 ,1,**, 张武汉2,**, 党小景1, 荣慧3, 叶琴3, 胡长敏1, 张瑛1, 何强
,1,**, 张武汉2,**, 党小景1, 荣慧3, 叶琴3, 胡长敏1, 张瑛1, 何强 ,2,*, 王德正
,2,*, 王德正 ,1,*
,1,*Genetic analysis of stigma traits with genic male sterile line by mixture model of major gene plus polygene in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
JIANG Jian-Hua ,1,**, ZHANG Wu-Han2,**, DANG Xiao-Jing1, RONG Hui3, YE Qin3, HU Chang-Min1, ZHANG Ying1, HE Qiang
,1,**, ZHANG Wu-Han2,**, DANG Xiao-Jing1, RONG Hui3, YE Qin3, HU Chang-Min1, ZHANG Ying1, HE Qiang ,2,*, WANG De-Zheng
,2,*, WANG De-Zheng ,1,*
,1,*通讯作者:
收稿日期:2020-08-18接受日期:2020-12-1网络出版日期:2020-12-31
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-08-18Accepted:2020-12-1Online:2020-12-31
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
江建华, E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (2657KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
江建华, 张武汉, 党小景, 荣慧, 叶琴, 胡长敏, 张瑛, 何强, 王德正. 水稻核不育系柱头性状的主基因+多基因遗传分析[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 47(7): 1215-1227. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.02057
JIANG Jian-Hua, ZHANG Wu-Han, DANG Xiao-Jing, RONG Hui, YE Qin, HU Chang-Min, ZHANG Ying, HE Qiang, WANG De-Zheng.
我国65%以上人口以稻米为主食, 在人口持续增加而耕地却以数万公顷逐年减少的情况下, 大幅提高单位面积产量是保障粮食安全的必然选择[1,2]。始于20世纪70年代的杂交水稻较同熟期常规稻增产20%, 其商业化种植使水稻生产力有了大幅提高[3]。我国杂交水稻年种植面积约1670万公顷, 年制种面积高达18万公顷[4]。虽然杂交水稻的制种产量从1976年的0.27 t hm-2增加到现在的2.7 t hm-2, 部分高产田块达4 t hm-2 [5], 但随着城市化进程加快, 劳动力短缺, 制种成本不断增加。提高制种产量是降低杂交水稻成本、增加种植效益的决定性因素。研究表明, 阻碍杂交水稻制种产量增加的主要因素是不育系异交结实率低[6]。不育系柱头外露是限制杂交水稻制种异交结实率的关键因素[7]。代贵金等[8]认为柱头外露率和制种产量成极显著正相关; 田大成等[9]发现水稻闭颖后外露柱头颖花平均结实率为64%, 远高于非外露颖花的15.7%; 李庆荣[10]发现柱头外露颖花的结实率占制种异交结实率的70%~80%; 杨保汉[11]发现自然条件下不育系柱头外露率每提高1个百分点, 其结实率可提高0.74~0.92个百分点, 每公顷制种产量可增加47~68 kg。可见, 水稻异交结实率与其柱头性状密切相关。
水稻柱头性状主要包括柱头长度、花柱长度、柱花总长度以及柱头外露率。柱花总长度与柱头外露率呈显著[12,13,14]或极显著[15,16]正相关, 柱头长度、花柱长度以及柱花总长度间也表现出极显著正相关[16,17]。相比较于水稻其他性状, 作为水稻重要异交性状的柱头性状, 其研究进展是严重滞后的。当前对于柱头性状的研究主要集中于柱头外露率, 研究者利用F2群体[12,18-21]、RIL群体[22,23,24,25,26,27]和自然群体[16,28]等在水稻12条染色体上共检测到112个控制该性状的QTL, 并将qSER-7[18]、qSE7[29]和qSE11[30]分别精细定位于28.4 kb、322.9 kb和350.7 kb的区间。而关于柱头长度性状的研究则较少, 研究者利用F2群体[31]、RIL群体[22,31]、BIL群体、DH群体[31]以及自然群体[16-17,28,32]等在水稻的11条染色体(除11号染色体外)上检测到28个控制STL的QTL, 在水稻1号、2号、3号、4号、6号、7号、10号和11号染色体上检测到21个控制SYL的QTL[16-17,22,31-32], 在水稻的9条染色体(除8号、9号和10号染色体外)上检测到16个控制TSSL的QTL[15,17,32-34], 但仅Liu等[34]将qSTL3精细定位于水稻3号染色体短臂19.8 kb区间。说明当前对于柱头性状的研究较少且未深入。这也可能是导致至今未见利用相关研究结果辅助选育长柱头、高外露率不育系等育种材料报道的原因。
本研究以课题组自行选育的短柱头、低外露率的粳型光温敏核不育系7001S[35]为母本, 长柱头、高外露率的籼型温敏核不育系紫泰S为父本, 在陵水进行杂交和自交, 以获得的7001S/紫泰S组合F1、F2和F2:3构成的遗传群体为研究对象, 利用广泛应用于水稻[36]、油菜[37]、大豆[38]、番茄[39]、小麦[40]等各种农作物的主基因+多基因混合模型[41]对2个世代的4个柱头性状进行遗传分析, 同时, 对2个世代(不同年份) 4个柱头性状间的相关性进行分析, 旨在揭示柱头性状的遗传基础及其相关性, 以期为水稻柱头性状的QTL定位和全基因组关联分析提供互补验证, 同时也为长柱头、高柱头外露率的水稻温敏核不育系的创制提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
无色短柱头、低柱头外露率的粳型光温敏核不育系7001S (P1) (图1-A和图2-A)、紫色长柱头、高柱头外露率的籼型温敏核不育系紫泰S (P2) (图1-B和图2)及其杂交、自交所衍生的7001S/紫泰S组合F1、F2和F2:3构成的遗传群体材料。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图17001S和紫泰S植株和穗子的表现
Fig. 1Phnotypes of plants and panicles between 7001S and Zitai S
1.2 试验方法
2016年冬季在海南陵水以7001S (P1)为母本, 紫泰S (P2)为父本, 杂交获得7001S/紫泰S F1, 2017年正季将F1种植于安徽省农业科学院水稻研究所庐江基地(31o30¢23¢¢N, 117o18¢9¢¢E), 自交获得F2种子, 2018年正季将P1、P2、F1和F2种植于庐江基地(E1), 5月12日播种, 6月17日移栽。2019年正季将P1、P2、F1和F2:3 (由2018年F2各单株收2粒种子混合而成)种植于庐江基地(E2), 5月13日播种, 6月14日移栽。P1、P2和F1分别种植4行, F2和F2:3群体均种植50行, 每行9株, 株行距16.7 cm × 26.7 cm, 常规栽培管理。柱头长度(stigma length, STL)是指水稻雌蕊上毛刷状部分的长度, 花柱长度(style length, SYL)是指毛刷状底部与子房交界处之间的长度[16], 柱花总长度(the sum of stigma and style length, TSSL)是指柱头长度和花柱长度之和(图2-B)。
