2.
The evolution process and regulation of China's regional development pattern
FAN Jie1,2, WANG Yafei1,2, LIANG Bo1,21. 2.
收稿日期:2019-11-20修回日期:2019-12-3网络出版日期:2019-12-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-11-20Revised:2019-12-3Online:2019-12-25
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
樊杰(1961-),男,陕西西安人,研究员,博士生导师,中国地理学会会员(S110005375M),主要从事经济地理学与区域综合研究E-mail:fanj@igsnrr.ac.cn。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (5095KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
樊杰, 王亚飞, 梁博. 中国区域发展格局演变过程与调控. 地理学报[J], 2019, 74(12): 2437-2454 doi:10.11821/dlxb201912002
FAN Jie.
1 引言
区域研究是地理学永恒的一个主题[1,2,3]。在地理学发展史上,区域研究一度被轻视,地理学的基本学科属性和核心价值随之受到很大影响。近年区域研究的复兴,对地理学的复兴起到了推动作用[4,5]。在工业文明时期,区域发展的研究局限于区域经济增长及其相关方面,主要是经济地理学关注的领域[6,7]。随着区域发展内涵的扩大,特别是可持续发展目标指向的区域发展、生态文明建设的区域发展、全面实现现代化过程中的区域发展,区域发展研究正在成为综合地理学研究的主题,这也使地理学不同学科领域从不同视角研究区域发展成为可能、也成为必然[8,9]。高质量区域发展无疑将成为中国地理学在新时代研究区域、彰显和提升地理学价值的经典但具有全新内涵的方向,其核心命题仍将是区域发展的格局和过程,或者说是可持续地理过程和格局[10,11]。现有侧重于国家、省级层面等宏观尺度的区域发展的格局和过程研究,普遍采用人均GDP[12,13]、人口或城镇化率[14,15]等指标,主要关注区域发展阶段划分[12]、空间相关与区域收敛[16,17]、区域差距的演变[18,19]、区域经济驱动力分析[20]等。一些****从自然地理分 异[21]、经济与人口重心的耦合态势[22]、低碳经济政策[23]等方面分析不同因素对区域发展格局演化的影响。这些研究通常局限于区域经济维度,缺少社会、生态等维度的综合分析。当区域可持续发展兴起以及区域协调发展战略提出以后,区域发展的可持续性、协调性的测度与解析受到广泛关注,社会、生态等综合分析逐渐被纳入其中[24,25,26]。但这些研究往往忽略了区域的功能定位以及区域发展模式的分异,在解析、调控未来高质量区域发展时就显得相对薄弱。
本文通过借鉴各国发展的经验教训,依托区域差距演变的倒“U”型统计规律,针对中国区域高质量发展对区域格局调控的要求,解析了1978年以来40年中国区域发展格局演变过程,探索未来中国高质量区域发展的科学内涵和区域模式,讨论了未来30年中国区域发展格局的调控重点。纵观1978-2050年区域格局演变历程(图1),① 西部大开发战略已实施20年左右的时间,建设重点是生态环境与基础设施建设,2020年之后的30年,西部大开发应进入高质量发展阶段,在促进区域协调发展中发挥重要作用。 ② 1978-2020年40多年间,是区域发展倒“U”字型结构的前半段,即区域经济发展水平差距不断扩大的阶段;2021-2050年还有30年的时间,应该实现区域协调发展,从历史的发展经验看,区域协调发展较一部分地区先富起来更艰难。③ 2020年是全面实现小康社会目标、开始启程向全面实现现代化目标迈进的转折点,过去的发展历程是“非高质量的”“不生态文明的”,未来要高质量区域发展、要按照生态文明建设要求实现区域现代化。因此,正确理解过去40年左右发展历程,研讨未来30年高质量区域发展理论模式,是实现区域发展科学转型的根本保障。
图1
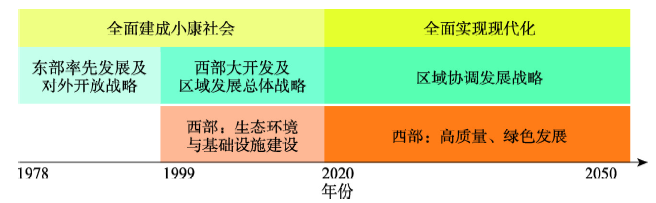 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1中国区域发展战略重点的演变历程
Fig. 1The evolution of strategy focus of China's regional development
2 1978年以来中国区域发展格局变化过程
2.1 中国区域发展与区域间差距持续扩大
1978-2018年,中国区域发展迅猛、格局变化剧烈,成为全球地表经济地理格局发生变化程度最大、对全球经济地理格局影响最大的区域[27]。40年来,从人口集聚过程看,城镇人口由1.72亿人增加到8.13亿人;从经济发展过程来看,地表承载的经济产出密度由1.56×104美元/km2增加到1.25×106美元/km2,经济总量在全球的占比由1.75%上升到15.4%,人均国民总收入(GNI)的排序由全球第175位提高到第68位;从基础设施布局来看,铁路营业里程从5.17×104 km增加到1.27×105 km,高速公路从无到有,2018年增长到1.36×105 km;从资源开发程度来看,全国城市建成区面积5.4×104 km2,比1981年末增长6.7倍;从对环境扰动程度来看,2018年碳排放总量接近100亿t,较1980年增长7倍。中国区域发展深刻地改变着全球经济地理格局(图2)。图2
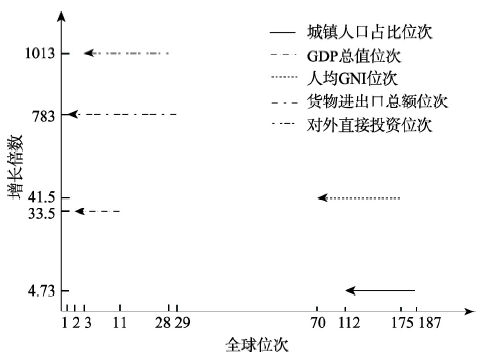 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2中国区域发展主要指标的全球排序
Fig. 2The global ranking of the main indicators of regional development in China
在过去40年,中国区域发展的方针是“让一部分地区先富起来”,尽管在跨入21世纪后试图通过区域发展总体战略①(①区域发展总体战略:由“西部大开发、东北及老工业基地振兴、中部崛起、东部率先发展”构成)调整这一方针,试图采取“先富起来带动欠发达地区,实现区域协调发展”,但总体上说效果并不显著。2007年樊杰在中共中央政治局集体学习讲解“国外区域发展情况与中国区域协调发展”时,对区域协调发展给出了4个内涵的定义[28,29]:即人均GDP的区域差距趋于缩小,区域经济发展与自然承载力相适应,区域经济发展的比较优势得以发挥,区域间基本公共服务均等化。尽管该时的区域发展内涵已经扩大,但在这个发展阶段,用人均GDP衡量区域差距依然是关键指标,先富起来的地区与欠发达地区之间的经济发展差距仍在持续扩大(图3)。2010年开始实施主体功能区规划,明确承担不同功能的区域发展应是“经济社会生态效益相统一” ②(②《生态文明建设总体方案》确定的国土空间开发原则是:“人口资源环境相均衡,经济社会生态效益相统一”,后者是指,无论承担何种主体功能的区域,不能只强调某一方面的效益,重点生态功能区也要有相应的经济效益。按照综合空间均衡理论[29],经济效益应达到使该类型区实现与其他功能区平衡的水平),但居民收入水平之间的差距依然在扩大。用经典的经济地理学理论阐释,过去中国区域发展正在经历着区域发展差距变化的倒“U”字型曲线的前半段,各种生产要素依然向获取更多收益的区域集聚,而人口集聚过程滞后于经济集聚过程,从而导致区域经济差距尚未达到最大值、依然处于不断拉大的过程中。
图3
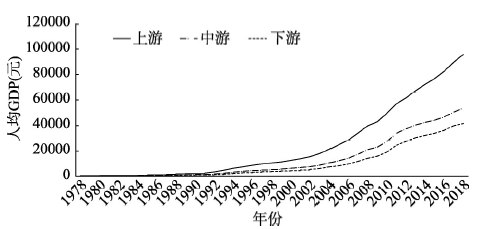 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图31978-2018年中国上、中、下游省区人均GDP的变化情况
注:上、下游相应为经济最发达、欠发达的前与后8位省区。
Fig. 3The change of per capita GDP in upstream, middle and downstream provinces from 1978 to 2018
世界各国区域发展格局演变的规律证实了倒“U”字型曲线的存在,而区域发展差距从扩大到缩小出现的拐点区间,通常是发生在人均GDP 10000美元左右的发展阶段。也就是说,此后的发展将出现区域经济差距趋于缩小的态势。这一过程不只是客观规律的表达,其实更是对调控政策“阀门”出现时机的揭示,当区域发展到这个阶段时,政策就应该转变为缩小区域发展差距,如果国家整体经济水平不能持续提升,长期停滞在10000美元左右的发展阶段,区域经济发展差距问题始终得不到解决,成为“中等收入陷阱”的特征表现之一;反之,如果要提升国家经济的整体水平,区域政策的着力点和区域发展战略就应当转向为积极缩小区域发展差距。区域发展差距的演变与国家经济整体发展状况具有相辅相成的互动关系。2018年底中国人均GDP达到6.46×104元人民币,折合9752美元,2020年达到10000美元的转折点是可预期的,这就意味着,中国的区域发展也应该进入一个拐点区间。中国区域发展进入人均GDP 10000美元拐点又面临着同世界任何一个国家历史上不同的发展背景,即其他国家都是在工业文明的要求下的转型,而中国是在生态文明建设总体要求下实现区域发展转型,这就需要区域发展模式的创新,以及支撑模式创新的理论创新。
2.2 中国区域发展格局的顺时针旋转过程
以1978-2018年中国31个省(市、区)人均GDP和城镇化率为样本,结合数据分布情况,逐年将全国各省区划分为上游、中游、下游三类区域,刻画中国区域发展格局的演变趋势(图4)。经济发展水平的区域分布格局在东南方向上发生旋转,以东北—西南向的经济发展水平差异演变成沿海—内陆向、进而演变为目前东南—西北向的经济发展水平差异的格局特征。人均GDP上游地区和下游地区的比值由1978年的2.45增长到2006年的最大值2.91,随后缓慢减少至2018年的2.27;但其绝对差值由1978年为407元,持续扩大至2018年的53817元,按照可比价格换算后,增长了18.85倍。京津、江浙沪、闽粤等主要沿海省区人均GDP长期处于高值区域,且平均增长速率高于全国水平近2个百分点;西藏、云南、贵州、广西等西南省区处于低值区域,平均增长速度长期低于或接近全国水平。从城镇化率表征的人口集聚程度来看,人口集聚的过程要滞后于经济集聚,如此导致经济发展水平上游区域与下游区域的差距越发拉大。图4
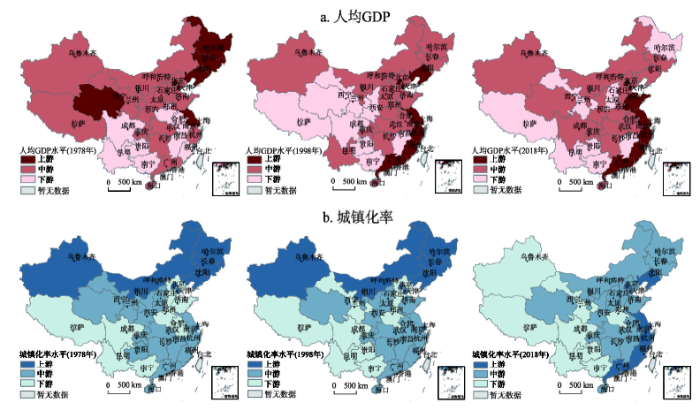 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图41978-2018年中国区域发展格局演变
Fig. 4Evolution of China's regional development pattern from 1978 to 2018 (a. per capita GDP, b. urbanization rate)
以人均GDP为例,对全国省区按照其演变格局特征分为以下几类:① 全国排位长期保持稳定类型,包括稳定上游型、稳定中游型、稳定下游型;② 显著上升型,包括从中下游跃至上游的前进飞跃型和从下游不断追赶至中游的后进追赶型;③ 显著下降型,包括从上游退至中下游的前退失利型和从中游退至下游的后退落后型。分析每种类型研究区的人均GDP差异及变化,并与全国进行对比,得到各种类型区对中国区域差异变化的贡献率(表1)。结果表明,稳定型的区域,特别是稳定的高值区和低值区,对区域差距的变化贡献很大,在各阶段贡献率均超过了50%,这也促成了中国人均GDP两端的极端化。中国的人均GDP格局近些年来已经趋于稳定,可见这种稳定态的地理格局仍将在未来一段时间持续驱动中国的区域差距变化。
Tab. 1
表1
表1区域发展格局演变对区域发展差距变化的贡献率(以人均GDP为指标)
Tab. 1
| 区域类型 | 1978-1998年 | 1998-2018年 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 区域简称 | 贡献率(%) | 区域简称 | 贡献率(%) | ||
| 稳定上游型 | 沪、京、津、苏 | 34.56 | 沪、京、津、粤、浙、苏、闽 | 31.81 | |
| 稳定下游型 | 黔、川 | 17.93 | 青、甘、黔 | 22.73 | |
| 后退落后型 | 藏、甘、陕、赣 | 17.58 | 黑、冀、晋、云、桂 | 22.29 | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
对内改革和对外开放是中国区域发展格局演变的两大驱动力,以非公有制经济和外向型经济为指标探究对内改革和对外开放两大驱动力的影响作用。由于数据的可获得性以及统计口径原因,连续性的单一指标难以获得,因此采取多指标合成法③ (③非公有制经济水平指标包括:私营企业从业人员占总人口比例、个体从业人员占总人口比例、工商登记注册的私营企业和个体就业人数及其占总人口比例、私营工业企业主营业务收入、私营工业企业利润总额等;经济外向度水平评价指标包括:实际外商直接投资及其它投资、进出口总额(按境内目的地、货源地分)、进出口总额(按经营单位所在地分)、年末登记的外商投资额、签订对外承包工程合同数额、国际旅游收入、外国游客人数等。),加权计算得分,对驱动力进行评价。按照与人均GDP与城镇化率相同的分级方法和重心计算方法,逐年将非公有制经济水平与经济外向度水平划分为上游、中游、下游三类区域,并计算各级重心移动轨迹。研究表明,非公有制经济上游地区由环渤海区域逐渐扩大为东部沿海区域,整体上呈现南移趋势;而外向型经济水平分布格局基本稳定,东南沿海始终是外向型经济发展最具优势和潜力的主要区域(图5)。
图5
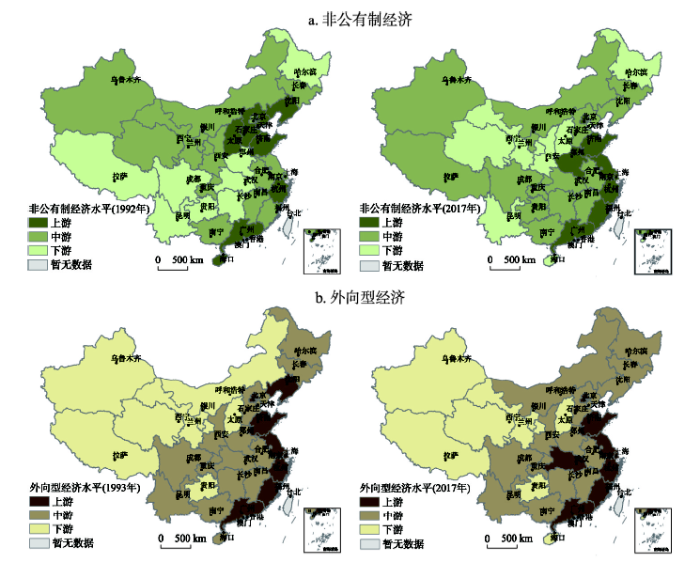 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5中国非公有制经济与外向型经济发展格局演变
Fig. 5Evolution of the non-public economy (a) and the export-oriented economic (b) pattern
将非公有制经济、外向型经济与人均GDP、城镇化率进行叠加,结果表明(图6),非公有经济和外向型经济对城镇化、人均GDP具有强烈的驱动作用。非公有制经济和外向型经济对经济人口格局的驱动作用体现在其二者重心之间的距离逐步缩小,经济人口重心持续向两个驱动力重心的方向迁移(表2)。从重心距离的缩短程度来看,非公有制经济对经济和人口格局的驱动作用稍大于外向型经济,自20世纪90年代以来二者重心间的距离均缩短了近50%。同时,两个驱动力在前期的驱动作用均大于后期,目前二者重心间的距离已经趋于稳定,表明经济人口格局演变已由加速运动转为低速运动。从逐级重心来看,各级驱动力指标重心均位于该级经济人口指标重心运动轨迹的前方,即上游驱动重心为东部各省经济人口提供了向南迁移的引力,下游驱动重心为西部各省经济人口提供了向北迁移的引力。各级经济人口重心均向着其驱动力重心所在方向迁移,从宏观上就表现为中国的经济人口格局大致呈顺时针旋转的演变趋势。
图6
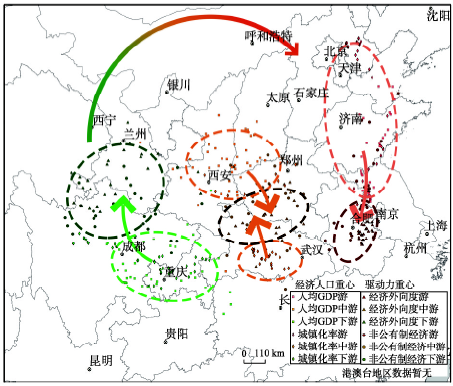 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6中国外向型与非公有经济驱动区域发展格局变化图示
Fig. 6China's export-oriented and non-public sector driving regional development pattern change
Tab. 2
表2
表2中国区域发展重心与驱动力重心间的标准化距离
Tab. 2
| 年份 | 人均GDP—外向型经济 | 人均GDP—非公有制经济 | 城镇化率—外向型经济 | 城镇化率—非公有制经济 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 2001 | 0.870 | 0.636 | 0.838 | 0.555 |
| 2009 | 0.817 | 0.539 | 0.633 | 0.479 |
| 2017 | 0.761 | 0.554 | 0.632 | 0.481 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 中国区域发展稳定性菱形结构
现阶段以非公有制经济和外向型经济为代表的驱动力格局与以人均GDP、城镇化率表征的经济人口格局趋于一致,中国区域发展格局逐渐趋于稳定。逐步形成了以京津冀、长三角、珠三角、成渝地区四大核心区域为顶点、相邻区域的连线为边界合围成的大致菱形结构(图7a)。改革开放以来,菱形顶点、菱形内部、菱形外部的经济发展分别表现出集聚、稳定、分散的变化趋势,其中南端顶点的广东省经济总量占比由1978年的5.46%增长到2018年的10.50%。菱形顶点区域作为全国人才、技术、资本的集聚地,持续发挥着引领全国经济发展、参与全球各国竞争与合作的重要作用,经济持续集聚,近年来稳定在45%左右。菱形内部的经济占比总体稳定在32%左右,菱形外部经济持续分散,GDP占比由27%降至23%,其中东北地区由1978年的13.68%下降到6.45%,成为下降的主要贡献区(图7b)。中国的东西经济比重差异在改革开放初期就已经显著,并持续扩大,东部地区与中、西部地区的经济比重差异分别由1978年的20.92%、29.45%扩大到2018年的30.89%、35.30%,而东部地区内部也分异明显,主要的经济份额由东北地区向东南地区转移。中国的南北经济差异在改革开放初期并不明显,但扩大速率快于东西差异,由8.05%扩大到21.84%。南北差异的扩大速率是东中、东西差异扩大速率的1.38倍、2.36倍,使得南北差异目前已接近东西差异的水平。中国经济发展的区域差异正逐步由以东西差异为主导转变为以东西差异和南北差异二者并存为主要特征(图7c)。图7
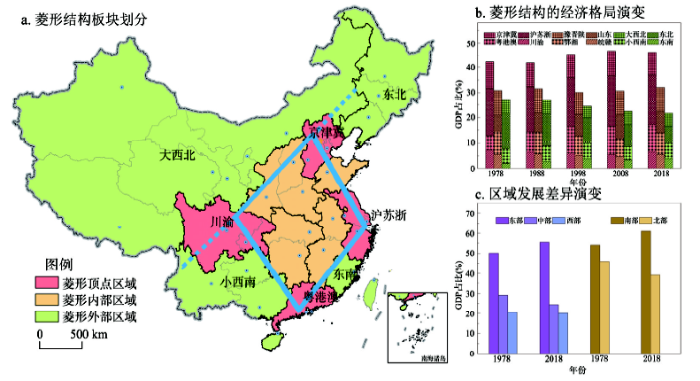 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7中国区域发展格局的菱形结构
Fig. 7The diamond structure of China's regional development pattern
3 高质量区域发展的科学内涵与模式探索
