 ,4,*, 安申群1,2, 马春玥1,21
,4,*, 安申群1,2, 马春玥1,21 2
3
4
Estimation of leaf chlorophyll content in cotton based on the random forest approach
Ershat ABLET1,2, Mamat SAWUT1,2,3,*, Baidengsha MAIMAITIAILI ,4,*, AN Shen-Qun1,2, MA Chun-Yue1,21
,4,*, AN Shen-Qun1,2, MA Chun-Yue1,21 2
3
4
通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2018-04-22接受日期:2018-08-20网络出版日期:2018-09-20
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-04-22Accepted:2018-08-20Online:2018-09-20
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (3099KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
依尔夏提?阿不来提, 买买提?沙吾提, 白灯莎?买买提艾力, 安申群, 马春玥. 基于随机森林法的棉花叶片叶绿素含量估算[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(1): 81-90. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84058
Ershat ABLET, Mamat SAWUT, Baidengsha MAIMAITIAILI, AN Shen-Qun, MA Chun-Yue.
叶绿素在植物光合作用中起着能量传递和捕获的作用, 且可反映植物氮、磷利用效率以及光合速率的强弱[1,2,3], 并指示植物生长发育状况。高光谱遥感技术作为一种无损、廉价、无污染的技术方法, 近年来广泛应用于叶绿素信息在植被长势、生理胁迫状况中的监测及作物估产[4,5]。
国内外****在高光谱估算农作物叶绿素含量方面取得了一定的成果, 估算方法可概括为以下两类。一类是经验模型。从原始光谱或各种转换数据的基础上选取敏感波段或以建立的植被指数为变量, 构建估算模型[6]; 第二类是物理模型。通过冠层和地物特性来反演光谱, 将获取的结果通过辐射传输等物理模型进行解释[7]。Li等[8]通过自创新技术(WREP)从连续小波转换的水稻和小麦反射光谱中提取红边参数, 并估算两种作物的叶片叶绿素含量; 毛博慧等[9]采用遗传算法寻优选出486、599、699和762 nm波长处的光谱反射值, 组合计算了12 个植被指数, 并以DVI (726, 699)、SAVI (762, 599)指数构建苗期冬小麦叶绿素含量估算模型。丁永军等[10]对番茄叶绿素含量进行估算, 并将原始光谱数据进行一阶导数转换、吸光度光谱转换和包络线去除处理, 采取多种共线性诊断选取四类光谱的敏感波段, 构建多元线性回归模型, 其中, 在去包络线模型中, 建模集R2为0.88, 检验集决定系数R2为0.82, 即模型具有较好的预测能力。姚霞等[11]对红边位置进行提取, 分析比较利用不同算法所提取的红边位置对氮素营养监测模型的准确性和可靠性产生的影响。Yi等[12]人对水稻光谱进行主成份分析再建立估算水稻氮含量的线性回归模型和人工神经网络回归模型, 发现通过主成份分析和人工神经网络结合建立的回归模型估算能力更强。上述研究丰富了农作物参数反演方法, 为今后大尺度估算作物叶绿素含量的准确性提供了一定的科学依据。
以往研究大部分直接选取相关系数较高的特征参数建立估算模型, 这可能导致变量的选择随机和单一, 缺乏定量化, 模型估算能力并未达到最佳效果。用随机森林法可计算SPAD值对特征波段的重要性评分并选出最佳估算参数, 对参数进行定量化, 提高模型估算精度。因此本研究以棉花叶绿素相对含量为研究对象, 对原始光谱数据进行包络线去除处理、立方根转换和倒数转换, 通过相关性分析选取跟SPAD值相关性较高的特征波段, 并用随机森林法寻优选择最佳估算参数, 建立偏最小二乘回归模型和BP神经网络回归模型。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
新疆玛纳斯县新疆农业科学院试验站位于新疆玛纳斯县中部的包家店镇(85°19′~86°25′E, 44°16′~ 44°22′ N), 面积为0.4 hm2, 属于典型的中温带大陆性气候区, 其特点是冬季时间长, 寒冷; 夏季时间短, 酷热。该地区光照较强, 昼夜温差较大, 年均气温7.2℃, 年均降水量193.3 mm, 年平均无霜期168.5 d。试验田被划分为60个小区, 供试棉花主要品种为新陆早57号、新陆中21号、农垦5号等。种植模式为“1膜3带6行”, 膜宽为2.35 m, 行距为60 cm, 株距为10 cm。2017年4月28日播种, 5月5日灌出苗水, 化学调控与其他管理措施按照当地高产栽培要求进行。研究区位置和采样点分布情况如图1所示。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1研究区位置和采样点分布图
Fig. 1Location of study area and distribution of sampling plots
1.2 光谱数据的测定与处理
对花铃期的棉花, 使用ASD FieldSpecHandHeld便携式光谱仪在晴朗无云无风条件下测取北京时间11:30-15:30, 波长为350~1050 nm的光谱, 光谱仪探头距离棉花叶片冠层高度25 cm, 并保持垂直向下, 设置光谱扫描时间为8 s, 每个样点测6次。其间, 每测3次进行一次白板标定, 确保数据的精确性, 并用Viewspec PRO计算出每样点6条曲线的平均值作为该点光谱反射值。为减少光照条件引起的乘性因素, 对光谱数进行包络线去除处理(continuum-removal transformation, Rcr)、倒数转换(Reciprocal transformation, 1/R)和立方根转换(cube-root transformation, ?R)。此3种光谱转换可增强可见光区域光谱差异, 突出光谱的吸收、反射特征[11]。其中去除包络线处理可压抑背景光谱, 并扩大弱吸收特征信息[13,14,15]。
1.3 SPAD值的测定
在60个样区内用叶绿素计(SPAD-502Plus, Konica Minoita, Japan)测定棉花冠层叶片SPAD值, 每个样点随机测量5~6次, 取平均值作为该样点最终叶片叶绿素含量值。测定时间与光谱测定同步, 位置与光谱测定保持一致。1.4 随机森林法
随机森林法(random forest, RF)是高维学数据分析方法之一, 主要用于高维数据分类和回归, 并可计算出自变量对因变量重要性评分[16,17,18], 本文以DPS数据处理系统计算随机森林变量重要性评分。首先对棉花SPAD值与四类反射光谱数据的相关性进行分析, 在原始光谱和转换光谱中分别选取12个特征波段, 运用随机森林法对光谱进行敏感波段寻优, 并建立偏最小二乘回归模型和BP神经网络模型。进行随机森林重要性评分时, 以袋外数据对b棵回归树进行测试分析, 可分别得均方残差MMSE,1、MMSE,2、MMSE,3、……、MMSE,b, 在各袋外数据集中, 将随机扰动方法对变量Xk进行置换, 形成新袋外测试集[19,20]。用袋外测试集对b棵回归树进行测试, 得出随机置换后的均方误差矩阵。第k个输入变量重要性评分为MMSE,1、MMSE,2、MMSE,3、……、MMSE,b与均方误差矩阵第k行之差的均值与b棵回归树标准误差SE的比值, 可得变量Xk的均方残差平均减小量。
1.5 模型建立与检验
采用DPS数据处理系统, 通过随机森林法筛选出来的特征波段建立估算棉花冠层叶绿素含量的偏最小二乘法回归(PLSR)模型和BP神经网络(BP ANN)回归模型。其中, PLSR方法在回归建模过程中采用数据降维、信息综合和筛选技术。在估算叶绿素含量时, 其主要思想为, 减少光谱维数的同时, 明确叶绿素含量变化的主控因子, 使模型具备更好的鲁棒性[21,22]。BP神经网络模型主要由输入层、隐含层和输出层3层组成[23], 通过调整权值将网络误差最小化, 把学习结果反馈到隐含层, 改变其权系数矩阵, 进而达到预期学习目的[24]。将通过相关性分析选出来的, 跟SPAD值相关性较高的高光谱参数作为神经网络的输入层, SPAD值作为输出层, 经过多次训练, 隐含层节点数和最大代次数调节为最佳估算精度, 建立估算棉花叶片SPAD值BP神经网络回归模型。分别采用决定系数(R2)、均方根误差(RMSE)、相对误差(RE)对模型评估, 以保证模型稳定性和估算精度。R2越接近1, 表明模型的稳定性越好, 且精度高; RMSE和RE越小, 模型的估算能力越精确, 预测方程所得预测值与实测值拟合效果更好。PLSR模型中, 原始光谱和包络线光谱的6个特征波段分别作为自变量, SPAD值作为因变量, 在已获取的60组数据中随机选取29组数据作为训练样本, 24组作为检验样本创建回归模型; BP神经网络模型将通过随机森林法选出的原始光谱和去除包络线光谱的特征波段作为神经网络的输入层, SPAD值作为输出层, 经过多次训练, 隐含层节点数定为10, 训练时最大代次数定为1000。2 结果与分析
2.1 棉花叶片光谱曲线特征
由图2可看出, 不同SPAD值的棉花反射率曲线变化趋势基本相同, 且具有明显变化规律。在350~680 nm波段范围内的反射率比680~1050 nm波段范围内低, 总体上继承了棉花叶片光谱反射率的特征。在350~680 nm波段范围内随着SPAD值的增加, 光谱反射率显著降低, 光谱差异较大, 其中在490~550 nm波段范围反射率平稳上升, 绿光区域的550 nm处出现绿色强反射, 产生峰值, 678 nm处形成叶绿素吸收谷; 在680~1050 nm范围内, 680~750 nm处反射率随波长呈现急剧增高趋势, 而在750~1050 nm波段范围内反射率随SPAD值增高未表现出明显梯度型差异, 光谱曲线变化趋于平稳。棉叶的健康状况直接决定了SPAD值的大小, 而SPAD值直接影响着叶片的反射率。由此可知, 叶绿素含量的差异会引起棉花叶片光谱曲线特征的变化, 叶片反射率会随着SPAD值的增加而降低, 呈负相关。图2
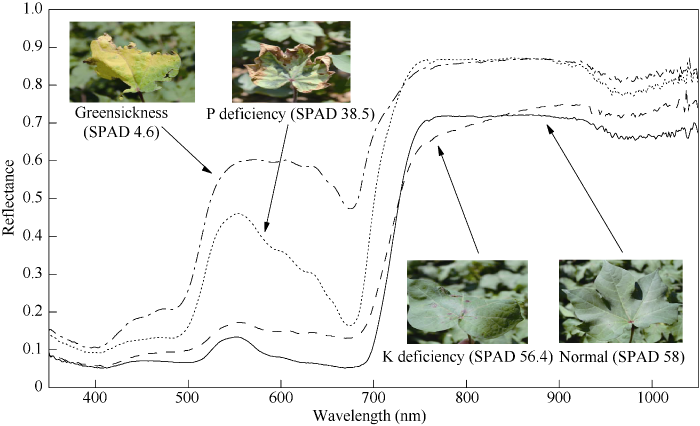 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2棉花叶片光谱
Fig. 2Spectra of cotton leaves
2.2 棉花冠层光谱和叶绿素含量的相关性分析
为了进一步明确棉花SPAD值相应的敏感波段, 将棉花叶片SPAD值和原始光谱在内的四类光谱数据做Pearson相关性分析和波段之间的自相关性分析, 由图3和图4所示, 棉花叶片SPAD值和反射率紧密相关。在605~690 nm和745~1050 nm区域内的反射率与SPAD值相关性达0.01的显著水平, 相关系数最高值为-0.619, 此波段范围主要受叶绿素吸收的影响, 均呈负相关。与原始光谱相比, 经过变换后的棉花反射率与SPAD值相关性相差较大, 其中去除包络线光谱和SPAD值呈极显著相关, 相关系数峰值的绝对值为0.799, 相关性最高值的呈现区域跟原始光谱数据大致相似, 相关性效果优于倒数转换数据和立方根转换数据。去除包络线光谱达0.01显著水平的敏感波段均集中于570~730 nm波段范围内, 可知, 包络线去除法更有利于发现棉花SPAD值相应的敏感波段。倒数光谱和立方根光谱虽然增强效果不明显, 但是敏感波段的出现区域跟原始光谱和去除包络线光谱保持一致, 从图可看出四类光谱数据的相关性最高值均出现在550~750 nm波段范围内, 说明此光谱范围与棉花SPAD值之间存在着高度相关, 为选取特征波段的最佳区间。图3
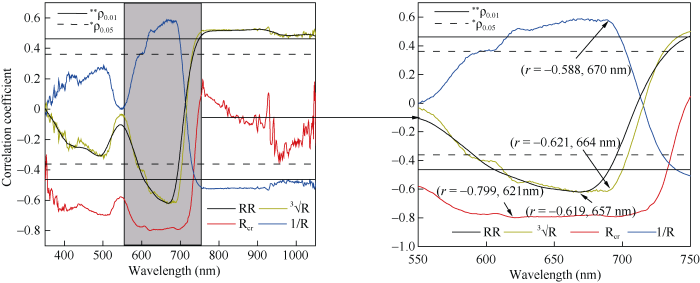 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3不同转换光谱曲线与叶SPAD值的相关性
R: 相关系数; RR: 原始光谱; Rcr: 包络线光谱; ?R: 立方根光谱; 1/R: 倒数光谱。