柱头长度相关性状的测量方法: 植株盛花期从主茎穗(最高穗)上取10个正张开的颖花(每天取样时间为10:00—14:00); 从颖花中剥取8个完整的雌蕊, 置于带有摄像头(MDX4)的体式显微镜(MZ11, 广州市明美光电技术有限公司)视野中拍照; 利用图像处理系统(MicroShot v1.2)在图片上测量柱头长度相关性状(图2-A, B); 计算单株所有16个柱头(每个雌蕊2个柱头)长度相关性状的平均值, 作为该单株(株系)柱头长度相关性状的表型值。P1、P2和F1各株系调查8个雌蕊, 即16个柱头长度相关性状的数据作为该株系表型值; F2和F2:3分别调查了350个和320个单株, 每单株调查16个柱头长度相关性状的数据作为该单株表型值。
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2水稻雌蕊各部位、7001S和紫泰S柱头表现以及柱头外露表现
A: 7001S和紫泰S的柱头长度比较; B: 水稻雌蕊各部位名称; C: 水稻柱头无外露、单外露以及双外露的表现; D: 紫泰S田间柱头外露表现。
Fig. 2Phenotypes of pistils and the stigmas in rice
A: stigma morphology of 7001S and Zitai S; B: names of rice pistil parts defined in this study; C: phenotypes of single, dual, and no stigma exsertion in a spikelet; D: phenotype of exserted stigma in Zitai S. STL: stigma length; SYL: style length; TSSL: the sum of stigma and style length.
柱头外露率(percentage of exserted stigma, PES)是在家系开花结束后10 d调查, 具体方法参照Miyata等[12]略作改动, 简言之, 柱头外露率等于主茎穗的外露柱头数除以总柱头数(总颖花数的2倍)所得的百分数(图2-C, D)。P1、P2和F1分别调查10个单株的主茎穗, 10个单株主茎穗的均值即为该株系柱头外露率表型值; F2和F2:3分别调查了350个和320个单株, 各单株分别调查主茎穗和2个分蘖穗, 3个穗子柱头外露率的均值为该单株柱头外露率的表型值。
1.3 数据分析
用SPSS软件(SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)进行柱头性状统计分析及性状间的相关性分析。遗传力的计算方法: H2 = [VF2 - 1/3(VP1 + VP2 + VF1)]/VF2。F2和F2:3群体4个柱头相关性状的次数分布按盖钧镒[42]的方法进行整理, 采用曹锡文等[41]研制的植物数量性状分离分析软件SEA-G4F2 (P1、P2、F1和F2)和SEA-G4F3 (P1、P2、F1和F2:3)中的极大似然法和IECM算法, 估算2个世代4个柱头相关性状获得1对主基因(one major gene model, 1 MG)、2对主基因(two major genes model, 2 MG)、多基因(polygene model, PG)、1对主基因+多基因(mixed one major gene and polygene model, MX1)和2对主基因+多基因(mixed two major genes and polygene model, MX2)共5类24种遗传模型的极大对数似然函数值和AIC (Akaike’s information criterion)值。根据最佳模型选择原则, AIC值最小的模型为相对最适模型, 若出现模型间AIC值差异不大时, 则会出现几个备选模型, 此时需通过样本分布与理论分布间的均匀性检验和Kolmogorov-Smirnov检验来比较各备选模型适合性概率的大小, 从而确定最适模型, 同时可得到最适模型相应的各成分分布参数, 包括各主基因的加性、显性、上位性效应, 多基因的加性、显性、上位性效应以及主基因遗传率和多基因遗传率等。其中主基因遗传率h2mg (%) = σ2mg/σ2p × 100; 多基因遗传率h2pg (%) = σ2pg/σ2p × 100; 式中σ2mg、σ2pg和σ2p分别为主基因方差、多基因方差和表型方差。
2 结果与分析
2.1 水稻柱头相关性状的遗传分析
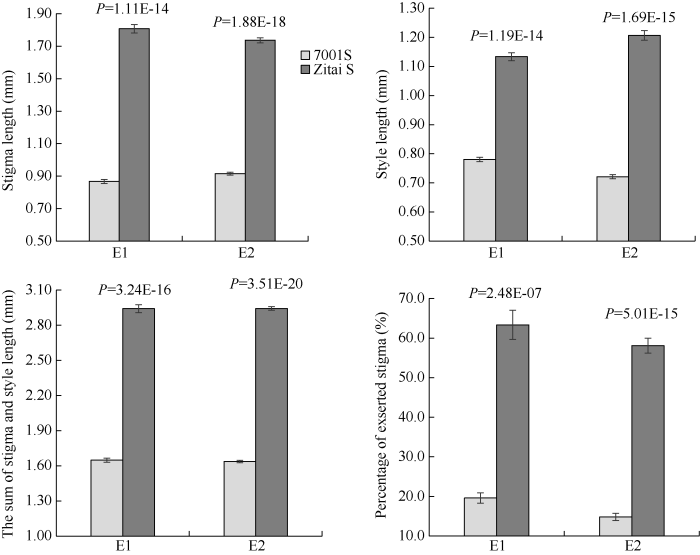
2.1.1 柱头相关性状表型特征及次数分布 E1和E2中紫泰S的STL、SYL、TSSL和PES均极显著高于7001S (表1和图3)。7001S / 紫泰S F1的4个柱头相关性状均介于双亲之间, 其中STL、SYL和TSSL的接近于双亲均值, 而PES的偏向于高值亲本。4个性状在分离世代群体(F2和F2:3)中的变异系数介于14.29%~54.94%, 说明该组合中的目标性状有较好的遗传多样性。2个环境中4个性状的遗传力均超过78%, 说明这4个性状以遗传为主。但是从表2的P1、P2和F1联合方差分析的结果来看, 除TSSL外, 环境效应以及基因型与环境之间的互作效应对柱头性状的表型值也存在一定影响。分离群体中, 除F2中的STL外, 其余性状在2个分离群体中均出现双向超亲个体, 表现出连续正态分布, 适于进行遗传分析(表1)。Table 1
表1
表17001S、紫泰S组合F2和F2:3群体柱头相关性状描述
Table 1
| 性状 Trait | 环境 Environment | 亲本Parent | F1 | F2/F2:3群体 F2/F2:3 population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7001S | 紫泰S Zitai S | 变幅 Range | 均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 变异系数CV (%) | 遗传力 H2 (%) | 偏度值Skewness | 峰度值 Kurtosis | |||
| 柱头长度 STL | E1 | 0.867 | 1.808 | 1.438 | 0.993-2.079 | 1.468 ± 0.226 | 15.40 | 78.71 | 0.088 | -0.467 |
| E2 | 0.915 | 1.737 | 1.303 | 0.752-1.880 | 1.180 ± 0.221 | 18.71 | 86.09 | 0.807 | 0.334 | |
| 花柱长度 SYL | E1 | 0.780 | 1.134 | 0.825 | 0.441-1.402 | 0.793 ± 0.162 | 20.43 | 93.44 | 0.559 | 0.138 |
| E2 | 0.721 | 1.207 | 0.953 | 0.554-1.399 | 0.862 ± 0.170 | 19.78 | 95.30 | 0.853 | 0.298 | |
| 柱花总长度 TSSL | E1 | 1.648 | 2.941 | 2.263 | 1.524-3.116 | 2.261 ± 0.323 | 14.29 | 86.42 | 0.055 | -0.269 |
| E2 | 1.636 | 2.943 | 2.256 | 1.464-3.100 | 2.042 ± 0.337 | 16.49 | 96.72 | 0.202 | 0.169 | |
