华南农业大学资源环境学院,广州 510642
School of Resources and Environment, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou 510642, China
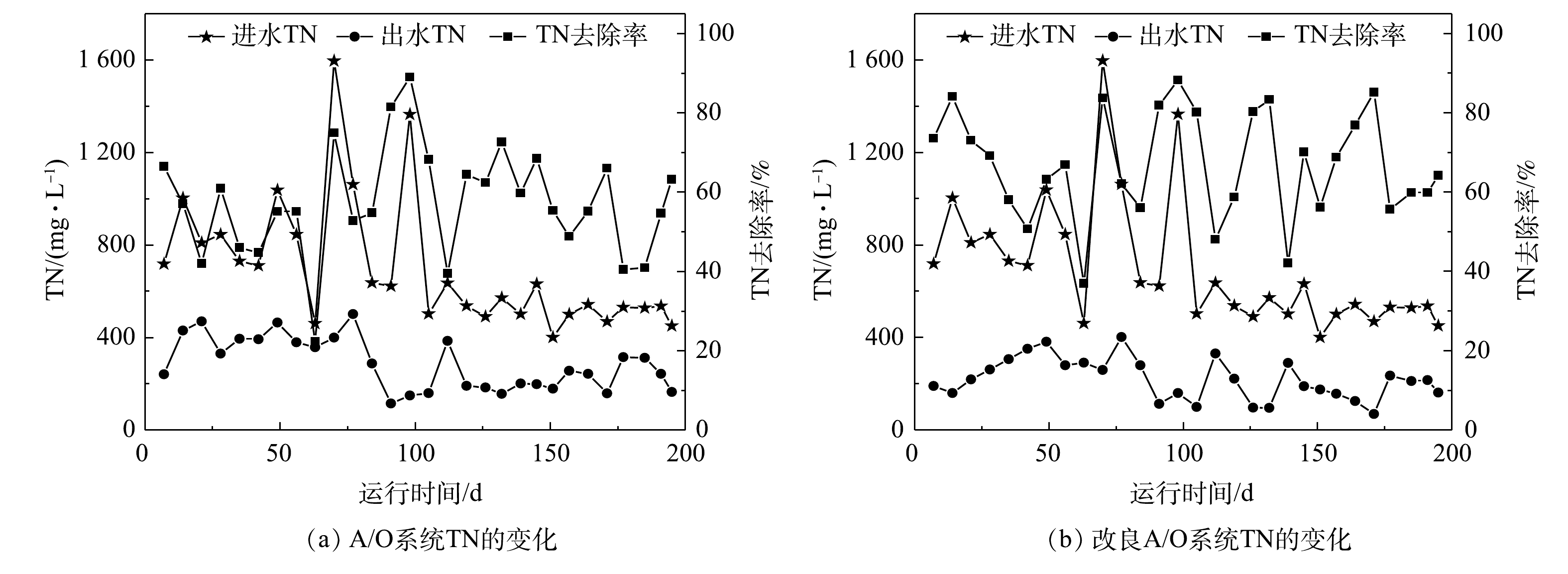
-N去除率分别为42.5%~97.4%、36.9%~88.3%和94.2%~99.4%,均优于A/O工艺的去除效果且具有显著提升。综合考虑对污染物的去除效果以及企业运行成本,在水力停留时间为10 d时,改良A/O工艺出水水质达到最优,出水COD平均去除率可达75.3%,对
。此外,可结合多级改良A/O工艺和组合工艺进一步优化出水水质。除微生物同化作用以及硝化反硝化途径外,系统中含氮类物质还可通过狐尾藻植物去除。改良A/O工艺中狐尾藻植物能够大量生长,含水量为88.8%~89.0%,TP和TN质量分数分别为3.4~5.2 g·kg
,TN质量分数要远高于普通富营养化水体栽培的狐尾藻,这说明狐尾藻在改良A/O工艺中能够更好的吸收污染水体中的含氮物质。以上结果可为改良A/O工艺对猪场沼液的优化处理提供参考。
In order to improve the removal efficiency of pollutants from piggery biogas slurry by traditional A/O system and realize the operation mode of high efficiency and low cost, the process was optimized by adding elastic packing to A/O system and planting myriophylla. The results showed that when the influent COD, TN and
-N were 42.5%~97.4%, 36.9%~88.3% and 94.2%~99.4% respectively, which were better than those of A/O system and had a significant improvement. In addition, the effluent quality can be further optimized by combining multi-stage improved A/O system and combined system. Considering the removal efficiency of pollutants and the operation cost of the enterprise, the HRT of 10 d was most suitable for the actual operation of the improved A/O system, the average removal rate of COD in the effluent was 75.3%, the average removal rate of
. In addition to microbial assimilation and nitrification and denitrification, nitrogen-containing substances in the system could also be removed by myriophylla. In the improved A/O system, myriophylla could grow in large quantities with water content of 88.8%~89.0%, TP and TN contents of 3.4~5.2 g·kg
, respectively, and the concentration of TN was much higher than that of myriophylla in eutrophic water, which showed that myriophylla in the improved A/O system had better absorption performance toward nitrogen in the polluted water. The above results provide a reference for the optimization of piggery biogas slurry treatment by improved A/O system.