Fig. 3Correlation of different conversion spectral curves with SPAD value
R: correlation coefficient; RR: raw reflectance; Rcr: continuum-removal reflectance; ?R: cube-root reflectance; 1/R: reciprocal reflectance.
图4
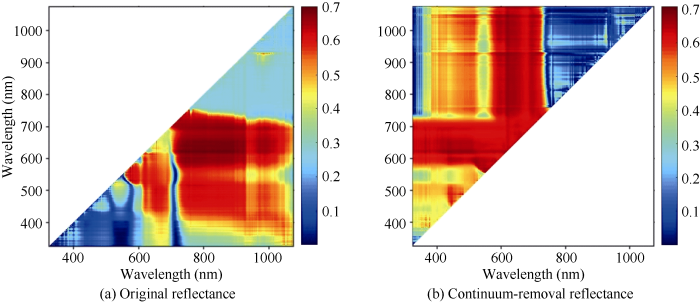 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4光谱自相关矩阵
Fig. 4Inter-correlation matrix of spctra
对原始光谱和去除包络线光谱的751个波段进行两两组合, 得出决定系数R2, 并用Matlab-R2016a绘制相对决定系数等值线图。图中颜色从深蓝色到深红色表示决定系数由小到大, 相同色调越深说明相关系数越大。由图4可知, 基于自相关性分析的原始光谱和去除包络线光谱的决定系数最高值均在620~690 nm和740~920 nm范围, 其余波段范围R2较小, 即相关性较低。去除包络线光谱在可见光波段范围内颜色最深, 即相关性显著, 且在570~750 nm波段范围内, 数据冗余最小, 信息含量最丰富, 结果与Pearson相关性结果吻合。
经相关分析可选出相关性较高的波段作为随机森林分类的参考值, 经过反复实验和比较分析, 最后随机森林生成树的变量(NTree)设置为300, 节点处变量数设置3, 对敏感波段重要性VIM值(variable importance measure)进行了评价。由表1和图5可知, VIM值越大, 说明敏感波段(自变量)在估算SPAD值(因变量)时有更重要的作用。原始光谱数据中, VIM值最大的波段为614 nm, VIM值最小的波段为689 nm和786 nm, VIM值最大的6个波段对应的变量依次为X12、X1、X6、X3、X4、X11, 这些特征波段均出现在610~700 nm和900~950 nm波段范围内; 在去除包络线光谱中, VIM值最大的波段为695 nm, VIM值最小的波段为612 nm, VIM值最大的6个波段对应的变量依次为X'10、X'12、X'1、X'11、X'4、X'8, 相比原始光谱敏感波段的出现范围较分散。通过随机森林法筛选出来的这些敏感波段可视为对模型贡献较大的变量。
Table 1
表1
表1特征波段的选取
Table 1
| 原始光谱RR | 包络线去除光谱Rcr | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变量名Variable name | 特征波段Characteristic band (nm) | 相关系数Correlation coefficient | VIM值 VIM value | 变量名Variable name | 特征波段Characteristic band (nm) | 相关系数Correlation coefficient | VIM值 VIM value |
| X1 | 614 | -0.498 | 0.03420 | X'1 | 407 | -0.670 | 0.00729 |
| X2 | 616 | -0.520 | 0.00652 | X'2 | 479 | -0.681 | 0.00326 |
| X3 | 653 | -0.603 | 0.01130 | X'3 | 488 | -0.694 | 0.00326 |
| X4 | 670 | -0.633 | 0.01031 | X'4 | 508 | -0.699 | 0.00461 |
| X5 | 689 | -0.628 | 0.00461 | X'5 | 577 | -0.732 | 0.00326 |
| X6 | 697 | -0.544 | 0.01458 | X'6 | 585 | -0.750 | 0.00326 |
| X7 | 700 | -0.482 | 0.00652 | X'7 | 612 | -0.779 | 0 |
| X8 | 759 | 0.513 | 0.00565 | X'8 | 621 | -0.799 | 0.00461 |
| X9 | 786 | 0.516 | 0.00461 | X'9 | 651 | -0.793 | 0.00326 |
| X10 | 826 | 0.519 | 0.00799 | X'10 | 695 | -0.792 | 0.00799 |
| X11 | 905 | 0.529 | 0.00799 | X'11 | 712 | -0.760 | 0.00652 |
| X12 | 941 | 0.509 | 0.05238 | X'12 | 723 | -0.697 | 0.00790 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图5
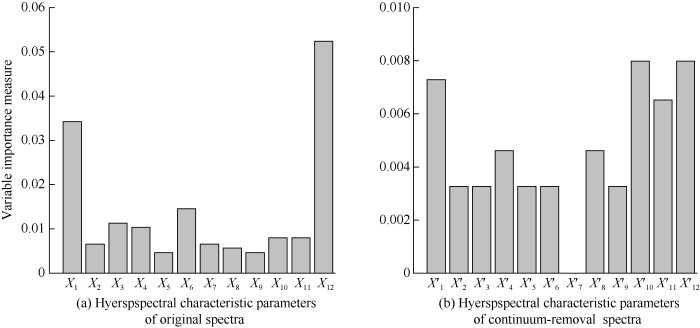 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5变量重要性评估
Fig. 5Variable importance measure
2.3 模型的构建与检验
运用随机森林法选出的6 个特征波段和建模样本实测叶绿素含量数据分别建立PLSR模型和BP神经网络模型, 模型评价参数如表2所示。从建模效果看, 基于原始光谱建立的两种模型中R2都低于0.8, RMSE相差不大, 说明两种模型的稳定性较低, 预测效果接近; 基于包络线数据的两种模型中BP神经网络模型的R2为0.90, RMSE降低至0.91, 表明数据转换后模型的稳定性和估算精度有了一定的提高。从预测值和实测值之间的拟合分析可以看出(图6), 基于去除包络线数据的点和原始光谱相对均匀地分布在1︰1直线的两侧, 表明利用去除包络线光谱建立的两种模型的拟合效果更好。
Table 2
表2
表2建模结果比较
Table 2
| 模型 Model | 建模Calibration (RR) | 建模集Calibration (Rcr) | 验证集Validation (RR) | 验证集Validation (Rcr) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | RE (%) | R2 | RMSE | RE (%) | |
| 偏最小二乘模型PLSR BP神经网络模型BP ANN | 0.68 0.69 | 1.62 1.59 | 0.63 0.90 | 1.73 0.91 | 0.64 0.78 | 2.06 1.60 | 3.01 2.27 | 0.92 0.83 | 0.88 1.26 | 1.30 1.89 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
图6
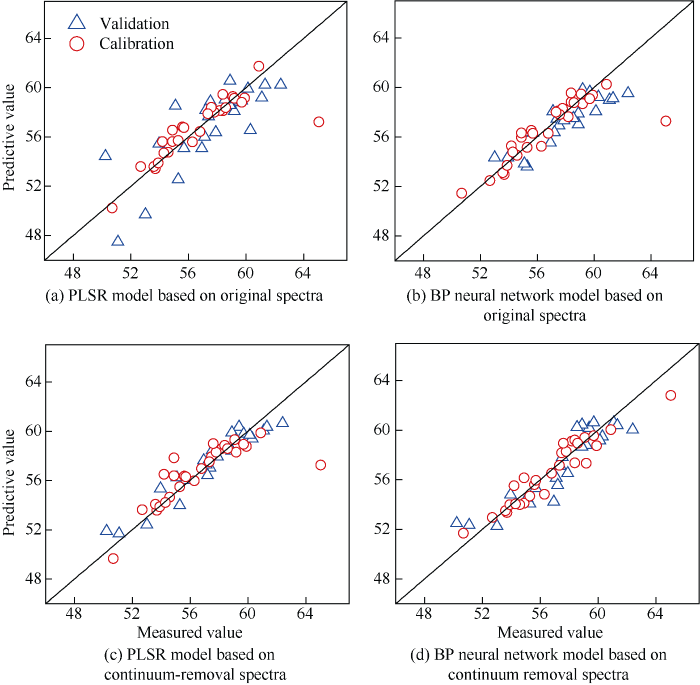 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6PLSR和BP神经网络模型对实测值与预测值的拟合分析结果
Fig. 6Fitting analysis results between measured values and predicted values by PLSR and BP neural network models
为了进一步验证模型的估算精度, 利用验证样本对两种模型进行验证(表 1), 从验证效果看, 基于原始建立的两种模型中R2分别为0.64、0.78, 均小于0.8, 与建模效果保持一致, RE分别为3.01%、2.27%, 说明这两种模型稳定性和估算能力都较低, 不能作为估算棉花叶片叶绿素含量的最佳模型, 这可能是由于实测光谱受外界因素干扰, 因目标物的粒度、密度、纹理、粗糙度等物理特性所故; 包络线光谱建立的PLSR和BP神经网络模型R2分别为0.92和0.83, 说明两种模型的稳定性较好; 在PLSR模型中, RMSE从原始光谱的2.06降到0.88, RE从3.01%降到1.30%, 说明PLSR模型的估算能力比BP神经网络模型更优异。从模型的验证效果
来看, PLSR模型效果比BP神经网络更好。因此, 本研究选取PLSR模型对棉花SPAD值进行估算。从预测值和实测值的拟合度可以看出(图6), 基于原始光谱的数据点与包络线相比分布较为离散, 估算精度较低。
3 讨论
冠层尺度的叶绿素含量的统计估算方法有不同的表现形式, 最常用的办法就是构建地面实测生化要素含量和田间、机载或者星载传感器测得的冠层反射率的统计关系[25,26,27]。另一种办法是将叶片尺度上的光谱指数与色素含量的关系直接用在冠层尺度上[28,29,30]。本研究按照第一种方法, 以田间测定来获取光谱数据和SPAD值, 进行了冠层尺度上的叶绿素相对含量估算。以田间尺度的光谱反射率作为应用条件建立了估算模型, 其中, PLSR模型具有运算量小、速度快、变量更少的特点, 且适用于对模型精度要求不高的场合; 神经网络模型是依赖于大量输入的统计学算法的数学模型, 与线性方法相比, 神经网络模型在解决非线性问题上的应用较为广泛, 且能够识别叶片色素和光谱指数之间复杂非线性关系[31]; 至于两种模型的样本数, 贾学勤等****利用PLSR模型对180组冬小麦样进行地上干生物量高光谱估测, 其模型的决定系数R2为0.692; 尼加提等人采用PLSR模型估算春小麦叶片叶绿素含量, 其样本数为55, 模型的决定系数R2达到0.8; 郭云开等****利用BP神经网络模型对40个土壤样本进行铜含量高光谱反演, 最后模型的拟合度为0.721; 余蛟洋等使用BP神经网络模型估算苹果叶片SPAD值, 采用的样本数总共是120组, 模型最后的决定系数达到0.95, 总之, 应用这两种模型的研究者们采用的样本数都不一致[20,32-36]。因此本研究按照以往研究者们的经验具备了53组样本, 29组为建模, 24组为检验, 最后两种模型的估算精度分别为PLSR模型R2为0.92; BP神经网路模型R2为0.83, 估算效果均优异, 但是如何控制样本数才能达到最佳效果需进一步探讨。在植被光谱分析中, 对原始光谱的预处理可更好地挖掘生物参量特征波段, 从而建立更加稳定精确的回归模型。本文对原始光谱数据进行倒数转换、立方根和去除包络线处理, 通过相关性分析可知, 包络线光谱较原始光谱在特征波段与棉花SPAD值的相关性更好, 基于去除包络线光谱所构建模型的验证精度高于原始光谱特征参数建立的模型, 去除包络线光谱更适合估算棉花叶片的SPAD值, 且倒数转换和立方根转换对光谱信息的获取未表现出明显的作用, 相关系数也未得到显著提高, 此结果对棉花SPAD值估算的研究意义较小。综合以上研究结果发现, 高光谱数据的衍生变化对模型的估算效果起到了一定的优化作用。高光谱数据特征选择常用的方法主要有PCA、判别分析、光谱微分处理技术与ICA等, 其中随机森林法具有容易实现、简捷、调整参数少、经济等优点[37,38,39]。因此本研究通过随机森林法进行了变量重要性选择, 且对特征波段进行了定量化处理, 更精确地评估出了对SPAD值影响较大的特征波段, 有效地提高了模型的估算精度。
不同建模算法对估算模型预测精度的影响较大, 验证结果说明PLSR模型的估算精度高于BP神经网络模型, 估算效果较为优异。主要是因为包络线去除法对数据进归一化处理, 可释放一些原本被遮蔽的光谱吸收特征信息, 从而改善模型精度, 此结果与众多****的研究相一致[40,41,42]。而BP神经网络算法的网络权值初始化随机, 且其程序运行结果、选用的输入参数均存在差异, 致使其模型精度较低[43]。因此在以后的研究中, 需要重点考虑BP神经网络输入参数的选择。
4 结论
(1) 在605~690 nm和745~1050 nm区域内, 反射率与SPAD值极显著负相关(P<0.01), 此波段范围主要受叶绿素吸收的影响。(2) 经去除包络线光谱变换和立方根转换后的棉花反射率与SPAD值相关性比原始光谱高, 且以去除包络线光谱变换最高; 倒数转换后棉花反射率与SPAD值相关性较原始光谱低。
(3) 通过随机森林法筛选出的去除包络线光谱波段建立的PLSR和BP神经网络模型的估算能力均高于原始光谱波段; 且PLSR估算能力高于BP神经网络模型。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1005.2009.00698URL [本文引用: 1]