| 柱头外露率 PES | E1 | 19.60 | 63.33 | 48.35 | 2.16-79.59 | 31.73 ± 17.43 | 54.94 | 80.23 | 0.547 | -0.178 |
| E2 | 14.82 | 58.09 | 43.32 | 2.83-74.34 | 35.85 ± 16.33 | 45.55 | 90.16 | 0.143 | -0.792 | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
Table 2
表2
表27001S、紫泰S和7001S/紫泰S F1 4个柱头性状的联合方差分析
Table 2
| 性状 Trait | 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 DF | 平方和 SS | 均方 MS | F值 F-value | F0.05 | F0.01 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柱头长度 STL (mm) | 基因型间Genotypes | 2 | 12.44 | 6.22 | 833.66** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| 环境间Environments | 1 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 8.98** | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| 基因型×环境互作Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 9.22** | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| 花柱长度 SYL (mm) | 基因型间Genotypes | 2 | 2.92 | 1.46 | 727.96** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| 环境间Environments | 1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 26.65** | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| 基因型×环境互作Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 36.98** | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| 柱花总长度 TSSL (mm) | 基因型间Genotypes | 2 | 27.06 | 13.53 | 1512.51** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| 环境间Environments | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.08 | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| 基因型×环境互作Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| 柱头外露率 PES (%) | 基因型间Genotypes | 2 | 19,545.70 | 9772.85 | 265.44** | 3.17 | 5.03 |
| 环境间Environments | 1 | 377.86 | 377.86 | 10.26** | 4.02 | 7.13 | |
| 基因型×环境互作Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.52 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 3.17 | 5.03 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图32个环境下7001S和紫泰S 4个柱头相关性状的表现 缩写同
Fig. 3Phenotypic evaluations of four stigma related-traits in E1 and E2 of 7001S and Zitai S Abbreviations are the same as those given in
2.1.2 柱头相关性状遗传模型的建立 根据5类24种模型以及柱头性状的次数分布, 算出该性状所有24种遗传模型的极大似然值和AIC值(表略)。AIC值最小的模型为最佳可能模型, 当出现与最小AIC值接近的模型时, 将这些模型与最佳可能模型一起都作为该性状的备选模型。再对备选模型的样本分布和理论分布进行适合性检验(U12, U22, U32, nW2, Dn)以确定最佳模型。结果E1中STL的MX2-ADI-AD模型AIC值最小, 为-127.50, 但MX1-AD-ADI、MX2-ADI-ADI和MX2-AD-AD模型的AIC值与之相近, 故上述4个模型作为E1中STL的备选模型。应用与E1中STL相同的方法进行其他柱头性状备选模型的选择。2个环境下4个柱头性状备选模型的极大似然值和AIC值见表3。
Table 3
表3
表34个柱头性状备选模型配合表型分布的极大似然函数值和AIC值(IECM算法)
Table 3
| 性状 Trait | 环境 Env. | 世代 Generation | 备选模型 Candidate model | 极大对数似然函数值 Max. log likelihood value | AIC值 AIC value | 适合性检验a Test of goodness-of-fit a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柱头长度 STL | E1 | F2 | MX1-AD-ADI | 69.20 | -122.40 | 0/0/2/0/0 |
| MX2-ADI-ADI | 72.90 | -121.90 | 0/0/2/0/0 | |||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 72.70 | -127.50 | 0/0/2/0/0 | |||
| MX2-AD-AD | 66.60 | -123.20 | 0/1/1/1/1 | |||
| E2 | F2:3 | PG-ADI | 227.00 | -442.00 | 0/0/1/1/0 | |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 236.50 | -457.00 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| MX2-ADI-ADI | 238.60 | -453.10 | 0/0/1/1/0 | |||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 238.40 | -458.80 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| 花柱长度 SYL | E1 | F2 | 2MG-ADI | 118.90 | -217.80 | 1/1/1/2/0 |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 118.40 | -222.80 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 121.70 | -217.40 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| MX2-AD-AD | 106.20 | -194.40 | 3/2/2/3/0 | |||
