全文HTML
--> --> --> 含氰化合物因其来源广泛、品种多、络合能力强,是一种在化工、焦化、冶金和电镀行业中应用广泛的重要工业原料。但氰化物对于人体和生物有剧毒,能引起对人体内必需金属酶的抑制[1-2]。工业生产过程中,氰化物会通过生产废水排放进入自然界中。我国每年的含氰废水产生量巨大,仅以黄金冶炼行业为例,含氰废水年排放量就高达1.2×108 t[3]。随着人们对以氰化物为附加值的产品需求不断增加,产生的含氰废水成分愈加复杂。与此同时,为了更好的保障人们的健康安全,国家对各种氰化物的排放标准也在不断提高,对产生含氰废水的企业也提出了更高的环保要求,也对含氰废水的处理提出了更高的挑战[4]。对于化工、电镀、制药等行业来说,其生产过程中产生的含氰废水一般具有较高浓度(TCN≥1 000 mg·L?1),并且含有大量有机腈,降解难度更大。采用次钠氯碱法等传统工艺需要额外加入大量药剂,极大地增加了处理的运行成本[5];且由于氰化物浓度高会导致扩散缓慢,处理效率也受到了抑制。基于上述原因,针对高浓度含氰废水,需要开发更高效的处理技术并对现有技术进行优化。
目前工业上应用较多的处理方法有氯氧化法[6]、H2O2氧化法[7]、因科法[8]、电化学法[9]等。这些方法在具有一定优势的同时也具有一些共性缺点,如运行成本高(H2O2氧化法中H2O2原料价格偏高)[10]、易造成二次污染(氯氧化法处理废水后可能存在余氯)[11]、具有安全隐患(因科法需要转运SO2)[12]等。此外,对于高浓度含氰废水,其处理效率受到明显抑制[13],主要原因在于在以试剂为氧化剂的工艺中,过高的氰化物浓度会限制在各相之间的反应速率并影响催化剂的活性[14-15]。
电化学法尽管存在建设成本高昂等问题,但其以电子为反应试剂,无需加药,无二次污染产生,故具有较好的应用前景。在此情况下,对于电化学反应器的设计就显得更为重要,通过巧妙的电化学反应器设计以实现安全、高效、经济的最终目的,并限制电极的电催化活性和稳定性变化产生的影响[16]。有研究[17]表明,高效的电化学反应器应具备空时收率高、电极比表面积大和传质效率高等特点。因此,电化学反应器的设计主要从提高传质效率和增大电化学活性面积2个方面来解决。传统的电化学反应器通常采用平行板式电极,即水流方向与电极板放置方向平行,这种模式下的传质非常有限。基于上述情况,很多研究利用多孔电极可穿透的特点,使水流方向垂直于电极,并迫使污染物与电极发生接触,并发现传质效率提升了2~6倍[18]。也有很多研究者通过加入三维电极的方法增加电极的有效面积[19],但这无疑也会进一步增加反应器的成本。管式电极可以比板式电极提供更大的活性面积,同时水流在管内的湍流程度更强,进而提高了传质,而搭配微孔管式电极则可以实现污染物与电极的强迫接触,进而进一步提升传质效率。