叶绿(Chlorophyll.Chl)合成是决定植物光合效率的重要性状,是决定作物产量的重要因素.参与植物Chl合成、分解代谢及信号调控的基因数目众多,其中任何一个基因发生突变都有可能引起Chl含量的变化,从而表现为各种叶色异常甚至导致植株死亡.自然或人工创造突变体,对于Chl相关基因的功能分析非常必要.目前,Chl突变体己广泛应用于基础研究和生产实践.文章就该研究领域内的最新研究进展进行了概述.
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1005.2009.00698URL [本文引用: 1]

叶绿(Chlorophyll.Chl)合成是决定植物光合效率的重要性状,是决定作物产量的重要因素.参与植物Chl合成、分解代谢及信号调控的基因数目众多,其中任何一个基因发生突变都有可能引起Chl含量的变化,从而表现为各种叶色异常甚至导致植株死亡.自然或人工创造突变体,对于Chl相关基因的功能分析非常必要.目前,Chl突变体己广泛应用于基础研究和生产实践.文章就该研究领域内的最新研究进展进行了概述.
DOI:10.11937/bfyy.201522003URL [本文引用: 1]

以"美国大速生"生菜为试材,采用营养液水培试验方法,对不同氮浓度水平下的生菜叶片全氮含量和叶绿素与叶片光谱反射率的相关性进行分析,以研究高光谱技术应用于叶菜类蔬菜的营养监测的可行性。结果表明:光谱反射率数据呈单峰曲线状并且随叶片氮浓度增加而增大;在生菜的生长过程中叶片光谱反射率、叶绿素含量、全氮三者具有显著线性相关关系;叶绿素含量在光谱技术中能够指示叶片全氮量的多少,利用可见光区域叶片最大光谱反射率可以实现反演生菜叶片全氮含量和叶绿素含量。
DOI:10.11937/bfyy.201522003URL [本文引用: 1]

以"美国大速生"生菜为试材,采用营养液水培试验方法,对不同氮浓度水平下的生菜叶片全氮含量和叶绿素与叶片光谱反射率的相关性进行分析,以研究高光谱技术应用于叶菜类蔬菜的营养监测的可行性。结果表明:光谱反射率数据呈单峰曲线状并且随叶片氮浓度增加而增大;在生菜的生长过程中叶片光谱反射率、叶绿素含量、全氮三者具有显著线性相关关系;叶绿素含量在光谱技术中能够指示叶片全氮量的多少,利用可见光区域叶片最大光谱反射率可以实现反演生菜叶片全氮含量和叶绿素含量。
DOI:10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)04-0975-07URL [本文引用: 1]

农业遥感中,利用光谱指数方法反演作物叶绿素含量一直得到广泛地应用。利用PSR-3500光谱仪及SPAD-502叶绿素仪同步获取了冬小麦冠层光谱数据及对应叶片的叶绿素相对含量(SPAD值),并利用高斯光谱响应模型将PSR获取的地面连续光谱数据重采样为多光谱Landsat-TM7及高光谱Hyperion光谱数据,然后分别计算基于两种传感器的归一化差值植被指数(normalized difference vegetation index,NDVI)、综合叶绿素光谱指数(MCARI/OSAVI,the ratio of the modified transformed chlorophyll absorption ratio index(MCARI)to optimized soil adjusted vegetation index(OSAVI))、三角形植被指数(triangle vegetation index,TVI)及通用植被指数(vegetation index based on universal pattern decomposition method,VIUPD),再将四种光谱指数与叶绿素含量进行回归分析。结果表明,针对重采样后的TM和Hyperion两种传感器数据,VIUPD反演叶绿素含量精度(决定系数R2)最高,反演能力最稳定,这与其"不受传感器影响"的特性密不可分;MCARI/OSAVI反演精度和稳定性次之,是因为引入的OSAVI削弱了土壤背景的影响;宽波段指数NDVI和TVI对模拟TM数据有较好的反演精度,对Hyperion数据反演精度却很低,可能是因为两种指数的构成形式简单,考虑的影响因素较少。以冬小麦为例,对利用光谱指数反演植被叶绿素含量的精度和稳定性进行了研究并分析了其影响因素,经比较发现利用植被指数VIUPD进行植被叶绿素含量反演时,其精度和稳定性最好。
DOI:10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)04-0975-07URL [本文引用: 1]