| E2 | F2:3 | 2MG-ADI | 220.90 | -421.90 | 0/0/2/0/0 | |
| 2MG-AD | 210.90 | -409.80 | 2/2/2/2/0 | |||
| MX1-AD-ADI | 220.80 | -427.60 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 219.10 | -412.20 | 0/0/0/0/0 | |||
| 柱花总长度 TSSL | E1 | F2 | MX2-AD-AD | -60.20 | 130.39 | 0/0/1/0/0 |
| MX2-A-AD | -62.25 | 130.50 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| MX2-EAED-AD | -64.11 | 132.22 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| MX2-EEAD-AD | -65.47 | 134.94 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| E2 | F2:3 | 2MG-ADI | 18.46 | -16.92 | 0/0/0/1/0 | |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 9.54 | -5.08 | 0/0/0/0/0 | |||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 5.01 | 15.98 | 0/0/0/0/0 | |||
| MX2-EAED-AD | -3.10 | 18.20 | 3/3/1/3/0 | |||
| 柱头外露率 PES | E1 | F2 | 2MG-ADI | -1627.49 | 3276.98 | 1/1/0/1/0 |
| MX1-AD-ADI | -1631.22 | 3278.44 | 0/0/0/0/0 | |||
| MX2-ADI-ADI | -1620.71 | 3265.42 | 0/0/0/0/0 | |||
| MX2-ADI-AD | -1619.79 | 3257.57 | 0/0/0/0/0 | |||
| E2 | F2:3 | 2MG-AD | -1482.84 | 2977.69 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |
| MX1-AD-ADI | -1482.98 | 2979.95 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| MX1-A-AD | -1483.46 | 2976.92 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |||
| MX1-EAD-AD | -1484.77 | 2979.55 | 0/0/1/0/0 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
经适合性检验, E1中STL的MX2-AD-AD模型20个适合性检验统计量有4个达到显著(α=0.05), 而MX1-AD-ADI、MX2-ADI-ADI和MX2-ADI-AD均只有2个统计量达到显著, 但MX2-ADI-AD模型理论分布配合实际分布适合性的概率值比MX1-AD-ADI和MX2-ADI-ADI模型高, 说明MX2-ADI-AD模型较其他3个备选模型的适合性好。因此, 7001S/紫泰S组合E1中STL的最佳遗传模型为MX2-ADI-AD。说明该性状E1中表现出受2对主效基因和微效基因共同控制, 其中2对主效基因表现出加性-显性-上位性效应, 而微效基因表现出加性-显性效应。E2中STL的PG-ADI和MX2-ADI-ADI模型20个适合性检验统计量均有2个达到显著(α=0.05); 而MX1-AD-ADI和MX2-ADI-AD模型均只有1个统计量达到显著(α=0.05), 但MX2-ADI-AD模型理论分布配合实际分布适合性的概率值比MX1-AD-ADI模型高, 说明MX2-ADI-AD模型比MX1-AD-ADI模型适合性好。因此, 7001S/紫泰S组合E2中STL的最佳遗传模型也为MX2-ADI-AD。说明该性状E2中也表现出受2对加性-显性-上位性主基因+加性-显性多基因控制。
图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
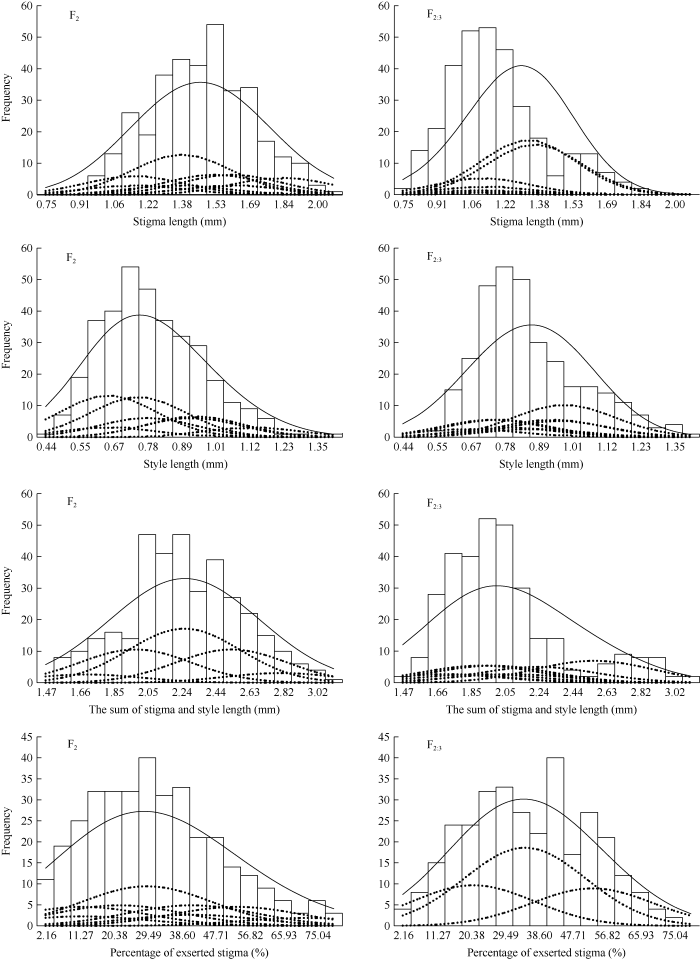
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图47001S/紫泰S组合F2 (E1)和F2:3 (E2)群体4个柱头相关性状的次数分布和拟合混合分布及其成分分布
Fig. 4Frequency distribution, fitted mixed distribution and its component distribution for four stigma related-traits of F2 (E1) and F2:3 (E1) population in the cross 7001S/Zitai S
应用与STL相同方法, 对其他3个性状进行最佳遗传模型的选择。对于SYL, 2个环境中的最佳遗传模型均为MX2-ADI-AD, 说明SYL在E1和E2中均表现出受2对加性-显性-上位性主基因+加性-显性多基因控制。对于TSSL, E1中最佳遗传模型为MX2-EEAD-AD, 即TSSL在E1中表现出受2对主效基因和微效基因共同控制, 其中2对主效基因的加性效应值和显性效应值分别相等, 而微效基因表现出加性-显性效应; E2中TSSL最佳遗传模型为MX2-ADI-AD, 说明TSSL在E2中表现为2对加性-显性-上位性主基因+加性-显性多基因控制。对于PES, E1中最佳遗传模型为MX2-ADI-ADI, 即PES在E1中表现出受2对主效基因和微效基因共同控制, 2对主效基因和微效基因均表现出加性-显性-上位性效应; E2中PES最佳遗传模型为MX1-AD-ADI模型, 即表现出受1对主效基因和微效基因共同控制, 主效基因表现出加性-显性效应, 而微效基因则表现出加性-显性-上位性效应。
E1中TSSL和E2中PES分别有5个和3个成分分布, 其余性状在2个环境中均表现出9个成分分布。4个柱头性状在各自最佳遗传模型下理论分布拟合曲线与实际分布曲线如图4所示。
2.1.3 柱头性状的遗传参数 表4列出了4个柱头性状在2个环境中各自最佳模型下的遗传参数估计值。从一阶参数看, E1中STL的|i|+|jab|+|jba|+|l|>|da|+|db|>|ha|+|hb|, 说明主效基因中的上位性效应要大于加性效应和显性效应, 以上位性效应为主; E2中STL的|i|+|jab|+|jba|+|l|>|ha|+|hb|>|da|+|db|, 说明主效基因中的上位性效应要大于显性效应和加性效应, 以上位性效应为主; 2个环境中的|i|+|jab|+|jba|+|l|+ |ha|+|hb|+|da|+|db|与|[d]|+|[h]|值基本一致, 说明STL中微效基因也起重要作用。对于SYL, E1和E2中|i|+|jab|+|jba|+|l|>|ha|+|hb|>|da|+|db|, 说明主基因效应中是以上位性效应为主; 与STL一样, 主效基因的各效应值之和与微效基因的各效应值之和基本一致, 说明SYL中微效基因效应也起重要作用。E1中TSSL的|d|>|[d]|+|[h]|, 说明主效基因的加性效应大于微效基因的加性效应和显性效应之和; E2中|i|+|jab|+|jba|+|l|>|ha|+|hb|>|da|+|db|, 说明2对主基因以上位性效应为主; |i|+|jab|+|jba|+|l|+|ha|+|hb|+|da|+ |db|=2.87, |[d]|+|[h]|=2.97, 说明TSSL中微效基因也起重要作用。对于PES, E1中|da|+|db|>|i|+|jab|+|jba|+|l|>|ha|+|hb|, E2中|d|>|h|, 说明PES是以加性效应为主。
