 ,1,2,3, 李吉龙
,1,2,3, 李吉龙 ,1,2,3,4, 熊礼阳1,2,3, 那嘉明1,2,3
,1,2,3,4, 熊礼阳1,2,3, 那嘉明1,2,3Scientific attributes and expression methods of geographical boundary
TANG Guoan ,1,2,3, LI Jilong
,1,2,3, LI Jilong ,1,2,3,4, XIONG Liyang1,2,3, NA Jiaming1,2,3
,1,2,3,4, XIONG Liyang1,2,3, NA Jiaming1,2,3通讯作者:
收稿日期:2021-06-11修回日期:2021-10-14
| 基金资助: |
Received:2021-06-11Revised:2021-10-14
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
汤国安(1961-), 男, 博士, 教授, 博导, 主要从事地理信息科学方面的研究。E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1774KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
汤国安, 李吉龙, 熊礼阳, 那嘉明. 论地理边界的科学属性与表达. 地理学报, 2021, 76(11): 2841-2852 doi:10.11821/dlxb202111017
TANG Guoan, LI Jilong, XIONG Liyang, NA Jiaming.
1 地理边界的概念
地理对象在空间的展布具有其属性的相似性与差异性。既有一条海岸线将地面划分为陆地与海洋、一条国境线将地域分为两个不同的国家、一条山脊线将山体两侧划分为不同的流域这样相对清晰、明确的地理分界线,也有诸如以“胡焕庸线”将中国分为东西两个不同的人口密度区、中国红壤—黄壤分界线这样相对模糊、综合的地理界线。可以说,无论是地理学的单要素研究还是系统综合研究,对地理边界类型的系统分类并在空间上确定其位置,是地理学研究的题中要义。地理边界划分不清会影响地理认知,而且不能够充分揭示和表达地理空间分异规律,进而无法反映地理边界、地理格局与地理规律之间的相互联系。因此,对地理边界科学内涵、外在表现与清晰划分的认识,是地理学根本性的理论问题。一般的“边界(boundary)”概念,在《现代汉语词典》[1]中解释为“地区和地区之间的界线”;《韦氏英语词典》[2]将边界定义为“可以表示或修正限制或范围的线”。事实上,在不同的学科领域,边界概念也有具体的表述。例如:在拓扑学中,边界指的是闭包减去拓扑空间子集的内部[3];在热力学中,边界指的是包围或标定热力学系统所占据空间区域的,物质、热量或功可以流过的,实际存在的或假想出来的二维闭合曲面[4]。
地理学的研究尺度范畴是地球表层空间,地理边界正是在这个范畴内来解决地学问题。地理边界具有基本地理属性,较之于其他边界具有一定的特殊性。《现代地理学辞典》将地理边界定义为“将相邻地域单位加以区分的线或带,一般处在地理要素或地理综合性特征变化梯度最大的带段”[5]。该定义强调以下几点:① 地理边界所区分的对象是相邻且不同的地域单位;② 地理对象的属性在不同地域单位上表现出显著的差异性;③“最大变化梯度”蕴含了地理现象相对变化的概念,但是仅以梯度变化作为地理边界的划界依据缺乏地理边界的结构基础[6];④ 边界的表现形式一般为突变的“线”或渐变的“带”,这体现了地理边界的过渡性和模糊性。此外,中国****指出地理边界是由量变到质变的点的连续,界线两侧是相似性和差异性相互交织的地带[7,8];而美国国家地理学会(National Geographic Society)将地理边界定义为:将地球上不同区域分开的线,并将地理边界划分自然边界、政治边界和其他边界等几种类型。也有****提到在地理边界的定义和概念中,需要考虑两种大类的地理边界:一是固定的自然边界(如海岸线、河流、山脉等);二是由人工自定义的大范围边界(如空气污染边界、城市边界等)[9]。综上所述,虽然地理边界定义的表达可以明确为:地理边界是一个具有若干不同过渡属性(显性突变、模糊渐变等)、用以区分各类地域单元的线或者过渡带。
然而,在地理界线的实际划分中却存在着诸多亟待澄清的理论与方法问题。首先,地理边界是某种地理现象或过程在空间上相似性与差异性的映射。无论以何种视角对地理边界的概念进行阐述,都应充分考虑这种映射关系中的尺度问题、匹配模式问题以及地域单元修正问题[10]。其次,地理边界作为刻画客观世界的一种方式,其客观存在性是必然的,然而不同的划分方式会导致不同的边界划分结果,这又使得地理边界研究中往往具有相当的主观性。无论是客观还是主观,二者是互相依赖的,即客观的刻画方式大多都是以对地理现象或过程的主观认知为基础,而主观的刻画方式则必须借助于地理边界存在的客观属性才能有针对性地确定边界划分方案。因此,如何将主客观划分思想结合,并将定性与定量的划分方案进行有效关联,是当前研究的一个重要方向,地理信息科学的发展为这一问题提供了有效的解决方案。
GIS是地理学的第三代语言[11],它以数字化的方式抽象表达了极其复杂的现实世界[12,13],同时GIS相关理论与方法的发展为地理边界的研究提供了定性、定量与定位相结合的研究思路,以及更加多样的表达方式。GIS的核心之一是模型语言,可使传统地理边界研究转变成更加定量化的模型知识进行研究,进而又形成了GIS背景下以离散化、模型化为核心的地理边界概念[14,15]。
2 地理边界的科学内涵
地理学是研究地理要素和地理综合体的空间分异规律、时间演变过程及区域特征的一门学科[16],地理边界划分是对地表系统的空间分异规律、时间演变过程及区域特征模式的高度抽象与成果凝练,是地理学中最基本的研究问题,而地理边界问题,本身又是一个极为复杂、极为抽象、极为综合的理论难题[17],其背后隐含着深邃的科学内涵。首先,地理边界可以全面揭示地理的时空同质性、异质性与相似性特征。Tobler[18]曾指出,“所有事物都与其他事物相关,但是近处的事物比远处的事物更相关”,即地理学第一定律。Goodchild[19]随后提出了地理学第二定律:“空间的隔离造成了地物之间的差异,即空间异质性”。例如景观异质性是指景观或其属性的变异程度[20],而地理系统作为自然与人文景观的综合体也不例外,异质性是地理系统的一个本质属性,景观与异质性二者的研究密不可分[21]。因此,空间与时间所构成的时空异质性是地理现象中重要的客观特征,而这种特征最直接的表现形式往往体现在地理边界上。朱阿兴等[22]基于地理环境提出的“地理学第三定律”,即“地理环境越相似,地理特征越相近”,该定律不同于地理学第一和第二定律,具有一定的独立性,其更强调地理现象中多要素相互作用,且涉及的是目标地理要素与其他地理要素组合在所在点上的相互关系或相互作用[23],而这种关系或作用可以直接通过地理环境体的边界来体现。具体而言,点位上的相互作用决定了地理边界的复杂程度,而地理边界又可反过来反映地理现象中多要素相互作用的状态。
