2.
3.
Geographical thinking on the relationship between beautiful China and land spatial planning
CHEN Mingxing1,2, LIANG Longwu1,2, WANG Zhenbo1,2, ZHANG Wenzhong1,2, YU Jianhui1,2, LIANG Yi31. 2.
3.
收稿日期:2019-11-6修回日期:2019-12-7网络出版日期:2019-12-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-11-6Revised:2019-12-7Online:2019-12-25
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
陈明星(1982-),男,安徽巢湖人,博士,研究员,主要从事城市化与区域发展研究E-mail:chenmx@igsnrr.ac.cn。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (2675KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
陈明星, 梁龙武, 王振波, 张文忠, 余建辉, 梁宜. 美丽中国与国土空间规划关系的地理学思考. 地理学报[J], 2019, 74(12): 2467-2481 doi:10.11821/dlxb201912004
CHEN Mingxing.
1 引言
美丽中国建设是中国“十八大”报告提出的重要战略思想和任务,是实现“两个一百年”奋斗目标和中华民族伟大复兴中国梦的新路径,旨在实现经济、政治、文化、社会和生态综合美丽发展。2018年5月,习近平总书记在全国生态环境保护大会上明确了建设美丽中国的“时间表”和“路线图”:“确保到2035年,生态环境质量实现根本好转,美丽中国目标基本实现”,“到本世纪中叶,人与自然和谐共生,生态环境领域国家治理体系和治理能力现代化全面实现,建成美丽中国”[1]。美丽中国概念提出以来,学术界从不同学科视角积极开展了相关研究工作,主要包括美丽中国理论内涵[2,3]、美丽中国评估方案[4]、美丽中国经验总结[5]、美丽中国评价指标体系[6]、美丽中国与国土空间管制[7]、美丽中国与旅游发展[8]等。2019年5月,《关于建立国土空间规划体系并监督实施的若干意见》指出,整体谋划新时代国土空间开发保护格局,科学布局生产空间、生活空间、生态空间,这和美丽中国建设总体目标一致。国土空间规划统是统筹区域资源空间配置、开发管理和布局优化的总体方案,在引领区域协调发展上具有重要意义[9,10]。随着世界各国对合理开发利用国土空间重视程度的提升,国土空间规划已经成为国际上国家治理体系的重要组成部分。1999年欧盟正式通过“欧洲空间发展远景(ESDP)”空间规划,形成了有关欧盟地域未来发展的共同目标和理念,深入解析了21世纪空间规划框架和内涵[11]。2006年美国政府为了解决21世纪美国国内人口的急剧增长、基础设施需求、经济发展和环境等问题,制定未来美国国土发展的“美国2050”国土空间规划[12]。中国也陆续编制了主体功能区规划、土地利用规划、城乡规划、新型城镇化规划等一系列重要的和空间相关规划[13]。随着新时代“多规合一”改革,国土空间规划编制迎来了重大改革和发展机遇期,要求做好国土空间规划顶层设计,发挥国土空间规划在国家规划体系中的基础性作用,为国家发展规划落地实施提供空间保障,成为国家可持续发展的空间蓝图,并且针对2020年、2025年和2035年不同时间节点上提出了明确目标。地理学长期以来为国土空间规划理论和实践研究做了大量基础性研究工作[14]。
美丽中国建设与国土空间规划已成为当前地理学发展息息相关的两件大事,为地理学尤其是人文与经济地理学的发展提供了重大机遇。目前,美丽中国建设与国土空间规划都是新生事物,学术界对美丽中国和国土空间规划编制尚没有形成统一认知,更鲜有文献分析美丽中国与国土空间规划之间的有机联系。基于此,本文提出美丽中国目标与国土空间规划编制的若干认知,梳理了国土空间规划需要加强的理论基础探讨,构建了国土空间规划编制的方法论框架,为开展国土空间规划编制工作提供理论与方法论支撑,为实现“美丽中国”建设提供思路借鉴。
2 美丽中国是国家第二个一百年发展新的引领目标
2.1 两个一百年与美丽中国建设的提出
1949年建国以来,中国的发展取得了举世瞩目的重大成就,迈入了中国特色社会主义新时代。为了实现中国梦,中国政府提出“两个一百年”奋斗目标,即在中国共产党成立100年时,中国要全面建成小康社会,在新中国成立100年时,中国要建成富强民主文明和谐美丽的社会主义现代化国家。随着发展阶段的改变,国家发展战略在面临的现实需求、所处的发展阶段、发展目标、思路及空间治理等方面产生了关键性转变(表1)。在社会主义新时代背景下,美丽中国建设为国家第二个一百年的发展提供了新目标与发展愿景,也为国土空间规划编制提供了最重要的引领目标。Tab. 1
表1
表1社会主义特色新时代的新目标与新变化
Tab. 1
| 类别 | 1949年-21世纪初 | 社会主义特色新时代 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 新目标 | 新变化 | ||
| 面临现实需求不同 | 主要解决人的温饱和小康问题 | 面向人民对美好生活的向往 | 不仅要吃饱吃好,还要享受高品质的生活 |
| 发展阶段演替 | 强调工业文明 | 实现生态文明 | 尊重自然,绿水青山就是金山银山,坚持绿色发展 |
| 发展目标升级 | 侧重经济增长,提供更加丰富物质基础 | 建设美丽中国 | 多维度发展,倡导以人为本,包括经济、社会和生态等目标 |
| 发展思路转变 | 各地区均要实现高速经济增长 | 各地区存在地域功能的差异 | 因地制宜,优化开发、重点开发、限制开发和禁止开发类型 |
| 空间治理变革 | 国土空间的条块化多头管理 | 国土空间规划统筹管理 | 统筹生产、生活和生态空间,实现空间治理现代化 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2 美丽中国不仅仅是生态美丽,而是综合的大美丽内涵
从“美丽中国”概念提出以来,中国各级政府陆续加强生态环境保护工作,全面开展环境污染防治、城市生态双修以及人居环境改善工作,已经形成“美丽浙江”[15]、“美丽福建”[16]、“美丽江西”[17]和“美丽云南”[18]等具有地方特色的美丽中国建设模式。但是在探索美丽中国建设过程中,也有地区存在“美丽中国建设只要做好生态建设”的思想误区。“美丽中国”建设应是一个集合概念,旨在创建资源节约型、环境友好型的“两型”社会和打造“生产空间集约高效、生活空间宜居适度、生态空间山清水秀”的美好家园,进而全面推进中国经济、政治、文化、社会和生态“五位一体”总布局的全面发展。经济建设是根本,政治建设是保证,文化建设是灵魂,社会建设是条件,生态文明建设是基础[19],只有做到经济绿色增长、政治体制完善、文化传承复兴、社会和谐幸福、生态文明发展,才能完成美丽中国“五位一体”建设总目标,进而实现中华民族的伟大复兴和永续发展(图1)。图1
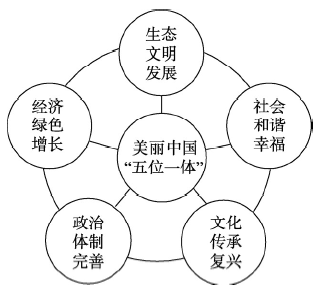 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1美丽中国“五位一体”建设目标
Fig. 1"Five in one" construction goal of beautiful China
2.3 美丽中国建设不能千城一面,要构建不同尺度和不同地域差异化评估指标体系
中国工业化和城市化的高速发展虽然有效地促进了城市扩张,提升了经济水平,改善了城市居民生活状况[20],但是也引发了诸如生态破损[21]、雾霾爆表[22]以及综合性环境污染[23]等“城市病”问题,城市可持续发展因此受到阻碍。地方政府“唯GDP论”的政绩观思想使得城市空间规划只看重经济发展,而忽视了城市质量,东中西部城市建设“千城一面”[24],缺乏地区文化,城市居民归属感和幸福度都较低。美丽中国建设正是要突破现有城市建设“美学平庸”困境,改善城市风貌,展现区域特色文化。在美丽中国建设过程中,东中西部地区要因地制宜建设美丽中国,充分发挥区域优势,重点打造地域特色;国家、省域、市域、县域和乡镇不同尺度层面的国土空间规划编制目标与重点应是有差别的,国家层面重点是顶层设计,侧重发展战略、方向和总体思路等,以及规划编制规程、审批和考核等组织管理工作,市县级和乡镇尺度侧重具体实施和落地,促进每一块国土空间都能得到合理有序的利用,省级单元做好中间衔接,既重视战略方向,也对下一级国土空间规划又要具有实际指导意义,做好美丽中国顶层设计和分层实施工作(图2)。因此,在美丽中国建设效果评估过程中,要根据不同空间尺度,不同地域差异构建多维度、多层次、多目标、多标准的美丽中国评估指标体系。图2
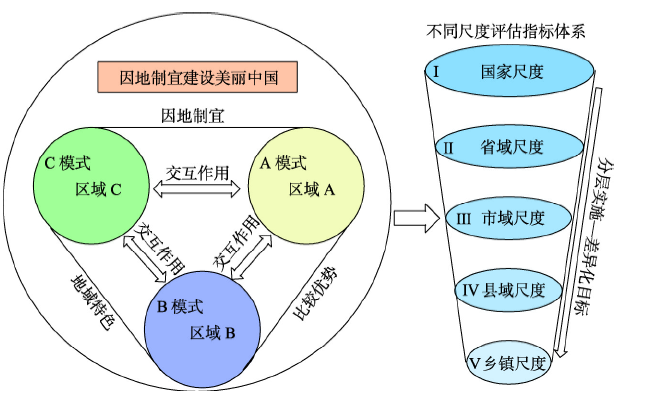 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2美丽中国“因地制宜”建设思想示意图
Fig. 2Construction idea of "adapting measures to local conditions" in beautiful China
在不同空间尺度美丽中国建设过程中,国家层面要加强顶层设计和组织领导,出台指导性战略规划和阶段性政策文件;省域层面要制定“美丽中国”建设实施纲要,引领全省美丽建设;市域层面要制定具体行动计划,统筹布局全市多要素美丽建设;县域层面要积极落实美丽建设方案,创建美丽中国样板区;乡镇层面要全面推进美丽中国建设,成为美丽中国梦的发源地。在不同地域美丽中国建设过程中,不同地域自然本底存在较大差异,其美丽中国建设应该有所侧重。
3 国土空间规划的重大改革及其与美丽中国建设关系
3.1 从多头管理向一张蓝图转变,实现多学科交叉的国土空间规划创新
国土空间规划旨在统筹区域空间协调可持续发展,防控国土空间结构失调和无序发展源[25]。1978年改革开放以来,中国政府愈加重视国土空间规划,由国家发改委、原国土资部、住房与城乡建设部、生态环境部、国家海洋局等国家部委主持编制了主体功能区规划、土地利用规划、国土规划、城乡规划、生态环境保护规划、海洋功能区规划等不同类型、不同层级的重大国土空间规划,有力支撑了经济社会持续快速发展,但也出现了一系列亟需解决的突出问题。基于此,党十八届五中全会提出以各类功能区规划为基础统筹空间规划,从多头管理向“一张蓝图”转变,推进“多规合一”,实现多学科交叉的国土空间规划创新型发展(图3)。国土空间规划过去多头管理、多头调研和多头规划,部门间相互矛盾、相互掣肘的困境有望得到根本性改观。通过机构调整的顶层设计,实现了由自然资源部统一部署和管理国土空间。为了实现新时代美丽中国建设总目标,国土空间规划还需要地理学、规划学、资源环境科学等多学科交叉融合,并在体制机制、理论体系、组织管理、应用技术、模式路径和思想观念等方面进行创新。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3美丽中国目标下国土空间规划“多规合一”
Fig. 3The compilation system of "multi compliance and integration" of land and space planning under the goal of beautiful China
3.2 国土空间规划是美丽中国目标引领下实现空间治理现代化的重要途径
美丽中国是新时代中国现代化建设的新目标和发展愿景,为国土空间规划指引了重要方向,以满足人民对美好生活的向往。在美丽中国的目标引领下,国土空间规划则是实现美丽中国的重要手段,为美丽中国建设提供了重要途径和空间保障。科学编制国土空间规划、促进美丽中国建设是衡量国家执政能力和水平的重要标志之一[26]。在过去多头管理的众多规划并行过程中,审批程序繁杂、规划相互打架导致规划建设成本过高,影响了国家治理体系和治理能力的现代化发展[27],尤其是空间治理现代化。国土空间规划的重大改革举措符合“统一实施国土空间用途管制”的空间规划体系初心[28]。地理科学在美丽中国建设和国土空间规划方面具有长期的科学基础,国家重大战略也为地理学科发展提供了前所未有的重要机遇(图4)。图4
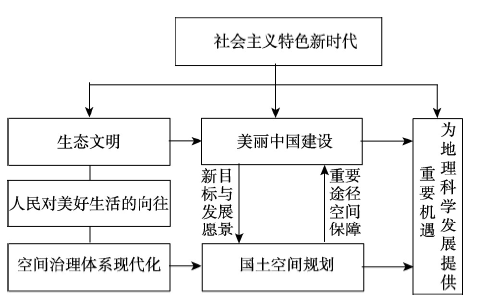 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4美丽中国与国土空间规划关系
Fig. 4The relationship between beautiful China and land spatial planning
3.3 从历史数据模型外推转向美丽中国目标引领与历史数据分析相结合的规划目标预测
国土空间是一个由人口、社会、经济、创新、全球化、基础设施等人文要素,以及生态环境、水资源、能源、土地资源、环境、气候等自然要素交互作用形成的动态复杂人地关系巨系统[29]。国土空间规划是在准确认知国土空间动态复杂巨系统及其内部多种要素正负反馈机制和动态演变规律的前提下,基于历史过程演化数据构建多元、线性、非线性、动态及离散化情景模拟和趋势预测模型,对未来国土空间开发利用进行科学预测与合理规划[30]。国土空间规划发展目标预测从历史过程外推预测未来,转向将未来美丽中国发展目标引领与历史数据分析相结合。统筹国土空间开发利用,推动经济社会有序发展[31]。通过“坚持以人民为中心、实现高质量发展和高品质生活、建设美好家园”,“科学布局生产、生活、生态‘三生’空间”,“到2035年,全面提升国土空间治理体系和治理能力现代化水平,基本形成生产空间集约高效、生活空间宜居适度、生态空间山清水秀,安全和谐、富有竞争力和可持续发展的国土空间格局”等美丽中国建设愿景目标引领和约束国土空间规划,“目标导向、过程约束”,持续加强自然环境保护,整体谋划新时代国土空间开发保护新格局。4 美丽中国与国土空间规划的地理学理论与认识基础
4.1 人地关系地域系统
国土空间规划的物质基础和保障是协调和谐、多元有序的人地关系,必须将人地关系系统全要素作为一个整体进行统筹规划和管理。1979年吴传钧先生提出人地关系地域系统理论,指出人地关系系统是地理环境和人类活动两大系统交互作用所组成的动态复杂性巨系统[32]。由于人类活动过度导致人类社会与自然生态环境各组成要素呈现不平衡和不协调的发展态势,进而导致诸多生态环境破坏和城市发展问题。人地关系地域系统理论旨在阐述人地关系系统全要素交互作用模式以及促进人地关系系统全要素协调发展和综合优化。4.2 点—轴系统
点—轴系统理论是由中国著名人文地理****陆大道先生于1984年在乌鲁木齐召开的 “全国经济地理和国土规划学术讨论会”上首次提出的。此后,陆大道先生基于中国宏观区域发展长期研究与深入实践经验,进一步阐述了“点—轴空间结构的形成过程”“发展轴的结构与类型”“点—轴渐进式扩散”“点—轴—聚集区”等多方面内涵,发表了一系列研究成果,并形成了完整的点—轴系统理论体系[33,34]。点—轴系统理论在等多学科、多领域中得到广泛运用[35,36,37,38],成为中国人文地理学界最卓有成效的两大应用性成果[39],应用到《全国国土总体规划纲要》中,是中国国土开发“T”字型结构的科学依据。4.3 主体功能区
主体功能区理论是主体功能区划的科学基础,是中国开展国土空间规划的重要指导思想之一。地理****根据不同地区资源环境承载能力、国土空间开发密度以及未来规划利用潜能等综合情况,划分出优化开发区域、重点开发区域、限制开发区域以及禁止开发区域4种国土空间开发类型[40]。主体功能区划坚持“以人为本”原则,重点强调人与自然复杂系统的和谐共生与协调发展,已经成为科学发挥政府部门调控作用和市场经济调节效应以及推动区域协调发展新格局的重要理论依据,以及有效地引领社会组织正确认知和合理规划建设国土空间的行动指南[41]。4.4 可持续发展与资源环境承载力
可持续发展思想最早由世界环境与发展委员会定义为“满足当代人需要的同时不影响后代人的需要”[42]。近年来,国际科学联盟和联合国分别提出“未来地球”研究计划[43]和2030全球可持续发展目标SDGs[44]。1978年以来,中国经济取得了长期高速增长,但也面临着产能过剩等突出结构性问题[45]。同时,也导致了生态破损[46,47]、环境污染[48]等诸多问题。城市群地区为了提升可持续发展能力呈现出可持续爬升规律[49]。资源环境承载力研究是可持续发展思想的进一步深入,得到国家高度重视[50]。是希望系统并量化评估出自然与人文要素耦合圈交互作用中资源、环境与生态等各类属性所能承载人类生产与生活的能力[51]。关注资源环境与经济发展交互耦合效应,为可持续发展提供支撑[52,53],是国土空间规划编制的重要基础[54]。4.5 新型城镇化
城镇化进程一度出现了过于重视速度,忽视了城镇化质量的冒进式现象[55]。2007年,提出城镇化要以人的发展为核心[56]。2011年,提出健康城镇化包括健康的人的发展、健康的城乡关系和健康的资源环境[57]。加速城镇化也不再适宜作为城镇化发展方针[58]。2014年“新型城镇化规划”发布,突出强调城镇化要以人为核心[59]。健康城镇化是支撑新型城镇化转型的重要学术理念。国家层面也曾使用“城镇化健康发展规划”,但最终明确为“新型城镇化规划”。为与国家战略保持一致,也避免名词过多,健康城镇化也就转变为新型城镇化,其本质上是一致的。新型城镇化理论内涵包括人本性、协同性、包容性和可持续性等4个方面特性[60]。这和过去更多追求物的城镇化、单要素增长、部分受益和不可持续的发展模式有着显著区别。新型城镇化要合理利用土地资源[61],认知地域差异[62],重视气候变化和资源环境[63]以及树立全球化视野[64]。中国新型城镇化仍处于起步阶段,还需要较为长期的发展提质过程,以及持续深入的学术研究支撑。城市群已成为中国经济社会发展的主体区域,提出的“5+9+6”城市群空间格局[65],对国土空间规划具有重要意义[66]。4.6 乡村地域多体系统
2008年提出城乡地域系统、阐述了城镇系统与乡村系统的耦合,强调乡村转型与城乡融合发展[67]。城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。乡村是国土空间的重要组成部分,也是经济社会发展的重要基础[68]。5 地理学视角下国土空间规划编制思路框架的思考
在“美丽中国”建设愿景目标下,国土空间规划如何编制,以实现国土空间的格局优化和资源要素的科学配置?地理学的传统优势决定了其在国土空间规划中的重要角色和作用。地理学从三分法来看包括自然地理学、人文地理学以及地理信息系统(包括遥感等),从地理学经典思维传统来看,主要包括空间思维、区域思维和综合思维。这对于国土空间规划的编制具有重要借鉴意义。从地理学思维传统和分支学科出发,提出国土空间规划编制的思路框架(图5)及其主要内容(图6):国土空间自然本底、经济社会基础、区域间相互联系、国土空间规划愿景与路径、公众参与与动态评估以及智能决策系统,为开展国土空间规划编制工作提供思路启示。图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5地理学视角下国土空间规划编制的思路框架
Fig. 5Framework of land spatial planning from the perspective of Geography
图6
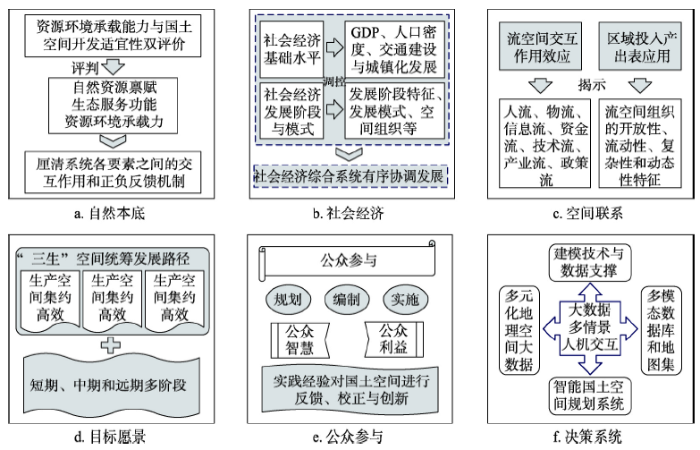 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6国土空间规划编制框架的主要内容
Fig. 6Main contents of the framework of land spatial planning
5.1 国土空间自然本底:资源环境承载能力与国土空间开发适宜性“双评价”
新时代国土空间规划编制的前提和基础是厘清国土空间自然本底条件,即对国土空间自然资源禀赋、生态服务功能和地理环境承载力等多要素本底条件具有全面性认知和综合性评价。以资源环境承载能力为基础,根据资源禀赋、生态条件和环境容量,明晰国土开发的限制性和适宜性,并提出适用于国土空间规划编制的“双评价”(资源环境承载能力与国土空间开发适宜性评价)方法。采用“双评价”方法对国土空间系统资源、环境、生态进行深刻分析,进而耦合人类活动进行综合性评价,加快划定生态保护红线、永久基本保护农田红线、城镇开发边界三条控制线等基础性工作。5.2 国土空间经济社会基础:国土开发强度与社会经济发展阶段模式
除了自然本底条件,社会经济则是国土空间规划中人类活动主体以及需要调控的对象。国土空间格局是自然资源环境与社会经济系统交互耦合作用的综合反映。改革开放以来,随着中国城镇化与工业化的快速发展,国土空间开发强度持续提升,但社会经济发展与资源环境保护之间的矛盾也日益凸显[69]。国土空间规划编制关注区域社会经济基础和社会经济发展阶段与模式,以及社会经济行为过程的整合优化和协调发展。科学测算和深入分析国土空间开发强度,依据国土开发强度以及资源环境承载能力,综合引导国土空间的有序开发和高效利用。5.3 国土空间相互联系:流空间交互作用与区域间投入产出表等应用
随着经济社会快速发展以及交通技术的不断进步,不同城市间、区域间联系越来越紧密。在国土空间规划编制过程中,需要充分考虑流空间下交互作用对国土空间所带来的影响,突破过去强调物理空间的规模等级结构,为要素在国土空间的充分流动创造条件。投入产出表旨在揭示不同地区产业联系机理,为了定量化探究流空间组织对国土空间全要素的影响机理机制,分析人流、物流、信息流、资金流等流空间组织的开放性、流动性、复杂性和动态性特征,提升区域各要素联系的空间流动和配置效率,构建协调有序、快速高效的国土空间联系网络[70]。5.4 国土空间愿景路径:国土空间规划愿景与发展路径设计
为了实现国土空间的综合优化目标,国土空间规划要充分依托对国土空间自然本底、社会经济及区域间联系的科学认知,进而提出不同空间尺度城乡区域的生产空间、生活空间、生态空间的布局与统筹发展路径。国土空间规划要结合“美丽中国”建设的总目标和分阶段目标,围绕国土空间高质量发展要求,提出不同尺度和层级下国土空间规划的短期、中期和远期多阶段的发展愿景,设计科学合理的空间发展路径,构建“生产空间集约高效、生活空间宜居适度、生态空间山清水秀”的“三生空间”新格局。5.5 公众参与与动态评估:公众参与与规划评估、反馈与校正
在国土空间规划编制过程中,要强调理念科学创新和公众参与机制,坚持政府主导、专家引领、公众参与的科学决策模式,激励社会公众参与国土空间规划工作和提供国土空间规划效果评估服务,广泛征求“公众智慧”和协调“公众利益”,群策群力打造科学高效的国土空间规划。同时,也要尝试建立全国、省域、市域和县域多层级的“国土空间规划委员会”,集合各部门的规划编制职能,负责国土空间规划编制、申述受理、冲突协调以及监督管理等工作,对规划实施内容、进展和效果等进行动态督查和评估。拓展社会公众对空间规划申述渠道,逐步使公众成为空间规划的重要监督者、推动者和评估者,对国土空间规划进行反馈、校正与创新。5.6 国土空间规划智能决策系统:大数据技术与智能空间规划系统
大数据应用最早主要集中在社会科学领域[71],近年来也逐步将大数据技术融入地理学科学研究[72,73]。目前,大数据技术为社会经济综合评价提供了技术和数据支撑[74],已经广泛应用在城市空间智慧规划的创新研究[75,76,77],但是大数据在国土空间规划编制中的应用研究仍然处于探索期。通过大数据挖掘和建模技术,将大数据与国土空间开发、自然资源、生态环境以及经济社会等多要素调研考察与材料分析相结合,整合多元化地理空间大数据资料建立数据库、地图集,研发可通过人机交互实现多情景模拟的大数据云计算平台,进而集成可视化、能分析、可人机交互、有效预警的国土空间规划综合智能决策系统。6 结论
(1)美丽中国和国土空间规划为地理科学发展提供了前所未有的重要机遇,两者之间紧密关联。提出若干认知:美丽中国是“经济—政治—文化—社会—生态”综合的大美丽,美丽中国建设要根据不同尺度目标和不同地域特色来构建差异化的评估指标体系,国土空间规划需要多学科交叉融合的规划编制方法论创新,美丽中国是国土空间规划编制的重要引领目标,国土空间规划是美丽中国目标下实现空间治理现代化的重要途径。(2)国土空间规划既有很好基础,又是一项全新事物。做好国土空间规划实践工作,离不开基础理论指导,也需要进一步加强人地关系地域系统、点—轴系统、主体功能区划、可持续发展与资源环境承载力、新型城镇化、乡村地域多体系统等理论层面的深入探讨。
(3)初步提出了国土空间规划编制的思路框架,应至少包括以下六个方面内容:国土空间的自然地理本底条件,经济社会发展基础,区域间相互联系,国土空间规划的愿景、目标与路径、公众参与与动态评估,以及基于大数据构建国土空间规划智能决策系统。
7 讨论
美丽中国与国土空间规划是当前国家对地理科学提供的重大需求,对相关战略需求的科技支撑亟待加强。未来仍有诸多方面需要进一步加强探讨:(1)美丽中国是生态文明理念下国家发展的新目标,体现社会主义新时代的新特征与新要求,主要针对的是“人对美好生活的向往”,体现以人为本的特点,和过去单纯追求数量、规模有着本质性区别。不仅重要宏观尺度,要协调好生态保护与经济社会发展的关系,改变过去由规模驱动的发展模式,探索绿色发展新模式。也要重视中微观小尺度,美丽中国与国土空间规划要规划和人生活息息相关的高品质社区生活圈的建设。对美丽中国概念内涵与外延的界定、思想演进的历史脉络梳理、美丽中国建设的路线图阐释、各地区差异化美丽中国样本的实践推进等还需要深入研究。
(2)美丽中国与国土空间规划是紧密联系的两件大事。不能脱离美丽中国大目标来谈国土空间规划,也不能只谈美丽中国目标,而忽视国土空间规划工作。要将美丽中国与国土空间规划有机结合,以加强两者之间关系的综合研究。
(3)国土空间规划离不开定量化分析,但是不能陷入计量主义陷阱。不仅需要进行数据定量分析,还应基于专业知识经验对经济社会发展和国土空间等方面的重大深层次问题和趋势性规律的研判,两者相结合才能编制出更为科学的国土空间规划。
(4)国土空间规划应海陆全覆盖,加强陆海统筹,高度重视蓝色国土的空间规划。中国海岸线绵长、海域辽阔,沿海地区应加快实施海洋领土专项空间规划,推进美丽海洋建设和海陆统筹规划。
(5)目前,我国国土空间规划体系主要是依据各层级行政区开展。这种编制思路有利于规划的尽快编制和实施。但是,国土空间规划编制思路一定是开放性的,需要在全球和更大区域空间尺度上谋划国土空间治理的精细化和科学化。因此,适时推进跨行政区的国土空间规划是重要环节。例如,跨行政区的长江经济带、城市群一体化发展地区或流域性高度关联区域等的国土空间规划统一编制。
(6)美丽中国建设与国土空间规划编制都急需跨学科、跨领域的交叉综合,开展理论方法的创新和实践探索。目前,中国科学院率先启动了A类战略性先导科技专项“美丽中国生态文明建设科技工程”,希望为国家生态文明与美丽中国建设提供有效的科技支撑。地理科学,尤其是人文与经济地理学,因其学科特质和传统,在其中将扮演重要角色。地理科学的发展也需要面向国土空间规划这一现实战略需求进一步发挥其学科价值、扩大社会服务、巩固学科源流等作用。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904001URL [本文引用: 1]

