 , 王璐, 杨扬
, 王璐, 杨扬
西北工业大学航空学院,西安 710072
AN IMPROVED SPH ALGORITHM FOR LARGE DENSITY RATIOS MULTIPHASE FLOWS BASED ON RIEMANN SOLUTION1)
YangQiuzu, XuFei , WangLu, YangYang
, WangLu, YangYang
中图分类号:O359
文献标识码:A
通讯作者:
收稿日期:2018-12-28
网络出版日期:2019-05-18
版权声明:2019力学学报期刊社 所有
基金资助:
展开
摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
-->0
PDF (34100KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章收藏文章
本文引用格式导出EndNoteRisBibtex收藏本文-->
引 言
许多关于流体流动的自然现象以及工程实际问题多涉到两种及两种以上流体,如水面波浪飞溅破碎、气垫船高速行驶、炸药水下爆炸、石油开采[1-4]等,采用真空或者考虑气体的存在分别对这类问题进行研究,两者得到的最后结果物理差别巨大,甚至直接影响到数值计算结果的正确与否,因此开发研究此类多相流问题的数值计算模型对许多工程应用具有重要意义.虽然采用网格方法解决流体动力学问题已很成熟[5-8],但用于模拟大变形流体动力学问题存在局限,需要进行特殊处理才能获得很好的计算结果[9-12].作为无网格方法中一种[13-16],光滑粒子水动力学(smoothedparticlehydrodynamics,SPH)程序化实现简单、高效,在计算流体动力学领域被广泛应用[17-20].尽管传统SPH在模拟上述单相流或小密度比多相流问题上效果很好,但将其扩展应用于计算大密度比多相流问题,却在异相界面周围存在压力震荡、数值不稳定等问题,为了处理这类数值问题,研究者们对传统SPH方法进行了许多改进.2001年,Richie和Thomas[21]通过将局部压力加权平均求解粒子压力,进而通过粒子压力求解粒子密度,来建立多相流SPH模型,但计算中需要考虑流体内部能量;2003年,Colagrossi等[22]为了保持粒子质量、密度和体积的一致性和减小多相流压力场震荡,采用了"粒子密度重新初始化"方法,同时又引入了XSPH技术,人为施加的干预技术较多;2008年,Colagrossi等[23]将Flebbe等[24]提出的"粒子分布密度"法引入到了多相流运动方程中估算粒子密度,考虑流体可压,该模型要求不同流体相粒子的体积相同、体积变化率相等;2009年,Grenier等[25]提出采用Shepard核函数计算流体密度,但需要先计算粒子体积,计算比较耗时;2010年,Adami等[26]也同样将"粒子分布密度"方法引入运动方程,同时又通过密度加权平均压力来处理界面压力梯度,但在计算大密度比多相流问题时误差偏大;2013年,Monaghan等[27]在模拟大变形多相流问题时(如Rayleigh-Taylor不稳定性问题),将多相流异相界面附近粒子人工处理为刚性,虽能稳定界面,但界面粒子只能单方向移动失去了流体真实物理流动性质;2015年,Chen等[28]对文献[26]的方法进行了改进,虽未引入非物理耗散也可以模拟大密度比多相流,但仅考虑了密度不连续,没有考虑压力梯度的影响;2016年,Lind等[29]提出弱可压相与不可压相SPH耦合算法来模拟大密度比多相流问题,在可压相引入人工黏性来减小数值震荡;在不可压相施加位移迁移技术减小粒子聚集;2018年,Wan等[30]为阻止粒子穿透提出一种人为只对轻质流体施加内聚力的SPH多相流模型;Kruisbrink等[31]为保证多相流异相界面稳定,在SPH动量方程中人为添加了一个额外修正项;Rezavand等[32]则提出了一种不涉及到速度散度项的不可压SPH多相流模型,采用算术平均对粒子密度和黏性分布进行了光滑处理.
可以看到上述已有多相流SPH模型虽能实现多相流数值模拟,但多采用的处理技术是非物理的,在减少震荡的同时增大了剪切黏性、降低了计算精度、人为增加了耗散,不符合守恒定律.Inutsuka[33]利用卷积积分重组SPH,将粒子对间作用看成间断处的黎曼解问题进行求解,提出了一种基于黎曼解、无人工黏性的SPH新算法;为求解激波管问题Monaghan[34]也将黎曼解与SPH相结合,不仅有效解决了间断处的数值震荡,而且提高了计算精度,但处理强冲击问题仍存有震荡;于是,Parshikov[35]采用声波近似黎曼解来描述粒子对间作用,解决强冲击震荡问题,同时也扩宽了其适用范围[36-37].但目前尚未有文献报道将无耗散黎曼解引用到多相流SPH模型中来求解大密度比黏性多相流问题.
本文正是鉴于黎曼解处理间断问题的优势,将其扩展应用于多相流SPH计算模型中,并对黎曼数值耗散项进行改进,用以描述多相流真实物理黏性,该改进的多相流SPH计算模型没有人为添加额外处理技术,能够准确捕捉多相流界面、模拟大密度比大黏性比多相流问题,最后通过4个典型多相流问题算例(包括方形液滴震荡、Rayleigh--Taylor不稳定、单气泡上浮、双气泡上浮)验证了改进的模型在处理具有挑战性的多相流问题上的有效性.
1 SPH基本原理
SPH方法的基本思想是将连续物质场离散成一组运动粒子的集合,每个粒子具有自己的物理特征(如速度、压力、能量和质量等),每个质点代表一个已知物理特性的插值基点,用规则的内插函数计算全部粒子的函数值,从而近似描述整个物质场问题的解.基于该方法将表示粒子$i$物理量的函数$f({ {x}}_i )$以及导数$\nabla f({ {x}}_i )$表示为以下形式[17]$$f(x_i ) = \int\limits_\varOmega {f({x}')} W({ {x}}_i - { {{x}'}},h)\;{\rm d}{ {{x}'}}\approx \\ \sum\limits_j {f({ {x}}_j )} W({ {x}}_i - { {x}}_j ,h)V_j\tag{1}$$
$$ \nabla f({ {x}}_i ) = \int\limits_\varOmega {f({ {{x}'}})} \nabla W({ {x}}_i - { {{x}'}},h)\;{\rm d}{ {{x}'}}\approx \\ \sum\limits_j {\left( {f({ {x}}_j ) - f({{ x}}_i )} \right)} \nabla W({ {x}}_i - { {x}}_j ,h)V_j \tag{2} $$
其中,$W({ {x}} - { {{x}'}},h)$和$\nabla W({ {x}} - {{ {x}'}},h)$分别为光滑核函数及其梯度,$h$为核函数影响区域的光滑长度(本文取1.25倍粒子间距),${{\varOmega}}$为光滑函数的支持域,$V_j = m_j / \rho _j $为$j$粒子体积,$m_j$和$\rho _j $分别表示$j$粒子的质量和密度.
2 SPH多相流模型
本文多相流模型采用基于质量与动量守恒的Navier--Stokes方程来描述,用SPH格式离散流体运动方程,利用黎曼解处理间断问题的优势,将其引入到SPH多相流模型中.2.1 一般SPH多相流离散方程
多相流的运动采用Navier--Stokes控制方程的拉格朗日形式描述,具体如下[22]$$\frac{{\rm d}\rho }{{\rm d}t} = - \rho \nabla \cdot {{v}}\tag{3}$$
$$ \frac{{\rm d}{{v}}}{{\rm d}t} = - \frac{1}{\rho }\nabla p + {{g}}\tag{4} $$
式中,$\rho, {v},p$和$g$分别表示流体密度、速度、压力和重力加速度.
为了求解式(3)、式(4)控制方程,本文添加弱可压状态方程进行联立求解[22]
\begin{equation} \label{eq5} p = \frac{\rho _0 c^2}{\gamma }\left[ {\left( {\frac{\rho }{\rho _0 }} \right)^\gamma - 1} \right] + p_0\tag{5} \end{equation}
式中,$\rho _0,c,p_0$分别是流体参考密度、参考声速、背景压力;$\gamma$为常数,无特殊指出同一算例中轻质流体取1.4,重质流体取7.0;参考声速的选取参考文献[38].
基于SPH方法离散控制方程式(3)、式(4)如下
$$\frac{{\rm d}\rho _i}{{\rm d}t} = \rho _i \sum\limits_j {({ {v}}_i - { { v}}_j )} \cdot \nabla _i W_{ij} ({ {r}}_i - { {r}}_j ,h)V_j =\\ 2\rho _i \sum\limits_j ( v_i - {{\bar { v}}}_{ij} ) \cdot \nabla _i W_{ij} ({ {r}}_i - { {r}}_j ,h)V_j \tag{6}\\ $$
$$\frac{{\rm d}{ {v}}_i }{{\rm d}t} = - \frac{1}{\rho _i }\sum\limits_j {(p_i + p_j )} \nabla _i W_{ij} ({ {r}}_i - { {r}}_j ,h)V_j + { {g}}_i= \\ - \frac{2}{\rho _i }\sum\limits_j {\bar {p}_{ij} } \nabla _i W_{ij} ({ {r}}_i - { {r}}_j ,h)V_j + { {g}}_i \tag{7}$$
式中,$\rho _i, {v}_i,p_i,{g}_i,{\bar {v}}_{ij}\mbox{和}\bar{p}_{ij}$和分别表示$i$粒子的密度、速度、压力、重力加速度以及$i$和$j$粒子的平均速度和平均压力;其中核函数的选取对SPH的计算十分重要,传统的一些核函数容易引起拉伸不稳定,如三次样条和高斯核函数等,为了避免出现拉伸不稳定,本文采用Wendland提出的核函数[39]
\begin{equation} \label{eq7} W({ {r}},h) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{ll} \alpha \left( {2 - q} \right)^4\left( {2q + 1} \right),&0 \le q < 2 \\ 0,&q \ge 2 \\ \end{array}} \right.\tag{8} \end{equation}
其中,$q = \left| {{ {r}}_i - { {r}}_j } \right| / h$,一维问题$\alpha = 3 / (64h)$,二维问题$\alpha = 7 / (64 h^2)$,三维问题$\alpha = 21 / (256 h^3)$.