从表4二阶遗传参数看, 2个环境中4个柱头性状的主基因遗传率介于71.13%~97.09%, 多基因遗传率介于0~22.21%, 说明这4个柱头性状均以主基因遗传为主。
Table 4
表4
表44个柱头性状遗传参数估计值
Table 4
| 遗传参数 Genetic parameter | 柱头长度STL | 花柱长度SYL | 柱花总长度TSSL | 柱头外露率PES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | |
| MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-EEAD- AD | MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-ADI- ADI | MX1-AD- ADI | |
| 一阶参数Univalent parameter | ||||||||
| da | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.05 | -0.28 | 0.06 | -22.32 | 15.99 |
| db | 0.05 | 0.01 | -0.02 | -0.01 | -0.03 | -7.61 | ||
| ha | 0.13 | 0.11 | -0.19 | 0.13 | 0.50 | -2.71 | -4.31 | |
| hb | 0.06 | 0.30 | -0.12 | 0.12 | 0.19 | -1.63 | ||
| i | -0.05 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.05 | -0.14 | 7.56 | ||
| jab | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.07 | -0.19 | 1.59 | ||
| jba | -0.01 | -0.03 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.32 | -2.04 | ||
| l | -0.25 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 1.44 | -0.71 | ||
| [d] | -0.70 | -0.47 | -0.28 | -0.28 | -0.06 | -0.68 | ||
| [h] | 0.10 | -0.53 | 0.15 | -0.50 | -0.08 | -2.29 | ||
| 二阶参数Bivalent parameter | ||||||||
| σ2p | 0.051 | 0.049 | 0.026 | 0.029 | 0.104 | 0.113 | 304.86 | 266.70 |
| σ2mg | 0.040 | 0.045 | 0.020 | 0.030 | 0.080 | 0.110 | 271.96 | 189.71 |
| σ2pg | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 8.42 | 52.40 |
| h2mg (%) | 81.81 | 92.86 | 71.64 | 93.00 | 76.02 | 97.09 | 89.21 | 71.13 |
| h2pg (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 22.21 | 0.00 | 10.99 | 0.00 | 2.76 | 19.65 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2 水稻柱头性状间的相关性分析
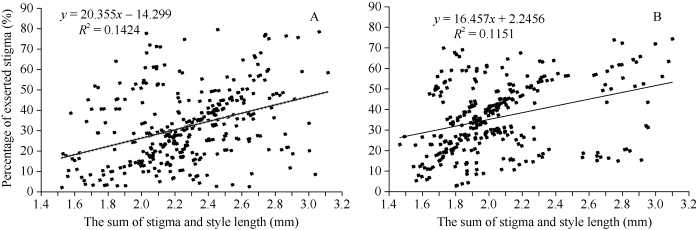
由表5可知, 4个柱头性状在7001S/紫泰S F2群体和F2:3群体中均表现出极显著正相关, 其中F2群体4个性状间的相关系数介于0.262 (SYL和PES)和0.895 (STL和TSSL)之间, F2:3群体4个性状间的相关系数介于0.281 (STL和PES)和0.885 (STL和TSSL)之间。柱花总长度和柱头外露率在2个世代中的表型相关系数分别为0.377 (F2)和0.339 (F2:3), 呈极显著正相关(2个性状的散点图见图5), 决定系数(R2)分别达到14.24%和11.51%, 说明在柱头外露率的变异中, 有11%以上是由柱头长度的变异引起的。这种极显著的线性正相关具有明显的生物学意义。Table 5
表5
表54个柱头性状间的相关性系数
Table 5
| 性状 Trait | 柱头长度 STL | 花柱长度 SYL | 柱花总长度 TSSL | 柱头外露率 PES |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柱头长度 STL | — | 0.472** | 0.885** | 0.281** |
| 花柱长度 SYL | 0.369** | — | 0.760** | 0.306** |
| 柱花总长度 TSSL | 0.895** | 0.816** | — | 0.339** |
| 柱头外露率 PES | 0.352** | 0.262** | 0.377** | — |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
本研究利用由2个核不育系杂交衍生的未经人工选择的F2 (350个单株)和F2:3 (320个单株)群体对4个柱头性状间的相关性进行了分析。结果表明, 4个性状两两之间均表现出极显著正相关, 这说明柱头性状是一个复杂性的综合性状。其中STL与SYL和TSSL间的相关系数均达到0.76以上, 呈紧密相关, 这与Zhou等[16]和Dang等[17]利用不同水稻材料构成的自然群体进行分析所得的结果一致, 说明STL、SYL和TSSL可能是由相同的基因位点(QTL)控制的。TSSL与PES间的相关系数分别为0.377 (F2)和0.339 (F2:3), 达极显著正相关, 这与前人的研究结果一致[12,13,14,15]。同时, 本研究还发现STL与PES间也表现出极显著正相关。说明育种家可以通过增加水稻温敏核不育系的柱花总长度(TSSL)来达到提高柱头外露率(PES)的目的。同时, 柱花总长度的增加, 必然会导致柱头长度(STL)的增加。柱头毛刷状部分是柱头接收花粉的器官, 柱头长度的增加、柱头外露率的提高必然导致杂交水稻异交结实率的增加, 从而增加杂交水稻的制种产量[12,43]。图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图57001S/紫泰S组合F2 (A)和F2:3 (B)群体柱花总长度和柱头外露率的散点图
Fig. 5Scattered dot of TSSL and PES in F2 (A) and F2:3 (B) population of 7001S/Zitai S