基于以上研究背景,针对西部某医药农药中间体化工企业所产生的高浓度含氰废水面临的处理问题,开发了管式电化学反应器工艺对高浓度含氰废水进行预处理的中试应用研究,使预处理过后的废水中氰化物得到有效控制,同时选择市场上广泛使用的次钠氯碱法和二氧化氯氧化法在处理效果和经济性上作对比,并对管式电化学反应器在处理高浓度含氰废水过程的运行参数进行优化。
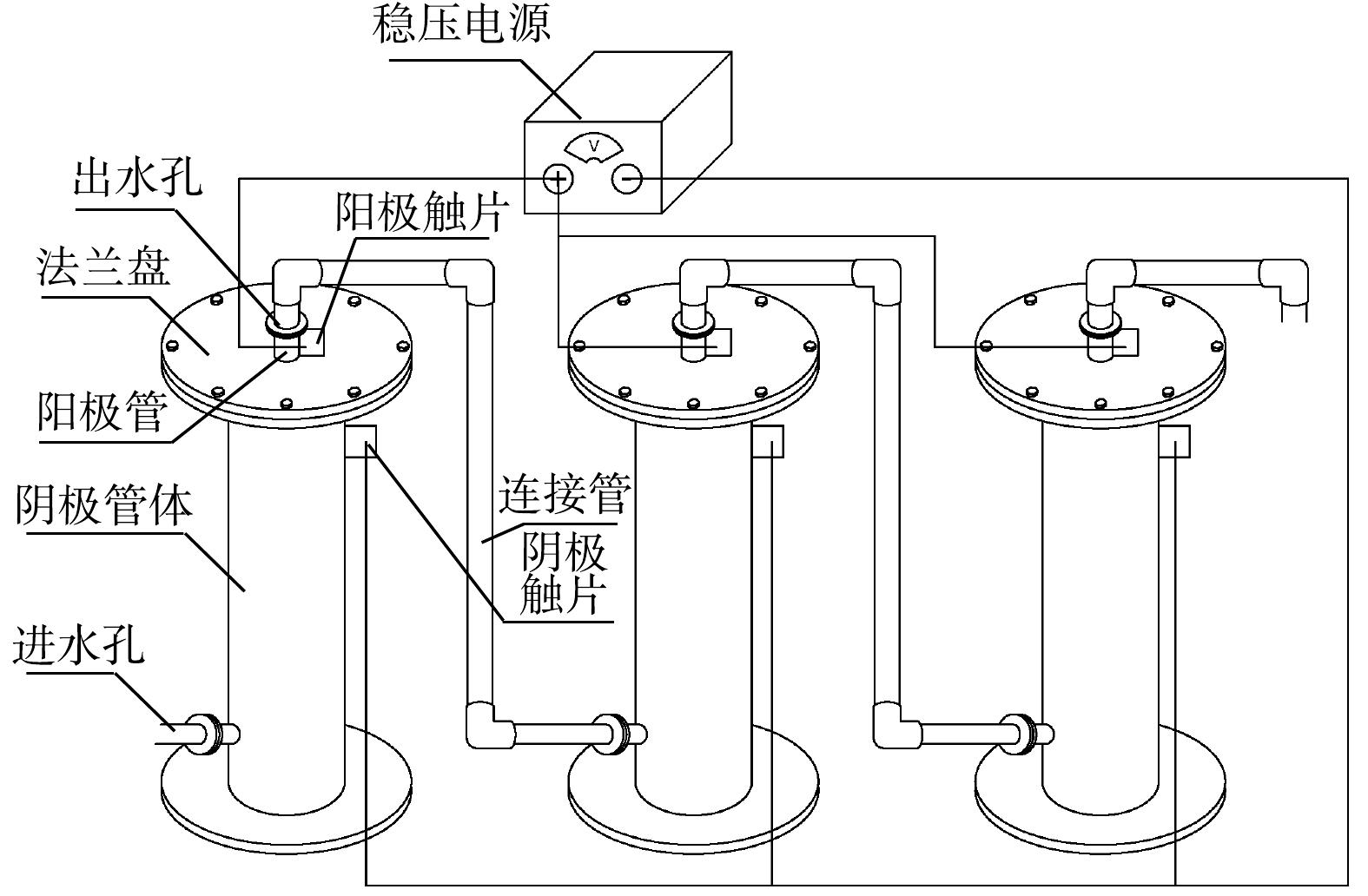
1.1. 管式电化学装置的构建
管式电化学反应器的构建如图1所示。反应器采用管式上流结构,长为105 cm/85 cm(阴极/阳极),阳极置于反应器中间,阴极为外部的不锈钢套管,两者之间的距离为2 cm,阳极由钛管/钛网上负载二氧化铅(PbO2)或二氧化钌(RuO2)而得,反应器直径为20 cm,采用法兰连接,法兰盘之间用1 cm厚的硅胶垫绝缘,并通过稳压恒流电源(JK10500k)为电极提供并控制电流;通过隔膜泵(QBY65-50)进行水流循环。钛基RuO2阳极由微孔钛管(孔径约10 μm)采用溶胶凝胶法进行制备,参考之前的制备方法[20],并通过加压诱导修饰微孔孔道,钛基PbO2阳极由钛网管(孔径约为2 mm)采用电沉积法进行制备,具体方法参考已有的研究[21],优化为双电流密度二次电沉积法,使α- PbO2和β- PbO2依次沉积于钛基体上。2种管式电化学反应器分别命名为ETR-Ru和ETR-Pb。
1.2. 高浓度含氰生产废水的处理
西部某化工厂的高浓度含氰化工生产废水具体水质为:pH为7~8;总氰化物(TCN)的质量浓度约为20 000 mg·L?1;耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)的质量浓度约为35 000 mg·L?1;总氮(TN)质量浓度约为17 000 mg·L?1;氨氮(NH3-N)质量浓度约为400 mg·L?1;废水中的总溶解性固体(TDS)的质量浓度约为12 000 mg·L?1,废水中无机盐包括Na2SO4、NaNO3和NaCl,且已知其中含有的首要污染物间苯二甲腈(IPN) 为500 mg·L?1。废水统一调节pH至9进行处理,处理水量为每次200 L。将40套管式电化学反应器阵列式连接,每10套串联为一组,并将4组并联到一起,在电源开启前先将泵速调至最大,废水尽快泵入且充满反应器,设置电流密度为20 mA·cm?2,处理时间为4 h,处理过程中通过隔膜泵进行循环,设置循环泵的流量为6.7 L min?1,即每处理1 h,处理水量在反应器中循环2次,搭载不同阳极的反应器分别命名为ETR-Pb和ETR-Ru。作为对比,以相同的水质和水量,按照传统的氯碱法进行[22-24],所用投药比例与实际工程使用的一致[23, 25]。所用药剂分2步投加,每步反应充分,消除反应不均带来的影响。次钠氯碱法按照CN?