全文HTML
--> --> --> 施氏矿物(schwertmannite)是BIGHAM等[1]于1990年在酸性矿山废水中发现的一种结晶度差的次生羟基硫酸铁沉淀[2-3],并在1994年被命名[4],化学式为Fe8O8(OH)8?2x(SO4)x(1≤x≤1.75)[5]。有研究表明,施氏矿物是降解有机污染物的高效催化剂,常被用来催化降解甲基橙[6-8]、罗丹明B[9]、苯酚[10-11]等有机污染物。甲基橙作为典型的偶氮染料被广泛应用于纺织印染行业,由于其具有可生化性差、色度大和难降解等特点,其降解行为备受关注。施氏矿物是亚稳态的[12-13],溶液体系中存在的一价阳离子(Na+,K+,
首先,施氏矿物生物合成后,通过在滤液中加入
1.1. 施氏矿物初始生物合成
将A. ferrooxidans LX5 (CGMCC No. 0727)菌体在150 mL改进型9K液体培养基中活化3次后,通过离心得到浓缩30倍A. ferrooxidans LX5细胞悬浮液[23-24]。采用QIAO等[23]提供的方法,在149 mL溶解有6.67 g FeSO4·7H2O的溶液中,加入1 mL A. ferrooxidans LX5细胞悬浮液,置于28 ℃、180 r·min?1的恒温振荡器中反应,合成施氏矿物,待Fe2+氧化完全后,抽滤收集矿物并分析其矿物生成量、形貌、XRD及其比表面积,滤液用于后续研究。1.2. NaBH4对次生铁矿物合成的影响
分别量取上述所得滤液120 mL置于5个250 mL锥形瓶中,设置NaBH4加入浓度为0.42、0.83、1.25、1.67和2.08 g·L?1的5个处理组,并设置对照组(记为CK),每个处理组3个重复,置于恒温振荡器中反应,各处理组在Fe2+氧化完全后再经过滤,滤液再次加入NaBH4后进行下个批次实验,共3个批次。实验过程中定时监测各处理组中的pH,并取样测定Fe2+及总Fe含量。将5个处理组对应3个批次生成的共15个矿物分别在50 ℃下干燥,过100目标准筛后收集保存。1.3. 次生铁矿物催化过硫酸钠降解去除甲基橙
根据矿物生成量,选择加入1.25 g·L?1和1.67 g·L?1 NaBH4的2个处理组各3个批次合成的矿物,与初始合成的施氏矿物共计7个矿物,使用光化学反应仪(XPA-7G8,南京胥江机电厂,中国),在254 nm紫外光照射下开展次生铁矿物催化过硫酸钠(Na2S2O8)降解甲基橙的实验。反应温度稳定在(23±1) ℃,使用100 W的汞灯作为254 nm紫外光源。配制0.1 mmol·L?1的甲基橙溶液,称取7个矿物各10 mg于石英管,加入50 mL甲基橙溶液,并设置纯紫外光照射降解甲基橙的对照处理组(记为CK紫外光)。每个处理组3个重复。分别在10、30、60、90、120、150和180 min时取样3 mL,过0.45 μm滤膜后,利用721型可见分光光度计在470 nm波长下测定吸光度,根据吸光度计算甲基橙的降解率。