.
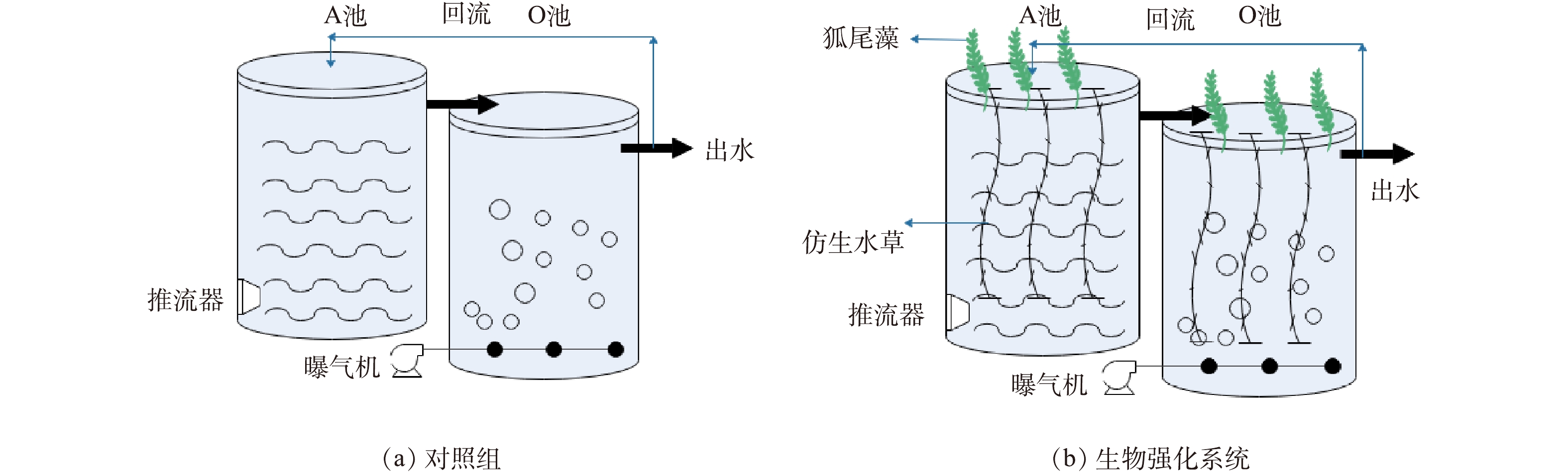
Device diagram of the A/O system
对比A/O系统与改良A/O系统中COD的变化
Comparison of COD changes between A/O system and improved A/O system
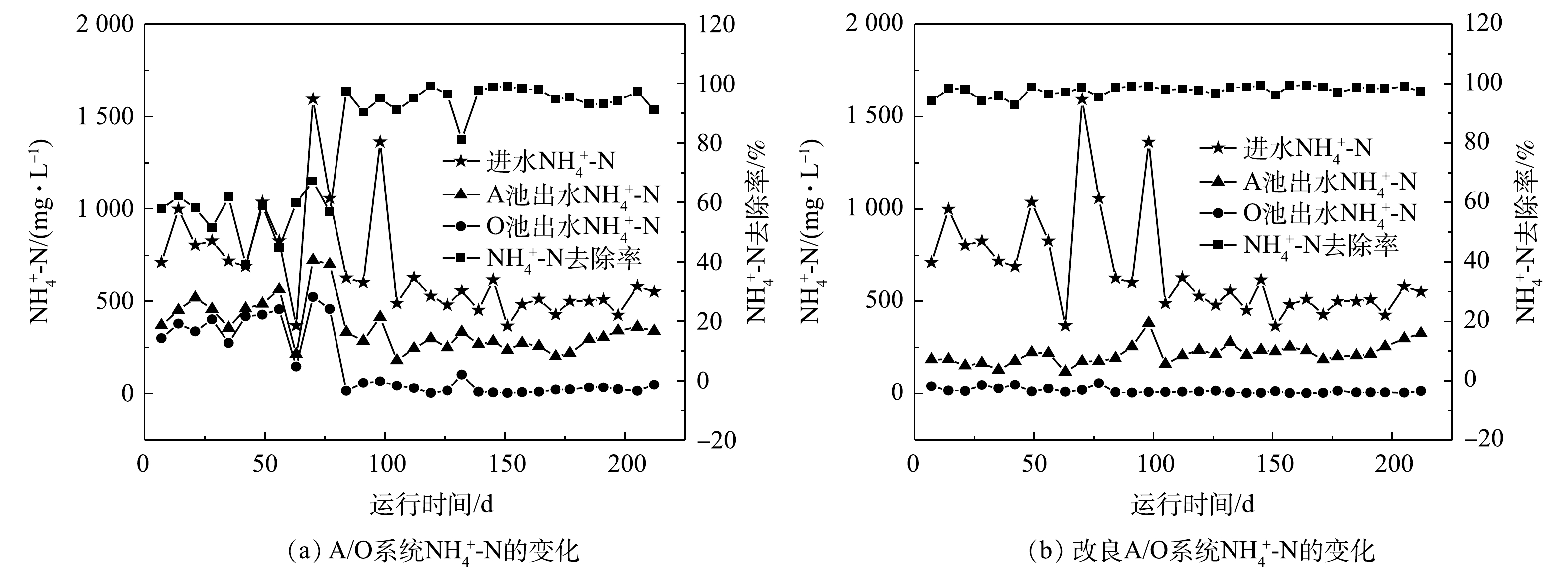
-N changes between A/O system and improved A/O system
-N changes between A/O system and improved A/O system
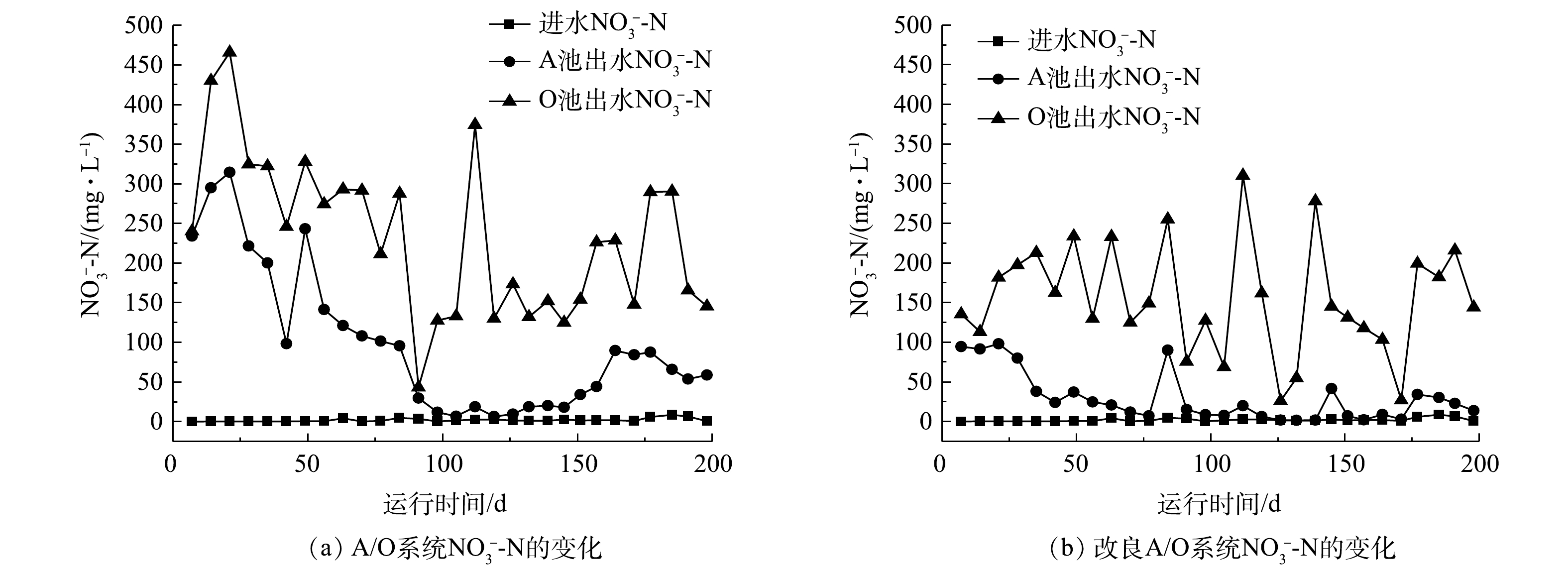
对比A/O系统与改良A/O系统中TN的变化
Comparison of TN changes between A/O system and improved A/O system
| [1] | 涂敏. 规模化养猪场粪污处理与综合利用综述[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2019, 25(15): 139-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2019.15.055 |
| [2] | ZHANG M M, LUO P, LIU F, et al. Nitrogen removal and distribution of ammonia-oxidizing and denitrifying genes in an integrated constructed wetland for swine wastewater treatment[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2017, 104: 30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.04.022 |
| [3] | MIYOKO W, TOMOKO Y, YASUYUKI F, et al. Treatment of swine wastewater in continuous activated sludge systems under different dissolved oxygen conditions: Reactor operation and evaluation using modelling[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 250: 574-582. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.078 |
| [4] | ZHANG D, WANG X X, ZHOU Z G. Impacts of small-scale industrialized swine farming on local soil, water and crop qualities in a hilly red soil region of subtropical China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(12): 1524. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14121524 |
| [5] | XU Z C, SONG X Y, LI Y, et al. Removal of antibiotics by sequencing-batch membrane bioreactor for swine wastewater treatment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 684: 23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.241 |
