 ,1,2,*
,1,2,*Differences in Physicochemical Properties between Flour and Starch of Wheat Grain
LI Chun-Yan1,*, ZHANG Wen-Xia1,2,*, ZHANG Yu-Xue1, YAO Meng-Hao1, DING Jin-Feng1, ZHU Xin-Kai1, GUO Wen-Shan1, FENG Chao-Nian ,1,2,*
,1,2,*通讯作者:
第一联系人:
收稿日期:2017-10-17接受日期:2018-03-20网络出版日期:2018-04-02
| 基金资助: |
Received:2017-10-17Accepted:2018-03-20Online:2018-04-02
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (576KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
李春燕, 张雯霞, 张玉雪, 姚梦浩, 丁锦峰, 朱新开, 郭文善, 封超年. 小麦籽粒淀粉与面粉的理化特性差异[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(7): 1077-1085. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01077
LI Chun-Yan, ZHANG Wen-Xia, ZHANG Yu-Xue, YAO Meng-Hao, DING Jin-Feng, ZHU Xin-Kai, GUO Wen-Shan, FENG Chao-Nian.
小麦籽粒中的主要成分是淀粉(直链淀粉和支链淀粉)、蛋白质和脂肪等生物大分子物质, 此外还含有少量的矿物质、糖类和维生素。根据直链淀粉含量可将小麦分为糯质小麦(Waxy蛋白亚基全缺失)、部分糯质小麦(Waxy蛋白亚基部分缺失)和非糯质小麦(Waxy蛋白亚基不缺失)[1,2]。籽粒中直、支链淀粉含量与结构的差异, 影响着淀粉的理化特性[3,4]。直链淀粉含量影响淀粉的成胶性、糊化特性和凝胶化作用[5,6], 直链淀粉含量高的淀粉比含量低的淀粉难糊化[7]。糯小麦理化特性中各项黏度参数值低于其亲本材料, 还具有膨胀和吸水能力强及回生度低的特征[8,9,10,11], 亦有研究认为糯小麦峰值黏度高于非糯小麦[12]。
小麦面粉主要用来制作面条、馒头、面包和蛋糕等, 面制食品的品质除与淀粉组分及其含量有关外, 还与面粉中α-淀粉酶活性、蛋白质、糖分、脂肪含量有关[13,14,15], 如面粉脱脂脱蛋白质后溶解度、膨胀势和黏度参数增加[13]。食品生产过程中, pH值及盐类、极性高分子有机化合物等外源添加剂也会影响淀粉的理化特性, 面粉中添加蔗糖后糊化温度显著提高[16]。前人研究主要是以面粉或淀粉为材料, 因其成份及α-淀粉酶活性不同, 研究结论不尽一致, 特别是在糯与非糯小麦黏度参数差异上观点不一。因此, 本研究选用糯小麦与非糯小麦, 分析其差异形成的原因, 并试验外源添加剂对面粉黏度特性的影响, 以期为小麦食品品质研究与改良提供依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
选用生产上示范推广的糯小麦扬糯麦1号和宁糯麦1号, 非糯小麦扬麦16和典型遗传种质材料中国春, 种子由江苏省里下河地区农业科学研究所和江苏省农业科学院提供。1.2 面粉的制备方法
采用Quadrumat Junior小型实验室制粉机(Branbender, 德国)磨制100目面粉, 用于面粉理化特性分析。1.3 淀粉的制备方法
参照陆大雷等[17]描述的方法略做改进提取小麦淀粉。称取100 g小麦籽粒, 用去离子水浸泡48 h, 豆浆机粉碎过100目筛, 静置2 h, 弃上清液, 1500 ×g离心10 min, 去除沉淀上层灰色杂质, 重复3次, 得到脱蛋白淀粉。当脱蛋白淀粉蛋白质含量高于0.5%时, 再用Solarbio碱性蛋白酶(北京索莱宝科技有限公司, 货号B8360)脱蛋白。脱蛋白淀粉加无水乙醇, 充分搅拌, 1500 ×g离心10 min, 重复3次; 在沉淀中加入甲醇和丙酮等体积混合液, 充分搅拌, 1500 ×g离心10 min, 重复3次, 通风晾干制得纯淀粉。
1.4 淀粉理化特性参数测定方法
对于参数测定每个品种重复3次。1.4.1 蛋白质和淀粉组分含量测定方法 称取1.000 g样品, 采用Kjeltec 2300型全自动凯氏定氮仪(Foss, 瑞典)测定蛋白质含量(干基); 采用双波长法测定直、支链淀粉含量[18], 采用淀粉总量检测试剂盒(Megazyme 公司, 货号K-TSTA-50A)测定糯小麦面粉的总淀粉含量, 减去面粉中直链淀粉含量即为支链淀粉含量。
1.4.2 淀粉粒粒度分布测定方法 采用Malvern Mastersizer 2000激光衍射粒度仪(Malvern, 英国)分析淀粉粒的粒度分布。根据淀粉粒粒径将淀粉分为A型(粒径>10 μm)、B型(粒径2~10 μm)和C型(粒径<2 μm), 计算各品种3种淀粉粒的数目百分率。
1.4.3 破损淀粉含量测定方法 采用SD matic型破损淀粉测定仪(Chopin Technologies, 法国)测定破损淀粉含量[3], 用碘吸收率(Ai%)表示破损淀粉含量。
1.4.4 膨胀势、溶解度和透光率 参照陆大雷等[17]描述的方法测定膨胀势、溶解度和透光率。
1.4.5 黏度特性 利用RVA Super3型快速黏度仪(Newport Scientific, 澳大利亚)测定黏度参数。选用模式标准方法1和标准分析方法1[4]。利用16% (w/v)蔗糖溶液、5% (w/v)氯化钠(NaCl)溶液、5 mmol L-1硝酸银(AgNO3)溶液和5 mmol L-1二硫苏糖醇(DTT)溶液各1 L, 代替蒸馏水, 测定面粉在有机物、无机盐、氧化剂和还原剂中的黏度特性[15]。
1.4.6 热力学特性 称取5 mg淀粉样品, 按1∶2 (w/w)比例加入蒸馏水配成淀粉乳, 密封后置4°C冰箱隔夜平衡。平衡后的样品糊化温度范围为20~100°C, 升温速率为10°C min-1。采用Q10差示扫描量热仪(TA Instruments, 美国)测定淀粉热力学特性[19]。
糊化后的样品在4°C下储藏7 d 后进行回生特性测定, 扫描范围为20~100°C, 升温速率为10°C min-1。
回生度DR% = ΔH / ΔH′ × 100%
式中, ΔH表示热焓值, ΔH′表示回生时的热焓值。
1.5 统计分析
利用Microsoft Excel 2010软件处理数据, DPS 7.05软件进行方差分析, LSD法比较不同小麦品种理化特性参数差异。2 结果与分析
2.1 蛋白质、淀粉含量及淀粉粒数目分布
糯与非糯小麦面粉蛋白质含量平均为12.63%, 宁糯麦1号最高, 为13.65%, 扬麦16最低, 为11.54%, 4个小麦品种淀粉中蛋白质含量仅为0.32%, 品种间差异不显著。糯小麦淀粉中直链淀粉含量平均为0.62%, 非糯小麦淀粉中直链淀粉含量为29.23%。4个品种淀粉中支链淀粉含量均表现为糯小麦高于非糯小麦, 淀粉中直链淀粉含量高于相应面粉中的含量(表1)。Table 1
Table 1Contents of protein,amylose and amylopectin and the percentages of three types of starch granule in different wheat cultivars(%)
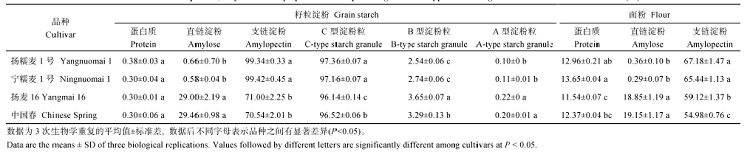 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
4个小麦品种均以C型淀粉粒为主, 数目百分比为96.14%~97.36%, 糯小麦C型淀粉粒数目百分比显著高于非糯小麦, B型和A型淀粉粒数目百分比显著低于非糯小麦(表1)。
2.2 破损淀粉、溶解度、膨胀势及透光率
2个糯小麦品种面粉的破损淀粉(Ai%)含量平均为70.76%, 显著低于非糯小麦破损淀粉含量(90.98%)。淀粉中破损淀粉含量低于面粉中破损淀粉的含量, 品种间宁糯麦1号破损淀粉含量最低, 扬麦16破损淀粉含量最高, 与品种相对应面粉变化趋势基本一致。非糯小麦淀粉中破损淀粉含量较面粉中破损淀粉含量下降的幅度小于糯小麦(表2)。Table2
Table2Differences in the contents of damaged starch,solubility,swelling power and transmittance between grain starch and flour in different wheat cultivars
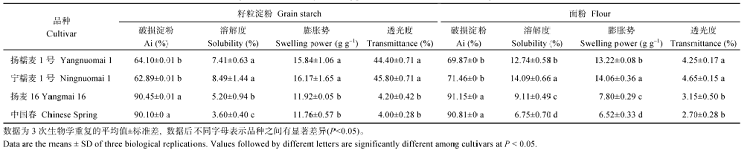 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
两种类型小麦均表现出面粉溶解度大于淀粉溶解度, 糯小麦面粉的溶解度高于非糯小麦, 其中宁糯麦1号面粉的溶解度最大, 达到14.09%, 扬糯麦1号其次, 中国春最低, 仅为6.75%。这3个品种的淀粉溶解度分别为8.49%、7.41%和3.60% (表2)。
糯小麦膨胀势显著高于非糯小麦, 淀粉的膨胀势又高于面粉, 品种间表现为宁糯麦1号>扬糯麦1号>扬麦16>中国春(表2)。
