周智2, 3,,,
张美丽1,
张蓬涛2, 3,
张贵军2,
张秦瑞4
1.河北农业大学资源与环境科学学院 保定 071000
2.河北农业大学国土资源学院 保定 071000
3.河北省农田生态环境重点实验室 保定 071000
4.四川轻化工大学 宜宾 644000
基金项目:2021年度河北省社会科学发展研究课题(20210201298)资助
详细信息
作者简介:温雪静, 研究方向为土地整治工程与土地利用规划。E-mail: wxj18731236073@qq.com
通讯作者:周智, 主要研究方向为土地整治工程与土地利用规划。E-mail: zhouzhi797825@163.com
中图分类号:X24计量
文章访问数:47
HTML全文浏览量:14
PDF下载量:28
被引次数:0
出版历程
收稿日期:2021-06-19
录用日期:2021-09-17
网络出版日期:2021-11-08
刊出日期:2021-12-09
Identification of key areas of territorial ecological restoration in Taihang Mountains — A case study of Tang County
WEN Xuejing1,,ZHOU Zhi2, 3,,,
ZHANG Meili1,
ZHANG Pengtao2, 3,
ZHANG Guijun2,
ZHANG Qinrui4
1. College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding 071000, China
2. College of Land and Resources, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding 071000, China
3. Key Laboratory of Farmland Ecological Environment of Hebei Province, Baoding 071000, China
4. Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, Yibin 644000, China
Funds:This study was supported by the Hebei Social Science Development Research Project in 2021 (20210201298).
More Information
Corresponding author:E-mail: zhouzhi797825@163.com
摘要
HTML全文
图
参考文献
相关文章
施引文献
资源附件
访问统计
摘要
摘要:诊断与修复国土空间关键区域是推进生态文明建设的必由之路。但目前我国站在“整体视角、系统治理、全域修复”的角度识别关键区域, 并加以保护的研究较为欠缺。本文选择典型生态型贫困区域太行山区唐县为研究区, 综合生境质量和生态服务价值确定生态质量, 进而确定生态源地, 运用最小累计阻力模型构建生态阻力面, 基于电路理论构建生态廊道及识别待修复关键区域, 并提出生态夹点区域优先保护、生态障碍点区域优先修复、生态断裂点区域加强维护、低生态质量区域提高生境质量防止破坏程度持续加深的修复建议。研究表明: 1) 2000年、2010年和2018年唐县遥感生态指数分别为0.57、0.64和0.56, 生态质量均处于良等, 生态质量为先上升后下降。2)综合3期生境质量和生态服务价值评价结果, 确定稳定性较好的生态源地共10处, 面积91.22 km2, 占总面积的6.4%, 主要分布在研究区北部和西南部, 土地利用类型为林地和水域; 识别生态夹点区域15处, 生态障碍点区域42处, 生态断裂点区域28处, 低生态质量区域面积178 km2, 约占全域总面积1/10。本文从整体连通性角度, 系统识别太行山区唐县国土空间修复关键区域, 并提出保护与修复措施, 为太行山区生态修复提供现实参考。
关键词:生态修复/
生境质量/
生态服务价值/
遥感生态指数/
MCR模型/
电路理论/
关键区域/
唐县
Abstract:Diagnosing and restoring key areas of territorial space is fundamental to promote the construction of ecological civilization. From the perspective of “holistic perspective, system governance and global restoration”, the identification of key areas and suggestions for restoration can make up for some deficiencies existing in current research. In this paper, Tang County, a typical eco-poverty area in Taihang Mountain, is selected as the research area. The ecological quality was determined by integrating habitat quality and ecological service value, and then determine the ecological patch with the best stability as the ecological source, the ecological resistance surface is constructed by using the minimum cumulative resistance model, the ecological corridor is constructed based on the circuit theory. In addition to the ecological pinch points, ecological obstacle points and ecological break points included in the existing studies, the low ecological key areas are supplemented to identify, which are obtained from the lowest grade patches extracted during ecological quality evaluation. Some suggestions were put forward, such as priority protection in ecological pinch area, priority restoration in ecological obstacle area, strengthening maintenance in ecological break area, and improving habitat quality in low ecological quality area to prevent further damage. Aiming at the ecological patches with high habitat quality and ecological service value, it is recommended that these patches should be ecologically protected by prohibiting the encroachment of non-ecological construction projects. For the key ecological areas where the land use types are woodland, grassland and farmland, it is recommended to plant plants adapted to the native environment to increase vegetation abundance, return farmland to forests, and return to grassland for ecological restoration. It is recommended to build culverts and tunnels for the smooth movement of organisms in the area of obstacles caused by the cutting effect of traffic roads. The distribution of low ecological quality areas is relatively scattered, so the degraded landscape during ecological restoration can be combined with the surrounding landscape to achieve the effect of improving ecological quality. In addition, attention should be paid to the environmental protection of rural residential areas and construction land. The restoration of construction land should actively respond to the rural revitalization strategy. It can develop sightseeing agriculture in some areas, control the development intensity of the southeast of the research area, and speed up the greening construction of villages. In this way, ecological restoration of low ecological quality areas will be carried out. The research showed that: The remote sensing ecological index of Tang County in 2000, 2010 and 2018 were 0.57, 0.64 and 0.56, respectively. The ecological quality was all in good grade, and the ecological quality increased firstly and then declined. We identified 10 of ecological sources with good stability, with an area of 91.22 km2, accounting for 6.4% of the total area, which mainly distributed in the north and southwest of the study area. The land use types were forest land and water area. We also identified 15 of ecological pinch points, 42 of ecological barrier points and 28 of ecological break points, and the area of low ecological quality was 178 km2, accounting for about 1/10 of the total area. From the perspective of overall connectivity, this study systematically identified the key areas of territorial space restoration in Tang County of Taihang Mountain, and put forward protection and restoration measures, which could provide a realistic reference for ecological restoration in Taihang Mountain.