过去40年中国区域发展格局变化的核心问题在于以人均GDP表征的区域差距绝对值仍在不断拉大,在此过程中最为突出的表现是人口集聚明显滞后于经济集聚。2018年区域发展处于上游的省区GDP占全国的比重为44.20%,远高于29.59%的人口比重。尽管人口与经济格局变动并未同步,但其方向仍为一致,与自然承载力、尤其是与考虑到地理区位以及系统整体性的地域功能适宜性的格局趋于一致。但离高质量的区域发展要求仍有较大差距,表现为生态环境、社会福祉的提升明显滞后于经济发展。2018年《可持续发展目标指数和指示板全球报告》指出,中国与经济发展相关的消除贫困和促进经济增长可持续目标位于前列,而城市可持续发展、减少不平等、保护陆地和海洋生态等与环境、社会相关的目标排名均位于中后位[30]。明确高质量区域发展的科学内涵,探索功能指向的高质量区域发展模式以及空间治理体系,是扭转拐点之前区域差距不断扩大的重要基础。3.1 高质量区域发展的科学内涵
高质量区域发展是以区间效益等值为基本目标,立足功能分异的区域模式,兼顾长期与短期效益最优的发展方式。其核心内涵主要包括(图8):首先,高质量区域发展追求区间效益等值,要求缩小经济差距且将生态、社会价值化,其重要标志是人均差距的不断缩小。与拐点之前性质不同的是,这种人均差距是指人均综合效益的差距,由经济效益、社会效益和生态效益共同构成[31,32]。其次,高质量区域发展既要寻求短期效益最优,又要顾及长远效益最优。区域作为人地关系地域系统,其发展状态取决于人类社会与自然环境两大系统的耦合状态,高质量区域发展首先要建立在人类社会与自然环境两大系统的可持续发展之上,在短期侧重于增强经济竞争力的同时,也要促进生态系统的可持续性以及社会公平性[33,34]。图8
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8高质量区域发展的科学内涵
Fig. 8Scientific connotation of high quality regional development
显然,任何长短期以牺牲生态效益或社会效益实现区域经济效益持续增长的弱可持续或不可持续的方式,都是非高质量的区域发展(图9a)。高质量区域发展在短期和长期均要求实现经济效益、社会效益、生态效益的同向发展(图9b),这与强可持续的观点在一定程度上保持了一致[35,36,37,38]。更为重要的是,高质量区域发展综合效益的实现建立在与区域相适应的功能导向的基础上,根据资源环境承载能力、发展基础和未来潜力,明确各区域在全国层面的主体功能定位[39,40]。针对主体功能定位,发挥区域比较优势,采用不同区域发展模式,从而实现国家层面远期人均综合效益的最大化。在近期无法有效消除不同功能区域间人均差距的前提下,采用基本公共服务均等化方式促进区域高质量发展。
图9
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图9非高质量发展与高质量区域发展的对比
Fig. 9Evolutionary process of non-high quality development and high quality regional development
3.2 功能指向的高质量区域发展模式
通过对高质量区域发展科学内涵的探讨可知,高质量区域发展是关于综合效益最大化的目标函数,由地域功能组织、时间或发展阶段等参数共同确定。对于某一区域R来说,其高质量区域发展的目标函数可表示为:式中:
高质量区域发展函数解析的关键在于:
(1)高质量区域发展的综合效益U是有关时间t的增函数,但对于每个时刻t均存在一个最优值E,这与区域R的功能组织方案及其各功能区采取的发展模式密切相关。区域R合理的功能组织,也就是每一个子区域ri的主体功能定位,取决于其资源环境承载能力、发展基础和未来潜力。正是由于功能的合理组织,使得综合效益U通常远大于子区域ri的最大效益
(2)不同功能的综合效益
图10
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图10不同功能指向的高质量区域发展模式
Fig. 10Pattern differentiation of high quality regional development in different function zones
(3)对于高质量区域发展的任一功能区域,生态效益
式中:
(4)不同功能区ri、rj的人均综合效益
3.3 主体功能区统领空间治理体系
实现不同功能区高质量发展的区域模式,必须建立在强有力的空间治理体系的前提下。未来30年,面向全面实现现代化的目标,打造高品质国土空间、建成美丽中国,调控和优化区域发展格局既是目标、也是路径。特别是面对世界百年未有之大变局、面对高质量发展的新要求,调控和优化国土空间格局将更加依赖空间治理体系和治理能力的现代化。在中国的治理能力和治理体系现代化建设中,空间治理是相对薄弱和落后的。未来,应以主体功能区的“区划—战略—规划—制度”为主线,健全空间治理体系,提升空间治理能力。目前,主体功能区是唯一能够纵向自国家到地方、横向涉及几乎所有与国土空间利用相关部门的空间治理手段,顶层有着对全国国土空间的总体结构设计和指引,在基层对每个县域有着主体功能定位和约束的基础制度,同时又给出了从国家层面管控中国国土有序开发和保护的总体蓝图。① 区域发展格局是一个复杂、开放和动态的系统,优化和调控需要科学依据、需要对格局形成与演变规律有准确的把握。主体功能区划是科学认知国土空间开发保护格局的成果,具有规划属性,可作为空间治理的基础底图和基本依据。② 主体功能区是中国经济发展和生态环境保护的大战略[41],主体功能区三大战略格局具有顶层设计、长周期稳定的特征,在各类空间布局规划和方针政策制定中,特别是对降尺度的各层级地域单元确定发展战略和规划部署时,具有了指引作用。应发挥主体功能区战略作为发展规划与空间规划之间旋转门的职能,从而实现发展规划和发展战略对空间规划有效的上位指引。③ 通过健全国土空间规划体系,推动主体功能区战略的精准落地。把主体功能区规划作为国土空间规划的有机组成部分和空间治理的上位规划内容,通过国土空间规划体系,将主体功能定位有效传导、精准落地,传导的方式是功能—结构,而且可以成为总规与专项规划、总体布局图与专项布局总图的衔接基础,也是未来动态监测和实施评估的主要依据。④ 充分发挥主体功能区基础性制度的作用,成为各类区域政策的基本遵循,具体内容包括:
(1)管理“人”的制度。改变以往无论是城市化地区还是生态脆弱地区,领导干部政绩考核都采用一样的指标体系的做法,按照功能定位确定领导干部绩效考核指标体系和标准;按照功能定位引导人口在空间上的合理流动,实现人口与经济相均衡的区域格局。
(2)管理“自然”的制度。按照主体功能区制度制定并动态调整区域环境容量总量管控方案,使中国的环境质量管理真正做到为各地区在全国可持续发展中承担的功能不同、而有不同的环境质量目标的管控途径;对土地、水资源的空间配置,亦然是按照主体功能定位实施。通过对不同功能区进行资源环境承载力监测预警,实现对中国可持续发展的状态进行动态跟踪、对区域政策进行及时调整。
(3)管理“钱”的制度。对生态功能区生态产品和粮食主产区的农作物产品,通过政府财政专项转移支付,实现承担不同功能的区域都能够在实现生态效益和社会效益最大化的同时,也获得必要的经济效益,最终达到综合效益在区域间的均衡。此外,投资的区域指向也应依托主体功能区战略格局和区域布局,实现国家直接投资和引导社会投资的空间指向合理化。
(4)管理“产业”的制度。基于功能区建立产业正面和负面清单,弥补市场机制对产业空间布局中的失灵环节,增强国家和地方产业发展竞争力。
4 未来30年中国区域发展格局的调控重点
未来30年区域发展格局演化目标,是形成与全面实现现代化目标相符的国土空间开发保护格局。按照区域发展格局演变规律和区域高质量发展的理论模型,未来区域发展格局优化的重点是:① 实现人口与经济的空间均衡,逐步实现各省区在全国人口和经济总量中所占比重基本相等、并最终实现各地市在本省区两个占比基本相等;② 实现人口经济与地域功能适宜性的空间均衡,以人口经济不超越由资源、环境、生态和灾害等不同可持续属性指标构成的自然承载力可承载范围为底线,同时,与由自然承载力、战略区位、系统整体性等构成的地域功能适宜性的空间分布相吻合;③ 实现区域发展数量增长与质量增长的空间均衡。为此,未来30年聚焦优化国土开发保护格局的目标,调控的重点聚焦在重点城市化地区、相对欠发达地区、重要安全保障区等3类区域以及区域间互动关系等方面。4.1 重点城市化地区
顺应人口经济向“菱形”顶点区域集聚、以及人口经济格局顺时针方向旋转的基本态势,以城市群、都市圈和中心城市地区作为重点城市化地区,通过人口与经济的同步集聚实现区域发展格局在进一步的集聚过程中的均衡过程。调控重点是:(1)中国人口经济分布格局顺时针方向旋转的过程,到2035年依然延续,主要表现是东南半壁——长三角到珠三角的区域经济比重将持续提升。尽管外向型经济的拉力有可能削弱,但区域已经形成起来经济基础和比较优势将发挥越来越大的作用。顺应这一态势,一方面,推进菱形区的顶点城市群区域的极化过程,在国家尺度上,推动人口经济向长三角地区、粤港澳大湾区2个东南地区的高度城市化区域,以及北方的京津冀地区和西部的成渝—关中地区的集聚。另一方面,在2035年前突出协调沿海和内陆发展为重点,2035-2050年以解决南北向差距为重点,前者重点推进菱形内部区域的长江中游城市群、以及小西南地区(滇桂黔)的经济增长。
(2)在集聚中趋于均衡是未来区域发展格局演变、也是调控优化的主导趋势。除国家尺度上的菱形4顶点区域城市群人口和经济比重持续提升外,在区域板块和省级尺度上,加速人口经济向城市群地区及其内部的都市圈集聚;在地市级尺度上,引导人口经济向中心城市集聚。其中,长三角、珠三角和京津冀的核心区域是中国参与全球竞争和国际分工合作的枢纽区,在城市基础设施和公共服务设施覆盖范围内,紧凑集约的城市建成区与周边低密度居民点构成的城镇化区域、以及开敞绿色空间复合并存,共同构成全域城镇化发展格局。同过去30年集聚过程不同的是,经济集聚的同时必须实现人口同步集聚,最终达到经济占比与人口占比大致相同。
(3)为实现城市群、都市圈和中心城市在功能上持续提升,根据国家在政治、经济、社会、军事、文化和对外交往等方面的宏观战略需求,在符合国家战略、体现国家意志、肩负国家使命、引领区域发展、跻身国际竞争领域、代表国家形象的现代化大都市中,在全国自上而下统一布局,打造一批国家中心城市,以履行国家职能,提升国家级城市群、都市圈等都市区域的中心功能。国家中心城市建设首先要转变以规模等级为核心的评价标准,应重点关注城市履行国家职能的潜力和影响力。此外,国家中心城市建设要和国际化进程结合起来,通过配套设施、优惠政策、配套资金的完善,营造成为全球从事相关行业人才的首选地。
4.2 相对欠发达地区
在中国“菱形”区域发展格局中,未来从全国尺度上看,菱形左上边线的延长线划分的大西北(甘肃、新疆、宁夏、内蒙古、西藏和青海)将是实现现代化的难点区域。如果着眼类型区域,存在较大城乡发展差距的乡村地区、以及全国相对贫困地区(通常也是乡村)也是难点地区。我们将这些区域统称为相对欠发达地区。促进中国相对欠发达地区发展,一方面要依托上述重点城市化区域的发展,通过吸纳人口和经济带动作用;另一方面则是创新相对欠发达地区发展模式,调控的重点如下:(1)用30年时间打赢扶持相对贫困地区发展的持久战。按照全国人均收入水平的50%~60%以下衡量中国相对贫困人口,其总数以及区域分布依然相对稳定,解决相对贫困问题依然严峻。以青藏高原为主攻地和先行示范区为例,这里是中国面积最大的集中连片特殊困难地区,抓住川藏铁路的建设机遇,将长江经济带拓展到拉萨、林芝等青藏高原腹地,促进内陆与青藏高原的同频共振。引导当地人口向非农产业发展的核心区和城镇集聚,进一步降低自然保护区、牧区的人口密度和资源环境压力。建设地球第三极国家公园群,以强度小于1%的土地低密度开发、实现对99%以上的国土空间严格的生态保护,把当地老百姓纳入国家公园建设与经营当中,解决牧民持续增收和区域可持续发展问题。
(2)依托多种资源优势,以科技创新和现代管理方式创新促进绿色发展,切实助推大西北地区进入高质量发展的新阶段。大西北地区要通过新一轮大开发到2050年与全国同步全面实现现代化,未来30年必须要进入经济转型升级和高质量发展的新阶段。面向全球市场发展的新形势以及全国人民群众日益增长的物质财富及其日趋成熟的市场需求,依托自然资源禀赋的优势,结合科技创新与现代组织管理方式的创新,紧扣资源的绿色开发与产业绿色布局,按照科学路径进行合理布局和配置。重点包括以生态绿色为基底的全域现代化旅游业、以生物技术和生命科学为先导的现代生物产业、建立全国绿色能源配额制和绿色能源指标采购机制的能矿业与资源加工产业链。
(3)推进城乡等值发展,创新城市周边半城镇化模式,打造具有中国特色的新农村发展的新面貌。打造各具特色、但满足人的居住生活和事业发展的综合价值相等的中国新型城、乡协调格局,实现乡村也一样让人的生活更美好。从人口流动上,城乡必须是双向合理的流动,建立城市能够留住乡村转移人口的机制,同时要创新城市人口转移下乡的制度保障。城乡必须是各具文化特质,各具自然生态特点、各具社会形态、建筑风格和规划品质、以及与各自人口构成和产业特质相适应的居民点。乡村在基础和公共服务设施建设水平方面应满足乡村人民生活福祉现代化的要求。推进中国城郊边缘区及近邻大都市周边的乡村区域、旅游休闲资源良好的非城市地区、分散的能源矿产资源开发区、以农副产品加工为支撑的农村工业发达区、通过经营方式转型的林业工人工作和生活区等开展的新农村区域的半城镇化建设,实行城市规划与管理,推动主要就业形式、收入来源构成、公共服务和基础设施条件、生活方式和社区文化等方面与城镇化地区相接近,将半城镇化打造为中国城镇化空间形态的一种补充形式。
4.3 重要安全保障区
从国土空间和区域发展格局的角度,主要包括保障生态安全、粮食安全、能源安全和国防安全的关键地区。调控重点:(1)中国生态空间内人口规模仍然偏大、农业空间内人口密度仍然偏高,是未来安全保障区建设的难点,也应当作为调控的重点。进一步疏散生态敏感和重要地区、粮食安全保障和重要农产品供给地区的超载人口,采取有效疏散途径,适度地降低人口规模与密度。通过“大集聚”实现“大疏解”,引导人口流动和空间演进过程,通过提升全国整体城镇化水平,引导每个区域都能按照主体功能定位,遵循生活空间宜居、生产空间集约、生态空间秀美的要求,确定区域发展目标和路径,实现国土空间开发保护格局的系统优化。能源安全区主要是应对清洁能源、可再生能源的结构转型,在空间上有效开发和合理利用太阳能、风能和水能资源。
(2)坚持国土安全和边境稳定高于一切,包括生态安全、粮食安全等在内,如果存在与国土安全和边境稳定的冲突,也应当取舍和让位。加大政策扶持力度,繁荣边境经济,完善体制机制,提高人口吸引力,避免人口外流。要以边境旅游和边民互市为抓手,发展红色旅游体验地、边境前哨参观教育地、边境民俗文化旅游产业,完善统管放行机制,把扶持集体经济发展作为抵边富民的重要途径,建设“以我为主”的边疆经济体系。不断提高边疆民族特色小镇的建设品质,加快实施抵边村建设,将人口和居民点抵边推进,形成人口和城镇的相对集中带。促进富民工程与守边基础设施融合发展,实现军民融合共建村镇、繁荣产业经济,构建军民融合的稳边固边基本格局,建设美丽富饶的新边疆。
此外,围绕以上3个重点调控的区域类型,协调区域间相互作用关系,也是区域发展格局优化不可或缺的内容。① 把引导人口合理流动作为区域间互动的关键,实现人口与经济空间均衡。国家尺度上建立疏解超载区域人口的机制,重点提升疏解人口迁徙能力和再就业能力的培育。省级尺度上应合理配置人口的空间分布,按照主体功能定位形成人口分布的中心—边缘模式[40]。城乡间建立人口相互流动机制,带动城乡一体化发展。② 把经济收益分配作为空间均衡政策的重要抓手,建立生态与农业产品的国家购买和生态农产品补偿制度,在动态调控中助推农业和生态区域实现生态、社会与经济效益相统一。③ 启用市场机制,通过洁净能源配额制、碳排放市场交易、生态安全体系建构的共同责任分担机制等,实现生态产品的价值化和市场交易过程。④ 发挥社会主义制度优越性,在继续强化省区市间横向对口支援的互动渠道的同时,将各种类型的所有制企业纳入支援的网络系统,形成先富带后富的新格局。
5 结论
调控和优化区域发展格局,一直是中国每个重要的发展阶段都高度关注的国家战略。中华人民共和国成立到改革开放的30年时间里,“156”项重点工程的区域布局、“三线”建设的空间配置、两次大规模成套设备引进在全国的选址落地,以及农业区划和基础设施网络系统的总体布局,为改革开放后经济腾飞奠定了基础。改革开放以来,从4个经济特区到沿海14个开放城市再到沿海地带全面开放等开放空间路线图的设计、4个板块构成的区域发展总体战略的实施、主体功能区战略和基础制度、以及京津冀—长三角与长江带—粤港澳大湾区等战略区域的发展,为全面建成小康社会提供了坚实的保障。改革开放40年,中国区域发展格局演变过程在实现经济向具有比较优势的区域集聚、以最快的速度推动中国整体经济实力提升的同时,人口集聚相对滞后,导致区域间经济发展水平的差距持续扩大。充分发挥区域经济比较优势推动国家经济整体迅猛提升、人口集聚相对滞后经济集聚过程而导致区域经济发展水平扩大,是这个发展阶段最主要的特征。与此同时,人口经济相对集聚过程趋于同自然本底条件相均衡,社会发展普遍滞后于经济发展、特别是发达地区社会发展水平与经济发展水平的滞后程度更大,区域生态环境质量的改善并没有能够同区域经济发展水平提升同向或同步、特别是发达地区普遍存在环境质量恶化及人口经济集聚超越环境容量的现象,成为这个发展阶段“非高质量”发展的主要表现。区域发展不充分、不平衡的表现严重制约了人居环境和人民福祉的改善,也成为投资环境和营商环境——特别是现代经济的发展环境的短板,自然生态系统的可持续性也有所降低。
未来30年,面向全面实现现代化的目标,应把实现区域发展格局演变尽快步入拐点区间、进而走向区域发展差距缩小作为战略取向,人口与经济均衡集聚,在集聚中实现区域均衡和协调发展;在经济持续增长过程中实现与生态、社会效益的同向与基本同步的增长,通过地域功能导向下的区域高质量发展模式实现区域发展综合效益的均衡;建立以主体功能区统领的现代空间治理体系,在现代治理法制化、科学化、系统化和精准化中实现对区域发展格局的合理调控和优化。区域发展已经从区域经济过程、拓展到区域生态过程和区域社会过程,区域发展已经从区域内拓展为区域间相互依赖、空间升降尺度间的相互作用的过程,区域发展格局的适应与响应也演变成为近远程互馈、社会与环境耦合、发展与治理互动等的全链条和全格局,这为地理学的研究与应用提出了重大的社会需求和科学问题,特别是面对世界百年未有之大变局,地理学必须在深刻揭示国土空间开发保护格局演变规律的基础上,为预判、调控和优化区域发展格局提供系统的科学方案,包括增强数据库和模型库等基础能力,优化和调整主体功能区划方案,创建与国土空间规划和空间治理体系相适应的人才培养和学科设置新模式等,在生态文明和美丽中国建设中实现地理学学科价值。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001URL [本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001URL [本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.05.001URL [本文引用: 1]

