2.
Comparison of spatial structure and linkage systems and geographic constraints: A perspective of multiple traffic flows
WANG Jiao'e1,2, DU Delin1,2, JIN Fengjun1,21. 2.
收稿日期:2019-01-2修回日期:2019-11-3网络出版日期:2019-12-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-01-2Revised:2019-11-3Online:2019-12-25
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
王姣娥(1981-),女,湖南涟源人,研究员,主要从事交通地理与区域发展研究E-mail:wangje@igsnrr.ac.cn。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (4081KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
王姣娥, 杜德林, 金凤君. 多元交通流视角下的空间级联系统比较与地理空间约束. 地理学报[J], 2019, 74(12): 2482-2494 doi:10.11821/dlxb201912005
WANG Jiao'e.
1 引言
随着全球化和信息化的不断推进以及交通技术的进步,各类要素在全球范围内快速流动,城市间的相互联系、相互作用和相互依赖程度不断加深,对城市体系和城市空间级联系统产生了深刻影响[1,2]。在“流空间”背景下,城市关系理论向“网络范式”转型, 关注点逐步转向由金融流、信息流、旅客流和物流等所构建的城市网络结构、功能和关系[3,4,5]。城市网络的本质是城市间的联系,即城市外部关系,其研究需要解决各种流的测度。目前,众多****已通过基础设施[6,7,8]、企业组织[9,10]和社会文化[11]等路径刻画了不同要素流,对不同空间尺度的城市网络进行了大量研究,其中,基础设施包括航空等交通基础设施和互联网等远程通讯设施[12]。交通既是构成区域空间结构的重要组成部分,也是区域发展的重要支撑条件,对引导和优化区域发展的空间秩序具有重要意义。作为“流空间”网络的一种重要表达形成,交通流可以直接反映城市间的联系密度、强度和等级结构,因此是研究城市等级体系和网络结构的重要手段。目前,学术界已有基于单一类型交通流的城市网络研究,主要包括航空流[13,14,15]、铁路(高铁)流[16,17,18]以及公路(高速公路)流[19,20],其中航空流是早期研究世界城市网络的重要手段[13,14],但基于多元交通流来表现城市网络结构异同性的研究相对较少。由于不同交通运输方式在技术经济特征、投资主体、运营和管理机构等方面存在一定差异,在地理空间上也会表现出不同的格局与结构特征,有****基于航空流和铁路(高铁)流对中国城市网络结构和组织模式进行了比较研究[5, 21],或进一步结合公路流数据,对比分析了航空、铁路和公路视角下城市网络的层级特征[22],但整体仍侧重于单个交通网络的分析,缺少对各类交通运输网络异同性的比较。此外,随着中国交通建设的高速化和网络化持续推进,交通运输体系不断完善,高速交通地位越来越重要,交通方式间的协调发展成为学术界和管理部门关注的焦点,比较多元交通流视角下的空间级联系统及城市网络组织结构具有重要的现实意义。
鉴于此,本文基于全国地级市(包括直辖市、地级行政区和省辖县级行政单元)研究尺度,采用长途汽车、高铁和航空时刻表数据构建交通组织网络,刻画表征公路、高铁和航空的城际空间运输联系,旨在比较分析多元交通流视角下的空间级联体系结构及其表达的城市网络组织体系,并揭示地理、行政、管理的空间约束作用。
2 理论框架设计与研究方法
2.1 概念与理论框架
空间组织是人类为实现发展目标而实施的一系列空间建构行动及其所产生的空间关联关系。金凤君基于空间组织的经济、文化和环境3方面的增益效应提出功效空间的概念,并以此为基础提出空间级联系统,即各类功效空间在相互联系和作用过程中逐渐形成的有层级关系、相互联系、不断追求均衡又不断打破均衡的动态空间系统[23,24]。空间级联系统体现在各类经济社会的空间活动中,城市体系和各类运输服务组织网络均属于典型的空间级联系统[24,25,26]。在系统中,各功效空间形成一定的结构层次和关联形式,即空间级联秩序。空间级联秩序是空间级联系统的基本特质,主要包括数量规则、时间演进、逻辑演绎和空间关联4方面内容[23]。在此秩序中,枢纽功效空间具有核心地位,层级间联系主要通过枢纽功效空间来实现。图1表达了空间级联系统在不同空间尺度的组织模式以及层级间的联系。图1
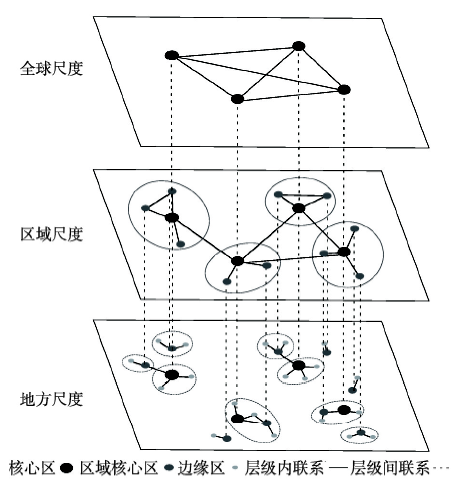 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1空间级联系统的组织模式与层级联系结构
Fig. 1Organizational pattern and hierarchical structure of spatial cascading system
作为空间级联系统的典型代表以及城市网络研究的常用视角,航空、铁路和公路运输的技术经济特征差异在空间上表现为适宜运输的距离不同,运营和管理体制的差异也促使形成不同的组织模式。航空运输适宜于大尺度、反映较高层次社会经济联系的空间级联体系研究,对短距离或低层级的级联关系刻画不足;铁路(高铁)是促使形成区域间交通经济带的重要运输方式,但其反映的空间级联系统在一定程度受制于设施空间,即受制于交通基础设施站点和线路的空间布局,对未设置站点的城市欠缺考量,由于中国西部地区的高铁网络尚不完善,则基于高铁的全国城市网络研究所反映的空间级联系统具有一定的局限性;公路运输在短距离内优势显著,可以实现“门对门”服务,适合刻画地方尺度的空间级联体系,但对长距离的级联关系反映不足。整体上,航空、铁路和公路适宜于在不同空间尺度反映不同层级的空间级联关系,3种运输网络在空间上既存在重叠性又存在差异性,其综合性研究可以更全面系统地解析空间级联系统的等级结构以及联系强度。
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 研究数据与网络构建 长途汽车数据主要通过调用欣欣旅游网(研究以地级市为基本单元。获取数据后,首先对同一城市的站点进行数据合并,即原数据站点对站点的连接关系投影到城市对城市的尺度。考虑到长途汽车、高铁和航空的运输组织模式、经停站点的时间以及对旅客出行的影响程度,本文采用如下方法来构建3种交通的运输网络:对长途汽车和高铁列车所经过的城市节点“A-B-C”分解为城市集合中任意2个城市之间的连接关系,即“A-B”、“A-C”和“B-C”,对少数中转或经停航班参考已有文献[27]将“A-B-C”分解为“A-B”和“B-C”。最后以城市为节点、运输联系频率为边,构建3种方式的对称矩阵M,公式为:
式中:n代表长途汽车(高铁或航空)覆盖的城市总量;aij代表城市
Tab. 1
表1
表12018年中国多元交通运输网络统计特征
Tab. 1
| 交通网络 | 城市数量 (个) | 城市发送/到达量(趟/日) | 城市对数量 (对) | 城市对运输联系(趟/日) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 标准差 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 标准差 | |||
| 长途汽车 | 361 | 544.4 | 6962 | 1 | 726.16 | 9208 | 10.7 | 780 | 0.25 | 30.90 |
| 高铁列车 | 229 | 164.0 | 1128 | 4 | 175.12 | 6856 | 23.2 | 694 | 1 | 42.84 |
| 航空运输 | 192 | 119.2 | 1452 | 1 | 230.42 | 2237 | 5.1 | 106 | 0.14 | 8.46 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
由于不同交通工具的单次载客量不同,运输组织模式也存在差异,因此仅采用频率数据会存在一定的差异。为便于直接比较,本文根据年均客运总量和年均运输频次,对每种交通工具的单次平均运量及在城市对间的分布进行粗略估算。根据2017年国内年旅客运量[28]和客运航班起飞架次,在对少数中转航班进行航段拆分的基础上,结合航空运输的“点对点”特征,可得出每架航班运量平均约117人。根据2017年国内高铁旅客运量[28]和开行列车数量,可估算每趟高铁载客约816人,考虑高铁列车具有串珠状的运输组织结构,根据高铁列车时刻表,每趟高铁列车平均停靠约9个站点,从而得出每趟高铁列车在各站点的平均上下旅客约91人,城市间的平均旅客运输约30人/趟。在公路运输方面,根据2017年全国公路营运载客汽车量(81.61万)和客位数(2099.18万)[28],参考得到平均每辆汽车客位约26人。综上所述,本文拟定航空、高铁和长途汽车的单次平均城际运量约117人/架、30人/趟和26人/趟,按此值将3种运输方式的频次比较转换为流量比较。
2.2.2 客流组织系数 为对比公路、高铁与航空组织网络的结构差异,构建客流组织系数,表示该城市对的运输联系强度占所有城市对联系总和的比重。客流组织系数常用于反映城市间的联系强度,值越大,表明城市对在网络中的地位越高。公式为[29,30]:
式中:RSLij表示城市i至城市j的客流组织系数;tij表示城市i至城市j的长途汽车(高铁或航空)班次。由于RSL的值过小,为便于比较,统一扩大1000倍[21, 30]。
2.2.3 社区结构 社区结构是一种刻画网络局部集聚特性的研究方法,是基于节点间的拓扑距离将网络划分为若干个子网络(即社区),在社区内部节点的联系紧密,而社区之间的联系相对较弱。基于社区结构,可以比较长途汽车、高铁和航空对城市间空间经济联系的影响,揭示3种网络的空间结构特征。本文主要采用Newman提出的“模块度”来衡量网络社区结构强度,模块度值越高则划分结果越好,反之则表示网络的社区结构特征不明显。模块度公式为[31,32]:
式中:Q表示模块度值;Aij表示城市i至城市j的长途汽车(高铁或航空)班次;ki和kj分别表示连接至城市i和城市j的班次总量;Ci和Cj分别是城市i和城市j分配的社区;m是网络中可能存在的最大线路数;当Ci = Cj时,
3 交通网络的地理格局与空间级联系统比较
3.1 地理空间格局
公路、铁路和航空3种交通网络的地理空间格局表现各异。其中,长途汽车网络具有强烈的空间依赖特征,高铁网络表现出明显的廊道效应,航空网络则体现了全国或大区域尺度的空间联系(图2)。从网络规模分析,长途汽车、高铁和航空网络规模依次降低;从地理格局分析,长途汽车依托发达的公路网络和较为完善的组织运输,已覆盖全国所有地级行政单元,在空间上形成了省域尺度内短距离、高频率的紧密联系;高铁运输依托铁轨线路和站点进行组织,发展时间相对较短,约覆盖全国2/3的城市,西部地区覆盖度较低,运输联系与“四纵四横”铁路客运专线走向基本一致;航空网络覆盖全国约1/2城市,涉及城市对数量约为长途汽车和高铁网络的25%和33%,基本形成了全国尺度下的跨区域空间联系网络框架。从三大地带分析,长途汽车和航空网络覆盖的城市数量呈“西部>中部>东部”的格局,而高铁网络则呈“东部>中部>西部”,这与高铁从东至西扩张、尚处于建设发展阶段以及更遵循社会经济联系耦合性密切相关。进一步对比运输联系的前十位城市和城市对(表2),长途汽车网络和高铁网络的顶层联系主要体现在以珠三角和长三角为代表的省域和区域尺度,而航空网络则在全国层面形成以“京沪穗蓉”为核心的跨区域联系网络。图2
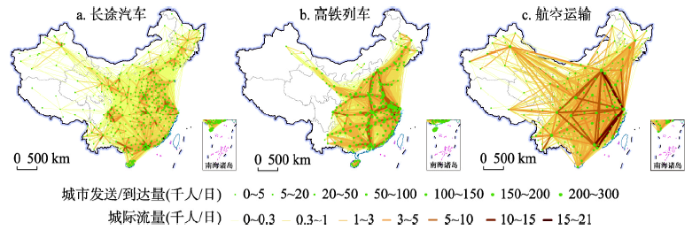 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图22018年中国长途汽车、高铁列车与航空运输的地理格局与运输联系
Fig. 2The networks of inter-city coach, high-speed train and flight in China in 2018
Tab. 2
表2
表22018年中国多元交通网络运输班次前十位城市和城市对比较
Tab. 2
| 位序 | 城市 | 城市对 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长途汽车 | 高铁列车 | 航空运输 | 长途汽车 | 高铁列车 | 航空运输 | ||
| 1 | 深圳 | 广州 | 上海 | 广州—深圳 | 南京—无锡 | 北京—上海 | |
| 2 | 广州 | 南京 | 北京 | 漳州—厦门 | 上海—南京 | 上海—深圳 | |
| 3 | 武汉 | 上海 | 广州 | 广州—东莞 | 上海—苏州 | 上海—广州 | |
| 4 | 东莞 | 武汉 | 西安 | 深圳—东莞 | 南京—苏州 | 北京—成都 | |
| 5 | 南京 | 无锡 | 昆明 | 广州—佛山 | 南京—常州 | 北京—深圳 | |
| 6 | 上海 | 长沙 | 成都 | 深圳—惠州 | 上海—无锡 | 上海—成都 | |
| 7 | 郑州 | 北京 | 深圳 | 广州—珠海 | 无锡—常州 | 上海—重庆 | |
| 8 | 南宁 | 杭州 | 重庆 | 厦门—泉州 | 广州—深圳 | 北京—广州 | |
| 9 | 中山 | 深圳 | 杭州 | 深圳—佛山 | 上海—常州 | 上海—青岛 | |
| 10 | 珠海 | 常州 | 南京 | 广州—中山 | 无锡—苏州 | 昆明—西双版纳 | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3.2 网络层级结构
长途汽车网络表现出省域尺度的“核心—边缘”结构,高铁网络呈轴线结构,航空网络则形成以“京沪穗蓉”这一菱形结构为核心的全国尺度网络框架。根据客流组织系数(RSL),以组间差异大、组内差异小的原则,将3种网络的城市对划分为5个层级(图3、表3),其中,前4层级城市对地位较高,以较少数量占据网络较多的班次资源,是网络的主要运输干线,长途汽车、高铁和航空网络分别以约4.8%、6.6%和22.9%的城市对占据了约51.8%、41.7%和69.9%的运输频率。空间上,省界对长途汽车网络具有明显的约束作用,其前4层级城市对中80.6%属于省内城市连接,同时半数左右连接本省省会或直辖市,即空间结构主要以省会或直辖市为核心。高铁网络前4层级城市对主要为“四纵四横”客运网络沿线城市之间的连接,尤其是京沪高铁和京广高铁。航空运输对经济技术的要求较高、受地理空间的限制较小,网络干线主要由远距离的各区域经济中心组成,前4层级城市对中67.6%为直辖市、省会或计划单列市之间的连接,并且主要围绕北京、上海、广州、深圳、成都等城市形成“菱形结构”。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图32018年中国多元交通网络的空间级联关系表达
Fig. 3The network hierarchies of the three transport networks in China in 2018
Tab. 3
表3
表32018年中国多元交通网络的城市空间层级结构特征
Tab. 3
| 交通网络(RSL) | 第一层级(≥ 5) | 第二层级(3~5) | 第三层级(1~3) | 第四层级(0.5~1) | 第五层级(0~0.5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长途汽车 | 城市对(个) | 4(0.04) | 12(0.13) | 162(1.76) | 260(2.82) | 8770(95.25) |