Key words:Ecological restoration/
Habitat quality/
Ecological service value/
Remote sensing ecological index/
MCR model/
Circuit theory/
Key areas/
Tang County
HTML全文
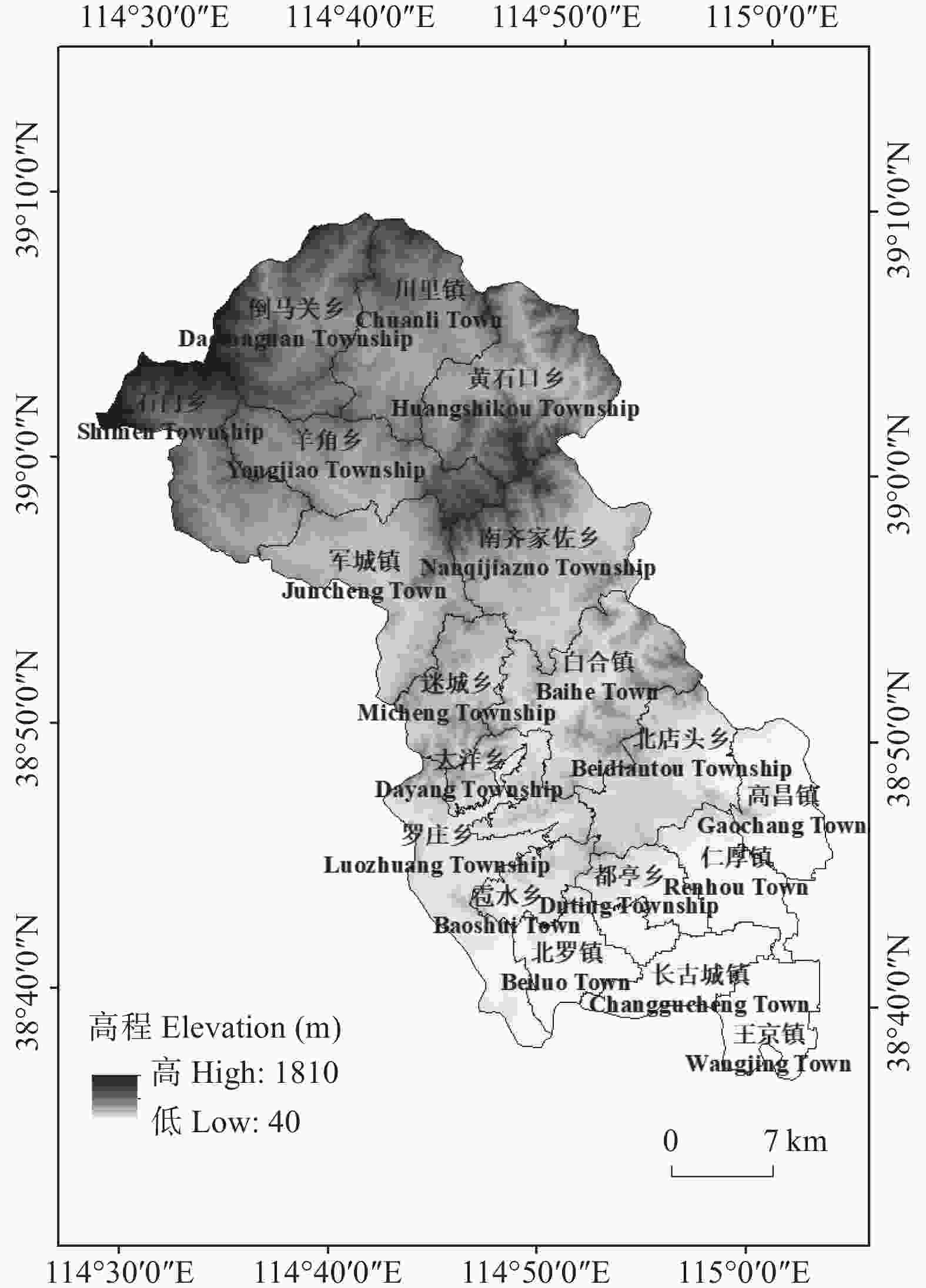
图1唐县地理位置及高程图
Figure1.Position and elevation map of Tang County
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片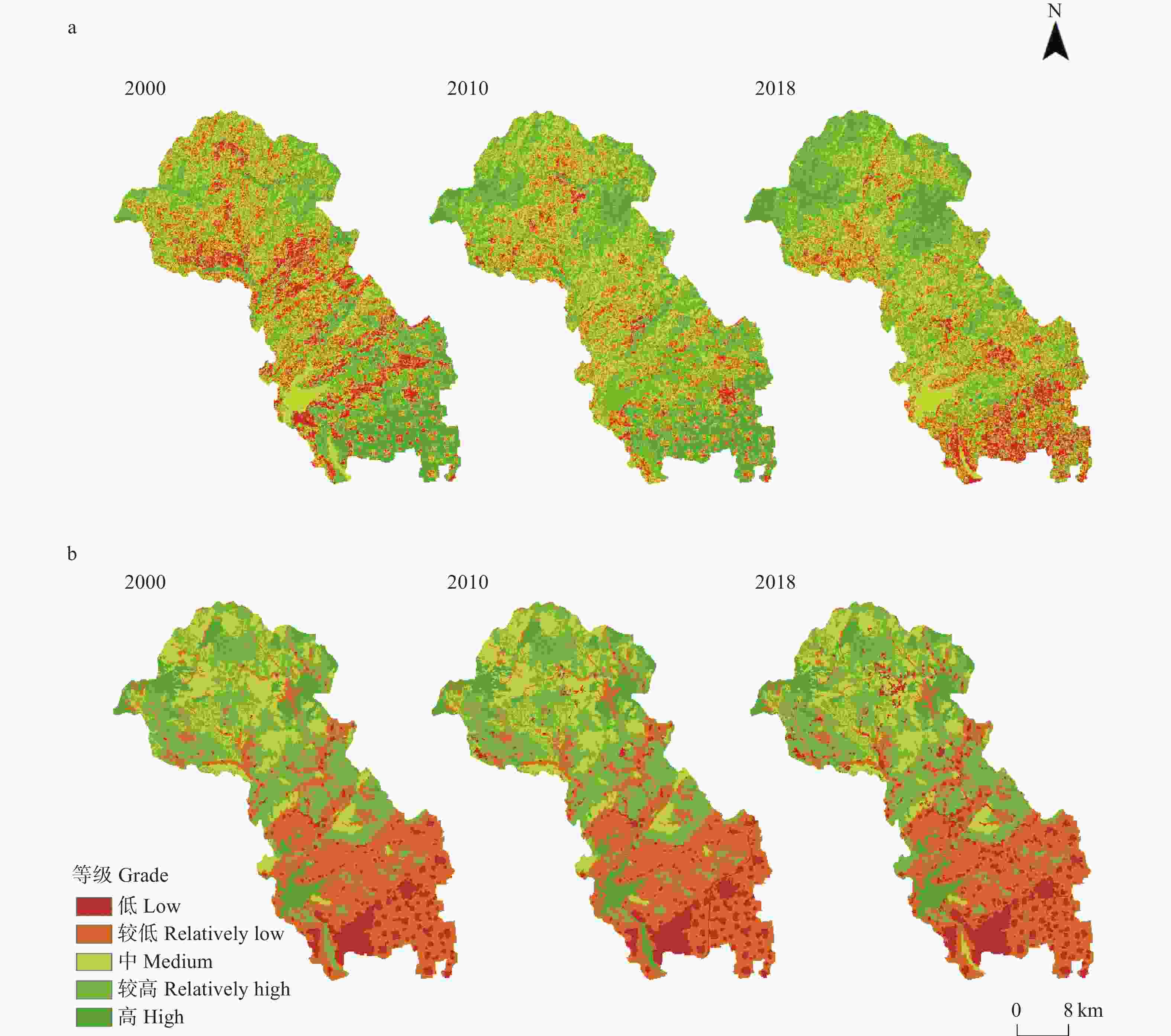
图22000年、2010年和2018年唐县生境质量(a)、生态服务价值(b)各等级空间分布情况
Figure2.Spatial distribution of each level of habitat quality (a), ecological service value (b) in the study area in 2000, 2010 and 2018
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片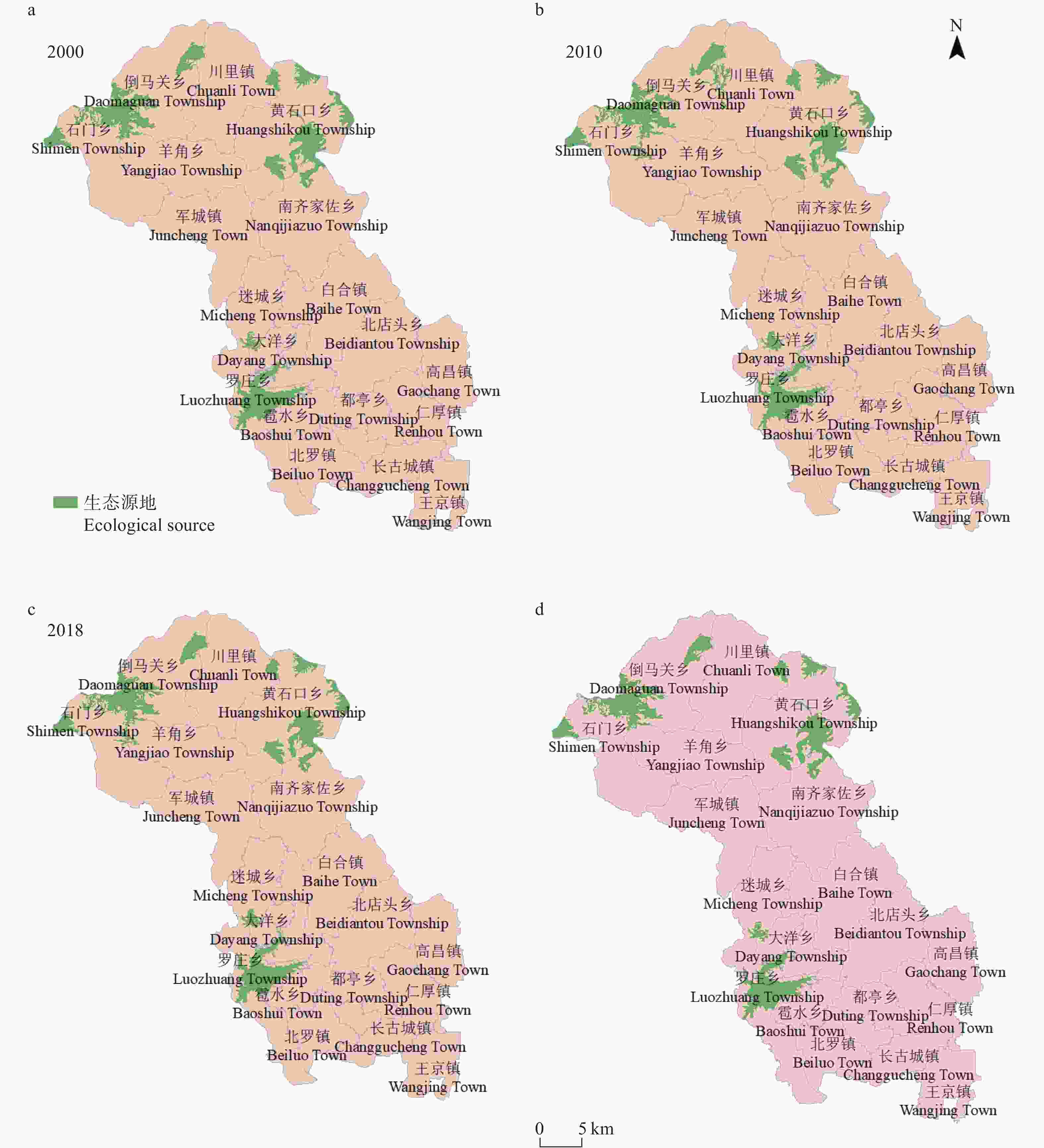
图32000年、2010年和2018年唐县生态源地的分布(a?c)和选取的研究区生态源地分布(d)
Figure3.Distribution of ecological sources in 2000, 2010 and 2018 (a?c), and the selected ecological sources in the study area (d)
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片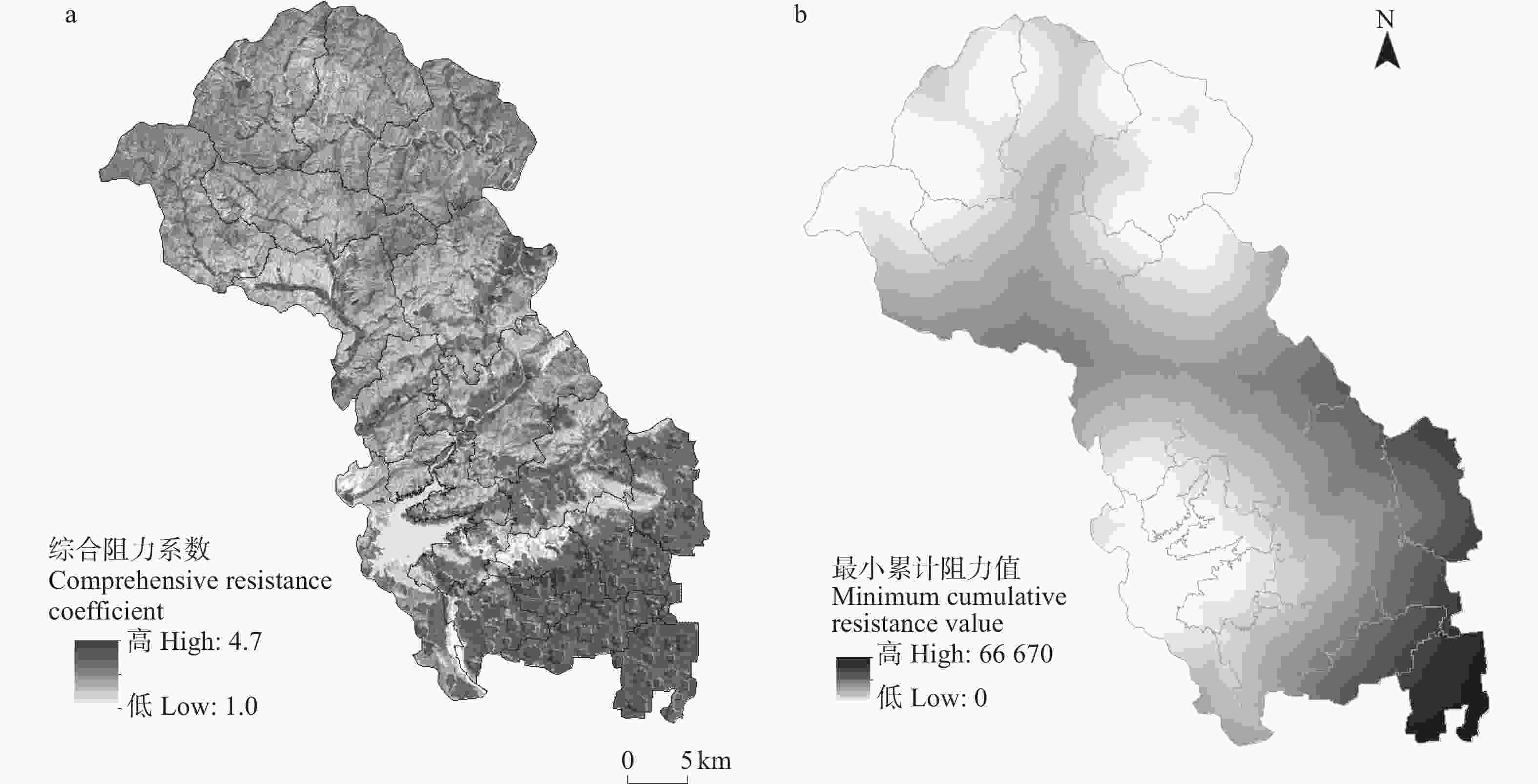
图4研究区综合阻力值(a)和最小累计阻力值(b)
Figure4.Comprehensive resistance value (a) and minimum cumulative resistance (MCR) value (b) of the study area
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片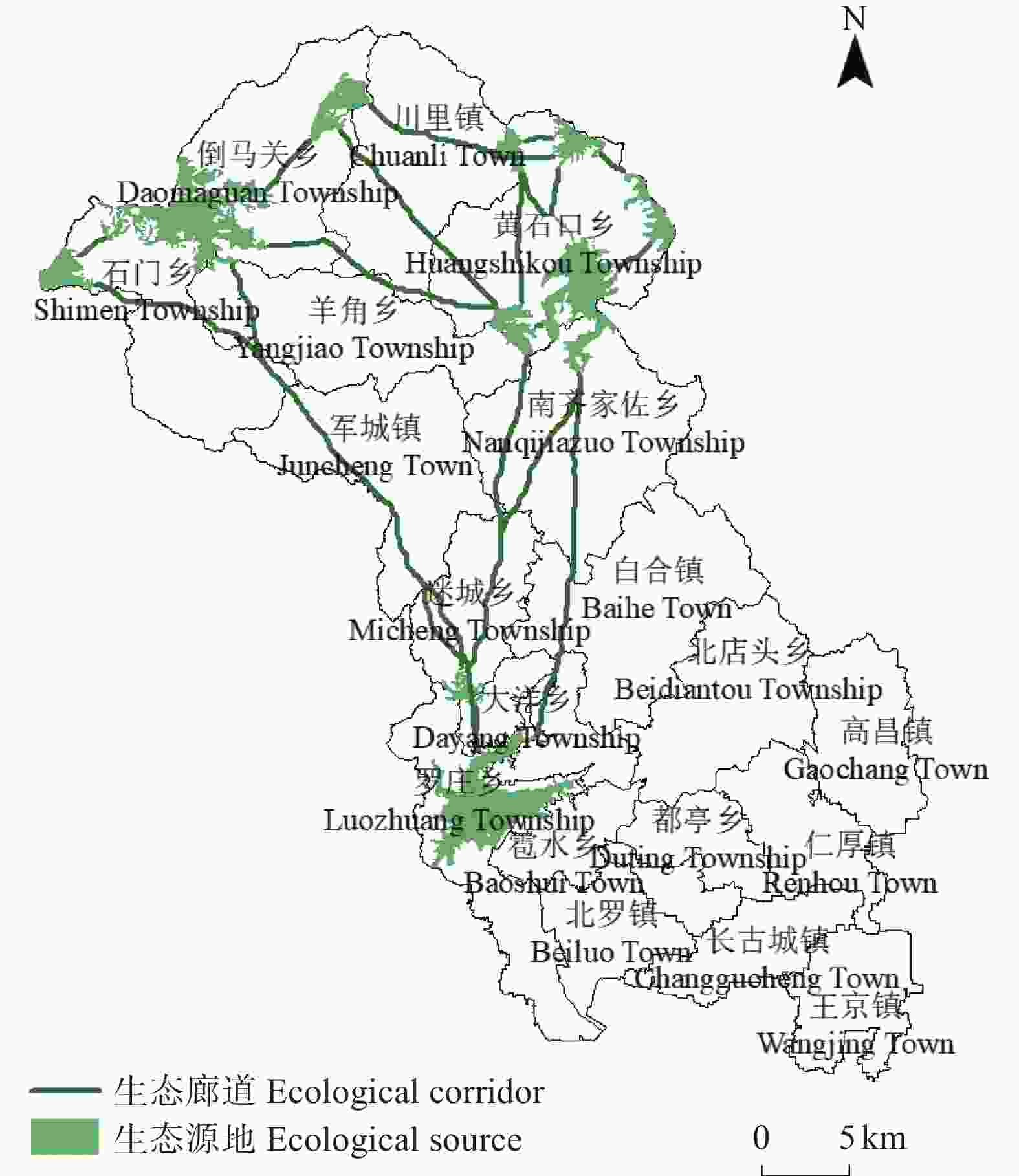
图5研究区生态廊道的空间分布
Figure5.Spatial distribution of ecological corridors in the study area
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片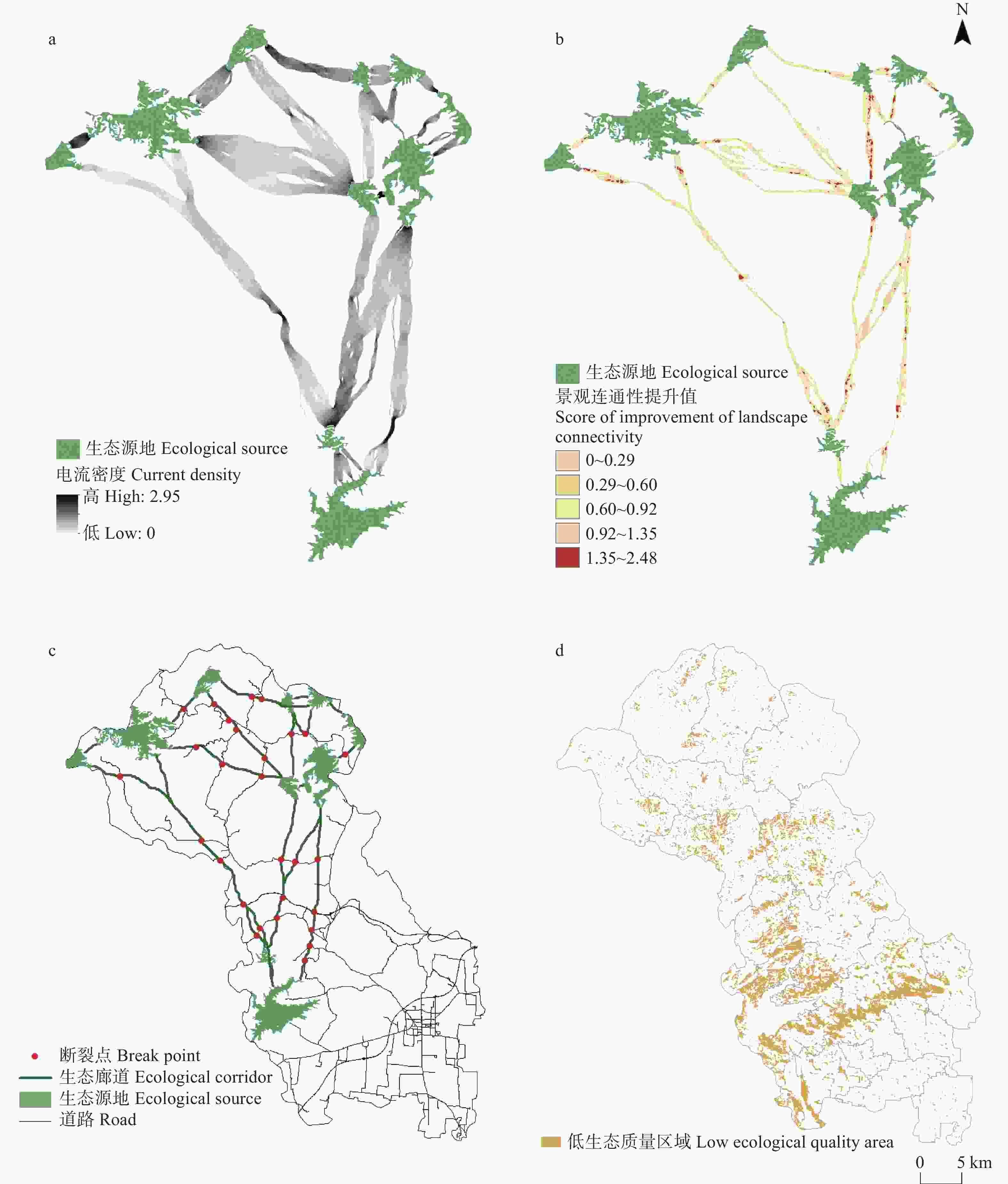
图6生态夹点(a)、生态障碍点(b)、生态断裂点(c)和低生态质量区域(d)分布
Figure6.Distribution of ecological pinch (a), ecological barrier points (b), ecological break points (c) and low ecological quality area (d)
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片表1唐县不同土地利用类型的生态服务价值系数表
Table1.Coefficients of ecological service value of different land use types
| 生态系统一级服务功能 Ecosystem first level service function | 生态系统二级服务功能 Ecosystem secondary service function | 林地 Woodland | 草地 Grassland | 耕地 Farmland | 水域 Water area | 未利用地 Unused land | 建设用地 Built-up land |
| 供给服务 Supply service | 食物生产 Food production | 2250.86 | 1560.00 | 4925.14 | 1782.86 | 0 | 0 |
| 原料生产 Raw material production | 5170.28 | 2295.43 | 1092.00 | 512.57 | 0 | 0 | |
| 水资源供给 Water supply | 2674.28 | 1270.28 | ?5816.57 | 18 474.85 | 0 | 0 | |
| 调节服务 Regulation service | 气体调节 Gas regulation | 17 003.99 | 8067.42 | 3966.85 | 1716.00 | 44.57 | 0 |
| 气候调节 Climate regulation | 50 878.25 | 21 327.41 | 2072.57 | 5103.43 | 0 | 0 | |
| 净化环境 Environment purification | 14 909.13 | 7042.28 | 601.71 | 12 368.56 | 222.86 | 0 | |
| 水文调节 Hydrological regulation | 33 294.84 | 15 622.28 | 6663.42 | 227 849.00 | 66.86 | 0 | |
| 支持服务 Support service | 土壤保持 Soil conservation | 20 703.42 | 9828.00 | 2317.71 | 2072.57 | 44.57 | 0 |
