2.北控水务集团有限公司,北京 100102
1.College of Chemical Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing 100029, China
2.Beijing Enterprises Water Group Limited, Beijing 100102, China
在(30±2) °C的条件下,通过精确控制供氧量,以氧气为气源培养E1反应器,以空气为气源培养E2反应器,探究了不同气源对一段式短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺启动、负荷提升及稳定运行效果的影响。结果表明:以氧气为气源的E1反应系统一段式短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化效果更佳,E1反应器中的
。通过不同气源对一段式短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺启动与运行的作用效应对比,证明了以氧气为气源应用于一段式短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺的可行性与优势。以上研究结果可为其在厌氧氨氧化工程的应用提供参考。
Through precise control the oxygen supply amount at (30±2) °C, the E1 reactor with oxygen as the gas source and E2 reactor with air as the gas source were cultivated. These two sets of one-stage partial nitrification-anammox EGSB reactors were compared to explore the effects of different gas sources on the start-up, load increase and stable running of the one-stage partial nitrification-anammox process. The results showed that one-stage partial nitrification-anammox in E1 reaction system with oxygen as gas source performed better, the removal rates of
-N and TN in E1 reactor were over 95% and 85%, respectively. The time to achieve the load increase was about 10 days; After one-stage shortcut nitrification anammox, ΔTN/Δ
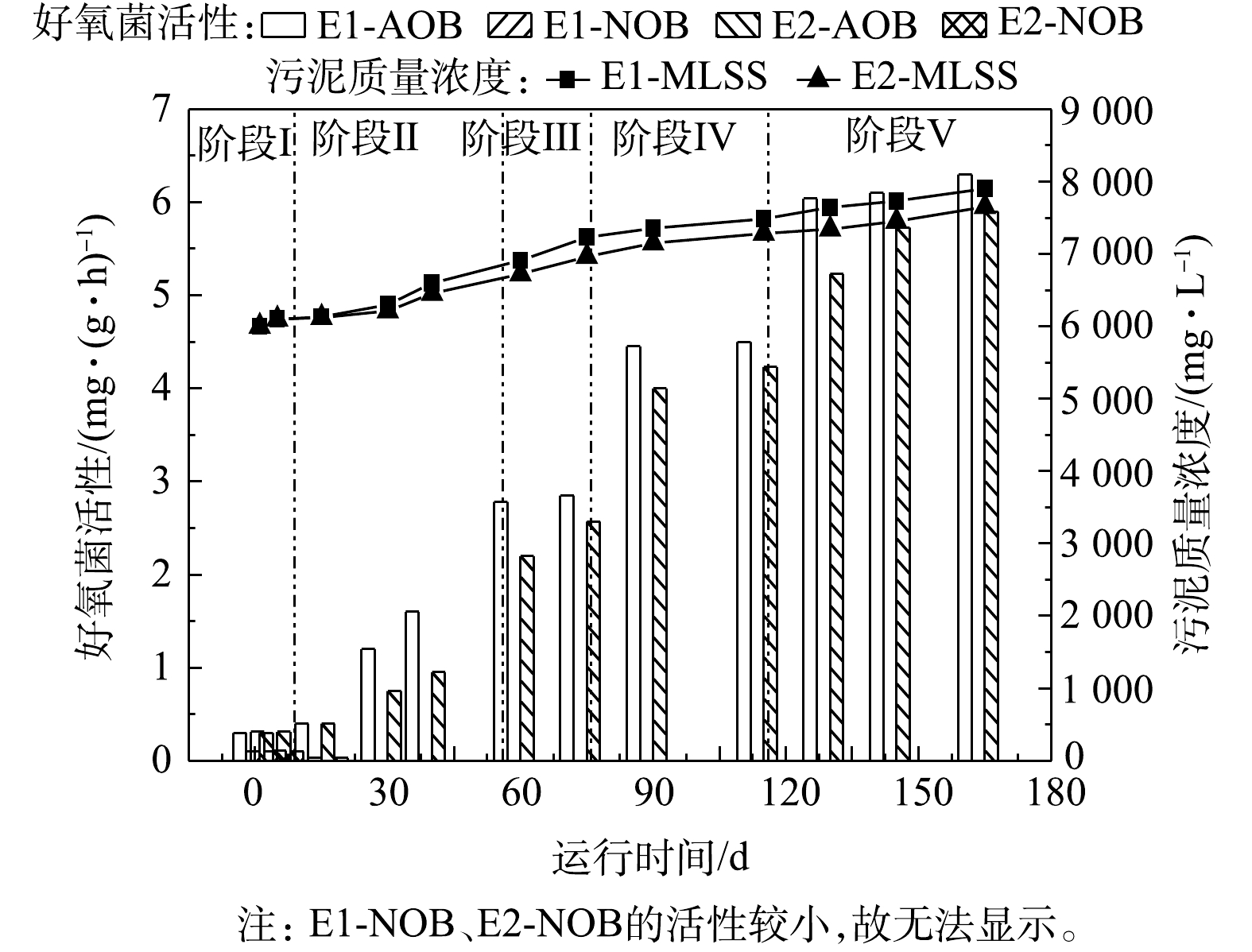
-N were stable at 0.88 and 0.11 in E1 reaction system, respectively; the AOB activity in E1 and E2 reactors increased from 0.3 mg·(g·h)
, respectively. Through comparison of the effects of different gas sources on the start-up and running of one-stage partial nitrification-anaerobic process, the feasibility and advantages of the oxygen as gas source in one-stage partial nitrification-anaerobic system were proved. This result can provide references for its application in anaerobic ammonia oxidation.
.
