重庆大学, 三峡库区生态环境教育部重点实验室, 重庆 400045
Key Laboratory of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region’s Eco-Environment, Ministry of Education, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400045, China
对排水管网和污水处理厂的一体化管理,可极大提升城市排水系统运行的高效性和安全性。作为厂网一体化运营理念的一部分,铁盐的综合使用愈发受到关注。在城市排水系统中,铁盐可在污水输送、污水处理及污泥处理过程中发挥作用。围绕铁盐的迁移转化路径、铁盐在污水输送和污水处理厂中的作用机制,以及系统末端铁盐的回收这4个方面,综述了城市排水系统中铁盐综合使用的研究进展。最后根据当前的研究现状,总结了铁盐综合使用中面临的挑战并给出了相关建议,并从厂网一体化铁盐自动加药控制和末端铁盐的进一步回收两方面进行了展望。
The integrated management of drainage network and sewage treatment plant has greatly improved the efficiency and safety of urban drainage system. As a part of plant-network integrated operation concept, the comprehensive use of iron salt has attracted more and more attention. In urban drainage systems, iron salt can play a role in sewage conveyance, sewage treatment and sludge treatment. This paper summarizes the research progress of comprehensive use of iron salt in urban drainage system from four aspects: the migration and transformation path of iron salt, the action mechanism of iron salt in sewage conveyance and sewage treatment plant, and the recovery of iron salt at the end of the system. Finally, according to the current research status, the challenges faced in the comprehensive use of iron salt are summarized, and the usage suggestions are given,and the research prospects are put forward on plant-network integrated automatic dosing control and terminal further recovery of iron salt.
.
Migration and transformation path of iron salt in urban drainage systems
Variation of sulfide species proportion with pH
| [1] | 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 2020年中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020. |
| [2] | MATILAINEN A, VEPS?L?INEN M, SILLANP?? M. Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: A review[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 159(2): 189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2010.06.007 |
| [3] | PIKAAR I, SHARMA K R, HU S, et al. Reducing sewer corrosion through integrated urban water management[J]. Science, 2014, 345(6198): 812-814. doi: 10.1126/science.1251418 |
| [4] | SHARMA K R, YUAN Z, DE HAAS D, et al. Dynamics and dynamic modelling of H2S production in sewer systems[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(10/11): 2527-2538. |
| [5] | GUISASOLA A, DE HAAS D, KELLER J, et al. Methane formation in sewer systems[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(6/7): 1421-1430. |
| [6] | LIU Y, SHARMA K R, NI B, et al. Effects of nitrate dosing on sulfidogenic and methanogenic activities in sewer sediment[J]. Water Research, 2015, 74: 155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.017 |
| [7] | AI T, HE Q, XU J, et al. A conceptual method to simultaneously inhibit methane and hydrogen sulfide production in sewers: The carbon metabolic pathway and microbial community shift[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 246: 119-127. |
| [8] | WIENER M S, SALAS B V, QUINTERO-Nú?EZ M, et al. Effect of H2S on corrosion in polluted waters: A review[J]. Corrosion Engineering, Science, and Technology, 2006, 41(3): 221-227. doi: 10.1179/174327806X132204 |
| [9] | ZHANG L, DE SCHRYVER P, DE GUSSEME B, et al. Chemical and biological technologies for hydrogen sulfide emission control in sewer systems: A review[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(1/2): 1-12. |
| [10] | YOUSEFI A, ALLAHVERDI A, HEJAZI P. Accelerated biodegradation of cured cement paste by Thiobacillus species under simulation condition[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2014, 86: 317-326. |
| [11] | HVITVED-JACOBSEN T, VOLLERTSEN J, NIELSEN A H. Sewer Processes: Microbial and Chemical Process Engineering of Sewer Networks[M]. Los Angeles: CRC Press, 2013. |
| [12] | JIANG G, SUN J, SHARMA K R, et al. Corrosion and odor management in sewer systems[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 37(4): 33. |
