全文HTML
--> --> --> 锑(Sb)是一种天然存在于自然界中的有毒准金属元素[1],因其与化合物有着良好的阻燃特性,在人类的生产和生活中有着广泛的用途[2]。中国作为世界上最大的锑储量和产量大国,其中产量约占世界的71%,锑污染已成为中国的典型环境污染问题[3]。锑在天然水体中通常以Sb(OH)3和湖南锡矿山的锑矿开采地区,附近的河流因受到锑矿石堆场渗透水的影响,锑浓度为0.33~11.4 mg·L?1[5],远远高于国家地表水环境质量标准的5 μg·L?1[6]。随着大量锑资源的开采,锑矿废水成为环境中最主要的锑污染来源[7-9],因此,对锑矿废水中Sb(Ⅴ)的去除显得尤为紧迫。高效去除、成本低廉、运行简易是科研技术人员对锑废水治理的追求目标[10]。目前,去除水溶液中锑的技术主要有混凝/絮凝[11]、离子交换[12]、电化学处理[13]、生物修复[14]、吸附[15]等。吸附是一种简单易行的废水处理技术,一般适合于处理量大、浓度范围广的水处理体系,该方法性能优良、成本低廉,因此,与其他方法相比,其具有更强的实用性[16]。已有研究[6, 17]表明,Sb(Ⅴ)吸附剂主要分为3大类:无机吸附剂,其主要是铁、锰、铝等金属氧化物或黏土矿物,通过物理或化学吸附将Sb(Ⅴ)固定在其表面;有机吸附剂,其主要包括炭材料和生物吸附剂,前者主要是活性炭、石墨烯和碳纳米材料,但活性炭对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附效果并不突出,而石墨烯和碳纳米材料成本又过高,后者主要是植物或生物吸附剂,通过生物质表面的羟基、羧基和氨基以静电吸附或表面络合来吸附Sb(Ⅴ);复合吸附剂,其主要利用无机溶剂对生物质改性或有机溶剂对无机吸附剂进行改性处理后的一种复合吸附剂,其吸附能力远高于单一的吸附剂。
近年来,生物炭作为一种新型的环境功能吸附材料,以其来源广泛、价格低廉、比表面积大、表面有着丰富的官能团等优点而倍受科学家关注[18-19]。传统生物炭表面通常带负电荷[20],对金属阳离子(Zn2+、Pd2+等)有着较好吸附效果[21],然而对以(氧)阴离子形式存在的污染元素而言,其吸附效果并不理想[22]。现有方法通过在生物炭表面负载金属离子,利用化学试剂等对原始生物炭进行改性处理[23-24],可有效增强生物炭吸附阴离子的效果。但这些改性方法的成本较高,且表面负载的金属离子、化学试剂易解吸造成二次污染等特点,在具体的工程应用中会显得不切实际。
笔者所在的课题组前期已使用工业废弃物磷石膏对酒糟生物炭进行了改性处理,并通过设置不同热解温度烧制生物炭样品,发现经磷石膏改性的生物炭能有效吸附以阴离子形式存在的磷酸根离子[25]和Cr(Ⅵ)[18]。本着以废治废的目的,本研究尝试使用上述改性的生物炭去除高浓度锑废水中以(氧)阴离子形式存在的Sb(Ⅴ),并研究其作为含锑废水中Sb(Ⅴ)吸附剂的潜在应用价值,分别考察了不同改性温度、投加量和溶液pH对吸附效果的影响,以确定生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)的最佳吸附条件,并探讨了改性生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附行为,并与其他吸附剂对水中Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附性能进行了对比,同时考察了改性生物炭的吸附稳定性,以期为有关锑矿废水中Sb(Ⅴ)的去除提供科学依据与理论指导。