| 运输班次(趟/日) | 2457(2.50) | 4569(4.65) | 25527(25.96) | 18335(18.65) | 47434(48.24) | |
| 高铁列车 | 城市对(个) | 0(0.00) | 7(0.10) | 105(1.53) | 341(4.94) | 6403(93.43) |
| 运输班次(趟/日) | 0(0.00) | 4109(2.58) | 24499(15.38) | 37734(23.69) | 92940(58.35) | |
| 航空运输 | 城市对(个) | 10(0.45) | 28(1.25) | 224(10.01) | 250(11.18) | 1725(77.11) |
| 运输班次(趟/日) | 747(6.53) | 1207(10.55) | 4052(35.41) | 1998(17.46) | 3438(30.05) | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
进一步从首位联系分析,可以发现长途汽车、高铁和航空网络包含的首位城市数量依次减少,分别为145个、81个和36个,揭示了3种方式的核心城市对全网络的整合能力依次变强(图4)。省界对长途汽车和高铁的首位联系具有明显的约束,分别有87.3%和81.7%属于省内城市对,而航空网络中该比例仅为38.0%。在空间上,基于首位联系的长途汽车网络更加凸显了省域尺度的“核心—边缘”结构;高铁网络联系则主要遵循京沪、京广等高铁干线的约束,尤其武汉作为京广和沪汉蓉的交点,集中的首位联系最多,在高铁网络中的地位得到明显提升;航空网络则进一步体现了核心城市的全局控制能力,上海和北京成为约1/3城市的首位联系。
图4
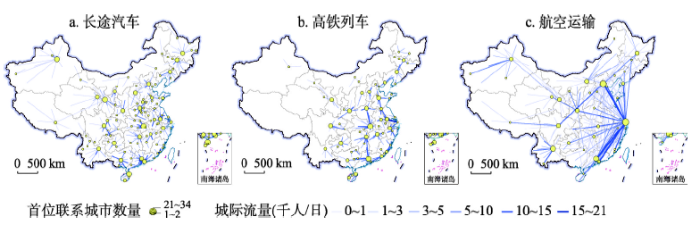 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图42018年中国多元交通网络中的首位联系比较
Fig. 4The dominant flow of the three transport modes in China in 2018
3.3 社区结构
长途汽车和高铁网络具有明显的社区结构(模块度分别为0.631和0.427),航空网络的社区结构不明显(模块度仅为0.124,图5)。依据模块度分析,长途汽车网络可划分为13个社区,各社区较大程度地沿袭了省级行政边界,部分省份整体或者省内大部分城市即为一个单独社区,如社区10为福建省;部分社区为相邻省份的大部分城市组合形成的区域性功能组团,如社区1由上海、江苏、浙江和安徽4省市组成;此外,部分位于省区边界的城市由于地理位置或自然环境等因素,被划分至邻省的社区中,例如内蒙古的呼伦贝尔、兴安盟和通辽3盟市更易接受相邻的黑龙江、吉林和辽宁的经济辐射,因而脱离本省框架,进入以东北三省为主体的社区7中。高铁网络可划分为9个社区,各社区受省界的约束明显较小,社区结构主要沿高铁干线分布,例如社区1主要由京沪和济青等高铁沿线的城市组成。由于地理空间和设施空间的限制,内蒙古和海南的高铁网络与其他区域分割,成为2个独立的社区(7和9)。相比之下,航空网络的社区结构不明显,仅可划分为5个社区,且大部分社区突破地理空间限制,在地理空间上呈不连续分布特征。图5
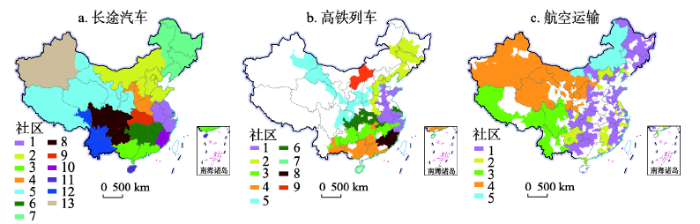 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图52018年中国多元交通网络中的社区结构比较
Fig. 5The community structure of the three transport networks in China in 2018
4 多元交通网络的空间异同性分析
4.1 网络布局的一致性与差异性
从个人出行视角出发,交通方式间的替代性是形成竞争关系的基础,当城际出行同时存在多种交通方式时,居民出行存在多种选择机会,从而形成潜在的竞争关系。以具有多种交通出行选择的城市对为基础,不同方式之间形成重叠网络,可以反映交通流网络间的相似性和竞争关系。与重叠网络相对,交通方式间不重叠的城市对形成相异网络,可以反映网络间的差异性和互补关系。3种方式在重叠和相异网络的频率分布如表4所示。Tab. 4
表4
表4多元交通网络中重叠与相异的概率(%)
Tab. 4
| 交通网络 | 重叠网络 | 相异网络 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长途汽车与 高铁列车 | 长途汽车与 航空运输 | 高铁列车与 航空运输 | 三者 重叠 | 长途汽车与 高铁列车 | 长途汽车与 航空运输 | 高铁列车与 航空运输 | 三者完全 相异 | ||
| 长途汽车 | 54.0 | 11.5 | - | 5.7 | 46.0 | 88.5 | - | 40.2 | |
| 高铁列车 | 76.7 | - | 10.7 | 9.1 | 23.3 | - | 89.3 | 21.8 | |
| 航空运输 | - | 70.7 | 54.2 | 44.6 | - | 29.3 | 45.8 | 19.7 | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
长途汽车、高铁和航空运输相互之间竞争激烈,尤其航空网络中80.3%的班次分布于重叠网络,相比之下长途汽车网络中59.8%的班次分布于重叠网络,频率占比最低,这与公路运输受到高铁和航空的市场挤压有较大关系。两两相比,长途汽车与高铁的网络相似性最高、竞争最明显,其次分别为长途汽车与航空和高铁与航空。三者重叠网络的规模较小,尤其长途汽车和高铁网络中仅有不到10%的班次分布于三者重叠网络。3种方式在完全相异网络的班次分布较少,其中长途汽车的班次比重约40%,高铁和航空网络中仅20%左右的班次与另2种交通方式均不重叠。
4.2 重叠网络空间特征
长途汽车、高铁列车和航空三者重叠网络包含较多距离较远、社会经济发达、联系紧密的城市对,大部分城市对在航空网络中的地位最高。三者重叠网络涉及519组城市对,平均距离约900 km,其中43.7%为省会、直辖市以及计划单列市之间的联系。重叠城市对数量分别占3种网络的5.6%、7.6%和23.2%,相比于频率占比(5.7%、9.1%和44.6%)较低,尤其航空的频率占比约是其城市对占比的2倍,可见此类城市对多为航空网络中频率较高的城市对。对比客流组织系数(图6)可以发现,长途汽车仅在少数城市对(31组)的RSL值最高,高铁略多(70组),航空在80%以上城市对的RSL值最高,进一步表明航空运输在大部分城市对具有重要地位。图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图62018年中国多元交通完全重叠网络的地理空间格局
Fig. 6The totally overlapping network of the three transport modes in China in 2018
以100 km为基本单元绘制长途汽车、高铁和航空在三者重叠网络的流量距离分布特征(图7),可以发现当3种交通方式同时运营时,长途汽车市场受到明显挤压,竞争优势较低,高铁和航空的竞争优势具有距离分布差异,800 km以内高铁的流量最高,超过800 km则航空最高,这与基于实际客流数据分析的临界点基本一致[21]。
图7
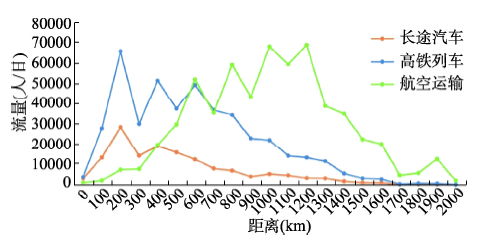 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图72018年中国多元交通完全重叠网络的旅客流量距离分布特征
Fig. 7Distance distribution in the overlapping network of the three transport modes in China in 2018
4.3 相异网络空间特征
长途汽车、高铁以及航空在完全相异网络具有明显的空间互补关系(图8)。3种方式分别包括5164组、3317组和805组城市对,可见长途汽车仍是众多城市对间的主要运输方式,在客运市场具有重要地位。空间上,长途汽车班次频率主要集中于省会或直辖市与周边短距离的城市对,尤其高铁尚不通达的区域;高铁则以京广高铁和沪昆高铁等沿线的城市对地位较高;航空网络以跨区域核心城市之间的直接联系的地位较高,尤其东西方向(如北京—乌鲁木齐)和南北方向(如北京—三亚)。图8
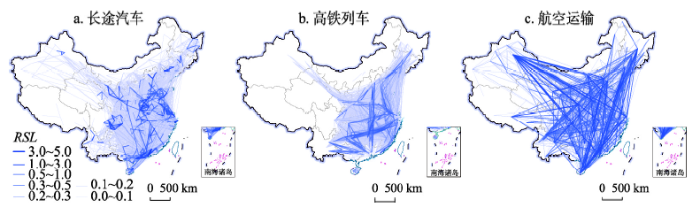 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图82018年中国多元交通完全相异网络的地理空间格局
Fig. 8The totally non-overlapping networks of the three transport modes in China in 2018
进一步对比流量距离分布特征(图9),3种方式在完全相异网络表现出明显的距离互补,以300 km和1400 km为临界点,300 km以内长途汽车流量最高,300~1400 km高铁的流量最高,超过1400 km则以航空的流量最高。整体上,3种方式在相异网络中的80%的流量分别集中于0~500 km、200~1200 km和800~2600 km,揭示了长途汽车、高铁和航空的运输优势分别集中于短途、中途和长途客运。
图9
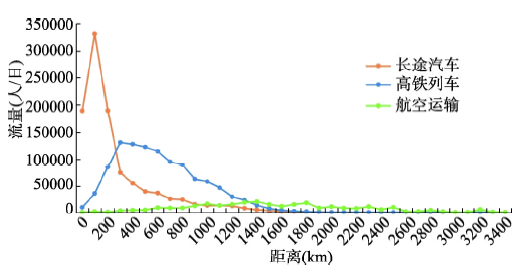 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图92018年中国多元交通完全相异网络的旅客流量距离分布特征
Fig. 9Distance distribution in the totally non-overlapping network of the three transport modes in China in 2018
5 地理空间约束下的多元交通流表达
5.1 距离衰减效应
长途汽车、高铁和航空运输的技术经济特征差异,导致3种方式适合运输的距离依次延伸。对比频率距离分布特征(图10),可以发现长途汽车、高铁和航空受到的距离约束依次降低,200 km以内长途汽车运输频次的分配率最高,200~700 km高铁最高,700 km以上则以航空最高。长途汽车网络的距离衰减效应最显著,其80%以上的班次集中在500 km以内,以100~200 km为峰值。高铁与长途汽车的变化趋势相似,200 km以后分配率不断降低,但相比于长途汽车的距离衰减效应较弱,整体上80%的高铁班次集中于700 km以内。作为非平面交通网络,航空运输本身不受地面空间约束,但有最低的适合飞行距离和最远可飞行距离,中间更多的受经济社会联系、旅游资源等与客运市场相关的资源影响,因而频率分布表现出随距离先增后减、非均匀的变化趋势。图10
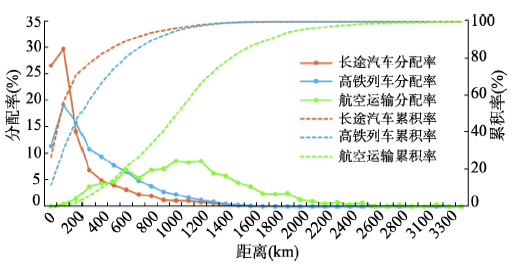 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图102018年中国多元交通网络的距离分布规律比较
Fig. 10Distance distribution characteristics of the three transport networks in China in 2018
5.2 地理邻近性
地理邻近性对不同交通网络的组织模式和结构形态各异,其中长途汽车受到的影响最显著,其次为高铁,航空网络受到的约束最小。长途汽车适宜于短途运输,其高频率层级联系网络主要由省内城市对组成,社区结构体现了明显的自然与行政双重地理空间的约束,例如由于自然地理单元的完整性以及社会经济联系,蒙东三盟市更倾向于融入东北三省组成的社区结构。地理邻近有助于交流联系,形成相近的历史发展和社会文化等,例如广东和广西作为珠江流域相邻省份,在历史文化等方面具有诸多共性,同时社会联系紧密,因而在长途汽车网络和高铁网络中均被划入同一社区。相比于长途汽车,地理邻近性对高铁网络的影响程度较小,其网络模块度略低、划分的社区数略少。高铁网络各社区主要由主干铁路沿线的相邻城市组成。航空网络由于具有超平面空间特征,受地理邻近性影响最小,并在中长距离更具有运输优势,因此未形成显著的社区结构,网络层级结构和首位联系也主要体现了全国尺度的空间联系。5.3 管理体制约束
管理体制的差异是形成交通网络不同结构的重要因素,映射在地理空间上即形成一定约束作用。中国高速公路实行以省划界、分省收费的管理运营体制,地方在高速公路规划、投资、建设以及管理等方面具有较大权限[23, 33-34],由此导致依托公路尤其高速公路的长途汽车网络形成地方化的发展结构,社区范围也在较大程度上沿袭了省级行政边界。中国铁路运输由国家层面统一管理,中国铁路总公司承担了建设、运营、调度以及投融资等核心职能,其下辖的18个地方铁路集团公司是铁路行业的企业主体,对铁路组织网络具有重要影响[5, 35]。中国航空运输管理体制经历了从严格管制到开放竞争的市场化过程[36],各航空公司拥有自主设计航线、制定票价等方面的权力,彼此之间竞争激烈,市场因素促使航空公司对经济社会联系等方面的关注度更高[5]。6 结论与讨论
交通运输组织网络作为典型的空间级联系统,对区域空间联系、城市体系结构塑造产生着重要影响,基于多元交通流视角的耦合性和差异性研究一直较少。本文比较分析了多元交通流网络的空间级联体系结构及其表达的城市网络组织体系,揭示了设施空间、地理空间、行政空间、管理体制的约束作用。研究发现:多元交通方式的集成表达是刻画空间级联系统的一种重要方式,任一单一交通方式均具有局限性。各种交通运输方式适合在不同空间尺度和行政区划范围内刻画和表达城市网络组织关系及空间级联系统。其中,长途汽车适合省域尺度内部的短距离表达,高铁适合在区域尺度的短距离至中等距离表达,航空运输适合在全国尺度的长距离表达,这与目前基于单一方式或多种方式对比的研究结论基本一致[5, 18-22]。3种方式在空间上的重叠性与互补性是对空间级联系统的一种有益表达。
地理空间约束对不同交通运输的组织模式表现不一。其中,自然地理条件、路网设施空间、地理距离、管理体制是影响陆路交通网络结构和组织的重要因素。长途汽车和高铁运输具有较强的距离衰减效应,其网络组织均具有明显的空间依赖性。长途汽车网络受省级行政空间和管理体制的约束,呈地方化发展模式,表现为“核心—边缘”的组织结构;高铁受设施空间、管理体制的约束更为明显,表现为轴线空间组织结构,围绕高铁干线形成多个区域性功能组团,空间上仍具有邻近特征;航空网络具有“超空间”运输特性,受自然条件和距离约束小,主要表现为全国尺度的“菱形结构”,其中社会经济联系、旅游资源等相关因素成为影响网络结构的关键。
相较于现有研究,本文得到的长途汽车、高铁以及航空运输适宜的空间尺度以及形成的组织模式存在一定的共性,创新之处在于进一步从耦合性和差异性的角度分析3种方式之间的竞合关系,从地理空间约束的视角解读交通流的表达,这是对现有多元交通流网络研究的一个补充和完善,为城市体系及空间级联系统的研究提供借鉴和参考。如何利用多元交通流视角对空间级联系统进行全面、精准的刻画,研究仍方兴未艾。本文受制于数据可得性,仅从运输联系频次视角进行研究,虽是管中窥豹,但仍具有一定的意义。需要指出的是,中国高铁仍处于快速建设发展过程中,未来高铁的建设与规划势必会对中国城市体系尤其是西部城市进一步产生影响,该议题仍值得持续关注研究。未来可从时间和空间尺度综合探讨高铁建设对其他交通方式的影响机制,对于即将建设高铁的区域,可参考发展相对成熟区域的交通网络组织模式协调其各类交通资源配置。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1177/0042098010377367URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1177/0042098010377365URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201708013URL [本文引用: 5]