| [13] | EPA. Hydrogen Sulfide Corrosion in Wastewater Collection and Treatment Systems[M]. Washington, DC: U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, 1991. |
| [14] | FIRER D, FRIEDLER E, LAHAV O. Control of sulfide in sewer systems by dosage of iron salts: Comparison between theoretical and experimental results, and practical implications[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 392(1): 145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.11.008 |
| [15] | 季斌, 秦慧, 陈威, 等. 铁盐应用于污水协同除磷研究进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2018, 44(2): 11-14. |
| [16] | LI R, WANG W, LI B, et al. Acidogenic phosphorus recovery from the wastewater sludge of the membrane bioreactor systems with different iron-dosing modes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 280: 360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.060 |
| [17] | 董建威, 何强, 司马卫平. 含盐废水生物/化学除磷模型及除磷剂的强化效果[J]. 中国给水排水, 2014, 30(21): 106-109. |
| [18] | CHARLES W, CORD-RUWISCH R, HO G, et al. Solutions to a combined problem of excessive hydrogen sulfide in biogas and struvite scaling[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2006, 53(6): 203-211. doi: 10.2166/wst.2006.198 |
| [19] | BABATUNDE A O, ZHAO Y Q. Constructive approaches toward water treatment works sludge management: An international review of beneficial reuses[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2007, 37(2): 129-164. doi: 10.1080/10643380600776239 |
| [20] | SUN J, PIKAAR I, SHARMA K R, et al. Feasibility of sulfide control in sewers by reuse of iron rich drinking water treatment sludge[J]. Water Research, 2015, 71: 150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.12.044 |
| [21] | WANG B, SIVRET E C, PARCSI G, et al. Reduced sulfur compounds in the atmosphere of sewer networks in Australia: Geographic (and seasonal) variations[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2014, 69(6): 1167-1173. doi: 10.2166/wst.2013.798 |
| [22] | PARK K, LEE H, PHELAN S, et al. Mitigation strategies of hydrogen sulphide emission in sewer networks: A review[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2014, 95: 251-261. |
| [23] | HVITVED-JACOBSEN T, VOLLERTSEN J, MATOS J S. The sewer as a bioreactor: A dry weather approach[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 45(3): 11-24. |
| [24] | PADIVAL N A, WEISS J S, ARNOLD R G. Control of Thiobacillus by means of microbial competition: Implications for corrosion of concrete sewers[J]. Water Environment Research, 1995, 67(2): 201-205. doi: 10.2175/106143095X131358 |
| [25] | NIELSEN A H, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T, VOLLERTSEN J. Kinetics and stoichiometry of sulfide oxidation by sewer biofilms[J]. Water Research, 2005, 39(17): 4119-4125. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.07.031 |
| [26] | SUN J, HU S, SHARMA K R, et al. Stratified microbial structure and activity in sulfide-and methane-producing anaerobic sewer biofilms[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(22): 7042-7052. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02146-14 |
| [27] | BACHE D H, PAPAVASILOPOULOS E N. Viscous behaviour of sludge centrate in response to polymer conditioning[J]. Water Research, 2000, 34(1): 354-358. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00143-8 |
| [28] | CHURCHILL P, ELMER D. Hydrogen sulfide odor control in wastewater collection systems[J]. Journal of New England Water Environment Association, 1999, 33(1): 57-63. |
| [29] | YANG W, VOLLERTSEN J, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T. Anoxic sulfide oxidation in wastewater of sewer networks[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2005, 52(3): 191. doi: 10.2166/wst.2005.0076 |
| [30] | GADEKAR S, NEMATI M, HILL G A. Batch and continuous biooxidation of sulphide by Thiomicrospira sp. CVO: Reaction kinetics and stoichiometry[J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(12): 2436-2446. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.007 |