分别称取7个矿物各10 mg于石英管,每个矿物称2次,并加入50 mL甲基橙溶液。然后,配制浓度为0.1 mol·L?1的Na2S2O8溶液,每个矿物的石英管中分别加入50 μL和250 μL Na2S2O8溶液,即设置Na2S2O8的浓度分别为0.1 mmol·L?1和0.5 mmol·L?1,并设置不加矿物,只加Na2S2O8的对照处理组(记为CK过硫酸钠)。每个处理3个重复,取样时间和方法同上。其中,在Na2S2O8浓度为0.5 mmol·L?1的实验中各处理组中的甲基橙降解迅速,在90 min时降解效率即可达到100%,故不再延长取样时间至180 min。
1.4. 各指标测定方法
用邻菲罗啉比色法测定样品中Fe2+、总Fe含量;用扫描电子显微镜(JSM-7001F,日本东京)观察矿物形貌;用X射线衍射仪(MiniFlex II,日本东京)分析矿物矿相;用比表面积分析仪(Tristar3020,Micromeritics Instrument Corporation,USA)测定矿物比表面积。2.1. 初始合成施氏矿物的表征分析
在施氏矿物初始合成过程中,总Fe沉淀率为26%,与刘奋武等[17]的研究结果相近,矿物合成量为5.72 g·L?1(以干物质计)。通过分析矿物的XRD衍射图谱(图1(a))可知,其为施氏矿物,比表面积为4.94 m2·g?1。由图1(b)可以看出,合成的施氏矿物为表面粗糙、具有毛刺状结构的微小球体,直径为1~2 μm,其形貌与前人报道的结果[25-26]相似。2.2. NaBH4对生物成矿后滤液pH的影响
5个处理组在3个批次实验过程中的pH变化情况如图2所示。各处理组在一个批次实验结束后立即开始下一批次实验,其中CK处理组与NaBH4加入量为2.08 g·L?1的处理组反应时间一致。CK处理组中在整个实验过程中pH基本保持不变(2.00)。添加NaBH4的各处理组中的pH均表现为先上升、后下降且在一定时间后趋于稳定的变化趋势,随着反应批次增加,各处理组pH上升幅度均有增大,pH稳定所需要的时间也逐渐延长。在第3批次中(图2(c))pH变化差异最大,在NaBH4加入量为0.42 g·L?1和0.83 g·L?1的2个处理组中的pH分别在108 h和360 h时稳定,而NaBH4加入量为1.25、1.67和2.08 g·L?1的3个处理组,pH在600 h后仍未稳定。NaBH4是强碱弱酸盐,加入水中会导致pH上升。为探究NaBH4加入后各处理组的pH上升情况是否与NaBH4和H2O的反应有关,用H2SO4配制pH为2.00的酸性溶液,分别量取120 mL置于5个250 mL锥形瓶中,对应5个处理组的加入量分别加入NaBH4,振荡1 h后测得pH分别为3.25、8.90、9.22、9.34和9.43,均高于第1批次实验中,5个处理组加入NaBH4 1 h后的pH最大值(NaBH4加入量为2.08 g·L?1处理组的pH为2.32)。由此可见,在酸性溶液中加入NaBH4,
2.3. 加入NaBH4后各处理组Fe2+和总Fe的变化情况
CK处理组在整个实验过程中几乎无Fe2+,添加NaBH4的5个处理组均有Fe2+产生。在第1批次实验中(图3(a)),各体系生成的Fe2+含量与NaBH4加入量呈正相关关系(Pearson相关系数r=0.998,在0.01级别,相关性显著),且加入NaBH4的各处理组Fe2+均能被氧化完全。在第2批次实验中(图3(b)),各处理组产生的Fe2+含量与第1批次相近,但Fe2+完全氧化所需要时间较长。