Beautiful China construction (BCC) is of fundamental importance for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation and a Chinese practice of the 2030 UN sustainable development agenda. The Chinese government has made strategic arrangements for the BCC with a five-pronged approach. President Xi Jinping proposed the schedule and roadmap for the BCC at the National Ecological Environmental Protection Conference. But at present, the theoretical basis, evaluation index system, evaluation criteria and construction effect of the BCC are not clear. This paper puts forward the basic connotation of the BCC from a broad and narrow perspective, regards the theory of man-earth harmony and Five-dimensional integration as the core theoretical basis of the BCC, and further constructs the evaluation index system of the BCC, which includes five dimensions: ecological environment, green development, social harmony, institutional improvement and cultural heritage, and uses the United Nations human development index (HDI) evaluation method to scientifically evaluate the construction effect of 341 prefecture-level cities (states) in China in 2016. The results show that the average value of the BCC Index (Zhongke Beauty Index) is 0.28, which is generally at a low level. The average of the sub-indexes of the ecological environment beauty index, the green development beauty index, the social harmony beauty index, the system perfect beauty index and the cultural heritage beauty index are respectively 0.6, 0.22, 0.29, 0.22, and 0.07. The sub-index values are all low, and the regional development is quite different, which indicates that the construction process of Beautiful China is generally slow and unbalanced. In order to implement the schedule and roadmap for the BCC with high quality and high standards, it is recommended that we construct and publish a general evaluation system for the BCC process, carry out dynamic monitoring and phased comprehensive evaluation of the BCC process, compile and publish the evaluation standards for BCC technology, do a good job in the comprehensive zoning of Beautiful China, carry out pilot projects for the construction of Beautiful China's model areas according to local conditions, and incorporate the achievements of Beautiful China into the assessment indicators of all levels of government.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904001URL [本文引用: 1]