To determine the direction and the field of research is the soul of discipline development. Humanistic and Economic Geography is a subject changing in both research field and even research direction. Recognition of research fields and disciplines for Humanistic and Economic Geography is essential. On the basis of combing the main branch development stage of Humanistic and Economic Geography in China for decades, the paper summarized the response of Humanistic and Economic Geography to the transformation development background of the social. On the one hand, the intersectionality of the discipline should be insisted, with the theory of ‘man-land’system as the direction and the combination of theory with practice being adhered. Humanistic and Economic Geography scholars should be with a new attitude and new vision, to think about the future development of discipline key fields, the development idea and the innovation of the theory and method. For the major problems which disciplines involved in a long time, strategic and consultative, predictive and summative work will gradually increase. In the paper, the development trend of some important fields such as information and social space economic organization, the new pattern of regional economy and‘New Urbanization’were expounded; some new ideas about ‘international hot spots’and ‘international frontier’, the theory research and the relationship between the theory and practice were proposed; and then the author put forward the suggestion that‘Humanistic Geography’to be renamed as‘Humanistic and Economic Geography’.
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.05.001URL [本文引用: 1]

To determine the direction and the field of research is the soul of discipline development. Humanistic and Economic Geography is a subject changing in both research field and even research direction. Recognition of research fields and disciplines for Humanistic and Economic Geography is essential. On the basis of combing the main branch development stage of Humanistic and Economic Geography in China for decades, the paper summarized the response of Humanistic and Economic Geography to the transformation development background of the social. On the one hand, the intersectionality of the discipline should be insisted, with the theory of ‘man-land’system as the direction and the combination of theory with practice being adhered. Humanistic and Economic Geography scholars should be with a new attitude and new vision, to think about the future development of discipline key fields, the development idea and the innovation of the theory and method. For the major problems which disciplines involved in a long time, strategic and consultative, predictive and summative work will gradually increase. In the paper, the development trend of some important fields such as information and social space economic organization, the new pattern of regional economy and‘New Urbanization’were expounded; some new ideas about ‘international hot spots’and ‘international frontier’, the theory research and the relationship between the theory and practice were proposed; and then the author put forward the suggestion that‘Humanistic Geography’to be renamed as‘Humanistic and Economic Geography’.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408006URL [本文引用: 1]