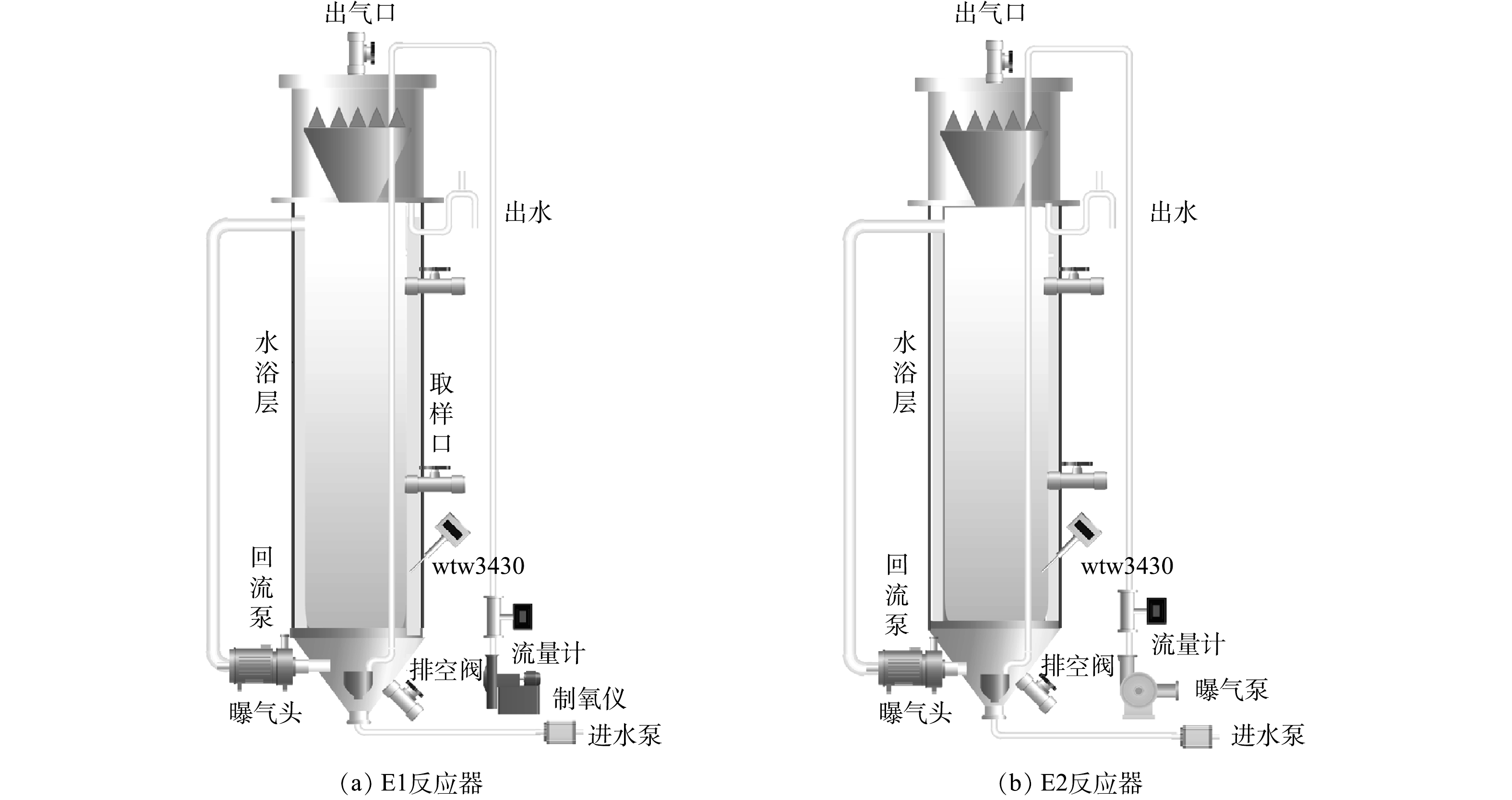
EGSB experimental device
Performance of E1 reactor during the start-up process
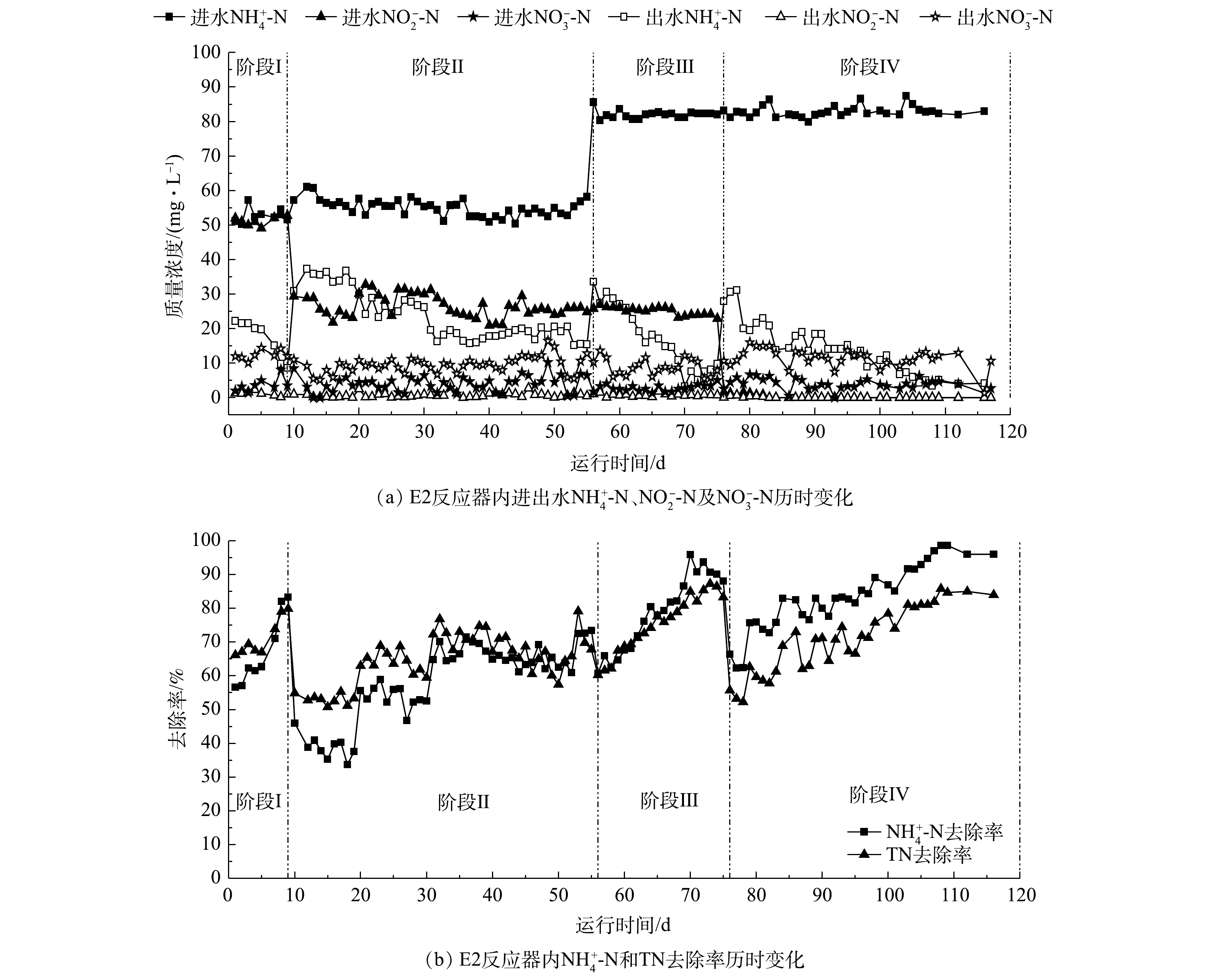
Performance of E2 reactor during the start-up process
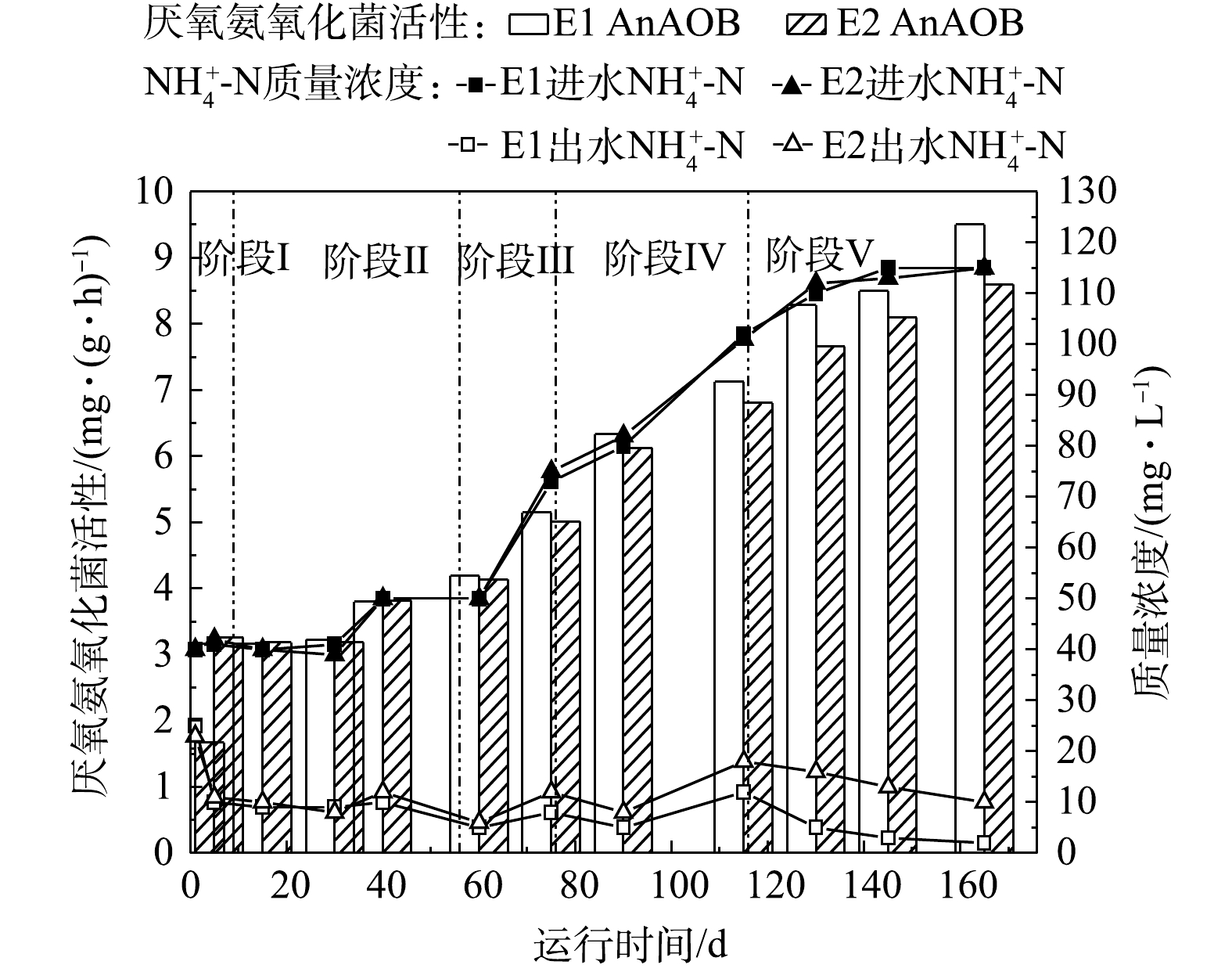
Ammonia nitrogen removal at each stage in the E1 and E2 reactors
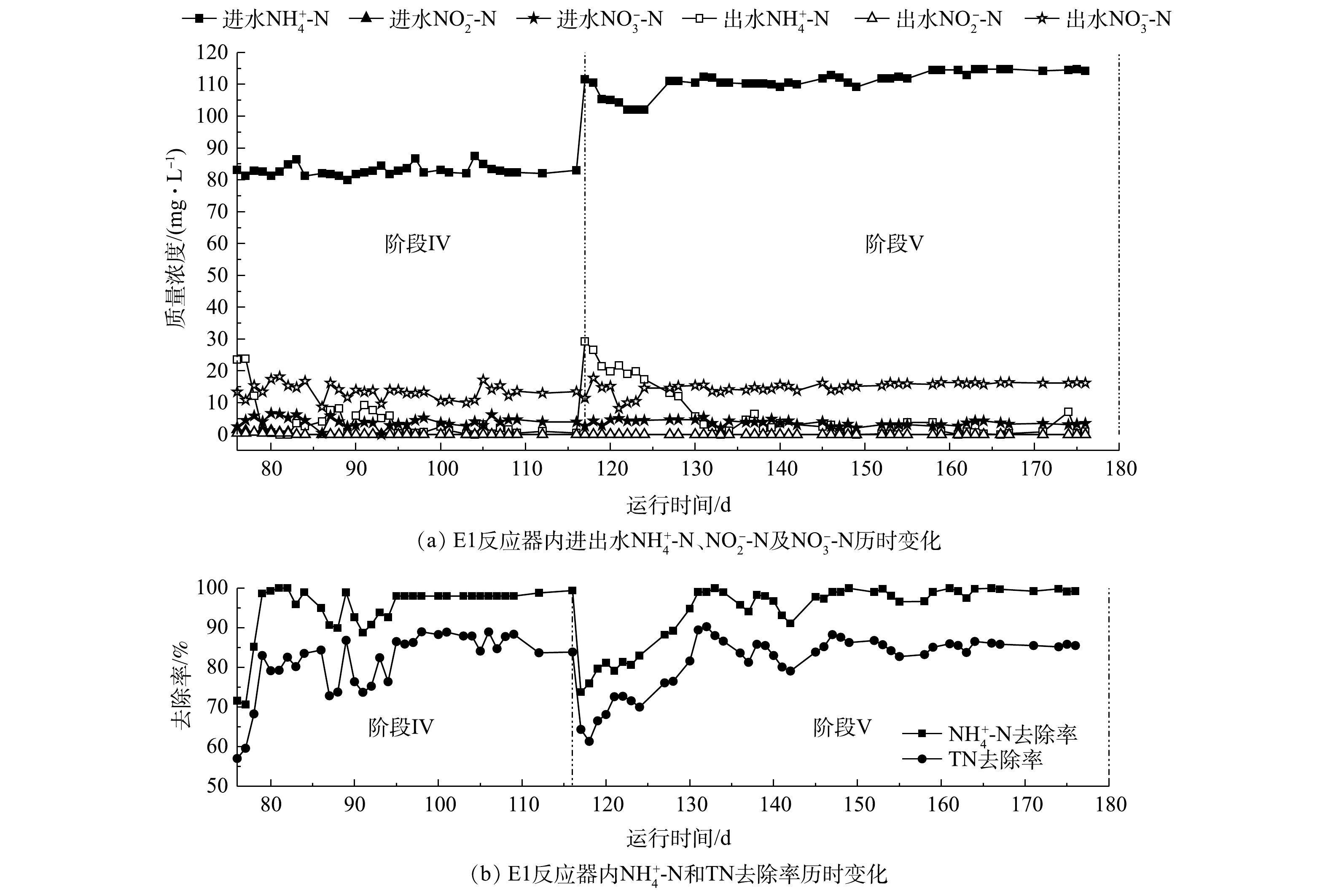
Performance of E1 reactor during the stable running process
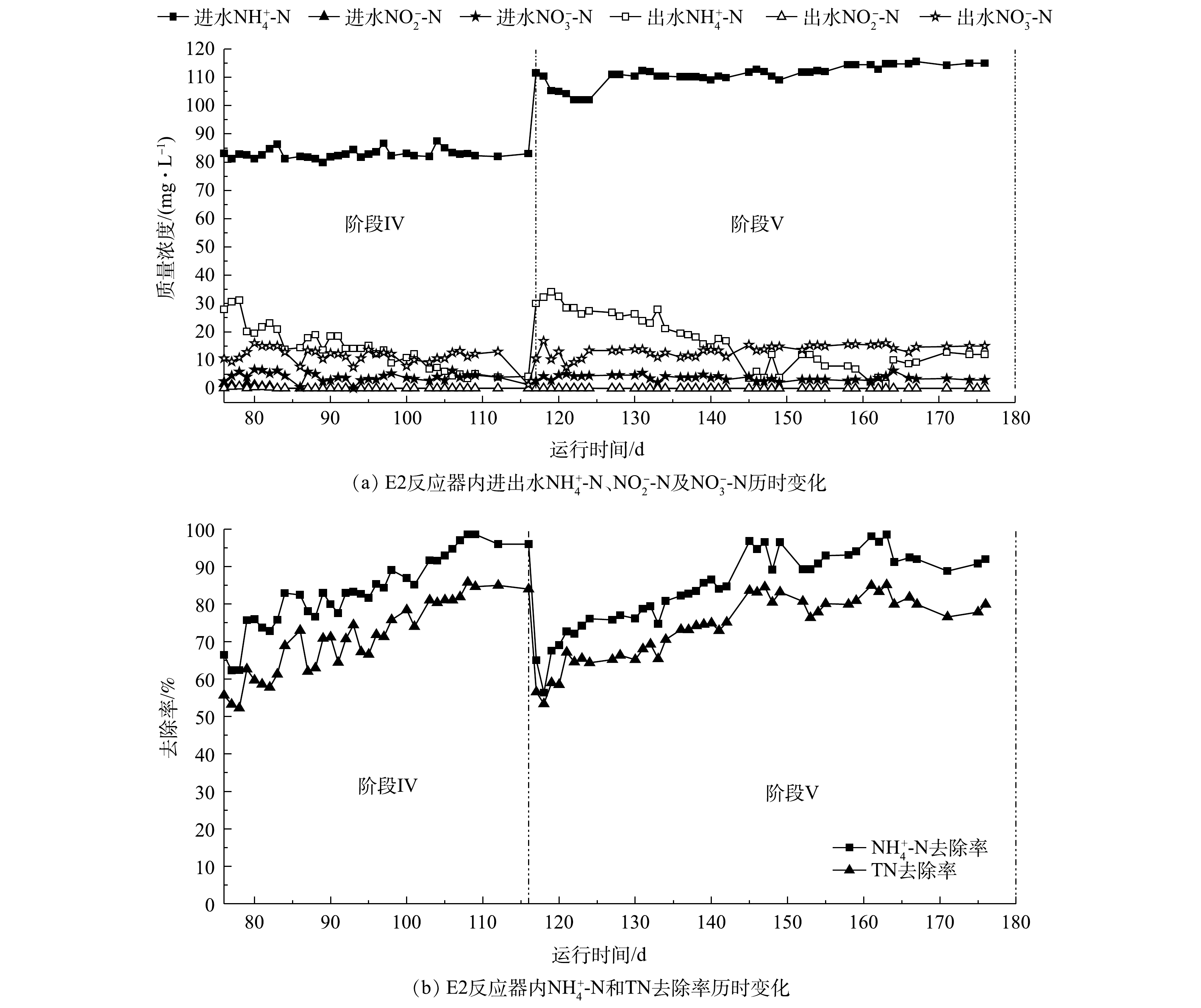
Performance of E2 reactor during the stable running process
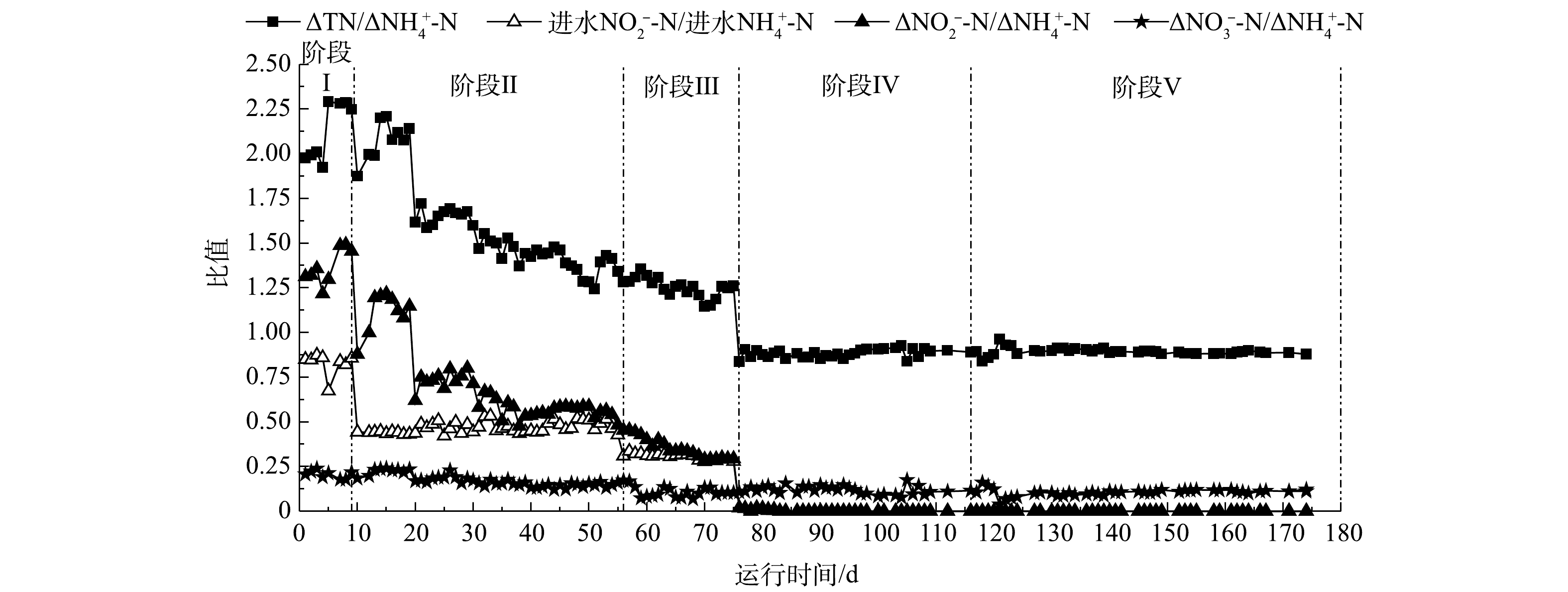
Changes of stoichiometric ratio in E1 reactor
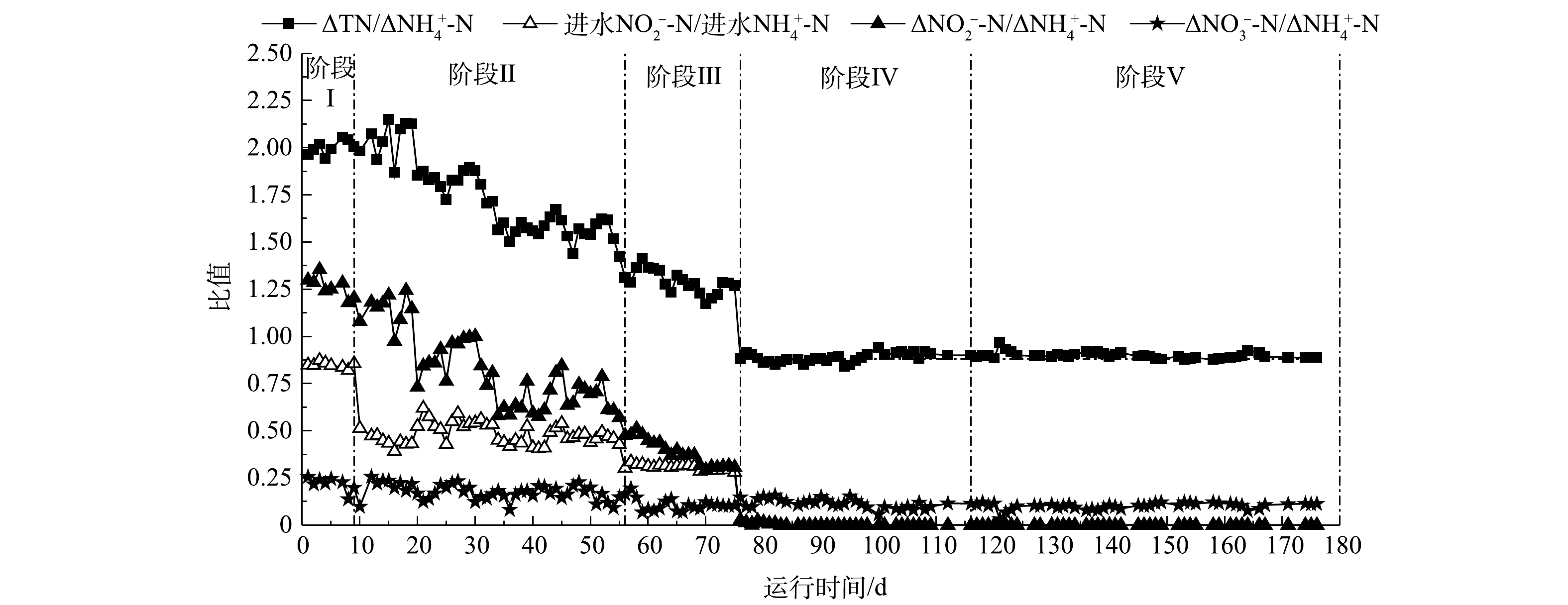
Changes of stoichiometric ratio in E2 reactor
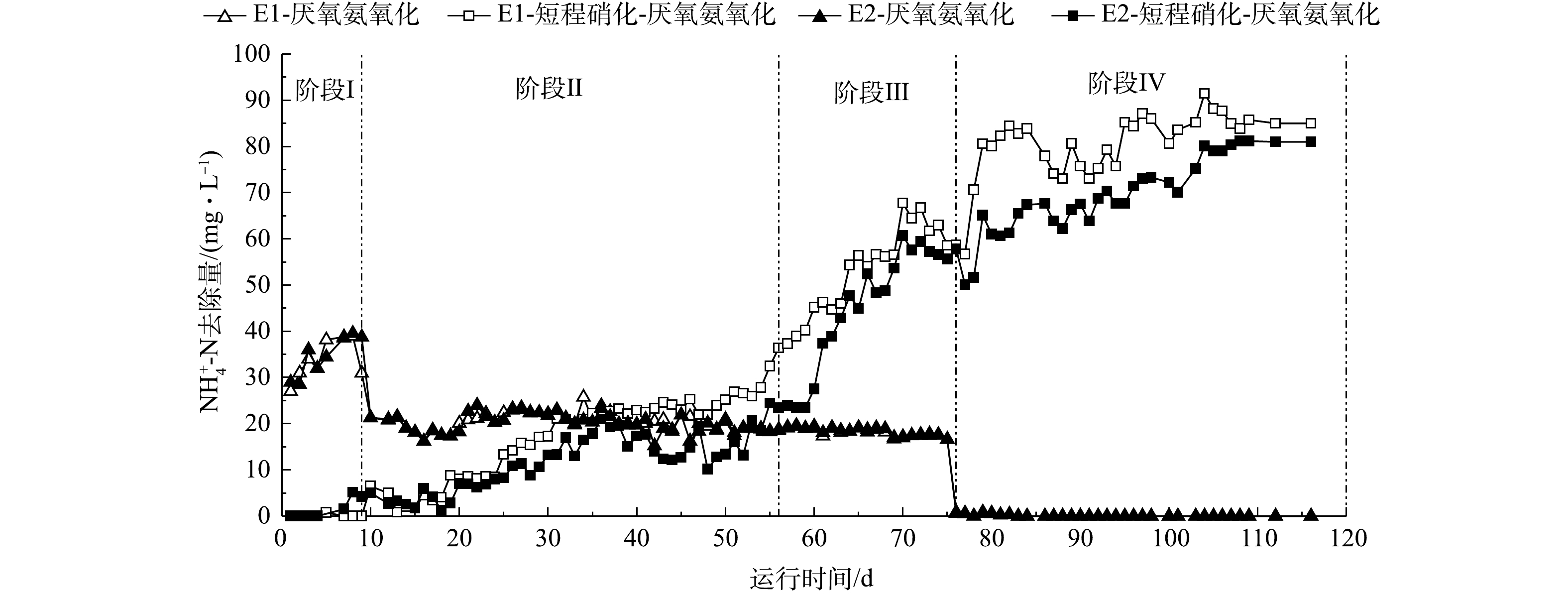
Activities of functional bacteria at each stage
Activities of AnAOB at each stage
| [1] | KUENUEN J G. Anammox bacteria: From discovery to application[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6(4): 320-326. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1857 |
| [2] | YANG W, HE S L, HAN M, et al. Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure in the start-up and substrate inhibition stages of an anammox reactor[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2018, 126(1): 88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.02.004 |