Beautiful China construction (BCC) is of fundamental importance for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation and a Chinese practice of the 2030 UN sustainable development agenda. The Chinese government has made strategic arrangements for the BCC with a five-pronged approach. President Xi Jinping proposed the schedule and roadmap for the BCC at the National Ecological Environmental Protection Conference. But at present, the theoretical basis, evaluation index system, evaluation criteria and construction effect of the BCC are not clear. This paper puts forward the basic connotation of the BCC from a broad and narrow perspective, regards the theory of man-earth harmony and Five-dimensional integration as the core theoretical basis of the BCC, and further constructs the evaluation index system of the BCC, which includes five dimensions: ecological environment, green development, social harmony, institutional improvement and cultural heritage, and uses the United Nations human development index (HDI) evaluation method to scientifically evaluate the construction effect of 341 prefecture-level cities (states) in China in 2016. The results show that the average value of the BCC Index (Zhongke Beauty Index) is 0.28, which is generally at a low level. The average of the sub-indexes of the ecological environment beauty index, the green development beauty index, the social harmony beauty index, the system perfect beauty index and the cultural heritage beauty index are respectively 0.6, 0.22, 0.29, 0.22, and 0.07. The sub-index values are all low, and the regional development is quite different, which indicates that the construction process of Beautiful China is generally slow and unbalanced. In order to implement the schedule and roadmap for the BCC with high quality and high standards, it is recommended that we construct and publish a general evaluation system for the BCC process, carry out dynamic monitoring and phased comprehensive evaluation of the BCC process, compile and publish the evaluation standards for BCC technology, do a good job in the comprehensive zoning of Beautiful China, carry out pilot projects for the construction of Beautiful China's model areas according to local conditions, and incorporate the achievements of Beautiful China into the assessment indicators of all levels of government.
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.07.007URL [本文引用: 1]