2.2 基于黎曼解改进的SPH多相流模型
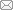
基于黎曼解SPH方法与传统SPH方法的不同之处是控制方程中描述两个相互作用粒子间的压力和速度项不同.假设这种相互作用存在于两个粒子连线的中间,粒子之间的相互作用沿着从粒子$i$到粒子$j$的单位矢量构建,类似于连续介质力学中处理接触不连续性的方法.本文采用的是一阶黎曼求解器,它是通过3个波分开的4个状态来近似黎曼解,如图1示,两个相关粒子的物理量构成左右状态,粒子$i$和$j$上的初始左和右状态为[35]$$U_i = \left( {\rho _{\rm L} ,u_{\rm L} ,P_{\rm L} } \right) = \left( {\rho _i ,{ {v}}_i \cdot { {e}}_{ij} ,P_i } \right)\tag{9}$$
$$U_j = \left( {\rho _{\rm R} ,u_{\rm R} ,P_{\rm R} } \right) = \left( {\rho _j ,{ {v}}_j \cdot { {e}}_{ij} ,P_j } \right)\tag{10}$$
式中,${ {e}}_{ij} = ({ {r}}_j - { {r}}_i ) / r_{ij} $,$r_{ij} $为$i$和$j$粒子的间距.
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1一阶黎曼求解器结构图
-->Fig. 1Wave solution of first order Riemann solver
-->
假设两个中间状态相等,$(u_{\rm L}^* ,P_{\rm L}^ * ) = (u_{\rm R}^ * ,P_{\rm R}^ * ) =(v_{ij}^*,p_{ij}^ * )$,通过黎曼求解器确定中间状态,解得粒子间断处的速度$v_{ij}^ * $跟压力$p_{ij}^ * $为
$${ {v}}_{ij}^ * = \frac{{ {v}}_i + { {v}}_j }{2} + \frac{1}{2}\frac{P_L - P_R }{\bar {\rho }_{ij} \bar {c}_{ij} }{ {e}}_{ij}\tag{11}$$
$$P_{ij}^ * = \frac{p_i + p_j }{2} + \frac{1}{2}\bar {\rho }_{ij} \bar {c}_{ij} (u_{\rm L} - u_{\rm R} )\tag{12}$$
式中,$\bar{\rho }_{ij}$和$\bar {c}_{ij} $为$i$和$j$粒子的平均密度与声速.
将解得的间断处黎曼解(11)和(12)替换式(6)、式(7)中$i$和$j$粒子的平均速度$\bar {v}_{ij} $、压力值$\bar {p}_{ij}$,得到基于黎曼解的多相流SPH控制方程为
$$\frac{\mbox{d}\rho _i }{\mbox{d}t} = 2\rho _i \sum\limits_j {({ {v}}_i - { {v}}_{ij}^ * )} \cdot \nabla _i W_{ij} V_j\tag{13}$$
$$\frac{\mbox{d}{ {v}}_i }{\mbox{d}t} = - \frac{2}{\rho _i }\sum\limits_j {p^ * } \nabla _i W_{ij} V_j + g_i\tag{14}$$
式(13)、式(14)中黎曼解的引入虽能抑制数值震荡,但数值黏性太大,严重影响流体的真实运动.Zhang等[40]通过引入一个耗散控制参数对式(14)进行了改进,虽能对冲击问题进行有效模拟,但没法表达流体的真实物理黏性,适用范围有限.本文不仅要解决黎曼本身的数值耗散,同时要扩展其应用范围,用于求解黏性多相流问题.为了在计算中考虑流体的真实物理黏性,于是对式(12)第二项进行改进,使其适用于求解黏性大密度比多相流问题,做如下转换
\begin{equation} \label{eq14} \dfrac{1}{2}\bar {\rho }_{ij} \bar {c}_{ij} (u_{\rm L} - u_{\rm R}) \to \left\{ {\begin{array}{ll} K\dfrac{\bar {\mu }_{ij} }{h}(u_{\rm L} - u_{\rm R} ),&r_{ij} > 0 \\ 0,&r_{ij} \le 0 \\ \end{array}} \right.\tag{15} \end{equation}
式中,$K$取$2.5(2 + d)$,$d$为计算维数;$\bar {\mu }_{ij} $取$\dfrac{2\mu _i \mu _j }{\mu _i + \mu _j }$,$\mu _i$和$\mu _j $表示粒子$i$和$j$的真实黏性系数[25]. 最后,式(12)间断处压力为
\begin{equation} \label{eq15} P_{ij}^ * = \frac{p_i + p_j }{2} + \frac{K}{h}\frac{\mu _i \mu _j }{\mu _i + \mu _j }(u_{\rm L} - u_{\rm R} )\tag{16} \end{equation}
2.3 黎曼型固壁边界条件
本文将Adami等[41]虚粒子固壁边界条件与单侧黎曼问题相结合来施加多相流固壁边界,假设$i$和$j$粒子对分别为流体粒子和固壁边界粒子,考虑固壁法向作用,基于黎曼解粒子$i$和$j$左右初始状态为$$U_i = \left( {\rho _{\rm L} ,u_{\rm L} ,P_{\rm L} } \right) = \left( {\rho _i ,-{ {v}}_i \cdot { {n}},P_i } \right)\tag{17}$$
$$U_j = \left( {\rho _{\rm R} ,u_{\rm R} ,P_{\rm R} } \right)=\\ \left( {\rho _j ,{ {v}}_i \cdot { {n}} + 2{ { v}}_j ,P_{\rm L} - \rho _i { {g}} \cdot { {r}}_{ij} } \right)\tag{18}$$
式中,${ {n}}$为固壁单位外法线方向;${ {v}}_j$为固壁自身运动速度,本文所有算例固壁静止取${ {v}}_j \mbox{ =}0$;对于自由滑移边界取$u_{\rm R}= 0$;$\rho _j$通过状态方程式(5)进行求解.
2.4 异相界面处理
考虑异相界面尺度的影响时,在异相界面间存在表面张力.本文采用CFS[35]表面张力模型,作为体力施加在界面两侧2$h$范围内不同相流体粒子上,根据Morris等[42]描述单位体积表面张力如下\begin{equation} \label{eq18} F^{\rm s} = \sigma \kappa \hat{ n}\delta ^{\rm s}\tag{19} \end{equation}
式中,$\sigma,\kappa,\hat{ n},\delta ^{\rm s}$分别表示表面张力系数、多相流界面曲率、界面单位外法线和迪拉克函数.为了计算界面单位法向,采用色函数标记粒子
\begin{equation} \label{eq19} C_i = \left\{ {\begin{array}{ll} 0,&i\subset A\\ 1,&i\subset B\\ \end{array}} \right.\tag{20} \end{equation}
光滑处理色函数,利用变分原理界面法向量为
\begin{equation} \label{eq20} { {n}}_i = \sum\limits_{j = 1}^N {(\bar {C}_j - \bar {C}_i )} \cdot \nabla _i W_{ij} V_j\tag{21} \end{equation}
式中,$\bar {C}_i = \sum\limits_j {C_j } W_{ij} V_j $.为避免边缘效应的影响,单位法向量取
\begin{equation} \label{eq21} \widehat{{ {n}}}_i = \left\{ {\begin{array}{ll} { {n}}_i / \left| {{ {n}}_i } \right|,&\mbox{if }\left| {{ {n}}_i } \right| > \varepsilon , \\ 0,&\mbox{otherwise} \\ \end{array}} \right.\tag{22} \end{equation}
其中, $\varepsilon $通常取$0.01h$.采用法线散度表示曲率,并采用CSPM修正[26],得
$$\kappa = - \left( {\nabla \cdot \widehat{{ { n}}}} \right)_i =\\ {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^N {\min (N_i ,N_j )} (\widehat{{ {n}}}_j - \widehat{{ {n}}}_i ) \cdot \nabla _i W_{ij} V_j }\bigg/\\ \sum\limits_{j = 1}^N {\min (N_i ,N_j )} W_{ij} V_j \tag{23}$$ $\delta ^{\rm s}$表征表面张力的分布情况,为满足连续性条件,取$\delta ^s=\left| { {n}}\right|$;于是得到粒子$i$表面张力为
$$ F_i^{\rm s} = -\sigma (\nabla \cdot \hat{ {n}})_i { {n}}_i\tag{24} $$
为了防止多相流界面不同相粒子的相互穿透,只在界面两侧2$h$范围增加微小界面力[38]
\begin{equation} \label{eq24} F_i^{\rm C} = \zeta \frac{1}{\rho _i }\sum\limits_j {(P_{\rm L} + P_{\rm R} )\nabla _i W_{ij} } V_j\tag{25} \end{equation}
式中,本文算例无特殊指出时$\zeta $取0.08.
最终,基于黎曼解改进的多相流SPH控制方程为
$$\frac{\mbox{d}\rho _i }{\mbox{d}t} = 2\rho _i \sum\limits_j {({ {v}}_i - { {v}}_{ij}^ * )} \cdot \nabla _i W_{ij} V_j\tag{26}$$
$$\frac{\mbox{d}{ {v}}_i }{\mbox{d}t} = - \frac{2}{\rho _i }\sum\limits_j {p^ * } \nabla _i W_{ij} V_j - \frac{\sigma }{\rho _i }(\nabla \cdot \widehat{ n})_i { {n}}_i+ \\ \frac{\zeta}{\rho _i }\sum\limits_j {(P_{\rm L} + P_{\rm R} )} \nabla _i W_{ij} V_j + { {g}}_i \tag{27}$$
2.5 时间积分与时间步
蛙跳法时间积分计算效率高、储存量小,因此本文采用蛙跳法积分求解,为保证数值计算稳定、精度高,时间步长需满足CFL条件[40]、黏性耗散[41]、表面张力[37]对时间步的限制$$\Delta t \le \min \left( {\frac{h}{c + v_{\max } }} \right)\tag{28}$$
$$\Delta t \le 0.125\min \left( {\frac{\rho _i h^2}{\mu _i }} \right)\tag{29}$$
$$\Delta t \le 0.5\min \left( {\frac{\rho _i h^3}{2\pi \sigma }} \right)^{1/2}\tag{30}$$
3 改进的SPH多相流算例验证
本节将对本文基于黎曼解改进的多相流SPH模型的可靠性进行验证.首先利用方形液滴震荡算例,对该模型在处理异相界面上施加的表面张力、界面力的有效性进行验证,进而通过模拟小密度比小黏性比Rayleigh--Taylor不稳定问题、大密度比大黏性比单气泡上浮、双气泡上浮算例,对改进的多相流SPH模型的适用性、准确性进行验证.3.1 异相界面处理方法的验证
方形液滴震荡问题遵循Laplace定律,是检验多相流界面处理方法的可靠算例.该算例模拟过程中没有任何外力参与,仅靠流体内部作用与表面张力相抵,最后达到稳定平衡状态.模拟开始时刻二维无重力、边长为$L = 1\mbox{m}$的方形气泡A静止于边长为$2L$的方形液箱无重力液体B中间,具体如图2示.取周围液体B密度$\rho _{\rm B} = 1000~\mbox{kg} / \mbox{m}^{3}$,黏性$\mu _{\rm B} = 0.5~\mbox{Pa}\cdot{\rm s}$,液气密度比$\rho _{\rm B} / \rho _{\rm A} = 1000$,黏性比$\mu _{\rm B} / \mu _{\rm A} = 100$,表面张力系数$\sigma =1.0$;为防止应力不稳定、负压情况的发生,背景压力取$P_0 =50\;\mbox{Pa} $,采用$100\times 100$个粒子、时间步取0.0001s进行模拟. 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2方形气泡初始状态简图
-->Fig. 2The state diagram of square bubble
-->
图3是气泡发生震荡过程中的3个关键时刻瞬态图.由于表面张力与界面曲率成正比,初始方形气泡只有4个角部界面附近受到表面张力作用(图3(a)),受表面张力的驱动,气泡方形角逐渐变圆滑(图3(b)),四周边界向外凸出,最后演化为稳定圆形气泡(图3(c)).