可见,上述地理学定律描述了地理系统所遵循的普遍规律,具有较强的客观性。虽然这些定律均未具体提及地理边界,但是从上述分析中不难发现,地理边界是客观存在的,即地理边界是同质性与异质性的综合表现,而相似性导致了地理边界的复杂性。因此,地理边界由地理环境/属性的时空同质性、异质性和相似性共同决定。
其次,地理边界及其划分过程是地理系统非线性的最直观体现。地理现象是必然性与偶然性融合的复杂现象,势必具有一定的复杂性与非线性特征[24]。以地貌系统为例,Phillips[25]认为地貌系统在空间和时间域上通常表现出复杂的、明显的随机性,其往往由单个过程响应机制的累积影响引起的。由于非线性机制太多而无法利用单一因素加以解释,或者一系列空间和时间尺度上的响应关系存在多种因素控制,进而产生混沌、耗散、分叉和突变等非线性特征,这些特征共同导致了地理系统中输入与输出之间的复杂关系。无论从微观还是宏观视角,在一个完整的地理系统中,地域单元不可避免的在空间中相互依赖、相互作用,就会呈现极为复杂的非线性发展关系[6]。
事实上地理系统的非线性是一种复杂的地理系统变化特征,并且是可以进行分类的[26]。区域即是在客观认识地理系统的时空差异的基础上,按一定的指标和方法划分出来的。对于一个系统而言,边界并不依赖于某个具体客观存在的地理实体[27]。然而,地理边界作为地表系统非线性特征的表现之一,本质上是地理空间物质和能量的地域变化客观性的反映,这种变化也遵循从量变到质变的客观世界普遍法则[28,29]。因此,对地理边界的划分不仅是人们认识客观世界的必要途径,更是一种认知地理现象与规律的重要手段。
此外,地理边界是地理系统自组织过程的重要桥梁。地理边界是地表系统“无序”与“有序”矛盾斗争的结果。对于地理系统整体而言,其内部各种地理要素的时空变化特征通常是非线性、非平稳的[30,31],这进一步会导致地理系统混沌无序的状态。地理耗散结构理论认为,地理系统是一个远离平衡态的开放系统,具有显著的自组织特征,它通过与外界不断地交换物质与能量,有可能在一定条件下形成新的稳定的有序结构,从而实现从“无序”向“有序”的转化[32]。而地理边界作为地理要素在空间和时间动态变化中的重要临界条件,实质上有效“分割”了这些非线性、非平稳的地理现象及过程。作为地理系统中物质与能量交换最频繁的地带,地理边界直观反映了物质、能量或信息交换与动态平衡的变化。
地理边界在区分地理现象和过程的同时,也是相邻区域间物质迁移、能量转换、信息传递等相互作用和相互联系的纽带[33]。当地理系统内的某些现象或属性的变化达到一定临界条件,其地理边界也将动态调整。这种调整映射了该变化过程的深层次机理。
可以看出,无论实体划分、单元划分、类型划分还是区域划分都与地理边界息息相关。地理边界存在的科学内涵充分体现了地理时空变化规律,反映了潜在的自然与人文变化格局,在揭示地理空间单元之间的过渡渐变特征、剖析地理要素在地理系统空间中的复杂性、探索地理边界动态变化与地理要素之间的关系等具有重要的地学意义。
3 地理边界的基本属性
地理边界基本属性集中体现在主观与客观、突变与渐变、稳定与变化的矛盾对立统一。3.1 主观与客观辩证统一性
地理边界并不具象地存在于地理空间,而是基于地理空间分异规律进行的抽象。由于研究的目标、标准、技术方法、划界因子的复杂多样,且不同****认知视角的差异[34],这将导致最终划定的边界出现主观性的差异化结果。但从另一角度看,地理边界的存在是地理对象、现象空间差异性的客观实在,有的地理边界由于自然阻隔或地理对象本身的显著特征,使得地理现象在时空上易于区分界定;而在地理学中更多的现象需要通过一定的科学依据与技术手段才能将相应的地理边界进行科学划定。但无论地理边界具有怎样的表现形式,地理边界的客观性不受主观判断差异性影响。3.2 稳定与变化辩证统一性
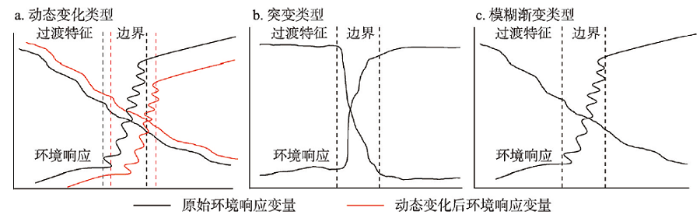
地理边界的划定离不开一个或一组划界因子或指标[28],而一个地理系统内部与外部的物质能量交换始终处于时空的动态变化之中。因此,指标会在一定的时空尺度内发生变化,这最终将导致地理边界产生迁移或结构上的变化。地理学第二定律也指出,地理要素的空间变化是不可控制的,即地理现象在空间的变化是必然的,当外部的环境变量与地理系统的响应变量达到矛盾对立统一,边界将保持动态稳定(图1a)。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1地理边界的过渡属性类型
注:修改自文献[37]。
Fig. 1Types of transition properties for geographical boundaries
地理边界稳定与变化的矛盾对立统一还体现在地理边界的尺度依赖性特征。对于同一个地理现象或地物的边界,在大尺度视野下观察较为平滑简约,在小尺度视野上观察则具有复杂的边缘带状结构[35]。同时,地理边界的划分往往基于不同尺度的时空数据展开。因此,不同的时间和空间尺度下,地理边界划分所计算的指标一般具有特定的尺度效应(如数据尺度、分析尺度、表达尺度),且表现出不同层次的等级结构,使得最终的边界划分结果也随之出现尺度依赖性。据此,认知地理边界的多尺度特征,构建多尺度的地理边界模型对于完整表征地理现象与过程的同质性、异质性和相似性具有重要的作用。
3.3 突变与渐变辩证统一性
法国数学家托姆(Rene Thom)提出的突变论(Catastrophe Theory)思想,指出在一切自然过程中,突变是基本的,而且渐变也是由无数小的突变组成的[36]。将突变论的思想移植于地理学中即为地理突变论。地理突变论认为,若干微小的、连续的突变特征可产生“积累效应”,到达一定程度(表现为某个临界值或临界值组合)就会使系统产生突变(图1b)。地理学中,若地理要素具有清晰的走向和标志(如地理阻隔),会导致地理环境明显突变现象,例如中国内流区与外流区以阴山—贺兰山—祁连山—巴颜喀拉山—冈底斯山为界。然而,由于地表分异现象多为连续渐变过渡的,很少出现跳跃,故大多数地理界线表现出边界的模糊性,常表现为具有一定宽度的且成因复杂的过渡带(图1c),不会出现“非此即彼”的特征。此外,突变论指出,在严格控制条件下,如果质变中经历的中间过渡态是稳定的,那么它就是一个渐变过程[38]。由此可见,地理边界的突变、渐变实质上是一个量变到质变的过程。无论是自然现象还是人文现象本质上都是由无数个突变组成的,而更多的是通过渐变的形式表现。突变、渐变的对立统一在GIS视角下也可以基于集合论和模糊数学等理论进行剖析和表达。
4 地理边界的基本类型
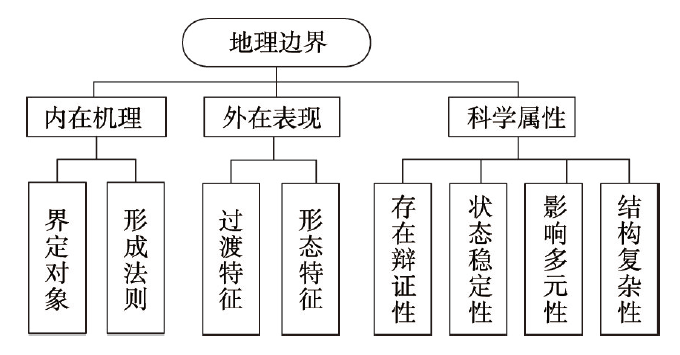
由于地理边界划分涉及对地理过程、现象和对象的特征阐述,同时又需要根据地理边界固有属性建立与环境之间的响应关系,因此我们依据科学性、系统性的基本原则,从内部机理、外在表现以及科学属性这3个方面对地理边界的类型划分进行梳理(图2)。具体如下:图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2地理边界类型划分依据示意图
Fig. 2Schematic diagram of the basis of geographical boundaries classification