这可能与A. ferrooxidans LX5的活性有关,随着NaBH4加入量的增加,各处理组中Na+含量增加,导致A. ferrooxidans LX5菌体活性减弱或细胞裂解死亡[27]。在第3批次实验中(图3(c)),各处理组Fe2+氧化情况相差较大,NaBH4加入量为0.42 g·L?1与0.83 g·L?1 2个处理组中的Fe2+分别在72 h和312 h氧化完全,这表明A. ferrooxidans LX5仍能发挥生物氧化作用。而NaBH4加入量为1.25、1.67和2.08 g·L?1 3个处理组分别在反应了696、624和624 h后,Fe2+氧化率仅为28.68%、34.94%和26.80%。为探究第3批次反应后各处理组内A. ferrooxidans LX5的活性,将反应结束后各处理组的滤液各15 mL分别加入到135 mL溶有6.67 g FeSO4·7H2O的溶液中,同时设置加入新活化菌液和不加菌的处理,比较在48 h后的Fe2+氧化情况。结果表明,反应48 h后,加入新活化菌液的处理Fe2+已经氧化完全,而不加菌处理的Fe2+氧化率仅为1.04%,添加第3批次反应后滤液的各处理Fe2+氧化率为1.18%~4.09%。可见,经过了3个批次的反应,各处理组内A. ferrooxidans LX5已经基本失活,无法快速氧化Fe2+,因此,3个批次后再开展次生铁矿物的强化合成意义不大。
总Fe含量变化情况如图4所示,CK处理组在整个实验过程总Fe基本不变,其他处理组均呈现下降趋势。在第1批次中(图4(a)),加入NaBH4后,5个处理组总Fe含量均下降,且与NaBH4加入量呈现负相关(Pearson相关系数r=?1.000,在0.01级别,相关性显著)。在第2批次中(图4(b)),5个处理组总Fe下降趋势与第1批次相同。在进入第3批次后(图4(c)),总Fe沉淀量的差异变的明显,在实验结束时,5个处理组的总Fe沉淀率分别达到14.57%、37.63%、47.00%、62.67%和60.91%。
2.4. 各处理组次生铁矿物生成量的比较
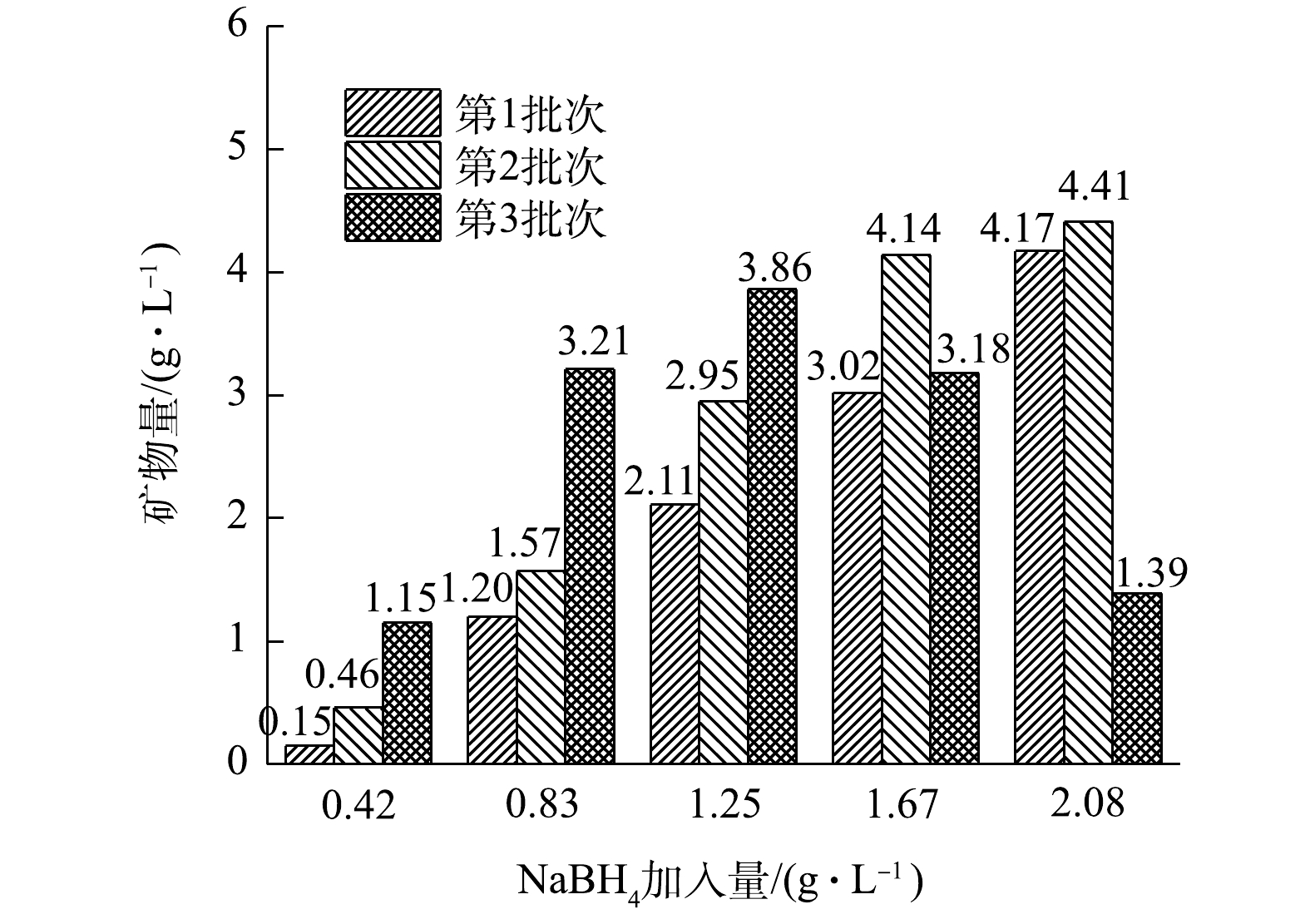
各处理组生成的矿物量情况如图5所示。在NaBH4加入量为0.42、0.83和1.25 g·L?1的3个处理组中,随着NaBH4反应批次增加,矿物生成量有所增加,在3个处理组中第2批次矿物生成量分别比第1批次提高了3.07、1.31和1.40倍,第3批次矿物生成量比第1批次分别高了7.67、2.68和1.83倍。在1.25 g·L?1处理组中,第3批次的Fe2+虽然没有被氧化完全,但其矿物生成量仍比前2个批次高,而在1.67 g·L?1和2.08 g·L?1的2个处理组中,由于第3批次的反应中体系中Fe2+没有被氧化完全,导致矿物生成量减少,没能超过同处理组的第2批次矿物生成量。经过3个批次反应后,添加NaBH4的5个处理组中的矿物生成总量分别为1.76、5.98、8.92、10.34与9.97 g·L?1。为探究5个处理组的矿物生成量与A. ferrooxidans LX5的关系,将施氏矿物合成后的滤液过0.22 μm滤膜后(去除A. ferrooxidans LX5),分别取120 mL加入到5个250 mL锥形瓶中,按照5个处理组的加入量加入NaBH4,并对应第1批次实验中各处理组的反应时间,实验结束后抽滤获得次生铁矿物,矿物生成量分别为0.28、1.02、1.66、2.20和2.55 g·L?1。