农业遥感中,利用光谱指数方法反演作物叶绿素含量一直得到广泛地应用。利用PSR-3500光谱仪及SPAD-502叶绿素仪同步获取了冬小麦冠层光谱数据及对应叶片的叶绿素相对含量(SPAD值),并利用高斯光谱响应模型将PSR获取的地面连续光谱数据重采样为多光谱Landsat-TM7及高光谱Hyperion光谱数据,然后分别计算基于两种传感器的归一化差值植被指数(normalized difference vegetation index,NDVI)、综合叶绿素光谱指数(MCARI/OSAVI,the ratio of the modified transformed chlorophyll absorption ratio index(MCARI)to optimized soil adjusted vegetation index(OSAVI))、三角形植被指数(triangle vegetation index,TVI)及通用植被指数(vegetation index based on universal pattern decomposition method,VIUPD),再将四种光谱指数与叶绿素含量进行回归分析。结果表明,针对重采样后的TM和Hyperion两种传感器数据,VIUPD反演叶绿素含量精度(决定系数R2)最高,反演能力最稳定,这与其"不受传感器影响"的特性密不可分;MCARI/OSAVI反演精度和稳定性次之,是因为引入的OSAVI削弱了土壤背景的影响;宽波段指数NDVI和TVI对模拟TM数据有较好的反演精度,对Hyperion数据反演精度却很低,可能是因为两种指数的构成形式简单,考虑的影响因素较少。以冬小麦为例,对利用光谱指数反演植被叶绿素含量的精度和稳定性进行了研究并分析了其影响因素,经比较发现利用植被指数VIUPD进行植被叶绿素含量反演时,其精度和稳定性最好。
DOI:10.1111/pce.12815URLPMID:27650474 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Canopy chlorophyll content (CCC) is an essential ecophysiological variable for photosynthetic functioning. Remote sensing of CCC is vital for a wide range of ecological and agricultural applications. The objectives of this study were to explore simple and robust algorithms for spectral assessment of CCC. Hyperspectral datasets for six vegetation types (rice, wheat, corn, soybean, sugar beet and natural grass) acquired in four locations (Japan, France, Italy and USA) were analysed. To explore the best predictive model, spectral index approaches using the entire wavebands and multivariable regression approaches were employed. The comprehensive analysis elucidated the accuracy, linearity, sensitivity and applicability of various spectral models. Multivariable regression models using many wavebands proved inferior in applicability to different datasets. A simple model using the ratio spectral index (RSI; R815, R704) with the reflectance at 815 and 704鈥塶m showed the highest accuracy and applicability. Simulation analysis using a physically based reflectance model suggested the biophysical soundness of the results. The model would work as a robust algorithm for canopy-chlorophyll-metre and/or remote sensing of CCC in ecosystem and regional scales. The predictive-ability maps using hyperspectral data allow not only evaluation of the relative significance of wavebands in various sensors but also selection of the optimal wavelengths and effective bandwidths.
DOI:10.1016/0034-4257(93)90011-LURL [本文引用: 1]

A review of recent progress in the field of imaging spectrometry is presented based on the 14 articles comprising the special issue of this journal. The results presented were achieved through research done with data from the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS), the first imaging spectrometer to cover the full solar reflected portion of the spectrum. The majority of the early work in imaging spectrometry prior to AVIRIS focused largely on geological applications and specifically surface mineral identification. In the past 5 years, the range of applications has expanded into the scientific disciplines of ecology, hydrology, oceanography, and atmospheric science. Significant progress has also been made in sensor design and calibration, and information extraction. NASA plans to place high spectral resolution sensors in earth orbit within the next few years; two have been flown already on recent planetary missions and have proven to be of great value to the study of planetary surfaces and atmospheres. The work presented in this issue will lead directly to more effective utilization of imaging spectrometry in the study of the earth. We present a discussion of future trends in imaging spectrometry at the conclusion of this article.
DOI:10.1016/0034-4257(89)90069-2URL [本文引用: 1]

Remotely sensed data are being used to estimate foliar chemical content as a result of our need for the information and our increasing ability to understand and measure foliar spectra. This paper reviews how stepwise multiple regression and deconvolution have been used to extract chemical information from foliar spectra, and concludes that both methods are useful, but neither is ideal. It is recommended that the focus of research be modeling in the long term and experimentation in the short term. Long-term research should increase our understanding of the interaction between radiation and foliar chemistry so that the focus of research can move from leaf model to canopy model to field experiment. Short-term research should aim to design experiments in which remotely sensed data are used to generate unambiguous and accurate estimates of foliar chemical content.
DOI:10.1016/0034-4257(90)90100-ZURL [本文引用: 1]

PROSPECT is a radiative transfer model based of Allen's generalized “plate model” that represents the optical properties of plant leaves from 400 nm to 2500 nm. Scattering is described by a spectral refractive index (n) and a parameter characterizing the leaf mesophyll structure (N). Absorption is modeled using pigment concentration (C a+b), water content (C w), and the corresponding specific spectral absorption coefficients (K a+b and K w). The parameters n, K a+b, and K w have been fitted using experimental data corresponding to a wide range of plant types and status. PROSPECT has been tested successfully on independent data sets. Its inversion allows one to reconstruct, with reasonable accuracy, leaf reflectance, and transmittance features in the 400–2500 nm range by adjusting the three input variables N, C a+b, and C w.
DOI:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.04.024URL [本文引用: 1]

Red edge position (REP), defined as the wavelength of the inflexion point in the red edge region (680-760 nm) of the reflectance spectrum, has been widely used to estimate foliar chlorophyll content from reflectance spectra. A number of techniques have been developed for REP extraction in the past three decades, but most of them require data-specific parameterization and the consistence of their performance from leaf to canopy levels remains poorly understood. In this study, we propose a new technique (WREP) to extract REPs based on the application of continuous wavelet transform to reflectance spectra. The REP is determined by the zero-crossing wavelength in the red edge region of a wavelet transformed spectrum for a number of scales of wavelet decomposition. The new technique is simple to implement and requires no parameterization from the user as long as continuous wavelet transforms are applied to reflectance spectra. Its performance was evaluated for estimating leaf chlorophyll content (LCC) and canopy chlorophyll content (CCC) of cereal crops (i.e. rice and wheat) and compared with traditional techniques including linear interpolation, linear extrapolation, polynomial fitting and inverted Gaussian.
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.z1.025URL [本文引用: 1]

光谱分析技术是作物生长检测的主要手段,为了解决大田漫反射采集所造成的光谱基线漂移和偏移问题,研究采集了冬小麦冠层325~1 075 nm范围反射光谱,采用多元散射校正方法对小麦原始光谱进行预处理。采取遗传算法对光谱特征参数寻优并结合相关分析结果,选取486、599、699和762 nm波长处反射率值并组合计算了RVI(ratio vegetation index),DVI(difference vegetation index),NDVI(normalized difference vegetation index)和SAVI(soil-adjusted vegetation index)共12个植被指数,分析了各植被指数与叶绿素含量值之间的相关关系,结果显示:DVI和SAVI可抑制苗期土壤背景干扰并对叶绿素含量响应较为敏感,与叶绿素含量相关性最优的参数分别为DVI(762,599)、SAVI(762,599)、DVI(762,699)和SAVI(762,699),与叶绿素含量的相关系数都达到0.6以上。基于相关性最优光谱植被指数DVI(762,699)和SAVI(762,599)利用最小二乘-支持向量回归建立冬小麦叶绿素含量预测模型,建模集决定系数为0.681,验证集决定系数为0.611。该模型可用于无损检测冬小麦苗期叶绿素含量,以期为后续施肥决策提供支持。
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.z1.025URL [本文引用: 1]

光谱分析技术是作物生长检测的主要手段,为了解决大田漫反射采集所造成的光谱基线漂移和偏移问题,研究采集了冬小麦冠层325~1 075 nm范围反射光谱,采用多元散射校正方法对小麦原始光谱进行预处理。采取遗传算法对光谱特征参数寻优并结合相关分析结果,选取486、599、699和762 nm波长处反射率值并组合计算了RVI(ratio vegetation index),DVI(difference vegetation index),NDVI(normalized difference vegetation index)和SAVI(soil-adjusted vegetation index)共12个植被指数,分析了各植被指数与叶绿素含量值之间的相关关系,结果显示:DVI和SAVI可抑制苗期土壤背景干扰并对叶绿素含量响应较为敏感,与叶绿素含量相关性最优的参数分别为DVI(762,599)、SAVI(762,599)、DVI(762,699)和SAVI(762,699),与叶绿素含量的相关系数都达到0.6以上。基于相关性最优光谱植被指数DVI(762,699)和SAVI(762,599)利用最小二乘-支持向量回归建立冬小麦叶绿素含量预测模型,建模集决定系数为0.681,验证集决定系数为0.611。该模型可用于无损检测冬小麦苗期叶绿素含量,以期为后续施肥决策提供支持。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.13.005URL [本文引用: 2]

【Objective】 Red edge position (REP, 680-780 nm) has been used for evaluating crop leaves nitrogen status. The objectives of this paper were to extract REP with different algorithms, to analyze the precision and stability of the monitoring model, to ascertain the optimum REP algorithm and relevant quantitative model for nitrogen status. 【Method】 On the basis of hyperspectral reflectance and leaf nitrogen status at different growth stages under varied nitrogen rates, planting densities and wheat cultivars, this study systematically analyzed the quantitative relationships and statistical characters between red edge position on various algorithms and canopy leaf nitrogen status, and then developed the monitoring models by comparing accuracy and reliability of nitrogen estimation. 【Result】 The results showed that the monitoring models developed from the linear extrapolation method (LEM) could stably indicate canopy leaf nitrogen content (LNC) and leaf nitrogen accumulation (LNA) in wheat. 【Conclusion】 The results have provided a stable and effective approach for monitoring canopy leaf nitrogen status in wheat.
DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.13.005URL [本文引用: 2]

【Objective】 Red edge position (REP, 680-780 nm) has been used for evaluating crop leaves nitrogen status. The objectives of this paper were to extract REP with different algorithms, to analyze the precision and stability of the monitoring model, to ascertain the optimum REP algorithm and relevant quantitative model for nitrogen status. 【Method】 On the basis of hyperspectral reflectance and leaf nitrogen status at different growth stages under varied nitrogen rates, planting densities and wheat cultivars, this study systematically analyzed the quantitative relationships and statistical characters between red edge position on various algorithms and canopy leaf nitrogen status, and then developed the monitoring models by comparing accuracy and reliability of nitrogen estimation. 【Result】 The results showed that the monitoring models developed from the linear extrapolation method (LEM) could stably indicate canopy leaf nitrogen content (LNC) and leaf nitrogen accumulation (LNA) in wheat. 【Conclusion】 The results have provided a stable and effective approach for monitoring canopy leaf nitrogen status in wheat.
DOI:10.1080/01431160902912061URL [本文引用: 1]