(1)基于内在机理划分。主要包括边界的界定对象和形成法则。其中,界定对象主要包括类型与区域[39,40,41],因此可划分为类型边界和区域边界,例如地貌类型边界、地貌区划边界等;后者有自然因素形成的地理边界,人为因素形成的地理边界以及自然人文综合因素形成的地理边界,例如分水岭、“胡焕庸线”以及区域旅游资源边界等。
(2)基于外在表现划分。① 过渡特征:根据地理环境的差异性和复杂性可将地理边界的过渡属性分为因自然阻隔(如山脉、河流等)等原因所形成的具有显性突变特征的地理边界、具有连续平稳过渡的模糊渐变特征的地理边界、以及更为复杂的交替过渡特征的地理边界。例如,流域边界、秦岭—淮河一线与水土流失分区边界等。② 形态特征:地理边界呈现出千姿百态的形状,例如根据规则度可将地理边界分为规则边界、不规则边界等。
(3)基于科学属性划分。① 存在辩证性:地理边界本身是抽象的,可以指一个客观存在的实体对象,也可以根据实际研究目的加以限定,因此可划分为客观边界与主客观综合边界等,例如亚欧板块与非洲板块的边界、城镇开发边界等;② 状态稳定性:任何地理边界都不是绝对稳定的,可划分为稳定边界、动态变化边界等,例如山体边界、季风区与非季风区边界等;③ 影响多元性:边界的划分受到多种环境要素的影响,根据这些要素的数量和关系划分为简单要素边界、复杂要素边界,例如海陆边界、综合自然地理区划边界等;④ 结构复杂性:地表系统具有一定的层次嵌套结构,可以根据不同研究尺度对边界进行进一步的划分,例如,不同等级的流域边界等。
5 地理边界的数学表达与划分方法
5.1 数学表达
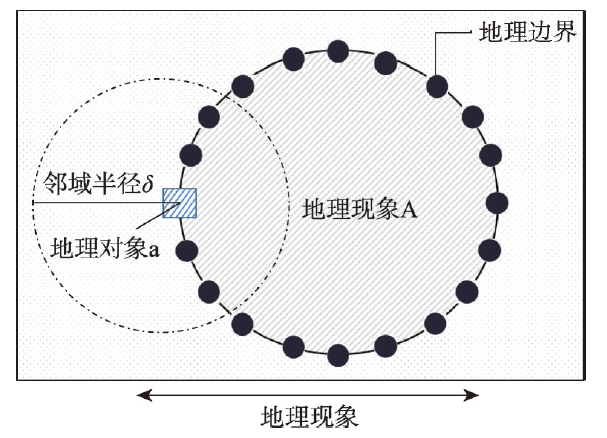
地理系统作为复杂的空间系统,其表达须借助数学方法进行科学抽象[42],地理边界的表达也需如此。从数学上讲,地理边界问题可以视作是一类确定范围的问题,即集合,而邻域又是集合上的一种基础拓扑结构。因此,地理边界的数学内涵是以集合及其邻域特征作为支撑的,实质上是将地理过程或现象分割为一系列的邻域,通过定义邻域内部任意小的集合来表达。也就是说,如果对于地理空间的某个对象a的任意邻域内既有属于某一地理现象A集合的点,也有不属于A的点,那么a可以视为A的一个地理边界点,A的所有边界点组成的集合称为A的地理边界(图3)。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3地理边界的简单数学表达示意图
Fig. 3Schematic diagram of a simple mathematical representation of geographical boundaries
地理边界最显著的特征就是其过渡属性,例如显性突变、模糊渐变、复杂交替变化等,这些属性本质上均是地理边界划分过程不确定性的体现。不确定性是客观世界的一种固有属性。地理边界的划分过程受到多种因素的影响,例如语义、数据、尺度、模型和表达等,这些因素直接或间接影响着边界划分的科学性与准确性,同时关系着各个相关领域的决策制定与应用。模糊集和粗糙集在度量和评价地理不确定性问题上具有广泛的应用。因此,利用模糊集和粗糙集进行模糊或复杂交替变化的地理边界表达,不仅可以客观评价划分结果,而且可以对边界划分的不确定性加以量化和控制。此外,由于地理边界的多种类型,可以根据边界划定的不同依据和目标还存在其他数学模型或表达方法。本文依据地理边界最具代表性的过渡属性,即显性突变、模糊渐变、复杂交替变化,分别应用势函数、模糊集和粗糙集等理论方法对地理边界的数学内涵加以建模和表达,目的是能够更加清晰认识地理现象与过程的定量表现形式,而且可以更好地服务于地理边界模型的构建(表1)。
Tab. 1
表1
表1常见的地理边界数学模型表达与对比
Tab. 1
| 过渡属性 | 数学模型 | 表达原理 | 示意图 | 模型特点与划分方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 显性突变 | 势函数 | 根据突变理论,势函数 式中: (1) 当 (2) 使势函数( 对于显性突变属性的地理边界,由势函数衍生出的平衡曲面与分叉集共同确定。 | 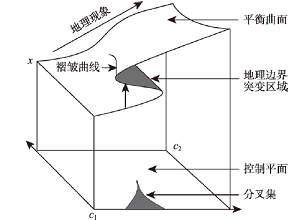 | 模型特点:适用有明显地理阻隔环境下的显性突变地理边界表达。 划分方法:采用突变理论与突变级数法进行地物显著差异分析并定位。 |
| 模糊渐变 | 模糊集 | 模糊集通过构建模糊隶属函数计算隶属度的大小来确定划界单元的归属。已知论域 式中:称映射 在地理边界的表达中, | 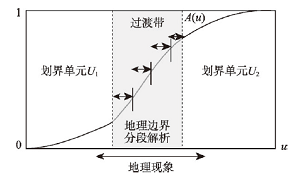 | 模型特点:更加自然表示地理现象,适用于模糊地理边界模糊划分。划分方法:通过构建模糊隶属度函数(根据专家知识、数据集特征给出)提取地物类型边界,建立模糊边界划分模型。 |
| 复杂交替 | 粗糙集 | 针对复杂交替特征的地理现象采用粗糙集进行边界表达: 式中:论域 | 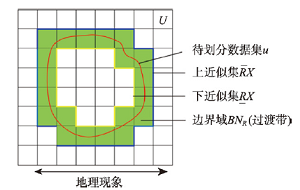 | 模型特点:完全由数据驱动,不涉及隶属函数的构造,在表达地理边界的特征上更加客观。划分方法:根据地物相关数据集,确定上下近似集,计算得到的边界域即为最终划定的地理边界(过渡带)。 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
5.2 划分方法
客观地认识和划定地理边界,是揭示地理环境时空规律的重要途径。地理边界的划分方法由地理边界的类型及其相应的数学模型确定,同时地理边界的分类和数学表达过程又是对划分方法不断改进优化的过程。数学表达虽然为地理边界划分提供了重要的理论依据,但其仍然是一个复杂的问题[43],且一直以来都是地理学研究中的重要问题之一,加之地理边界本身的属性特征,使得研究的难点更为突出。因此,根据不同的划分目的,采取何种方法和技术手段进行地理边界的划分至关重要。5.2.1 传统地理边界划分方法 传统的地理边界划分通常是围绕地理区划展开的,划分方法与区划方法基本一致,主要包括主导因素法、叠置法、地理相关分析法和景观制图法等[8]。目前已有诸多研究从地理区划的角度对地理边界的划分方法进行了阐述。在地理区划的研究中,地理边界是反映地理空间单元差异最为重要的地理对象,国内外的地理区划研究几乎都提到了区划单元边界的重要性,而地理边界是地理区域存在的必要条件[44]。
目前,围绕地理区划的地理边界划分已有许多研究成果。郑度等[7,8]系统总结了中国的区划工作,并对自然区划方法进行了梳理与思考,特别指出界线的确定一直是区划的难点。即使在中国区划全面发展的时期,由于受到当时技术手段、资料等条件的限制,很多重要的地理边界的确定带有假定、推测的成分,指标选择与指标体系构建也需要进一步改进完善[45]。可见,以区划为基础的地理边界划定既需要科学理论支撑,也需要技术方法突破。此外,高江波等[34]总结认为受先验知识制约,传统区域划分主要采用专家集成方法,而这种方法在分区指标和具体界线走向等问题的确定上,主观性较强,经验判断起了主要作用,在界线划分上定量化程度不够。虽然这些研究在宏观方面具有引导性,但是微观方面需要进一步具体和翔实的信息[16]。同时,由于地理系统的非线性特征以及地理边界本身的过渡属性特征,迫切需要集定性、定量、定位为一体的划分模型与方法,进而弥补和完善传统地理边界划分方法。