As traffic flow reflects the socio-economic relations between cities, it is widely applied as a key factor in studies on city networks. Based on the inter-city railway and air passenger flow in 2010, this article made a comparison of the spatial structure and passenger flow organization of inter-city networks from the perspective of railway and air passenger flow, in terms of node, linkage, and community. The results are as follows: (1) Both city networks based on railway and air passenger flow present a hierarchical structure with Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou being the top three, while the nodes in the lower classes of two networks are different. (2) The spatial structure of linkages between cities based on railway passenger flow displays strong neighborhood effect. In contrast, the cities' own characteristics play a dominant role in the organization of air passenger flow. (3) Most of the dominant railway passenger flow is directed to the capital city in each province, forming several disperse regional systems separated by the provincial boundaries. In terms of air passenger flow, the regional systems are integrated by vertical linkages between them. (4) Although the community structure is not obvious from the perspective of air passenger flow, there are seven communities of significant geographical characteristics being detected in the railway network. The main differences between two networks are attributed to the management systems and technical characteristics of the modes of transportation.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201708013URL [本文引用: 5]

As traffic flow reflects the socio-economic relations between cities, it is widely applied as a key factor in studies on city networks. Based on the inter-city railway and air passenger flow in 2010, this article made a comparison of the spatial structure and passenger flow organization of inter-city networks from the perspective of railway and air passenger flow, in terms of node, linkage, and community. The results are as follows: (1) Both city networks based on railway and air passenger flow present a hierarchical structure with Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou being the top three, while the nodes in the lower classes of two networks are different. (2) The spatial structure of linkages between cities based on railway passenger flow displays strong neighborhood effect. In contrast, the cities' own characteristics play a dominant role in the organization of air passenger flow. (3) Most of the dominant railway passenger flow is directed to the capital city in each province, forming several disperse regional systems separated by the provincial boundaries. In terms of air passenger flow, the regional systems are integrated by vertical linkages between them. (4) Although the community structure is not obvious from the perspective of air passenger flow, there are seven communities of significant geographical characteristics being detected in the railway network. The main differences between two networks are attributed to the management systems and technical characteristics of the modes of transportation.
DOI:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2007.12.005URL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract
This paper contextualises and reviews the burgeoning research in which data on air passenger flows are used to analyse a network of world cities. Rather than taking the relevance of such airline statistics on trust, we consider their advantages and drawbacks in the context of the different approaches devised in the empirical research at large. To assess the potential of data on air passenger flows in this context, we construct a taxonomy of approaches that distinguishes between information on global corporate organization and large-scale infrastructure networks. While this evaluation suggests that information on air passenger flows may indeed be a prime data source in this context, it is equally clear that the relevance of such research is potentially undermined by inadequate statistics. It is argued that future research should explore and/or construct alternative airline datasets that allow for more meaningful analyses.DOI:10.1177/0042098010372684URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/xb201208003URL [本文引用: 1]