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3方形气泡演化过程
-->Fig. 3The evolution of square bubble
-->
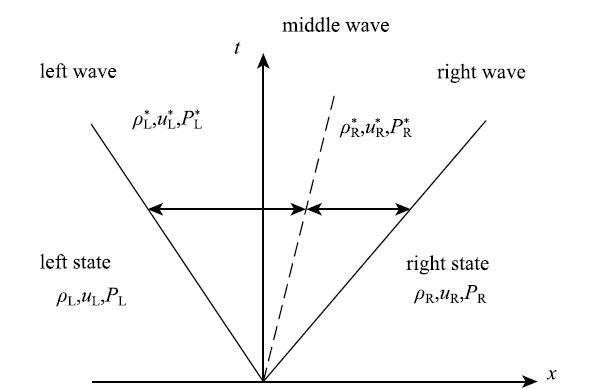
当异相界面表面张力与内部粒子间作用达到平衡状态时,理论上液体B与气泡A内外压力差为一定值$\bar {p}_{\rm A} - \bar {p}_{\rm B} = \sigma \sqrt \pi / L$,图4为3种不同粒子间距(0.02 m,0.01 m和0.005 m)分布下内外压力差随时间的演化过程,压力差$(\bar {p}_{\rm A} - \bar {p}_{\rm B} )$随着方形气泡的演化,成上下震荡,但振动幅度越来越小,最终达到趋于一个稳定值,且可以看到粒子间距越小稳定值越接近于$\sigma \sqrt \pi / L = 1.77$,符合Laplace定律,说明本文计算模型随粒子间距的减小计算结果收敛,同时也验证了本文模型中异相界面施加的表面张力与界面力准确有效.
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4气泡内外压力差$\nabla p$随时间的变化
-->Fig. 4The variation of $\nabla p$ between inner and outer bubble with time
-->
3.2 Rayleigh--Taylor 不稳定模拟
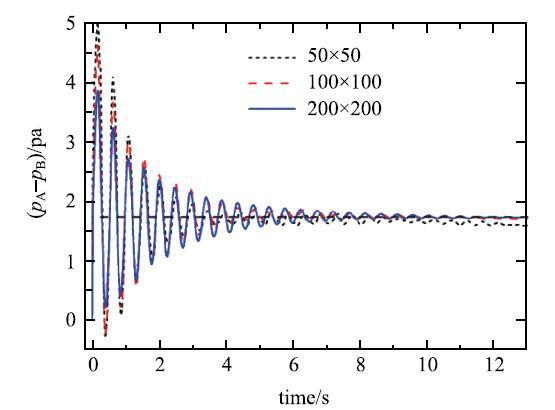
虽然Rayleigh--Taylor不稳定多相流问题的各相密度比、黏性比不大,但它的异相界面在受轻微扰动后会发生大翻卷变形,对多相流模型处理大变形异相界面的精度要求高、黏性耗散控制要求比较严,因此本文首先利用Rayleigh--Taylor不稳定算例来检验本文改进的多相流SPH模型.该算例的两种流体处于如图5示的$1~\mbox{m}\times \mbox{2~m}$液箱内,密度是$1~\mbox{kg} / \mbox{m}^{3}$轻质流体分布在下方,密度是$1.8~\mbox{kg} / \mbox{m}^{3}$的较重流体处在上方,重力加速度$g = 1.0~\mbox{m} / \mbox{s}^2$,初始两种流体的分界线是$y = 1 - 0.15\sin (2\pi x1L)$. 两种流体采用相同的雷诺数,取$Re = \sqrt {L^3g} / \upsilon = 420$(其中$\upsilon = \mu / \rho )$,状态方程中采用相同的系数$\gamma = 7.0$,液箱上下、左右壁均设为无滑移边界,鉴于初始两相流体界面曲率不大,不考虑表面张力的影响,德邦数$Bo = \infty $,异相界面力系数$\zeta = 0.05$,模拟采用$150\times 300$个粒子离散流体域,时间步取$1.0\times 10^{ - 6}~\mbox{s}$.
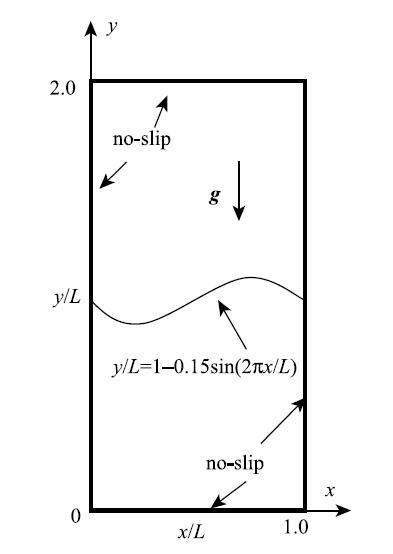 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5Rayleigh--Taylor不稳定初始设置
-->Fig. 5Initial setup of Rayleigh-Taylor instability
-->
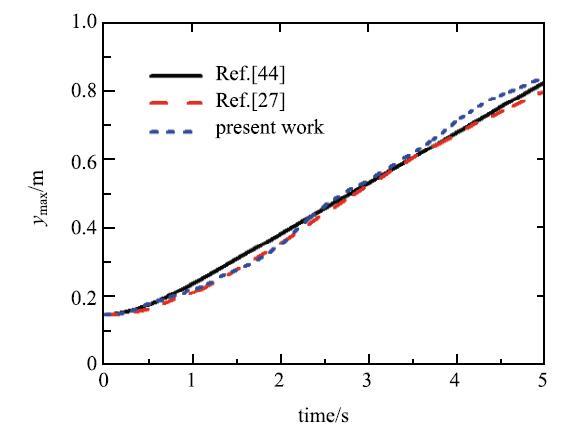
受初始不稳定的重力扰动影响,两种流相发生相互缠绕翻卷,成蘑菇状,图6展示了$t$=5s时刻本文计算结果与文献结果的对比,可以看到本文模型和文献[43]模型能够有效阻止Rayleigh--Taylor不稳定问题异相间的相互渗透、清晰的捕捉到复杂的强翻卷大变形异相界面,而Monaghhan等[27]未能将异相界面局部细节变形模拟出来.图7展示出本文模拟结果与文献[27,44]计算出的低密度流体最高点随时间的竖向位移曲线,结果吻合很好,说明本文改进的多相流SPH模型能量耗散少且可以模拟出多相流真实的物理黏性.
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6$t$=5 s时Rayleigh--Taylor不稳定多相流分布
-->Fig. 6Phase distribution of Rayleigh-Taylor instability at $t$=5 seconds
-->
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7轻质液相最高点竖向位移--时间曲线
-->Fig. 7The time variation of the highest point of the low-density fluid
-->
3.3 单气泡上浮数值模拟
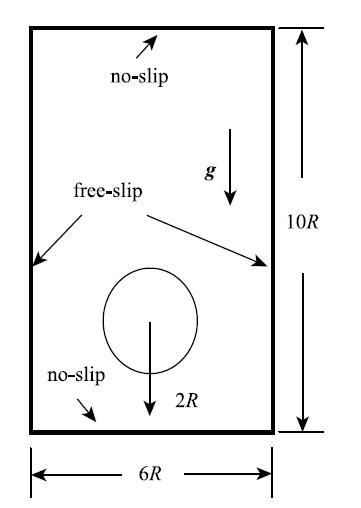
数值模拟多相流问题的难点在于异相界面的处理上,界面两侧流体物理属性差别越大,界面越难被清晰捕捉,计算过程越不稳定.本节单气泡上浮算例是一个大的密度比和黏性比的多相流问题,能否对气泡上浮形态演化过程进行准确捕捉,对任何多相流计算模型来说都具有挑战性.本算例取初始半径$R = 0.1~\mbox{m}$的气泡静置于高$10R$、宽$6R$的液箱内,位置如图8所示,液箱上下壁为无滑移边界、左右为自由滑移边界,取周围液体为水,密度$\rho _{\rm B} = 1000~\mbox{kg} / \mbox{m}^{3}$,重力加速度$g=9.8~$m/s$^2$,取$Re = \rho _{\rm B} R\sqrt {gR} / \mu _{\rm B} = 1000$的雷诺数,考虑表面张力对气泡形状的影响,德邦数取$Bo = 200$,液气密度比$\rho _{\rm B} / \rho _{\rm A} = 1000$、黏性比$\mu _{\rm B} / \mu _{\rm A} = 100$. 本算例采用$150\times 250$个粒子离散计算域,时间步取$1.0\times 10^{ - 6}\;\mbox{s}$.