糯与非糯小麦面粉的透光率变化在2.70%~ 4.65%之间, 糯小麦面粉透光率高于非糯小麦, 差异显著, 2个糯小麦淀粉的平均透光率为45.10%, 显著高于相应面粉的透光率; 非糯小麦淀粉的平均透光率为4.10%, 略高于相应面粉的透光率(表2)。
2.3 淀粉与面粉的黏度特性
2.3.1 不同品种淀粉和面粉的黏度特性 糯小麦面粉RVA谱在3.6 min左右达到峰值黏度, 之后迅速下降, 冷却过程中曲线只有小幅度上升, 最终黏度低于峰值黏度。糯小麦淀粉RVA谱变化趋势与面粉基本一致, 品种间有差异, 扬糯麦1号淀粉与面粉峰值黏度差异不显著, 宁糯麦1号淀粉峰值黏值显著高于面粉。非糯小麦面粉到达峰值黏度的时间早于淀粉。扬麦16淀粉的低谷黏度和最终黏度高于面粉, 反弹值低于面粉; 中国春淀粉的低谷黏度高于面粉, 反弹值、最终黏度低于面粉(图1)。图1
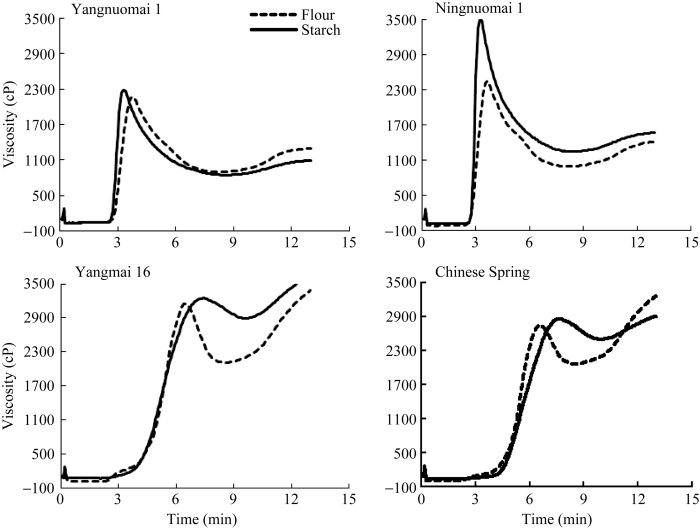 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1小麦籽粒淀粉与面粉RVA图谱
Fig. 1Viscosity curves of grain starch and flour in different wheat cultivars
2个糯小麦面粉的糊化温度与相应淀粉相似, 而2个非糯小麦的面粉糊化温度均有不同程度的下降(1.95~14.47°C, 数据未列出), 说明非糯小麦淀粉到达峰值黏度所需要的温度高于面粉。
2.3.2 不同处理对籽粒面粉黏度特性的影响 用抑制α-淀粉酶活性的AgNO3氧化剂处理后, 4个小麦品种均表现峰值黏度、低谷黏度和最终黏度显著增加(图2), 糯小麦峰值黏度值增加最显著, 扬糯麦1号增加72.39%, 宁糯麦1号增加63.97%。
图2
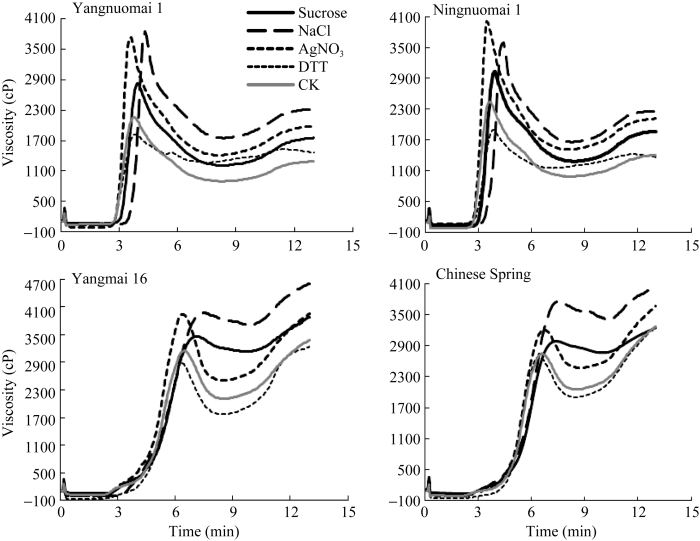 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2不同处理对小麦籽粒面粉黏度的影响
Fig. 2Viscosity curves of flour in different wheat cultivars under different treatments
用改变蛋白质分子结构的DTT还原剂处理后, 非糯小麦峰值黏度、低谷黏度和最终黏度略低于未处理的面粉, 糯小麦面粉经DTT处理后峰值黏度显著低于未处理的面粉, 扬糯麦1号峰值黏度下降15.70%, 宁糯麦1号峰值黏度下降22.71%, 最终黏度和低谷黏度略高于或接近未处理的面粉。
添加蔗糖和氯化钠处理使4个品种面粉的峰值黏度、低谷黏度和最终黏度显著增加, 糯小麦峰值黏度增加较非糯小麦更显著。氯化钠促进峰值黏度、低谷黏度和最终黏度增加的效应大于蔗糖。蔗糖和氯化钠处理后均延长了小麦面粉到达峰值黏度的时间, 氯化钠延时的作用更显著。
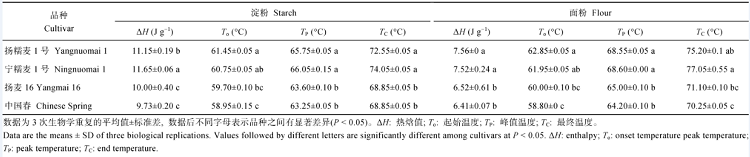
2.4 淀粉与面粉的热力学特性
小麦淀粉热焓值为宁糯麦1号>扬糯麦1号>扬麦16>中国春; 面粉热焓值显著低于淀粉热焓值, 4个品种面粉热焓值比淀粉平均降低34%, 但面粉的起始温度、峰值温度和最终温度高于相应淀粉。糯小麦面粉和淀粉的热焓值高于非糯小麦, 具有较高的起始温度、峰值温度和最终黏度(表3)。Table 3
Table 3Differents in thermal properties between wheat starch and flour among cultivars
 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
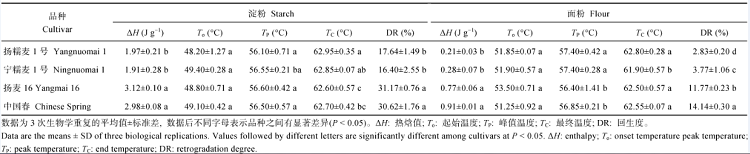
将糊化后的样品置4°C冰箱冷藏7 d后, 回生参数均低于其热力学参数值, 其中起始温度、峰值温度和最终温度均降低10°C左右。糯小麦面粉的平均回生度为3.30%, 显著低于非糯小麦12.96%的回生度, 同一品种面粉的回生度显著低于淀粉(表4)。
Table 4
Table 4Different in retrogradation properties between wheat starch and flour among cultivars
 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
3 讨论
刘希伟等[20]根据淀粉粒径, 将淀粉粒分为A型(>10 μm)和B型(<10 μm)。本研究以2 μm和10 μm为界限, 将淀粉粒分为A型(>10 μm)、B型(2~10 μm)和C型(<2 μm), 糯小麦中C型淀粉粒百分比高于非糯小麦, 与Zhang等[21]认为糯小麦中小型淀粉粒偏多的观点一致。破损淀粉含量影响面粉的吸水率, 提高对酶的敏感性, 改变面粉的特性[22]。与以往研究结果[3]一致, 本研究也发现非糯小麦破损淀粉含量高于糯小麦, 同一品种面粉的破损淀粉含量略高于淀粉的破损淀粉含量, 这可能是因为面粉是通过机械碾压制取, 淀粉是通过种子浸泡后水磨获得, 造成面粉中淀粉粒的破损程度增加, 也可能是引起面粉与淀粉糊化特性差异的原因之一。Tester等[23]认为, 支链淀粉可增加淀粉的吸水膨胀, 加速颗粒糊化, 而直链淀粉和脂肪的作用是抑制或延缓膨胀和糊化; 但也有研究表明, 淀粉糊的透光程度直接受淀粉膨胀程度的影响, 具有较高膨胀势的淀粉透光率也较高[24,25]。本试验结果表明, 4个小麦品种淀粉膨胀势和透光度的变化趋势一致, 均为宁糯麦1号>扬糯麦1号>扬麦16>中国春, 其中糯小麦淀粉透光率高达45%, 说明糯小麦因直链淀粉与脂肪复合物含量低, 对淀粉膨胀抑制作用小, 淀粉膨胀程度和透光率显著提高。4个品种淀粉的膨胀势、透光度高于面粉, 主要是因为脱蛋白质和脱脂肪后的淀粉粒接触到更多水分子, 有利于淀粉粒的膨胀, 膨胀势增加; 面粉中蛋白质、脂肪等物质的存在, 阻碍了光束的通过, 从而使得面粉的透光率降低。另外, 面粉的溶解度高于淀粉, 糯小麦高于非糯小麦。面粉溶解度高于淀粉的原因可能是面粉中存在一些易溶于水的糖类和无机盐类物质, 这些物质的溶解增加了溶质的质量, 糯小麦面粉溶解度也与其籽粒中具有较高的糖类物质有关[26]。Schirmer等[27]认为, 糯性淀粉具有较强的蓄水能力和较高的黏度特性, 膨胀的淀粉粒特别容易破裂, 高直链淀粉含量能够阻止大量淀粉粒的膨胀, 导致黏度降低。本研究中糯小麦品种面粉的低谷黏度、最终黏度、反弹值、峰值时间和糊化温度均低于非糯小麦, 而稀澥值高于非糯小麦。扬糯麦1号淀粉与面粉峰值黏度差异不大, 宁糯麦1号淀粉峰值黏度显著高于面粉峰值黏度, 推测2个糯小麦品种支链淀粉的精细结构上可能存在差异。
面粉中的α-淀粉酶活性影响淀粉的糊化特性[28]。姚金宝等[15]认为, 无论是糯小麦还是非糯型品系, 加氧化剂AgNO3处理的RVA峰值黏度和最终黏度明显高于不加AgNO3处理的品系, 对糯小麦品系的影响较大, 这主要是AgNO3抑制α-淀粉酶活性的缘故, 本研究结果与之一致, AgNO3处理对2个糯小麦面粉中α-淀粉酶活性的抑制作用大于对非糯小麦, 说明糯小麦面粉中α-淀粉酶活性显著高于非糯小麦, 是抑制糯小麦面粉峰值黏度升高的主要原因; 此外, 扬糯麦1号淀粉峰值粘度显著低于宁糯麦1号峰值粘度, 推测一方面可能与支链淀粉精细结构有关, 另一方面可能与扬糯麦1号淀粉中α-淀粉酶活性高有关, 具体原因有待深入研究。在淀粉糊化加热过程中, 支链淀粉粒吸水膨胀形成分散相, 蛋白质吸水变性和部分直链淀粉溶于热水形成黏稠相, 还原剂DTT处理后, 打破了二硫键削弱谷蛋白基质作用, 糊液稳定性变差, 淀粉粒容易破裂, 表现为稻米峰值黏度和崩解值下降[14], 本试验结果与前人研究结果基本一致, 因品种类型不同而异, 对糯小麦的影响程度大于非糯小麦, 这与糯小麦蛋白质含量高有关[10]。外源添加蔗糖以及氯化钠均影响了面粉的黏度特性, 添加蔗糖提高糊化温度[16]。本研究明确了氯化钠处理对面粉峰值黏度、低谷黏度、最终黏度影响的效应高于蔗糖处理, 由此说明面粉中α-淀粉酶活性、糖含量、蛋白结构、以及食品生产过程中添加的有机化合物、盐类等均会影响面粉的黏度特性, 这是导致淀粉与面粉黏度特性差异的原因之一。
Yasui等[29]研究表明, 糯小麦淀粉与其非糯亲本相比具有高的糊化温度和热焓值。本研究中糯小麦热焓值高于非糯小麦, 同一品种面粉与淀粉的热力学参数存在差异, 表现为小麦面粉的热焓值低于淀粉。其原因可能是面粉中的蛋白质和戊聚糖能与面粉体系中的淀粉竞争自由水, 导致淀粉吸收的自由水减少, 从而使面粉的糊化热焓值降低[30]。直链淀粉含量是影响淀粉回生特性最主要的因素, 较高的直链淀粉含量具有较强的回生趋势[20,31]。本试验结果表明, 糯小麦面粉以及淀粉的回生度均低于非糯小麦, 与直链淀粉含量表现一致。相同品种面粉糊化的起始温度、峰值温度和最终温度均高于淀粉, 而热焓值和回生度则低于淀粉, 主要原因是面粉中的蛋白质妨碍了淀粉分子之间的相互聚拢, 不利于微晶束的形成, 此外, 面粉中直链淀粉-脂质复合物的存在也会降低回生度[13,32-33]。
4 结论
不同类型小麦淀粉与面粉理化特性存在差异, 淀粉的破损淀粉含量低于面粉, 淀粉糊化的起始温度、峰值温度和最终温度均低于面粉, 热焓值和回生度高于面粉, 淀粉的膨胀势和透光度显著高于面粉, 溶解度低于面粉。除了直、支链淀粉含量外, 面粉中蛋白质、脂肪、糖类物质以及面粉中α-淀粉酶活性是造成面粉与淀粉理化特性差异的主要原因。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/BF00225757URLPMID:24162229 [本文引用: 1]