解松峰等[40]认为与传统的遗传分析方法相比, 主基因+多基因混合遗传模型进行分析所得的结果更加客观, 育种家可通过表型值快速判断目标性状的遗传组成。近些年主基因+多基因遗传模型更是被频繁用于各种农作物[36-40,44]。本研究利用植物数量性状分离分析软件中的SEA-G4F2 (P1、P2、F1和F2)和SEA-G4F3 (P1、P2、F1和F2:3)对4个柱头性状进行了主基因+多基因遗传分析。结果发现, STL、SYL和TSSL均表现出受2对主效基因+微效基因控制, 且除E1中TSSL的2对主基因表现出等效的加性效应和等效的显性效应外, 其余的2对主效基因间均表现出加性-显性-上位性效应, 这也进一步从遗传上证实了STL、SYL和TSSL之间的显著相关性, 说明在该群体中这3个性状极可能是由相同的主效位点(QTL)控制的。而2个世代PES的最适模型并不一致, E1中PES表现出受2对主基因控制, 2对主基因间表现为加性-显性-上位性效应, 而E2中则表现出受1对加性-显性主效基因控制, 说明较之于柱头长度相关性状, PES更易受到环境因素的影响[18]。结合P1、P2和F1联合方差分析结果发现, 4个柱头性状均是以基因型遗传为主, 但同时也受环境效应的影响(表2)。除TSSL外, 环境效应对STL、SYL和PES的影响均达到了极显著水平, 且STL和SYL同时受到基因型×环境互作效应的极显著影响。从而导致2个环境TSSL和PES检测到的主效基因数量以及主效基因间作用方式的不同, 需要通过其他方法, 如多环境下的QTL定位等, 进行进一步的验证。
当前, 对于柱头性状的研究主要集中于PES, 而对STL、SYL和TSSL的研究较少[15-17,22,28,31-34]。因此, 对于4个柱头性状遗传效应的研究也主要集中于PES。从一阶遗传参数来看, PES以加性效应为主, 这与Yan等[29]和Li等[45]研究结果是一致的。而STL、SYL和TSSL则以上位性效应遗传为主, 说明这3个性状的遗传较PES复杂。同时, 本研究发现的TSSL以上位性效应为主的结果与刘强明[15]利用CSSL群体所得出的以加性效应遗传为主的结果是不一致的, 这可能是由于材料类型的不同造成的。从二阶遗传参数来看, 2个环境中4个性状主基因遗传率介于71.13% (E2中PES)和97.09% (E2中TSSL)之间, 说明这4个性状均以主效基因遗传为主, 而除F2:3群体中的PES受1对主基因+多基因控制外, 其余均表现出受2对主基因+多基因控制; 且除F2群体中TSSL的2对主基因表现为等效的加性效应和等效的显性效应外, 其余2对主效基因间均表现出加性-显性-上位性效应。综上结果一方面, 说明4个柱头性状为数量性状, 研究材料以及环境等因素可能会对检测到的主基因数量以及作用方式产生影响[28,29,30]; 但另一方面, 本研究同时利用F2和F2:3群体在2个环境下对4个柱头性状进行遗传分析, 其结果可以互相验证。从本研究结果分析, 7001S/紫泰S组合中的STL、SYL和TSSL是由2个主效位点控制的, 且控制这3个性状的主效位点可能为相同位点, 且这2个位点中至少有1个位点同时也是控制PES的主效位点。王春娥等[44]曾同时利用主基因+多基因模型和QTL定位对大豆豆腐和豆乳得率进行了遗传分析和QTL定位, 认为这2种方法检测到的主基因数量具有相对一致性。说明主基因+多基因混合遗传模型与QTL定位间存在紧密联系, 两者相辅相成。实践中可以利用遗传分析的结果对QTL定位的结果进行校对, 便于育种家根据表型快速得到目标性状的遗传组成; 同时, 也可以用QTL定位的结果来校正遗传分析的结果, 这样可进一步更加准确了解QTL定位所反映目标性状的遗传组成。本研究利用主基因+多基因模型对柱头4个相关性状进行遗传分析, 其中柱头外露易于观察, 水稻开花后田间可直接观察, 但柱头性状较小, 田间肉眼很难直接进行比较, 需取样室内测量。育种家在高异交率温敏核不育选育的过程中, 可将田间柱头外露率的观察和室内柱头长度性状的调查相结合, 通过长柱头(毛刷长度和柱花总长度)、高外露率的选择进而改良水稻的异交率。同时, 育种家在进行长柱头、高外露率温敏核不育系选育过程中, 要充分考虑主效基因和微效基因的影响, 及时开展早期有效的单株选择, 重点关注高代单株性状的后期稳定表现, 排除或降低环境因素对目标性状选择造成的影响。主基因+多基因遗传分析对4个柱头相关性状的遗传组成、遗传规律特征及遗传参数进行了解析, 这将会为水稻柱头性状的改良提供有意义的遗传信息, 为下一步通过QTL初定位及精细定位、阐明性状间的遗传调控网络和分子设计育种提供重要理论依据。
4 结论
2个环境中4个柱头性状两两间均表现出极显著正相关, 相关系数介于0.262 (E1中PES和SYL)和0.895 (E2中STL和TSSL)之间。STL、SYL和TSSL均表现出受2对主基因+多基因控制, 除E1中TSSL表现为等加性-等显性主基因+加性-显性多基因控制外, 其余均表现为加性-显性-上位性主基因+加性-显性多基因。E1中PES表现出受2对加性-显性-上位性主基因+加性-显性-上位性多基因控制, 而E2中则表现出受1对加性-显性主基因+加性-显性-上位性多基因。2个环境中4个性状均以主基因遗传为主。本研究结果为创制长柱头、高柱头外露率核不育系材料提供了理论支持, 同时也为柱头长度相关性状主效位点的挖掘以及分子标记辅助选择提供理论依据。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:31140005 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s00122-006-0454-4URLPMID:17131105 [本文引用: 5]

Stigma exsertion is one of the important traits which contribute to the efficient improvement of commercial seed production in hybrid rice. In order to understand the genetic factors involved in the stigma exsertion of an indica variety--IR24--a QTL analysis was conducted using the F2 population between a japonica variety--Koshihikari--and a breeding line showing exserted stigma selected from the backcross population between IR24 as a donor and japonica varieties. As a result, a highly significant QTL (qES3), which had been predicted in the recombinant inbred population of IR24, was confirmed at the centromeric region on chromosome 3. qES3 increases about 20% of the frequency of the exserted stigmas at the IR24 allele and explains about 32% of the total phenotypic variance. A QTL near-isogenic line for qES3 increased the frequency of the exserted stigma by 36% compared to that of Koshihikari in a field evaluation, which suggests that qES3 is a promising QTL for the development of a maternal line for hybrid rice.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 5]