| [31] | NIELSEN A H, VOLLERTSEN J, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T. Determination of kinetics and stoichiometry of chemical sulfide oxidation in wastewater of sewer networks[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(17): 3853-3858. |
| [32] | GUTIERREZ O, MOHANAKRISHNAN J, SHARMA K R, et al. Evaluation of oxygen injection as a means of controlling sulfide production in a sewer system[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(17): 4549-4561. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.07.042 |
| [33] | GANIGUE R, GUTIERREZ O, ROOTSEY R, et al. Chemical dosing for sulfide control in Australia: An industry survey[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(19): 6564-6574. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.054 |
| [34] | GUTIERREZ O, PARK D, SHARMA K R, et al. Effects of long-term pH elevation on the sulfate-reducing and methanogenic activities of anaerobic sewer biofilms[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(9): 2549-2557. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.008 |
| [35] | NIELSEN A H, LENS P, VOLLERTSEN J, et al. Sulfide-iron interactions in domestic wastewater from a gravity sewer[J]. Water Research, 2005, 39(12): 2747-2755. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.048 |
| [36] | NIELSEN A H, HVITVED-JACOBSEN T, VOLLERTSEN J. Effects of pH and iron concentrations on sulfide precipitation in wastewater collection systems[J]. Water Environment Research, 2008, 80(4): 380-384. doi: 10.2175/106143007X221328 |
| [37] | ZHANG L, VERSTRAETE W, DE LOURDES MENDOZA M, et al. Decrease of dissolved sulfide in sewage by powdered natural magnetite and hematite[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 573: 1070-1078. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.206 |
| [38] | ZHANG L, KELLER J, YUAN Z. Inhibition of sulfate-reducing and methanogenic activities of anaerobic sewer biofilms by ferric iron dosing[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(17): 4123-4132. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.013 |
| [39] | ZHANG L, KELLER J, YUAN Z. Ferrous salt demand for sulfide control in rising main sewers: Tests on a laboratory-scale sewer system[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2010, 136(10): 1180-1187. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000258 |
| [40] | ZHANG L, DERLON N, KELLER J, et al. Dynamic response of sulfate-reducing and methanogenic activities of anaerobic sewer biofilms to ferric dosing[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012, 138(4): 510-517. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000481 |
| [41] | LIN H, KUSTERMANS C, VAIOPOULOU E, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of iron and alkalinity generation for efficient sulfide control in sewers[J]. Water Research, 2017, 118: 114-120. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.069 |
| [42] | PIKAAR I, FLUGEN M, LIN H, et al. Full-scale investigation of in-situ iron and alkalinity generation for efficient sulfide control[J]. Water Research, 2019, 167: 115032. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115032 |
| [43] | YAN X, SUN J, KENJIAHAN A, et al. Rapid and strong biocidal effect of ferrate on sulfidogenic and methanogenic sewer biofilms[J]. Water Research, 2020, 169: 115208. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115208 |
| [44] | KULANDAIVELU J, CHOI P M, SHRESTHA S, et al. Assessing the removal of organic micropollutants from wastewater by discharging drinking water sludge to sewers[J]. Water Research, 2020, 181: 115945. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115945 |
| [45] | KULANDAIVELU J, GAO J, SONG Y, et al. Removal of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs from wastewater due to ferric dosing in sewers[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(11): 6245-6254. |