可见,在无A. ferrooxidans LX5的情况下,将NaBH4加入滤液中也能产生矿物沉淀,但A. ferrooxidans LX5的存在可以进一步提高矿物生成量。在第1批次中,当NaBH4加入量为0.83、1.25、1.67和2.08 g·L?1时,矿物生成量分别提高了17.65%、27.11%、37.27%和63.53%。
2.5. 次生铁矿物的矿相、形态和比表面积
选择NaBH4加入量为1.25 g·L?1和1.67 g·L?1 2个处理组对应的3个批次所生成的6种矿物,对其进行了XRD、SEM表征且测定了其比表面积,将XRD表征结果与施氏矿物(PDF#47-1775)和黄钠铁矾(PDF#30-1203)的JCPDS标准卡片衍射峰进行比较[28-29]。由图6可知:2个处理组中第1批次生成的次生铁矿物均具有施氏矿物的特征衍射峰,且峰较宽,这说明2种矿物是施氏矿物;第2批次生成的2种矿物的XRD图谱中,虽然施氏矿物的特征衍射峰依然存在,但在其他位置出现数条黄钠铁矾的特征峰,表明这2种矿物是黄钠铁矾和施氏矿物的混合物。这可能是由于NaBH4加入量的增加,Na+浓度增高,导致生成黄钠铁矾。第3批次生成的矿物的XRD图谱中显示的均为黄钠铁矾的特征峰[30],由此可见,2个处理组中第3批次合成的矿物是黄钠铁矾。NaBH4加入量为1.25 g·L?1和1.67 g·L?1的2个处理组合成的次生铁矿物的形貌各不相同(图7),2个处理组对应的同一批次矿物形貌相差较小,同一处理组不同批次之间矿物形貌相差较大。第1批次合成的次生铁矿物(图7(a)和图7(d))仍具有施氏矿物的形貌特征,即微小的球形结构,表面带有毛刺状,颗粒之间互相粘连形成几个或几十个团聚在一起的结构,与前文2.1中初始合成的施氏矿物相比,没有明显差别。而第2批次合成的次生铁矿物(图7(b)和图7(e))是球状结构与不规则块状结构粘连在一起的混合物,且增加NaBH4加入量可增加生成的次生铁矿物中立方体(假立方体)的块状结构。而第3批次合成的次生铁矿物(图7(c)和图7(f))已经全部由块状结构组成。结合XRD和SEM结果可知,立方体(假立方体)块状结构为黄钠铁矾。
就矿物比表面积而言(表1),NaBH4加入量为1.25 g·L?1和1.67 g·L?1的2个处理组中3个批次合成的矿物比表面积为第2批次>第1批次>第3批次,而在相同批次中,NaBH4加入量为1.67 g·L?1的处理组合成的矿物比表面积大于投加量为1.25 g·L?1处理组对应的矿物比表面积。由此可见,加入NaBH4不仅能够进一步沉淀总Fe,促进次生铁矿物的合成,而且能够增加次生铁矿物的比表面积。其中,第2批次合成的矿物比表面积增加更为显著,但在第3批次中,由于矿物以黄钠铁矾为主,比表面积会大幅度减小。值得一提的是,尽管在第2批次合成的矿物中已经有黄钠铁钒的生成,但相对于第1批次生成的矿物,比表面积仍然呈现增加的趋势。由此可见,在第2批次合成的矿物中,施氏矿物对矿物比表面积的贡献较大。综合矿物矿相、比表面积、矿物生成量可以得出,在初始合成施氏矿物滤液中适量引入NaBH4,可以在提高矿物生成量的同时,得到比表面积较大的施氏矿物。
