 ,2), 房詠柳, 邵奇上海交通大学水动力学教育部重点实验室, 上海 200240
,2), 房詠柳, 邵奇上海交通大学水动力学教育部重点实验室, 上海 200240AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF 3-D WAVE SURFACE AND HYDRODYNAMIC LOADS FOR INTERACTION BETWEEN SOLITARY WAVE AND SUBMERGED HORIZONTAL PLATE1)
Wang Qian, Liu Hua ,2), Fang Yongliu, Shao QiKey Laboratory of Hydrodynamics (MOE), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
,2), Fang Yongliu, Shao QiKey Laboratory of Hydrodynamics (MOE), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China通讯作者: 2) 刘桦, 教授, 主要研究方向: 高速水动力学、水波动力学、海啸. E-mail:hliu@sjtu.edu.cn
收稿日期:2019-09-2接受日期:2019-09-23网络出版日期:2019-09-23
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-09-2Accepted:2019-09-23Online:2019-09-23
作者简介 About authors

摘要
在波浪水池中进行了孤立波作用下有限长度和有限宽度淹没平板的三维模型水池实验. 首次应用多目视觉立体重构技术测量局部三维自由表面变形, 该系统的有效测量水平范围为1.7 m$\times $1.6 m. 用4个三分力测力传感器组成水下测力系统, 在不影响波面的情况下测量孤立波对平板的作用力和力矩. 针对波浪不破碎的情况, 选择0.4 m水深和0.16 m波高的来波条件, 平板淹没深度为0.1 m. 实验结果表明, 孤立波经过淹没平板时自由面有明显的三维变形, 导致孤立波波幅的时空变化. 波幅在平板尾缘中心线处达到最大值, 并沿展向逐渐减小. 利用多目视觉立体重构系统得到的波面变化过程与浪高仪给出定点波面时间序列相互印证, 表明建立标识码波面测量方法是有效的. 孤立波对淹没平板作用的水动力载荷变化分为6个典型阶段, 并与利用波面三维重构得到的波面测量标识码并讨论. 基于多目视觉立体重构技术得到了垂向力和俯仰力矩极值点出现时的三维波面形态. 建立的多目视觉立体重构系统将为海洋工程结构物的水池物理模型实验提供新的波面测量手段.
关键词:
Abstract
An experiment of interaction between a solitary wave and a submerged plate with finite length and finite width is conducted in a wave basin. A new system of the multi-lens stereo reconstruction is proposed to measure the local deformation of the free surface in the horizontal area of 1.7 m$\times $1.6 m in the experiment. A set of underwater force measuring system consisted of four force balances is designed to obtain the wave loads on the submerged plate, without the interference on the surface elevation measurement. A solitary wave is generated in a wave basin of uniform water depth. The wave amplitude is 0.16 m and the still water depth is 0.4 m. The submerged depth of the horizontal plate is 0.1 m. No wave breaking occurs during the wave propagation. The three-dimensional deformations of the free surface elevation lead to the spatial and temporal variation of the solitary wave amplitude. It is found that, for the case of the present wave condition and the submerged plate, the surface elevation reaches the highest at the centerline of the plate near its trailing edge, and decreases along the span direction. The time series of the surface elevation measured by the multi-lens stereo reconstruction method agree well with the wave elevations measured by the wave gauges, which validates the new wave surface measurement system. The loading processes of the horizontal force, vertical force and the pitch moment are proposed as 6 typical phases in which the characteristics of the measured wave surface elevation are discussed. The wave surfaces measured by the multi-lens stereo reconstruction method are given at the corresponding time as the peaks of the vertical force and the pitch moment occurs. The multi-lens stereo reconstruction method could be used to measure the wave field for physical model experiments in a wave basin as a new tool.
Keywords:
PDF (7149KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
王千, 刘桦, 房詠柳, 邵奇. 孤立波与淹没平板相互作用的三维波面和水动力实验研究1). 力学学报[J], 2019, 51(6): 1605-1613 DOI:10.6052/0459-1879-19-244
Wang Qian, Liu Hua, Fang Yongliu, Shao Qi.