In this study, a wide range of leaf nitrogen concentration levels was established in field-grown rice with the application of three fertilizer levels. Hyperspectral reflectance data of the rice canopy through rice whole growth stages were acquired over the 350 nm to 2500 nm range. Comparisons of prediction power of two statistical methods (linear regression technique (LR) and artificial neural network (ANN)), for rice N estimation (nitrogen concentration, mg nitrogen g611 leaf dry weight) were performed using two different input variables (nitrogen sensitive hyperspectral reflectance and principal component scores). The results indicted very good agreement between the observed and the predicted N with all model methods, which was especially true for the PC-ANN model (artificial neural network based on principal component scores), with an RMSE65=650.347 and REP65=6513.14%. Compared to the LR algorithm, the ANN increased accuracy by lowering the RMSE by 17.6% and 25.8% for models based on spectral reflectance and PCs, respectively.
DOI:10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00182-1URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.5846/stxb201507091460URL [本文引用: 1]

研究采用芦苇和香蒲叶片光谱及实测叶绿素含量数据,选取波段谱带范围为可见光波段400-760nm(为了避免近红外波段受叶片水分含量的影响,降低构建模型的稳定性),利用相关分析与逐步回归分析的统计学分析方法,建立叶面尺度下不同包络线去除衍生转换光谱:BD(band depth)、CRDR(continuum-removed derivative reflectance)、BDR(band depth ratio)、NBDI (normalized band depth index)与叶绿素含量估算模型.通过对入选波段的统计表明在550-750nm,特别是700-750nm(红边)波段范围内产生了较多的有效波段,是今后进行生物参量反演的重点波段范围.舍一交叉验证结果表明芦苇、香蒲和混合样本绿素含量估测的最佳模型分别为BD、CRDR和NBDI模型,其交叉验证决定系数依次为0.87、0.83和0.81,交叉验证均方根误差RMSE依次为0.16、0.15和0.33.并在此基础上利用独立样本非参数检验和多因子方差分析,探讨相关因素对于叶绿素含量估算模型精度的影响.结果表明物种差异、数据类型差异对于叶绿素回归模型的影响较大,而光谱类型差异及光谱数据与数据类型交互作用对于回归模型精度的影响较小.
DOI:10.5846/stxb201507091460URL [本文引用: 1]

研究采用芦苇和香蒲叶片光谱及实测叶绿素含量数据,选取波段谱带范围为可见光波段400-760nm(为了避免近红外波段受叶片水分含量的影响,降低构建模型的稳定性),利用相关分析与逐步回归分析的统计学分析方法,建立叶面尺度下不同包络线去除衍生转换光谱:BD(band depth)、CRDR(continuum-removed derivative reflectance)、BDR(band depth ratio)、NBDI (normalized band depth index)与叶绿素含量估算模型.通过对入选波段的统计表明在550-750nm,特别是700-750nm(红边)波段范围内产生了较多的有效波段,是今后进行生物参量反演的重点波段范围.舍一交叉验证结果表明芦苇、香蒲和混合样本绿素含量估测的最佳模型分别为BD、CRDR和NBDI模型,其交叉验证决定系数依次为0.87、0.83和0.81,交叉验证均方根误差RMSE依次为0.16、0.15和0.33.并在此基础上利用独立样本非参数检验和多因子方差分析,探讨相关因素对于叶绿素含量估算模型精度的影响.结果表明物种差异、数据类型差异对于叶绿素回归模型的影响较大,而光谱类型差异及光谱数据与数据类型交互作用对于回归模型精度的影响较小.
DOI:10.1080/2150704X.2015.1007246URL [本文引用: 1]

Modern imaging spectrometers produce an ever-growing amount of data, which increases the need for automated analysis techniques. The algorithms employed, such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Tetracorder and the Mineral Identification and Characterization Algorithm (MICA), use a standardized spectral library and expert knowledge for the detection of surface cover types. Correct absorption feature definition and isolation are key to successful material identification using these algorithms. Here, a new continuum removal and feature isolation technique is presented, named the ‘Geometric Hull Technique’. It is compared to the well-established, knowledge-based Tetracorder feature database together with the adapted state of the art techniques scale-space filtering, alpha shapes and convex hull.
DOI:10.1023/A:1010933404324URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s11912-000-0027-7URLPMID:8931062 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Our purpose is to examine how applicable current quality of life instruments are in advanced cancer. Quality of life (QOL) is difficult to define and measure; it is a multidimensional, dynamic and subjective concept. An acceptable QOL instrument for advanced disease should be simple to administer and easy to explain, complete and analyse. In our view, the present instruments used in oncology do not serve the needs of advanced cancer patients. Based on our review, we believe a single question posed on a linear or categorical scale should be used to assess QOL in advanced cancer in preference to other available methods.
DOI:10.1198/tast.2009.08199URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7229.2017.01.017URL [本文引用: 2]

提高短期电力负荷预测精度是保障电网安全稳定运行的技术措施之一,通过选取影响负荷的最优输入变量集合,建立高斯过程回归(Gaussian process regression,GPR)短期负荷预测模型。负荷预测建模输入变量的选取对预测精度有很大影响,首先采用随机森林(random forest,RF)算法给出输入变量重要性评分(variable importance measure,VIM),并对各输入变量影响程度进行排序,基于序列前向搜索策略确定最优输入变量集合,避免人工经验选取的不足。其次针对共轭梯度(conjugate gradient,CG)法求解高斯过程回归模型超参数时易陷入局部最优解,且存在优化性能依赖于初值选取、迭代次数难以确定的问题,采用改进粒子群优化(particle swarm optimization,PSO)算法搜索模型超参数,形成优化高斯过程回归预测模型。最后,算例测试表明该模型的有效性。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7229.2017.01.017URL [本文引用: 2]

提高短期电力负荷预测精度是保障电网安全稳定运行的技术措施之一,通过选取影响负荷的最优输入变量集合,建立高斯过程回归(Gaussian process regression,GPR)短期负荷预测模型。负荷预测建模输入变量的选取对预测精度有很大影响,首先采用随机森林(random forest,RF)算法给出输入变量重要性评分(variable importance measure,VIM),并对各输入变量影响程度进行排序,基于序列前向搜索策略确定最优输入变量集合,避免人工经验选取的不足。其次针对共轭梯度(conjugate gradient,CG)法求解高斯过程回归模型超参数时易陷入局部最优解,且存在优化性能依赖于初值选取、迭代次数难以确定的问题,采用改进粒子群优化(particle swarm optimization,PSO)算法搜索模型超参数,形成优化高斯过程回归预测模型。最后,算例测试表明该模型的有效性。
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.22.027URL [本文引用: 1]

叶绿素含量是影响作物生长及产量的主要因素。该研究以2017年6月小型试验田获取的抽穗期春小麦叶绿素含量及其对应的光谱反射率为数据源,对红边(627-780 nm)、黄边(566-589 nm)、蓝边(436-495 nm)、绿边(495-566 nm)、吸收谷和反射峰的最大反射率及反射率总和等16个高光谱特征参数与叶绿素含量之间的相关性进行了分析,并结合偏最小二乘回归法(partial least-squares regression,PLSR)对叶绿素含量进行高光谱建模及验证。结果表明:1)对特定的16个光谱特征参数而言,光谱特征参数绿边最大反射率与春小麦叶绿素质量分数之间的决定系数最低(R^2〈0.5);决定系数较高(R^2≥0.5)的光谱特征参数包括蓝边最大反射率、蓝边反射率总和、黄边最大反射率、黄边反射率总和、红边最大反射率、红边反射率总和、绿边反射率总和、820-940 nm反射率总和及最大反射率、500-670 nm归一化吸收深度和560-760 nm归一化吸收深度,其中820-940 nm反射率总和决定系数达到最高(R^2为0.8);2)利用16个特征参量进行PLSR建模后,发现波段范围在820-940 nm的最大反射率及反射率总和所建立的PLSR估算模型为最优模型,其精度参数R^2p=0.8、RMSEp=2.0 mg/g、RPD=3.2。因此,该模型具有极好的预测能力。该研究为相关研究及当地精准农业提供科学支持和应用参考。
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.22.027URL [本文引用: 1]

叶绿素含量是影响作物生长及产量的主要因素。该研究以2017年6月小型试验田获取的抽穗期春小麦叶绿素含量及其对应的光谱反射率为数据源,对红边(627-780 nm)、黄边(566-589 nm)、蓝边(436-495 nm)、绿边(495-566 nm)、吸收谷和反射峰的最大反射率及反射率总和等16个高光谱特征参数与叶绿素含量之间的相关性进行了分析,并结合偏最小二乘回归法(partial least-squares regression,PLSR)对叶绿素含量进行高光谱建模及验证。结果表明:1)对特定的16个光谱特征参数而言,光谱特征参数绿边最大反射率与春小麦叶绿素质量分数之间的决定系数最低(R^2〈0.5);决定系数较高(R^2≥0.5)的光谱特征参数包括蓝边最大反射率、蓝边反射率总和、黄边最大反射率、黄边反射率总和、红边最大反射率、红边反射率总和、绿边反射率总和、820-940 nm反射率总和及最大反射率、500-670 nm归一化吸收深度和560-760 nm归一化吸收深度,其中820-940 nm反射率总和决定系数达到最高(R^2为0.8);2)利用16个特征参量进行PLSR建模后,发现波段范围在820-940 nm的最大反射率及反射率总和所建立的PLSR估算模型为最优模型,其精度参数R^2p=0.8、RMSEp=2.0 mg/g、RPD=3.2。因此,该模型具有极好的预测能力。该研究为相关研究及当地精准农业提供科学支持和应用参考。
DOI:10.11766/trxb200907100306URL [本文引用: 1]