[本文引用: 5]
DOI:10.1016/j.molp.2017.01.001URLPMID:28110091 [本文引用: 7]

Stigma exsertion, a key determinant of the rice mating system, greatly contributes to the application of heterosis in rice. Although a few quantitative trait loci associated with stigma exsertion have been fine mapped or cloned, the underlying genetic architecture remains unclear. We performed a genome-wide association study on stigma exsertion and related floral traits using 6.5 million SNPs characterized in 533 diverse accessions of Oryza sativa. We identified 23 genomic loci that are significantly associated with stigma exsertion and related traits, three of which are co-localized with three major grain size genes GS3, GW5, and GW2. Further analyses indicated that these three genes affected the stigma exsertion by controlling the size and shape of the spikelet and stigma. Combinations of GS3 and GW5 largely defined the levels of stigma exsertion and related traits. Selections of these two genes resulted in specific distributions of floral traits among subpopulations of O. sativa. The low stigma exsertion combination gw5GS3 existed in half of the cultivated rice varieties; therefore, introducing the GW5gs3 combination into male sterile lines is of high potential for improving the seed production of hybrid rice.
URLPMID:27555858 [本文引用: 6]
DOI:10.1186/s12284-019-0304-zURLPMID:31289958 [本文引用: 3]

BACKGROUND: Stigma exsertion rate (SER) is a key determinant of outcrossing in hybrid rice seed production. A quantitative trait locus (QTL) for stigma exsertion rate in rice, qSER-7, has previously been detected on chromosome 7 by using a F2 population derived from two indica cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) maintainers, Huhan 1B and II-32B. RESULTS: The chromosomal location of qSER-7 was precisely delimited by fine-scale mapping. Near-isogenic lines (NILs) were established, one of which isolated the locus in the qSER-7(II-32B) line, which contains an introgressed segment of II-32B in the Huhan 1B genetic background, and exhibits a significantly higher stigma exsertion rate than that of the recurrent parent. Using 3192 individuals from the BC4F2 segregation population, the QTL qSER-7 was narrowed down to a 28.4-kb region between the markers RM3859 and Indel4373 on chromosome 7. According to the rice genome annotation database, three genes were predicted within the target region. Real-time PCR analysis showed significantly higher expression levels of LOC_Os07g15370 and LOC_Os07g15390 in II-32B than in Huhan 1B. LOC_Os07g15370(OsNRAMP5) was a previously reported gene for Mn and Cd transporter. The stigma exertion rates of OsNRAMP5-overexpressing plants were significantly higher than that of wild type plants, in contrast, a T-DNA insertion mutant osnramp5 showed a lower stigma exertion rate. CONCLUSIONS: In the present study, the QTL qSER-7 was isolated to a region between the markers RM3859 and Indel4373. Two candidate genes were selected based on the expression difference between the two parents, which can facilitate the further cloning of the gene underlying the quantitative trait associated with qSER-7 as well as the marker-assisted transfer of desirable genes for stigma exsertion rate improvement in rice.