Papers published in Acta Geographica Sinica are academically regarded as of high quality, speciality and practice-oriented studies. Reviewing these papers can help us better sketch the contours of the development of economic geography in China. This article examined 421 economic geography papers published in Acta Geographica Sinica from 1934 to 2013 based on the number of papers, evolution tracks, research paradigm, topics, and the development of sub-disciplines, and concluded that economic geography research in China has made considerable progress. But this progress remains uneven among sub-disciplines of economic geography. It has shown a close link to new issues in economic development, changing from studies on economic growth to sustainable development, from studies pertinent to nature elements to those pertinent to anthropogenic elements, and the study areas having shifted from industries providing tangible goods to economic activities on services aspects. Sub-disciplines focused on regional, industrial, and agricultural studies before the 1980s, while a growing number of papers have since then been published on transportation, service industries, and urban studies. Research ideas in the 80 years originated from various sources, leading to research by using multiple spatial scales and dynamic quantificational methods. In summary, Chinese economic geographical research has always stood close to the nation's requirements, leaning towards macro studies, economic growth, and practical characteristics. However, studies at the micro scale, with comprehensive features and theoretical deductions are emerging increasingly.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408006URL [本文引用: 1]

Papers published in Acta Geographica Sinica are academically regarded as of high quality, speciality and practice-oriented studies. Reviewing these papers can help us better sketch the contours of the development of economic geography in China. This article examined 421 economic geography papers published in Acta Geographica Sinica from 1934 to 2013 based on the number of papers, evolution tracks, research paradigm, topics, and the development of sub-disciplines, and concluded that economic geography research in China has made considerable progress. But this progress remains uneven among sub-disciplines of economic geography. It has shown a close link to new issues in economic development, changing from studies on economic growth to sustainable development, from studies pertinent to nature elements to those pertinent to anthropogenic elements, and the study areas having shifted from industries providing tangible goods to economic activities on services aspects. Sub-disciplines focused on regional, industrial, and agricultural studies before the 1980s, while a growing number of papers have since then been published on transportation, service industries, and urban studies. Research ideas in the 80 years originated from various sources, leading to research by using multiple spatial scales and dynamic quantificational methods. In summary, Chinese economic geographical research has always stood close to the nation's requirements, leaning towards macro studies, economic growth, and practical characteristics. However, studies at the micro scale, with comprehensive features and theoretical deductions are emerging increasingly.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1033.2013.00147URL [本文引用: 1]

The achievements in the forward-looking human-economic geographic studies on the interactions between natural sphere and human sphere as well as the distribution and evolution mechanism of human living and production activities on the earth’s surface have been playing a prominent role in guiding the scientific decision- making and promoting the orderly territorial development. The Eighteenth National Congress of the Communist Party of China has put the optimization of spatial development pattern as the primary task of ecological civilization; this provides an unprecedented opportunity of development and huge demand for human-economic geography. Based on the analyses of the microscopic differentiation and humanizing tendency caused by the emphasis on mechanism and process studies, and the requirements of multidisciplinary supporting system for the construction of ecological civilization, this paper discusses the comprehensive values of human-economic geography as a research field, and re-recognizes the basic categories of the subject from the aspects of factors and mechanisms, interface and process, functions and structure, scale and its conversion. Specifically, this paper discusses the topics such as: (1) the Equilibrium Model for the balance between comprehensive benefits of economy, ecology and society and the stereo system of production, distribution and consumption; (2) carrying capacity evaluation method, oriented toward the interaction between human system and natural system; (3) the theory for the emergence of territorial functions and the identification method; (4) the research innovation by which the planar space of territorial functions is incorporated into the theoretical framework of spatial structures. Finally, in response to the challenges from the replacements among different subjects, four aspects of disciplinary development path are put forward for the future, including: paying equal attention to academic and ideological contents, making comprehensive use of computer methods and experimental methods, emphasizing on the unity of basic theories and applied research, and integrating the innovation of interdisciplinary researches and the dependence on classical paths.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1033.2013.00147URL [本文引用: 1]

The achievements in the forward-looking human-economic geographic studies on the interactions between natural sphere and human sphere as well as the distribution and evolution mechanism of human living and production activities on the earth’s surface have been playing a prominent role in guiding the scientific decision- making and promoting the orderly territorial development. The Eighteenth National Congress of the Communist Party of China has put the optimization of spatial development pattern as the primary task of ecological civilization; this provides an unprecedented opportunity of development and huge demand for human-economic geography. Based on the analyses of the microscopic differentiation and humanizing tendency caused by the emphasis on mechanism and process studies, and the requirements of multidisciplinary supporting system for the construction of ecological civilization, this paper discusses the comprehensive values of human-economic geography as a research field, and re-recognizes the basic categories of the subject from the aspects of factors and mechanisms, interface and process, functions and structure, scale and its conversion. Specifically, this paper discusses the topics such as: (1) the Equilibrium Model for the balance between comprehensive benefits of economy, ecology and society and the stereo system of production, distribution and consumption; (2) carrying capacity evaluation method, oriented toward the interaction between human system and natural system; (3) the theory for the emergence of territorial functions and the identification method; (4) the research innovation by which the planar space of territorial functions is incorporated into the theoretical framework of spatial structures. Finally, in response to the challenges from the replacements among different subjects, four aspects of disciplinary development path are put forward for the future, including: paying equal attention to academic and ideological contents, making comprehensive use of computer methods and experimental methods, emphasizing on the unity of basic theories and applied research, and integrating the innovation of interdisciplinary researches and the dependence on classical paths.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408003URL [本文引用: 1]

In combination with the author's review of frontier issues in human geography in recent years, this paper clarifies that uncovering the spatiotemporal difference rules of human-environment system interaction in the geographic pattern is the highest-level scientific puzzle in modern geography, and is the understanding of key issues which could decide the prospect of future geography. Four practical methods including "process induction, regional comparison, qualitative analysis, logical judgment" until now for integrated human-environment system researches are proposed. Aiming at four frontier fields including regional equilibrium, resources and environment carrying capacity, territorial function, and spatial structure, academic ideas including the driving forces of regional development pattern changes, the impact carrier of natural sphere on human activity sphere, the rules and methods for integrated geographic zoning, and the changing laws of "living-production-ecology" spatial structure, are discussed. Finally, this paper discusses the significance and key issues of regional sustainable development in the framework of "Future Earth", and presents that the integrated method system and basic theoretical system of comprehensive research in complexity science based on "integration of both natural and social sciences" and "interpenetration of both basic researches and decision-making application", will profoundly influence research progress of the process and framework of human-environment system.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408003URL [本文引用: 1]

In combination with the author's review of frontier issues in human geography in recent years, this paper clarifies that uncovering the spatiotemporal difference rules of human-environment system interaction in the geographic pattern is the highest-level scientific puzzle in modern geography, and is the understanding of key issues which could decide the prospect of future geography. Four practical methods including "process induction, regional comparison, qualitative analysis, logical judgment" until now for integrated human-environment system researches are proposed. Aiming at four frontier fields including regional equilibrium, resources and environment carrying capacity, territorial function, and spatial structure, academic ideas including the driving forces of regional development pattern changes, the impact carrier of natural sphere on human activity sphere, the rules and methods for integrated geographic zoning, and the changing laws of "living-production-ecology" spatial structure, are discussed. Finally, this paper discusses the significance and key issues of regional sustainable development in the framework of "Future Earth", and presents that the integrated method system and basic theoretical system of comprehensive research in complexity science based on "integration of both natural and social sciences" and "interpenetration of both basic researches and decision-making application", will profoundly influence research progress of the process and framework of human-environment system.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/xb201304007URL [本文引用: 2]