1.1. 改性生物炭的制备
本研究使用的生物炭样品为课题组前期制备的原始生物炭和改性生物炭,其中改性生物炭的制备使用经过预处理的磷石膏与酒糟按1∶2的质量比例混匀,再与等体积的水混合均匀,在105 ℃下烘干后,放置于管式炭化炉中设置不同温度进行烧制[18]。经不同热解温度(300、400、500、600 ℃)烧制后,磷石膏改性后的酒糟生物炭样品分别标记为MC300、MC400、MC500和MC600,未改性的原始酒糟生物炭样品分别标记为BC300、BC400、BC500和BC600。1.2. 吸附实验
根据前期的研究发现,锑矿区矿井水以及周边矿石堆场渗滤水体中均含有较高浓度的锑,锑矿区矿井水中Sb含量最高达13.35 mg·L?1[26],本研究将基于该浓度而设置相对更高浓度的初始Sb(Ⅴ)溶液开展吸附实验。本吸附实验所用溶液均使用去离子水配制,用焦锑酸钾(K2H2Sb2O7·4H2O)配置243.6 mg·L?1 的Sb(Ⅴ)标准储备液。每组实验均设置3个平行样和1个空白样。1)不同热解温度生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)吸附影响。分别称取MC300、MC400、MC500、MC600和BC300、BC400、BC500、BC600样品0.05 g于50 mL离心管,加入24.36 mg·L?1 的Sb(Ⅴ)溶液至40 mL,于25 ℃、200 r·min?1条件下振荡24 h后,高速离心过滤,收集滤液;采用ICP-OES(VISTA-MPX)测定滤液中Sb浓度,校正计算吸附量,选取吸附效果最佳的生物炭进行后续实验。
2)生物炭投加量对Sb(Ⅴ)吸附影响。分别称取0.025、0.05、0.10和0.20 g生物炭样品(基于步骤1)的实验结果),加入24.36 mg·L?1 的Sb(Ⅴ)溶液至40 mL,其他操作均与上述一致;通过吸附量大小选取吸附效果最佳的投加量进行后续实验。
3)不同pH对Sb(Ⅴ)吸附效果影响。基于1)和2)的实验结果,分别称取0.10 g的MC600和BC600,取24.36 mg·L?1 的Sb(Ⅴ)溶液至40 mL,同时调节体系pH分别为3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12,其余步骤与上述一致;通过吸附量大小研究不同pH对Sb(Ⅴ)吸附的影响。
4)吸附平衡实验。吸附动力学:分别称取0.10 g的MC600和BC600于50 mL离心管中,取24.36 mg·L?1的Sb(Ⅴ)溶液至40 mL,同时调节体系pH至预设值。在25 ℃、200 r·min?1条件下振荡,于不同时间(0.1、0.25、0.5、1、2、4、8、16、24、36、48 h)取出,高速离心过滤,并测定其滤液中Sb浓度。