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8单气泡初始状态设置
-->Fig. 8The initial setup of single bubble
-->
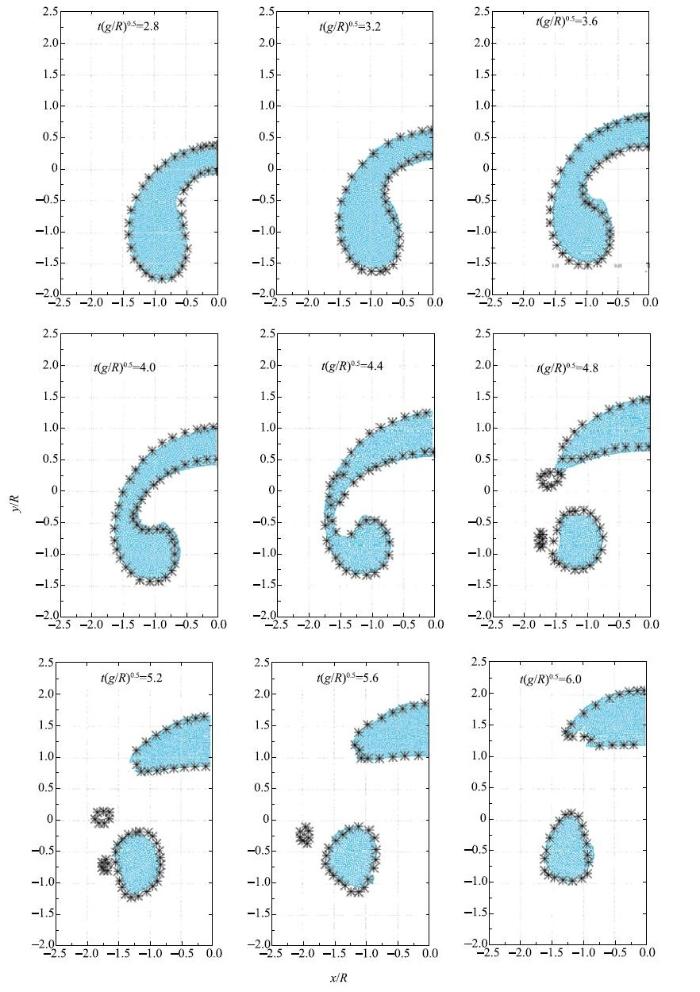
初始静止的圆形气泡,由于受到水的浮力作用向上浮动,图9展示出了气泡上升过程的9个瞬间时刻演变图(蓝色粒子表示气泡,图9未显示水粒子),可以看到本文模型清晰地捕捉到了气液界面. 不平衡水压拖动气泡向上运动,水上涌将气泡压为蘑菇状,随着上浮射流变宽,气泡两个尾趾向上翻卷,后气泡被撕裂出两个小气泡,尾随气泡独立上升.在这一系列的演化过程中,气液界面始终光滑连续,即使发生撕裂依然保持界面稳定.图9中,"*"号是文献[25]展示的水平集模型计算结果,本文计算结果基本与之吻合,两者方法本质不同结果略有差别(水平集模型采用的是网格方法).在$t(g/h)^{0.5}=4.4$之前,本文结果在气泡两侧的夹缩部位略窄于水平集模型结果,形成的旋涡更大,在$t(g/h)^{0.5}=4.8$时也未产生过小气泡,在文献[25]中采用SPH方法计算结果与水平集模型结果对比可以看到同样差异.为了研究黎曼解对SPH多相流问题计算结果的影响,分别给出黎曼解与SPH有无结合的单气泡上浮计算结果,图10(a)、图10(b)为$t(g/h)^{0.5}=6.0$时刻流场压力云图,可以看出黎曼解与SPH相结合计算结果压力场分布十分均匀,无噪声出现,且撕裂产生的两个小气泡较大.由此可以证明,本文模型虽没有添加人工黏性或耗散,对于大密度比、大黏性比多相流问题仍能够进行准确模拟,且异相界面捕捉清晰,压力场计算稳定.
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图9单气泡上浮演变过程("*"来自水平集模型结果[
-->Fig. 9Single bubble shape evolution process (marked by asterisk: level-set solver [
-->
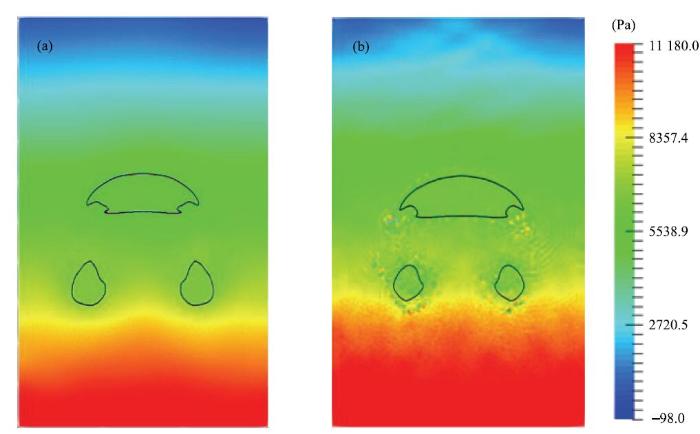 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图10与黎曼解结合(a)和没有与黎曼解结合(b)流场压力分布
-->Fig. 10The pressure distribution in theflow field: (a) using the Riemann solution; (b) without using the Riemann solution
-->
3.4 双气泡上浮数值模拟
上节单气泡上浮算例仅涉及到单气泡界面撕裂过程,而本节竖向双气泡上浮算例更具挑战性,涉及到了气泡的撕裂、融合再撕裂等更为复杂的一系列动态过程,多相流模型对异相界面追踪捕捉的稳定与否直接关系到本节多相流算例计算的成败.本算例初始状态如图11所示,下气泡半径$R = 0.1~\mbox{m}$、上气泡半径$1.5R$,初始置于高$H = 15R$、宽$B = 10R$的液箱内,液箱液体密度采用水的密度$\rho _{\rm B} = 1000~\mbox{kg} / \mbox{m}^{3}$,液气密度比$\rho _{\rm B} / \rho _{\rm A} = 10$、黏性比$\mu _{\rm B} / \mu _{\rm A} = 2.0$,以小半径气泡为参考雷诺数取$Re = 633$. 为检验本文计算模型的收敛性,采用$200\times 300$和$320\times 480$两种分辨率的粒子离散计算域,时间步长分别取$50~\mu \mbox{s}$和$10~\mu \mbox{s}$; 同时考虑表面张力对上浮气泡界面的影响, 取$Bo =\infty $和$Bo =80$分别进行模拟计算,观察双气泡上浮的动态演化过程.
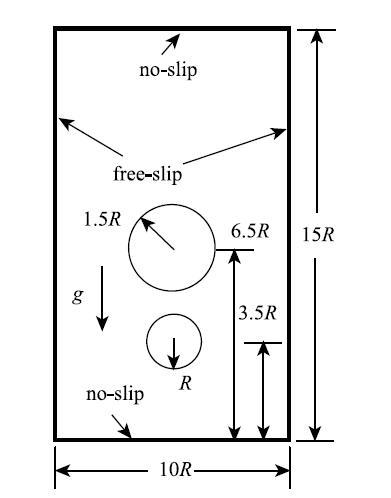 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图11双气泡初始状态设置
-->Fig. 11The initial setup of double bubble
-->
图12是不考虑表面张力的影响(即$Bo = \infty)$,双气泡上浮过程中的6个瞬间形态图,开始两个轻质气泡在浮力作用下同时向上浮动,下部向上凸进, 两个气泡演化为蘑菇状,进而小尺寸气泡被大尺寸气泡吸引拉长、后被吞进,小气泡分裂出的两个尾趾尾随上升,两个气泡间液膜越来越薄,进而大小气泡顶端融合,后又从对称处撕裂的一系列演化过程.图12每张图中左侧蓝色粒子是低分辨率计算结果,右侧红色是高分辨率计算结果,与文献[32]中采用水平集计算模型的结果对比(左侧红色轮廓线是采用Level-Set计算),可以看到高分辨率计算结果与文献结果更加吻合,说明本文模型计算结果收敛,对于这种复杂多相流界面的融合撕裂过程都能够准确捕捉.考虑表面张力对上浮气泡界面演变过程的影响(改取$Bo =80)$,图13是上浮过程中的6个瞬间拍照,每张图中右侧被粒子填充区域是本文高分辨率计算所得的气泡形态,左侧红色轮廓线是水平集结果[32],两者吻合一致.综合对比图12与图13,水平集受网格方法限制,小尺度气泡产生的尾趾一致保持与气泡连续,而本文结果尾趾提早分裂与文献[32]采用ISPH方法结果更加吻合;同时可以看到,表面张力对气泡演变形状有影响,使界面表现的更加圆润,抑制了大尺度气泡大旋涡的产生.本节双气泡上浮算例的模拟更加肯定了本文多相流SPH模型处理多相流问题的适用性,对于像本算例异相界面复杂的演变过程也能够清晰、稳定的捕捉到.