As important carriers of regional strategy and policy, prefecture-level regions have played an increasingly significant role in the development of China's economy. However, few studies have grasped the essence of economic development stage and spatio-temporal evolution process at a prefectural level. Thus they may lead to a biased policy and ineffective implementation. Based on Chenery's economic development theory, this paper identifies China's economic development stages at both national and prefectural levels. Both Global Moran's I index and Getis-Ord Gi* index are employed to investigate the spatial-temporal evolution of China's economic development from 1990 to 2010. Major conclusions can be drawn as follows: (1) China's economic development is generally in the state of agglomeration. It stepped into primary production stage in 1990, and middle industrialized stage in 2010, with a "balanced-unbalanced-gradually rebalanced" pattern in the process. (2) China's rapid economic growth experienced a spatial shift from coastal regions to inland regions. Most advanced cities in central and western China can be roughly categorized into regional hub cities and resource-dependent cities. (3) Hot-spots in China's economic development moved northward and westward. The interactions between cities and prefectures became weaker in eastern China, while cities and prefectures in central and western China were still on the stage of monomer development, with limited effects on the surrounding cities. (4) While the overall growth rate of China's economy gradually slowed down during the past two decades, the numbers of cities and prefectures in central and western China grew much faster than those in coastal areas. (5) Regions rich in resources, such as Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia, became the new hot-spots of economic growth in recent years. For these regions, however, more attention should be paid to its unbalanced industrial structure and the lagging social development in the backdrop of the rapid economic growth driven predominantly by the exploitation of resources.
DOI:10.11821/xb201304007URL [本文引用: 2]

As important carriers of regional strategy and policy, prefecture-level regions have played an increasingly significant role in the development of China's economy. However, few studies have grasped the essence of economic development stage and spatio-temporal evolution process at a prefectural level. Thus they may lead to a biased policy and ineffective implementation. Based on Chenery's economic development theory, this paper identifies China's economic development stages at both national and prefectural levels. Both Global Moran's I index and Getis-Ord Gi* index are employed to investigate the spatial-temporal evolution of China's economic development from 1990 to 2010. Major conclusions can be drawn as follows: (1) China's economic development is generally in the state of agglomeration. It stepped into primary production stage in 1990, and middle industrialized stage in 2010, with a "balanced-unbalanced-gradually rebalanced" pattern in the process. (2) China's rapid economic growth experienced a spatial shift from coastal regions to inland regions. Most advanced cities in central and western China can be roughly categorized into regional hub cities and resource-dependent cities. (3) Hot-spots in China's economic development moved northward and westward. The interactions between cities and prefectures became weaker in eastern China, while cities and prefectures in central and western China were still on the stage of monomer development, with limited effects on the surrounding cities. (4) While the overall growth rate of China's economy gradually slowed down during the past two decades, the numbers of cities and prefectures in central and western China grew much faster than those in coastal areas. (5) Regions rich in resources, such as Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia, became the new hot-spots of economic growth in recent years. For these regions, however, more attention should be paid to its unbalanced industrial structure and the lagging social development in the backdrop of the rapid economic growth driven predominantly by the exploitation of resources.
DOI:10.11821/xb200906008URL [本文引用: 1]

This article, taking Jiangsu Province as an example, describes the spatial changes of the diverse economy of Jiangsu at county level since the 1990s through the related analysis of ESDA as well as other tools such as Moran's I, Getis-Ord General G, Getis-Ord Gi and the function of variogram and its amount of fractal dimension as scale index. Based on four time discontinuity surfaces, some conclusions are drawn as follows. (1) Considering the overall spatial economic framework, the county economy of Jiangsu province shows a strong trend of spatial natural correlation. The similar areas cluster in space. The space structure of the hotspot distribution tends to be the circular space structure centered on Wuxi and Suzhou. (2) The development of the spatial economic growth framework is likely to be more stochastic and unstable in the aspect of spatial distribution. Hotspot areas are changing frequently without obvious appearance of geographical concentration. (3) According to the space-time mechanism, the Jiangsu spatial economic framework tends to be more continuous and self-organized, the random of the spatial differential pattern keeps decreasing and the mechanism of the structural differentiation caused by natural correlation in space is becoming more and more remarkable. The homogeneousness of economic development in the direction of northeast-southwest is typical for its relatively small spatial difference. As to the opposite direction, the spatial difference is great. (4) The driving force of the evolvement of Jiangsu economic framework can be identified through the following aspects: the basis of historical development, the economic location and the policies on regional development.
DOI:10.11821/xb200906008URL [本文引用: 1]

This article, taking Jiangsu Province as an example, describes the spatial changes of the diverse economy of Jiangsu at county level since the 1990s through the related analysis of ESDA as well as other tools such as Moran's I, Getis-Ord General G, Getis-Ord Gi and the function of variogram and its amount of fractal dimension as scale index. Based on four time discontinuity surfaces, some conclusions are drawn as follows. (1) Considering the overall spatial economic framework, the county economy of Jiangsu province shows a strong trend of spatial natural correlation. The similar areas cluster in space. The space structure of the hotspot distribution tends to be the circular space structure centered on Wuxi and Suzhou. (2) The development of the spatial economic growth framework is likely to be more stochastic and unstable in the aspect of spatial distribution. Hotspot areas are changing frequently without obvious appearance of geographical concentration. (3) According to the space-time mechanism, the Jiangsu spatial economic framework tends to be more continuous and self-organized, the random of the spatial differential pattern keeps decreasing and the mechanism of the structural differentiation caused by natural correlation in space is becoming more and more remarkable. The homogeneousness of economic development in the direction of northeast-southwest is typical for its relatively small spatial difference. As to the opposite direction, the spatial difference is great. (4) The driving force of the evolvement of Jiangsu economic framework can be identified through the following aspects: the basis of historical development, the economic location and the policies on regional development.
DOI:10.11821/xb200503002URL [本文引用: 1]

With fast development of regional economy and society of China, the "Three Macro-Regional Development Zones", which is still in effect, is now hard to meet the requirements of the new situation under the guidance of integrated-considering regional development. According to the demands of the scientific viewpoint of development and the "five-integrated-considerations", after introducing what is a full regional economic system and the actual full four-layer regional economic system of USA, this paper puts forward a new zoning project of the "Three Macro-Regional Development Zones" and the 10 comprehensive economic districts of the regional economy of China: the "New Three Macro-Regional Development Zones" include the Northeast and East Coastal developing zone, the Middle and Near-Reach-West developing zone, and the Far-Reach-West developing zone; the 10 comprehensive economic districts are composed of the Northeast District, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Shandong Coastal District, the Shanghai-Jiangsu-Zhejiang Coastal District, the Guangdong-Fujian-Hainan Coastal District, the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Yellow River District, the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River District, the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Pearl River District, Inner Mongolia District, Xinjiang District, and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau District.
DOI:10.11821/xb200503002URL [本文引用: 1]

With fast development of regional economy and society of China, the "Three Macro-Regional Development Zones", which is still in effect, is now hard to meet the requirements of the new situation under the guidance of integrated-considering regional development. According to the demands of the scientific viewpoint of development and the "five-integrated-considerations", after introducing what is a full regional economic system and the actual full four-layer regional economic system of USA, this paper puts forward a new zoning project of the "Three Macro-Regional Development Zones" and the 10 comprehensive economic districts of the regional economy of China: the "New Three Macro-Regional Development Zones" include the Northeast and East Coastal developing zone, the Middle and Near-Reach-West developing zone, and the Far-Reach-West developing zone; the 10 comprehensive economic districts are composed of the Northeast District, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Shandong Coastal District, the Shanghai-Jiangsu-Zhejiang Coastal District, the Guangdong-Fujian-Hainan Coastal District, the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Yellow River District, the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River District, the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Pearl River District, Inner Mongolia District, Xinjiang District, and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau District.
DOI:10.11821/xb200904001URL [本文引用: 1]

From the essential meaning of urbanization, this paper establishes a comprehensive evaluation index system, including four aspects changing: population, economy, society and land. Based on the method of entropy, the measure and evolution of China's urbanization are analyzed since 1981. The results show that China's comprehensive urbanization level continues improving. Economic growth and geographical landscape are the main features of rapid evolution of urbanization, followed by the population urbanization, and the medical care level of social urbanization is the least advanced. The evolution of all the four subsystems has unique characteristics. The analysis of multiple regression model shows that the driving factors have been diversified. The market force is the most powerful driving force of China's urbanization, followed by intrinsic force, administration force, exterior force. From different stages of urbanization, the effects of market force, exterior force and the administration force on urbanization are increasing, while intrinsic force is decreasing. China's urbanization is the main endogenous process, hence more policies should be formulated to strengthen the market economy reform and coordinate urban and rural development.
DOI:10.11821/xb200904001URL [本文引用: 1]

From the essential meaning of urbanization, this paper establishes a comprehensive evaluation index system, including four aspects changing: population, economy, society and land. Based on the method of entropy, the measure and evolution of China's urbanization are analyzed since 1981. The results show that China's comprehensive urbanization level continues improving. Economic growth and geographical landscape are the main features of rapid evolution of urbanization, followed by the population urbanization, and the medical care level of social urbanization is the least advanced. The evolution of all the four subsystems has unique characteristics. The analysis of multiple regression model shows that the driving factors have been diversified. The market force is the most powerful driving force of China's urbanization, followed by intrinsic force, administration force, exterior force. From different stages of urbanization, the effects of market force, exterior force and the administration force on urbanization are increasing, while intrinsic force is decreasing. China's urbanization is the main endogenous process, hence more policies should be formulated to strengthen the market economy reform and coordinate urban and rural development.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/xb201012010URL [本文引用: 1]

This paper proposes to combine the standard analysis method of economic convergence with spatial econometrics to explore regional convergence based on a total of 240 cities in China. To investigate the kind of spatial autocorrelation and agglomeration, the Moran's I statistic is used, finding that the existence of strongly positive global autocorrelation of GDP per capita and what's more, the local spatial structure is rather stable. The findings suggest that the non-spatial models applied to analyse β-convergence suffer from the risk of misspecification and a spatial model is competent. The results based on the spatial models indicate the existence of absolute convergence between cities. Taking into account effects results in a significant faster rate of convergence. The sensitivity test of the absolute convergence with respect to assumption of a common steady state and robustness over space suggest that the finding of absolute convergence is not stable. The mechanism of diminishing return and technology spillover is both important for absolute convergence. Finally, a set of regional policies are discussed.
DOI:10.11821/xb201012010URL [本文引用: 1]

This paper proposes to combine the standard analysis method of economic convergence with spatial econometrics to explore regional convergence based on a total of 240 cities in China. To investigate the kind of spatial autocorrelation and agglomeration, the Moran's I statistic is used, finding that the existence of strongly positive global autocorrelation of GDP per capita and what's more, the local spatial structure is rather stable. The findings suggest that the non-spatial models applied to analyse β-convergence suffer from the risk of misspecification and a spatial model is competent. The results based on the spatial models indicate the existence of absolute convergence between cities. Taking into account effects results in a significant faster rate of convergence. The sensitivity test of the absolute convergence with respect to assumption of a common steady state and robustness over space suggest that the finding of absolute convergence is not stable. The mechanism of diminishing return and technology spillover is both important for absolute convergence. Finally, a set of regional policies are discussed.
DOI:10.11821/xb201106001URL [本文引用: 1]

It is commonly believed that so far as countries at the early stage of economic development are concerned, capital usually flows from areas with unfavorable conditions to those with favorable conditions, which leads to the Matthew effect and the widening of regional development gap. Inter-bank credit flows are an important form of inter-regional capital flows. This paper used a measuring method to disclose the direction of the inter-bank credit flows between eastern China which has favorable conditions and central and western China which have unfavorable conditions during the period of widening of regional development gaps (1978-2003), and analyzed the causes. It was found that in the years of inter-regional capital flows, no net credit outflows from the underdeveloped areas to the developed areas but the reverse patterns were found. This indicated that the inter-bank credit flow narrowed rather than widened the regional development gap at least to some extent. Further analysis found that the credit control by the Central Government and the changes of market environments formed two periods of inter-bank credit flows before and after 1994 respectively.
DOI:10.11821/xb201106001URL [本文引用: 1]