吸附等温线:分别称取0.10 g的MC600和BC600于50 mL离心管中,取一系列Sb(Ⅴ)储备液(0.608、1.218、2.436、6.09、12.18、24.36、60.9、121.8 mg·L?1)至40 mL,同时调节体系pH至预设值,振荡24 h后取出,高速离心过滤,测定其滤液中Sb浓度。
1.3. 改性生物炭的基本特征测定
选取MC600和BC600样品进行理化性质分析,比表面积和孔径使用全自动比表面积与孔隙度分析仪(ASAP2020[M])进行分析,pH的测定是由生物炭与水按1∶20的质量比结合后使用pH计(PHS-3C)测定,表面电位则是通过莫尔文Zate计测量。1.4. 解吸实验
选取吸附初始浓度为60.9 mg·L?1和121.8 mg·L?1 Sb(Ⅴ)溶液后的MC600样品烘干(40 ℃),分别称取0.10 g(每个样3组平行),加入40 mL去离子水,于25 ℃、200 r·min?1条件下振荡24 h后,高速离心过滤,测定滤液中Sb浓度,计算解吸量。而后重新加入去离子水于相同条件进行解吸,每个样品重复解吸3次。1.5. 数据处理
吸附量根据式(1)计算。式中:Q为元素的吸附量,mg·kg?1;A为溶液初始浓度,mg·L?1;Y为吸附平衡浓度,mg·L?1;V为加入的溶液体积,L;m为生物炭质量,g。
解吸量根据式(2)计算。
式中:Qt为元素的解吸量,mg·kg?1;Ct为浸提液中元素的浓度,mg·L?1;V为浸提液体积,L;m为生物炭质量,g。
吸附动力学拟合根据拟一级动力方程(式(3))、拟二级动力学方程(式(4))、Elovich方程(式(5))、双常数方程(式(6))计算。
式中:qt为t时的吸附量,mg·kg?1;k1、k2为拟一、二级动力学吸附速率常数;t为吸附时间,h;qe为平衡吸附量,mg·kg?1;α为初始吸附速率,kg·(mg·h)?1;β为解吸系数,kg·mg?1;k、n为双常数方程动力学参数。
吸附等温线拟合根据Langmuir模型(式(7))、Freundlich模型(式(8))、Langmuir-Freundlich模型(式(9))计算。
式中:Q为最大吸附量,mg·kg?1;b为平衡吸附常数,L·kg?1;qe为平衡时的吸附量,mg·kg?1;x为平衡时浓度,mg·L?1;k为Freundlich模型的亲和系数;n为Freundlich和Langmuir-Freundlich模型的经验常数。
2.1. 生物炭的基本性质
经磷石膏改性后,MC600的比表面积和孔隙大小均有显著提高,BC600和MC600的比表面积分别为0.92 m2·g?1和13.67 m2·g?1,孔隙体积为5×10?4 m3·g?1和9.6×10?3 m3·g?1。比表面积越大,孔隙越多,这说明生物炭吸附能力越强[27]。此外,改性使得生物炭的Zeta电位也发生了明显变化,由改性前的?36.6 mV变为0.949 mV,表明生物炭表面所带电荷从改性前的负电荷变成了改性后的正电荷,这对吸附(氧)阴离子也是非常有利的[28]。MC600的pH(10.10)较BC600的pH(9.02)略有升高,且BC600和MC600的pH均为碱性。由于锑矿区矿井水本身受到含锑硫化物矿物的影响,最初是呈酸性的,但在复杂的野外环境中,受不同地质背景的影响,矿井水的酸碱性会发生变化[29]:在碳酸盐岩地质背景环境中,矿井水在水-岩相互作用下会逐渐被碳酸盐岩中和,呈弱碱性;而在石英砂岩等地质背景下,矿井水会持续酸化,呈酸性。因此,本研究的生物炭为碱性特征,在某种程度上还可用作锑矿区酸性矿井水的水体中和剂。2.2. 最佳吸附条件的确定