| [46] | GUTIERREZ O, PARK D, SHARMA K R, et al. Iron salts dosage for sulfide control in sewers induces chemical phosphorus removal during wastewater treatment[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(11): 3467-3475. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.03.023 |
| [47] | GE H, ZHANG L, BATSTONE D J, et al. Impact of iron salt dosage to sewers on downstream anaerobic sludge digesters: Sulfide control and methane production[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 139(4): 594-601. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000650 |
| [48] | SCHIPPERS A, JRGENSEN B B. Biogeochemistry of pyrite and iron sulfide oxidation in marine sediments[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(1): 85-92. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00745-1 |
| [49] | LUEDECKE C, HERMANOWICZ S W, JENKINS D. Precipitation of ferric phosphate in activated sludge: A chemical model and its verification[J]. Water Pollution Research & Control Brighton, 1988, 21(4/5): 325-337. |
| [50] | REBOSURA M, SALEHIN S, PIKAAR I, et al. A comprehensive laboratory assessment of the effects of sewer-dosed iron salts on wastewater treatment processes[J]. Water Research, 2018, 146: 109-117. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.09.021 |
| [51] | REBOSURA M, SALEHIN S, PIKAAR I, et al. Effects of in-sewer dosing of iron-rich drinking water sludge on wastewater collection and treatment systems[J]. Water Research, 2020, 171: 115396. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115396 |
| [52] | SALEHIN S, KULANDAIVELU J, REBOSURA M, et al. Opportunities for reducing coagulants usage in urban water management: The oxley creek sewage collection and treatment system as an example[J]. Water Research, 2019, 165: 114996. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.114996 |
| [53] | KULANDAIVELU J, SHRESTHA S, KHAN W, et al. Full-scale investigation of ferrous dosing in sewers and a wastewater treatment plant for multiple benefits[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 250: 126221. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126221 |
| [54] | WILFERT P, MANDALIDIS A, DUGULAN A I, et al. Vivianite as an important iron phosphate precipitate in sewage treatment plants[J]. Water Research, 2016, 104: 449-460. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.08.032 |
| [55] | WILFERT P, DUGULAN A I, GOUBITZ K, et al. Vivianite as the main phosphate mineral in digested sewage sludge and its role for phosphate recovery[J]. Water Research, 2018, 144: 312-321. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.020 |
| [56] | SALEHIN S, REBOSURA M, KELLER J, et al. Recovery of in-sewer dosed iron from digested sludge at downstream treatment plants and its reuse potential[J]. Water Research, 2020, 174: 115627. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115627 |
| [57] | CHEN Y, CHENG J J, CREAMER K S. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(10): 4044-4064. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.057 |
| [58] | WU Y, LUO J, ZHANG Q, et al. Potentials and challenges of phosphorus recovery as vivianite from wastewater: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 226: 246-258. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.138 |
| [59] | FREDERICHS T, VON DOBENECK T, BLEIL U, et al. Towards the identification of siderite, rhodochrosite, and vivianite in sediments by their low-temperature magnetic properties[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 2003, 28(16/17/18/19): 669-679. |
| [60] | REBOSURA M, SALEHIN S, PIKAAR I, et al. The impact of primary sedimentation on the use of iron-rich drinking water sludge on the urban wastewater system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 402(2): 124051. |
| [61] | GANIGUé R, JIANG G, LIU Y, et al. Improved sulfide mitigation in sewers through on-line control of ferrous salt dosing[J]. Water Research, 2018, 135: 302-310. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.022 |





















 下载:
下载: 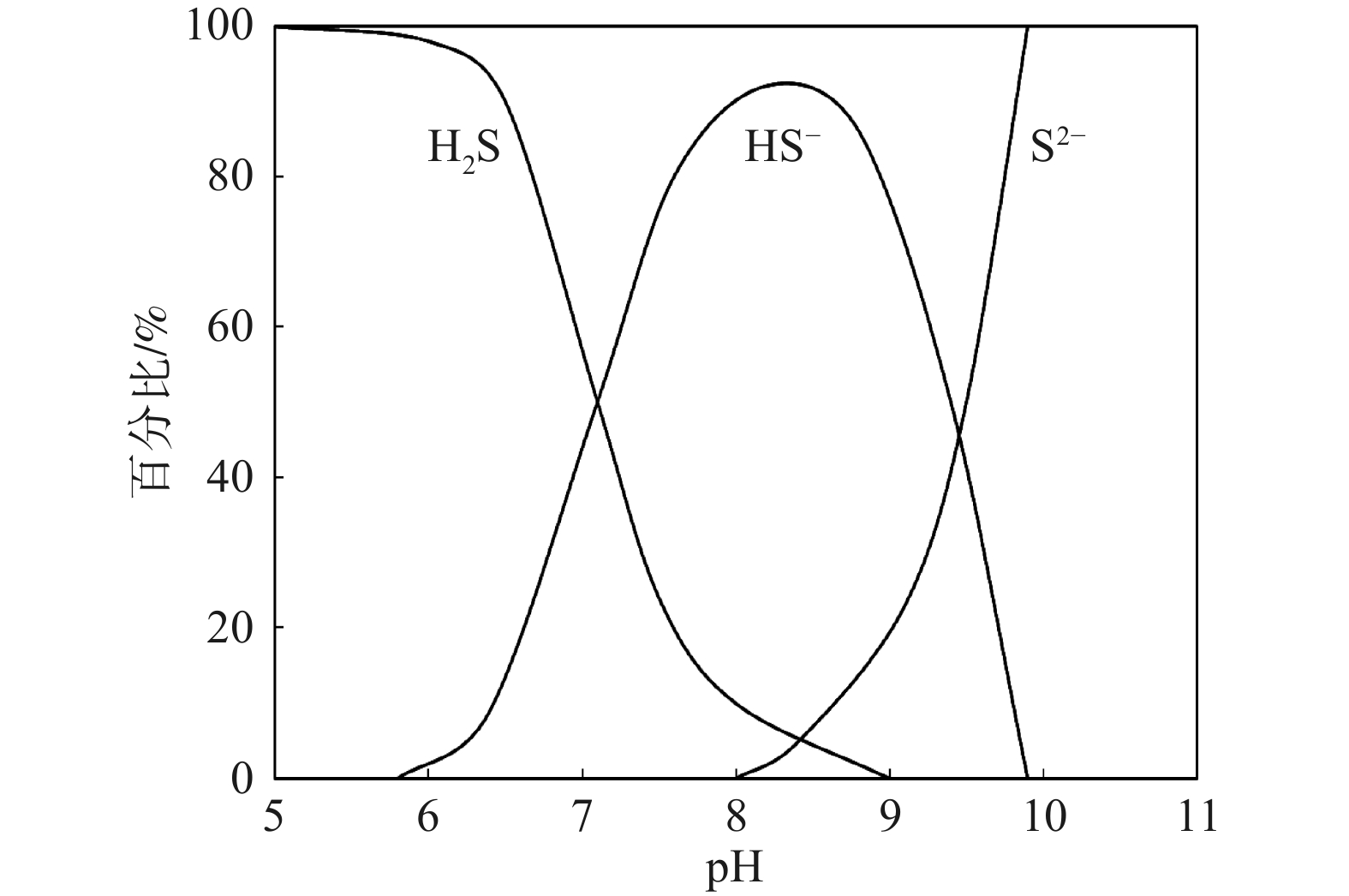
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图