5.2.2 基于定量研究的地理边界划分方法 随着地理学的发展,涌现了诸多的定量分析方法和丰富的数据获取方式,并有许多研究将多种多样数学模型和表达方法应用到地理界线的划分中,特别是GIS已经成为定量地理边界划分中不可或缺的技术手段。GIS的相关理论技术方法可以将地理边界划分过程中涉及的时空环境要素及相关信息进行挖掘量化和建模,并且适宜通过可视化的方式将划分结果快速有效地呈现。然而,当前的GIS理论与技术是在地理边界划分中仍存在相当的不足和局限,如何将传统的地理学家在地理界线划分中的智慧与经验进行科学的抽象及有效的建模,就是亟待解决的问题。现阶段应用高分辨率地理数据直接提取地理边界已有相关研究开展[46,47],这种方法极大简化了地理边界的划分过程,但对于具有模糊渐变等属性的地理边界划分仍然存在很多局限,都需要一定的科学理论支撑与方法突破才能实现。
早在1989年,Mark等[48]提出一种类概率曲面模型用于土壤类型边界的划分,可视作基于模糊数学思想定量化划分地理边界的早期研究。随后,由Burrough等[49]主编的《Geographic Objects with Indeterminate Boundaries》论文集出版,该书指出自然对象均具有不确定且模糊的边界,同时对地理边界的基本概念、表达语言、定量化概念框架进行了系统阐述,形成了完整的研究体系,这些研究都为定量地理边界划分提供了重要基础。此后,模糊数学理论广泛应用于地理边界的划分中,例如Wang等[50]基于GIS提出了模糊表达(Fuzzy Representation)的地理界线划分方法;Jiang[51]对地理对象的模糊边界进行了可视化表达研究;曹菡等[15]使用模糊隶属函数构建了模糊边界地理现象的模型;Lu等[52]采用贝叶斯区域分割法(Bayesian Areal Wombling)提出了模糊地理边界的分析模式。空间统计建模理论与方法的发展促使了地理边界向更加定量模型化的研究转变。例如晏路明[53,54,55]分别采用Fuzzy综合评判、可拓工程、Fisher判别准则等方法划定福建省境内中、南亚热带之间的界线;李双成等[56,57]分别使用策略性循环尺度转换(SCS)和空间小波变换划分生态地理界线;洪滔等[58]通过改进基于单纯形法直接优化投影寻踪技术建立自然地理界线划分的判别模型。近几年,仍有新的地理边界划分方法不断涌现,例如多面语义[59]、地理探测器(Geodetector)[60,61]等边界划分方法。纵观现有研究,定量地理边界划分方法脱离不开数学理论的指导,无论是针对何种过渡属性地理边界的划分大体上都可分为:由数据直接提取边界法、基于模糊数学理论的划分方法、基于空间统计建模的划分方法以及近几年出现的新型划分方法,但均存在一定的优缺点(表2)。
Tab. 2
表2
表2定量地理边界划分方法对比
Tab. 2
| 方法 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 直接法 | 由数据驱动,划分思路简便,适用于具有显性突变或明显地理阻隔的地理边界划分研究中 | 使用局限,面对复杂的地理现象或过程,划分捉襟见肘 |
| 模糊数学法 | 符合地理认知,能够更加自然表示地理现象、对象或过程,适用于具有模糊过渡特征的边界划分 | 模糊隶属函数可以根据专家知识或实验数据给出,或根据数据集属性特征的聚类得到,划分结果存在差异 |
| 空间统计建模法 | 充分顾及划界指标的重要性,同时兼顾划分过程中的尺度依赖性,适用于多种过渡属性的边界划分 | 需要有领域知识和统计知识,且通常需要假设空间分布数据具有统计上不存在空间自相关和平稳性,然而对于地理边界划分过程而言,其空间属性关联不可避免 |
| 新型划分法 | 通常采用启发式学习方式来进行边界划分,并从数据本身入手,在符合地理认知的基础上,具有稳定的划分效率与准确性 | 需要大量的初始参数,如网络拓扑结构、权值和阈值,划分过程黑盒等 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
虽然目前基于定量分析和GIS技术的地理界线划分研究具有较多的成果,但若脱离定性分析难免出现单纯定量化的研究模式,也会使得地理边界的划分结果与实际可能会存在一定的偏差。因此,发展定量、定性以及定位相结合的研究体系仍然是地理边界划分中不可或缺的重要方面。认识论、方法论和本体论是地理学研究范式的重要支撑,是科学体系的基本模式、基本结构与基本功能[62]。如今针对地理边界的研究缺乏系统认知,方法上也缺少统一的标准或指导思想,对于地理边界本身所刻画的客观世界也存在争议,这些问题归根结底是现有地理边界的研究不足以将地理边界理论与方法进行模型化统一整合导致的。因此,在当前GIS及时空大数据环境下,亟待发展可对地理边界定性、定量、定位有效划分的标准模型——地理边界模型,该目标的实现将是对地理学研究的重要贡献。
6 结论与讨论
地理边界问题是地理学最基本的理论问题,地理边界是自然的客观实在,但其外在表现又极具复杂性,充分体现了地表系统多要素综合作用、多尺度耦合影响的地理效应。科学、系统地梳理地理边界的基本概念、存在条件、科学内涵与基本属性,对于地理边界的科学内涵的分析,科学指导界线划分,具有重要意义。本文按照科学性、系统性的原则与依据,依据内在机理、外在表现以及科学属性等不同视角,对地理边界的基本类型进行了划分,该分类系统可望深化对地理边界基本特征的认识,有利于实际专题地图制图中分类、分区的实现。
地理边界的数学本源是集合论。本文基于过渡属性对地理边界进行数学表达是一种最直观有效的方式,借助于势函数、模糊集与粗糙集理论,建立起地理边界表达从定性向定量转变的桥梁,不仅可以更加充分认识与理解地理现象与过程的定量表现形式,而且可以更好地服务于未来地理边界模型的构建。