Starch granule proteins (SGPs) of common wheat ( Triticum aestivum L.) were analyzed by two electrophoretic techniques: sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis ( SDS-PAGE ) and two-dimensional electrophoresis (2D-PAGE). These analyses identified three kinds of SGPs which were tentatively designated SGP-1 , SGP-2 and SGP-3. SDS-PAGE resolved the products of three homoeologous genes for SGP-1 into three protein fractions, SGP-A1, -B1 and -D1. While SDS-PAGE resolved SGP-3 into one fraction, 2D-PAGE separated it into three protein fractions encoded by homoeologous genes Sgp-A3 , B3 and - D3 . SGP-2 was detected as one protein by SDS-PAGE and was present as one protein on 2D-PAGE. Aneuploid (nullisomic-tetrasomic and ditelosomic) analyses in the cultivar Chinese Spring showed that the genes for two SGPs ( SGP-1 and -3) were located on the short arms of group-7 chromosomes. The results obtained from deletion lines for chromosome arms 7AS, 7BS and 7DS suggested that the gene order along the arms is 鈥榗entromere- Sgp-1-Sgp-3-Wx 鈥. An electrophoretic survey of wheat germ plasm identified a few cultivars lacking one of the proteins SGP-A1, -B1, -D1, SGP-A3 and -B3. The null alleles Sgp-A1b, Sgp-B1b and Sgp-D1b will be useful for the production of a variant wheat lacking SGP-1 .
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2007.07.013URL [本文引用: 3]