Building Beautiful China is an important starting point for accelerating the reform of the ecological civilization system and realizing the sustainable development of the Chinese nation. At present, the country has set the timetable and roadmap of the construction of Beautiful China. It is of great significance to fully understand the current progress of Beautiful China research to guide future study. The current research on Beautiful China is at an exploratory stage, mainly focusing on the background and connotation of Beautiful China, the discussion of the index system, and the construction path. Among them, the connotation and theoretical basis of Beautiful China is the main body and focus of the present research, but a mature system is yet to be developed. The research of evaluation index system is in the exploration stage, and a unified understanding and standards have not been formed. The research content of the construction path is rather vague, and operability is limited. Future research needs to prioritize the following aspects. The first is to clarify the definition and connotation of Beautiful China, to build a theoretical system, and to answer the question of "what is". The second is to build a differential, development-oriented indicator system that is accessible, can be assessed, and can be implemented, to answer the question of "what to build". The third is to sum up local experiences, build a Beautiful China construction path system, and answer the question of "how to build".
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.07.007URL [本文引用: 1]

Building Beautiful China is an important starting point for accelerating the reform of the ecological civilization system and realizing the sustainable development of the Chinese nation. At present, the country has set the timetable and roadmap of the construction of Beautiful China. It is of great significance to fully understand the current progress of Beautiful China research to guide future study. The current research on Beautiful China is at an exploratory stage, mainly focusing on the background and connotation of Beautiful China, the discussion of the index system, and the construction path. Among them, the connotation and theoretical basis of Beautiful China is the main body and focus of the present research, but a mature system is yet to be developed. The research of evaluation index system is in the exploration stage, and a unified understanding and standards have not been formed. The research content of the construction path is rather vague, and operability is limited. Future research needs to prioritize the following aspects. The first is to clarify the definition and connotation of Beautiful China, to build a theoretical system, and to answer the question of "what is". The second is to build a differential, development-oriented indicator system that is accessible, can be assessed, and can be implemented, to answer the question of "what to build". The third is to sum up local experiences, build a Beautiful China construction path system, and answer the question of "how to build".
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S0743-0167(97)00052-1URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201608012URL [本文引用: 1]

On January 22nd and 23rd, 2016, "High level Forum of the Development of Chinese Human and Economic Geography under the background of change" was held in Beijing. More than 30 professors attended this forum. On the conference, they discussed on the major progress of the development of China's Human and Economic Geography, and the existing problems, restraint factors, opportunities, international path, developing direction, prospects in the development of the discipline. In recent years, Human and Economic Geography has boomed, facing many important opportunities for development. To establish an academic community for joint researches on major issues and collaborative innovation is a significant route. We should embrace domestic and international characteristics, to promote China's Human and Economic Geography to go to the world arena. In the meantime, the construction of various series of talents and the growth of young and middle-aged talents are also of great significance.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201608012URL [本文引用: 1]

On January 22nd and 23rd, 2016, "High level Forum of the Development of Chinese Human and Economic Geography under the background of change" was held in Beijing. More than 30 professors attended this forum. On the conference, they discussed on the major progress of the development of China's Human and Economic Geography, and the existing problems, restraint factors, opportunities, international path, developing direction, prospects in the development of the discipline. In recent years, Human and Economic Geography has boomed, facing many important opportunities for development. To establish an academic community for joint researches on major issues and collaborative innovation is a significant route. We should embrace domestic and international characteristics, to promote China's Human and Economic Geography to go to the world arena. In the meantime, the construction of various series of talents and the growth of young and middle-aged talents are also of great significance.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.105URLPMID:30469058 [本文引用: 1]

China experiences severe particulate matter pollution associated with rapid economic growth and accelerated urbanization. In this study, concentrations of PM2.5 (fine particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter?≤?2.5?μm) throughout China, and specifically in nine typical urban agglomerations and one economic region, were statistically analyzed using high-resolution ground-based PM2.5 observations from June 2014 to May 2018. The spatial variation of PM2.5 was also explored via spatial autocorrelation analysis. High annual mean PM2.5 concentrations were predominantly concentrated in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Central Plain, Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountain, and Cheng-Yu urban agglomerations, as well as the Huaihai Economic Region. The proportion of air quality nationwide monitoring sites where annual average PM2.5 concentrations exceeded the Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) Grade II annual standard were 82.8%, 77.1%, and 70.8% in 2015, 2016, and 2017, respectively. Moreover, the frequency of PM2.5 concentrations meeting the CAAQS Grade I 24-h standard increased in five national-level urban agglomerations, and the average annual PM2.5 decreased from 2015 to 2017 with a reduction rate of over 20%. The southern Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei agglomeration and surrounding areas revealed the highest PM2.5 pollution in four seasons. Monthly mean PM2.5 typically exhibited a characteristic "U" shape. Diurnal mean PM2.5 concentrations were generally consistent with typical urban agglomerations, with maximum and minimum PM2.5 values occurring at approximately 08:00-12:00 and 15:00-17:00, respectively, except for the Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountain urban agglomeration (NSTM-UA) (14:00 and 08:00, respectively). A positive spatial autocorrelation of PM2.5 concentrations was observed in all urban agglomerations (except NSTM-UA); high-high agglomeration centers of PM2.5 pollution were located far inland with a circular distribution, and low-low agglomeration centers formed at the periphery of the high-high agglomeration region. This study is key for understanding the difference in PM2.5 concentrations among urban agglomerations and region-oriented air pollution control strategies are highly suggested.
DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.088URLPMID:31096175 [本文引用: 1]

Numerous environmental problems have been seen due to the "high energy consumption, high pollution, high emissions" economic model in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration (BTHUA). The coupling coordination degree model is applied to provide a coordination of urbanization and ecological environment composite system (CUECS) value while a geographic detector is applied to explore the dominant factors controlling it. This study reached the following conclusions. (1)The CUECS types are mainly low coordination, but which generally exhibit positive evolutionary trend. The change trends can be characterized as urbanization lags followed by system equilibrium followed by ecological environmental lags. (2)The CUECS conforms to a core-edge distributional pattern that comprises plain high mountain low, inland high coastal low. Industrialization played a key role in the development of BTHUA, the landform type was the important factor controlling CUECS. (3) Social consumer goods, gross domestic product, the disposable income of urban residents (all per capita) are the core factors controlling CUECS within different spatial units. Urbanization rate, per capita social consumer goods, the proportion of tertiary industrial population are the core factors controlling CUECS during different urbanization development stages. (4)The relative impacts of urbanization and ecological environmental subsystems on CUECS are (in decreasing order of importance) population urbanization, economic urbanization, social urbanization, ecological environment subsystem. Therefore, green urbanization remains the primary path for sustainable development within the urban agglomeration. It is unsuitable for rapid urbanization development model in the mountainous areas that encapsulate ecological and environmental security as their main functions, so the government urgently needs to amend its 'one size fits all' policy system.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.05.001URL [本文引用: 1]

In recent years, China’s industrialization and urbanization have entered a new transformational stage of development. The contradictions between innovation-driven development and institutional constraints are intensified, and the problems of resource shortage and inefficiency of resource allocation are becoming increasingly prominent. Therefore, multiple planning integration that merges economic and social development planning, urban spatial planning, and land use planning into an overall planning system has received wide attention from academics and governments at all levels. Promoting multiple planning integration and innovating the theories and technical methods of regional planning, as well as constructing the spatial planning system of national territory with Chinese characteristics, have become an important issue in further reform. This study analyzed the practical problems of planning segregation and essential characteristics of multiple planning contradictions and discussed the strategic positioning of multiple planning integration. Then we constructed a basic theoretical framework of multiple planning integration with “three primaries” and “three separations”. Finally, the technical approaches and long-term mechanisms for gradual multi-plan adjustments were proposed. It can be concluded that the essence of multiple planning integration is to integrate and coordinate all plans at the strategic level of regional spatial structure optimization, and guide the optimization of urban-rural land allocation so that it can achieve spatial consistency, functional integration, and coordination in the development process. Multiple planning integration is neither to prepare a plan nor to focus on solving the greatest common divisor of existing multiple plans, but to promote the formation of a regional planning system with the characteristics of overall-and sub-planning, clear hierarchy, and functional specificity.
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.05.001URL [本文引用: 1]