| [6] | LI X, LI Y Y, LI Y, et al. Enhanced nitrogen removal and quantitative analysis of removal mechanism in multistage surface flow constructed wetlands for the large-scale treatment of swine wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 246: 575-582. |
| [7] | LUO P, LIU F, ZHANG S N, et al. Nitrogen removal and recovery from lagoon-pretreated swine wastewater by constructed wetlands under sustainable plant harvesting management.[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 258: 247-254. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.017 |
| [8] | 郑效旭, 李慧莉, 徐圣君, 等. SBR串联生物强化稳定塘处理养猪废水工艺优化[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(6): 1503-1511. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201902016 |
| [9] | MCKIE M J, BERTOIA C, EDMONDS L T, et al. Andrews. Pilot-scale comparison of cyclically and continuously operated drinking water biofilters: Evaluation of biomass, biological activity and treated water quality[J]. Water Research, 2019, 149: 488-495. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.033 |
| [10] | 王欢, 李旭东, 曾抗美. 猪场废水厌氧氨氧化脱氮的短程硝化反硝化预处理研究[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(1): 114-119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.01.020 |
| [11] | JIA S J, CHEN X Q, SUENAGA T, et al. Spatial and daily variations of nitrous oxide emissions from biological reactors in a full-scale activated sludge anoxic/oxic process.[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2019, 127(3): 333-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.08.003 |
| [12] | WANG Q B, CHEN Q W. Simultaneous denitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal in a full-scale anoxic-oxic process without internal recycle treating low strength wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 39(1): 175-183. |