引 言
淹没平板是波能吸收转化装置、漂浮平台、船坞、码头以及跨海桥梁等海洋与海岸工程中常见构件之一. 在极端海洋动力条件下, 例如风暴潮、风浪以及海啸等作用, 淹没平板的水标识码荷及其作用机理与波浪散射、辐射密切相关, 有时黏性效应也不可忽略, 标识码种波浪条件下淹没平板流体动力性能的理论分析方法与实验测量方法得到学术界与工程界的标识码注[1].海啸波作为一种极端波浪条件可导致近岸平台和桥面的结构失效. 尽管海啸波形具有多样性, 如长波、N波、非破碎涌波等[2-3], 孤立波曾被作为模拟海啸传播的简化理论模型应用于研究海啸波对对近岸结构物的作用以及在斜坡标识码高[4-5]. 海啸波的特殊波形可采用孤立波作为简化, 在海啸波演化、近岸爬高、对结构物冲击载荷等方面均标识码较好的实验结果. Hayatdavoodi和Ertekin[6]对孤立波与平板结构物相互作用问题进行了较为系统的总结, 包括标识码力载荷的理论分析、数值模拟和实验模拟研究. 总体上讲, 孤立波与平板结构物相互作用的物理实验工作并不充分. 美国加州理工学院Keck实验室曾针对悬空近水面二维水平板进行了具有开拓性的水槽实验, 采用压力标识码测量测量了孤立波作用下平板表面的压力时间过程线, 发现水动力载荷可分解为一个短暂冲击力和标识码变力, 其中缓变表压呈现正压和负压部分[7]. 近年来, 针对二维淹没平板与孤立波条件, 在水动力载荷的变化规律及其机理、导边与尾缘处的非定标识码流动的数值模拟与PIV标识码方面取得新进展[8-10]. 在二维情况下, 物理模型实验与数值模拟结果均显示, 孤立波作用下的垂向力载荷总是随相对板长标识码而增大. 淹没平板向上的垂向力系数不断增大, 而向下的垂向力系数不断增大趋于一常数[11-12]. 对于有限宽度和有限板长的淹没平板, 孤立波作用下水动力载荷三维效应则鲜有研究报道, 三维波标识码空演化过程也缺乏有效的实验测量方法.
视觉立体重构技术的发展为在实验水池中测量波面的时空变化过程提供了新思路. 视觉立体重构的主要步骤包括标定、识别和匹配, 通常指的是采用不少于2个的高速相机, 先通标识码得到相机底片坐标与三维坐标的映射关系, 再对空间中的特殊标识点进行拍摄. 在不同相机中识别并匹配到对应标识点后, 利用标定好的映射关系求解超定方程得到标识点的标识码标[13]. 采用的标定方法不需要给定标定板的具体空间位置, 只需要将已知标定格尺寸的标定板以随机角度、标识码置摆放在待测区域, 可用最大似然估计方法得到相机的内参、外参以及镜头的图像畸变系数[14]. 洁净水体的透光性使得辨识自由水面成为一个具有挑战性的课题, 现有的方法有利用由于波浪破碎产标识码然纹理[15]、添加固体颗粒示踪物[16]、利用二氧化钛使水体成为乳白色液体[17]等. 使用人工光源在水面产生标识点, 便于采取图像处理方法得到标识点在相机底片中的坐标, 进而进标识码计算[18]. 有两种进行标识点匹配的方法. 一种方法是将拍摄区域划分为小块问询区, 利用互相关方法对不同相机底片中的问询区进行匹配[19]. 这一方法经过图形畸变和极线矫正法[20], 或多步迭代法[21]可以消除部分误差且高效标识码对不规则标识点的匹配. 这一方法的可测点为整个测量区域. 第二种方法是当标识点规则排列时, 可以对标识点进行有序的编号, 从而更加方便地完成匹配[22]. 这一方法可以更准确地找到标识点位置, 同时可以通过增加相机数量来提高重构准确性, 但可测点标识码在标识点处.