| 维持养分循环 Nutrient circulation maintaning | 1582.28 | 757.71 | 690.86 | 156.00 | 0 | 0 | |
| 维持生物多样性 Biodiversity maintaning | 18 853.70 | 8936.57 | 757.71 | 5682.85 | 44.57 | 0 | |
| 文化服务 Cultural service | 美学景观 Aesthetic landscape | 8267.99 | 3944.57 | 334.29 | 4212.00 | 222.86 | 0 |
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表2唐县生态阻力面因子权重与阻力系数
Table2.Factor weights and resistance coefficients of ecological resistance surface of Tangxian County
| 阻力系数 Resistance coefficient | 阻力因子 Resistance factor | |||
| 土地利用类型 Land use type | 生境质量 Habitat quality | 高程 Altitude (m) | 坡度 Slope (°) | |
| 1 | 林地和水域 Woodland and water area | 0.8~1.0 | 40~191 | 0~5 |
| 2 | 草地 Grassland | 0.6~0.8 | 191~368 | 5~15 |
| 3 | 耕地 Farmland | 0.4~0.6 | 368~565 | 15~25 |
| 4 | 未利用地 Unused land | 0.2~0.4 | 565~830 | 25~35 |
| 5 | 建设用地 Built-up land | 0~0.2 | 830~1810 | >35 |
| 权重 Weight | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表32000—2018年唐县综合生境质量各等级面积占比
Table3.Area proportion of each grade of comprehensive habitat quality in the study area from 2000 to 2018
| 等级 Grade | 2000 | 2010 | 2018 | |||||
| 面积 Area (km2) | 占比 Proportion (%) | 面积 Area (km2) | 占比 Proportion (%) | 面积 Area (km2) | 占比 Proportion (%) | |||
| 低 Low | 149.12 | 9.5 | 52.49 | 3.6 | 108.14 | 7.6 | ||
| 较低 Relatively low | 298.29 | 20.0 | 211.73 | 15.0 | 242.00 | 17.1 | ||
| 中等 Medium | 366.26 | 25.9 | 374.97 | 26.4 | 395.22 | 27.8 | ||
| 较高 Relatively high | 322.03 | 23.7 | 455.18 | 32.2 | 417.61 | 29.5 | ||
| 高 High | 281.17 | 20.9 | 322.50 | 22.8 | 253.90 | 18.0 | ||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV参考文献
| [1] | 彭建, 吕丹娜, 董建权, 等. 过程耦合与空间集成: 国土空间生态修复的景观生态学认知[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(1): 3?13 doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200102 PENG J, LYU D N, DONG J Q, et al. Processes coupling and spatial integration: Characterizing ecological restoration of territorial space in view of landscape ecology[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2020, 35(1): 3?13 doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200102 |
| [2] | 费建波, 夏建国, 胡佳, 等. 生态空间与生态用地国内研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(11): 1626?1636 FEI J B, XIA J G, HU J, et al. Research progress of ecological space and ecological land in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(11): 1626?1636 |
| [3] | 高世昌. 国土空间生态修复的理论与方法[J]. 中国土地, 2018, (12): 40?43 GAO S C. Theory and method of land space ecological restoration[J]. China Land, 2018, (12): 40?43 |