The change of urban regional spatial structure influenced by information technology has become a hotspot of research at home and abroad. This study tries to analyze China's city network characteristics from the social network space perspective by using Sina microblog as an example. The result shows that China's city network based on the micro-blog social space has a clear hierarchical structure and level distinction. Firstly, the result shows the existence of regional characteristics, performance as a visible regional development pattern which contains "Three Main-regions and Four Sub-regions" according to the analysis of the level distinction in the city network and the connection rate between cities. Specifically speaking, the three main regions contain the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region represented by Beijing, Pearl River Delta region represented by Guangzhou and Shenzhen, and the Yangtze River Delta region represented by Shanghai, Hangzhou and Nanjing. The four sub-regions contain Chengdu-Chongqing region, west coast of the Taiwan Straits region represented by Fuzhou and Xiamen, Wuhan region represented by Wuhan and Changsha, Northeast China represented by Shenyang, Harbin and Changchun. Secondly, the result shows there is a significant difference of the network links among Eastern, Central and Western China. Links within Eastern China and the links between Eastern, Central and Western China constitute almost all of the current network systems. It is also found that the high-level cities have an absolute dominance in the city network pattern, and that Beijing is the contact center in China's city network, with an overwhelming advantage. Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen are the sub-contact centers in the China's city nework.
DOI:10.11821/xb201208003URL [本文引用: 1]