| [13] | 晏广, 邱兆富, 曹国民, 等. A/O系统处理低C/N奶牛场废水中的抗生素[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(7): 1817-1826. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201909163 |
| [14] | 陈锦良. 基于A/O工艺的微电解耦合反硝化污泥深度处理猪场沼液研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2018. |
| [15] | LIU J B, ZHANG P Y, TIAN Z Y, et al. Pollutant removal from landfill leachate via two-stage anoxic/oxic combined membrane bioreactor: Insight in organic characteristics and predictive function analysis of nitrogen-removal bacteria[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 317: 69-76. |
| [16] | 孙亚平, 林运通, 梁瑜海, 等. 组合工艺对高浓度猪场废水的深度处理[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(S2): 169-174. |
| [17] | 张洪刚, 洪剑明. 人工湿地中植物的作用[J]. 湿地科学, 2006, 4(2): 146-154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5948.2006.02.012 |
| [18] | 金树权, 周金波, 包薇红, 等. 5种沉水植物的氮、磷吸收和水质净化能力比较[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(1): 156-161. |
| [19] | LIU F, ZHANG S N, LUO P, et al. Purification and reuse of non-point source wastewater via Myriophyllum-based integrative biotechnology: A review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 248: 3-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.181 |
| [20] | 钟爱文, 曹特, 张萌, 等. 光照和黑暗条件下苦草和穗花狐尾藻对铵态氮的吸收[J]. 湖泊科学, 2013, 25(2): 289-294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2013.02.017 |
| [21] | 孙宏, 李宁, 汤江武, 等. 狐尾藻在养殖污水净化中的作用原理及相关应用进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2020, 56(3): 37-42. |
| [22] | 吴晓梅, 叶美锋, 吴飞龙, 等. 狐尾藻净化生猪养殖场沼液的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(4): 796-803. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1188 |
| [23] | 赵宪章, 董文艺, 王宏杰, 等. 组合填料强化多级AO工艺处理低温污水脱氮效果[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(3): 49-53. |