| [4] | 苏冲, 董建权, 马志刚, 等. 基于生态安全格局的山水林田湖草生态保护修复优先区识别?以四川省华蓥山区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(23): 8948?8956 SU C, DONG J Q, MA Z G, et al. Identifying priority areas for ecological protection and restoration of mountains-rivers-forests-farmlands-lakes-grasslands based on ecological security patterns: a case study in Huaying Mountain, Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(23): 8948?8956 |
| [5] | 习近平. 关于《中共中央关于全面深化改革若干重大问题的决定》的说明[J]. 北京周报: 英文版, 2014, 57(6): 6?16 XI J P. Explanation on the decision of the CPC Central Committee on several major issues of comprehensively deepening reform[J]. Beijing Review, 2014, 57(6): 6?16 |
| [6] | 袁大鹏, 陈奇乐, 石垚, 等. 河北典型样带土地利用生态安全格局研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(11): 1767?1778 YUAN D P, CHEN Q L, SHI Y, et al. Ecological security pattern of land use in a typical transect of Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(11): 1767?1778 |
| [7] | 黎晓亚, 马克明, 傅伯杰, 等. 区域生态安全格局: 设计原则与方法[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(5): 1055?1062 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2004.05.029 LI X Y, MA K M, FU B J, et al. The regional pattern for ecological security (RPES): designing principles and method[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(5): 1055?1062 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2004.05.029 |
| [8] | 黄润, 葛向东. 六安市生态安全关键地段的识别与分析[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2005, 21(3): 75?79 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2005.03.018 HUANG R, GE X D. Recognition and analysis on the key area for ecological security in Lu’an City[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2005, 21(3): 75?79 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2005.03.018 |
| [9] | 王志涛, 门明新, 崔江慧. 沽源县未利用地生态重要性空间识别及其地形梯度特征分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(2): 256?264 WANG Z T, MEN M X, CUI J H. Spatial recognition of ecological importance and analysis of terrain gradients characteristic of unused lands in Guyuan County[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(2): 256?264 |
| [10] | 方莹, 王静, 黄隆杨, 等. 基于生态安全格局的国土空间生态保护修复关键区域诊断与识别?以烟台市为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(1): 190?203 doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200116 FANG Y, WANG J, HUANG L Y, et al. Determining and identifying key areas of ecosystem preservation and restoration for territorial spatial planning based on ecological security patterns: a case study of Yantai City[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2020, 35(1): 190?203 doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200116 |