∶NaClO=1∶4.5,即有效氯与氰根质量比为4∶1进行投加,反应1 h后,再按照CN?∶NaClO=1∶8,即有效氯与氰根质量比为7∶1继续投加次氯酸钠溶液,且持续反应3 h。ClO2氧化法通过ClO2发生器向调节水池注入ClO2,比例以有效氯计,与次钠氯碱法投入量和投加次数一致,由于ClO2的有效氯含量高达263%[26],投药量与NaClO相比会有大幅减少。这2种方法均采用将废水泵入钢结构调节池之后实施。采用ClO2发生器(水夫水泵联动型CPF-200CX)实现ClO2的投加。所有实验均平行进行3次。之后进行运行参数优化实验,在初始pH=9的情况下,以5、10、20、50 mA·cm?2对废水处理8 h,并在0.5、1、1.5、2、4、8 h采样检测;再将废水pH调至8、9、10、11、12,以20 mA·cm?2处理4 h并取样检测。考虑到电解质种类也会在电化学反应器处理的过程中影响最终的处理效果,通过生产过程的工艺调整,在废水中其他水质参数不变的情况,以Na2SO4、NaNO3和NaCl为唯一电解质(12 000 mg·L?1),在pH为9的情况下以20 mA·cm?2处理4 h并取样检测以观察不同电解质下处理效果的差别。1.3. 表征和测试方法
采用国家标准方法中的硝酸银滴定法测定水中总氰化物的含量[27]。化学需氧量和氨氮的测定均按照国家标准使用紫外可见分光光度计(Photolab 6600UV-VIS)进行测定[28-29],采用高效液相色谱仪(HPLC)测定水中首要污染物间苯二腈的浓度(Waters G2)[30],操作条件为色谱柱C-18 (150 mm×4.6 mm),柱温为35 ℃,流动相为超纯水和甲醇,设置液流比为65∶35,流速1.00 mL·min?1,检测波长为288 nm。2.1. 处理效果的比较
图2为次钠氯碱法、ClO2氧化法和2种管式电化学反应器对实际含氰废水的处理情况。由图2可以看出,各工艺对于含氰废水处理的情况有较大差异,以钛基RuO2为阳极的管式电化学反应器相比于其他工艺效果更佳,TCN去除率可达81.74%,相比之下,传统的次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化法对废水中TCN的去除率分别只有59.20%和61.13%。这是由于TCN去除的主要机理是通过产生强氧化基团将游离CN?氧化为不稳定的CNO?,之后CNO?再进一步变成N2和

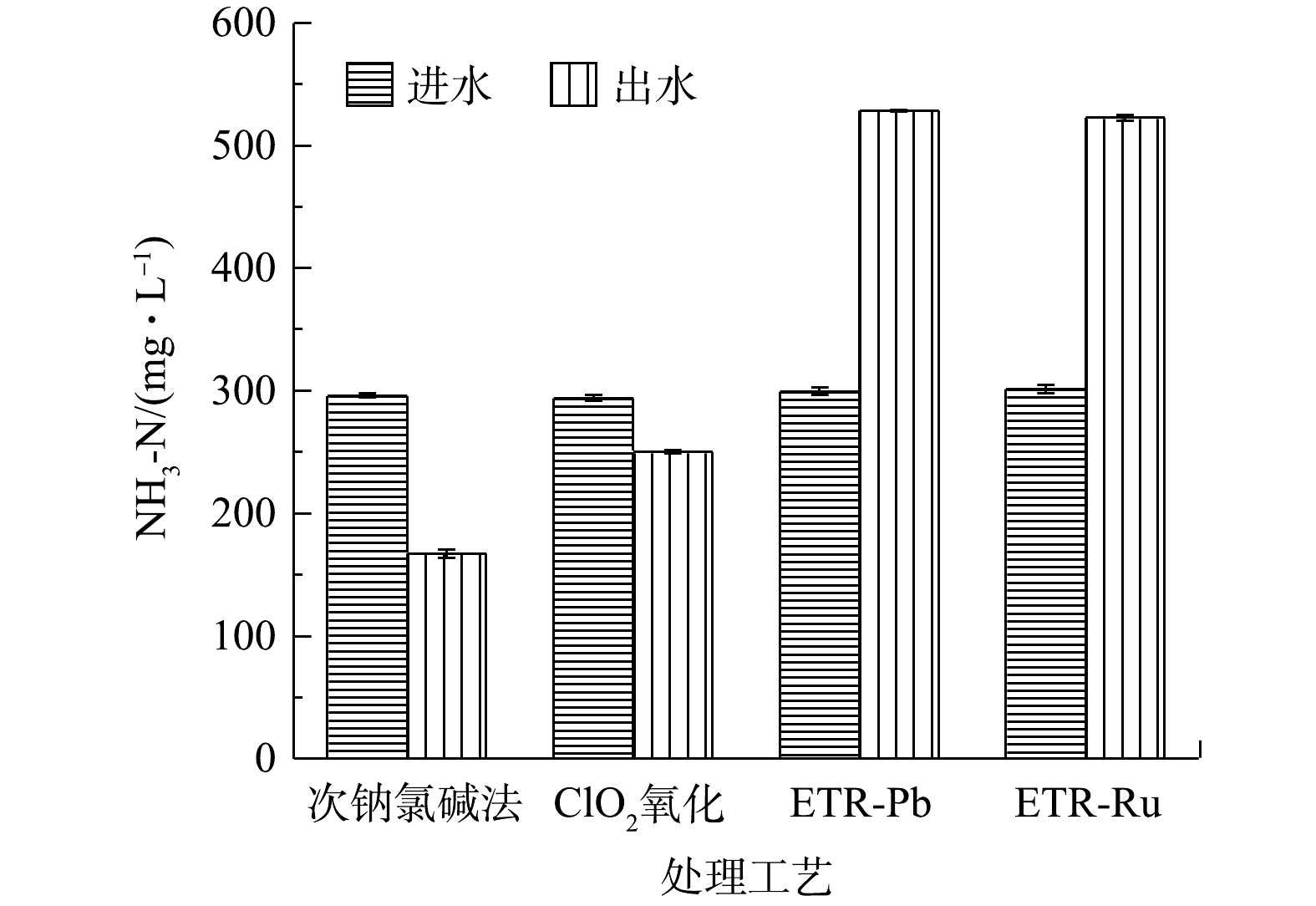