The change of urban regional spatial structure influenced by information technology has become a hotspot of research at home and abroad. This study tries to analyze China's city network characteristics from the social network space perspective by using Sina microblog as an example. The result shows that China's city network based on the micro-blog social space has a clear hierarchical structure and level distinction. Firstly, the result shows the existence of regional characteristics, performance as a visible regional development pattern which contains "Three Main-regions and Four Sub-regions" according to the analysis of the level distinction in the city network and the connection rate between cities. Specifically speaking, the three main regions contain the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region represented by Beijing, Pearl River Delta region represented by Guangzhou and Shenzhen, and the Yangtze River Delta region represented by Shanghai, Hangzhou and Nanjing. The four sub-regions contain Chengdu-Chongqing region, west coast of the Taiwan Straits region represented by Fuzhou and Xiamen, Wuhan region represented by Wuhan and Changsha, Northeast China represented by Shenyang, Harbin and Changchun. Secondly, the result shows there is a significant difference of the network links among Eastern, Central and Western China. Links within Eastern China and the links between Eastern, Central and Western China constitute almost all of the current network systems. It is also found that the high-level cities have an absolute dominance in the city network pattern, and that Beijing is the contact center in China's city network, with an overwhelming advantage. Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen are the sub-contact centers in the China's city nework.
DOI:10.1016/j.drugpo.2016.09.006URLPMID:27780655 [本文引用: 1]

Shanghai was considered to be a "capital of opium" in modern China, hence the history of opium in the city has received significant attention. In the Shanghai International Settlement, where Chinese and foreigners lived as neighbours, drugs were considered by the administration as both "trouble maker", and important financial resource. This paper explores how the Shanghai Municipal Council (SMC), the most senior governing body in the settlement, used its position to maximize political and economic profit from the trade and consumption of opium.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.07.008URL [本文引用: 1]

With the accelerated development of globalization and the revolutionary advances of information technology, advanced producer services (APS) have become the main driving force of the region's economic growth and an important source of product innovation, and its positive role in the construction of urban network has gained extensive attention from scholars at home and abroad. By systemically analyzing the changes of the urban network research carrier, it can be found that the layout behavior of the producer services enterprises provides an important breakthrough point for the world's city network research. Meanwhile, due to the advantages of the relational data access, urban network construction from the perspective of producer services industry has become an important frontier of city research in the western countries. On the whole, the close correlation between the producer services aggregation and city level is an important foundation of network construction based on producer services, the acting forces of network construction includes the industry attributes of producer services, location selection of the producer services enterprise, and urban development conditions, such as innovative elements, technical facilities, etc. Through the detailed studies of network construction models, the network features, and the dynamic evolution, it can be found that the layout of producer services industry can be applied to the interpretation of urban network in China under the impact of globalization and informatization. Domestic scholars have recognized its importance, and current researches are focused on introducing the method, rather than being concerned with intrinsic mechanisms and evolution characteristics. As the division of labor in global industries deepens, China no longer just plays a role in manufacturing; the country's producer services will start to cluster in large scales. Domestic research on urban network based on producer services just started, and should be strengthened. Based on practical needs, this paper further proposes directions for future research. With China's more active participation in globalization, the theoretical framework of urban network based on producer services need to be established, the systematic studies of urban network based on producer services at regional level is certainly insufficient, and the driving mechanisms and future trends of the urban network require in-depth investigations.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.07.008URL [本文引用: 1]