| [11] | 李青圃, 张正栋, 万露文, 等. 基于景观生态风险评价的宁江流域景观格局优化[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(7): 1420?1437 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201907011 LI Q P, ZHANG Z D, WAN L W, et al. Landscape pattern optimization in Ningjiang River Basin based on landscape ecological risk assessment[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74(7): 1420?1437 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201907011 |
| [12] | 何珍珍, 王宏卫, 杨胜天, 等. 渭干河-库车河绿洲景观生态安全时空分异及格局优化[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(15): 5473?5482 HE Z Z, WANG H W, YANG S T, et al. Spatial-temporal differentiation and pattern optimization of landscape ecological security in the Ugan-Kuqa River Oasis[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(15): 5473?5482 |
| [13] | GUO R, WU T, LIU M R, et al. The construction and optimization of ecological security pattern in the Harbin-Changchun urban agglomeration, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(7): 1190 doi: 10.3390/ijerph16071190 |
| [14] | 张远景, 俞滨洋. 城市生态网络空间评价及其格局优化[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(21): 6969?6984 ZHANG Y J, YU B Y. Analysis of urban ecological network space and optimization of ecological network pattern[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(21): 6969?6984 |
| [15] | DONG R C, ZHANG X Q, LI H H. Constructing the ecological security pattern for sponge city: a case study in Zhengzhou, China[J]. Water, 2019, 11(2): 284 doi: 10.3390/w11020284 |
| [16] | 殷炳超, 何书言, 李艺, 等. 基于陆海统筹的海岸带城市群生态网络构建方法及应用研究[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(12): 4373?4382 YIN B C, HE S Y, LI Y, et al. Development and application of an ecological network model for a coastal megalopolis based on land-sea integration[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 4373?4382 |
| [17] | 胡炳旭, 汪东川, 王志恒, 等. 京津冀城市群生态网络构建与优化[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(12): 4383?4392 HU B X, WANG D C, WANG Z H, et al. Development and optimization of the ecological network in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 4383?4392 |
| [18] | 谢花林, 李秀彬. 基于GIS的区域关键性生态用地空间结构识别方法探讨[J]. 资源科学, 2011, 33(1): 112?119 XIE H L, LI X B. A method for identifying spatial structure of regional critical ecological land based on GIS[J]. Resources Science, 2011, 33(1): 112?119 |
| [19] | 陈小平, 陈文波. 鄱阳湖生态经济区生态网络构建与评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(5): 1611?1618 CHEN X P, CHEN W B. Construction and evaluation of ecological network in Poyang Lake Eco-economic Zone, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(5): 1611?1618 |