青海柴达木盆地气候干旱,蒸降比为10~20,地形封闭,属漠境草原盆地景观。由于气候干旱、蒸发强烈、地势低洼、含盐地下水接近地表使得土壤盐渍化较为严重。土壤盐渍化造成了资源破坏、农业生产损失,对生物圈和生态环境构成威胁。
DOI:10.11766/trxb200907100306URL [本文引用: 1]

青海柴达木盆地气候干旱,蒸降比为10~20,地形封闭,属漠境草原盆地景观。由于气候干旱、蒸发强烈、地势低洼、含盐地下水接近地表使得土壤盐渍化较为严重。土壤盐渍化造成了资源破坏、农业生产损失,对生物圈和生态环境构成威胁。
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.16.016URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

目前中国西北干旱、半干旱地区的土壤盐渍化情况日益趋于严重,动态、快速而精确地监测与评价土壤盐渍化显得尤为重要。微波遥感所具有的优点使其成为探测土壤盐分分布的新兴而有潜力的方法。快速获取大范围地表土壤盐渍化的空间分布是一个迫切急需解决的科学难题。该文目的是试验与评价C波段RADARSAT-2 SAR(synthetic aperture radar)数据反演土壤盐渍化的性能。以受盐渍化影响较严重的内蒙古河套灌区解放闸灌域为试验区,基于SAR后向散射系数和土壤盐分实测值,利用多元线性回归(multiple linear regress,MLR)、地理加权回归(geographically weighted regression,GWR)和BP人工神经网络(back propagation artificial neural networks,BP ANN)方法建立土壤含盐量的定量反演模型,重点构建了8∶140∶1结构的3层BP ANN模型,经模型验证发现MLR、GWR模型均偏向于弱相关,其标准误差SE分别为0.55、0.47 mg/g-1,而ANN(BP)模型的内部、外部检验标准误差SE分别为0.24、0.33 mg/g,优于前2种模型,其反演的盐渍化面积占比65.4%,与地面验证结果基本一致。该文建立的考虑土壤水分影响、组合雷达后向散射系数反演土壤盐分的人工智能模型,无需复杂的介电常数模型,能够在一定程度上满足土壤盐渍化监测的需要,可促进微波遥感在土壤盐渍化监测中的开拓应用。
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.16.016URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

目前中国西北干旱、半干旱地区的土壤盐渍化情况日益趋于严重,动态、快速而精确地监测与评价土壤盐渍化显得尤为重要。微波遥感所具有的优点使其成为探测土壤盐分分布的新兴而有潜力的方法。快速获取大范围地表土壤盐渍化的空间分布是一个迫切急需解决的科学难题。该文目的是试验与评价C波段RADARSAT-2 SAR(synthetic aperture radar)数据反演土壤盐渍化的性能。以受盐渍化影响较严重的内蒙古河套灌区解放闸灌域为试验区,基于SAR后向散射系数和土壤盐分实测值,利用多元线性回归(multiple linear regress,MLR)、地理加权回归(geographically weighted regression,GWR)和BP人工神经网络(back propagation artificial neural networks,BP ANN)方法建立土壤含盐量的定量反演模型,重点构建了8∶140∶1结构的3层BP ANN模型,经模型验证发现MLR、GWR模型均偏向于弱相关,其标准误差SE分别为0.55、0.47 mg/g-1,而ANN(BP)模型的内部、外部检验标准误差SE分别为0.24、0.33 mg/g,优于前2种模型,其反演的盐渍化面积占比65.4%,与地面验证结果基本一致。该文建立的考虑土壤水分影响、组合雷达后向散射系数反演土壤盐分的人工智能模型,无需复杂的介电常数模型,能够在一定程度上满足土壤盐渍化监测的需要,可促进微波遥感在土壤盐渍化监测中的开拓应用。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.12.029URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

土壤盐渍化是干旱、半干旱农业区主要的土地退化问题,及时、精准、动态地监测盐渍土盐分,对于治理、防治盐渍土和进行农业可持续发展至关重要。以松嫩平原西部长岭县为例,利用盐渍土高光谱数据构建盐渍土盐分遥感预测模型。电导法测得土壤盐量,用ASD高光谱仪野外采集高光谱数据,利用光谱导数变换选择能够表征盐渍土盐分信息的最佳波段,即550、720、760、820和940 nm。通过比较3层和4层72种不同神经网络结构,最终选择5-6-1 结构的3层神经网络预测盐渍土盐分(R2 = 0.895,RMSE = 0.089)。与传统回归相比(R2 = 0.81,RMSE = 0.25),运用高光谱数据与人工神经网络方法相结合,能够提高盐渍土的预测精度,说明人工神经网络在构建光谱反射率与土壤参数关系研究中具有突出优势。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.12.029URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

土壤盐渍化是干旱、半干旱农业区主要的土地退化问题,及时、精准、动态地监测盐渍土盐分,对于治理、防治盐渍土和进行农业可持续发展至关重要。以松嫩平原西部长岭县为例,利用盐渍土高光谱数据构建盐渍土盐分遥感预测模型。电导法测得土壤盐量,用ASD高光谱仪野外采集高光谱数据,利用光谱导数变换选择能够表征盐渍土盐分信息的最佳波段,即550、720、760、820和940 nm。通过比较3层和4层72种不同神经网络结构,最终选择5-6-1 结构的3层神经网络预测盐渍土盐分(R2 = 0.895,RMSE = 0.089)。与传统回归相比(R2 = 0.81,RMSE = 0.25),运用高光谱数据与人工神经网络方法相结合,能够提高盐渍土的预测精度,说明人工神经网络在构建光谱反射率与土壤参数关系研究中具有突出优势。
DOI:10.1016/0034-4257(94)90157-0URL [本文引用: 1]

High spectral resolution data from the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS) acquired over several forest stands in west-central Oregon were analyzed with respect to variations in forest canopy biochemical content (kg ha 611 ), foliar biochemical concentration (mg cm 2 leaf area), and leaf area index (LAI). The Lowtran-7 atmospheric radiative transfer code was used to convert AVIRIS at-sensor radiance into reflectance factor. The correlation of reflectance factor and first-difference AVIRIS spectra with total nitrogen (TN), lignin, starch, total chlorophyll content (kg ha 611 ), and LAI is presented. Correlogram structure in the 1200–2400 nm region is compared with the occurrence of known absorption features associated with organic molecular bonds which comprise foliar biochemical constituents. Regression equations relating the first-difference AVIRIS data to chemical variables and LAI were developed. The chlorophyll red edge spectral region was strongly related to LAI, canopy TN content, and canopy chlorophyll content. Generally good correspondence was found between wavelength selections for TN and lignin (concentration and content) and overtones of fundamental CH and NH absorptance features. The AVIRIS data were not significantly correlated with either starch concentration or starch content, although wavelength selections for starch were consistent with those made in previous laboratory-based studies.
DOI:10.2307/1941934URL [本文引用: 1]

We examined seasonal changes in canopy chemical concentrations and content in conifer forests growing along a climate gradient in western Oregon, as part of the Oregon Transect Ecosystem Research (OTTER) study. The chemical variables were related to seasonal patterns of growth and production. Statistical comparisons of chemical variables with data collected from two different airborne remote-sensing platforms were also carried out. Total nitrogen (N) concentrations in foliage varied significantly both seasonally and among sites; when expressed as content in the forest canopy, nitrogen varied to a much greater extent and was significantly related to aboveground net primary production (r = 0.99). Chlorophyll and free amino acid concentrations varied more strongly than did total N and may have reflected changes in physiological demands for N. Large variations in starch concentrations were measured from pre- to post-budbreak in all conifer sites. Examination of remote-sensing data from two different airborne instruments suggests the potential for remote measurement of some canopy chemicals. Multivariate analysis of high-resolution spectral data in the near infrared region indicated significant correlations between spectral signals and N concentration and canopy N content; the correlation with canopy N content was stronger and was probably associated in part with water absorption features of the forest canopy. The spectral bands that were significantly correlated with lignin concentration and content were similar to bands selected in the other laboratory and airborne studies; starch concentrations were not significantly related to spectral reflectance data. Strong relationships between the spectral position of specific features in the visible region and chlorophyll were also found.
DOI:10.1109/36.563280URL [本文引用: 1]

Airborne imaging spectrometers can record spatially-explicit information on the absorption features associated with foliar biochemicals in a forest canopy. The spectra of a single species pine canopy were recorded by the National Aeronautics and Spac...
DOI:10.1016/0034-4257(88)90007-7URL [本文引用: 1]

Remote detection and measurement of the nitrogen and lignin contents of forest canopies could allow predictions of biogeochemical processes such as productivity, decomposition, and nutrient turnover rates. Spectral absorption features characteristic of proteins (containing nitrogen), lignin and other leaf constituents occur throughout the shortwave infrared region (1200 2400 nm). The lignin and nitrogen concentration of dried and ground deciduous leaves have been predicted from reflectance spectra obtained in the laboratory. The optimum wavelengths for prediction were selected using stepwise multiple linear regression. The prediction errors were comparable to chemical techniques. Analysis of the reflectance spectra of fresh, whole leaves has been limited thus far to conifer leaves but indicate spectral features predictive of nitrogen and lignin also found in airborne spectra. Airborne Imaging Spectrometer (AIS) were evaluated for whole forest canopy physical and chemical properties. Variations in spectral brightness were associated with variations in total water content of the foliar biomass. Comparison of forest spectra with spectrally flat targets revealed absorption features common to the canopy spectra between 1500 and 1700 nm which were tentatively attributed to absorption by lignin and starch. The AIS and laboratory data indicate strongly that absorption in the infrared region is influenced by biochemical characteristics.
DOI:10.1016/0034-4257(95)00135-NURL [本文引用: 1]

An experiment was designed to determine whether chlorophyll and nitrogen concentrations could be predicted from reflectance (R) spectra of fresh bigleaf maple leaves in the laboratory, and, if so, whether the predictive spectral features could be correlated with chlorophyll and nitrogen concentration or content of simple canopies of maple seedlings. The best predictors for nitrogen and chlorophyll of fresh leaves appeared with first-difference transformations of log 1/R, and the bands selected were similar to those found in other studies. Shortwave infrared bands were best predictors for nitrogen, visible bands best for chlorophyll. In the shortwave infrared region, however, the absolute differences in reflectance at critical bands was extremely small, and the bands of high correlation were narrow. High spectral and radiance resolution are required to resolve these differences accurately. The best shortwave infrared bands from the leaf scale were not good predictors of chemical content or concentration at the canopy scale ; variability in canopy reflectance in the shortwave infrared region was at least an order of magnitude beyond that necessary to detect signals from chemicals. The variability in first-difference log 1/R on the canopy scale was related to the arrangement of trees with respect to direct solar radiation, instrument noise, leaf fluttering and small changes in atmospheric moisture.
DOI:10.1080/01431160601024242URL [本文引用: 1]