| [3] | VAN DE GRAAF A A, MULDER A, BRUIJN P D, et al. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bedreactor[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 1995, 16(3): 177-249. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.1995.tb00281.x |
| [4] | SIEGRIST H, SALZGEBER D, EUGSTER J, et al. Anammox brings WWTP closer to energy autarky due to increased biogas production and reduced aeration energy for N-removal[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2008, 57(3): 383-388. doi: 10.2166/wst.2008.048 |
| [5] | KARKAL B, KUENUEN J G, VAN L M C, et al. Engineering. Sewage treatment with anammox[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5979): 702-703. doi: 10.1126/science.1185941 |
| [6] | MIAO Y Y, PENG Y Z, ZHANG L, et al. Partial nitrification-anammox (PNA) treating sewage with intermittent aeration mode: effect of influent C/N ratios[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 664-672. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.072 |
| [7] | MIAO L, WANG K, WANG S, et al. Advanced nitrogen removal from landfill leachate using real-time controlled three-stage sequence batch reactor (SBR) system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 159: 258-265. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.058 |
| [8] | MOLINUEVO B, GARCIA M C, KARAKASHEV D, et al. Anammox for ammonia removal from pig manure effluents: Effect of organic matter content on process performance[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(7): 2171-2175. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.10.038 |
| [9] | WANG G, XU X, ZHOU L, et al. A pilot-scale study on the start-up of partial nitrification-anammox process for anaerobic sludge digester liquor treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 241: 181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.125 |
| [10] | KELUSKARR, NERURKARA, DESAI A, et al. Development of a simultaneous partial nitrification, anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitrification (SNAD) bench scale process for removal of ammonia from effluent of a fertilizer industry[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 130: 390-397. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.066 |
| [11] | YUAN S H, ZHAO X H, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Achieving high-rate autotrophic nitrogen removal via canon process in a modified single bed tidal flow constructed wetland[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 237: 329-335. |
| [12] | ZHANG Z, CHEN S, WU P, et al. Start-up of the Canon process from activated sludge under salt stress in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR)[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(16): 6309-6314. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.040 |