选用非糯性强筋、中筋、弱筋小麦品种和糯性小麦品种(系),研究 了淀粉理化特性的差异.结果表明,糯性与非糯性小麦RVA图谱具有明显的差异.峰值黏度、低谷黏度、最终黏度、峰值时间、糊化温度等黏度特征值,糯小麦均 显著低于非糯性品种,同一类型不同品种间RVA图谱差异主要是在峰值黏度之后的曲线变化;破损淀粉含量为强筋>中筋>弱筋>糯小麦.糯性与非糯性小麦品种 面粉的X-衍射图谱均呈现A型特征,晶体结构差异主要表现在峰值的大小,结晶度变化范围为28.97%~36.97%.相关分析表明,直链淀粉含量、直/ 支比、破损淀粉含量对淀粉黏度特性有重要的影响,而结晶度对黏度特性影响不显著.
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2007.07.013URL [本文引用: 3]

选用非糯性强筋、中筋、弱筋小麦品种和糯性小麦品种(系),研究 了淀粉理化特性的差异.结果表明,糯性与非糯性小麦RVA图谱具有明显的差异.峰值黏度、低谷黏度、最终黏度、峰值时间、糊化温度等黏度特征值,糯小麦均 显著低于非糯性品种,同一类型不同品种间RVA图谱差异主要是在峰值黏度之后的曲线变化;破损淀粉含量为强筋>中筋>弱筋>糯小麦.糯性与非糯性小麦品种 面粉的X-衍射图谱均呈现A型特征,晶体结构差异主要表现在峰值的大小,结晶度变化范围为28.97%~36.97%.相关分析表明,直链淀粉含量、直/ 支比、破损淀粉含量对淀粉黏度特性有重要的影响,而结晶度对黏度特性影响不显著.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1094/CCHEM.1997.74.1.63URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1094/CCHEM.1997.74.1.72URL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract In our wheat breeding program to introduce the low amylose character of Tanikei A6099 to elite lines, five waxy lines were unexpectedly obtained from 249 doubled haploid lines of the F1 hybrid of Saikai 168 x Tanikei A6099. The amylose content of all the waxy lines was <1% and the blue value was <0.1. Starch granule-bound proteins were extracted and subjected to modified sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The waxy lines lacked the Wx protein. Starch paste viscosity measurements gave pasting profiles of waxy wheat starch that were quite different from those of nonwaxy wheats but similar to those of waxy maize. However, the peak viscosity of waxy wheats was much higher than that of the waxy maize.
URL [本文引用: 1]

Starches were isolated from 12 waxy and six nonwaxy genotypes of grown in adjacent field plots to minimize edaphic variation. (AP) in all of the starches appeared to be very similar in structure. For the colorimetric determination of (AM), a revised calibration curve was necessary because AP gave a lower lambda(max) (529 nm) and absorbance with I2/KI reagent than AP from other cereal starches used previously. The waxy starches contained AM (< 7.4%) and (120-630 mg/100 g), giving an AM-relationship (r = 0.990) different from that in the nonwaxy starches; the B-granules in the waxy starches had about half of the AM and found in the A-granules. The fatty acid composition of the in the waxy starches was much more saturated than in the nonwaxy starches, and it was negatively correlated with total content. swelling at 70 and 80 degrees C, after gelatinization (disordering) of AP is complete, is a property of the whole AP molecule. Swelling factors for the AP fraction, over the range of 4-35 for all starches from the present and previous studies, were inversely correlated with content (r = -0.918, n = 30).
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-1041.2001.02.003URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

以江苏白火麦(缺失Wx-Dl)和关东107(缺失Wx-Al和Wx-Bl)为亲本配制杂交组合,采用花粉和籽粒剖面染色、蛋白质电泳进行筛选和鉴定,人工创造得到自然界不存在的糯性小麦,并对其直链淀粉含量及淀粉品质性状进行研究。结果表明,所得到的两个糯性小麦吕系直链淀粉含量很低(小于1%),其糊化特性、膨胀势特性亦与普通小麦品种不同;RVA高峰粘度明显低于其亲本,其高峰粘度出现较快,而且反弹值不明显;其淀粉膨胀能力远大于亲本。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-1041.2001.02.003URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