图3为经过各工艺处理后废水中的氨氮质量浓度的变化情况。经过次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化法处理的废水中,NH3-N质量浓度分别下降了43.48%和14.98%;与之相反,经过管式电化学反应器处理的废水中,NH3-N质量浓度比原水升高了99.82%和73.33%。这可能是由以下2种原因导致的:一是因为废水中除游离氰之外的有机腈,如间苯二腈在电化学氧化中开始降解,腈基易发生亲核反应,从而转化为NH3-N并释放在水中;二是废水中游离CN?在具有强氧化能力的电化学体系中会不通过CNO?直接转化为NH3。而次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化产生的活性氯既对有机腈的降解效果有限,又不能直接将CN?转化为NH3,因此,废水中的NH3-N浓度会出现一定程度的削减。尽管经管式电化学反应器处理的废水NH3-N质量浓度升高,但从整个废水处理系统的宏观角度来看,有机腈的降解转化既为后续的生化处理有效的缓解了压力,也削弱了潜在的环境风险,故可从根本上对废水进行有效处理。
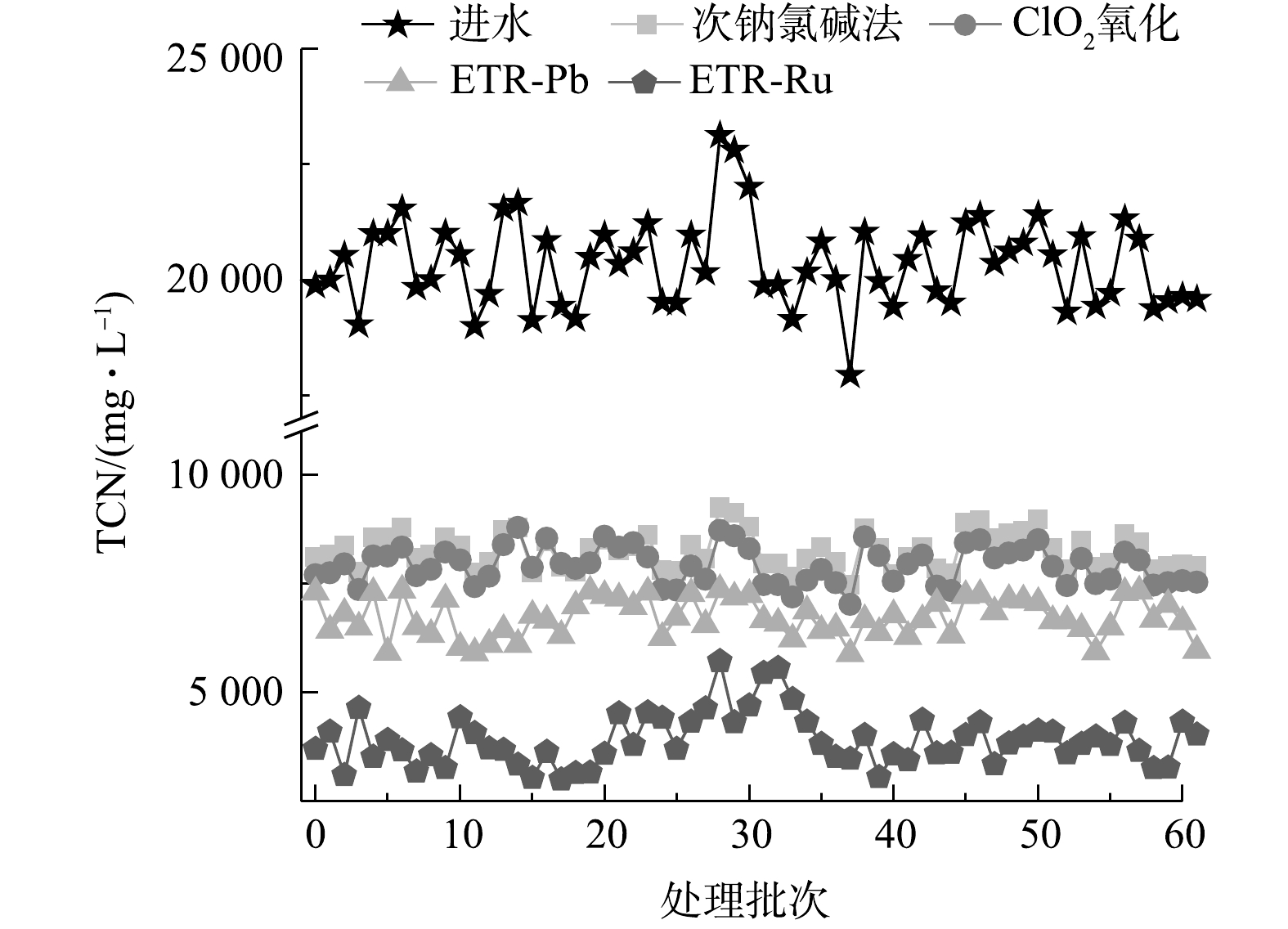
图4反映了各工艺在实际运行了60次的TCN处理效果,用以考察各工艺的长期运行效果和稳定性。从各工艺TCN处理效果上来看,ETR-Ru整体的处理效果远优于其他3种工艺,而次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化法之间的差异并不显著;从稳定性来看,在进水水质波动较大的情况下,次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化法对于水质变化的稳定性更高,ETR-Ru的稳定性则会随水质变化出现一定的波动。次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化法的运行是按照一定比例加入氧化剂,即更高浓度的TCN就会增加更多的氧化剂,导致了这2种方法稳定性较好,但同时也增加了投入。管式电化学反应器运行过程中保持电流密度恒定,产生的氧化基团数量在电流密度不变的情况下基本保持一致,其氧化能力并不会随水质波动而变化,因此,处理效果会随着进水情况的变化而波动。
2.2. 工艺能耗和经济性对比
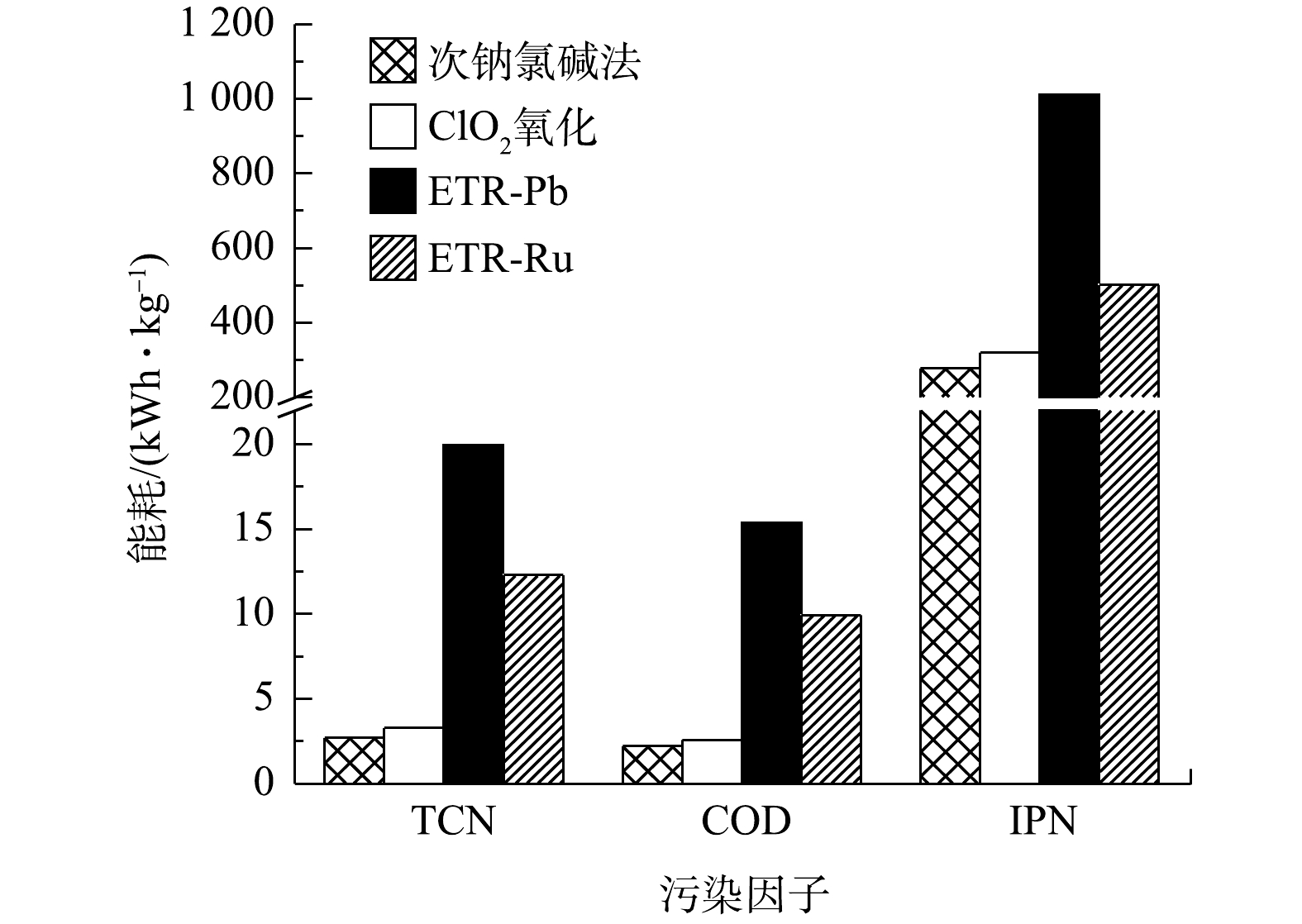
实际应用过程中,处理效果并不是影响某项技术是否能够得以应用和推广的唯一因素,能耗情况和经济成本同样是需要重点考虑的问题。图5列出了各工艺对废水中不同水质污染因子的单位能耗对比结果。由图5可以看出,管式电化学反应器处理的单元能耗要远高于次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化法。特别是其中ETR-Pb能耗最高,在去除TCN、COD和IPN时,能耗分别高达19.95、15.37和1 012 kWh·kg?1;与之相比,次钠氯碱法由于在实施过程仅通过计量泵加药及通过搅拌器搅拌使加入的次氯酸钠与废水充分接触,能耗控制在较低的水平,仅为ETR-Pb处理的13.53%(TCN)、14.24%(COD)和27.47%(IPN)。