It is commonly believed that so far as countries at the early stage of economic development are concerned, capital usually flows from areas with unfavorable conditions to those with favorable conditions, which leads to the Matthew effect and the widening of regional development gap. Inter-bank credit flows are an important form of inter-regional capital flows. This paper used a measuring method to disclose the direction of the inter-bank credit flows between eastern China which has favorable conditions and central and western China which have unfavorable conditions during the period of widening of regional development gaps (1978-2003), and analyzed the causes. It was found that in the years of inter-regional capital flows, no net credit outflows from the underdeveloped areas to the developed areas but the reverse patterns were found. This indicated that the inter-bank credit flow narrowed rather than widened the regional development gap at least to some extent. Further analysis found that the credit control by the Central Government and the changes of market environments formed two periods of inter-bank credit flows before and after 1994 respectively.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201702002URL [本文引用: 1]

With the implementation and deepening of household registration reform and liberalizing of factors flow under market economy system, the imbalance in regional development is becoming increasingly complex. Thus it is significant to conduct research on the impact of population flow on regional economic disparities. This paper selected the Yangtze River economic belt as a case study, and used population flow ratio (to divide the difference between resident population and registered population by resident population) to represent the migration size. Based on the county-level data of registered population and resident population in China's fourth, fifth and sixth censuses, we analyzed the spatial-temporal patterns of economic disparities and population flow, and explored population mobility effect on economic inequalities in the Yangtze River economic belt. With the Theil index, spatial analysis and regression modeling methods, the following conclusions could be drawn: (1) The economic disparities based on resident population were smaller than those besed on registered population. The former was shrinking with the elapse of time, while the latter was expanding. (2) The eastern zone showed the megalopolis characteristic and a center-periphery spatial economic structure, with the spatial aggregation of developed counties in the Yangtze River Delta as the planar core area, while there were several sub-center-periphery structures with center city as point core area in the central and western zones. (3) The impact of population flow on economic growth was significantly different between inflow and outflow counties. The increase of population flow rate promoted the economic growth of inflow areas remarkably in 2000 and 2010. While it retarded the economic growth of outflow areas in 2000, and enhanced it slowly in 2010. The county economic gaps in the Yangtze River economic belt was widening. (4) The impact of population flow on regional economy disparities was prominently weakened with the provincial and regional factors taken into account. (5) Population flow was the most prominent factor which affects the regional economic disparities, followed by economic structure embodied in the level of industrialization. The other factors were human capital, fiscal decentralization and regional strategy. Emphasizing labor return, promoting family migration and speeding up industrialization are key policies to prevent and even narrow the regional economic gaps in outflow areas.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201702002URL [本文引用: 1]

With the implementation and deepening of household registration reform and liberalizing of factors flow under market economy system, the imbalance in regional development is becoming increasingly complex. Thus it is significant to conduct research on the impact of population flow on regional economic disparities. This paper selected the Yangtze River economic belt as a case study, and used population flow ratio (to divide the difference between resident population and registered population by resident population) to represent the migration size. Based on the county-level data of registered population and resident population in China's fourth, fifth and sixth censuses, we analyzed the spatial-temporal patterns of economic disparities and population flow, and explored population mobility effect on economic inequalities in the Yangtze River economic belt. With the Theil index, spatial analysis and regression modeling methods, the following conclusions could be drawn: (1) The economic disparities based on resident population were smaller than those besed on registered population. The former was shrinking with the elapse of time, while the latter was expanding. (2) The eastern zone showed the megalopolis characteristic and a center-periphery spatial economic structure, with the spatial aggregation of developed counties in the Yangtze River Delta as the planar core area, while there were several sub-center-periphery structures with center city as point core area in the central and western zones. (3) The impact of population flow on economic growth was significantly different between inflow and outflow counties. The increase of population flow rate promoted the economic growth of inflow areas remarkably in 2000 and 2010. While it retarded the economic growth of outflow areas in 2000, and enhanced it slowly in 2010. The county economic gaps in the Yangtze River economic belt was widening. (4) The impact of population flow on regional economy disparities was prominently weakened with the provincial and regional factors taken into account. (5) Population flow was the most prominent factor which affects the regional economic disparities, followed by economic structure embodied in the level of industrialization. The other factors were human capital, fiscal decentralization and regional strategy. Emphasizing labor return, promoting family migration and speeding up industrialization are key policies to prevent and even narrow the regional economic gaps in outflow areas.
DOI:10.11821/xb200606003URL [本文引用: 1]

Interregional input-output analysis may depict accurately interregional economic linkage and driving forces of regional development. This paper focuses upon the driving forces of regional industrial development since the 1990s based on analysis of China interregional input-output model. The results show that most of the industries in the coastal areas depend upon external market. The industries with degree of dependence on induced output of external demand exceed 50%, accounting for more than 60% of the total in the coastal areas. On the contrary, in inland areas, most of the industries depend upon the internal market as driving forces of industrial development. The differences in driving forces of industrial development lead to differentiation in potential of industrial development and spatial concentration of industries, and thus many industries gather into the coastal areas. This indicates that development of western areas, revival of northeast industrial bases and growing-up of the midland face many challenges in fostering industrial competitiveness. Hence, the policy of regional development must pay more attention to upgrading of industrial competitiveness in these areas. In view of the external trade, the degree of industrial internationalization in the coastal areas has reached a rather high level. Therefore, the fluctuation of international market will directly influence industrial development, or bring more opportunities to the industrial development in the coastal areas.
DOI:10.11821/xb200606003URL [本文引用: 1]

Interregional input-output analysis may depict accurately interregional economic linkage and driving forces of regional development. This paper focuses upon the driving forces of regional industrial development since the 1990s based on analysis of China interregional input-output model. The results show that most of the industries in the coastal areas depend upon external market. The industries with degree of dependence on induced output of external demand exceed 50%, accounting for more than 60% of the total in the coastal areas. On the contrary, in inland areas, most of the industries depend upon the internal market as driving forces of industrial development. The differences in driving forces of industrial development lead to differentiation in potential of industrial development and spatial concentration of industries, and thus many industries gather into the coastal areas. This indicates that development of western areas, revival of northeast industrial bases and growing-up of the midland face many challenges in fostering industrial competitiveness. Hence, the policy of regional development must pay more attention to upgrading of industrial competitiveness in these areas. In view of the external trade, the degree of industrial internationalization in the coastal areas has reached a rather high level. Therefore, the fluctuation of international market will directly influence industrial development, or bring more opportunities to the industrial development in the coastal areas.
DOI:10.1007/s11442-008-0225-zURL [本文引用: 1]

With the rapid economic development during the last 30 years in China, more and more disparities have emerged among different regions. It has been one of the hot topics in the fields of physical geography and economic geography, and also has been the task for Chinese government to handle. Nevertheless, to quantitatively assess the impacts of physio-geographical patterns (PGP) on the regional development disparity has been ignored for a long time. In this paper, a quantitative method was adopted to assess the marginal effects of the PGP on spatio-temporal disparity using the partial determination coefficients. The paper described the construction of the evaluation model step by step following its key scientific thinking. Total GDP, per capita GDP, primary industrial output value and secondary industrial output value were employed in this study as the indicators to reflect the impacts of PGP on the regional development disparity. Based on the evaluation methods built by researchers, this study firstly analyzed the temporal impacts of the PGP on spatio-temporal disparity of the regional development in China during the past 50 years, and then explained the spatial differences at each development stage. The results show that the spatio-temporal disparity in China is highly related to the PGP, and that the marginal contribution rate could be employed as an effective way to quantitatively assess the impact of the PGP on spatio-temporal disparity of the regional development.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.01.012URL [本文引用: 1]

Regional gap is an important problem that the regional development of China is facing. The distribution of economy and population, as an embodiment of the spatial equilibrium process of regional development, has a close relation with the state of regional gap. Using gravity models, it works out the center of economic gravity and population gravity (abbr. CEG and CPG), illustrates the coupling process by measuring the overlapping of two centers of gravity and the consistency of their movement, and proves that the coupling process has a high correlation with the evolution of regional gap. Then, a model of the coupling mechanism of CEG and CPG is built. Based on the model, it illustrates the spatial equilibrium process of regional development by the transition of equilibrium location and the conversion of regional potential energy difference, and reveals how the internal and external factors affect the process. Therefore, the authors advance a “multistage inverted-U-curve evolution law” of regional gap. Finally, it analyses the mechanism of the periodic variation of regional gap in China since 1952, and brings up a discussion of the path to coordinating the regional development of China.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.01.012URL [本文引用: 1]

Regional gap is an important problem that the regional development of China is facing. The distribution of economy and population, as an embodiment of the spatial equilibrium process of regional development, has a close relation with the state of regional gap. Using gravity models, it works out the center of economic gravity and population gravity (abbr. CEG and CPG), illustrates the coupling process by measuring the overlapping of two centers of gravity and the consistency of their movement, and proves that the coupling process has a high correlation with the evolution of regional gap. Then, a model of the coupling mechanism of CEG and CPG is built. Based on the model, it illustrates the spatial equilibrium process of regional development by the transition of equilibrium location and the conversion of regional potential energy difference, and reveals how the internal and external factors affect the process. Therefore, the authors advance a “multistage inverted-U-curve evolution law” of regional gap. Finally, it analyses the mechanism of the periodic variation of regional gap in China since 1952, and brings up a discussion of the path to coordinating the regional development of China.
DOI:10.11821/xb201012012URL [本文引用: 1]

Low-carbon economy has become a worldwide trend. This paper applies a dynamic multi-regional computable general equilibrium (CGE) model to conduct research into the impacts of carbon tax policy on regional economic development in China based on a China Interregional Input-Output Table 2002. Simulation results show that different regions endure different impacts when a uniform carbon tax policy is implemented. It exerts negative influences on less developed regions and positive economic influences on coastal areas, which will widen regional economic disparity. Regional differentiated carbon tax policies may alleviate differences of impacts of CO2 emission reduction on regional economy and then help to marrow regional economic gap. Therefore, regional differentiated carbon tax policies, from the viewpoint of efficiency and equality, may be a win-win choice for developing low-carbon economy and promoting harmonious development of regional economy in China.
DOI:10.11821/xb201012012URL [本文引用: 1]

Low-carbon economy has become a worldwide trend. This paper applies a dynamic multi-regional computable general equilibrium (CGE) model to conduct research into the impacts of carbon tax policy on regional economic development in China based on a China Interregional Input-Output Table 2002. Simulation results show that different regions endure different impacts when a uniform carbon tax policy is implemented. It exerts negative influences on less developed regions and positive economic influences on coastal areas, which will widen regional economic disparity. Regional differentiated carbon tax policies may alleviate differences of impacts of CO2 emission reduction on regional economy and then help to marrow regional economic gap. Therefore, regional differentiated carbon tax policies, from the viewpoint of efficiency and equality, may be a win-win choice for developing low-carbon economy and promoting harmonious development of regional economy in China.
DOI:10.11821/xb200002002URL [本文引用: 1]

The sustainable development pattern of China, calculated by province from the databases of the Population, Environment and Sustainable Development Atlas of China (PESDAC), are expressed by six indexes and their maps visually. The spatial distribution characteristics are described according to the indexes and the maps. The paper is organized as follows. Firstly, the research situaction on Chinese Sustainable Development by home and abroad is introduced. Then, the dessipative structure theory is applied to the research on evolution of regional Population, Resource, Environment and Development (PRED) system. A comprehensive index named SDI is put forward with its non-linear model. Thirdly, based on the databases of the PESDAC, the indexes of population, resource, environment, development of economy and society by province are derived quantitatively. Fourthly, they are visualized into six maps. Next, a spatial analysis of the pattern of China’s sustainable development is made. Finally, the causes are analyzed and some answers to the question are given. The conclusions are drawn as follows on the overall spatial characteristics of the sustainable development of China. The social and economic development pattern is divided into three zones from east to west obviously. The ecology and environment situation is related to regional economy closely. There is a difference between North China and South China because of their natural condition; The natural resource lies mainly in the west of China. It is short relatively in the middle of China. But the resource per capita is least in the east of China;The distribution of SDI has the same pattern as the attraction to population, its shape is like two circles with the same center in Hubei province. But there is a slight difference between SDI and the attraction to population, it reflects a value deflection by which people decide to migrate nowadays. Poverty scatters mainly in the middle of China, but there is one third of poverty population not living in the counties assigned by government.
DOI:10.11821/xb200002002URL [本文引用: 1]