Two nitrogen experiments on rice were conducted in 2002, and the reflectances (350 to 2500 nm) and pigment contents (chlorophylls a and b, total chlorophylls and carotenoids) for leaf and panicle samples at different growth stages were measured in the laboratory. After performing an outlier analysis, the number of samples were 843 for leaves and 188 for panicles. Absorption features at 430, 460, 470, 640 and 660 nm for different pigments, and the relative reflectance of the green peak around 550 nm calculated by the continuum emoved method, as well as the red edge position (REP) of rice leaves and panicles were selected as the independent variables, and measured pigment contents were selected as the dependent variables. Then, back propagation neural network (BPN) models, a kind of artificial neuron network (ANN), and multivariate linear regression models (MLR) were trained and tested. The main objective of this study was to compare the predictive ability of the ANN models to that of the MLR models in estimating the content of pigments in rice leaves and panicles. Results showed that all BPN models gave higher coefficients of determination (R2) and lower absolute errors (ABSEs) and root mean squared errors (RMSEs) than the corresponding MLR models, in both calibration and validation tests. Further significance tests by paired t tests and bootstrapping algorithms indicated that most of the BPN models outperformed the MLR models. When trained by combination data that did not meet the assumption of normal distribution, the BPN models appeared to not only have a better learning ability, but also had a more accurate predictive power than the MLR models. The estimation of leaf pigments was more accurate than that of panicle pigments, independent of which model was used.
DOI:10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2018)01-0246-07URL [本文引用: 1]

传统食品掺假分析多集中于检测特定已知或者怀疑可能存在的掺假物,然而由于掺假形式的多样性以及新的掺假物不断出现,使得传统检测方法具有局限性。目前,全蛋粉作为鲜蛋理想替代品掺假现象十分严重,然而不管是国内还是国外,其掺假检测都鲜有研究。因此,为了探索一种快速检测全蛋粉掺假的方法,研究尝试使用最近快速发展起来的具有绿色、无损等优点的高光谱技术来检测全蛋粉掺假的可行性。从不同地区收集不同品牌的鸡蛋全蛋粉,按不同比例分别掺入淀粉、大豆分离蛋白、麦芽糊精以及三种掺假物的混合物进行试验样品的制备。样品进行光谱采集后,采用ENVI软件选取感兴趣区域(ROI)后提取出平均光谱。根据获得的光谱数据建立全波段下支持向量机(SVM)模型进行掺假的判别并采用偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)模型建立全波段与掺假浓度之间的关系。结果显示,采用径向基核函数所建立的SVM模型,其分类的正确率达到90%以上,基于PLSR建立掺假模型实际值与预测值相关系数R2P均高于0.90。为了简化模型,采用回归系数法(RC)及连续投影法(SPA)提取特征波长,根据特征波长下的光谱数据建立RC-PLSR和SPA-PLSR模型,结果显示,经简化的模型依然具有良好的性能,说明使用高光谱技术来检测全蛋粉掺假是可行且高效的。
DOI:10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2018)01-0246-07URL [本文引用: 1]

传统食品掺假分析多集中于检测特定已知或者怀疑可能存在的掺假物,然而由于掺假形式的多样性以及新的掺假物不断出现,使得传统检测方法具有局限性。目前,全蛋粉作为鲜蛋理想替代品掺假现象十分严重,然而不管是国内还是国外,其掺假检测都鲜有研究。因此,为了探索一种快速检测全蛋粉掺假的方法,研究尝试使用最近快速发展起来的具有绿色、无损等优点的高光谱技术来检测全蛋粉掺假的可行性。从不同地区收集不同品牌的鸡蛋全蛋粉,按不同比例分别掺入淀粉、大豆分离蛋白、麦芽糊精以及三种掺假物的混合物进行试验样品的制备。样品进行光谱采集后,采用ENVI软件选取感兴趣区域(ROI)后提取出平均光谱。根据获得的光谱数据建立全波段下支持向量机(SVM)模型进行掺假的判别并采用偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)模型建立全波段与掺假浓度之间的关系。结果显示,采用径向基核函数所建立的SVM模型,其分类的正确率达到90%以上,基于PLSR建立掺假模型实际值与预测值相关系数R2P均高于0.90。为了简化模型,采用回归系数法(RC)及连续投影法(SPA)提取特征波长,根据特征波长下的光谱数据建立RC-PLSR和SPA-PLSR模型,结果显示,经简化的模型依然具有良好的性能,说明使用高光谱技术来检测全蛋粉掺假是可行且高效的。
URL [本文引用: 1]

为了探究多种植被指数组合与偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)结合对于提高冬小麦地上干生物量估测精度的影响,本研究以氮运筹试验为基础,比较分析了18种植被指数与冬小麦地上干生物量的相关性,筛选出相关性较好的植被指数,建立多种植被指数组合的PLSR模型,并对模型进行评价比较。结果表明:除叶绿素归一化植被指数(NPCI)外各植被指数均与冬小麦地上干生物量有良好的相关性,中分辨率陆地叶绿素成像指数(MTCI)、绿色归一化植被指数(GNDVI)、改进红边比值植被指数(MSR705)和特征色素简单比值指数c (PSSRc)4个植被指数相关系数绝对值均达到0.800以上;多植被指数组合构建的PLSR模型中,以PSSRc、MSR705和MTCI 3个植被指数建立的复合式模型建模集(=0.719,=0.316)和验证集(=0.696,=0.346)表现最佳。因此,多种植被指数组合与偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)结合能有效提高冬小麦地上干生物量的估测精度,为更好地实现冬小麦地上干生物量高光谱遥感估测提供有效技术途径。
URL [本文引用: 1]

为了探究多种植被指数组合与偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)结合对于提高冬小麦地上干生物量估测精度的影响,本研究以氮运筹试验为基础,比较分析了18种植被指数与冬小麦地上干生物量的相关性,筛选出相关性较好的植被指数,建立多种植被指数组合的PLSR模型,并对模型进行评价比较。结果表明:除叶绿素归一化植被指数(NPCI)外各植被指数均与冬小麦地上干生物量有良好的相关性,中分辨率陆地叶绿素成像指数(MTCI)、绿色归一化植被指数(GNDVI)、改进红边比值植被指数(MSR705)和特征色素简单比值指数c (PSSRc)4个植被指数相关系数绝对值均达到0.800以上;多植被指数组合构建的PLSR模型中,以PSSRc、MSR705和MTCI 3个植被指数建立的复合式模型建模集(=0.719,=0.316)和验证集(=0.696,=0.346)表现最佳。因此,多种植被指数组合与偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)结合能有效提高冬小麦地上干生物量的估测精度,为更好地实现冬小麦地上干生物量高光谱遥感估测提供有效技术途径。
DOI:10.1080/01431169608949073URL [本文引用: 1]

Forest ecosystem modelling requires information about canopy chemistry. This is usually obtained through chemical analysis and laboratory spectrometric measurements. The potential of spectrometric remote sensing was investigated with two airborne campaigns organized in 1991 with AVIRIS (Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging spectrometer) and in 1993 with ISM (Infrared SpectroMeter) over the ''Landes forest (south-west France): AVIRIS covers the 400-2500 nm spectral range with 210 bands, whereas the ISM instrument is an airborne profiling spectrometer that operates in the 800-3200 nm spectral range with 128 bands. The study area consists of homogeneous parcels of maritime pines with a wide variety of ages from 2 to 48 years. Simultaneously with the airborne acquisition, foliar samples were collected in the field. These samples were chemically analysed for determining nitrogen, lignin and cellulose contents. Reflectance spectra of dried pine needles were obtained with the help of two laboratory spectrometers: (1) the Technicon lnfraAlyser-450 with 19 spectral bands centred on chemical absorption features; and (2) the NIR-6500 System with l0nm wide 1050 bands from 400 nm to 2500 nm. Predictive relationships of nitrogen, lignin and cellulose concentrations were established by using stepwise regression analysis on the laboratory spectral measurements. These predictive relationships were quite different, depending on the laboratory spectrometers and the year of sampling. Consequently, different correlations (r2) were obtained between predicted and actual chemical concentrations: 66-94 per cent for nitrogen, 37-79 per cent for lignin and 45-85 per cent for cellulose. The stability of predictive relationships from laboratory to remote sensing level was especially analysed. The application of laboratory derived predictive equations to airborne data led to encouraging results: best correlations (r2) were obtained for nitrogen (AVIRIS: 55 per cent -ISM: 66 per cent) and cellulose (AVIRIS: 63 per cent) but lignin could not be predicted. It was attempted to improve these results while talking into account atmospheric effects: whereas AVIRIS-derived correlations were not improved, ISM-derived correlations were improved for nitrogen from 66 per cent to 76 per cent and lignin from 9 per cent to 77 per cent. The better signal-to-noise ratio of ISM may be the reasons for the better results obtained with this instrument
DOI:10.1080/01431160412331269698URL [本文引用: 1]

Growing an ensemble of decision trees and allowing them to vote for the most popular class produced a significant increase in classification accuracy for land cover classification. The objective of this study is to present results obtained with the random forest classifier and to compare its performance with the support vector machines (SVMs) in terms of classification accuracy, training time and user defined parameters. Landsat Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) data of an area in the UK with seven different land covers were used. Results from this study suggest that the random forest classifier performs equally well to SVMs in terms of classification accuracy and training time. This study also concludes that the number of user-defined parameters required by random forest classifiers is less than the number required for SVMs and easier to define.
DOI:10.5589/m12-012URL [本文引用: 1]

The potential of a random forest (RF) classifier for radar-only crop classifications was evaluated for an eastern and western Canadian site. Overall classification accuracies were improved by approximately 4% 5% over traditional boosted decision trees with gains of up to 7% in the accuracies of specific classes. Accuracies above 85% were obtained for key crops including canola, soybeans, corn, and wheat. Variable importance measures generated by the RF classifier showed that the most important acquisitions occurred in late August to early September at peak biomass and after wheat harvest. The least important images were acquired in May and mid-July. The HV and VV polarizations had the most significant contributions, while the HH polarization contributed little throughout the season, except in late September when the HH response was largely driven by soil conditions. The sensitivity of three RF parameters (number of training pixels, number of trees, and number of variables to select from at each split) was evaluated and shown to have negligible influence on overall accuracy. The RF classifier provided large performance gains in terms of processing time relative to the decision tree classifier. The operational potential and implementation considerations for radar-only Canada-wide crop type mapping are discussed in the context of these results.
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.021URL [本文引用: 1]