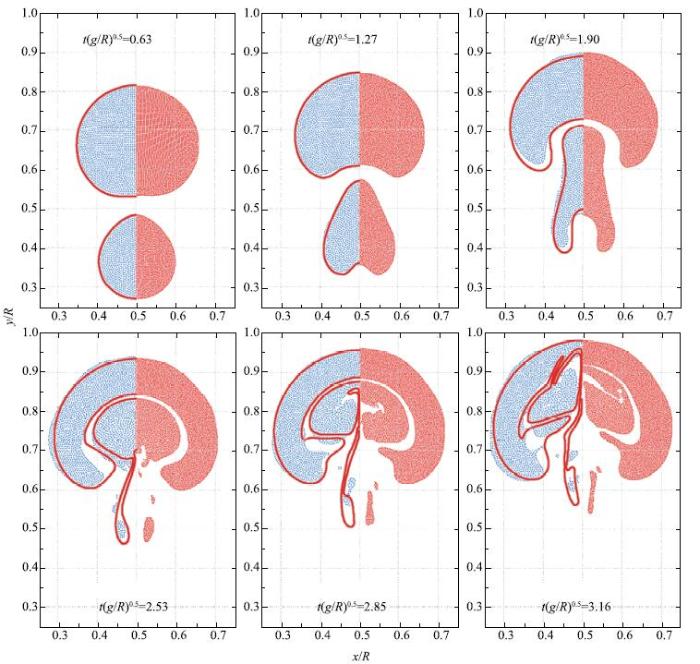 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图12$Bo = \;\infty $时双气泡上浮演变过程(红线是水平集模型计算结果[
-->Fig. 12Double bubbles shape evolution for $Bo = \;\infty $(marked by red line : level-set simulation [
-->
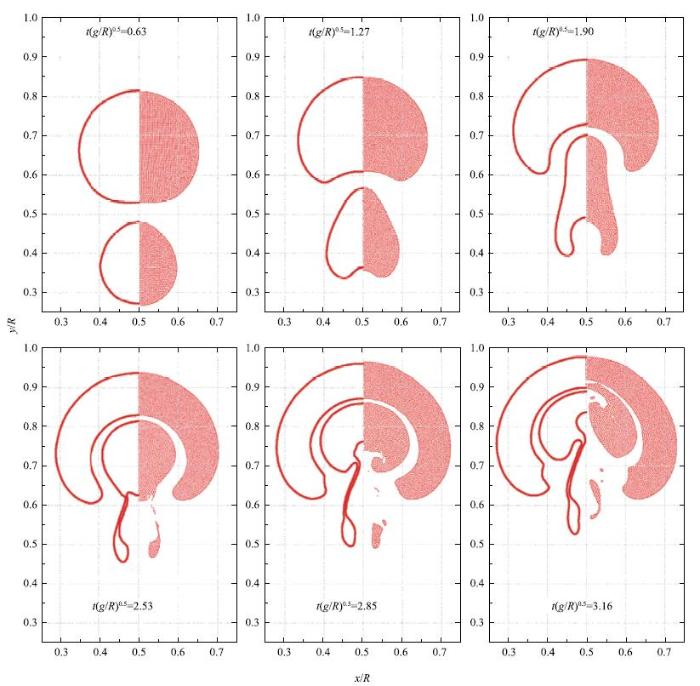 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图13$Bo =80$时双气泡上浮演变过程(左侧红线是水平集模型计算结果[
-->Fig. 13Double bubbles shape evolution for $Bo =80 $(marked by red line : level-set simulation [
-->
4 结论
本文充分发挥黎曼解在处理接触间断问题上的优势,将黎曼解与多相流SPH相结合,为减小黎曼耗散、描述多相流真实物理黏性,对黎曼动量方程进行了改进,模型中考虑了表面张力的影响,为防止异相粒子渗透,界面两侧施加了界面力,利用黎曼单侧问题施加SPH固壁边界,提出了一种能模拟大密度比多相流问题的新模型.采用该改进的模型对方形液滴震荡、Rayleigh--Taylor不稳定、单气泡、双气泡上浮问题进行了模拟,并与理论解、已有文献进行了对比.由此可以证明,本文改进的多相流SPH计算模型能够对密度比为1$\sim$1000、黏性比为1$\sim$100的多相流问题进行准确模拟,且无需添加人工耗散和人工黏性、计算稳定、界面捕捉清晰光滑.本文采用的是一阶黎曼求解器进行求解,对精度要求更高的多相流问题可引用高阶黎曼进行求解.The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
| [1] | . <p>多段压裂水平井技术是目前开采致密气最常用的方法之一,在致密气压裂水平井试井测试中常常伴随着一定的产水量,井筒气液两相流会增加井筒流体的流动阻力,加大井筒流体流动对试井解释的影响.为了明确井筒气液两相流对致密气藏压裂水平井试井的影响,提高产水致密气压裂水平井的试井解释精度,建立了一种井筒气液两相流与地层渗流耦合的试井模型,采用数值方法对模型进行求解,获得了考虑井筒气液两相流的压裂水平井试井理论曲线、压力场分布及裂缝产量分布.研究结果表明:井筒气液两相流会增加试井理论曲线中压力和压力导数值,造成靠近入窗点的压力扩散要快于远离入窗点的压力扩散,引起靠近入窗点的裂缝产量要高于远离入窗点的裂缝产量.现场实例分析进一步说明,不考虑井筒两相流可能会对产水压裂水平井的试井解释结果产生很大误差,主要表现为水平井筒假设为无限大导流能力会使得拟合得到的表皮系数偏大,将测试点视为入窗点会使得拟合得到的原始地层压力偏小.所建立的考虑井筒两相流的压裂水平井试井模型为产水致密气井试井资料的正确解释提供了重要技术保障.</p> . <p>多段压裂水平井技术是目前开采致密气最常用的方法之一,在致密气压裂水平井试井测试中常常伴随着一定的产水量,井筒气液两相流会增加井筒流体的流动阻力,加大井筒流体流动对试井解释的影响.为了明确井筒气液两相流对致密气藏压裂水平井试井的影响,提高产水致密气压裂水平井的试井解释精度,建立了一种井筒气液两相流与地层渗流耦合的试井模型,采用数值方法对模型进行求解,获得了考虑井筒气液两相流的压裂水平井试井理论曲线、压力场分布及裂缝产量分布.研究结果表明:井筒气液两相流会增加试井理论曲线中压力和压力导数值,造成靠近入窗点的压力扩散要快于远离入窗点的压力扩散,引起靠近入窗点的裂缝产量要高于远离入窗点的裂缝产量.现场实例分析进一步说明,不考虑井筒两相流可能会对产水压裂水平井的试井解释结果产生很大误差,主要表现为水平井筒假设为无限大导流能力会使得拟合得到的表皮系数偏大,将测试点视为入窗点会使得拟合得到的原始地层压力偏小.所建立的考虑井筒两相流的压裂水平井试井模型为产水致密气井试井资料的正确解释提供了重要技术保障.</p> |
| [2] | . |
| [3] | . 轮胎滚动引起跑道积水飞溅进入发动机将导致发动机喘振甚至熄火,已有的飞机滑跑试验和经验证明采用具有翻边设计的轮胎可减小溅水与地面的夹角,减小发动机进水的可能性,但对翻边抑制溅水相关机理的研究仍十分匮乏.采用有限元软件LS-DYNA中的SPH/FEM耦合方法对翻边轮胎溅水机理开展分析计算.首先改进了轮胎数值模型和加载方式并验证了模型的有效性,研究了翻边轮胎溅水随滑跑速度的变化规律.其次基于特征位置水粒子的速度变化,分析了翻边抑制溅水的作用机理,通过比较不同深度水深的溅水速度分布说明翻边的作用.最后基于翻边高度和角度对轮胎溅水影响的研究,对优化的翻边构型进行了探索. . 轮胎滚动引起跑道积水飞溅进入发动机将导致发动机喘振甚至熄火,已有的飞机滑跑试验和经验证明采用具有翻边设计的轮胎可减小溅水与地面的夹角,减小发动机进水的可能性,但对翻边抑制溅水相关机理的研究仍十分匮乏.采用有限元软件LS-DYNA中的SPH/FEM耦合方法对翻边轮胎溅水机理开展分析计算.首先改进了轮胎数值模型和加载方式并验证了模型的有效性,研究了翻边轮胎溅水随滑跑速度的变化规律.其次基于特征位置水粒子的速度变化,分析了翻边抑制溅水的作用机理,通过比较不同深度水深的溅水速度分布说明翻边的作用.最后基于翻边高度和角度对轮胎溅水影响的研究,对优化的翻边构型进行了探索. |
| [4] | . 对于水下发射过程来说,掌握水动力载荷形成机理与结构响应特征是一个亟待解决的问题.研究该问题需要考虑含相变的复杂多相流动,变约束的结构运动以及这二者之间的耦合效应.本文采用松耦合的方法,以流体求解器为主体,将自编的固体结构程序接入流体求解器中,在每个时间步长内分别对流体动力学方程和固体结构动力学方程进行求解,通过流固界面之间的数据交换实现耦合计算.其中,流体求解器基于雷诺平均纳维斯托克斯方程,采用单流体模型处理多相流问题,引入空化模型描述空化相变,采用修正的湍流模型模拟混合物的湍流效应,并采用动网格技术处理移动边界问题.航行体的刚体运动和结构振动分开求解.结构求解器采用等效梁模型描述结构的振动,通过坐标变换给出了随体坐标系下的结构振动方程,求解方法采用时域积分法.所建立的流固耦合方法不仅能够捕捉到自然空化的演化情况,还可获得航行体所受水动力、结构振动响应以及截面的弯矩,获得了实验的验证.基于该方法研究了结构刚度、发射速度对空泡溃灭与结构振动耦合效应的影响规律.结果表明,同步溃灭是影响结构载荷的主要因素,包括溃灭压力幅值,溃灭压力作用位置,以及溃灭压力与结构振动的相位关系. . 对于水下发射过程来说,掌握水动力载荷形成机理与结构响应特征是一个亟待解决的问题.研究该问题需要考虑含相变的复杂多相流动,变约束的结构运动以及这二者之间的耦合效应.本文采用松耦合的方法,以流体求解器为主体,将自编的固体结构程序接入流体求解器中,在每个时间步长内分别对流体动力学方程和固体结构动力学方程进行求解,通过流固界面之间的数据交换实现耦合计算.其中,流体求解器基于雷诺平均纳维斯托克斯方程,采用单流体模型处理多相流问题,引入空化模型描述空化相变,采用修正的湍流模型模拟混合物的湍流效应,并采用动网格技术处理移动边界问题.航行体的刚体运动和结构振动分开求解.结构求解器采用等效梁模型描述结构的振动,通过坐标变换给出了随体坐标系下的结构振动方程,求解方法采用时域积分法.所建立的流固耦合方法不仅能够捕捉到自然空化的演化情况,还可获得航行体所受水动力、结构振动响应以及截面的弯矩,获得了实验的验证.基于该方法研究了结构刚度、发射速度对空泡溃灭与结构振动耦合效应的影响规律.结果表明,同步溃灭是影响结构载荷的主要因素,包括溃灭压力幅值,溃灭压力作用位置,以及溃灭压力与结构振动的相位关系. |
| [5] | . In this paper we present a three-dimensional Navier-Stokes solver for incompressible two-phase flow problems with surface tension and apply the proposed scheme to the simulation of bubble and droplet deformation. One of the main concerns of this study is the impact of surface tension and its discretization on the overall convergence behavior and conservation properties.Our approach employs a standard finite difference/finite volume discretization on uniform Cartesian staggered grids and uses Chorin's projection approach. The free surface between the two fluid phases is tracked with a level set (LS) technique. Here, the interface conditions are implicitly incorporated into the momentum equations by the continuum surface force method. Surface tension is evaluated using a smoothed delta function and a third-order interpolation. The problem of mass conservation for the two phases is treated by a reinitialization of the LS function employing a regularized signum function and a global fixed point iteration. All convective terms are discretized by a WENO scheme of fifth order. Altogether, our approach exhibits a second-order convergence away from the free surface. The discretization of surface tension requires a smoothing scheme near the free surface, which leads to a first-order convergence in the smoothing region.We discuss the details of the proposed numerical scheme and present the results of several numerical experiments concerning mass conservation, convergence of curvature, and the application of our solver to the simulation of two rising bubble problems, one with small and one with large jumps in material parameters, and the simulation of a droplet deformation due to a shear flow in three space dimensions. Furthermore, we compare our three-dimensional results with those of quasi-two-dimensional and two-dimensional simulations. This comparison clearly shows the need for full three-dimensional simulations of droplet and bubble deformation to capture the correct physical behavior. Copyright 漏 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. |
| [6] | . 从亚网格尺度稳定化方法的基本原理出发, 提出了适合时间推进求解非定常Navier-Stokes方程获得定常解的SGS稳定化方法. 基于一定程度的近似和简化, 获得了与时间步长相关的稳定化参数, 从而排除了传统SGS稳定化方法在求解高Re数、小时间步长问题时所引发的数值不稳定性. 把SGS稳定化方法应用于求解不可压湍流, 结合标准k-\varepsilon湍流模型和壁面函数法估计湍流黏性系数, 详细讨论了壁面函数法的实施、湍流输运方程的求解和保证湍流变量非负性的限制策略, 发展了时间推进求解不可压湍流的分离式算法. 二维外掠后台阶层流和湍流计算结果表明,该方法求解不可压黏性流动是可行的, 并且具有稳定性好、计算精度高的特点. . 从亚网格尺度稳定化方法的基本原理出发, 提出了适合时间推进求解非定常Navier-Stokes方程获得定常解的SGS稳定化方法. 基于一定程度的近似和简化, 获得了与时间步长相关的稳定化参数, 从而排除了传统SGS稳定化方法在求解高Re数、小时间步长问题时所引发的数值不稳定性. 把SGS稳定化方法应用于求解不可压湍流, 结合标准k-\varepsilon湍流模型和壁面函数法估计湍流黏性系数, 详细讨论了壁面函数法的实施、湍流输运方程的求解和保证湍流变量非负性的限制策略, 发展了时间推进求解不可压湍流的分离式算法. 二维外掠后台阶层流和湍流计算结果表明,该方法求解不可压黏性流动是可行的, 并且具有稳定性好、计算精度高的特点. |
| [7] | . 本文对近三十年来,国内外对于高精度数值方法研究中的热点--间断伽辽金方法在可压缩流数值模拟方面的应用研究进行了综述.首先对间断伽辽金方法的基本概念和特点作了简单介绍,然后对应用该方法解决双曲型及椭圆型问题的发展历程进行了回顾,并重点梳理了其在计算流体力学领域可压缩流数值模拟方面的应用发展以及研究现状,之后对该方法在对应的网格技术、激波捕捉方法、湍流流动模拟以及计算量需求方面目前仍然存在的研究难点和可能的发展趋势做出了总结和分析.最后给出了间断伽辽金方法在可压缩流数值模拟中的若干应用实例. . 本文对近三十年来,国内外对于高精度数值方法研究中的热点--间断伽辽金方法在可压缩流数值模拟方面的应用研究进行了综述.首先对间断伽辽金方法的基本概念和特点作了简单介绍,然后对应用该方法解决双曲型及椭圆型问题的发展历程进行了回顾,并重点梳理了其在计算流体力学领域可压缩流数值模拟方面的应用发展以及研究现状,之后对该方法在对应的网格技术、激波捕捉方法、湍流流动模拟以及计算量需求方面目前仍然存在的研究难点和可能的发展趋势做出了总结和分析.最后给出了间断伽辽金方法在可压缩流数值模拟中的若干应用实例. |
| [8] | . 采用改进的延迟分离涡方法数值模拟了高雷诺数下的柱体绕流,包括单圆柱绕流、单方柱绕流、串列双圆柱绕流和串列双方柱绕流,研究了不同雷诺数下圆柱绕流与方柱绕流的水动力特性.计算结果与实验数据及其他文献的数值计算结果吻合良好,研究表明,单方柱绕流在2:0×103 . 采用改进的延迟分离涡方法数值模拟了高雷诺数下的柱体绕流,包括单圆柱绕流、单方柱绕流、串列双圆柱绕流和串列双方柱绕流,研究了不同雷诺数下圆柱绕流与方柱绕流的水动力特性.计算结果与实验数据及其他文献的数值计算结果吻合良好,研究表明,单方柱绕流在2:0×103 |
| [9] | . 采用浸入边界法对细长柔性圆柱在线性剪切流条件下的涡激振动进行三维数值模拟.细长柔性圆柱振动采用三维索模型模拟,其两端铰接,质量比为6,长细比为50,无量纲顶张力为496.来流为线性剪切流,剪切率从0到0.024变化,最大雷诺数为250.研究发现:剪切流作用下柔性立管横流向振动表现为驻波模式,而顺流向振动表现为行波与驻波混合模式.随着剪切率增大,振动频谱呈现多频响应,振动能量逐渐向低频转移.阻力系数平均值随着展向变化,脉动阻力系数和升力系数的均方根值均表现为"双峰"模式.流固能量传递系数沿立管轴向的分布表明,振动激励区集中于高流速区,而振动阻尼区多位于低流速区.剪切率较小时,圆柱的泻涡为平行交叉模式;剪切率较大时,圆柱的泻涡为倾斜泻涡模式,且由于泻涡频率沿立管轴向变化,尾流发生涡裂现象,形成泻涡频率不同的胞格结构. 采用浸入边界法对细长柔性圆柱在线性剪切流条件下的涡激振动进行三维数值模拟.细长柔性圆柱振动采用三维索模型模拟,其两端铰接,质量比为6,长细比为50,无量纲顶张力为496.来流为线性剪切流,剪切率从0到0.024变化,最大雷诺数为250.研究发现:剪切流作用下柔性立管横流向振动表现为驻波模式,而顺流向振动表现为行波与驻波混合模式.随着剪切率增大,振动频谱呈现多频响应,振动能量逐渐向低频转移.阻力系数平均值随着展向变化,脉动阻力系数和升力系数的均方根值均表现为"双峰"模式.流固能量传递系数沿立管轴向的分布表明,振动激励区集中于高流速区,而振动阻尼区多位于低流速区.剪切率较小时,圆柱的泻涡为平行交叉模式;剪切率较大时,圆柱的泻涡为倾斜泻涡模式,且由于泻涡频率沿立管轴向变化,尾流发生涡裂现象,形成泻涡频率不同的胞格结构. |