以江苏白火麦(缺失Wx-Dl)和关东107(缺失Wx-Al和Wx-Bl)为亲本配制杂交组合,采用花粉和籽粒剖面染色、蛋白质电泳进行筛选和鉴定,人工创造得到自然界不存在的糯性小麦,并对其直链淀粉含量及淀粉品质性状进行研究。结果表明,所得到的两个糯性小麦吕系直链淀粉含量很低(小于1%),其糊化特性、膨胀势特性亦与普通小麦品种不同;RVA高峰粘度明显低于其亲本,其高峰粘度出现较快,而且反弹值不明显;其淀粉膨胀能力远大于亲本。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2007.12.032URL [本文引用: 1]

[目的]对Wx蛋白缺失影响小麦淀粉理化特性和面条加工品质的情况进行探讨.[方法]以6类 Wx蛋白组成的14个品种为试材,测定其淀粉理化特性和面条品质,进行统计分析.[结果]Wx亚基的数目对其酶蛋白和直链淀粉含量有显著影响,随着Wx亚 基数目的增加,Wx蛋白和直链淀粉含量相应升高,面粉膨胀势和峰值粘度呈现下降的趋势,但面条品质的变化并不表现完全一致.糯小麦绝大部分淀粉理化指标显 著较低.不同Wx亚基对淀粉理化特性和面条品质的影响也存在一定的差异,缺失Wx-B1亚基对直链淀粉合成的影响最大,其次是Wx-D1亚基,缺失Wx- A1亚基作用最小.3类单一Wx亚基缺失材料中,Wx-B1亚基缺失品种直链淀粉含量最低,膨胀势和RVA峰值粘度最高,面条评分最高.[结论]从不同 Wx亚基缺失类型小麦品种看,面条评分与直链淀粉含量、膨胀和糊化特性之间并不是简单的直线关系,尤其是直链淀粉含量,而是有一个合适的范围,在这个范围 内随着直链淀粉含量的下降,膨胀势和峰值粘度升高,面条评分上升,超出这一范围面条评分下降.
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2007.12.032URL [本文引用: 1]

[目的]对Wx蛋白缺失影响小麦淀粉理化特性和面条加工品质的情况进行探讨.[方法]以6类 Wx蛋白组成的14个品种为试材,测定其淀粉理化特性和面条品质,进行统计分析.[结果]Wx亚基的数目对其酶蛋白和直链淀粉含量有显著影响,随着Wx亚 基数目的增加,Wx蛋白和直链淀粉含量相应升高,面粉膨胀势和峰值粘度呈现下降的趋势,但面条品质的变化并不表现完全一致.糯小麦绝大部分淀粉理化指标显 著较低.不同Wx亚基对淀粉理化特性和面条品质的影响也存在一定的差异,缺失Wx-B1亚基对直链淀粉合成的影响最大,其次是Wx-D1亚基,缺失Wx- A1亚基作用最小.3类单一Wx亚基缺失材料中,Wx-B1亚基缺失品种直链淀粉含量最低,膨胀势和RVA峰值粘度最高,面条评分最高.[结论]从不同 Wx亚基缺失类型小麦品种看,面条评分与直链淀粉含量、膨胀和糊化特性之间并不是简单的直线关系,尤其是直链淀粉含量,而是有一个合适的范围,在这个范围 内随着直链淀粉含量的下降,膨胀势和峰值粘度升高,面条评分上升,超出这一范围面条评分下降.
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1003-0174.2002.04.003URL [本文引用: 2]

对 5个组合的 13个糯麦F6 (或F5)株系及其亲本的籽粒成分、直链淀粉含量和膨胀势进行测定 ,以及分析了它们的淀粉糊化过程和糊化参数 ,比较它们之间的差异。结果表明 :糯性小麦籽粒的蛋白质含量、湿面筋含量均高于相应的亲本 ;而淀粉含量则低于相应的亲本 ;糯性小麦株系的直链淀粉含量远远低于其亲本 ;糯麦淀粉的膨胀能力和吸水力大于其亲本 ;糯麦株系的RVA高峰粘度、低谷粘度、最后粘度、反弹值和峰值时间显著低于其亲本 ;糯麦株系面粉间的RVA粘度参数值大同小异。讨论了糯性小麦的应用前景。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1003-0174.2002.04.003URL [本文引用: 2]

对 5个组合的 13个糯麦F6 (或F5)株系及其亲本的籽粒成分、直链淀粉含量和膨胀势进行测定 ,以及分析了它们的淀粉糊化过程和糊化参数 ,比较它们之间的差异。结果表明 :糯性小麦籽粒的蛋白质含量、湿面筋含量均高于相应的亲本 ;而淀粉含量则低于相应的亲本 ;糯性小麦株系的直链淀粉含量远远低于其亲本 ;糯麦淀粉的膨胀能力和吸水力大于其亲本 ;糯麦株系的RVA高峰粘度、低谷粘度、最后粘度、反弹值和峰值时间显著低于其亲本 ;糯麦株系面粉间的RVA粘度参数值大同小异。讨论了糯性小麦的应用前景。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2005.05.002URL [本文引用: 1]

Starch properties play an important role in Chinese noodle quality. Eight genotypes from Japanese cultivar 'Kanto 107'/Chinese cultivar 'Baihuo' differing in the presence and absence of three Waxy proteins, Wx-A1, Wx-B1, and Wx-D1, were used to determine the effect of Waxy protein deficiencies on amylose content, starch pasting properties and Chinese fresh noodle quality by using the fractionation and reconstitution procedures. The results showed that amylose content and starch pasting properties were influenced significantly by different Waxy protein. For amylose content, it can be ranked as type 8 (waxy wheat, three proteins )>5 (Wx-B1 and Wx-D1 )>7 (Wx-A1 and Wx-B )>6 (Wx-A and Wx-D ) >3 (Wx-B1)鈮4 (Wx-D1)>2 (Wx-A1). The rank for peak viscosity is 8, 3, 5, 4, 6, 7, 2. Types with Wx-B1 or -D1 performed the best noodle-making quality. Waxy type has higher peak viscosity and breakdown than other types, while it has lower breakdown, pasting temperature and peak time. Amylose content was significantly and positively correlated with TPA parameters hardness, gumminess, and chewiness of cooked noodle (r = 0.83 - 0.87, P<0.01). It also had a significant and negative influence on noodle springiness, adhesiveness, cohesiveness, and resilience (r = -0.53 - -0.83). It was found that a positive and significant correlation among starch pasting property parameters such as hold though, final viscosity, setback, peak time, and pasting temperature and color, appearance, firmness, elasticity, stickiness, flavor and total score of cooked noodle (r = 0.53 - 0.91). Breakdown had a significant and negative influence on those noodle quality traits (r = -0.66 - -0.74).
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2005.05.002URL [本文引用: 1]

