) with a few gigabytes of memory. The algorithm is as accurate as SSAHA2, more accurate than BLAT, and is several to tens of times faster than both. AVAILABILITY: http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net
URLPMID [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

In order to understand the origin, phylogeny, and phylogeography of the species Cervus elaphus, we examined the DNA sequence variation of the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene of 51 populations of deer from the entire distribution area of Cervinae with an emphasis on Europe and Asia. Several methods, including maximum parsimony, maximum likelihood, and nested clade analysis, revealed that red deer originated from the area between Kyrgyzstan and Northern India. We found two distinct groups of red deer: a western group consisting of four subgroups and an eastern group consisting of three subgroups. Our mtDNA data do not support the traditional classification of red deer as only one species nor its division into numerous subspecies. The discrepancies between the geographical pattern of differentiation based on mtDNA cytochrome b and the existing specific and subspecific taxonomy based on morphology are discussed.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 2]

A phylogeny was constructed for red deer/wapiti (Cervus elaphus) subspecies using sequence data from the control region of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). The tree was rooted using Cervus nippon (sika deer), Cervus albirostris (Thorold's white-lipped deer), and several Odocoileinae species. A division between the mtDNA haplotypes of red deer (European) and wapiti (Asian/North American) corresponds to subspecies found on opposite sides of the Himalayan Mountains and Gobi, which suggests wapiti should be reconsidered for the status of C. canadensis. Using parsimony and distance analysis, red deer and wapiti are derived from a single recent common ancestor, which is consistent with current taxonomy that recognizes the subspecies of Cervus elaphus as monophyletic group. However, maximum-likelihood analysis using weighted transitional substitutions caused red deer to form a sister group to sika deer (Cervus nippon) and wapiti. A phenetic comparison revealed wapiti also share more nucleotide similarities with sika deer, although approximately 5% sequence divergence separates wapiti, sika, and red deer. Phylogenetic evidence from the cytochrome b sequences corroborated observations from the control region. Observations from this study suggest that the species status of wapiti should be reinstated.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

This method is designed to maximize recovery of PCR-amplifiable DNA from ancient bone and teeth specimens and at the same time to minimize co-extraction of substances that inhibit PCR. This is achieved by a combination of DNA extraction from bone powder using a buffer consisting solely of EDTA and proteinase K, and purification of the DNA by binding to silica in the presence of high concentrations of guanidinium thiocyanate. All steps are performed at room temperature (20-23 degrees C), thereby reducing further degradation of the already damaged and fragile ancient DNA and providing an optimal trade-off between DNA release and degradation. Furthermore, the purification step removes most of the various types of PCR inhibitors present in ancient bone samples, thereby optimizing the amount of ancient DNA available for subsequent enzymatic manipulation, such as PCR amplification. The protocol presented here allows DNA extraction from ancient bone and teeth with a minimum of working steps and equipment and yields DNA extracts within 2 working days.
DOIURLPMID

DNA that survives in museum specimens, bones and other tissues recovered by archaeologists is invariably fragmented and chemically modified. The extent to which such modifications accumulate over time is largely unknown but could potentially be used to differentiate between endogenous old DNA and present-day DNA contaminating specimens and experiments. Here we examine mitochondrial DNA sequences from tissue remains that vary in age between 18 and 60,000 years with respect to three molecular features: fragment length, base composition at strand breaks, and apparent C to T substitutions. We find that fragment length does not decrease consistently over time and that strand breaks occur preferentially before purine residues by what may be at least two different molecular mechanisms that are not yet understood. In contrast, the frequency of apparent C to T substitutions towards the 5'-ends of molecules tends to increase over time. These nucleotide misincorporations are thus a useful tool to distinguish recent from ancient DNA sources in specimens that have not been subjected to unusual or harsh treatments.
[本文引用: 5]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 4]