In recent years, China’s industrialization and urbanization have entered a new transformational stage of development. The contradictions between innovation-driven development and institutional constraints are intensified, and the problems of resource shortage and inefficiency of resource allocation are becoming increasingly prominent. Therefore, multiple planning integration that merges economic and social development planning, urban spatial planning, and land use planning into an overall planning system has received wide attention from academics and governments at all levels. Promoting multiple planning integration and innovating the theories and technical methods of regional planning, as well as constructing the spatial planning system of national territory with Chinese characteristics, have become an important issue in further reform. This study analyzed the practical problems of planning segregation and essential characteristics of multiple planning contradictions and discussed the strategic positioning of multiple planning integration. Then we constructed a basic theoretical framework of multiple planning integration with “three primaries” and “three separations”. Finally, the technical approaches and long-term mechanisms for gradual multi-plan adjustments were proposed. It can be concluded that the essence of multiple planning integration is to integrate and coordinate all plans at the strategic level of regional spatial structure optimization, and guide the optimization of urban-rural land allocation so that it can achieve spatial consistency, functional integration, and coordination in the development process. Multiple planning integration is neither to prepare a plan nor to focus on solving the greatest common divisor of existing multiple plans, but to promote the formation of a regional planning system with the characteristics of overall-and sub-planning, clear hierarchy, and functional specificity.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/xb201012009URL [本文引用: 1]

Since the theory of "Pole & Axis System" was proposed, great achievements have been made in its theoretical expansion and practical application. With the development of GIS and the wide application of spatial analysis techniques, further research of the theory of "Pole & Axis System" depends on innovation of regional spatial analysis methods and techniques. Based on the "Pole & Axis System" theory proposed by Professor Lu Dadao, a spatial analysis method of "Pole & Axis System" was introduced. The method combines point elements, including town node, traffic node (port, airport, railway station, highway intersection) with linear elements (waterway, railway, highway, land way) of regional spatial structure in various ways and analyzes the spatial accessibility and the spatial diffusion. It takes linear elements as diffusion route to analyze gradual diffusion of point elements and calculate spatial accessibility of "Pole & Axis System". "Pole & Axis Gradual Diffusion Model" is constructed as time-distance attenuation diffusion model according to exponential and linear diffusion pattern. Also the model selects "Weighted Average Travel Time" as evaluation indicator of spatial accessibility and adopts the minimal seed algorithm to calculate minimal travel time and shortest path from one cell to others in the region. Based on GIS, "Pole & Axis" spatial analysis information system is developed, in which several common formations of "Pole & Axis System" are simulated. Also spatial pattern and evolution of node diffusion and accessibility are analyzed. A case taking Yangtze River Delta as a test region is presented. It chooses 16 cities as point elements and uses land traffic network of 1985, 1995, 2006 and 2020 as axis elements. The case studies axial gradual spatial diffusion of city nodes based on land traffic network of different periods and generates diffusion maps of score and accessibility of every city node for different periods. The results show the following aspects: Firstly, diffusion scores and regional accessibility values of city nodes are increasing every year. Secondly, spatial diffusion is evolving from multiple cores into a single one and the diffusion axis is apparent. Thirdly, the Yangtze River Delta region is integrated gradually, but the disequilibrium between regions is enlarged. Finally, the "Z"-shaped high-speed traffic corridor of Nanjing, Shanghai, Hangzhou and Ningbo is formed.
DOI:10.11821/xb201012009URL [本文引用: 1]

Since the theory of "Pole & Axis System" was proposed, great achievements have been made in its theoretical expansion and practical application. With the development of GIS and the wide application of spatial analysis techniques, further research of the theory of "Pole & Axis System" depends on innovation of regional spatial analysis methods and techniques. Based on the "Pole & Axis System" theory proposed by Professor Lu Dadao, a spatial analysis method of "Pole & Axis System" was introduced. The method combines point elements, including town node, traffic node (port, airport, railway station, highway intersection) with linear elements (waterway, railway, highway, land way) of regional spatial structure in various ways and analyzes the spatial accessibility and the spatial diffusion. It takes linear elements as diffusion route to analyze gradual diffusion of point elements and calculate spatial accessibility of "Pole & Axis System". "Pole & Axis Gradual Diffusion Model" is constructed as time-distance attenuation diffusion model according to exponential and linear diffusion pattern. Also the model selects "Weighted Average Travel Time" as evaluation indicator of spatial accessibility and adopts the minimal seed algorithm to calculate minimal travel time and shortest path from one cell to others in the region. Based on GIS, "Pole & Axis" spatial analysis information system is developed, in which several common formations of "Pole & Axis System" are simulated. Also spatial pattern and evolution of node diffusion and accessibility are analyzed. A case taking Yangtze River Delta as a test region is presented. It chooses 16 cities as point elements and uses land traffic network of 1985, 1995, 2006 and 2020 as axis elements. The case studies axial gradual spatial diffusion of city nodes based on land traffic network of different periods and generates diffusion maps of score and accessibility of every city node for different periods. The results show the following aspects: Firstly, diffusion scores and regional accessibility values of city nodes are increasing every year. Secondly, spatial diffusion is evolving from multiple cores into a single one and the diffusion axis is apparent. Thirdly, the Yangtze River Delta region is integrated gradually, but the disequilibrium between regions is enlarged. Finally, the "Z"-shaped high-speed traffic corridor of Nanjing, Shanghai, Hangzhou and Ningbo is formed.
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.11.001URL [本文引用: 1]

This article examines the spatial development structure of the Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREB) with respect to the role of the YREB in the overall spatial development of China's geographical space and the characteristics of the spatial development structure of the YREB. Based on the analysis of the population and economic activity aggregation function of the YREB and the radiation effect of the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), as well as the impact of globalization and regional integration on the spatial development structure of China's geographical space, this study analyzed the strategic position of the YREB. It also summarizes the characteristics of the spatial development pattern of the YREB through the analysis of the volume structure, spatial structure, and causes of resources and environment carrying capacity, spatial development suitability, and Main Function Zoning (MFZ) and cross analysis among them, and a comparison with these at the national level. Finally, according to the innovative development requirements of the Fifth Plenary Session of the 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, this article preliminarily examines the effects that innovative factors will have on the future strategic position and spatial structure evolution of the YREB and proposes relevant suggestions.
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.11.001URL [本文引用: 1]

This article examines the spatial development structure of the Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREB) with respect to the role of the YREB in the overall spatial development of China's geographical space and the characteristics of the spatial development structure of the YREB. Based on the analysis of the population and economic activity aggregation function of the YREB and the radiation effect of the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), as well as the impact of globalization and regional integration on the spatial development structure of China's geographical space, this study analyzed the strategic position of the YREB. It also summarizes the characteristics of the spatial development pattern of the YREB through the analysis of the volume structure, spatial structure, and causes of resources and environment carrying capacity, spatial development suitability, and Main Function Zoning (MFZ) and cross analysis among them, and a comparison with these at the national level. Finally, according to the innovative development requirements of the Fifth Plenary Session of the 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, this article preliminarily examines the effects that innovative factors will have on the future strategic position and spatial structure evolution of the YREB and proposes relevant suggestions.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201504001URL [本文引用: 1]

As a country's brand-new geographical unit in global competition and international division of labor, urban agglomeration is the product of China's new industrialization and urbanization in a higher stage, as well as the main battlefield of the "One Belt and One Road" project. Meanwhile, the development of urban agglomerations dominates not only the economic arteries, but also the future of China's new urbanization. Hence, it is of great strategic significance to promoting China's new urbanization and socio-economic development. However, a series of problems have emerged in the selection and cultivation process of China's urban agglomerations, which needs appropriate technological paths and plans to facilitate the healthy development of China's urban agglomerations from the scientific point of view. Therefore, the "High-Level Forum on China's Urban Agglomeration Development", jointly organized by the Geographical Society of China, the China's City Forum of Hundred Experts, and the Institute of Geographic Science and Natural Resources Research, CAS, was held in Beijing on December 20, 2014. After a series of heated debates, contention and discussion, nearly 100 experts attending the forum agreed that: (1) urban agglomeration plays an important role and dominates China's new urbanization. The research and development of urban agglomerations is a complex scientific issue and a very long process, as well as a natural process which cannot go against the objective laws; (2) there is a fierce debate and discussion on the basic connotation and standards of spatial recognition range, the benefit and value orientation are different at the policy level and academic level; (3) during the selection and cultivation process, "urban agglomeration disease", such as indiscriminating enclosure, unlimited sprawl, spoiling cities by excessive enthusiasm, create something out of nothing and throwing cities together in groups, should be solved as soon as possible; (4) different organization plans for the future spatial pattern of China's urban agglomerations are forming; (5) distinctive development patterns and problems do exist among urban agglomerations with different development levels, for example, the collaborative development optimization mode of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, the expansion mode of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, the parallel development mode of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration, the spatial integration mode of Central and Southern Liaoning urban agglomeration, the intersecting parallels ("#") space pattern of Harbin-Changchun urban agglomeration, the strategic integration mode of Central Plains urban agglomeration, and the balanced organization mode of Guanzhong urban agglomeration.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201504001URL [本文引用: 1]

As a country's brand-new geographical unit in global competition and international division of labor, urban agglomeration is the product of China's new industrialization and urbanization in a higher stage, as well as the main battlefield of the "One Belt and One Road" project. Meanwhile, the development of urban agglomerations dominates not only the economic arteries, but also the future of China's new urbanization. Hence, it is of great strategic significance to promoting China's new urbanization and socio-economic development. However, a series of problems have emerged in the selection and cultivation process of China's urban agglomerations, which needs appropriate technological paths and plans to facilitate the healthy development of China's urban agglomerations from the scientific point of view. Therefore, the "High-Level Forum on China's Urban Agglomeration Development", jointly organized by the Geographical Society of China, the China's City Forum of Hundred Experts, and the Institute of Geographic Science and Natural Resources Research, CAS, was held in Beijing on December 20, 2014. After a series of heated debates, contention and discussion, nearly 100 experts attending the forum agreed that: (1) urban agglomeration plays an important role and dominates China's new urbanization. The research and development of urban agglomerations is a complex scientific issue and a very long process, as well as a natural process which cannot go against the objective laws; (2) there is a fierce debate and discussion on the basic connotation and standards of spatial recognition range, the benefit and value orientation are different at the policy level and academic level; (3) during the selection and cultivation process, "urban agglomeration disease", such as indiscriminating enclosure, unlimited sprawl, spoiling cities by excessive enthusiasm, create something out of nothing and throwing cities together in groups, should be solved as soon as possible; (4) different organization plans for the future spatial pattern of China's urban agglomerations are forming; (5) distinctive development patterns and problems do exist among urban agglomerations with different development levels, for example, the collaborative development optimization mode of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, the expansion mode of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, the parallel development mode of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration, the spatial integration mode of Central and Southern Liaoning urban agglomeration, the intersecting parallels ("#") space pattern of Harbin-Changchun urban agglomeration, the strategic integration mode of Central Plains urban agglomeration, and the balanced organization mode of Guanzhong urban agglomeration.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/xb200704001URL [本文引用: 1]