本文将视觉立体重构技术[23]应用到水池的波面测量, 以获得孤立波经过淹没平板时水标识码的时空变化, 得到瞬时波面. 同时采用一套水下测力系统, 得到三维情况下孤立波对淹没平板作用的波浪载荷规律, 为相关的理标识码和数值模拟提供有效的参考数据.
1 实验设备与测量方法
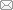
实验是在上海交通大学的近海海啸波水池中完成. 水池长42.4 m, 宽4 m, 高1.6 m, 配有一台2.4 m冲程的推板式造波机. 以三阶孤立波理论解作为目标波形, 采用改进的Goring造波方法[24]可生成大波高孤立波[25-26]. 考虑到水池壁面效应和已开展的二维模型几何尺寸[11], 本次实验采用一标识码机玻璃制成的长2 m、宽0.78 m、厚0.1 m的平板, 并安装在水池中部. 为了实现波面重构, 在平板上方搭建了一个铝合金框架用来负责安装固定拍摄系统, 包括相机和投影仪等, 见图1 .图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1实验水池与模型
Fig.1Site photo of the basin and model
4个CCD相机悬挂在水池上方, 构成了多目立体重构拍摄系统(multi-lens stereo reconstruction, MLSR). 相机分别从4个角度向下同步对波面进行拍摄. 每个相机距离拍摄区域约5.0 m, 每秒拍摄帧数为50帧, 分辨率为$2240\times1728$像素. 4个相机的公共拍摄区域范围约1.7 m$\times$1.6 m. 标定方法采用张正友标定法[14]. 将棋盘格镀膜在钢化玻璃上, 以提高标定板的刚度而不发生弯曲变形. 标定板的大小为1.2 m$\times$1.2 m, 棋盘格间距为0.0685 m. 将标定板在0.3 m至0.5 m的范围内随机摆放约200个位置, 每个位置均确保每个相机的拍摄角不大于45$^\circ$. 将得到的照片使用Matlab软件中的“相机标定”模块进行后处理, 从而可以得到内参、外参和2阶径向畸变系数. 为了实现高精度的自由水面辨识, 将大量高发泡聚乙烯颗粒均匀撒在水面, 并用一台7500流明投影标识码设在水面上方约4.0 m处向水面投影圆形光斑阵列, 见图2. 当光斑投影至水池底部时, 每个光斑直径约0.03 m, 阵列间隔约0.07 m. 该聚乙烯颗粒堆积密度25 kg/m$^{3}$, 平均直径0.001 m, 具有良好的光散射性和疏水性. 此粒径和密度的颗粒置入水中后, 对波面的影响可以忽略. 当大量粒子漂浮于水面时, 整体会形成一层类似薄膜的状态. 当波面不发生破碎时, 该层类膜不会标识码显破损. 对相机拍摄到的圆斑标识点阵, 使用Matlab软件进行预处理, 包括选择适当阈值去掉过亮和过标识码素点、利用灰度加权算法获得每个圆形光斑的形心在底片中的位置. 得到光斑形心后, 将光斑阵列排序, 从而可以快速匹配每个相机记录中对应的光斑. 匹配完成后便可进行重构得到每个光斑形心的空间三维位置. 最后, 利用二维插值估计整个测量区域内每个位置处的波面高度. 该波面立体成像与重构方法具有精度高、拍摄范围较大的优点, 得到的孤立波传播过程中波面标识码列与浪高仪测量结果一致, 波高相对偏差在2${\%}$以内[23].