| [20] | 俞孔坚. 景观生态战略点识别方法与理论地理学的表面模型[J]. 地理学报, 1998, 53(S1): 11?20 YU K J. Ecologically strategic points in landscape and surface model[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1998, 53(S1): 11?20 |
| [21] | 潘竟虎, 刘晓. 疏勒河流域景观生态风险评价与生态安全格局优化构建[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3): 791?799 PAN J H, LIU X. Landscape ecological risk assessment and landscape security pattern optimization in Shule River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(3): 791?799 |
| [22] | 李健飞, 李林, 郭泺, 等. 基于最小累积阻力模型的珠海市生态适宜性评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(1): 225?232 LI J F, LI L, GUO L, et al. Assessment on the ecological suitability in Zhuhai City, Guangdong, China, based on minimum cumulative resistance model[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(1): 225?232 |
| [23] | 柯新利, 李红艳, 刘荣霞. 武汉市耕地景观游憩功能与可达性的空间匹配格局[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2016, 25(5): 751?760 doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201605008 KE X L, LI H Y, LIU R X. Research on the spatial mathching pattern of cultivated land landscape recreation function and accessibility in Wuhan[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2016, 25(5): 751?760 doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201605008 |
| [24] | XU X B, YANG G S, TAN Y. Identifying ecological red lines in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt: a regional approach[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 96: 635?646 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.09.052 |
| [25] | WANG Y, GAO J X, ZOU C X, et al. Identifying ecologically valuable and sensitive areas: a case study analysis from China[J]. Journal for Nature Conservation, 2017, 40: 49?63 doi: 10.1016/j.jnc.2017.08.005 |
| [26] | 黄隆杨, 刘胜华, 方莹, 等. 基于“质量-风险-需求”框架的武汉市生态安全格局构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(2): 615?626 HUANG L Y, LIU S H, FANG Y, et al. Construction of Wuhan’s ecological security pattern under the “quality-risk-requirement” framework[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(2): 615?626 |
| [27] | 刘佳, 尹海伟, 孔繁花, 等. 基于电路理论的南京城市绿色基础设施格局优化[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(12): 4363?4372 LIU J, YIN H W, KONG F H, et al. Structure optimization of circuit theory-based green infrastructure in Nanjing, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 4363?4372 |
| [28] | MCRAE B H. Isolation by resistance[J]. Evolution, 2006, 60(8): 1551?1561 doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2006.tb00500.x |