ClO2氧化法由于采用ClO2发生器需要通电,其能耗略高于次钠氯碱法。而在相同电流密度的情况下,ETR-Ru和ETR-Pb的差异主要源于2种电极材料的导电性有差异,RuO2的电阻率比PbO2小[38],所用电压也就更低。这也表明在管式电化学反应器中,以Ti/RuO2为阳极的反应器优势更为明显。对于次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化法,能耗显然不能代表其在运行过程中的所有成本。表1列出了各工艺的处理成本组成。除了能耗成本以外,次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化需要外加大量的药剂,次钠氯碱法需要投加NaClO,ClO2氧化需要氯酸钠和HCl。由表1也可以看出,次钠氯碱法的药剂成本高达812.60 元·t ?1,北方冬季的寒冷天气还使NaClO反应的过程中需要通入一定量的蒸汽来保证反应正常运行;而ClO2发生器本身就有加热模块,管式电化学反应器在通电的过程,电极也会发热,从而不需要进行保温。由表2可以看出,在综合计算比较之后,管式电化学反应器的运行成本有较大的优势,ETR-Ru的运行成本仅为110.70 元·t ?1,占次钠氯碱法的13.10%。
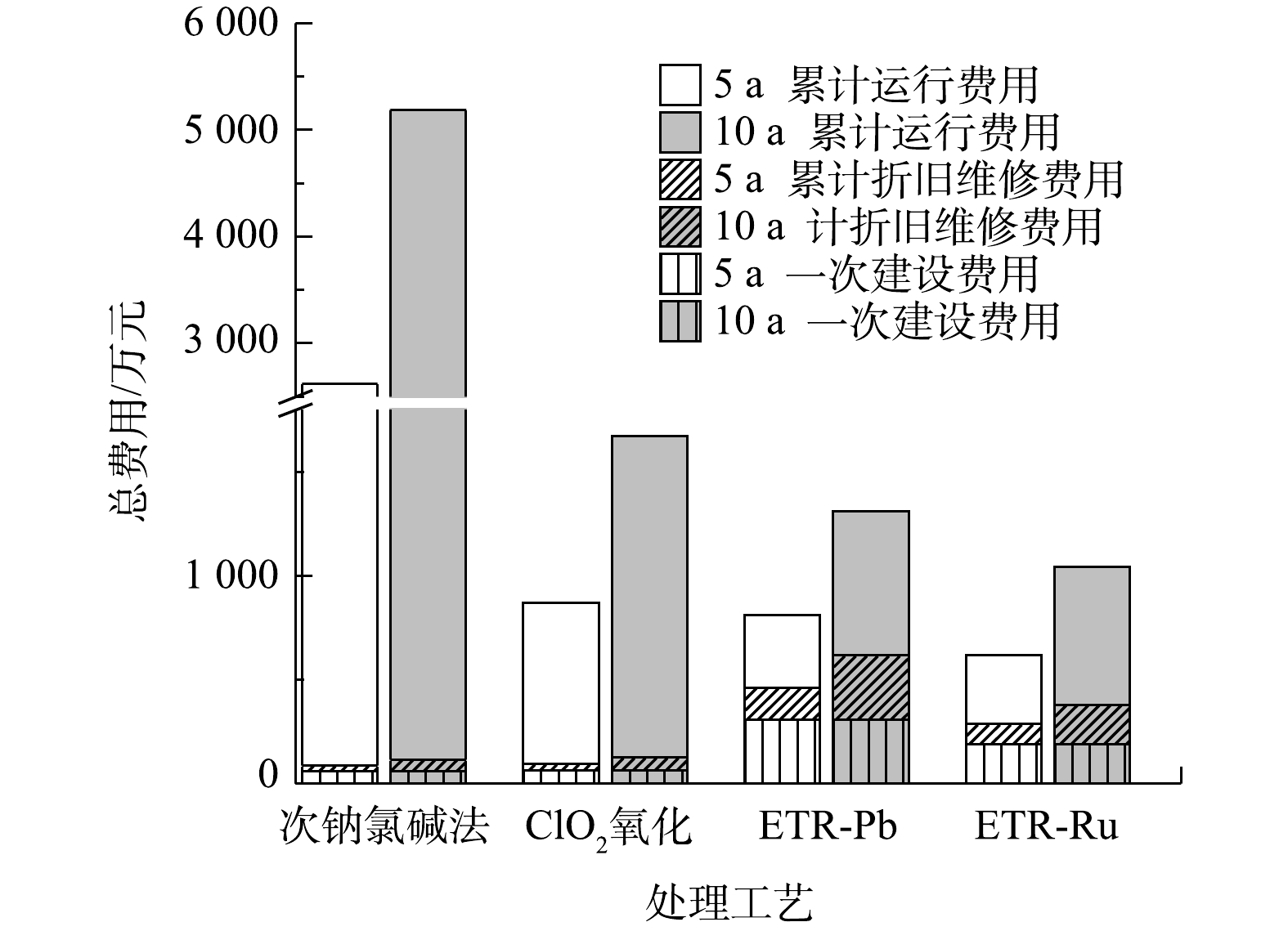
需要注意的是,考虑到管式电化学反应器的电极造价高昂,并且在安装过程较复杂,仅仅对比各工艺的处理成本,并据此比较各工艺的经济性也是片面的。在进行处理成本对比的同时,必须将建设成本考虑进去,以此来综合对比各工艺经济性的优劣。表2列出了各工艺的建设成本和具体构成。可以看出,管式电化学反应器的建设成本较次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化法有大幅度的增加,ETR-Pb的建设成本高达15.39 万元·t ?1,分别是次钠氯碱法和ClO2氧化建设成本的6.45倍和4.92倍。这主要是由于管式电化学反应器的电极的贵金属成分成本高昂造成的。次钠氯碱法只需要钢结构的池体,搅拌器和加药设备等常规设备,其他3种工艺均有特有的工艺设备。由表2还可以看出,在管式电化学反应器中,ETR-Ru相比于ETR-Pb的制造成本更为低廉。这是由于电极制备过程中的前驱体材料价格的差异所导致的,相比于ETR-Pb的电沉积工艺,ETR-Ru加工工艺更繁琐,因此,需要较高的人工成本。
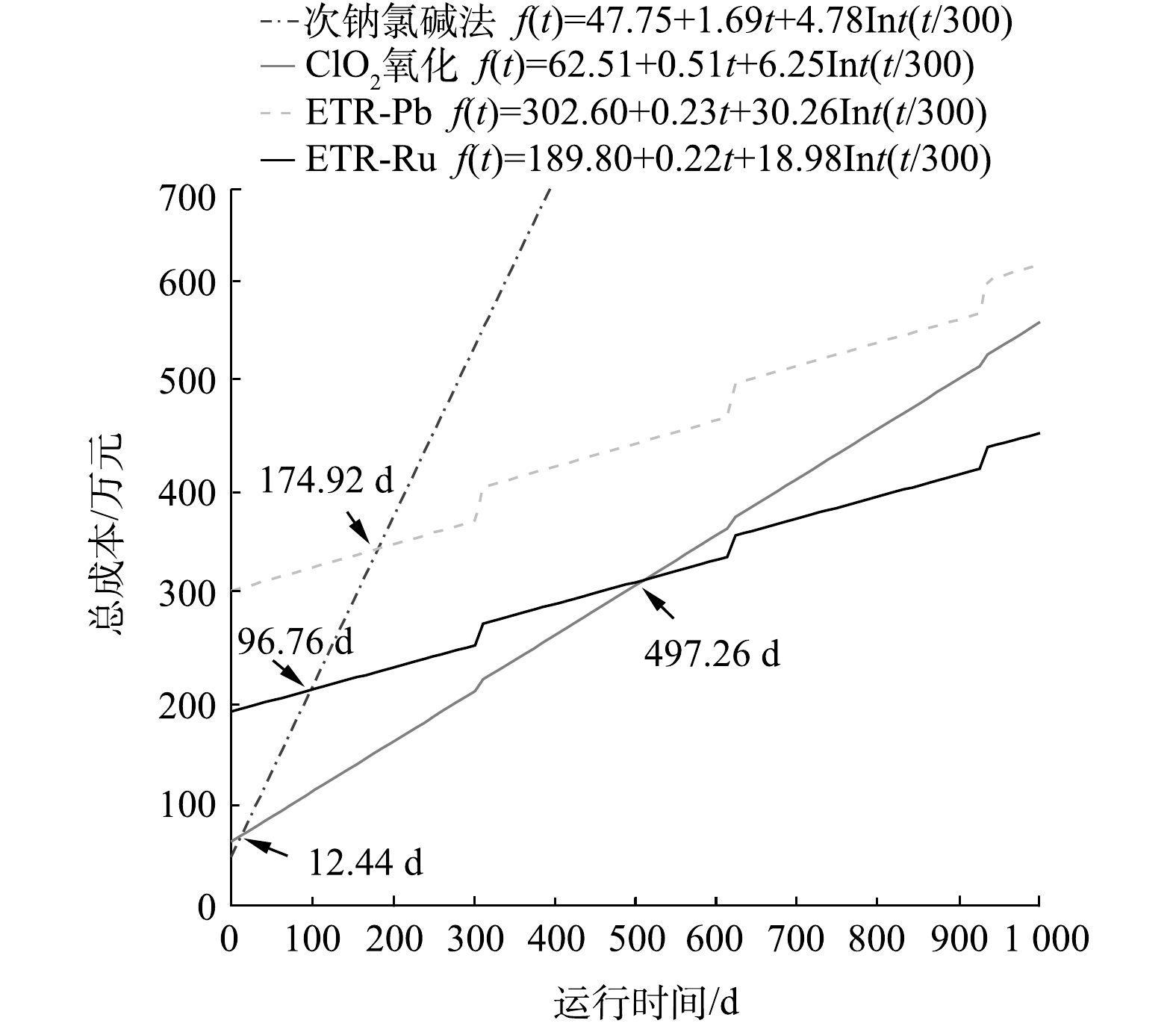