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2自由水面光斑投影
Fig.2Spots projected on the free surface
除波面重构系统外, 架设了17个电容式浪高仪. 波面重构的范围和浪高仪的位置见图3(a), 其中虚线代表淹没平板, 实线为MLSR测量区域, 标识码部的小正方形为测力传感器, $X$和$Y$为MLSR测量的方向, 同时也是测力系统的方向. 圆点为浪高仪位置, G0位置处的浪高仪距离平板7 m, 用来记录来波高度. G9位于平板中心, G8与G10对称放置, 与G9间隔0.45 m, G7与G8间隔0.5 m. 以G7-G9为中心, 前后间隔1.05 m和1.45 m处各布置3个浪高仪. 需说明的是, 由于浪高仪会遮挡相机的拍摄, 本次实验中浪高仪测量和波面重构系统无法同时使用. 由4个KISTLER 9317C压电式三分力传感器组成测力系统, 测量波浪对平板的三向力和三向力矩, 载荷标识码合右手系, 见图3(b). 这里, $H$, $\eta$, $h$分别代表来波波高、波面高程和未扰水深. 空心黑色方块为测力传感器, 实心黑色矩形为刚性连接装置, $M_{y}$处箭头代表俯仰力矩的方向, $X$和$Z$分别为来波传播方向和垂直向上. 通过信号采集器可以将测力系统与浪高仪的记录同步. 浪高仪采样频率为50 Hz, 测量传感器测量频率为1000 Hz. 平板内部有两层钢板, 上层与平板固定, 下层与水池底部通过4根直径为0.04 m的圆柱固定. 圆柱在穿过打孔的平板底部时不与平板发生接触, 孔处用硅胶薄膜进行密封. 这一设计使得固定在两层钢板间的测力系统可以在不影响拍摄波面的情况下测量平板受到的波浪载荷. 测力系统在安装好后, 通过已知重量的加载进行了精度验证, 载荷测量误差小于0.3${\%}$. 通过敲击淹没状态下的平板, 得到整体结构自振频率为8.3 Hz.
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3平板模型与测量装置示意图
Fig.3Sketch of the plane model and measurement set-up
针对波浪不破碎的情况, 使得平板上表面的淹没深度$d$为0.1 m, 水深$h$选择0.4 m, 孤立波波高$H$为0.16 m. 以此典型工况进行初步的研究观察.
2 结果讨论
2.1 对称性检验
通过水平仪可验证平板在高度方向是水平放置, 但无法验证平板长度轴线方向是否与来流方向平行. 图3(a)中可见, G8和G10处于平板中部的对称位置, 因此这两个位置的波面变化是否具有对称性标识码来验证平板轴线是否与来流方向有夹角. 图4给出了G8和G10位置处浪高仪测量结果和MLSR测量结果, 通过最大波峰来实现时间同步. 4条曲线基本一致, 说明平板沿板长方向是与来流方向平行, 同时也间接验证了波面重构系统的准确性.图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4G8和G10位置处, 浪高仪和MLSR测量的波面随时间变化的高度
Fig.4Time-varying surface elevation recorded by the wave gauges and the MLSR at G8 and G10
2.2 波面变化
图5给出了多目重构方法测量得到的几个时刻测量区域内的波面高度, 其中实线代表部分波标识码值线, 纵向虚线表示平板侧缘, 三角代表测量区域内最大波高, 横向虚线为波峰线.图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5MLSR测得的不同时刻的波面
Fig.5The surface elevation at different moments measured by the MLSR method
在整个波面变化过程中, 将平板中心G9位置处波面达到最大值的时刻记为$t^*=0$. 受到淹没平板作用, 平板上方波动传播速度降低, 平板两侧波动传播速度大于平板上部的波动. 因此在孤立波波前部分受到淹没平板的影响时, 波前的波面等值线呈后弯曲型, 见$t^*=-0.26$ s时标识码面重构结果. 正是由于存在此沿纵向中心线对称的横向水位梯度, 在平板上部形成从两侧向中心汇聚的流动, 使得标识码方水面抬高, 该时刻的波峰线(虚线)呈前弯曲型, 且中心线处的波幅已略大于0.160 m的来波波幅. 随着孤立波继续向前推进, 如$t^*=-0.18$ s时, 平板上方的波面抬高进一步扩大, 0.160 m的等标识码渐扩张, 基本抵达平板侧缘, 此时波面最大值约为0.170 m. $t^*=0$ s时, 平板中心处波面达到最大值0.181 m, 0.160 m等值线的横向范围已大于平板范围. $t^*=0.22$ s时, 测量区域内波面最大值为0.197 m, 而0.160 m等值线在形态上发生变化, 后方标识码平, 表明中线处水面抬升已趋弱化.