Starch properties play an important role in Chinese noodle quality. Eight genotypes from Japanese cultivar 'Kanto 107'/Chinese cultivar 'Baihuo' differing in the presence and absence of three Waxy proteins, Wx-A1, Wx-B1, and Wx-D1, were used to determine the effect of Waxy protein deficiencies on amylose content, starch pasting properties and Chinese fresh noodle quality by using the fractionation and reconstitution procedures. The results showed that amylose content and starch pasting properties were influenced significantly by different Waxy protein. For amylose content, it can be ranked as type 8 (waxy wheat, three proteins )>5 (Wx-B1 and Wx-D1 )>7 (Wx-A1 and Wx-B )>6 (Wx-A and Wx-D ) >3 (Wx-B1)鈮4 (Wx-D1)>2 (Wx-A1). The rank for peak viscosity is 8, 3, 5, 4, 6, 7, 2. Types with Wx-B1 or -D1 performed the best noodle-making quality. Waxy type has higher peak viscosity and breakdown than other types, while it has lower breakdown, pasting temperature and peak time. Amylose content was significantly and positively correlated with TPA parameters hardness, gumminess, and chewiness of cooked noodle (r = 0.83 - 0.87, P<0.01). It also had a significant and negative influence on noodle springiness, adhesiveness, cohesiveness, and resilience (r = -0.53 - -0.83). It was found that a positive and significant correlation among starch pasting property parameters such as hold though, final viscosity, setback, peak time, and pasting temperature and color, appearance, firmness, elasticity, stickiness, flavor and total score of cooked noodle (r = 0.53 - 0.91). Breakdown had a significant and negative influence on those noodle quality traits (r = -0.66 - -0.74).
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2006.05.012URL [本文引用: 2]

通过分析蛋白酶或还原剂二巯基苏糖醇(DTT)分别去除稻米蛋白质或打破蛋白质二硫键后,稻 米RVA(Rapid Visco Analyzer)特征谱形成和特征值的变化,研究蛋白质对淀粉RVA特征谱的影响,以及对米饭食味品质的作用。在淀粉糊化过程中,蛋白质使RVA特征谱 的峰值黏度、冷胶黏度等值升高,改变RVA线性上升段的斜率。蛋白质可能通过二硫键结合形成的蛋白质网络本身和通过吸水减少淀粉水合的有效水量,协同提高 糊化多相体系的浓度,增强分散相与黏稠相的互作。蛋白质影响米饭食味品质,可能通过改变米粒的吸水性而起作用。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2006.05.012URL [本文引用: 2]

通过分析蛋白酶或还原剂二巯基苏糖醇(DTT)分别去除稻米蛋白质或打破蛋白质二硫键后,稻 米RVA(Rapid Visco Analyzer)特征谱形成和特征值的变化,研究蛋白质对淀粉RVA特征谱的影响,以及对米饭食味品质的作用。在淀粉糊化过程中,蛋白质使RVA特征谱 的峰值黏度、冷胶黏度等值升高,改变RVA线性上升段的斜率。蛋白质可能通过二硫键结合形成的蛋白质网络本身和通过吸水减少淀粉水合的有效水量,协同提高 糊化多相体系的浓度,增强分散相与黏稠相的互作。蛋白质影响米饭食味品质,可能通过改变米粒的吸水性而起作用。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-1041.2005.06.007URLMagsci [本文引用: 3]

为了明确普通小麦缺失不同W x蛋白对直链淀粉含量的影响以及部分糯小麦品系的淀粉特性,采用单向改良SDS-PAGE方法对1个非糯×糯杂交组合F2分离群体的196个单籽粒进行了W x蛋白筛选,测定了这批籽粒的直链淀粉含量,同时测定了1个部分糯小麦品系(缺失W x-B 1和W x-D 1)和2个正常型小麦品系粗面粉的直链淀粉含量、膨胀势和RVA粘度。结果表明,缺失1对W x蛋白的直链淀粉含量比正常型降低3.29~7.15个百分点,缺失2对W x蛋白的比正常型降低9.45~13.82个百分点,缺失3对W x蛋白的直链淀粉含量几乎为0;缺失W x-B 1和W x-D 1的部分糯小麦品系粗面粉的直链淀粉含量比正常型降低5.62~7.49个百分点,膨胀势则增加4.51~4.72,RVA高峰粘度显著高于正常型。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-1041.2005.06.007URLMagsci [本文引用: 3]

为了明确普通小麦缺失不同W x蛋白对直链淀粉含量的影响以及部分糯小麦品系的淀粉特性,采用单向改良SDS-PAGE方法对1个非糯×糯杂交组合F2分离群体的196个单籽粒进行了W x蛋白筛选,测定了这批籽粒的直链淀粉含量,同时测定了1个部分糯小麦品系(缺失W x-B 1和W x-D 1)和2个正常型小麦品系粗面粉的直链淀粉含量、膨胀势和RVA粘度。结果表明,缺失1对W x蛋白的直链淀粉含量比正常型降低3.29~7.15个百分点,缺失2对W x蛋白的比正常型降低9.45~13.82个百分点,缺失3对W x蛋白的直链淀粉含量几乎为0;缺失W x-B 1和W x-D 1的部分糯小麦品系粗面粉的直链淀粉含量比正常型降低5.62~7.49个百分点,膨胀势则增加4.51~4.72,RVA高峰粘度显著高于正常型。
DOI:10.1021/bp00014a012URL [本文引用: 2]

Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to evaluate the effects of sugar and emulsifier interactions on gelatinization temperatures of three different starches. A constant weight ratio of starch to sugar to water (1:1.5:1.5), typical in high-ratio cake batters, was used in the DSC. Sucrose exhibited a greater effect than glucose on raising gelatinization temperatures. However, with lactose, typical complete gelatinization endotherms could not be observed because of the peak for large lactose crystal melting. Therefore, the solubility of the sugars may have an important effect on starch gelatinization. Low emulsifier concentrations (0.6%) did not appear to change DSC starch gelatinization temperatures. Sugars and emulsifiers may interact and affect the gelatinization temperature ranges.
URL [本文引用: 2]

以4个糯玉米品种为材料,比较分析了糯玉米粉、淀粉(脱蛋白)和脱脂淀粉(脱蛋白脱脂)的理化特性。结果表现,脱蛋白或脱蛋白脱脂处理不改变材料的结晶类型,各材料均表现为典型的"A"型衍射图谱。理化特性在糯玉米粉、淀粉和脱脂淀粉间存在显著差异。结晶度、膨胀势、回复值、峰值时间和糊化温度以糯玉米粉最高,脱脂淀粉最低;溶解度、峰值黏度和谷值黏度以淀粉最高,米粉最低;透光率以脱脂淀粉最高,米粉最低;但4个糯玉米品种的终值黏度变化趋势不甚明显。
URL [本文引用: 2]

以4个糯玉米品种为材料,比较分析了糯玉米粉、淀粉(脱蛋白)和脱脂淀粉(脱蛋白脱脂)的理化特性。结果表现,脱蛋白或脱蛋白脱脂处理不改变材料的结晶类型,各材料均表现为典型的"A"型衍射图谱。理化特性在糯玉米粉、淀粉和脱脂淀粉间存在显著差异。结晶度、膨胀势、回复值、峰值时间和糊化温度以糯玉米粉最高,脱脂淀粉最低;溶解度、峰值黏度和谷值黏度以淀粉最高,米粉最低;透光率以脱脂淀粉最高,米粉最低;但4个糯玉米品种的终值黏度变化趋势不甚明显。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.04.066URL [本文引用: 1]

利用差示扫描量热仪结合Avrami方程考察了8种不同小麦淀粉与面粉糊化和回生特性,探讨了直链淀粉和蛋白含量对其热力学行为产生的影响,并用SPSS软件计算其相关性。结果表明:对于淀粉与面粉体系,直链淀粉含量与糊化热焓值△H呈较显著的负相关,与Avrami指数n呈弱的负相关,而与速率常数k呈较显著的正相关,与最大回生度DR呈一定的正相关;对于面粉体系,蛋白含量与面粉糊化热焓值△Hf呈一定的负相关,与面粉体系Avrami指数nf和速率常数kf分别呈弱的正相关和较显著的负相关,与面粉体系最大回生度DRf呈弱的正相关。
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.04.066URL [本文引用: 1]