Major function oriented zoning (MFOZ hereafter) is the guideline for optimizing the spatial pattern of regional development in China, which entails both theoretical and methodological innovation in the academic field of economic geography. This study analyzes the basic features of territorial function and puts forward a spatially equilibrium model for regional development. It argues that there exists a trend of regional convergence in almost any indicator measuring the average level of regional development status. Based on this finding, the study illustrates that the formation of functional zone should be conducive to the reduction of regional inequality and that free flow of resources across region is the prerequisite to spatial equilibrium. It also investigates the impact of territorial functional evolution on spatial processes of equilibrium and suggests that the benefit to be derived from zoning proposal is contingent upon the method of regional division and correct understanding of temporal change of territorial function. After that, this study goes to examine the scientific foundation of several issues concerning the reconciliation of contradictory functions of development and protection, the selection of indicators and the spatial and temporal features of MFOZ. It is then followed by an interrogation of the rationality of achieving dual goals of efficiency and equality simultaneously through three-dimensional flow and spatial equilibrium. The paper ends with a discussion of the position, implementation and coordination of MFOZ from the perspective of institutional arrangements of spatial governance including law, planning and government policy.
DOI:10.11821/xb200704001URL [本文引用: 1]

Major function oriented zoning (MFOZ hereafter) is the guideline for optimizing the spatial pattern of regional development in China, which entails both theoretical and methodological innovation in the academic field of economic geography. This study analyzes the basic features of territorial function and puts forward a spatially equilibrium model for regional development. It argues that there exists a trend of regional convergence in almost any indicator measuring the average level of regional development status. Based on this finding, the study illustrates that the formation of functional zone should be conducive to the reduction of regional inequality and that free flow of resources across region is the prerequisite to spatial equilibrium. It also investigates the impact of territorial functional evolution on spatial processes of equilibrium and suggests that the benefit to be derived from zoning proposal is contingent upon the method of regional division and correct understanding of temporal change of territorial function. After that, this study goes to examine the scientific foundation of several issues concerning the reconciliation of contradictory functions of development and protection, the selection of indicators and the spatial and temporal features of MFOZ. It is then followed by an interrogation of the rationality of achieving dual goals of efficiency and equality simultaneously through three-dimensional flow and spatial equilibrium. The paper ends with a discussion of the position, implementation and coordination of MFOZ from the perspective of institutional arrangements of spatial governance including law, planning and government policy.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.01.001URL [本文引用: 1]

Future Earth initiative puts forward the academic thought, top-level design, core content, and methodology for systemic solutions of regional sustainable development, which provides a reference for future research of regional sustainable development in human-economic geography. Based on an analysis of the core concepts of Future Earth, this article elaborates the development opportunities and positioning of human-economic geography, and discusses the five grand challenges of Future Earth and their implications for exploring systemic solutions of regional sustainable development. It maintains that progress in the study of each of these challenges is essential to overall solve the problem of global sustainable development. This article also discusses the objective, perspective, and path of regional sustainable development system, and analyzes the academic thought of systemic solutions for regional sustainable development from the applied basic research and application practice. Using the Future Earth research initiative as a reference and based on the research framework of the regional sustainable development system, it examines the future development of human-economic geography from the three aspects of improving the ability of prediction and assessment, applied research on regulatory process and controlling mode, and institutional design with respect to Future Earth.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.01.001URL [本文引用: 1]

Future Earth initiative puts forward the academic thought, top-level design, core content, and methodology for systemic solutions of regional sustainable development, which provides a reference for future research of regional sustainable development in human-economic geography. Based on an analysis of the core concepts of Future Earth, this article elaborates the development opportunities and positioning of human-economic geography, and discusses the five grand challenges of Future Earth and their implications for exploring systemic solutions of regional sustainable development. It maintains that progress in the study of each of these challenges is essential to overall solve the problem of global sustainable development. This article also discusses the objective, perspective, and path of regional sustainable development system, and analyzes the academic thought of systemic solutions for regional sustainable development from the applied basic research and application practice. Using the Future Earth research initiative as a reference and based on the research framework of the regional sustainable development system, it examines the future development of human-economic geography from the three aspects of improving the ability of prediction and assessment, applied research on regulatory process and controlling mode, and institutional design with respect to Future Earth.
DOI:10.7189/jogh.09.020201URLPMID:31489184 [本文引用: 1]

While physiotherapists appear to be ideally positioned as key role players in achieving the health- and education-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), few studies have examined the complete scope of physiotherapy practice in addressing the SDGS. Considering the broad scope of physiotherapy practice, physiotherapists are a valuable resource that the South African government can utilise to address their workforce shortages in achieving inclusive primary education, promoting gender equality, reducing child mortality, improving maternal health, and combating HIV and AIDS, and other diseases.
URL [本文引用: 1]

China's national economy has experienced a long period of rapid growth, but prominent structural problems have already appeared. Instead of following the traditional research approach of investigating the speed of future economic growth through investment, consumption and export, this article analyzes the capacities of systems which support economic growth, including resource(energy), environment(bearing capacity) and the urbanization and development patterns on the basis of resources and environment. It includes seven aspects:① It points out that the long period of high-speed-but-low-efficiency economic growth has led to the structural problems at the current stage. ② It analyzes the serious situation of China's environmental pollution. ③ It argues that excessive consumption of natural resources may bring about severe national security issues. ④ It indicates that urbanization is the most important supporting factor of the high-speed economic development of our country.⑤ It holds that the development patterns of"world factory"of low-end products and relying on investment which have been practiced for a long period of time are important concepts and supports of the high-speed economic development of China. ⑥ It also argues that China has taken full advantage of backwardness which has limits in fact. ⑦ Finally, based on practice and international experience, it analyzes the relationships between the speed of economic growth and employment, the influence of the country, and economic transformation briefly. Based on these analyses, a meta-synthetic research is conducted and the following conclusions are arrived at:China's economic development will enter a stage of moderate-speed growth rather quickly. The economic growth of a moderate speed will create significant opportunities and spaces for building economic superpower and achieving a harmonious society in China.
URL [本文引用: 1]

China's national economy has experienced a long period of rapid growth, but prominent structural problems have already appeared. Instead of following the traditional research approach of investigating the speed of future economic growth through investment, consumption and export, this article analyzes the capacities of systems which support economic growth, including resource(energy), environment(bearing capacity) and the urbanization and development patterns on the basis of resources and environment. It includes seven aspects:① It points out that the long period of high-speed-but-low-efficiency economic growth has led to the structural problems at the current stage. ② It analyzes the serious situation of China's environmental pollution. ③ It argues that excessive consumption of natural resources may bring about severe national security issues. ④ It indicates that urbanization is the most important supporting factor of the high-speed economic development of our country.⑤ It holds that the development patterns of"world factory"of low-end products and relying on investment which have been practiced for a long period of time are important concepts and supports of the high-speed economic development of China. ⑥ It also argues that China has taken full advantage of backwardness which has limits in fact. ⑦ Finally, based on practice and international experience, it analyzes the relationships between the speed of economic growth and employment, the influence of the country, and economic transformation briefly. Based on these analyses, a meta-synthetic research is conducted and the following conclusions are arrived at:China's economic development will enter a stage of moderate-speed growth rather quickly. The economic growth of a moderate speed will create significant opportunities and spaces for building economic superpower and achieving a harmonious society in China.
DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.088URLPMID:31096175 [本文引用: 1]

Numerous environmental problems have been seen due to the "high energy consumption, high pollution, high emissions" economic model in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration (BTHUA). The coupling coordination degree model is applied to provide a coordination of urbanization and ecological environment composite system (CUECS) value while a geographic detector is applied to explore the dominant factors controlling it. This study reached the following conclusions. (1)The CUECS types are mainly low coordination, but which generally exhibit positive evolutionary trend. The change trends can be characterized as urbanization lags followed by system equilibrium followed by ecological environmental lags. (2)The CUECS conforms to a core-edge distributional pattern that comprises plain high mountain low, inland high coastal low. Industrialization played a key role in the development of BTHUA, the landform type was the important factor controlling CUECS. (3) Social consumer goods, gross domestic product, the disposable income of urban residents (all per capita) are the core factors controlling CUECS within different spatial units. Urbanization rate, per capita social consumer goods, the proportion of tertiary industrial population are the core factors controlling CUECS during different urbanization development stages. (4)The relative impacts of urbanization and ecological environmental subsystems on CUECS are (in decreasing order of importance) population urbanization, economic urbanization, social urbanization, ecological environment subsystem. Therefore, green urbanization remains the primary path for sustainable development within the urban agglomeration. It is unsuitable for rapid urbanization development model in the mountainous areas that encapsulate ecological and environmental security as their main functions, so the government urgently needs to amend its 'one size fits all' policy system.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117649URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201609001URL [本文引用: 1]

In view of the regional differentiation rules of land surface, research on terrestrial system (TS) has provided significant basis for the rational development of natural resources and layout of industries, and supported regional sustainable development as well. In this paper, the progress of TS research in China is overviewed and research frontiers in TS research in the near future under global change are explored. Since the 1950s, China has paid great attention to the TS study as its socio-economic development, and conducted research on physical geographical regionalization, eco-geographical regionalization and comprehensive regionalization. Along with the deepening of global change research, dynamics of TS have been highly concerned. During the studies, methodology has been developed from qualitative research of integration of experts' brainpower gradually to quantitative research based on field observation and experiments of the natural processes, including physical, chemical and biological processes, as well as application of information technology and mathematical simulation. Along with the emphasis on global change, TS would be combined with the ideology, objectives and key researches of Future Earth program, to focus on the mechanism and regional effects of interaction among land surface elements, the response of TS to global change, the quantitative recognition on regional unit boundary, and the combination of physical and human elements.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201609001URL [本文引用: 1]