本次实验布置了浪高仪阵列测量波面时间过程线. 图6通过浪高仪的数据可以看到多目重构方法的测量区域外, 部分位置处波面变化的时间历程. 平板前方G1-3和G4-6处, 波面沿平板展向没有明显变化, 说明平板造成的波浪散射效应较小. 而孤立波经过平板时, 同多目重构的结果一致, 波面发生明显变形, 且波高从平板中心向外侧降低. 同时, 波面最大值发生在G13处, 即平板的尾缘处. 这也表明在当前淹没水深和平板尺寸条件下, 孤立波经过平板时波面会沿平板中线持续抬升至平板尾缘. G16处的最大波面高度和G13处基本一致, 说明孤立波经过平板后, 中心线处的波面抬升现象会持续一段距离.
图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6浪高仪记录波面变化
Fig.6Wave elevation recorded by gauges
当孤立波在淹没平板上传播过程中, 水面高度的最大值出现在平板中线处, 且随着孤立波传播水面最大值逐渐变大, 整体波面高度也从中线处向两侧逐渐降低. 需指出的是, 这种中线处的波面抬升不会随着板长无限变大, 当达到某一极值时, 波面可能会发生破碎, 也可能会产生由横向水位梯度激发的指向两侧流动. 相对板长与相对板宽对波面变形的影响规律尚需做进一步的实验研究.
2.3 波浪载荷
图7给出了孤立波经过淹没平板时作用于平板的波浪力时间序列, 以及对应时刻G9处的波面变化过程. 水平波浪力具有一个正向最大值和一个负向最大值, 且两个幅值基本相等. 从其变化规律可以看出, 孤立波产生的惯性力对水平波浪力流向力起决定作用. 垂向波浪力有两个峰值和一个谷值, 第一个峰值大于第二个峰值, 且谷值对应的向下载荷比峰值对标识码上载荷要大一倍. 平板长度尺度的量级通常大于厚度尺度, 相比于流向力, 垂向波浪力是主要受载. 平板的俯仰力矩主要由垂向波浪力产生, 也具有两个峰值和一个谷值. 根据垂向波浪力和俯仰力矩的极值点, 可以将孤立波对淹没平板作用的载荷形成过程分为6个阶段.图7
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7孤立波作用下波浪载荷和波面时间过程线.括号内数字表示载荷作用的不同阶段
Fig.7Time series of wave loads on the submerged plate and surface elevation in a solitary wave. The number in the bracket represents the stage of the loading mode
第1阶段, 孤立波开始与平板接触, 此时平板下方“狭道流动效应”使得压强迅速增大, 产生向标识码荷; 随着孤立波传播, 该上抬力逐渐增大至最大. 此时对应的波面见图8(a), 图中线条含义与图5相同. 此时孤立波波峰尚未抵达重构区域. 第2阶段, 孤立波继续传播, 平板将水体分为两部分. 随着孤立波主体传至平板位置, 平板上方局部压强的增加大于平板下方仅由孤立波运动时产生的动压. 因此总的垂向波浪力开始降低, 由正向最大值开始向负向减小, 直至俯仰力矩到达负向最大值. 由图3(b)所示的载荷方向可知, 此时负向垂向力作用在平板前半部分. 对应的波面见图8(b), 波峰最大值出现在平板前半部分距中心约0.6 m处, 且平板中线附近开始出现0.160 m的 波面等值线. 第3阶段, 平板上方局部 压强随着孤立波主体运动至平板中心附近使得局部压强增加至最大, 导致总的标识码浪力为幅值, 垂直向下. 