URLPMID:31086492 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s00122-003-1227-yURLPMID:12845437 [本文引用: 4]

To understand the genetic basis of floral traits associated with the mating system in rice, we analyzed pistil, stamen and glume traits using a recombinant inbred line population, derived from a cross between an Asian cultivated rice ( Oryza sativa L.), Pei-kuh, and a wild rice ( Oryza rufipogon Griff.), W1944. Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) affecting floral morphology were detected by composite interval mapping using a linkage map constructed using 147 markers, mostly RFLPs. A total of 7, 4, 14 and 6 QTLs were detected for traits related to pistil, stamen, and size and shape of the glume, respectively. Comparison of 31 QTLs affecting these organs revealed ten QTLs affecting the different organs in four adjacent regions on chromosomes 2, 4, 5 and 10, but most QTLs (68%) were located separately on the whole chromosomes. Although four QTLs for stigma breadth, anther length and thickness of lemma and palea explained more than 25% of the total phenotypic variance, most QTLs (87%) had smaller effects. These results suggest that quantitative variation observed for pistil, stamen and glume traits is controlled by several distinct genes with small effects.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:20234878 [本文引用: 4]
DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-32629-2URLPMID:30266907 [本文引用: 3]

Stigma exsertion is a key determinant to increase the efficiency of commercial hybrid rice seed production. The major quantitative trait locus (QTL) qSE7 for stigma exsertion rate was previously detected on the chromosome 7 using 75 Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines (CSSLs) derived from a cross between the high stigma exsertion indica maintainer XieqingzaoB (XQZB) and low stigma exsertion indica restorer Zhonghui9308 (ZH9308). The C51 line, a CSSL population with an introgression from XQZB, was backcrossed with ZH9308 to produce the secondary F2 (BC5F2) and F2:3 (BC5F2:3) populations. As a result, the Near Isogenic Line (NIL qSE7(XB)) was developed. Analysis indicated qSE7 acted as a single Mendelian factor and decreased the stigma exsertion. We hypothesized qSE7 regulates single, dual, and total stigma exsertion rate, provided experimental support. qSE7 was mapped and localized between RM5436 and RM5499 markers, within a physical distance of 1000-kb. With use of new insertion-deletion (InDel) markers and analysis of the heterozygous and phenotypic data, it was ultimately dissected to a 322.9-kb region between InDel SER4-1 and RM5436. The results are useful for additional identification and isolation of this candidate gene controlling stigma exsertion rate, and provide a basis for further fine mapping, gene cloning, and Marker Assisted Selection (MAS) breeding later.
DOI:10.3389/fpls.2017.01818URLPMID:29163563 [本文引用: 2]

The rate of stigma exsertion (SE) is an important trait in rice breeding because the efficiency of hybrid rice seed production can be improved by increasing the percentage of stigmas that exsert. In this study, we developed a near isogenic line (NIL) from two parents, XieqingzaoB (XQZB) and Zhonghoi9308 (ZH9308), which have high and low SE rates in that order. In our previous study, we employed 75 chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) and analyzed quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for their influence on SE rate. The single gene QTL (qSE11), which is located on chromosome 11, was responsible for this trait. In this study, we focused on one of the CSSLs (C65), namely, the NIL (qSE11XB). It contains an introgression segment of XQZB in the genetic background of ZH9308, and exhibits a significantly higher SE rate than that of the parents. We demonstrated that qSE11 regulated both the single and the dual SE rates. They both contribute to the total SE rate. Genetic analysis revealed that qSE11 acted as a single Mendelian factor and that the allele from XQZB increased the SE rate. The validity of our conclusions was established when C65 was used to develop secondary F2 (BC5F2) and F2:3 (BC5F2:3) populations by backcrossing to ZH9308, with subsequent selfing. We entered 3600 plants from the F2 population and 3200 from the F2:3 populations into a genetic dissection program and dissected the major QTL qSE11 to a 350.7-kb region located on chromosome 11. This study will contribute to the future isolation of candidate genes of SE and will play a vital role in future hybrid rice seed production programs.
[本文引用: 5]
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0127938URLPMID:26030903 [本文引用: 3]

The efficiency of hybrid seed production can be improved by increasing the percentage of exserted stigma, which is closely related to the stigma length in rice. In the chromosome segment substitute line (CSSL) population derived from Nipponbare (recipient) and Kasalath (donor), a single CSSL (SSSL14) was found to show a longer stigma length than that of Nipponbare. The difference in stigma length between Nipponbare and SSSL14 was controlled by one locus (qSTL3). Using 7,917 individuals from the SSSL14/Nipponbare F2 population, the qSTL3 locus was delimited to a 19.8-kb region in the middle of the short arm of chromosome 3. Within the 19.8-kb chromosome region, three annotated genes (LOC_Os03g14850, LOC_Os03g14860 and LOC_Os03g14880) were found in the rice genome annotation database. According to gene sequence alignments in LOC_Os03g14850, a transition of G (Nipponbare) to A (Kasalath) was detected at the 474-bp site in CDS. The transition created a stop codon, leading to a deletion of 28 amino acids in the deduced peptide sequence in Kasalath. A T-DNA insertion mutant (05Z11CN28) of LOC_Os03g14850 showed a longer stigma length than that of wild type (Zhonghua 11), validating that LOC_Os03g14850 is the gene controlling stigma length. However, the Kasalath allele of LOC_Os03g14850 is unique because all of the alleles were the same as that of Nipponbare at the 474-bp site in the CDS of LOC_Os03g14850 among the investigated accessions with different stigma lengths. A gene-specific InDel marker LQ30 was developed for improving stigma length during rice hybrid breeding by marker-assisted selection.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