| [10] | . 格子Boltzmann方法可以有效地模拟水动力学问题,边界处理方法的选择对于可靠的模拟计算至关重要.本文基于多松弛时间格子Boltzmann模型开展了不同边界条件下,周期对称性结构和不规则结构中流体流动模拟,阐述了不同边界条件的精度和适用范围.此外,引入一种混合式边界处理方法来模拟多孔介质惯性流,结果表明:对于周期性对称结构流动模拟,体力格式边界条件和压力边界处理方法是等效的,两者都能精确地捕捉流体流动特点;而对于非周期性不规则结构,两种边界处理方法并不等价,体力格式边界条件只适用于周期性结构;由于广义化周期性边界条件忽略了垂直主流方向上流体与固体格点的碰撞作用,同样不适合处理不规则模型;体力-压力混合式边界格式能够用来模拟周期性或非周期性结构流体流动,在模拟多孔介质流体惯性流时,比压力边界条件有更大的应用优势,可以获得更大的雷诺数且能保证计算的准确性. . 格子Boltzmann方法可以有效地模拟水动力学问题,边界处理方法的选择对于可靠的模拟计算至关重要.本文基于多松弛时间格子Boltzmann模型开展了不同边界条件下,周期对称性结构和不规则结构中流体流动模拟,阐述了不同边界条件的精度和适用范围.此外,引入一种混合式边界处理方法来模拟多孔介质惯性流,结果表明:对于周期性对称结构流动模拟,体力格式边界条件和压力边界处理方法是等效的,两者都能精确地捕捉流体流动特点;而对于非周期性不规则结构,两种边界处理方法并不等价,体力格式边界条件只适用于周期性结构;由于广义化周期性边界条件忽略了垂直主流方向上流体与固体格点的碰撞作用,同样不适合处理不规则模型;体力-压力混合式边界格式能够用来模拟周期性或非周期性结构流体流动,在模拟多孔介质流体惯性流时,比压力边界条件有更大的应用优势,可以获得更大的雷诺数且能保证计算的准确性. |
| [11] | . 稳定和不稳定流形是研究动力系统全局特性的重要工具.一般系统的稳定和不稳定流形的曲率在全局范围内会有明显变化,应根据流形曲率的变化采用不同尺寸的网格单元计算全局流形.然而在现有二维流形算法中,流形网格单元的尺寸在全局范围内是统一的.为持续有效地计算全局稳定流形,提高计算网格对流形曲率变化的适应性.本文在偏微分方程算法的基础上提出一种二维稳定流形的自适应推进算法.该算法的基本思想是根据稳定流形曲率的变化自适应地调整网格单元的尺寸.该算法首先在系统的稳定特征子空间中确定稳定流形的一个初始估计,该初始估计的网格单元尺寸设置为初始大小.然后根据稳定流形网格前沿的曲率特点自适应地产生新的备选网格单元,继而根据相切性条件更新备选点的坐标,并将距离平衡点最近的备选点接受为已知点,最后更新稳定流形网格的前沿并自适应地产生新的备选网格单元,通过这个迭代过程使流形网格自适应地向前推进.本文算法通过引入流形单元尺寸自适应,成功实现了洛伦兹流形和类球面流形的计算,并与偏微分方程算法进行了对比,结果表明自适应推进算法的流形计算单元的尺寸可在全局范围内根据流形曲率自适应地调整.利用自适应推进算法计算二维稳定流形,可实现稳定流形的自适应推进. . 稳定和不稳定流形是研究动力系统全局特性的重要工具.一般系统的稳定和不稳定流形的曲率在全局范围内会有明显变化,应根据流形曲率的变化采用不同尺寸的网格单元计算全局流形.然而在现有二维流形算法中,流形网格单元的尺寸在全局范围内是统一的.为持续有效地计算全局稳定流形,提高计算网格对流形曲率变化的适应性.本文在偏微分方程算法的基础上提出一种二维稳定流形的自适应推进算法.该算法的基本思想是根据稳定流形曲率的变化自适应地调整网格单元的尺寸.该算法首先在系统的稳定特征子空间中确定稳定流形的一个初始估计,该初始估计的网格单元尺寸设置为初始大小.然后根据稳定流形网格前沿的曲率特点自适应地产生新的备选网格单元,继而根据相切性条件更新备选点的坐标,并将距离平衡点最近的备选点接受为已知点,最后更新稳定流形网格的前沿并自适应地产生新的备选网格单元,通过这个迭代过程使流形网格自适应地向前推进.本文算法通过引入流形单元尺寸自适应,成功实现了洛伦兹流形和类球面流形的计算,并与偏微分方程算法进行了对比,结果表明自适应推进算法的流形计算单元的尺寸可在全局范围内根据流形曲率自适应地调整.利用自适应推进算法计算二维稳定流形,可实现稳定流形的自适应推进. |
| [12] | . . |
| [13] | . |
| [14] | . 将大涡模拟(LES)和无网格的移动粒子半隐式法(MPS)相结合, 以求解湍流中的自由表面问题. 对N-S方程进行滤波计算可得到大涡模拟的控制方程, 大涡模拟的控制方程相对于以往的移动粒子半隐式法而言仅多出雷诺应力项, 通过亚粒子应力(sub-particle-scale,SPS)模型并引入Smagorinsky涡黏模型将雷诺应力模型化, 可实现移动粒子半隐式法的大涡模拟. 将MPS-LES应用至具有大变形自由表面的共振晃荡中, 其模拟结果同实验及其他数值模拟结果都相当接近. . 将大涡模拟(LES)和无网格的移动粒子半隐式法(MPS)相结合, 以求解湍流中的自由表面问题. 对N-S方程进行滤波计算可得到大涡模拟的控制方程, 大涡模拟的控制方程相对于以往的移动粒子半隐式法而言仅多出雷诺应力项, 通过亚粒子应力(sub-particle-scale,SPS)模型并引入Smagorinsky涡黏模型将雷诺应力模型化, 可实现移动粒子半隐式法的大涡模拟. 将MPS-LES应用至具有大变形自由表面的共振晃荡中, 其模拟结果同实验及其他数值模拟结果都相当接近. |
| [15] | . 求解含裂纹等不连续问题一直是计算力学的重点研究课题之一,以偏微分方程为基础的连续介质力学方法处理不连续问题时面临很大的困难.近场动力学方法是一种基于积分方程的非局部理论,在处理不连续问题时有很大的优越性.本文提出了求解含裂纹热传导问题的一种新的近场动力学与有限元法的耦合方法.结合近场动力学方法处理不连续问题的优势以及有限元方法计算效率高的优势,将求解区域划分为两个区域,近场动力学区域和有限元区域.包含裂纹的区域采用近场动力学方法建模,其他区域采用有限元方法建模.本文提出的耦合方案实施简单方便,近场动力学区域与有限元区域之间不需要设置重叠区域.耦合方法通过近场动力学粒子与其域内所有粒子(包括近场动力学粒子和有限元节点) 以非局部方式连接,有限元节点与其周围的所有粒子以有限元方式相互作用.将有限元热传导矩阵和近场动力学粒子相互作用矩阵写入同一整体热传导矩阵中,并采用Guyan缩聚法进一步减小计算量.分别采用连续介质力学方法和近场动力学方法对一维以及二维温度场算例进行模拟,结果表明,本文的耦合方法具有较高的计算精度和计算效率.该耦合方案可以进一步拓展到热力耦合条件下含裂纹材料和结构的裂纹扩展问题. . 求解含裂纹等不连续问题一直是计算力学的重点研究课题之一,以偏微分方程为基础的连续介质力学方法处理不连续问题时面临很大的困难.近场动力学方法是一种基于积分方程的非局部理论,在处理不连续问题时有很大的优越性.本文提出了求解含裂纹热传导问题的一种新的近场动力学与有限元法的耦合方法.结合近场动力学方法处理不连续问题的优势以及有限元方法计算效率高的优势,将求解区域划分为两个区域,近场动力学区域和有限元区域.包含裂纹的区域采用近场动力学方法建模,其他区域采用有限元方法建模.本文提出的耦合方案实施简单方便,近场动力学区域与有限元区域之间不需要设置重叠区域.耦合方法通过近场动力学粒子与其域内所有粒子(包括近场动力学粒子和有限元节点) 以非局部方式连接,有限元节点与其周围的所有粒子以有限元方式相互作用.将有限元热传导矩阵和近场动力学粒子相互作用矩阵写入同一整体热传导矩阵中,并采用Guyan缩聚法进一步减小计算量.分别采用连续介质力学方法和近场动力学方法对一维以及二维温度场算例进行模拟,结果表明,本文的耦合方法具有较高的计算精度和计算效率.该耦合方案可以进一步拓展到热力耦合条件下含裂纹材料和结构的裂纹扩展问题. |
| [16] | . . |
| [17] | . This paper shows how to formulate the two phase flow of a dusty gas using SPH. The formulation is very general and can be easily extended to deal with gas, solid and liquid phases in each of which there may be several species. |
| [18] | . Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a meshfree particle method based on Lagrangian formulation, and has been widely applied to different areas in engineering and science. This paper presents an overview on the SPH method and its recent developments, including (1)02the need for meshfree particle methods, and advantages of SPH, (2)02approximation schemes of the conventional SPH method and numerical techniques for deriving SPH formulations for partial differential equations such as the Navier-Stokes (N-S) equations, (3)02the role of the smoothing kernel functions and a general approach to construct smoothing kernel functions, (4)02kernel and particle consistency for the SPH method, and approaches for restoring particle consistency, (5)02several important numerical aspects, and (6)02some recent applications of SPH. The paper ends with some concluding remarks. |
| [19] | . 飞机水上迫降以及船体在高速行驶时,均会发生结构物砰击水面的现象,当结构物底面较为平坦,砰击水面时会捕获空气,在板底形成空气垫。研究空气垫的形成及影响,有助于对结构物进行更准确的载荷分析。该问题的研究涉及到气固液三相的相互作用,在数值模拟中仍是一个挑战,本文使用光滑粒子流体动力学(SPH)方法对该问题进行模拟。首先,与实验结果进行对比;其次,系统地研究了平板形成空气垫以及砰击水面的过程,考查了空气、水和平板的动能变化。对比了在SPH模拟中考虑空气与不考虑空气得到的水压力场和平板所受压力,说明了空气对结果的影响;最后,研究了平板宽度对空气垫形成的影响,从而进一步影响加速度。 . 飞机水上迫降以及船体在高速行驶时,均会发生结构物砰击水面的现象,当结构物底面较为平坦,砰击水面时会捕获空气,在板底形成空气垫。研究空气垫的形成及影响,有助于对结构物进行更准确的载荷分析。该问题的研究涉及到气固液三相的相互作用,在数值模拟中仍是一个挑战,本文使用光滑粒子流体动力学(SPH)方法对该问题进行模拟。首先,与实验结果进行对比;其次,系统地研究了平板形成空气垫以及砰击水面的过程,考查了空气、水和平板的动能变化。对比了在SPH模拟中考虑空气与不考虑空气得到的水压力场和平板所受压力,说明了空气对结果的影响;最后,研究了平板宽度对空气垫形成的影响,从而进一步影响加速度。 |
| [20] | . In ocean engineering, the applications are usually related to a free surface which brings so many interesting physical phenomena(e.g. water waves, impacts, splashing jets, etc.). To model these complex free surface flows is a tough and challenging task for most computational fluid dynamics(CFD) solvers which work in the Eulerian framework. As a Lagrangian and meshless method, smoothed particle hydrodynamics(SPH) offers a convenient tracking for different complex boundaries and a straightforward satisfaction for different boundary conditions. Therefore SPH is robust in modeling complex hydrodynamic problems characterized by free surface boundaries, multiphase interfaces or material discontinuities. Along with the rapid development of the SPH theory, related numerical techniques and high-performance computing technologies, SPH has not only attracted much attention in the academic community, but also gradually gained wide applications in industrial circles. This paper is dedicated to a review of the recent developments of SPH method and its typical applications in fluid-structure interactions in ocean engineering. Different numerical techniques for improving numerical accuracy, satisfying different boundary conditions, improving computational efficiency, suppressing pressure fluctuations and preventing the tensile instability, etc., are introduced. In the numerical results, various typical fluid-structure interaction problems or multiphase problems in ocean engineering are described, modeled and validated. The prospective developments of SPH in ocean engineering are also discussed. |
| [21] | . |
| [22] | . An implementation of the smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method is presented to treat two-dimensional interfacial flows, that is, flow fields with different fluids separated by sharp interfaces. Test cases are presented to show that the present formulation remains stable for low density ratios. In particular, results are compared with those obtained by other solution techniques, showing a good agreement. The classical dam-break problem is studied by the present two-phase approach and the effects of density-ratio variations are discussed. The role of air entrapment on loads is discussed. |
| [23] | // |
| [24] | . |