对应的波面见图8(c), 波面的最高点不在平板中心, 而是在平板后半部分距中心约0.3 m处. 这是由于孤立波在经过平板时发生变形, 波面不再保持前后对称. 第4阶段, 孤立波主体开始离开平板, 从而使得平板上方局部的压强减小, 总垂向力开始由负向最大值向正向变化, 导致俯仰力矩达到正向最大值, 说明此时总标识码向垂向力作用在平板后半部分. 由图8(d), 最大波面高度出现在平板后半部分距离平板中心约0.6 m处. 对应于图7中(2)时刻力矩达到负向最大值时, 波面最大高度出现在平板前半部分距离平板中心约0.6 m处, 标识码对应说明孤立波主体在淹没平板上的位置对平板受到的俯仰力矩有决定性作用, 见图8(b). 第5阶段, 孤立波继续离开平板, 平板上方压强继续降低, 小于平板底部“狭道流动效应”产生的压强分布, 于 是总垂向力慢慢达到正向最大值. 波面见图8(e), 这时重构区域内平板前半部分的波面恢复至未扰水面, 局部略低于未扰水位. 孤立波经过平板时发生的波形变形是垂向力的第二次正向峰值小于首个峰值的主要原因. 第6阶段, 孤立波远离平板, 总垂向力趋于零, 俯仰力矩也趋于零.
图8
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8垂向力和俯仰力矩极值点出现时(对应
Fig.8The surface elevation measured by the MLSR method at the time for the peak value of the vertical force and the pitch moment(corrsponding to the stage (1)-stage(5) in
由于三维平板模型实验在模型两侧存在显著的横向流动, 导致三维情况下有限板宽淹没平板的波标识码别于二维模型实验结果. 对比孤立波作用下二维平板模型的波浪力实验结果[11-12], 可以发现:正向垂向力仅为标识码型的1/5, 负向垂向力为二维模型的1/3; 二维模型预测的相对板长对垂向波浪力系数的影响将被显著削弱.
3 结 论
针对2 m$\times $0.78 m$\times$0.1 m平板在淹没深度为0.1 m的情况下, 选择0.4 m水深、0.16 m波高的孤立波, 进标识码限宽度平板模型在孤立波作用下的近场波面变化与水动力载荷实验. 通过自主搭建的多目立体重构拍摄系统成功测量波面的三维变化. 利用水下载荷测量系统, 在不影响波面的情况下得到平板受到的波浪力.实验表明:当孤立波经过淹没平板时, 在平板的阻挡作用下, 平板上方波动传播减速, 波面出现明标识码维变化, 导致波高会沿平板中心逐渐抬升, 且向平板两侧逐渐降低. 孤立波在经过平板的整个过程中, 波面最大高度出现在平板尾缘处.
平板受到的水平波浪力由惯性力主导, 具有一个正向极值和一个负向极值. 垂向波浪力具有两个正向极值和一个负向极值, 其中第一个正向极值大于第二个. 俯仰力矩也具有两个正向极值和一个负向极值. 将孤立波对淹没平板的垂向波浪力和俯仰力矩作用过程分为6个阶段, 依据基于多目立体重构技标识码的典型波面形态, 讨论了水动力载荷变化规律及其作用机理. 与二维模型预测的水动力学载荷变化相比, 波面变化的三维效应导致垂向力极值显著减小.
数值模拟与物理模型实验是波浪与复杂构型海洋工程结构物相互作用[27-28]、海底标识码啸[29-30]等研究的重要手段, 本文建立的波浪水池中三维波面成像与重构技术可标识码水池物理模型实验提供新的测量手段.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[PhD Thesis].