| [29] | 黄九明. 基于电路理论的济南市生态安全格局构建研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020 HUANG J M. Research on the construction of ecological security pattern of Jinan City based on circuit theory[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020 |
| [30] | MCRAE B H, DICKSON B G, KEITT T H, et al. Using circuit theory to model connectivity in ecology, evolution, and conservation[J]. Ecology, 2008, 89(10): 2712?2724 doi: 10.1890/07-1861.1 |
| [31] | 周浪, 李明慧, 周启刚, 等. 基于电路理论的特大山地城市生态安全格局构建?以重庆市都市区为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(2): 319?325, 334 ZHOU L, LI M H, ZHOU Q G, et al. Construction of ecological security pattern in very large mountainous city based on circuit theory — Taking Chongqing metropolitan area as an example[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(2): 319?325, 334 |
| [32] | 谢高地, 张彩霞, 张雷明, 等. 基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进[J]. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30(8): 1243?1254 doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.08.001 XIE G D, ZHANG C X, ZHANG L M, et al. Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015, 30(8): 1243?1254 doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.08.001 |
| [33] | VEMURI A W, COSTANZA R. The role of human, social, built, and natural capital in explaining life satisfaction at the countrylevel: Toward a national well-being index (NWI)[J]. Ecological Economics, 2006, 58(1): 119?133 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.02.008 |
| [34] | 谢高地, 甄霖, 鲁春霞, 等. 一个基于专家知识的生态系统服务价值化方法[J]. 自然资源学报, 2008, 23(5): 911?919 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2008.05.019 XIE G D, ZHEN L, LU C X, et al. Expert knowledge based on valuation method of ecosystem service in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2008, 23(5): 911?919 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2008.05.019 |
| [35] | 吴健生, 张理卿, 彭建, 等. 深圳市景观生态安全格局源地综合识别[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(13): 4125?4133 doi: 10.5846/stxb201208081123 WU J S, ZHANG L Q, PENG J, et al. The integrated recogni-tion of the source area of the urban ecological security pattern in Shenzhen[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 2013, 33(13): 4125?4133 doi: 10.5846/stxb201208081123 |
| [36] | 周敏, 齐增湘, 吕婧玮, 等. 废弃工矿区生态修复潜力分析?以水口山镇为例[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(4): 273?281 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2021.04.39 ZHOU M, QI Z X, LYU J W, et al. Analysis of ecological restoration potential in abandoned industrial and mining areas — Taking Shuikoushan Town as an example[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2021, 36(4): 273?281 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2021.04.39 |