为了将以上得出的建设成本和运行成本加以系统地比较,以西部某化工厂的实际情况为例,进行了函数拟合。该厂产出高浓度含氰废水量为20 m3·d?1。如经调研比较发现,若高浓度含氰废水水量大,则可通过工艺回用进一步降低浓度并回收利用水中的氰化物,从而实现废水中氰化物的循环利用并有效缩减成本。因此,对一般生产企业来讲,高浓度含氰废水的水量较小,进行核算的企业废水量符合氰工业产生废水的正常水平[39]。此外,由于设备的长时间使用造成的折旧维修,也应该列入成本计算范围,这其中主要是阳极在反应过程中造成的腐蚀和损耗。在该中试之前,对采用2种阳极的管式反应器进行了加速寿命实验。结果表明,2种阳极的正常使用时间都超过30 000 h。按照中试的运行时间折算,电极的寿命约为25 a。由于废水处理规模增加以及考虑反应器其他部件的损坏,每年以建设成本的10%(折旧率为10%)作为折旧维修费计入总成本。各工艺包含建设成本、运行成本和折旧维修费用的总投入与运行时间的函数关系如图6所示(Int为取整函数)。
由图6中可以看出,当运行时间超过498 d时,ETR-Ru的总成本最为低廉;而在运行时间小于12 d的情况下,ClO2氧化法的总成本最低。图7则反映了各工艺在运行5 a和10 a之后投入的对比。运行5 a后,次钠氯碱法、ClO2氧化法、ETR-Pb和ETR-Ru的总费用分别为2 620.50 万、869.28 万、810.54 万和616.80 万元。在运行10 a之后差距会变得更为明显。这也说明尽管管式电化学反应器的建设成本较高,但从较长的时间跨度来看,管式电化学反应器仍然具有明显的成本优势,这也为管式电化学反应器的应用提供了更广阔的市场前景和应用空间。
2.3. 管式电化学反应器运行参数优化
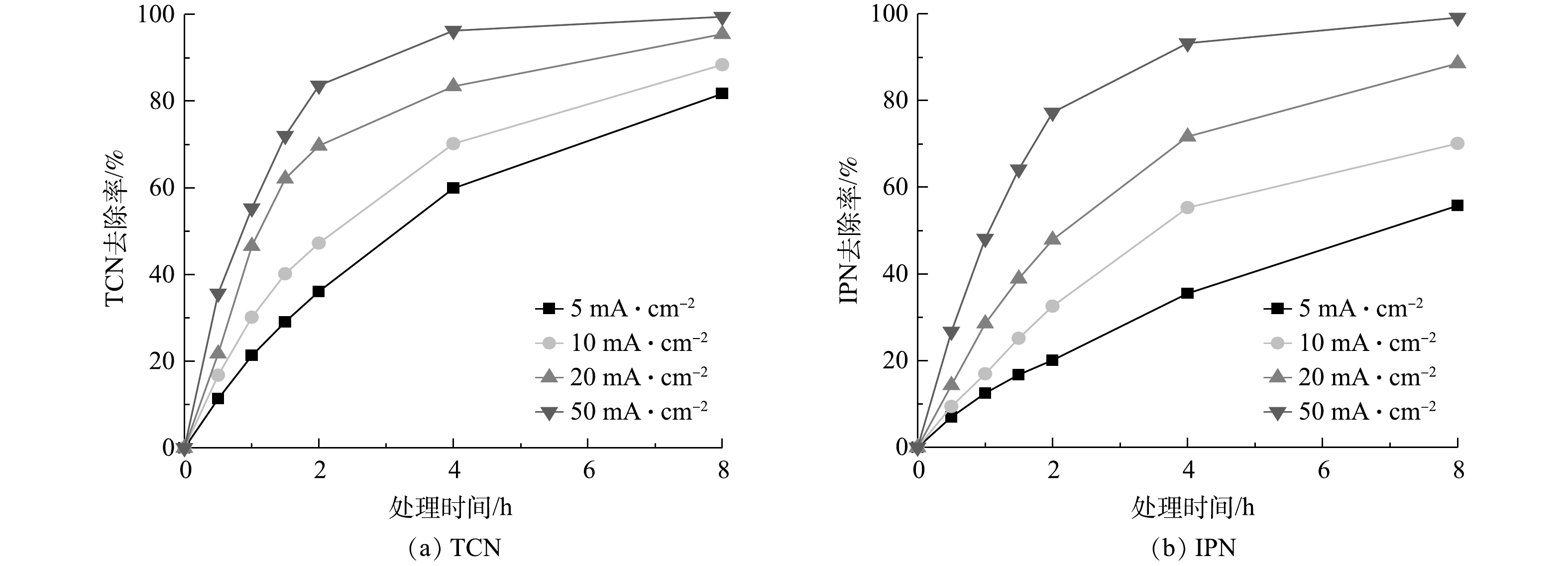
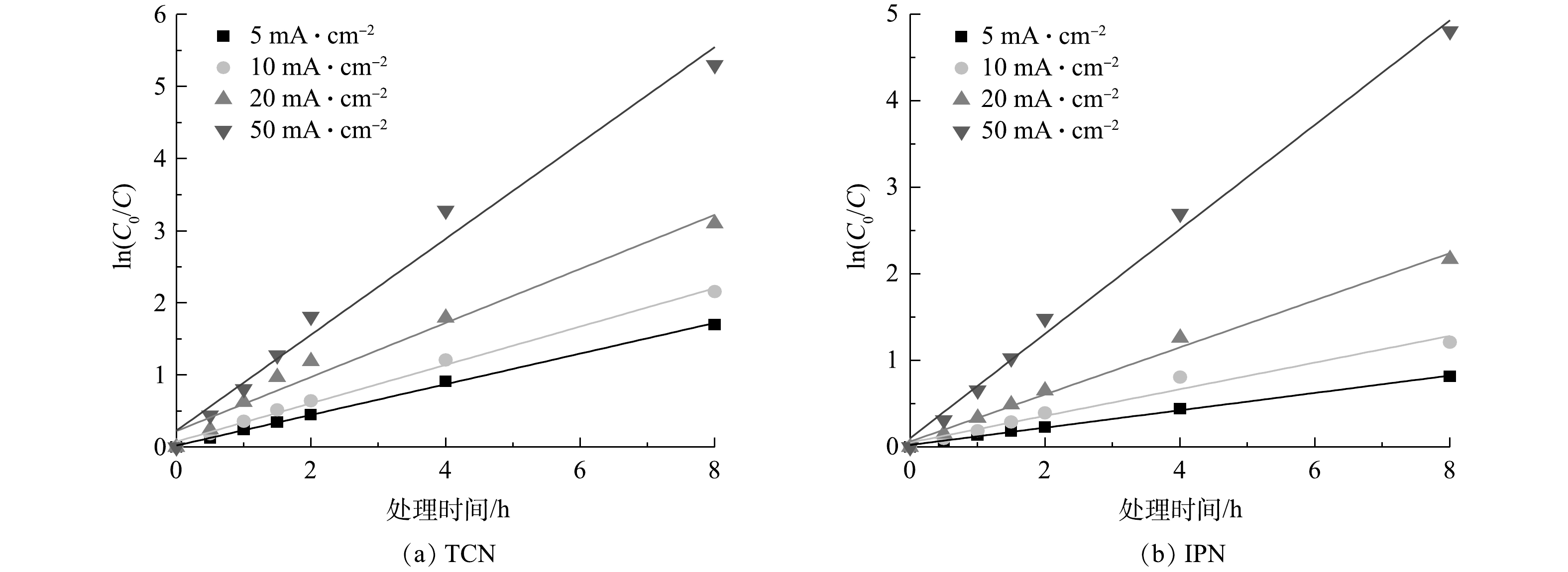
从以上实验和计算可得出,管式电化学反应器在处理高浓度含氰废水中在处理效果和经济性上具有一定的优势,而为使其更好地在实际应用中发挥作用,需对管式电化学反应器进行运行参数的优化。电流密度是管式电化学反应器的核心参数,图8反映了在不同电流密度下随处理时间变化TCN和IPN去除率的变化情况。由图8可以看出,当电流密度为5、10、20、50 mA·cm?1时,TCN和IPN的去除率随着电流密度的增加而增强。这是基于传统电化学氧化理论,在更大电流的情况,会产生更多的氧化活性位点。此外,还可以看到,TCN和IPN的去除速率会随着时间的推移而逐渐放缓,特别是在电流密度较大的情况下,这种现象更为明显。这主要是由2方面的原因引起的:一方面是随着降解的不断进行,废水中污染物的浓度逐渐降低,污染物与电极活性位点的碰撞几率降低,传质过程限制了反应速率的提高,导致了降解速率开始放缓;另一方面,对于TCN来说,水中的其他有机腈可能会在处理过程中转化为TCN,促使TCN的浓度积累,这也抵消了一部分TCN的去除。