在本研究中,通过加入1.67 g·L?1的NaBH4,在第1批次实验结束时就可以得到3.02 g·L?1的施氏矿物,生成量增加了52.80%,生成的施氏矿物比表面积为20.02 m2·g?1,提高了4.05倍。本研究所用NaBH4(优级纯)价格为1 250 元·kg?1,从滤液中每多合成1 g高比表面积施氏矿物,需要投入的成本为0.69元。
2.6. 次生铁矿物在紫外光下催化Na2S2O8去除甲基橙
NaBH4加入量为1.25 g·L?1和1.67 g·L?1的2个处理组各3个批次合成的矿物,与初始合成的施氏矿物共计7个矿物,在紫外光下催化Na2S2O8降解甲基橙的效果如图8所示。在无Na2S2O8的实验中(图8(a)),CK紫外光处理组在180 min时,甲基橙去除率为1%,加入次生铁矿物的7个处理组对甲基橙的去除率相差不大,为3.90%~9.28%。其中1.25 g·L?1处理组第1批次矿物(比表面积为0.84 m2·g?1)催化去除甲基橙的效果最差。在Na2S2O8加入量为0.1 mmol·L?1时(图8(b)),次生铁矿物的引入能够催化高级氧化去除甲基橙的过程。在反应120 min时,CK过硫酸钠处理组的甲基橙去除率为58.28%,当加入比表面积为0.84 m2·g?1的次生铁矿物时,去除率为72.83%,降解效果提升不明显。当矿物比表面积在4.94~42.74 m2·g?1时,去除率均能达到90%,而加入1.67 g·L?1处理组第1批次和第2批次矿物时,去除率分别可达98.12%和98.45%。在反应180 min时,CK过硫酸钠处理组对甲基橙的去除率为70.44%,加入1.25 g·L?1处理组中第3批次矿物对甲基橙的去除率为94.58%,其余处理组对甲基橙的去除率均达到100%。笔者认为,也许由于本研究中次生铁矿物的加入量为10 mg,加入量较大,当矿物比表面积差异较大时(4.94~42.74 m2·g?1),其对甲基橙催化去除效果的差异未能较好地体现出来。在Na2S2O8浓度为0.5 mmol·L?1的实验中,增大Na2S2O8浓度能够提高甲基橙降解速率,缩短反应时间,各处理组对甲基橙去除效果的差异变小,且均能在90 min时将甲基橙完全去除。可见,在Na2S2O8浓度较低时(0.1 mmol·L?1)引入次生铁矿物,可以提升甲基橙的去除率,对催化高级氧化去除偶氮染料更有价值。而在Na2S2O8达到一定浓度后(0.5 mmol·L?1),次生铁矿物加入对提升甲基橙高级氧化去除效果并不明显。
2)当NaBH4添加量为1.25~1.67 g·L?1时,第1批次得到的矿物是施氏矿物,第2批次获得矿物是施氏矿物和黄钠铁矾的混合物,第3批次获得矿物是黄钠铁矾,且第2批次合成的矿物比表面积最大,第3批次合成的矿物比表面积最小。
3)当Na2S2O8浓度为0.1 mmol·L?1时,次生铁矿物的引入可以明显提高甲基橙去除率;当Na2S2O8浓度为0.5 mmol·L?1时,次生铁矿物的引入并未明显提升甲基橙的去除。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: 





 点击查看大图
点击查看大图