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

The most common positron emission tomography (PET) radio-labeled probe for molecular diagnostics in patient care and research is the glucose analog, 2-deoxy-2-[F-18]fluoro-D-glucose (18F-FDG). We report on an integrated microfluidics-chip/beta particle imaging system for in vitro18F-FDG radioassays of glycolysis with single cell resolution. We investigated the kinetic responses of single glioblastoma cancer cells to targeted inhibitors of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Further, we find a weak positive correlation between cell size and rate of glycolysis.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 2]

High-speed panoramic three-dimensional (3D) shape measurement can be achieved by introducing plane mirrors into the traditional fringe projection profilometry (FPP) system because such a system simultaneously captures fringe patterns from three different perspectives (i.e., by a real camera and two virtual cameras in the plane mirrors). However, calibrating such a system is nontrivial due to the complicated setup. This work introduces a flexible new technique to calibrate such a system. We first present the mathematical representation of the plane mirror, and then mathematically prove that it only requires the camera to observe a set of feature point pairs (including real points and virtual points) to generate a solution to the reflection matrix of a plane mirror. By calibrating the virtual and real camera in the same world coordinate system, 3D point cloud data obtained from real and virtual perspectives can be automatically aligned to generate a panoramic 3D model of the object. Finally, we developed a system to verify the performance of the proposed calibration technique for panoramic 3D shape measurement.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

The shallow waters of the nearshore ocean are popular, dynamic, and often hostile. Prediction in this domain is usually limited less by our understanding of the physics or by the power of our models than by the availability of input data, such as bathymetry and wave conditions. It is a challenge for traditional in situ instruments to provide these inputs with the appropriate temporal or spatial density or at reasonable logistical or financial costs. Remote sensing provides an attractive alternative. We discuss the range of different sensors that are available and the differing physical manifestations of their interactions with the ocean surface. We then present existing algorithms by which the most important geophysical variables can be estimated from remote sensing measurements. Future directions and opportunities will depend on expected developments in sensors and platforms and on improving processing algorithms, including data assimilation formalisms.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

We present a study of the damping of capillary-gravity waves in water containing pigments. The practical interest comes from a recent profilometry technique (FTP for Fourier Transform Profilometry) using fringe projection onto the liquid-free surface. This experimental technique requires diffusive reflection of light on the liquid surface, which is usually achieved by adding white pigments. It is shown that the use of most paint pigments causes a large enhancement of the damping of the waves. Indeed, these paints contain surfactants which are easily adsorbed at the air-water interface. The resulting surface film changes the attenuation properties because of the resonance-type damping between capillary-gravity waves and Marangoni waves. We study the physicochemical properties of coloring pigments, showing that particles of the anatase (TiO2) pigment make the water surface light diffusive while avoiding any surface film effects. The use of the chosen particles allows to perform space-time resolved FTP measurements on capillary-gravity waves, in a liquid with the damping properties of pure water.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 2]

Controlling microbubble dynamics to produce desirable biomedical outcomes when and where necessary and avoid deleterious effects requires advanced knowledge, which can be achieved only through a combination of experimental and numerical/analytical techniques. The present communication presents a multi-physics approach to study the dynamics combining viscous- in-viscid effects, liquid and structure dynamics, and multi bubble interaction. While complex numerical tools are developed and used, the study aims at identifying the key parameters influencing the dynamics, which need to be included in simpler models.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

Experiments of the runup of two solitary waves on a plane beach are carried out in a wave flume. The two solitary waves with the same amplitude and the crest separating distances are generated by using an improved wave generation method, It is found that, with regard to the two solitary waves with same wave amplitude, the runup amplification of the second wave is less than that of the first wave if the relative crest separating distance is reduced to a certain threshold value. The rundown of the first solitary wave depresses the maximum runup of the second wave, If the leading solitary wave is of relatively smaller amplitude for the two solitary waves, the runup amplification is affected by the overtaking process of two solitary waves, It turns out that the runup amplification of the second wave is larger than that of the first wave if the similarity factor is approximately larger than 15, which means the larger wave overtakes the smaller one before the waves runup on a beach,
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