| [37] | 郝月, 张娜, 杜亚娟, 等. 基于生境质量的唐县生态安全格局构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(3): 1015?1024 HAO Y, ZHANG N, DU Y J, et al. Construction of ecological security pattern based on habitat quality in Tang County, Hebei, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(3): 1015?1024 |
| [38] | 李芹. 基于MCR模型的赣南稀土矿区景观生态安全格局研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2019 LI Q. Study on landscape ecological security patterns of rare earth mining areas in southern Jiangxi Province based on MCR model[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2019 |
| [39] | 孙枫, 章锦河, 王培家, 等. 城市生态安全格局构建与评价研究: 以苏州市区为例[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(9): 2476?2493 doi: 10.11821/dlyj020200990 SUN F, ZHANG J H, WANG P J, et al. Research on the construction and evaluation of urban ecological security pattern: Taking Suzhou City as an example[J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(9): 2476?2493 doi: 10.11821/dlyj020200990 |
| [40] | 吕剑成, 周磊, 洪武扬, 等. 城市土地生态适宜性分区划分研究——以常州市武进区为例[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2015, 24(9): 1560–1567 LYU J C, ZHOU L, HONG W Y, et al. Research on zoning of urban land ecological suitability — Taking Wujin District of Changzhou City as an example[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2015, 24(9): 1560–1567 |
| [41] | 汤峰, 王力, 张蓬涛, 等. 基于生态保护红线和生态网络的县域生态安全格局构建[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(9): 263?272 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.09.030 TANG F, WANG L, ZHANG P T, et al. Construction of county-level ecological security pattern based on ecological protection red line and network in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(9): 263?272 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.09.030 |
| [42] | 叶玉瑶, 苏泳娴, 张虹鸥, 等. 生态阻力面模型构建及其在城市扩展模拟中的应用[J]. 地理学报, 2014, 69(4): 485–496 YE Y Y, SU Y X, ZHANG H O, et al. Construction of ecological resistance surface model and its application in urban expansion simulation[J], Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(4): 485–496 |
| [43] | MCRAE B H, HALL S A, BEIER P, et al. Where to restore ecological connectivity? detecting barriers and quantifying restoration benefits[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(12): e52604 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052604 |
| [44] | MCRAE B H, SHAH V B, MOHAPATRA T K. Circuitscape User Guide[EB/OL]. Santa Barbara: The University of California, 2009. https://circuitscape.org/ |