| [13] | GUANG J X, ZHOU Y, YANG Q, et al. The challenges of mainstream deammonification process for municipal used water treatment[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(6): 2485-2490. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6423-6 |
| [14] | CAO Y, VAN L M C, DAIGGERG T, et al. Mainstream partial nitritation-anammox in municipal wastewater treatment: Status, bottlenecks, and further studies[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(4): 1365-1383. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-8058-7 |
| [15] | LACKNER S, GILBERT E M, VLAEMINCK S E, et al. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences: An application survey[J]. Water Research, 2014, 55: 292-303. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.02.032 |
| [16] | DE CLIPPELEIR H, VLAEMINEK S E, DE WILDE F, et al. One-stage partial nitritation/anammox at 15 degrees C on pretreated sewage: Feasibility demonstration at lab-scale[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(23): 10199-10210. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4744-x |
| [17] | HUNIK J H, TRAMPER J, WIJFFELS R H, et al. A strategy to scale up nitrification processes with immobilized cells of nitrosamines europaea and nitrobacter agilis[J]. Bioprocess Engineering, 1994, 11(2): 73-82. doi: 10.1007/BF00389563 |
| [18] | 谢丽, 殷紫, 尹志轩, 等. 一段式厌氧氨氧化工艺亚硝酸盐氧化菌抑制方法研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(7): 2647-2655. |
| [19] | LIU G Q, WANG J M. Long-term low DO enriches and shifts nitrifier community in activated sludge[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(10): 5109-5117. |
| [20] | MIAO Y Y, ZHANG L, YANG Y D, et al. Start-up single partial nitrification-anammox process treating low-strength sewage and its restoration from nitrate accumulation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 218: 771-779. |
| [21] | CALDERON K, GONZALEZ-MARTINEZ A, MONTERO-PUENTE C, et al. Bacterial community structure and enzyme activities in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) using pure oxygen as an aeration source[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 103(1): 87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.133 |
| [22] | 江雪姣. 纯氧曝气系统中活性污泥特性研究[J]. 文山学院学报, 2020, 33(3): 37-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9200.2020.03.008 |
| [23] | 徐冰清, 詹超, 程建光. 城市污水处理厂应用纯氧曝气技术的探讨[J]. 能源环境保护, 2010, 24(6): 35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8759.2010.06.010 |
| [24] | GRAAF V D A A, DE BRUIJN P D, ROBERTSON L A, et al. Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms in a fluidized bed reactor[J]. Microbiology, 1996, 142(8): 2187-2196. doi: 10.1099/13500872-142-8-2187 |