| [25] | . In the present work a new SPH model for simulating interface and free surface flows is presented. This formulation is an extension of the one discussed in Colagrossi and Landrini (2003) and is related to the one proposed by Hu and Adams (2006) to study multi-fluid flows. The new SPH scheme allows an accurate treatment of the discontinuity of quantities at the interface (such as the density), and permits to model flows where both interfaces and a free surface are present. The governing equations are derived following a Lagrangian variational principle leading to an Hamiltonian system of particles. The proposed formulation is validated on test cases for which reference solutions are available in the literature. |
| [26] | . In this paper, we propose a new surface-tension formulation for multi-phase smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). To obtain a stable and accurate scheme for surface curvature, a new reproducing divergence approximation without the need for a matrix inversion is derived. Furthermore, we introduce a density-weighted color-gradient formulation to reflect the reality of an asymmetrically distributed surface-tension force. We validate our method with analytic solutions and demonstrate convergence for different cases. Furthermore, we show that our formulation can handle phase interfaces with density and viscosity ratios of up to 1000 and 100, respectively. Finally, complex three-dimensional simulations including breakup of an interface demonstrate the capabilities of our method. |
| [27] | . In this paper, we describe an SPH algorithm for multi-fluid flow, which is efficient, simple and robust. We derive the inviscid equations of motion from a Lagrangian together with the constraint provided by the continuity equation. The viscous flow equations then follow by adding a viscous term. Rigid boundaries are simulated using boundary force particles in a manner similar to the immersed boundary method. Each fluid is approximated as weakly compressible with a speed of sound sufficiently large to guarantee that the relative density variations are typically 1%. When the SPH force interaction is between two particles of different fluids, we increase the pressure terms. This simple procedure stabilizes the interface between the fluids. The equations of motion are integrated using a time stepping rule based on a second-order symplectic integrator. When linear and angular momentum should be conserved exactly, they are conserved to within round-off errors. We test the algorithm by simulating a variety of problems involving fluids with a density ratio in the range 11000. The first of these is a free surface problem with no rigid boundaries. It involves the flow of an elliptical distribution with one fluid inside the other. We show that the simulations converge as the particle spacing decreases, and the results are in good agreement with the exact inviscid, incompressible theory. The second test is similar to the first but involves the nonlinear oscillation of the fluids. As in the first test, the agreement with theory is very good, and the method converges. The third test is the simulation of waves at the interface between two fluids. The method is shown to converge, and the agreement with theory is satisfactory. The fourth test is the RayleighTaylor instability for a configuration considered by other authors. Key parameters are shown to converge, and the agreement with other authors is good. The fifth and final test is how well the SPH method simulates gravity currents with density ratios in the range 230. The results of these simulations are in very good agreement with those of other authors and in satisfactory agreement with experimental results.Copyright (c) 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. |
| [28] | . In this paper, an improved SPH model for multiphase flows with complex interfaces and large density differences is developed. The multiphase SPH model is based on the assumption of pressure continuity over the interfaces and avoids directly using the information of neighboring particles' densities or masses in solving governing equations. In order to improve computational accuracy and to obtain smooth pressure fields, a corrected density re-initialization is applied. A coupled dynamic solid boundary treatment (SBT) is implemented both to reduce numerical oscillations and to prevent unphysical particle penetration in the boundary area. The density correction and coupled dynamics SBT algorithms are modified to adapt to the density discontinuity on fluid interfaces in multiphase simulation. A cut-off value of the particle density is set to avoid negative pressure, which can lead to severe numerical difficulties and may even terminate the simulations. Three representative numerical examples, including a Rayleigh-Taylor instability test, a non-Boussinesq problem and a dam breaking simulation, are presented and compared with analytical results or experimental data. It is demonstrated that the present SPH model is capable of modeling complex multiphase flows with large interfacial deformations and density ratios. (C) 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. |
| [29] | . A new two-phase incompressible–compressible Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) method has been developed where the interface is discontinuous in density. This is applied to water–air problems with a large density difference. The incompressible phase requires surface pressure from the compressible phase and the compressible phase requires surface velocity from the incompressible phase. Compressible SPH is used for the air phase (with the isothermal stiffened ideal gas equation of state for low Mach numbers) and divergence-free (projection based) incompressible SPH is used for the water phase, with the addition of Fickian shifting to produce sufficiently homogeneous particle distributions to enable stable, accurate, converged solutions without noise in the pressure field. Shifting is a purely numerical particle regularisation device. The interface remains a true material discontinuity at a high density ratio with continuous pressure and velocity at the interface. This approach with the physics of compressibility and incompressibility represented is novel within SPH and is validated against semi-analytical results for a two-phase elongating and oscillating water drop, analytical results for low amplitude inviscid standing waves, the Kelvin–Helmholtz instability, and a dam break problem with high interface distortion and impact on a vertical wall where experimental and other numerical results are available. |
| [30] | . A high concentration of the total dissolved gas (TDG) in a flow downstream high dams may cause the gas bubble disease in fishes. To better understand the spatial distribution of a supersaturated TDG, a numerical simulation approach for determining the TDG concentration is shown to be effective and convenient; however, the determination of the model parameters relies to a great extent on the... [Show full abstract] |