近年来,随着现代对地观测技术手段的提升和GIS理论与方法研究的深化,数据的来源与形式不断丰富,新的技术方法不断涌现,为地理边界的定性、定量、定位一体化研究开辟了新的途径。当前,地理边界问题探索虽已在地理学相关研究中广泛开展,但现阶段地理边界的划分在如何运用海量对地观测数据,非结构化的地学大数据时仍存在一定的难度,特别是当前GIS的发展存在着越来越背离地理学本源的错误倾向。很多GIS研究或开发工作者,由于对地理学区域分析基本理论与方法知识的欠缺,对各种地理边界基本概念、存在的内在机理及划分方法等存在相当程度的曲解,甚至误判。不少GIS平台软件,混淆地理类型划分与区域划分的区别,造成专题地图制图的错误。当前在时空大数据背景下,数据的形式、规模与内容发生了根本的改变,这也给地理边界的划分方法提出了新的挑战,如何在地球系统科学思想指引下,构建集科学性、系统性为一体的地理边界模型,都是摆在我们面前亟待解决的难题。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/PL00011456URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001 [本文引用: 2]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1007/s11442-021-1853-9URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/143141URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8306.2004.09402008.xURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/19475683.2018.1534890URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1191/0309133303pp340raURL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/02723646.2016.1211460URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/tgis.v23.1URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.11.032 [本文引用: 2]

<p>As is well known, there exist similarities and differences among geographical regions, and zonality is a universal theorem governing geographical patterns. Physio-geographical regional system is a hierarchical system, which is formed by division or combination of natural features based on geographic relativity and geographic zonality. Researches on physio-geographical regional system aim at observing and studying natural complex of the earth’s surface, revealing rules of regional differentiations and exploring formation, development, division, combination, relativity and demarcation of natural regions at different scales, from a regional point of view. As a radical method to obtain geographical information, physio-geographical regionalization has always been studied and widely used by geographers. Studies on physio-geographical regionalization in China have made great progress in principle, methodology, and theory since the 1930s. It could provide a scientific basis for social and economic development and planning, and conservation, improvement and rational utilization of natural environment. Based on brief review of physio-geographical regionalization at home and abroad, the paper summarizes the characteristics of researches in recent years: various types of elements; distinct ecologicalization in comprehensive natural regionalization; a complete series of spatial scales; scarce creativity in technology and methods; emphasizing regionalization methodology; enhancing application of regionalization schemes. Then, the paper analyzes academic problems in the present researches: lack of epistemological study; weak methodological study. Finally, the paper explores the prospects of physio-geographical regionalization: continuous increase in requirement at the national level; strengthening the standardization of regionalization, and raises several trends in geographical regionalization.</p>
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1137/1019036URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[0730:IEDADM]2.0.CO;2URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.01.002 [本文引用: 1]