| [24] | 晁雷, 孟佳, 王焕书, 等. 三种填料改良A/O工艺处理炼化废水的对比研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2019, 45(8): 103-107. |
| [25] | FENG L J, YANG G F, ZHU L, et al. Enhancement removal of endocrine-disrupting pesticides and nitrogen removal in a biofilm reactor coupling of biodegradable Phragmites communis and elastic filler for polluted source water treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 187: 331-337. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.03.095 |
| [26] | 傅金祥, 陈东宁, 李微, 等. 水力负荷对A/O生物滤池处理生活污水的影响[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 24(3): 447-450. |
| [27] | 李海华, 金艳艳, 刘保, 等. HRT及有机负荷对厌氧+好氧UF组合工艺处理养猪场粪污的试验研究[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2012, 46(6): 691-694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2012.06.019 |
| [28] | 李倩, 全天秀, 李祖明, 等. 狐尾藻营养活性成分的研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(11): 318-322. |
| [29] | 余红兵, 肖润林, 杨知建, 等. 五种水生植物生物量及其对生态沟渠氮、磷吸收效果的研究[J]. 核农学报, 2012, 26(5): 798-802. |
| [30] | XU W W, HU W P, DENG J C, et al. Effects of harvest management of Trapa bispinosa on an aquatic macrophyte community and water quality in a eutrophic lake[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 64: 120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.12.028 |
| [31] | 郑焕春, 周青. 微生物在富营养化水体生物修复中的作用[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(1): 197-202. |



























































































































































































































































































































































































 下载:
下载: 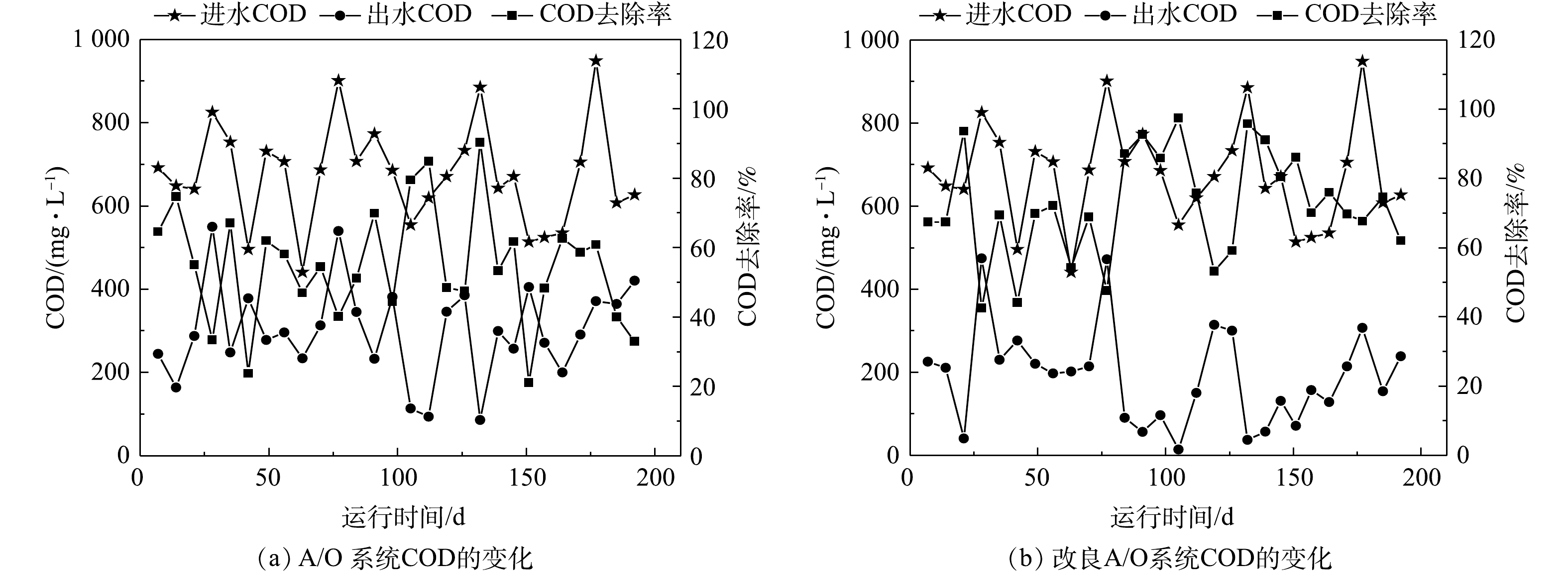













 点击查看大图
点击查看大图