With the accelerated development of globalization and the revolutionary advances of information technology, advanced producer services (APS) have become the main driving force of the region's economic growth and an important source of product innovation, and its positive role in the construction of urban network has gained extensive attention from scholars at home and abroad. By systemically analyzing the changes of the urban network research carrier, it can be found that the layout behavior of the producer services enterprises provides an important breakthrough point for the world's city network research. Meanwhile, due to the advantages of the relational data access, urban network construction from the perspective of producer services industry has become an important frontier of city research in the western countries. On the whole, the close correlation between the producer services aggregation and city level is an important foundation of network construction based on producer services, the acting forces of network construction includes the industry attributes of producer services, location selection of the producer services enterprise, and urban development conditions, such as innovative elements, technical facilities, etc. Through the detailed studies of network construction models, the network features, and the dynamic evolution, it can be found that the layout of producer services industry can be applied to the interpretation of urban network in China under the impact of globalization and informatization. Domestic scholars have recognized its importance, and current researches are focused on introducing the method, rather than being concerned with intrinsic mechanisms and evolution characteristics. As the division of labor in global industries deepens, China no longer just plays a role in manufacturing; the country's producer services will start to cluster in large scales. Domestic research on urban network based on producer services just started, and should be strengthened. Based on practical needs, this paper further proposes directions for future research. With China's more active participation in globalization, the theoretical framework of urban network based on producer services need to be established, the systematic studies of urban network based on producer services at regional level is certainly insufficient, and the driving mechanisms and future trends of the urban network require in-depth investigations.
DOI:10.1177/0002716207311877URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2012.02.015URL [本文引用: 1]

The importance of national states as an economic unit is descending following the process of economy globalization, and multinational company turns out to be the main organization carrier and the decision-making power decentralized to city since the 1970s. International completion among states materialized to city-centered regional completion, and city became the crucial actor in global governance system. As the organization node, world city constructed an economic control and social-economic connection network system according to different function and status in global production process. The paper deemed that under the guide of social network theory, based on the drawbacks of world city/global city and inter-city research of world city system, world city network research started with relational perspective, and discovered the inter-city relationship and the dynamic of world city network formation with quantitative analysis by infrastructure approach, corporation approach and social culture approach. The paper deemed world city network research as the response of academic studies to the effects of world city on transformation of information and communication technology, corporation organizations and global governance patterns. In conclusion, the paper discussed some reference and inspirations to related research fields in China on orders of inter-city relation, spatial organization logic, production and collection of relational data, spatial scales and types of urban economy.
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2012.02.015URL [本文引用: 1]

The importance of national states as an economic unit is descending following the process of economy globalization, and multinational company turns out to be the main organization carrier and the decision-making power decentralized to city since the 1970s. International completion among states materialized to city-centered regional completion, and city became the crucial actor in global governance system. As the organization node, world city constructed an economic control and social-economic connection network system according to different function and status in global production process. The paper deemed that under the guide of social network theory, based on the drawbacks of world city/global city and inter-city research of world city system, world city network research started with relational perspective, and discovered the inter-city relationship and the dynamic of world city network formation with quantitative analysis by infrastructure approach, corporation approach and social culture approach. The paper deemed world city network research as the response of academic studies to the effects of world city on transformation of information and communication technology, corporation organizations and global governance patterns. In conclusion, the paper discussed some reference and inspirations to related research fields in China on orders of inter-city relation, spatial organization logic, production and collection of relational data, spatial scales and types of urban economy.
DOI:10.2307/142321URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1177/00027640121958104URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1068/a300785URLPMID:12293871 [本文引用: 1]

"Traditionally, estimates of the number of people in small areas (the smallest geographical units for which data are available) have been disaggregated only by age and sex. More recently, much research effort has been directed towards developing some form of enhanced small-area population estimation, in which the population in a small area is disaggregated not only by age and sex, but also by a wide range of additional economic and social characteristics. Solutions to this problem currently include account-based demographic models, often used by local authorities."
DOI:10.1068/a300785URLPMID:12293871 [本文引用: 1]

"Traditionally, estimates of the number of people in small areas (the smallest geographical units for which data are available) have been disaggregated only by age and sex. More recently, much research effort has been directed towards developing some form of enhanced small-area population estimation, in which the population in a small area is disaggregated not only by age and sex, but also by a wide range of additional economic and social characteristics. Solutions to this problem currently include account-based demographic models, often used by local authorities."
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201412009URL [本文引用: 1]

As a new mode of transportation, the rapid development of high-speed rail (HSR) will bring a leap in the history of transportation and have a comprehensive impact on the regional structure, population mobility, geographical division of labors, regional linkages, land use, and so on. Therefore, it is significantly important to study the impacts of HSR on regional spatial interactions, especially under the background of regional economic integration. The paper researches the impact of high speed rail on the reconstruction of spatial economic linkages. Based on the GIS network analysis tools, this paper first calculates the time cost matrix of 333 prefecture-level administrative units and four municipalities, and then uses the gravity model to calculate the interurban economic linkages, and lastly analyzes the distribution of the total economic linkage and the economic linkages between any two cities. In order to analyze the impact of HSR on regional spatial interaction, this paper resumes three scenarios: the current transport network in 2012 without the HSR network (scenario 1), the current transport network in 2012 (scenario 3), and the planning HSR network in 2020 (scenario 3) based on the current transport network, to calculate the time cost matrix of 337 cities. Results indicate that: (1) Cities in the east have the highest economic linkages, and cities with the highest increase of economic linkages are located along the HSR lines, which will lead to regional restructuring; (2) The development of HSR lines will improve the economic linkages between cities, and the increasing rate during the first period (comparing scenario 2 with scenario 1) is much higher than that during the second period (comparing scenario 3 with scenario 2); (3) From different perspectives and regional scales, the development of HSR has different impacts on spatial difference; (4) It is possible for cities in a long distance to have high economic linkages with the construction of HSR lines, which could also change the linkage directions.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201412009URL [本文引用: 1]

As a new mode of transportation, the rapid development of high-speed rail (HSR) will bring a leap in the history of transportation and have a comprehensive impact on the regional structure, population mobility, geographical division of labors, regional linkages, land use, and so on. Therefore, it is significantly important to study the impacts of HSR on regional spatial interactions, especially under the background of regional economic integration. The paper researches the impact of high speed rail on the reconstruction of spatial economic linkages. Based on the GIS network analysis tools, this paper first calculates the time cost matrix of 333 prefecture-level administrative units and four municipalities, and then uses the gravity model to calculate the interurban economic linkages, and lastly analyzes the distribution of the total economic linkage and the economic linkages between any two cities. In order to analyze the impact of HSR on regional spatial interaction, this paper resumes three scenarios: the current transport network in 2012 without the HSR network (scenario 1), the current transport network in 2012 (scenario 3), and the planning HSR network in 2020 (scenario 3) based on the current transport network, to calculate the time cost matrix of 337 cities. Results indicate that: (1) Cities in the east have the highest economic linkages, and cities with the highest increase of economic linkages are located along the HSR lines, which will lead to regional restructuring; (2) The development of HSR lines will improve the economic linkages between cities, and the increasing rate during the first period (comparing scenario 2 with scenario 1) is much higher than that during the second period (comparing scenario 3 with scenario 2); (3) From different perspectives and regional scales, the development of HSR has different impacts on spatial difference; (4) It is possible for cities in a long distance to have high economic linkages with the construction of HSR lines, which could also change the linkage directions.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201602007URL [本文引用: 2]