Promoting coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is not only a major national strategy, but also a long-term complex process. It is necessary to apply scientific theories and respect the laws of nature to realize the strategic target of common prosperity, share a clean environment, share the burden of risk of development, and build a world-class metropolis for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. This article examines the scientific foundation and patterns of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Synergy theory, game theory, dissipative structure theory, and catastrophe theory are the theoretical basis of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Synergy theory is the core theory for the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. The coordinated development process of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is a non-linear spiral progress of game, coordination, mutation, game, resynchronization, and mutation. Each game-coordination-mutation process promotes the coordinated development of the urban agglomeration to a higher level of coordination, and the progress fluctuates. This process includes eight stages: assistance phase, cooperation phase, harmonization phase, synergy phase, coordination phase, resonance phase, integration phase, and cohesion phase. Further analysis shows that the real connotation of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is to realize the coordination of planning, transportation, industrial development, urban and rural development, market, science and technology, finance, information, ecology, and the environment, as well as the construction of a collaborative development community. The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration will achieve advanced collaboration from low-level collaborative phase through regional coordination on planning, construction of traffic network, industrial development, joint development of urban and rural areas, market consolidation, science and technology cooperation, equal development of financial services, information sharing, ecological restoration, and pollution control. This study may provide a scientific foundation and theoretical basis for the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502002 [本文引用: 1]

Major Function Oriented Zoning (MFOZ) is the blueprint for the future developmnt and protection pattern of China's territory, and has been raised to from major function zones planning to major function zoning strategy and major function zoning institution. From 2004 to 2014, the author organized a series of research projects to compose MFOZ for the country, studied basic theory of regional function and MFOZ technical process, and proposed that space controlling zones of national and provincial scales can be divided into four types: urbanized zones, foodstuff-security zones, ecological safety zones, cultural and natural heritage zones. On this basis, major function zones of county scale should be transferred to optimized, prioritized, restricted, and prohibited zones. In this paper, a regional function identification index system comprising nine quantitative indicators (including water resources, land resources, ecological importance, ecological fragility, environment capacity, disaster