利用差示扫描量热仪结合Avrami方程考察了8种不同小麦淀粉与面粉糊化和回生特性,探讨了直链淀粉和蛋白含量对其热力学行为产生的影响,并用SPSS软件计算其相关性。结果表明:对于淀粉与面粉体系,直链淀粉含量与糊化热焓值△H呈较显著的负相关,与Avrami指数n呈弱的负相关,而与速率常数k呈较显著的正相关,与最大回生度DR呈一定的正相关;对于面粉体系,蛋白含量与面粉糊化热焓值△Hf呈一定的负相关,与面粉体系Avrami指数nf和速率常数kf分别呈弱的正相关和较显著的负相关,与面粉体系最大回生度DRf呈弱的正相关。
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.09.030URLPMID:24076202 [本文引用: 1]

Morphological features, granule composition, and physicochemical properties of waxy wheat starch were compared with those of normal wheat starch. The morphologies and granule populations were found to be similar for the two starches. However, waxy wheat starch contained a smaller proportion of B-type granules, had a larger average granule diameter, and a higher degree of crystallinity than normal wheat starch, as measured by particle size analysis and differential scanning calorimetry. These differences resulted in a higher gelatinization temperature, transition enthalpy, peak viscosity, breakdown, swelling power, lower peak viscosity temperature and final viscosity in waxy wheat starch. These points suggest that waxy wheat starch should have greater resistance to retrogradation during cooling and higher water-holding capacity under dry conditions. Highlighting the differences in physicochemical properties of waxy and normal wheat starches should help point toward effective applications of waxy wheat starch in the food industry.
DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.075URLPMID:26920275 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract The influence of damaged starch (DS) on the quality of frozen dough and steamed bread were investigated. Characterization of the farinographical properties showed that DS levels affected water absorption, development, weakness, falling number and gluten index. Flour viscosity profiles indicated that pasting temperatures increased, but peak viscosity, low viscosity, breakdown, final viscosity and setback increased and then decreased with increasing amounts of DS. Compared to leavened dough, unleavened dough had significantly higher peak times, of T21 and T22, and was also affected by DS concentration. Steamed bread had a higher specific volume, relatively lower hardness, exhibited more whiteness, and a higher degree of gumminess and chewiness with higher DS levels. We compared two methods of making steamed bread and assessed the quality of the product. We found that an appropriate DS content improved the quality of frozen dough and steamed bread. This study provides the basis for future development and improvements to methods for making frozen dough products. Copyright 漏 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
URL [本文引用: 1]

ABSTRACT A method was developed for measuring the volume of water absorbed by starch-granules heated in excess water, based on the observation that blue dextran dye (molecular weight 2 X 106) will dissolve in supernatant and interstitial water but not in the
DOI:10.1016/0963-9969(96)00016-6URL [本文引用: 1]

Starch from wild rice ( Zizania palustris L) was isolated and yielded only 38.3% on a whole seed basis, compared with 64.4% starch yield from long grain brown rice ( Oryza sativa indica ). The granules were angular to polygonal in shape with a diameter of 2–8 μm, similar to starch granules from long grain brown rice. Scanning electron micrographs revealed the presence of smooth granular surfaces. Lipids were extracted by acid hydrolysis and by selective solvent extraction with chloroform-methanol 2:1 v/v at ambient temperature, followed by n-propanol-water 3:1 v/v at 90–100 °C. The acid-hydrolyzed extracts which represented the total starch lipids averaged 0.29%. The free lipid in the chloroform-methanol extract was 0.04%, whereas the free and bound lipids in the n-propanol-water extracts totalled 0.24%. The amylose content of wild rice starch was 29.4%, of which 28.6% was complexed by native lipids. The gelatinization temperature range was 51–64 °C and the enthalpy of gelatinization was 7.5 J/g. The viscoamylographic examination on starch pastes (6% w/v) showed high thermal stability during the holding cycle (at 95 ° C), and the absence of a set-back on cooling. Native starch was readily hydrolyzed by α-amylase (92.3% in 72 h) and 2.2 N HCl (99.0% in 20 days). Differential scanning calorimetry and acid hydrolysis studies on stored gels showed that wild rice starch was resistant to retrogradation.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.11.033URL [本文引用: 1]

Straight-grade flours roller-milled from seven waxy and two control (nonwaxy and partial waxy) wheats ( Triticum aestivum ) were wet-milled by dough-washing (DW) and dough-dispersion and centrifugation (DD&C) methods to give starch, gluten, tailings, and water-solubles fractions. Compared to the controls, flour yields of the waxy wheats were lower. The waxy flours contained more crude fat and pentosans and less total starch. Gluten proteins of the waxy flours appeared to be weaker. By the DW method, both of the controls but only two of the seven waxy flours could be wet-milled. The remaining five waxy flours failed in the DW method as their doughs lost cohesiveness and elasticity during kneading and washing under water. Those waxy flours were instead wet-milled by the modified DW method, where the doughs were gently hand-rubbed on a 125-m opening screen to facilitate the passage of the starch and water-solubles through while retaining the gluten agglomerates on the screen. The prime starch and tailings of the waxy flours were not separated as visibly as those of the controls during their centrifugal purification, which in turn led to a reduction in yields and purities of their prime starch and gluten fractions. On the other hand, the wet-milling characteristics of the waxy flours by the DD&C method were comparable to those of the controls because the DD&C method is apparently less dependent than the DW method on the gluten aggregation traits of flours.
DOI:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.11.032URL [本文引用: 1]

Starch-rich raw materials are widely used in the food industry. Their functionality and end-use applications are markedly influenced by starch characteristics. Starches with varying amylose (AM) and amylopectin (AP) content are of particular interest due to their ability to influence and modify the texture, quality and stability of starch-based food products. The present study shows the influence of the AM/AP content on physicochemical and morphological properties of a range of starches (Maize = 3%, 23%, 71%; Potato = 2%, 21%; Wheat = 28; Barley 3%, 25% AM content w/w of starch).Starches have been analyzed in terms of their chemical composition, water retention capacity, morphological characteristics, and pasting/thermal properties. The changes in starch granule morphology during gelatinization were monitored by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The different analysis revealed that waxy-starches (AP>90%) had a high water retention capacity (1.2-1.5 times higher) and developed higher paste viscosities (up to 40% for maize; 43% for barley). The swollen granules were highly susceptible to mechanical breakdown and solubilized faster. Higher AM contents showed inhibition of an extensive granule swelling and lowered the paste viscosity. The exceptional integrity of the high-AM starch even prevented its gelatinization at atmospheric pressure. Significant differences in physicochemical and morphological properties between the starches from regular, high-AM and waxy strains have become evident, no direct relationship between the AM/AP contents and the internal growth ring structures of the starch granules could be identified by CLSM. The waxy starches had a higher gelatinization temperature (up to 2 degrees C) and enthalpy (up to 20%), which indicates a higher crystalline and molecular order. (c) 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
DOI:10.1094/CCHEM-10-14-0209-RURL [本文引用: 1]