The sustainable development pattern of China, calculated by province from the databases of the Population, Environment and Sustainable Development Atlas of China (PESDAC), are expressed by six indexes and their maps visually. The spatial distribution characteristics are described according to the indexes and the maps. The paper is organized as follows. Firstly, the research situaction on Chinese Sustainable Development by home and abroad is introduced. Then, the dessipative structure theory is applied to the research on evolution of regional Population, Resource, Environment and Development (PRED) system. A comprehensive index named SDI is put forward with its non-linear model. Thirdly, based on the databases of the PESDAC, the indexes of population, resource, environment, development of economy and society by province are derived quantitatively. Fourthly, they are visualized into six maps. Next, a spatial analysis of the pattern of China’s sustainable development is made. Finally, the causes are analyzed and some answers to the question are given. The conclusions are drawn as follows on the overall spatial characteristics of the sustainable development of China. The social and economic development pattern is divided into three zones from east to west obviously. The ecology and environment situation is related to regional economy closely. There is a difference between North China and South China because of their natural condition; The natural resource lies mainly in the west of China. It is short relatively in the middle of China. But the resource per capita is least in the east of China;The distribution of SDI has the same pattern as the attraction to population, its shape is like two circles with the same center in Hubei province. But there is a slight difference between SDI and the attraction to population, it reflects a value deflection by which people decide to migrate nowadays. Poverty scatters mainly in the middle of China, but there is one third of poverty population not living in the counties assigned by government.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910008URL [本文引用: 1]

Methods for the evaluation of sustainable development capability are important and highly sought after tools for identifying the synergistic relationship between humans and the environment and guiding scientific decision-making for the implementation of ecological and environmental protection measures. Compared to traditional methods such as ecological footprint, environmental sustainability index, and human development index, emergy analysis and exergy analysis result in smaller errors and are more objective. These two methods can directly convert materials and services into energy units, without evaluation indicators and weight settings, and do not require raw dimensionless data. Exploring the coupling of emergy analysis and exergy analysis can provide a new perspective on and method for the analysis of regional sustainable development capabilities. Based on a literature review, a theoretical analysis framework was constructed. This study proposes an emergy and exergy coupling model for the analysis of sustainable development capability based on a thermodynamic theory. This analytical model has three indices, namely, self-organizing capability index (SO), ecological pressure index (EP), and sustainable development capability index (SC). The emergy and exergy input and output values of 17 typical developed countries in 1985 were screened via meta-analysis to calculate the SO and EP thresholds of the model, based on which sustainable development capability was divided into four stages. The model was tested via a comparative analysis of the sustainable development capability of China and the USA in 1985-2015. The results show that China was in the low self-organizing capacity and low ecological pressure stage before 2005. After 2005, it entered the low self-organizing capability and high ecological pressure stage. It has had low eco-efficiency and scale expansion driving characteristics. The USA is always in the high self-organizing capacity and high ecological pressure stage, and is characterized by high ecological efficiency, and economic and ecological decoupling. These results are consistent with the findings of the World Ecological Footprint Network and World Wildlife Fund, indicating that the proposed model is adaptive and reliable. In addition, the study results indicate that this model can express the ecological efficiency of an economic and social system in terms of "total annual exergy amount used/annual emergy input amount". Moreover, it can express the ecological pressure as "annual exergy loss of an economic and social system/annual eco-exergy produced by an ecosystem." This model connects the entropy path of an economic and social system to the ecosystem. Furthermore, it can identify sustainable development stage and analyze changes in sustainable development level and factors driving these changes. From an anthropological and ecological perspective, the model expresses the ecological efficiency of an economic and social system, evaluates the proportion of ecological space occupied, and can combine macroscopic scale with microscopic efficiency analysis, which is an improvement over conventional methods.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910008URL [本文引用: 1]

Methods for the evaluation of sustainable development capability are important and highly sought after tools for identifying the synergistic relationship between humans and the environment and guiding scientific decision-making for the implementation of ecological and environmental protection measures. Compared to traditional methods such as ecological footprint, environmental sustainability index, and human development index, emergy analysis and exergy analysis result in smaller errors and are more objective. These two methods can directly convert materials and services into energy units, without evaluation indicators and weight settings, and do not require raw dimensionless data. Exploring the coupling of emergy analysis and exergy analysis can provide a new perspective on and method for the analysis of regional sustainable development capabilities. Based on a literature review, a theoretical analysis framework was constructed. This study proposes an emergy and exergy coupling model for the analysis of sustainable development capability based on a thermodynamic theory. This analytical model has three indices, namely, self-organizing capability index (SO), ecological pressure index (EP), and sustainable development capability index (SC). The emergy and exergy input and output values of 17 typical developed countries in 1985 were screened via meta-analysis to calculate the SO and EP thresholds of the model, based on which sustainable development capability was divided into four stages. The model was tested via a comparative analysis of the sustainable development capability of China and the USA in 1985-2015. The results show that China was in the low self-organizing capacity and low ecological pressure stage before 2005. After 2005, it entered the low self-organizing capability and high ecological pressure stage. It has had low eco-efficiency and scale expansion driving characteristics. The USA is always in the high self-organizing capacity and high ecological pressure stage, and is characterized by high ecological efficiency, and economic and ecological decoupling. These results are consistent with the findings of the World Ecological Footprint Network and World Wildlife Fund, indicating that the proposed model is adaptive and reliable. In addition, the study results indicate that this model can express the ecological efficiency of an economic and social system in terms of "total annual exergy amount used/annual emergy input amount". Moreover, it can express the ecological pressure as "annual exergy loss of an economic and social system/annual eco-exergy produced by an ecosystem." This model connects the entropy path of an economic and social system to the ecosystem. Furthermore, it can identify sustainable development stage and analyze changes in sustainable development level and factors driving these changes. From an anthropological and ecological perspective, the model expresses the ecological efficiency of an economic and social system, evaluates the proportion of ecological space occupied, and can combine macroscopic scale with microscopic efficiency analysis, which is an improvement over conventional methods.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201402005URL [本文引用: 1]

The coordination development of industrialization, informatization, urbanization and agricultural modernization (so called "Sihua Tongbu" in Chinese, and hereinafter referred to as "new four modernizations"; China first put forward the term of "four modernizations" in the early 1960s, targeting the fields of industry, agriculture, national defense and science and technology) is practical need and strategic direction of integrating urban-rural development and regional development in recent China. This study mainly aims to explore the spatial pattern and influencing factors of coordination development of new four modernizations of China's prefecture-level regions. Firstly, we established a comprehensive evaluation index system to reveal the spatial pattern of coordination development of new four modernizations. And then, Pearson correlation analysis was used to explore the relationship between the coordinating degrees of new four modernizations and main indicators reflecting regional development state. Thirdly, a spatial econometric model was employed to explore the factors affecting the coordination development of the new four modernizations. Moreover, a set of rules based on the coordination development level of the new four modernizations has been established to identify the problematic region. The main contents and results were summed up as follows: (1) the respective development level of the new four modernizations and the coupling degree and coordinating degree of the new four modernizations shows obvious spatial difference. (2) The coordinating degree of new four modernizations is at relatively low level, and has significant positive correlation with per capita net income of farmers and per capita gross domestic product, and in contrast, it has significant negative correlation with both the income gap and consumption gap between urban and rural residents. (3) Socio-economic conditions, traffic location and physical geography conditions show obvious impacts on the coordinating state of new four modernizations, especially, on social investment, financial investment and financial support on agriculture and rural areas, as well as development level of large and medium-sized enterprise, road infrastructure density and social consumption, have robust and positive impacts on the coordinating state of new four modernizations. (4) A total of 145 prefecture-level cities have been identified as problematic regions according to their coordinating states of new four modernizations. These cities are mainly located in the traditional agricultural zones of central China, hilly areas of southwest China and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Our findings may contribute to the knowledge of coordination development of industrialization, informatization, urbanization and agricultural modernization in the new era of urban-rural transformation development. To promote the coordination development of new four modernizations needs for top-level design, common institutional innovation, and regional policy innovation specifically for problematic regions. In addition, more social investment, financial investment and financial support for agricultural and rural development should be encouraged, and more attention should be paid to expand domestic demand actively, optimize the export-oriented economic development strategy, and enhance the efficiency of the investment in urban construction and education development.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201402005URL [本文引用: 1]

The coordination development of industrialization, informatization, urbanization and agricultural modernization (so called "Sihua Tongbu" in Chinese, and hereinafter referred to as "new four modernizations"; China first put forward the term of "four modernizations" in the early 1960s, targeting the fields of industry, agriculture, national defense and science and technology) is practical need and strategic direction of integrating urban-rural development and regional development in recent China. This study mainly aims to explore the spatial pattern and influencing factors of coordination development of new four modernizations of China's prefecture-level regions. Firstly, we established a comprehensive evaluation index system to reveal the spatial pattern of coordination development of new four modernizations. And then, Pearson correlation analysis was used to explore the relationship between the coordinating degrees of new four modernizations and main indicators reflecting regional development state. Thirdly, a spatial econometric model was employed to explore the factors affecting the coordination development of the new four modernizations. Moreover, a set of rules based on the coordination development level of the new four modernizations has been established to identify the problematic region. The main contents and results were summed up as follows: (1) the respective development level of the new four modernizations and the coupling degree and coordinating degree of the new four modernizations shows obvious spatial difference. (2) The coordinating degree of new four modernizations is at relatively low level, and has significant positive correlation with per capita net income of farmers and per capita gross domestic product, and in contrast, it has significant negative correlation with both the income gap and consumption gap between urban and rural residents. (3) Socio-economic conditions, traffic location and physical geography conditions show obvious impacts on the coordinating state of new four modernizations, especially, on social investment, financial investment and financial support on agriculture and rural areas, as well as development level of large and medium-sized enterprise, road infrastructure density and social consumption, have robust and positive impacts on the coordinating state of new four modernizations. (4) A total of 145 prefecture-level cities have been identified as problematic regions according to their coordinating states of new four modernizations. These cities are mainly located in the traditional agricultural zones of central China, hilly areas of southwest China and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Our findings may contribute to the knowledge of coordination development of industrialization, informatization, urbanization and agricultural modernization in the new era of urban-rural transformation development. To promote the coordination development of new four modernizations needs for top-level design, common institutional innovation, and regional policy innovation specifically for problematic regions. In addition, more social investment, financial investment and financial support for agricultural and rural development should be encouraged, and more attention should be paid to expand domestic demand actively, optimize the export-oriented economic development strategy, and enhance the efficiency of the investment in urban construction and education development.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/xb200704001URL [本文引用: 2]

Major function oriented zoning (MFOZ hereafter) is the guideline for optimizing the spatial pattern of regional development in China, which entails both theoretical and methodological innovation in the academic field of economic geography. This study analyzes the basic features of territorial function and puts forward a spatially equilibrium model for regional development. It argues that there exists a trend of regional convergence in almost any indicator measuring the average level of regional development status. Based on this finding, the study illustrates that the formation of functional zone should be conducive to the reduction of regional inequality and that free flow of resources across region is the prerequisite to spatial equilibrium. It also investigates the impact of territorial functional evolution on spatial processes of equilibrium and suggests that the benefit to be derived from zoning proposal is contingent upon the method of regional division and correct understanding of temporal change of territorial function. After that, this study goes to examine the scientific foundation of several issues concerning the reconciliation of contradictory functions of development and protection, the selection of indicators and the spatial and temporal features of MFOZ. It is then followed by an interrogation of the rationality of achieving dual goals of efficiency and equality simultaneously through three-dimensional flow and spatial equilibrium. The paper ends with a discussion of the position, implementation and coordination of MFOZ from the perspective of institutional arrangements of spatial governance including law, planning and government policy.
DOI:10.11821/xb200704001URL [本文引用: 2]

Major function oriented zoning (MFOZ hereafter) is the guideline for optimizing the spatial pattern of regional development in China, which entails both theoretical and methodological innovation in the academic field of economic geography. This study analyzes the basic features of territorial function and puts forward a spatially equilibrium model for regional development. It argues that there exists a trend of regional convergence in almost any indicator measuring the average level of regional development status. Based on this finding, the study illustrates that the formation of functional zone should be conducive to the reduction of regional inequality and that free flow of resources across region is the prerequisite to spatial equilibrium. It also investigates the impact of territorial functional evolution on spatial processes of equilibrium and suggests that the benefit to be derived from zoning proposal is contingent upon the method of regional division and correct understanding of temporal change of territorial function. After that, this study goes to examine the scientific foundation of several issues concerning the reconciliation of contradictory functions of development and protection, the selection of indicators and the spatial and temporal features of MFOZ. It is then followed by an interrogation of the rationality of achieving dual goals of efficiency and equality simultaneously through three-dimensional flow and spatial equilibrium. The paper ends with a discussion of the position, implementation and coordination of MFOZ from the perspective of institutional arrangements of spatial governance including law, planning and government policy.
[EB/OL]. http://sdgindex.org/reports/2018/?from=singlemessage&isappinstalled=0.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