| [31] | . Summary We introduce a Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) concept for the stabilization of the interface between two fluids. It is demonstrated that the change in the pressure gradient across the interface leads to a force imbalance. This force imbalance is attributed to the particle approximation implicit to SPH. To stabilize the interface a pressure gradient correction is proposed. In this approach the multi-fluid pressure gradients are related to the (gravitational and fluid) accelerations. This leads to a quasi-buoyancy correction for hydrostatic (stratified) flows, which is extended to non-hydrostatic flows. The result is a simple density correction which involves no parameters or coefficients. This correction is included as an extra term in the SPH momentum equation. The new concept for the stabilization of the interface is explored in five case studies and compared with other multi-fluid models. The first case is the stagnant flow in a tank: the interface remains stable up to density ratios of 1:1000 (typical for water and air) in combination with artificial wave speed ratios up to 1:4. The second and third cases are the Rayleigh鈥揟aylor instability and the rising bubble, where a reasonable agreement between SPH and level-set models is achieved. The fourth case is an air flow across a water surface up to density ratios of 1:100, artificial wave speeds for water higher than that of air, and high air velocities. The fifth case is about the propagation of internal gravity waves up to density ratios of 1:100 and artificial wave speed ratios of 1:2. It is demonstrated that the quasi-buoyancy model may be used to stabilize the interface between two fluids up to high density ratios, with real (low) viscosities and more realistic wave speed ratios than achieved by other WCSPH multi-fluid models. Real wave speed ratios can be achieved, as long as the fluid velocities are not very high. Although the wave speeds may be artificial in many cases, correct and realistic wave speed ratios are essential in the modelling of heat transfer between two fluids (e.g. in engineering applications such as gas turbines). |
| [33] | . |
| [34] | . |
| [35] | . |
| [36] | . A new modification of the Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) method is presented. The performance of the proposed method is checked when used together with Local Lax-Friedrichs (LLF), Harten, Lax, van Leer (HLL) and exact Riemann solvers, and we derive the SPH equations for each applied solver. The validation problems include Sod’s problem, Sj02green test, blast wave tests, and collision of strong shocks problem. On the basis of our results, we conclude that the application of HLL and LLF approximate Riemann solvers is preferable, with LLF solver having a smallest compuational load. The conservative properties of the method are also strong. The linear momentum, the total mass, and the total energy are conserved within machine accuracy for all applied Riemann solvers. |
| [37] | . Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) is used to simulate the movement of a caisson breakwater in the surf zone. The open-source code SPHysics is used with a Riemann solver-based formulation. The friction force between the moving caisson and the bed is modelled with a transition from static to dynamic friction force. Results are presented for two-dimensional simulations and compared with experiments for the movement of a caisson breakwater under the forcing of periodic waves. Promising agreement with experimental data is obtained for the displacement and the horizontal forces on the caisson. It is demonstrated that the peak impact forces are better captured using finer resolution and that a Riemann solver-based formulation produces a better agreement with experiment for the predicted caisson displacement than conventional SPH. |
| [38] | . 基于虚功原理, 在Hu X Y等和Grenier N等的研究结果基础上推导了多相流光滑粒子流体动力学(smoothed particle hydrodynamics, SPH)控制方程, 采用精度较高的黏性力和表面张力模型, 发展了一套适用于具有大密度比和大黏性比界面的多相流SPH方法. 首先, 通过施加人工位移修正, 适当背景压力和异相界面力, 使得计算全程粒子分布相对均匀, 改善了界面处的失稳现象, 防止了异相界面处粒子的非物理性穿透; 在此基础上, 利用方形流体团振荡模型对表面张力模型进行了验证, 数值结果与解析解甚为吻合; 然后采用上浮气泡经典数值算例对比研究了不同黏性力计算方法、不同核函数的适用性以及人工位移修正的效果; 最后, 对单个气泡的上浮、变形、撕裂以及垂向两个气泡的追赶、融合等现象进行了模拟, 初步揭示了气泡上浮过程中各种有趣物理现象的细节过程和动力学机理. . 基于虚功原理, 在Hu X Y等和Grenier N等的研究结果基础上推导了多相流光滑粒子流体动力学(smoothed particle hydrodynamics, SPH)控制方程, 采用精度较高的黏性力和表面张力模型, 发展了一套适用于具有大密度比和大黏性比界面的多相流SPH方法. 首先, 通过施加人工位移修正, 适当背景压力和异相界面力, 使得计算全程粒子分布相对均匀, 改善了界面处的失稳现象, 防止了异相界面处粒子的非物理性穿透; 在此基础上, 利用方形流体团振荡模型对表面张力模型进行了验证, 数值结果与解析解甚为吻合; 然后采用上浮气泡经典数值算例对比研究了不同黏性力计算方法、不同核函数的适用性以及人工位移修正的效果; 最后, 对单个气泡的上浮、变形、撕裂以及垂向两个气泡的追赶、融合等现象进行了模拟, 初步揭示了气泡上浮过程中各种有趣物理现象的细节过程和动力学机理. |
| [39] | . |
| [40] | . We present a low-dissipation weakly-compressible SPH method for modeling free-surface flows exhibiting violent events such as impact and breaking. The key idea is to modify a Riemann solver which determines the interaction between particles by a simple limiter to decrease the intrinsic numerical dissipation. The modified Riemann solver is also extended for imposing wall boundary conditions. Numerical tests show that the method resolves free-surface flows accurately and produces smooth, accurate pressure fields. The method is compatible with the hydrostatic solution and exhibits considerably less numerical damping of the mechanical energy than previous methods. |
| [41] | . In this paper we present a new formulation of the boundary condition at static and moving solid walls in SPH simulations. Our general approach is both applicable to two and three dimensions and is very simple compared to previous wall boundary formulations. Based on a local force balance between wall and fluid particles we apply a pressure boundary condition on the solid particles to prevent wall penetration. This method can handle sharp corners and complex geometries as is demonstrated with several examples. A validation shows that we recover hydrostatic equilibrium conditions in a static tank, and a comparison of the classical dam break simulation with state-of-the-art results in literature shows good agreement. We simulate various problems such as the flow around a cylinder and the backward facing step at Re=100 to demonstrate the general applicability of this new method. |
| [42] | . A method for simulating two-phase flows including surface tension is presented. The approach is based upon smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). The fully Lagrangian nature of SPH maintains sharp fluid-fluid interfaces without employing high-order advection schemes or explicit interface reconstruction. Several possible implementations of surface tension force are suggested and compared. The numerical stability of the method is investigated and optimal choices for numerical parameters are identified. Comparisons with a grid-based volume of fluid method for two-dimensional flows are excellent. The methods presented here apply to problems involving interfaces of arbitrary shape undergoing fragmentation and coalescence within a two-phase system and readily extend to three-dimensional problems. Boundary conditions at a solid surface, high viscosity and density ratios, and the simulation of free-surface flows are not addressed |
| [43] | . 提出了一种适用于模拟多相流的光滑粒子法,该方法对密度方程在交界面处的离散格式进行了修正以适应多相流所涉及的大密度比问题,在不同相粒子之间施加了很小的排斥力以防止粒子穿透交界面,并采用了最新发展的双曲型光滑函数以消除应力不稳定问题.应用该多相流光滑粒子法模拟研究了单模态和多模态瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题.通过与文献中结果的对比研究表明:在模拟瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题时,本文方法的结果明显优于文献中的大部分光滑粒子法模拟结果,与Grenier等(2009 J.Comput.Phys.2288380)的结果相当,但本文方法比Grenier等的方法简单方便.对于单模态瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题,研究了交界面的形态,涡结构的演化过程以及贯穿深度随时间的变化关系.对于多模态瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题,研究了交界面演化过程中小尺度结构合并成大尺度结构的过程,水平方向的平均密度随高度的变化关系,以及贯穿深度随时间的变化关系. . 提出了一种适用于模拟多相流的光滑粒子法,该方法对密度方程在交界面处的离散格式进行了修正以适应多相流所涉及的大密度比问题,在不同相粒子之间施加了很小的排斥力以防止粒子穿透交界面,并采用了最新发展的双曲型光滑函数以消除应力不稳定问题.应用该多相流光滑粒子法模拟研究了单模态和多模态瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题.通过与文献中结果的对比研究表明:在模拟瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题时,本文方法的结果明显优于文献中的大部分光滑粒子法模拟结果,与Grenier等(2009 J.Comput.Phys.2288380)的结果相当,但本文方法比Grenier等的方法简单方便.对于单模态瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题,研究了交界面的形态,涡结构的演化过程以及贯穿深度随时间的变化关系.对于多模态瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题,研究了交界面演化过程中小尺度结构合并成大尺度结构的过程,水平方向的平均密度随高度的变化关系,以及贯穿深度随时间的变化关系. |
| [44] |