The evolution of inter-city network influenced by globalization and information technology has become a hot topic in city and urban research. This study tries to explore the evolution of nodal hierarchy and communities in inter-city network based on passenger train network during the rapid development period of High-speed Railway (HSR) in China since 2003. Results indicate that: (1) the evolved HSR network in China enlarged the disparities of weighted degree centrality between regions, but decreased the disparities of that between communities, and led to an increasing concentrated city hierarchy with fewer cities having high centrality value, and a growing similarity between the city hierarchies measured by the passenger train network and by city attributes (such as population and GDP); (2) the city hierarchy measured by passenger train network followed a rank-size distribution in the national and regional levels, as well as in some communities. (3) Spatially, cities with higher hierarchy in passenger train network and larger improvement in weighted centrality indicator were mostly located in the eastern region or the areas with the distance to the nearest HSR stations below 50 km, developed economy and high population density; the cities in 2013 could be divided into 14 communities, including the communities with cities mainly located along Beijing-Shanghai, Beijing-Wuhan and Wuhan-Chengdu, Wuhan-Guangzhou, Beijing-Jiujiang, Hangzhou-Xiamen, Lanzhou-Urumqi trunk rail lines, and located in Northeast China, Shanxi Province, Inner Mongolia. (4) The evolution of communities was mostly influenced by the natural environment and administrative areas, especially by the development of HSR network.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201602007URL [本文引用: 2]

The evolution of inter-city network influenced by globalization and information technology has become a hot topic in city and urban research. This study tries to explore the evolution of nodal hierarchy and communities in inter-city network based on passenger train network during the rapid development period of High-speed Railway (HSR) in China since 2003. Results indicate that: (1) the evolved HSR network in China enlarged the disparities of weighted degree centrality between regions, but decreased the disparities of that between communities, and led to an increasing concentrated city hierarchy with fewer cities having high centrality value, and a growing similarity between the city hierarchies measured by the passenger train network and by city attributes (such as population and GDP); (2) the city hierarchy measured by passenger train network followed a rank-size distribution in the national and regional levels, as well as in some communities. (3) Spatially, cities with higher hierarchy in passenger train network and larger improvement in weighted centrality indicator were mostly located in the eastern region or the areas with the distance to the nearest HSR stations below 50 km, developed economy and high population density; the cities in 2013 could be divided into 14 communities, including the communities with cities mainly located along Beijing-Shanghai, Beijing-Wuhan and Wuhan-Chengdu, Wuhan-Guangzhou, Beijing-Jiujiang, Hangzhou-Xiamen, Lanzhou-Urumqi trunk rail lines, and located in Northeast China, Shanxi Province, Inner Mongolia. (4) The evolution of communities was mostly influenced by the natural environment and administrative areas, especially by the development of HSR network.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201702004URL [本文引用: 1]

The multi-level perspective and multi-scalar city network have gradually become the critical pathways to understand spatial interactions and linkages. The road linkages represent distinguished characteristics of spatial dependence and distance decay, which is of great significance in depicting spatial relationships at regional scale. Based on the data of highway passenger flows between prefecture-level administrative units, this paper tries to identify the functional structures and regional impacts of China's city network, and further explores the spatial organization patterns of the existing functional regions, aiming to deepen the understanding of city network structure and provide new cognitive perspectives for the extant research. The empirical results are shown as follows: (1) It is immediately visible that the highway flows are extremely concentrated on the mega-regions of eastern coastal China and major economic zones in central and western China. And city networks based on highway flows demonstrate strong spatial dependence and hierarchical characteristics, which to a large extent has spatial coupling with the distributions of major mega-regions in China. It is a reflection of spatial relationships at regional scale and core-periphery structure. (2) A total of 19 communities that belong to important spatial configurations are identified through community detection algorithm, and we believe that they are urban economic regions within urban China. Their spatial metaphors can be concluded in three aspects. Firstly, many communities have the same boundaries with provincial level administrative units, which reveals that significant administrative region economy still exists in contemporary China. Secondly, trans-provincial linkages can be formed through spatial spillover effects of mega-regions within specific communities. Thirdly, cities located in the marginal areas of provinces and attracted by powerful center cities in neighboring provinces may become increasingly disconnected with their own provinces and be enrolled into communities of neighboring provinces, which make contribution to the formation of the trans-provincial core-periphery structures. (3) Each community, with its distinguished city network system, demonstrates strong spatial dependence and various spatial organization patterns. Regional patterns have emerged with the features of a multi-level, dynamic and networked system. (4) From the morphology perspective, the spatial pattern of regional city networks can be basically divided into monocentric structure, dual-nuclei structure, polycentric structure and low-level equilibration structure, with the monocentric structure as the major type.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201702004URL [本文引用: 1]

The multi-level perspective and multi-scalar city network have gradually become the critical pathways to understand spatial interactions and linkages. The road linkages represent distinguished characteristics of spatial dependence and distance decay, which is of great significance in depicting spatial relationships at regional scale. Based on the data of highway passenger flows between prefecture-level administrative units, this paper tries to identify the functional structures and regional impacts of China's city network, and further explores the spatial organization patterns of the existing functional regions, aiming to deepen the understanding of city network structure and provide new cognitive perspectives for the extant research. The empirical results are shown as follows: (1) It is immediately visible that the highway flows are extremely concentrated on the mega-regions of eastern coastal China and major economic zones in central and western China. And city networks based on highway flows demonstrate strong spatial dependence and hierarchical characteristics, which to a large extent has spatial coupling with the distributions of major mega-regions in China. It is a reflection of spatial relationships at regional scale and core-periphery structure. (2) A total of 19 communities that belong to important spatial configurations are identified through community detection algorithm, and we believe that they are urban economic regions within urban China. Their spatial metaphors can be concluded in three aspects. Firstly, many communities have the same boundaries with provincial level administrative units, which reveals that significant administrative region economy still exists in contemporary China. Secondly, trans-provincial linkages can be formed through spatial spillover effects of mega-regions within specific communities. Thirdly, cities located in the marginal areas of provinces and attracted by powerful center cities in neighboring provinces may become increasingly disconnected with their own provinces and be enrolled into communities of neighboring provinces, which make contribution to the formation of the trans-provincial core-periphery structures. (3) Each community, with its distinguished city network system, demonstrates strong spatial dependence and various spatial organization patterns. Regional patterns have emerged with the features of a multi-level, dynamic and networked system. (4) From the morphology perspective, the spatial pattern of regional city networks can be basically divided into monocentric structure, dual-nuclei structure, polycentric structure and low-level equilibration structure, with the monocentric structure as the major type.
DOI:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2018.03.015URL [本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804006URL [本文引用: 1]

Variations of locational conditions caused by transport infrastructure construction largely promoted the agglomeration of production factors and the local economy and reshaped the regional structure. Hence, measuring transport location has become one of the fundamental topics in geography. Recently, along with transport development, as well as the emergence of new technology, new models, new factors and new industrial forms, the locational conditions have been reconstructed and individual travel concept and patterns changed. The existing research on measuring transport location considers not only the location in the geographic context in terms of the spatial location and transport infrastructure network but also the location in the flow of space concerning the network connectivity, reliability and travel convenience. The research objects changed from various locations to the micro-location regarding group travel characteristics and differences at the individual level. The research contents included door-to-door trips in the accessibility of transport networks. Meanwhile, techniques of big data and GIS-T methods make measuring transport location more accurate.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804006URL [本文引用: 1]