In view of the regional differentiation rules of land surface, research on terrestrial system (TS) has provided significant basis for the rational development of natural resources and layout of industries, and supported regional sustainable development as well. In this paper, the progress of TS research in China is overviewed and research frontiers in TS research in the near future under global change are explored. Since the 1950s, China has paid great attention to the TS study as its socio-economic development, and conducted research on physical geographical regionalization, eco-geographical regionalization and comprehensive regionalization. Along with the deepening of global change research, dynamics of TS have been highly concerned. During the studies, methodology has been developed from qualitative research of integration of experts' brainpower gradually to quantitative research based on field observation and experiments of the natural processes, including physical, chemical and biological processes, as well as application of information technology and mathematical simulation. Along with the emphasis on global change, TS would be combined with the ideology, objectives and key researches of Future Earth program, to focus on the mechanism and regional effects of interaction among land surface elements, the response of TS to global change, the quantitative recognition on regional unit boundary, and the combination of physical and human elements.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908006URL [本文引用: 1]

As natural resources are experiencing rapid reduction and the environment is degenerating, resource environmental carrying capacity has attracted more and more attention in China. However, current research on resource environmental carrying capacity still stays at theoretical level leaving the gap with applications. Moreover, the study conclusions are usually not of policy implications and lack of operability. This study develops a comprehensive analytical framework for the co-development of industries, population, economy, resources and environment. The framework first evaluates the importance of all industries to local social economy and determines the direction of industrial structure adjustment, and then identifies the interaction relationships among the socioeconomic development, resource consumption and environment emission, and subsequently evaluates the resource environmental carrying capacity, which helps achieve the maximum socio-economic development under the premise of environmental protection and efficient resource utilization. The Tibet case study estimates the local resource environmental carrying capacity under different development scenarios and therefore determines the maximum population and economic scale through industrial structure adjustments under the constraints of resource and environment. The results show that to focus on the development of tourism can significantly improve the resource environmental carrying capacity of Tibet. The results could help make decision regarding local industrial structure adjustments to achieve sustainable development. In conclusion the proposed analytical framework provides an operational decision support tool for "socio-ecological" sustainability. It can be extended to other regions through minor parameter adjustments.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908006URL [本文引用: 1]

As natural resources are experiencing rapid reduction and the environment is degenerating, resource environmental carrying capacity has attracted more and more attention in China. However, current research on resource environmental carrying capacity still stays at theoretical level leaving the gap with applications. Moreover, the study conclusions are usually not of policy implications and lack of operability. This study develops a comprehensive analytical framework for the co-development of industries, population, economy, resources and environment. The framework first evaluates the importance of all industries to local social economy and determines the direction of industrial structure adjustment, and then identifies the interaction relationships among the socioeconomic development, resource consumption and environment emission, and subsequently evaluates the resource environmental carrying capacity, which helps achieve the maximum socio-economic development under the premise of environmental protection and efficient resource utilization. The Tibet case study estimates the local resource environmental carrying capacity under different development scenarios and therefore determines the maximum population and economic scale through industrial structure adjustments under the constraints of resource and environment. The results show that to focus on the development of tourism can significantly improve the resource environmental carrying capacity of Tibet. The results could help make decision regarding local industrial structure adjustments to achieve sustainable development. In conclusion the proposed analytical framework provides an operational decision support tool for "socio-ecological" sustainability. It can be extended to other regions through minor parameter adjustments.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-27-6-883URLPMID:18919987 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-27-6-883URLPMID:18919987 [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502001URL [本文引用: 1]

The "National New Urbanization Planning (2014-2020)" (hereinafter referred to as "Planning") marks a significant transformation in China's urbanization development process, with the core of human urbanization, and the general requirement of seeking advance in stability. This paper elaborates the authors' preliminary thoughts on the formation of the "Planning" mainly from the speed and quality aspects of the urbanization development. Urbanization level should be consistent with industrial restructuring, the amount of new jobs, the actual ability of absorbing rural population, and water-soil resource and environment capacity of the urban area, etc. The large scale and high speed urbanization development in China has resulted in severe environment pollution, great pressures on the infrastructure, and huge challenge to the supporting capacity of natural resources. Urbanization is an important frontier scientific issue with obvious cross disciplinary feature, which is also a complex system. The interdisciplinary human economic geography has outstanding advantages and solid research foundation in the field of urbanization research. Therefore, facing the significant realistic demand of the national new urbanization, we should do some in-depth research and tracking studies in this field.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502001URL [本文引用: 1]

The "National New Urbanization Planning (2014-2020)" (hereinafter referred to as "Planning") marks a significant transformation in China's urbanization development process, with the core of human urbanization, and the general requirement of seeking advance in stability. This paper elaborates the authors' preliminary thoughts on the formation of the "Planning" mainly from the speed and quality aspects of the urbanization development. Urbanization level should be consistent with industrial restructuring, the amount of new jobs, the actual ability of absorbing rural population, and water-soil resource and environment capacity of the urban area, etc. The large scale and high speed urbanization development in China has resulted in severe environment pollution, great pressures on the infrastructure, and huge challenge to the supporting capacity of natural resources. Urbanization is an important frontier scientific issue with obvious cross disciplinary feature, which is also a complex system. The interdisciplinary human economic geography has outstanding advantages and solid research foundation in the field of urbanization research. Therefore, facing the significant realistic demand of the national new urbanization, we should do some in-depth research and tracking studies in this field.
DOI:10.1007/s11442-019-1685-zURL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/141926URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/141926URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/xb201010001URL [本文引用: 1]

Cities have been greatly influenced by the wave of globalization during the past half century, which has made the World City and Global City into a world popular research heat topic. Most existing research has focused on the about 50 cities on the top of the world city system before the end of the 1980s, only very recently extended to the 220 major cities, while most cities in the developing countries are neglected out of the World City Map. Regarding the driving forces of the World City/Global City, the economic function, particularly the producer services of these cities at the global level, in which the roles transnational corporations play, have been over emphasized. The questions are naturally and automatically arising: Are the other cities besides the top ones influenced by globalization? Are those average cities also experiencing the process of globalization? In which ways and at what levels are those general cities globalizing or globalized? In order to seek answers to these questions, Taking all the cities in China at prefectural level and above as research objects, we constructed an evaluation indicator system, and explored the change of the urban globalization levels of each Chinese city based on the data covering the years of 1984, 1990, 1995, 2000, 2004 and 2007. We found that: (1) all China's cities has witnessed the rise of their urban globalization levels during the last more than 2 decades. (2) The major cities such as Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen and Guangzhou have seen the most rapid development of urban globalization. So not only the world top cities but also the average Chinese cities have been experiencing the process of globalization. We have also found that manufacturing function has been a very important driving force of many world factory cities in the course of their globalization process in China.
DOI:10.11821/xb201010001URL [本文引用: 1]

Cities have been greatly influenced by the wave of globalization during the past half century, which has made the World City and Global City into a world popular research heat topic. Most existing research has focused on the about 50 cities on the top of the world city system before the end of the 1980s, only very recently extended to the 220 major cities, while most cities in the developing countries are neglected out of the World City Map. Regarding the driving forces of the World City/Global City, the economic function, particularly the producer services of these cities at the global level, in which the roles transnational corporations play, have been over emphasized. The questions are naturally and automatically arising: Are the other cities besides the top ones influenced by globalization? Are those average cities also experiencing the process of globalization? In which ways and at what levels are those general cities globalizing or globalized? In order to seek answers to these questions, Taking all the cities in China at prefectural level and above as research objects, we constructed an evaluation indicator system, and explored the change of the urban globalization levels of each Chinese city based on the data covering the years of 1984, 1990, 1995, 2000, 2004 and 2007. We found that: (1) all China's cities has witnessed the rise of their urban globalization levels during the last more than 2 decades. (2) The major cities such as Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen and Guangzhou have seen the most rapid development of urban globalization. So not only the world top cities but also the average Chinese cities have been experiencing the process of globalization. We have also found that manufacturing function has been a very important driving force of many world factory cities in the course of their globalization process in China.
DOI:10.1007/s11442-015-1216-5URL [本文引用: 1]

Urban agglomerations are an inevitable outcome of China’s new national industrialization and urbanization reaching relatively advanced stages of development over the past 30 years. In the early 2000s, urban agglomerations became new geographical units for participating in global competition and the international division of labor, and China has spent the past decade promoting them as the main spaces for pushing forward its new form of urbanization. The convening of the first Central Work Conference on Urbanization and the National New-type Urbanization Plan (2014-2020) further defined the status of urban agglomerations as the main players in promoting China’s new type of national urbanization. Nevertheless, urban agglomerations remain a weak link in Chinese academia and are in urgent need of study. Only 19 articles on the theme of urban agglomerations were published in the journal Acta Geographica Sinica between 1934 and 2013, accounting for only 0.55% of all articles written during that period. Not only are there very few, they have also all been published within a relatively short period of time, with the first having been published only 10 years ago. The studies are also concentrated among only a few authors and institutions, and research is aimed at national requirements but is rather divergent. Even so, some studies on urban agglomerations have played a leading role and made important contributions to dictating the overall formation of urban agglomerations nationwide. Specifically, a proposed spatial pattern for urban agglomerations formed the basic framework for the spatial structure of China’s urban agglomerations and guided the government to make urban agglomerations the main urban pattern when promoting the new type of urbanization; proposed standards and technologies for identifying the spatial dimensions of urban agglomerations played an important role in defining the scope of national urban agglomerations; a series of studies in the area of urban agglomerations spurred more in-depth and practical studies in the field; and studies on issues related to the formation and growth of urban agglomerations provided warnings on the future selection and development of urban agglomerations. Taking the progress and results of these studies as a foundation, the foci of selecting and developing urban agglomerations in China are as follows: to be problem-oriented and profoundly reflect on and review new problems exposed in the selection and development of urban agglomerations; to concentrate on urban agglomerations and lay importance on the formation of a new “5+9+6” spatial structure for China’s urban agglomerations; to rely on urban agglomerations and promote the formation of a new pattern of national urbanization along the main axes highlighted by urban agglomerations; to be guided by national strategic demand and continue to deepen understanding of major scientific issues in the course of the formation and development of urban agglomerations, including studying the resource and environmental effects of high-density urban agglomerations, scientifically examining resource and environmental carrying capacities of high-density urban agglomerations, creating new management systems and government coordination mechanisms for the formation and development of urban agglomerations, studying the establishment of public finance systems and public finance reserve mechanisms for urban agglomerations, and studying and formulating technical specifications for urban agglomeration planning and standards for delineating urban agglomeration boundaries.
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.11.007URL [本文引用: 1]

The Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREB) is a significant supporting area for transforming the spatial pattern of regional development in China from the T-shaped structure to a new H-shaped structure. The hierarchical structure of the urban system of the Yangtze River Economic Belt presents a pyramid pattern featured by unbalanced division in function of the upper-, middle-, and lower reaches, unbalanced spatial structure of development, and deep pressures on the resources and environment. At present, problems of urban agglomeration development along the Yangtze River Economic Belt include the mismatch of space delimitation with development standard and strong government intervention. The overall development level is weaker than the coastal urban agglomerations, urban agglomeration development decreases from the downstream areas to the upstream areas, ecological and resources security situation is grim, cities within the agglomerations compete rather than cooperate, and there is a lack of overall coordination mechanism. Thus, this study recommends to use the river basin and transport system integration as a main theme, to promote integration and market development of urban agglomerations of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and build a new "1+2+3" staged or differented development pattern for urban agglomerations along the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Supported by different driving forces, the development should emphasize advantages and priorities of urban agglomerations at all levels according to the local conditions. The strategic development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in the future can take the following measures: set up a development committee for urban agglomeration integration of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and establish an overall coordination mechanism for river basin integration; follow principles of urban agglomeration development and avoid irrational enlargement of urban agglomerations that is separated from the local reality; build a urban system with linkages between urban agglomerations as the strategic base; establish public financing and public fiscal reserves mechanism for the development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt; strengthen cooperation for ecological environment protection and build eco-friendly urban agglomerations; speed up the innovation-driven development and build an innovative urban agglomeration; and prioritize the construction of a series of major projects and national-level new districts to support the development of urban agglomerations along the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.11.007URL [本文引用: 1]

The Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREB) is a significant supporting area for transforming the spatial pattern of regional development in China from the T-shaped structure to a new H-shaped structure. The hierarchical structure of the urban system of the Yangtze River Economic Belt presents a pyramid pattern featured by unbalanced division in function of the upper-, middle-, and lower reaches, unbalanced spatial structure of development, and deep pressures on the resources and environment. At present, problems of urban agglomeration development along the Yangtze River Economic Belt include the mismatch of space delimitation with development standard and strong government intervention. The overall development level is weaker than the coastal urban agglomerations, urban agglomeration development decreases from the downstream areas to the upstream areas, ecological and resources security situation is grim, cities within the agglomerations compete rather than cooperate, and there is a lack of overall coordination mechanism. Thus, this study recommends to use the river basin and transport system integration as a main theme, to promote integration and market development of urban agglomerations of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and build a new "1+2+3" staged or differented development pattern for urban agglomerations along the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Supported by different driving forces, the development should emphasize advantages and priorities of urban agglomerations at all levels according to the local conditions. The strategic development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in the future can take the following measures: set up a development committee for urban agglomeration integration of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and establish an overall coordination mechanism for river basin integration; follow principles of urban agglomeration development and avoid irrational enlargement of urban agglomerations that is separated from the local reality; build a urban system with linkages between urban agglomerations as the strategic base; establish public financing and public fiscal reserves mechanism for the development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt; strengthen cooperation for ecological environment protection and build eco-friendly urban agglomerations; speed up the innovation-driven development and build an innovative urban agglomeration; and prioritize the construction of a series of major projects and national-level new districts to support the development of urban agglomerations along the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
DOI:10.11821/xb200802001URL [本文引用: 1]

The agriculture, rural and farmer development are the principal and radical problems in the recent economic and social process in China. Nowadays, aiming at building a moderately prosperous society in all respects and modernizing the country, the project of new socialist countryside construction was advanced at the Fifth Plenary Session of the 16th Central Committee of the Party, which means advanced production, improved livelihood, a civilized social atmosphere, clean and tidy villages and efficient management. Though many researches have been conducted on the new socialist countryside construction and given some suggestions, there have been relatively few studies on the research of rural development theory. It is an original approach to the analysis of the elements and configuration of the whole rural development system to provide theoretical basis for choosing rural development models based on the view of system theory. The results are as the follows: (1) The regional system is a urban-rural integration, so it is very necessary to study rural development problem in the general framework of the whole regional system. (2) Regional rural development system is a complicated synthesis, including regional rural development core system and regional rural development exterior system. The former is composed of rural natural system, rural economic system, rural social system and rural ecological system, and the latter consists of regional development policies, international trade circumstance, etc. The essence of rural development is the process of mutual coupling and coordination of the two sub-systems. (3) The regional rural comprehensive ability lies on two aspects including the rural development inner ability and the exterior drive of urbanization and industrialization. The interaction mechanism obeys parallelogram principle in physics. The evolvement characteristics of rural development system are different in the different combinations of the inner and exterior driving forces. (4) According to the difference of rural development driving forces, rural development models are classified into two types, namely the dominant type of rural self-development and the dominant type of the exterior drive of industrialization and urbanization, and six sub-types at the second level, which are industry driving, villages and towns construction driving, labor force transfer driving, characteristic industry driving, eco-tourism development and specialized market organization driving. In conclusion, it is a scientific approach to the exploration of regional rural sustainable development models, based on the analysis of elements, construction, and function of regional rural development system and characteristics.
DOI:10.11821/xb200802001URL [本文引用: 1]

The agriculture, rural and farmer development are the principal and radical problems in the recent economic and social process in China. Nowadays, aiming at building a moderately prosperous society in all respects and modernizing the country, the project of new socialist countryside construction was advanced at the Fifth Plenary Session of the 16th Central Committee of the Party, which means advanced production, improved livelihood, a civilized social atmosphere, clean and tidy villages and efficient management. Though many researches have been conducted on the new socialist countryside construction and given some suggestions, there have been relatively few studies on the research of rural development theory. It is an original approach to the analysis of the elements and configuration of the whole rural development system to provide theoretical basis for choosing rural development models based on the view of system theory. The results are as the follows: (1) The regional system is a urban-rural integration, so it is very necessary to study rural development problem in the general framework of the whole regional system. (2) Regional rural development system is a complicated synthesis, including regional rural development core system and regional rural development exterior system. The former is composed of rural natural system, rural economic system, rural social system and rural ecological system, and the latter consists of regional development policies, international trade circumstance, etc. The essence of rural development is the process of mutual coupling and coordination of the two sub-systems. (3) The regional rural comprehensive ability lies on two aspects including the rural development inner ability and the exterior drive of urbanization and industrialization. The interaction mechanism obeys parallelogram principle in physics. The evolvement characteristics of rural development system are different in the different combinations of the inner and exterior driving forces. (4) According to the difference of rural development driving forces, rural development models are classified into two types, namely the dominant type of rural self-development and the dominant type of the exterior drive of industrialization and urbanization, and six sub-types at the second level, which are industry driving, villages and towns construction driving, labor force transfer driving, characteristic industry driving, eco-tourism development and specialized market organization driving. In conclusion, it is a scientific approach to the exploration of regional rural sustainable development models, based on the analysis of elements, construction, and function of regional rural development system and characteristics.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004URL [本文引用: 1]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004URL [本文引用: 1]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1186/s12910-016-0113-5URLPMID:27209083 [本文引用: 1]

Systems medicine is the name for an assemblage of scientific strategies and practices that include bioinformatics approaches to human biology (especially systems biology); "big data" statistical analysis; and medical informatics tools. Whereas personalized and precision medicine involve similar analytical methods applied to genomic and medical record data, systems medicine draws on these as well as other sources of data. Given this distinction, the clinical translation of systems medicine poses a number of important ethical and epistemological challenges for researchers working to generate systems medicine knowledge and clinicians working to apply it.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201603011URL [本文引用: 1]

The purpose of this study is to explore the employment center system in the central city of Shanghai by using commuting data obtained from mobile phone signaling data in Shanghai. Based on the signaling data it is possible to identify the phone users' home residence and where their employment is. We compile the employment density map using the employment places data in order to identify the employment centers in Shanghai. Then the employment center system is measured based on two perspectives, namely employment density and commuting connection. We measure the level, the hinterland and influence sphere of each employment center in Shanghai central city. Our main conclusions are as follows: firstly, the employment center system in Shanghai central city is a weak multi-centric system with a strong primary center. Secondly, centers with higher employment densities also contain stronger commuting connections to other areas, and the discrepancies of commuting connections between centers are even more significant. Thirdly, centers with higher levels also have larger hinterlands, but their influence spheres are not necessarily larger. Fourthly, the mixed degree of residential and employment land use is a more significant determinant of the residential and employment land use pattern balance of employment center than the level of the center. Finally, influence spheres are alternately distributed in areas that lack employment centers. To some extent, this paper helps to solve the problems of identifying employment centers and measuring commuting connections. Previous studies have been unable to perfectly identify such centers due to either an overly large spatial unit of measurement or lack of commuting data. This paper will be helpful for constructing multi-center employment system in the central city of Shanghai.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201603011URL [本文引用: 1]

The purpose of this study is to explore the employment center system in the central city of Shanghai by using commuting data obtained from mobile phone signaling data in Shanghai. Based on the signaling data it is possible to identify the phone users' home residence and where their employment is. We compile the employment density map using the employment places data in order to identify the employment centers in Shanghai. Then the employment center system is measured based on two perspectives, namely employment density and commuting connection. We measure the level, the hinterland and influence sphere of each employment center in Shanghai central city. Our main conclusions are as follows: firstly, the employment center system in Shanghai central city is a weak multi-centric system with a strong primary center. Secondly, centers with higher employment densities also contain stronger commuting connections to other areas, and the discrepancies of commuting connections between centers are even more significant. Thirdly, centers with higher levels also have larger hinterlands, but their influence spheres are not necessarily larger. Fourthly, the mixed degree of residential and employment land use is a more significant determinant of the residential and employment land use pattern balance of employment center than the level of the center. Finally, influence spheres are alternately distributed in areas that lack employment centers. To some extent, this paper helps to solve the problems of identifying employment centers and measuring commuting connections. Previous studies have been unable to perfectly identify such centers due to either an overly large spatial unit of measurement or lack of commuting data. This paper will be helpful for constructing multi-center employment system in the central city of Shanghai.
DOI:10.1016/j.cities.2015.05.001URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