It is an innovative work of comprehensive deepening reforms of China to establish the mechanism of monitoring and early-warning of carrying capacity. Based on the scientific connotation of the carrying capacity of national resources and environment and oriented to regional sustainable development, this article explores the"pressure-state-response" process of the interaction between the carrying body: the natural foundation (which consists of resources, environment, ecology and disasters) with the carrying object: the human production and life activities, and presents the academic thought that the early-warning of the national resources and environment carrying capacity is an overload early-warning according to the cap of the constraints of resources and environment or the population and economic rational scales or other key thresholds, and also presents a process early-warning in terms of the changes of the natural basic conditions or the tendencies of the impact of resource utilization and environmental changes. According to the exploration on the principles of early-warning carrying capacity, this article constructs the differential indicator system and the overall technical process of early-warning of marine and terrestrial resources and environment carrying capacity. Land resources stress index, water resources use intensity index, environmental stress strength index and vegetation coverage change range index are chosen as basic indicators to conduct an overall regional evaluation, and different specific indicators, such as the pollution level of dust-haze, the increase and decrease of arable land, equilibrium index of grass and livestock and the variation of eco-environmental quality, are chosen to conduct the specific evaluation respectively for the urbanized areas, major grain producing areas, pastoral and semi-pastoral areas and ecological function areas, and then the key thresholds of these indicators are determined to conduct classifying evaluation. Finally, this article integrates all the evaluations and puts forward an evaluation method which shows the differentials in terms of major function oriented zone and evaluation results of consistent expression, and then carries out the process evaluation using two indexes of resource utilization efficiency and environment pollution pressure to reflect auxiliary the early-warning state of China's resources and environment carrying capacity and sustainable development abilities, thus providing a scientific basis for the proposed recommendations for restrictive measures and the improvement of monitoring and early-warning mechanisms.
URL [本文引用: 1]

It is an innovative work of comprehensive deepening reforms of China to establish the mechanism of monitoring and early-warning of carrying capacity. Based on the scientific connotation of the carrying capacity of national resources and environment and oriented to regional sustainable development, this article explores the"pressure-state-response" process of the interaction between the carrying body: the natural foundation (which consists of resources, environment, ecology and disasters) with the carrying object: the human production and life activities, and presents the academic thought that the early-warning of the national resources and environment carrying capacity is an overload early-warning according to the cap of the constraints of resources and environment or the population and economic rational scales or other key thresholds, and also presents a process early-warning in terms of the changes of the natural basic conditions or the tendencies of the impact of resource utilization and environmental changes. According to the exploration on the principles of early-warning carrying capacity, this article constructs the differential indicator system and the overall technical process of early-warning of marine and terrestrial resources and environment carrying capacity. Land resources stress index, water resources use intensity index, environmental stress strength index and vegetation coverage change range index are chosen as basic indicators to conduct an overall regional evaluation, and different specific indicators, such as the pollution level of dust-haze, the increase and decrease of arable land, equilibrium index of grass and livestock and the variation of eco-environmental quality, are chosen to conduct the specific evaluation respectively for the urbanized areas, major grain producing areas, pastoral and semi-pastoral areas and ecological function areas, and then the key thresholds of these indicators are determined to conduct classifying evaluation. Finally, this article integrates all the evaluations and puts forward an evaluation method which shows the differentials in terms of major function oriented zone and evaluation results of consistent expression, and then carries out the process evaluation using two indexes of resource utilization efficiency and environment pollution pressure to reflect auxiliary the early-warning state of China's resources and environment carrying capacity and sustainable development abilities, thus providing a scientific basis for the proposed recommendations for restrictive measures and the improvement of monitoring and early-warning mechanisms.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/142491URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/142491URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001URL [本文引用: 1]

Compared with the increasingly obvious humanistic tendency in foreign human geography, China's human and economic geography still follows Academician Wu Chuanjun's theory, with human and economic geography as an interdisciplinary subject which is the study of the formation and evolution of the distribution pattern of human activities under the interaction of natural circle and human circle. And China's mainstream school on human and economic geography has been formed with studies on spatio-temporal rule of sustainable development on territories with different space scales, territories with important production and living, and territories with typical geospatial patterns as the main research points. "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction", developed by Academician Wu Chuanjun, is the important theoretical foundation not only for human and economic geography, but also for the comprehensive research on geography. The essence of the theory, which includes territorial functional, system structured, orderly process for spatio-temporal variation, and the difference and controllability of human-environment interaction system effect, is entirely harmonious with the forefront of thought of the "Future Earth" studies program. In recent decade, with scientific mode of urbanization, major function oriented zoning, road map for the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, rural hollowing and targeted poverty alleviation, revitalization of Northeast China and transformation of resource-based cities, and administrative area optimization as the main research objects, theoretical methods have been developed in the aspects of important sustainable process of human and economic geography, territorial function formation and ordering rules for comprehensive geographical pattern, formation and evolution mechanism of urban agglomeration and its resources and environmental effects, sustainable life cycle and the revitalization of the path for problem areas, the interaction between geopolitics, geo-economy and regions, and effect of cultural boundaries on sustainable development. China's human and economic geography has made great progress in discipline development, and the application results have produced profound influences on the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in recent years. With decades of hard work, China's human and economic geography has reached a world-class advanced level, so as to console the soul and spirit of Wu Chuanjun on the occasion of commemoration of the centenary of his birth.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001URL [本文引用: 1]

Compared with the increasingly obvious humanistic tendency in foreign human geography, China's human and economic geography still follows Academician Wu Chuanjun's theory, with human and economic geography as an interdisciplinary subject which is the study of the formation and evolution of the distribution pattern of human activities under the interaction of natural circle and human circle. And China's mainstream school on human and economic geography has been formed with studies on spatio-temporal rule of sustainable development on territories with different space scales, territories with important production and living, and territories with typical geospatial patterns as the main research points. "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction", developed by Academician Wu Chuanjun, is the important theoretical foundation not only for human and economic geography, but also for the comprehensive research on geography. The essence of the theory, which includes territorial functional, system structured, orderly process for spatio-temporal variation, and the difference and controllability of human-environment interaction system effect, is entirely harmonious with the forefront of thought of the "Future Earth" studies program. In recent decade, with scientific mode of urbanization, major function oriented zoning, road map for the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, rural hollowing and targeted poverty alleviation, revitalization of Northeast China and transformation of resource-based cities, and administrative area optimization as the main research objects, theoretical methods have been developed in the aspects of important sustainable process of human and economic geography, territorial function formation and ordering rules for comprehensive geographical pattern, formation and evolution mechanism of urban agglomeration and its resources and environmental effects, sustainable life cycle and the revitalization of the path for problem areas, the interaction between geopolitics, geo-economy and regions, and effect of cultural boundaries on sustainable development. China's human and economic geography has made great progress in discipline development, and the application results have produced profound influences on the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in recent years. With decades of hard work, China's human and economic geography has reached a world-class advanced level, so as to console the soul and spirit of Wu Chuanjun on the occasion of commemoration of the centenary of his birth.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502002URL [本文引用: 1]

Major Function Oriented Zoning (MFOZ) is the blueprint for the future developmnt and protection pattern of China's territory, and has been raised to from major function zones planning to major function zoning strategy and major function zoning institution. From 2004 to 2014, the author organized a series of research projects to compose MFOZ for the country, studied basic theory of regional function and MFOZ technical process, and proposed that space controlling zones of national and provincial scales can be divided into four types: urbanized zones, foodstuff-security zones, ecological safety zones, cultural and natural heritage zones. On this basis, major function zones of county scale should be transferred to optimized, prioritized, restricted, and prohibited zones. In this paper, a regional function identification index system comprising nine quantitative indicators (including water resources, land resources, ecological importance, ecological fragility, environment capacity, disaster risk, economic development level, population concentration and transport superiority) and one qualitative indicator of strategic choice is developed. Based on the single index evaluation, comprehensive evaluation using regional function suitability evaluation index is conducted, aiming at testing several key parameters including lower limit of protection zones and upper limit of development zones at the provincial level. In addition, a planning-oriented zoning method of major function zones is also discussed, which has brought the first MFOZ planning in China. According to the MFOZ caliber, it is forecasted that national spatial development intensity will rise from 3.48% in 2010 to 3.91% in 2020. Furthermore, according to caliber of the provincial integrated MFOZ planning, the area of optimized, prioritized and restricted zones accounts for 1.48%, 13.60% and 84.92%, respectively, and that of urbanized, foodstuff-security and ecological safety zones accounts for 15.08%, 26.11% and 58.81%, respectively. In combination of analyses of development level, resources and environmental carrying status and quality of the people's livelihood, the main characteristics of MFOZ were identified. Through verification, MFOZ draft of national and provincial scales, which is interactively accomplished with "MFOZ Technical Process" put forward by the author, is mostly above 80% identical with what have been forecasted.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502002URL [本文引用: 1]

Major Function Oriented Zoning (MFOZ) is the blueprint for the future developmnt and protection pattern of China's territory, and has been raised to from major function zones planning to major function zoning strategy and major function zoning institution. From 2004 to 2014, the author organized a series of research projects to compose MFOZ for the country, studied basic theory of regional function and MFOZ technical process, and proposed that space controlling zones of national and provincial scales can be divided into four types: urbanized zones, foodstuff-security zones, ecological safety zones, cultural and natural heritage zones. On this basis, major function zones of county scale should be transferred to optimized, prioritized, restricted, and prohibited zones. In this paper, a regional function identification index system comprising nine quantitative indicators (including water resources, land resources, ecological importance, ecological fragility, environment capacity, disaster risk, economic development level, population concentration and transport superiority) and one qualitative indicator of strategic choice is developed. Based on the single index evaluation, comprehensive evaluation using regional function suitability evaluation index is conducted, aiming at testing several key parameters including lower limit of protection zones and upper limit of development zones at the provincial level. In addition, a planning-oriented zoning method of major function zones is also discussed, which has brought the first MFOZ planning in China. According to the MFOZ caliber, it is forecasted that national spatial development intensity will rise from 3.48% in 2010 to 3.91% in 2020. Furthermore, according to caliber of the provincial integrated MFOZ planning, the area of optimized, prioritized and restricted zones accounts for 1.48%, 13.60% and 84.92%, respectively, and that of urbanized, foodstuff-security and ecological safety zones accounts for 15.08%, 26.11% and 58.81%, respectively. In combination of analyses of development level, resources and environmental carrying status and quality of the people's livelihood, the main characteristics of MFOZ were identified. Through verification, MFOZ draft of national and provincial scales, which is interactively accomplished with "MFOZ Technical Process" put forward by the author, is mostly above 80% identical with what have been forecasted.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904007URL [本文引用: 2]

China's Major Function Zoning, a prospective map comprehensively envisioning China's future conservation and development pattern, actually tells how urbanization areas, agricultural development areas and ecological security areas coordinate and evolve together to maintain the territorial development order in China, right in accordance with certain principles and rules. In this paper, the overall pattern and internal differences of the core-periphery structure are gauged by a feature point-axis-area-vector method in the proportion of the three areas, with an analysis in physiographical spatial differentiation, socio-economic spatial organization and interactions between the function zones. The result shows that the core-periphery structure is prevalent in all provinces of China: the local proportions of urbanization areas, agricultural development areas and ecological security areas follow a circling layer pattern spatially differentiated against the distances to the regional core, while the structure is complicated by differences in core location, axis direction, function attribute of edge area and internal function proportion. Through analysis of relevant factors, it can be concluded that the core-periphery structure of major function zones develops out of combined effects of physiographical spatial differentiation, socio-economic spatial organization and regional spatial connection. The core-periphery of the provinces of western China is greatly influenced by the main physiographical boundaries, while that of the eastern plains is primarily affected by existing urban system structure, socio-economic layout, and inter-regional connection strength. Where the natural geographical constraint is weaker, local socio-economic development and regional spatial connection affect the region more significantly.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904007URL [本文引用: 2]

China's Major Function Zoning, a prospective map comprehensively envisioning China's future conservation and development pattern, actually tells how urbanization areas, agricultural development areas and ecological security areas coordinate and evolve together to maintain the territorial development order in China, right in accordance with certain principles and rules. In this paper, the overall pattern and internal differences of the core-periphery structure are gauged by a feature point-axis-area-vector method in the proportion of the three areas, with an analysis in physiographical spatial differentiation, socio-economic spatial organization and interactions between the function zones. The result shows that the core-periphery structure is prevalent in all provinces of China: the local proportions of urbanization areas, agricultural development areas and ecological security areas follow a circling layer pattern spatially differentiated against the distances to the regional core, while the structure is complicated by differences in core location, axis direction, function attribute of edge area and internal function proportion. Through analysis of relevant factors, it can be concluded that the core-periphery structure of major function zones develops out of combined effects of physiographical spatial differentiation, socio-economic spatial organization and regional spatial connection. The core-periphery of the provinces of western China is greatly influenced by the main physiographical boundaries, while that of the eastern plains is primarily affected by existing urban system structure, socio-economic layout, and inter-regional connection strength. Where the natural geographical constraint is weaker, local socio-economic development and regional spatial connection affect the region more significantly.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