To realize the full potential of waxy wheat, the pasting properties of hard waxy wheat flours as well as factors governing the pasting properties were investigated and compared with normal and partial waxy wheat flours. Starches isolated from six hard waxy wheat flours had similar pasting properties, yet their corresponding flours had very different pasting properties. The differences in pasting properties were narrowed once endogenous a-amylase activity in waxy wheat flours was inhibited by silver nitrate. Upon action of protease, the extent of protein digestibility determined viscosity profile in waxy wheat flours. Waxy wheat starch granules swelled more extensively and were more prone to a-amylase degradation than normal wheat starch. A combination of endogenous a-amylase activity and protein matrix contributed to a large variation in pasting properties of waxy wheat flours.
DOI:10.1006/jcrs.1996.0046URL [本文引用: 1]

Starch was isolated from the endosperm of three recently developed waxy wheat lines and their parents. Their amylose and lipid contents, amylopectin structures and gelatinisation properties were evaluated. The endosperm starch from waxy wheat lines is composed essentially of amylopectin. The apparent amylose (1·2–2·0 g/100 g) and lipid contents (0·12–0·29 g/100 g) are much lower than the apparent amylose (26·0–28·4 g/100 g) and lipid contents (1·05–1·17 g/100 g) of their non-waxy parents. The amylopectin of waxy wheat lines is structurally identical to that of the parents. The peak gelatinisation temperature and gelatinisation enthalpy for waxy starch are significantly higher than for non-waxy starch, but the gelatinisation enthalpy for the amylopectin fraction of waxy starch is nearly identical to that of non-waxy starch.
DOI:10.1002/star.200400298URL [本文引用: 1]

Abstract The ageing of non-expanded wheat starch extrudates containing 37% and 51% water on a dry solids basis (d.s.b.) at 25°C was studied using Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), Wide Angle X-ray Diffraction (XRD), proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) relaxometry and Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analysis (DMTA). The retrogradation rate increased with water content (650.02h 611 at 37% water (d.s.b.) compared to 650.06h 611 at 51%). While a good correlation was found between the DSC, XRD and NMR data, the kinetics of retrogradation measured by DMTA was delayed. The findings were interpreted in terms of the different molecular processes probed by the different techniques. In addition to the kinetics, information on the physical structure of the partially crystalline retrograded materials were obtained. DSC suggested a broad bimodal melting behaviour, which was attributed to the melting of the crystalline structure followed by the dissociation of the double helices. XRD suggested that at both water contents, the recrystallisation of amylopectin led principally to the A-polymorph. DMTA suggested a significant interaction between the amorphous and crystalline phases, with a requirement of a minimum relative crystallinity index of 650.8 (e.g. 6580% of the crystallinity index of the fully retrograded material), before any increase in the elastic modulus (at 25°C) was measured.
DOI:10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00130-9URL [本文引用: 1]

The physico-chemical, morphological, thermal and rheological properties of the starches separated from different potato cultivars (Kufri Jyoti, Kufri Badshah and Pukhraj) were studied. The starches separated from the mealier cultivars (Kufri Jyoti and Kufri Badshah) showed lower transition temperatures ( T o; T p and T c), peak height indices (PHI), and higher gelatinization temperature range ( R) and enthalpies of gelatinization (Δ H gel) than the starch from the least mealy cultivar (Pukhraj). Swelling power, solubility, amylose content and transmittance values were observed to be higher for Kufri Jyoti and Kufri Badshah potato starches, while turbidity values were lower for these starches. The rheological properties of starches, measured using a dynamic rheometer, showed significant variation in the peak G′ , G″ and peak tan δ values. Kufri Badshah and Kufri Jyoti starches showed higher peak G′, G″ and lower peak tan δ values than Pukhraj starch during heating and cooling cycles. Kufri Jyoti and Kufri Badshah starches showed higher breakdown in G′ than starch from the Pukhraj potato cultivar. The large-sized granules of the starches from Kufri Badshah and Kufri Jyoti appeared to be associated with higher values of peak G′ and G″ and consistency coefficient. Starch from the least mealy cultivar (Pukhraj) showed higher retrogradation, which increased progressively during storage at 402°C for 120 h.
DOI:10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2017.04.011URL [本文引用: 1]

以普通玉米粉、普通玉米淀粉、高直链玉米粉和高直链玉米淀粉为材料,比较玉米粉和玉米淀粉在理化特性上的差异。结果表明:在扫描电镜(SEM)下,蛋白质、脂肪等物质附着、包埋或填充在淀粉颗粒的表面和空隙中;热特性(DSC)测试显示,高直链玉米粉和淀粉的T_0(起始温度)、Tp(峰值温度)和Tc(终止温度)高于普通玉米粉和淀粉,高直链玉米粉和淀粉的吸热焓小于普通玉米粉和淀粉,玉米粉的吸热焓大于淀粉;快速粘度分析(RVA)测试显示,普通玉米粉的最低粘度和峰值粘度小于普通玉米淀粉,高直链玉米则相反。普通玉米粉和高直链玉米粉的衰减值、最终粘度、回生值均大于淀粉;玉米粉的溶解度和膨胀势高于玉米淀粉。蛋白质、脂肪等非淀粉成分可以与淀粉颗粒结合,增加玉米粉的吸热焓,提高冷热稳定性、溶解度和膨胀势。
DOI:10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2017.04.011URL [本文引用: 1]

以普通玉米粉、普通玉米淀粉、高直链玉米粉和高直链玉米淀粉为材料,比较玉米粉和玉米淀粉在理化特性上的差异。结果表明:在扫描电镜(SEM)下,蛋白质、脂肪等物质附着、包埋或填充在淀粉颗粒的表面和空隙中;热特性(DSC)测试显示,高直链玉米粉和淀粉的T_0(起始温度)、Tp(峰值温度)和Tc(终止温度)高于普通玉米粉和淀粉,高直链玉米粉和淀粉的吸热焓小于普通玉米粉和淀粉,玉米粉的吸热焓大于淀粉;快速粘度分析(RVA)测试显示,普通玉米粉的最低粘度和峰值粘度小于普通玉米淀粉,高直链玉米则相反。普通玉米粉和高直链玉米粉的衰减值、最终粘度、回生值均大于淀粉;玉米粉的溶解度和膨胀势高于玉米淀粉。蛋白质、脂肪等非淀粉成分可以与淀粉颗粒结合,增加玉米粉的吸热焓,提高冷热稳定性、溶解度和膨胀势。
DOI:10.1007/s13197-016-2202-3URLPMID:4926931 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Starch and flour properties of different Indian durum wheat varieties were evaluated and related to noodle-making properties. Flours were evaluated for pasting properties, protein characteristics (extractable as well as unextractable monomeric and polymeric proteins) and dough rheology (farinographic properties), while starches were evaluated for granule size, thermal, pasting, and rheological properties. Flour peak and final viscosities related negatively to the proportion of monomeric proteins but positively to that of polymeric proteins whereas opposite relations were observed for dough rheological properties (dough-development time and stability). Starches from varieties with higher proportion of large granules showed the presence of less stable amylose-lipids and had more swelling power, peak viscosity and breakdown viscosity than those with greater proportion of small granules. Noodle-cooking time related positively to the proportion of monomeric proteins and starch gelatinization temperatures but negatively to that of polymeric proteins and amylose content. Varieties with more proteins resulted in firmer noodles. Noodle-cohesiveness related positively to the proportion of polymeric proteins and amylose-lipids complexes whereas springiness correlated negatively to amylose content and retrogradation tendency of starches.