这也说明合适的处理时间更能达到处理效果和经济效益的平衡。此外,在本研究中,当电流密度由20 mA·cm?1增加至50 mA·cm?1时,TCN的去除率增长变缓;当电流密度增加至一定程度后,会产生一些副反应,O2会从H2O和HO·中释放出来,与废水中的底物发生竞争降解,废水中TCN去除率的增长也就随之放缓[33]。此外,由于电化学氧化过程的能量利用效率限制,高电流密度还会造成大量能量转化为电极的放热过程,使能量利用效率降低。需要特别说明的是,根据稀电解质溶液的德拜-休克尔-昂萨格理论计算,在恒定电流的情况下,溶液中的电解质浓度直接影响电极与溶液接触的相界面的液接电势,液接电势又直接影响了电极表面活性位点的强弱[40]。所以,随着溶液中电解质浓度的减少,最合适的电流密度可能会向更高发生一定的偏移。图9为TCN和IPN在管式电化学反应器处理下被去除过程的一级动力学拟合结果。可以看出,废水中TCN和IPN的电化学去除符合一级动力学方程式。在电流密度为20 mA·cm?1时,TCN和IPN的一级反应动力学速率常数(k1)分别为0.375 s?1和0.272 s?1。这表明管式电化学反应器对于TCN的降解速率高于IPN,这主要是IPN的物质结构使其处理的难度大所致。
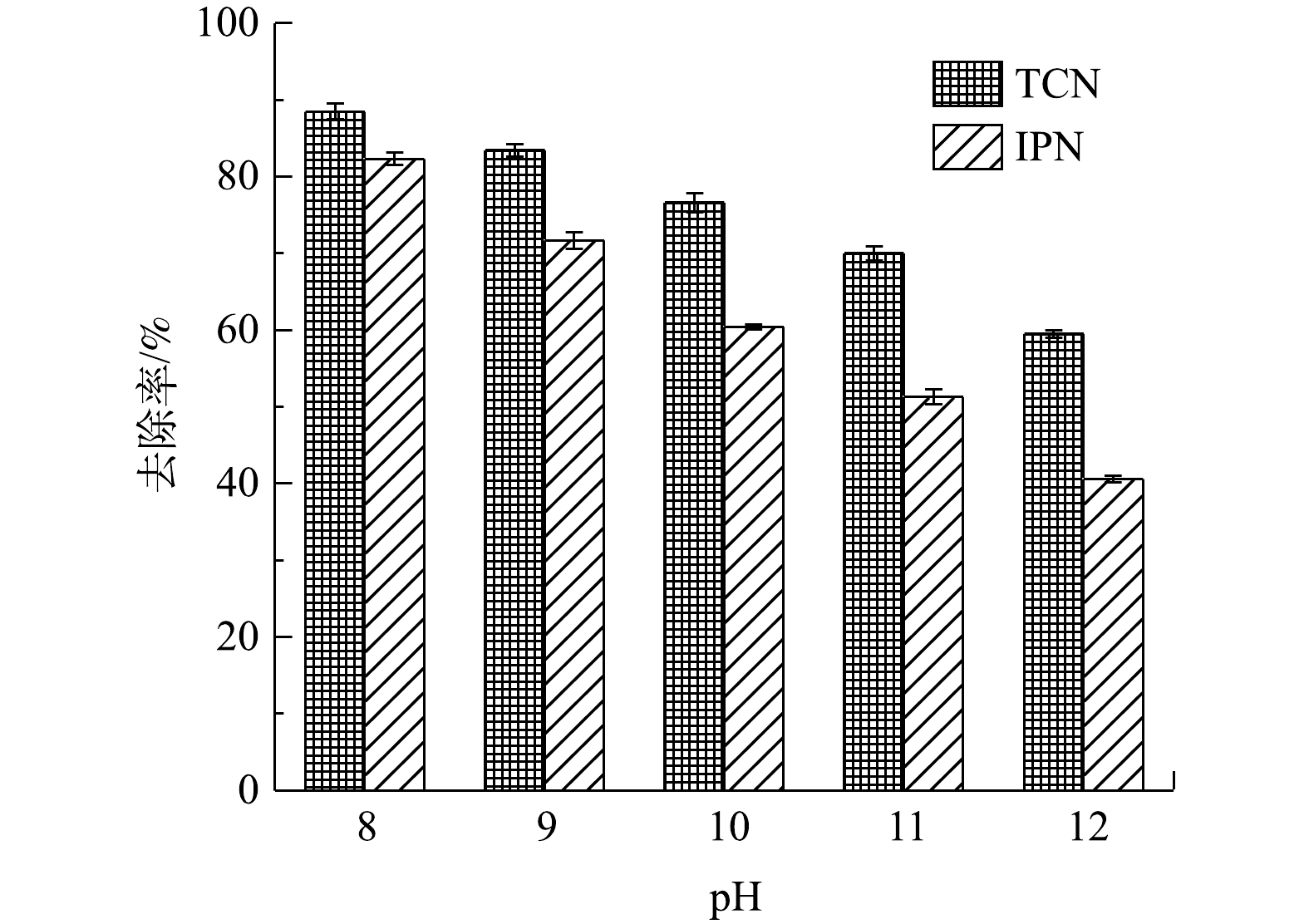
图10反映了分别以不同pH进行高浓度含氰废水处理过程IPN和TCN的变化情况。由于pH升高会导致阳极的析氧电位降低,从而导致更多副反应发生降低氧化效率,故传统的电化学氧化过程应该是在pH为3~4的酸性条件下进行以获得最佳效果[41]。但由于CN?在酸性条件下会生成HCN,故在处理含氰废水时,必须在pH>7的碱性条件下进行以保证运行安全。由图10可知,随着pH升高,TCN的去除率不断降低。这也证明了电化学体系中OH?的存在确实会极大影响电化学反应效率。此外,pH过高还会导致废水中络合物和沉淀物的产生;这一方面会严重影响传质,阻塞孔道,遮挡活性位点;另一方面也会缩短电极的使用寿命。但是,由图10中可以看出,当pH从8升高至9时,TCN和IPN的去除率分别只降低了5.1%和9.6%。这说明在OH?增加的过程中,对废水中污染物去除效率的影响并不是线性下滑的。考虑到实际操作过程中的安全情况,初始pH在8~9为运行过程中较适宜的条件。
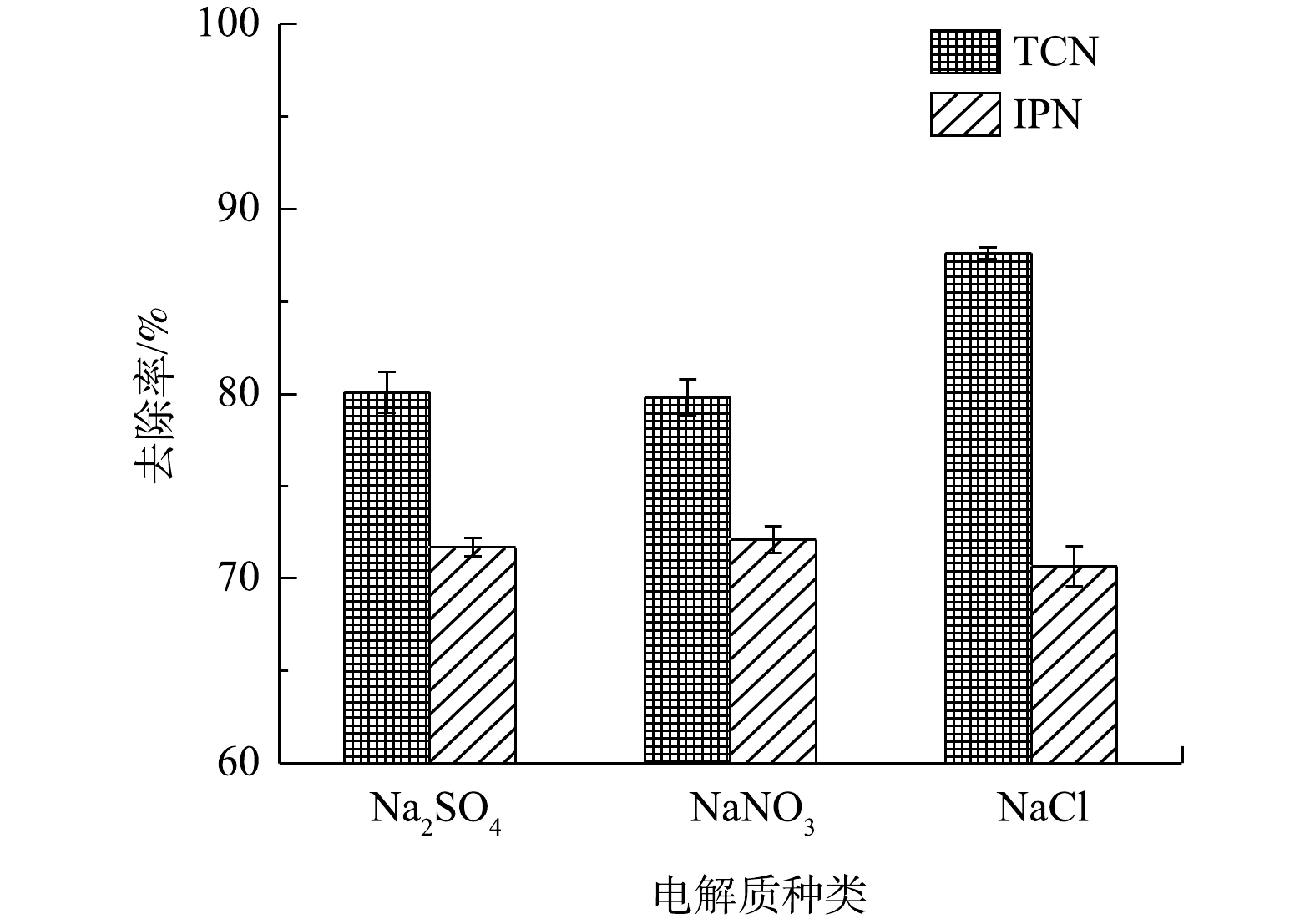
如上文所提到,在电化学氧化的过程中,废水中的氯离子可能会通过变成Cl2而有助于TCN的降解,并且由于自身的电势,阴离子会影响TCN的去除效果。图11反映了在以3种电解质(Na2SO4、NaNO3和NaCl)为废水中唯一电解质的情况下,管式电化学反应器对IPN和TCN去除效果的影响。由图11中可以看出,在以NaCl为唯一电解质时,对TCN的去除率为87.6%,明显高于以Na2SO4为电解质时对TCN的去除率(80.1%)和以NaNO3为电解质时对TCN的去除率(79.8%)。而同时,对于IPN的去除,3种电解质之间没有出现明显的差异。