Variations of locational conditions caused by transport infrastructure construction largely promoted the agglomeration of production factors and the local economy and reshaped the regional structure. Hence, measuring transport location has become one of the fundamental topics in geography. Recently, along with transport development, as well as the emergence of new technology, new models, new factors and new industrial forms, the locational conditions have been reconstructed and individual travel concept and patterns changed. The existing research on measuring transport location considers not only the location in the geographic context in terms of the spatial location and transport infrastructure network but also the location in the flow of space concerning the network connectivity, reliability and travel convenience. The research objects changed from various locations to the micro-location regarding group travel characteristics and differences at the individual level. The research contents included door-to-door trips in the accessibility of transport networks. Meanwhile, techniques of big data and GIS-T methods make measuring transport location more accurate.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910001URL [本文引用: 1]

Since the reform and opening-up in 1978, historic changes have been seen in the transportation geography pattern of China. Understanding its evolutionary characteristics and regularity is significant and meaningful for future transportation construction and territory development. This paper reviewed the process of transportation construction in China and investigated the evolutionary characteristics and spatial effects of transportation geography pattern with the technologies in big data mining and GIS. In addition, the regular rules of transportation geography evolution from the aspects of stages, structures, and orders are systematically analyzed. The investigation showed that China's transportation construction has entered the stage of quality improvement. The construction mode has upgraded from scale-expanding driven by investment to quality-improving driven by innovation. The development direction has changed from "prior development" to "integrated coordinated development". The rapid growth and development of transportation networks have significantly influenced the relationship between time and space. The resulting spatial convergence and superiority pattern are coupled with economic-social distribution, which facilitates the development of the economic-social spatial structure. Consequently, territory development that is traditionally centralized by corridors has changed into the networked mode centered on metropolises and metropolitan areas. In brief, the transportation geography pattern is of evolutionary principles. China has been evolving from the stage of ordered structure to the stage of cascade-order structure. Simultaneously, the economic-social pattern has changed from the axis structure to the hub-and-spoke structure with a preliminary ordered network. As transportation networks grow and expand, China's functional spatial structure and ordered network will be gradually stabilized and balanced.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910001URL [本文引用: 1]

Since the reform and opening-up in 1978, historic changes have been seen in the transportation geography pattern of China. Understanding its evolutionary characteristics and regularity is significant and meaningful for future transportation construction and territory development. This paper reviewed the process of transportation construction in China and investigated the evolutionary characteristics and spatial effects of transportation geography pattern with the technologies in big data mining and GIS. In addition, the regular rules of transportation geography evolution from the aspects of stages, structures, and orders are systematically analyzed. The investigation showed that China's transportation construction has entered the stage of quality improvement. The construction mode has upgraded from scale-expanding driven by investment to quality-improving driven by innovation. The development direction has changed from "prior development" to "integrated coordinated development". The rapid growth and development of transportation networks have significantly influenced the relationship between time and space. The resulting spatial convergence and superiority pattern are coupled with economic-social distribution, which facilitates the development of the economic-social spatial structure. Consequently, territory development that is traditionally centralized by corridors has changed into the networked mode centered on metropolises and metropolitan areas. In brief, the transportation geography pattern is of evolutionary principles. China has been evolving from the stage of ordered structure to the stage of cascade-order structure. Simultaneously, the economic-social pattern has changed from the axis structure to the hub-and-spoke structure with a preliminary ordered network. As transportation networks grow and expand, China's functional spatial structure and ordered network will be gradually stabilized and balanced.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1080/00420980701518990URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2009.02.001URL [本文引用: 2]

Abstract
There seems to be a renewed trade-off between processes of concentration and dispersal in airline networks. This development calls for a framework that allows for a systematic assessment of the overall evolution of the spatiality of airline networks. To this end, we develop an analytical framework based on a set of spatial interaction indices, which allows measuring the degree of hierarchical differentiation (i.e. dominance and connectivity) in a network. Moreover, a normalization of these indices through a systematic comparison with the corresponding values for a rank size distribution makes it possible to engage in meaningful longitudinal analyses and/or to compare the spatiality of networks with different numbers of nodes and/or links. Our framework is tested by applying it to data on air passenger flows within Europe, and its usefulness is discussed in the context of research on air traffic liberalization.DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.70.056131URLPMID:15600716 [本文引用: 1]

The connections in many networks are not merely binary entities, either present or not, but have associated weights that record their strengths relative to one another. Recent studies of networks have, by and large, steered clear of such weighted networks, which are often perceived as being harder to analyze than their unweighted counterparts. Here we point out that weighted networks can in many cases be analyzed using a simple mapping from a weighted network to an unweighted multigraph, allowing us to apply standard techniques for unweighted graphs to weighted ones as well. We give a number of examples of the method, including an algorithm for detecting community structure in weighted networks and a simple proof of the maximum-flow-minimum-cut theorem.
DOI:10.1088/1742-5468/2006/10/P10008URLPMID:19002269 [本文引用: 1]

The Cellular Potts Model (CPM) successfully simulates drainage and shear in foams. Here we use the CPM to investigate instabilities due to the flow of a single large bubble in a dry, monodisperse two-dimensional flowing foam. As in experiments in a Hele-Shaw cell, above a threshold velocity the large bubble moves faster than the mean flow. Our simulations reproduce analytical and experimental predictions for the velocity threshold and the relative velocity of the large bubble, demonstrating the utility of the CPM in foam rheology studies.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.08.008URL [本文引用: 1]

As the basic law of geography, the law of distance-decay is of great significance to the formation and evolution of spatial order. Using the data of Fujian expressway toll stations in October 2016, an expressway flow origin-destination matrix was identified with county areas as the basic unit. Cumulative proportion curve, spectrum analysis, and null model were used to simulate the distance-decay effect of expressway flow on the provincial and county scales. Then, combining spatial analysis and correlation analysis, the spatial differentiation characteristics and the distance-decay effect of expressway flow were discussed. The results show that: (1) The expressway flow is mainly concentrated in the 0~200 km and 0~200 min sections, which is in line with the economic radius of road transportation and the temporal and spatial fracture characteristics of traffic flow. (2) The expressway flow has a significant decreasing tendency on the provincial scale with the increase of distance. When using the road distance and power-law decay function, the distance decay coefficient is 2.674, which is significantly higher than the conventional value of 2. (3) The distance-decay rates of the expressway flow in different counties show a clear zonal pattern, corresponding well with the spatial distribution of expressway flow. (4) The law of distance-decay not only influences the evolution of spatial order, but also is influenced by the evolution of spatial order, and it is endogenous to the spatial patterns of socioeconomic activities. Under certain conditions, the strength of socioeconomic spatial connections will form a self accelerating feedback process with the increase of node size, population, and economic density, and the optimization of location conditions.
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.08.008URL [本文引用: 1]

As the basic law of geography, the law of distance-decay is of great significance to the formation and evolution of spatial order. Using the data of Fujian expressway toll stations in October 2016, an expressway flow origin-destination matrix was identified with county areas as the basic unit. Cumulative proportion curve, spectrum analysis, and null model were used to simulate the distance-decay effect of expressway flow on the provincial and county scales. Then, combining spatial analysis and correlation analysis, the spatial differentiation characteristics and the distance-decay effect of expressway flow were discussed. The results show that: (1) The expressway flow is mainly concentrated in the 0~200 km and 0~200 min sections, which is in line with the economic radius of road transportation and the temporal and spatial fracture characteristics of traffic flow. (2) The expressway flow has a significant decreasing tendency on the provincial scale with the increase of distance. When using the road distance and power-law decay function, the distance decay coefficient is 2.674, which is significantly higher than the conventional value of 2. (3) The distance-decay rates of the expressway flow in different counties show a clear zonal pattern, corresponding well with the spatial distribution of expressway flow. (4) The law of distance-decay not only influences the evolution of spatial order, but also is influenced by the evolution of spatial order, and it is endogenous to the spatial patterns of socioeconomic activities. Under certain conditions, the strength of socioeconomic spatial connections will form a self accelerating feedback process with the increase of node size, population, and economic density, and the optimization of location conditions.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2015.03.007URL [本文引用: 1]