risk, economic development level, population concentration and transport superiority) and one qualitative indicator of strategic choice is developed. Based on the single index evaluation, comprehensive evaluation using regional function suitability evaluation index is conducted, aiming at testing several key parameters including lower limit of protection zones and upper limit of development zones at the provincial level. In addition, a planning-oriented zoning method of major function zones is also discussed, which has brought the first MFOZ planning in China. According to the MFOZ caliber, it is forecasted that national spatial development intensity will rise from 3.48% in 2010 to 3.91% in 2020. Furthermore, according to caliber of the provincial integrated MFOZ planning, the area of optimized, prioritized and restricted zones accounts for 1.48%, 13.60% and 84.92%, respectively, and that of urbanized, foodstuff-security and ecological safety zones accounts for 15.08%, 26.11% and 58.81%, respectively. In combination of analyses of development level, resources and environmental carrying status and quality of the people's livelihood, the main characteristics of MFOZ were identified. Through verification, MFOZ draft of national and provincial scales, which is interactively accomplished with "MFOZ Technical Process" put forward by the author, is mostly above 80% identical with what have been forecasted.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3138/D235-3262-062X-4472URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/02693799608902098URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/gean.2005.37.issue-3URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/yj1999010008 [本文引用: 1]

By means of the method of extension engineering, this article sets up a matter-element model of distinguishing objects. The model can be used to define the most reasonable location of the north boundary to the south subtropical belt in Fujian Province, and to show the various transitional states near the boundary objectively and quantitatively.In the design of the model, some generally recognized temperature indices and typical samples are chosen according to physical geography theory, to guarantee the correctness of the single-index dependent function. In the construction of the multiple-index comprehensive dependent function, the method of principal component analysis(PCA) is employed to determine the weight assignation of related factors, so as to avoid subjectivity and to balance objectively the deviation of the single-index boundaries. The model gives the output with satisfying explanations in physical geography meaning.Finally, the paper discusses the controversies on the east and west sections of the boundary, and points out that it is difficult for traditional qualitative methods and classical mathematics to explain the transitive features of geographic boundary, while the matter-element model has its advantages in this respect.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010 [本文引用: 1]