| [25] | SUN S H, SONG Y, YANG X J, et al. Effects of temperature on anammox performance and community structure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 260: 186-195. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.090 |
| [26] | SUN S H, SONG Y, YANG X J, et al. Strategies for improving nitrogen removal under high sludge loading rate in an anammox membrane bioreactor operated at 25 °C[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 183: 106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2018.03.011 |
| [27] | 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. |
| [28] | 陈帅, 谭学军, 蒋玲燕. 浅谈纯氧曝气活性污泥法处理技术[J]. 城市道桥与防洪, 2012(1): 65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7716.2012.01.025 |
| [29] | 王小龙. 基于颗粒污泥的单级自养脱氮系统构建及其脱氮效能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. |
| [30] | SLIEKERS A O, DERWORT N, CAMPOS-GOMEZ J L, et al. Completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite in one single reactor[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(10): 2475-2482. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00476-6 |
| [31] | 赵良杰. 一段式部分亚硝化厌氧氨氧化工艺处理中低浓度氨氮废水技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2020. |
| [32] | 杨晓欢. 动态膜序批式反应器(DM-SBR)应用于一段式厌氧氨氧化的工艺研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2020. |
| [33] | 张凯, 张志华, 王朝朝, 等. Anammox富集与优化停曝比对MBR-SNAD工艺的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(6): 2370-2377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.06.017 |
| [34] | 李冬, 高雪健, 张杰, 等. 不同曝气密度对canon工艺启动的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(2): 829-836. |
| [35] | 杨京月, 郑照明, 李军, 等. 厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化底物竞争抑制特性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(8): 2947-2953. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.08.020 |
| [36] | MIAO Y Y, ZHANG L, YANG Y D, et al. Start-up of single-stage partial nitrification-anammox process treating low-strength swage and its restoration from nitrate accumulation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 218: 771-779. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.125 |


















































































































































































































































































































































































































 下载:
下载: 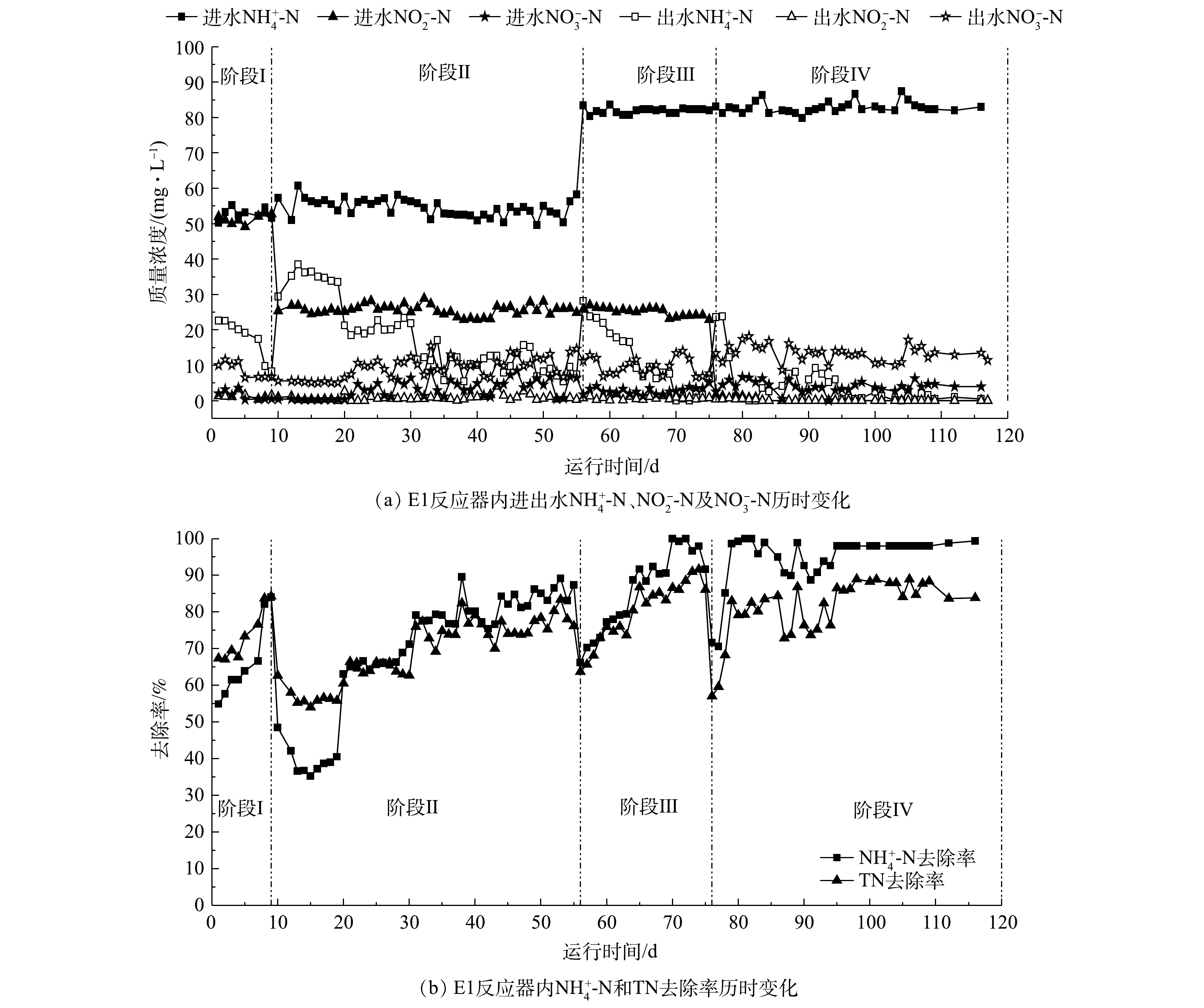



 点击查看大图
点击查看大图