以上2种现象说明,废水中的氯离子会在阳极被氧化为Cl2且在废水中释放,转化为活性氯,对游离氰进行氧化,而活性氯的氧化能力不足以对IPN进行氧化降解[42]。而


也就是说,管式电化学反应器在发生电化学反应的时候,Ti/RuO2电极可以较容易达到析氯的电位,而基本不可能对


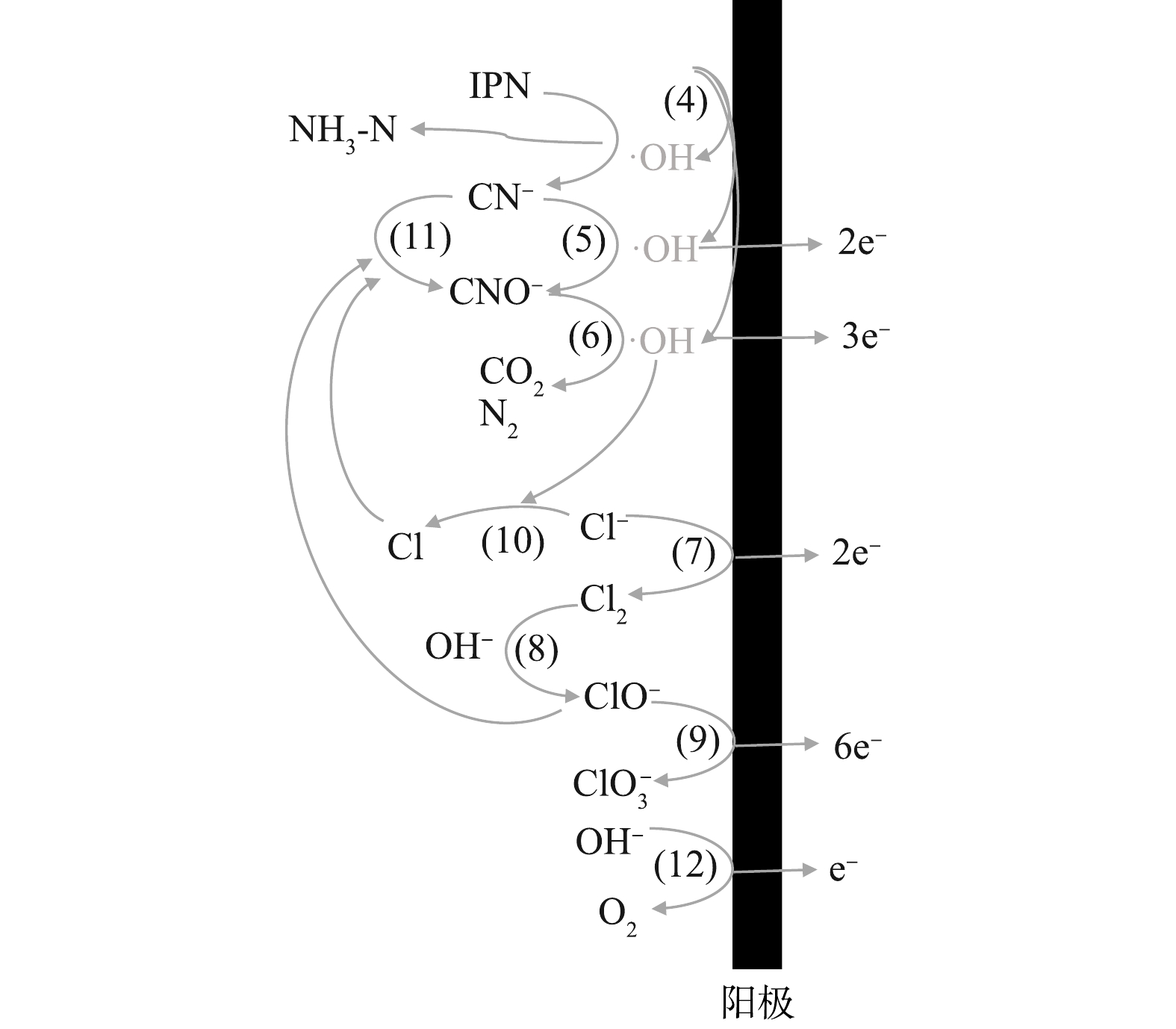
在阳极区,首先形成高电位(Ti/RuO2)或通过表面的空穴产生羟基自由基(Ti/PbO2)(式(4))[38]。废水中的间苯二腈等难降解有机物通过阳极上的氧化,腈基脱落转化为水中游离的CN?,这些转化的CN?与废水中本来存在的CN?一起先被氧化为CNO?,再被进一步氧化至完全矿化,如式(5)~式(6)所示[43]。电化学反应器的阳极表面还会发生析氯和析氧反应,如式(7)和式(12)所示。一方面,阳极析氯反应产生的Cl2会在碱性条件下转化为ClO?(式(8)),甚至有可能在阳极提供的电极电位下,发生如式(9)[44]的反应,在此过程中产生的活性氯基团(ClO?),也可以参与到CN?的氧化过程中,发生如式(11)的反应,这一定程度上提升了电化学去除CN?的效果,也就是上文中所提到的;另一方面,Cl?会与阳极产生的·OH反应,生成氯自由基(式(10))[45],尽管氯自由基本身也可以参与氧化CN?,但仍抑制了电化学体系的处理效率。此外,当运行的电流密度过大时,析氧反应(式(12))也会对处理效率起到抑制作用。尽管对于最终处理效率的作用不一,但从最终结果来看,废水中Cl?的存在对于CN?的去除的促进作用要强于其余的抑制作用。这可为电化学处理含氰废水提供参考。图12为管式电化学反应器阳极作用的机理图。
2)管式电化学反应器尽管单位能耗和投资成本(ETR-Ru为94 900 元·t?1)较高,但运行成本低廉,ETR-Ru的运行成本仅为次钠氯碱法的13.10%。
3) 电化学氧化去除废水中TCN和IPN符合一级反应动力学方程。在废水初始pH为8~9时,以20 mA·cm?1的电流密度进行降解,可以达到处理效果和经济效益的最佳平衡。机理探究过程验证了水中氯离子会促进TCN的去除。综合考虑建设成本和运行时间,ETR-Ru的经济性最佳。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 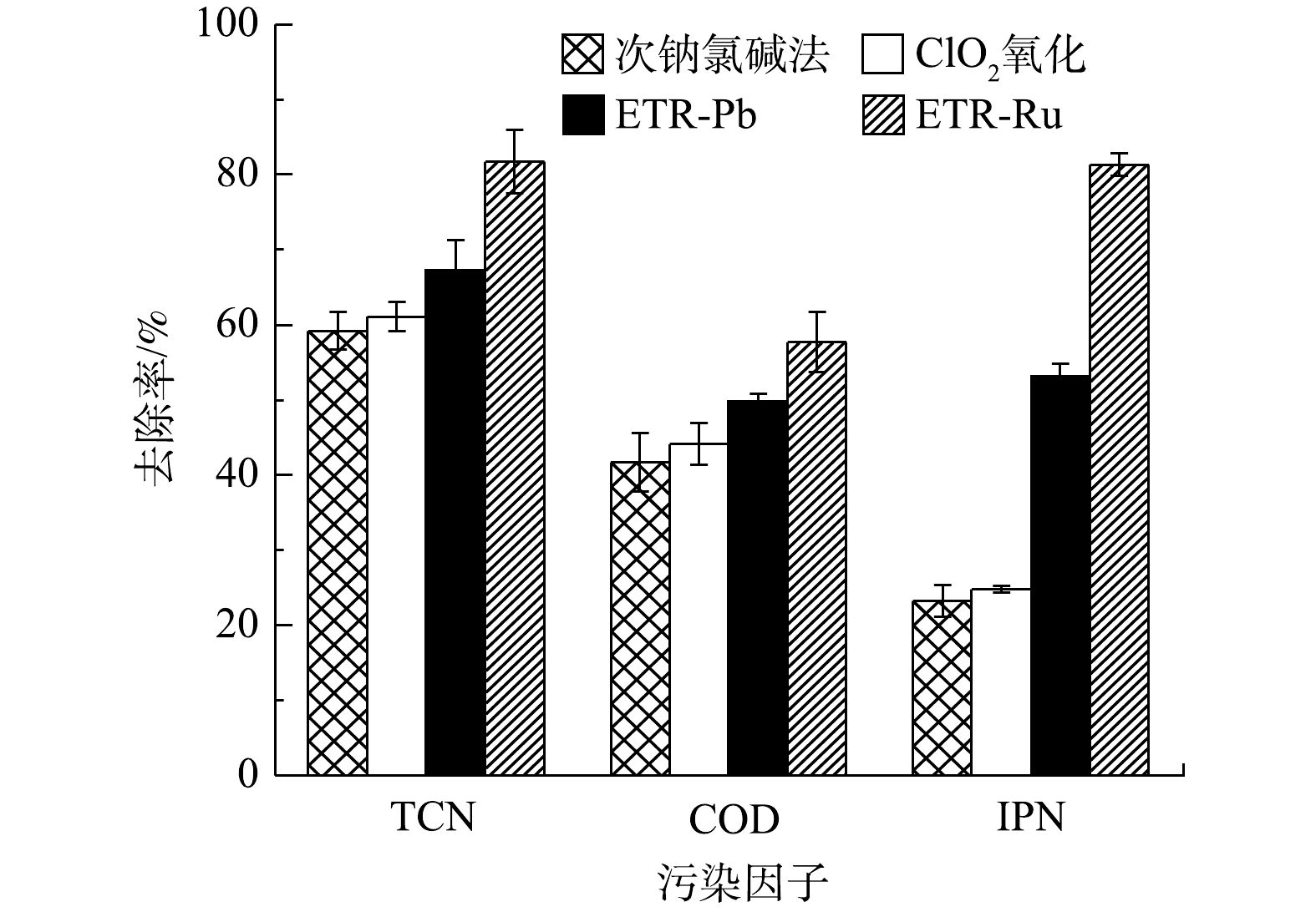
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图