Spatial stratified heterogeneity is the spatial expression of natural and socio-economic process, which is an important approach for human to recognize nature since Aristotle. Geodetector is a new statistical method to detect spatial stratified heterogeneity and reveal the driving factors behind it. This method with no linear hypothesis has elegant form and definite physical meaning. Here is the basic idea behind Geodetector: assuming that the study area is divided into several subareas. The study area is characterized by spatial stratified heterogeneity if the sum of the variance of subareas is less than the regional total variance; and if the spatial distribution of the two variables tends to be consistent, there is statistical correlation between them. Q-statistic in Geodetector has already been applied in many fields of natural and social sciences which can be used to measure spatial stratified heterogeneity, detect explanatory factors and analyze the interactive relationship between variables. In this paper, the authors will illustrate the principle of Geodetector and summarize the characteristics and applications in order to facilitate the using of Geodetector and help readers to recognize, mine and utilize spatial stratified heterogeneity.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701011 [本文引用: 1]

The northern border of the tropical zone of China has been the focus of studies on comprehensive physical regionalization. Based on different indexes and methods, the border was delineated by different scholars, but their results varied greatly. Based on the Geodetector model and regionalization thought of spatial stratified heterogeneity, the northern border of the tropical zone of China's mainland was investigated. Climatic elements were used as dominant demarcation partitioning indexes, combined with auxiliary indexes such as soil and multiple cropping types. The key results were as follows: (1) Using Geodetector, the northern border of the tropical zone was delineated. From west to east, the border goes through Lincang, Simao, Yuxi and Gejiu in Yunnan, Baise, Mashan, Guigang and Wuzhou in Guangxi, Zhaoqing, Guangzhou, Huizhou, Heyuan and Meizhou in Guangdong, and Zhangzhou, Quanzhou and Putian in Fujian. It generally agrees with the 12℃ isotherm of the coldest monthly mean temperature, soil border between lateritic red soil and red soil, and border of double cropping rice or its continuous thermophile dry framing and single (double) cropping rice or its continuous chimonophilous dry framing. (2) The q average value of all indexes for the border was 0.40. Using this model, regionalization principles—homogeneity of the within-strata value and heterogeneity of the between-strata value—were satisfied. The border meets the requirements of zonal heterogeneity between tropical and subtropical zones. Therefore, it is reasonable to use Geodetector in studies of comprehensive physical regionalization, and it can provide high-precision technical support.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