准确掌握农作物的空间种植分布情况,对于国家宏观指导农业生产、制定农业政策有重要意义。针对黑龙江省玉米与大豆生育期接近、光谱特征相似,较难区分的问题,以多时相16 m空间分辨率高分一号(GF-1)卫星宽覆盖(wide field of view,WFV)影像为数据源,选择归一化植被指数(normalized difference vegetation index,NDVI)、增强植被指数(enhanced vegetation index,EVI)、宽动态植被指数(wide dynamic range vegetation index,WDRVI)、归一化水指数(normalized difference water index,NDWI)4个特征,结合实地调查样本点,采用随机森林分类算法,提取黑龙江省黑河市嫩江县玉米与大豆种植面积。研究表明,区分玉米与大豆的最佳时段为9月下旬至10月上旬,即大豆已收获而玉米未收获的时段,在4个待选特征中,NDVI、NDWI与WDRVI指数组合表现最佳;随机森林算法与最大似然算法、支持向量机算法相比,分类精度更高,其总体分类精度为84.82%,Kappa系数为77.42%。玉米制图精度为91.49%,用户精度为93.48%;大豆制图精度为91.14%,用户精度为82.76%。该方法为大区域农作物的分类提供重要参考和借鉴价值。
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.021URL [本文引用: 1]

准确掌握农作物的空间种植分布情况,对于国家宏观指导农业生产、制定农业政策有重要意义。针对黑龙江省玉米与大豆生育期接近、光谱特征相似,较难区分的问题,以多时相16 m空间分辨率高分一号(GF-1)卫星宽覆盖(wide field of view,WFV)影像为数据源,选择归一化植被指数(normalized difference vegetation index,NDVI)、增强植被指数(enhanced vegetation index,EVI)、宽动态植被指数(wide dynamic range vegetation index,WDRVI)、归一化水指数(normalized difference water index,NDWI)4个特征,结合实地调查样本点,采用随机森林分类算法,提取黑龙江省黑河市嫩江县玉米与大豆种植面积。研究表明,区分玉米与大豆的最佳时段为9月下旬至10月上旬,即大豆已收获而玉米未收获的时段,在4个待选特征中,NDVI、NDWI与WDRVI指数组合表现最佳;随机森林算法与最大似然算法、支持向量机算法相比,分类精度更高,其总体分类精度为84.82%,Kappa系数为77.42%。玉米制图精度为91.49%,用户精度为93.48%;大豆制图精度为91.14%,用户精度为82.76%。该方法为大区域农作物的分类提供重要参考和借鉴价值。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2016.06.007URL [本文引用: 1]

考虑气候因子间多重共线性及其与粮食产量间复杂的非线性关系,本文在HP滤波分离出气候产量的基础上,尝试引入基于三次B样条变换(Spline-PLSR)和内部嵌入GRNN的两种非线性偏最小二乘模型(GRNN-PLSR),利用1961-2008年气候因子数据建立气候产量计算模型,以2009—2013年数据进行拟合检验,并与常用的C-D生产函数法计算的气候产量进行比较。结果表明,Spline-PLSR法在拟合气候因子变化对粮食产量影响时预测精度较高。而且,与C-D生产函数法相比,Spline-PLSR所需要素较少,操作简单,相对误差最高仅为13.6%;与GRNN-PLSR法拟合结果相比,Spline-PLSR相对误差波动较小,因此,基于三次B样条变换的非线性偏最小二乘法建模较适合拟合气候产量。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2016.06.007URL [本文引用: 1]

考虑气候因子间多重共线性及其与粮食产量间复杂的非线性关系,本文在HP滤波分离出气候产量的基础上,尝试引入基于三次B样条变换(Spline-PLSR)和内部嵌入GRNN的两种非线性偏最小二乘模型(GRNN-PLSR),利用1961-2008年气候因子数据建立气候产量计算模型,以2009—2013年数据进行拟合检验,并与常用的C-D生产函数法计算的气候产量进行比较。结果表明,Spline-PLSR法在拟合气候因子变化对粮食产量影响时预测精度较高。而且,与C-D生产函数法相比,Spline-PLSR所需要素较少,操作简单,相对误差最高仅为13.6%;与GRNN-PLSR法拟合结果相比,Spline-PLSR相对误差波动较小,因此,基于三次B样条变换的非线性偏最小二乘法建模较适合拟合气候产量。
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.14.015URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

为实现基于光谱分析土壤有机质含量的快速测定,该文以江汉平原公安县的土壤为研究对象,进行室内理化分析、光谱测量与处理等一系列工作,在土壤原始光谱反射率(raw spectral reflectance,R)的基础上,提取了其倒数之对数(inverse-log reflectance,LR)、一阶微分(first order differential reflectance,FDR)和连续统去除(continuum removal, CR)3种光谱指标,分析4种不同形式的光谱指标与有机质含量的相关性,对相关系数进行P=0.01水平上的显著性检验来确定显著性波段的范围,并基于全波段(400~2 400 nm)和显著性波段运用偏最小二乘回归(partial least squares regression, PLSR)建立了该区域土壤有机质高光谱的预测模型,通过模型精度的比较确定最优模型。结果表明,进行CR变换后,光谱曲线的特征吸收带更加明显,相关系数在可见光波段范围内有所提高;基于全波段的PLSR建模效果要优于显著性波段,其中以CR的预测精度最为突出,其模型的决定系数R2和相对分析误差RPD分别为0.84、2.58;显著性波段的PLSR模型与全波段对比在模型精度方面虽有一定差距,但从模型的复杂程度来比较,具有模型简单、运算量小、变量更少的特点;最后,综合比较了全波段和显著性波段4种光谱指标的反演精度,发现CR-PLSR模型的建模和预测的效果比R-PLSR、LR-PLSR、FDR-PLSR模型都要显著。该研究可为将CR-PLSR高光谱反演模型用于该区域土肥信息的遥感监测提供参考。
DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.14.015URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

为实现基于光谱分析土壤有机质含量的快速测定,该文以江汉平原公安县的土壤为研究对象,进行室内理化分析、光谱测量与处理等一系列工作,在土壤原始光谱反射率(raw spectral reflectance,R)的基础上,提取了其倒数之对数(inverse-log reflectance,LR)、一阶微分(first order differential reflectance,FDR)和连续统去除(continuum removal, CR)3种光谱指标,分析4种不同形式的光谱指标与有机质含量的相关性,对相关系数进行P=0.01水平上的显著性检验来确定显著性波段的范围,并基于全波段(400~2 400 nm)和显著性波段运用偏最小二乘回归(partial least squares regression, PLSR)建立了该区域土壤有机质高光谱的预测模型,通过模型精度的比较确定最优模型。结果表明,进行CR变换后,光谱曲线的特征吸收带更加明显,相关系数在可见光波段范围内有所提高;基于全波段的PLSR建模效果要优于显著性波段,其中以CR的预测精度最为突出,其模型的决定系数R2和相对分析误差RPD分别为0.84、2.58;显著性波段的PLSR模型与全波段对比在模型精度方面虽有一定差距,但从模型的复杂程度来比较,具有模型简单、运算量小、变量更少的特点;最后,综合比较了全波段和显著性波段4种光谱指标的反演精度,发现CR-PLSR模型的建模和预测的效果比R-PLSR、LR-PLSR、FDR-PLSR模型都要显著。该研究可为将CR-PLSR高光谱反演模型用于该区域土肥信息的遥感监测提供参考。
DOI:10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.09.016URL [本文引用: 1]

Reflectance spectroscopy provides an alternate method to classical physical and chemical laboratory soil analysis for estimation of a large range of key soil properties. Techniques including classical chemometrics approaches and specific absorption features studies have been developed for deriving estimates of soil characteristics from visible and near-infrared (VNIR, 400–120002nm) and shortwave infrared (SWIR, 1200–250002nm) reflectance measurements. This paper examines the performances of two distinct methods for clay and calcium carbonate (CaCO 3) content estimation (two key soil properties for erosion prediction) by VNIR/SWIR spectroscopy: i) the Continuum Removal (CR) has been used to correlate spectral absorption bands centred at 2206 and 234102nm with clay and CaCO 3 concentrations and ii) the partial least-squares regression (PLSR) method with leave-one-out cross-validation, which is a classical chemometrics technique, has been used to predict clay and CaCO 3 concentrations from VNIR/SWIR full spectra. We tried to respond to the question “should we use all bands in the 400–250002nm range or should we focus our analysis on selected spectral absorption bands to determine soil properties from reflectance data?” In this paper, the CR and PLSR methods were applied to VNIR/SWIR laboratory and airborne HYMAP reflectance measurements collected over the La Peyne Valley area in southern France. This study shows that the performance of both techniques is dependent on the spectral feature for the soil property of interest and on the level data acquisition (lab or airborne) face to the instrument specifications. When airborne HYMAP reflectance measurements are used, the PLSR technique performs better than the CR approach. As well, when the soil property of interest has no well-identified spectral feature, which is the case of clay, the PLSR technique performs better than the CR approach. In this last situation, PLSR is able to find surrogate spectral features that retain satisfactory estimations of the studied soil properties. However, parts of these spectral features remain difficult to explain or relate to area-specific correlations between soil properties, which means that extrapolation to larger pedological contexts must be envisaged with care. In the near future, VNIR/SWIR airborne hyperspectral data processed by the PLSR technique will allow for accurate mapping of clay and CaCO 3 contents, which will contribute significantly to the digital mapping of soil properties.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0171.2008.01.009URL [本文引用: 1]

为提高BP网络模型的泛化能力和学习精度,从神经网络的结构、参数设计,以及基本训练算法的选定等方面进行研究,给出了程序设计过程,提出了有效的解决方法。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0171.2008.01.009URL [本文引用: 1]

为提高BP网络模型的泛化能力和学习精度,从神经网络的结构、参数设计,以及基本训练算法的选定等方面进行研究,给出了程序设计过程,提出了有效的解决方法。