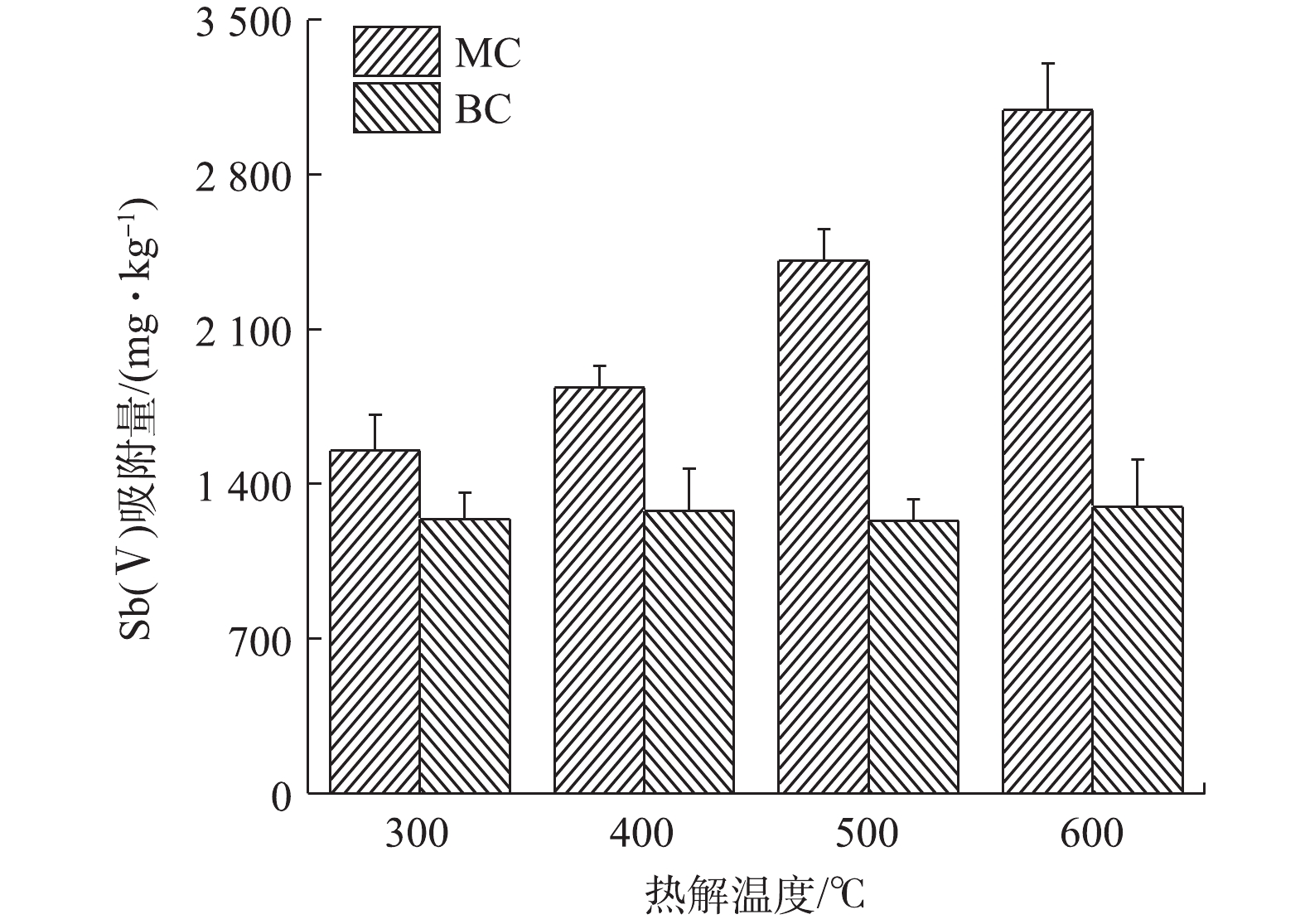
1)最佳生物炭材料的确定。在一定温度范围内,热解温度的升高,能在一定程度上增加生物炭的比表面积和孔隙度[30],从而提高生物炭对污染物的吸附能力。在本研究中,热解温度为600 ℃烧制的BC600,其比表面积仅为0.92 m2·g?1,而同等条件烧制的MC600,其比表面积显著增大为13.67 m2·g?1。由图1可知,随着生物炭热解温度的升高,未改性的生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量差异不大,约为1 250 mg·kg?1;但改性后生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量变化明显,与热解温度升高呈正比。可见,本研究所采用的改性方式对生物炭的吸附性能影响明显,改性后极大地提高了生物炭吸附Sb(Ⅴ)的能力,MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量达到3 092 mg·kg?1,表现出了良好的吸附效果。结合实际生产工艺,600 ℃是一个相对比较节能和节约生产成本的烧制温度;因此,本实验将选用MC600作为Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附剂进行后续去除实验,同时将热解温度相同的原始生物炭BC600作为对照样品开展后续的实验。2)生物炭最佳投加量的选择。吸附剂的投加量是影响吸附的一个重要因素:投加量不足,不能使水体中的污染物得到有效去除,达不到预期的污染治理效果。投加过量,会降低吸附剂的吸附效率,造成资源浪费,在实际应用中增加使用成本。图2为在初始Sb(Ⅴ)浓度是24.36 mg·L?1的条件下,MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量随投加量的变化。当MC600投加量由0.025 g增至0.10 g的过程中,MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量显著增加;而当MC600投加量大于0.10 g时,单位质量吸附剂对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量变化略有降低。这可能与单位质量生物炭的位点和活性基团的数量有关,一定量的生物炭表面位点和活性基团可促进Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附,但过量的位点和活性基团则会引起溶液中Sb(Ⅴ)离子与之发生竞争吸附,降低吸附效率。因此,本研究选取该生物炭的最佳投加量为0.10 g进行后续吸附实验。
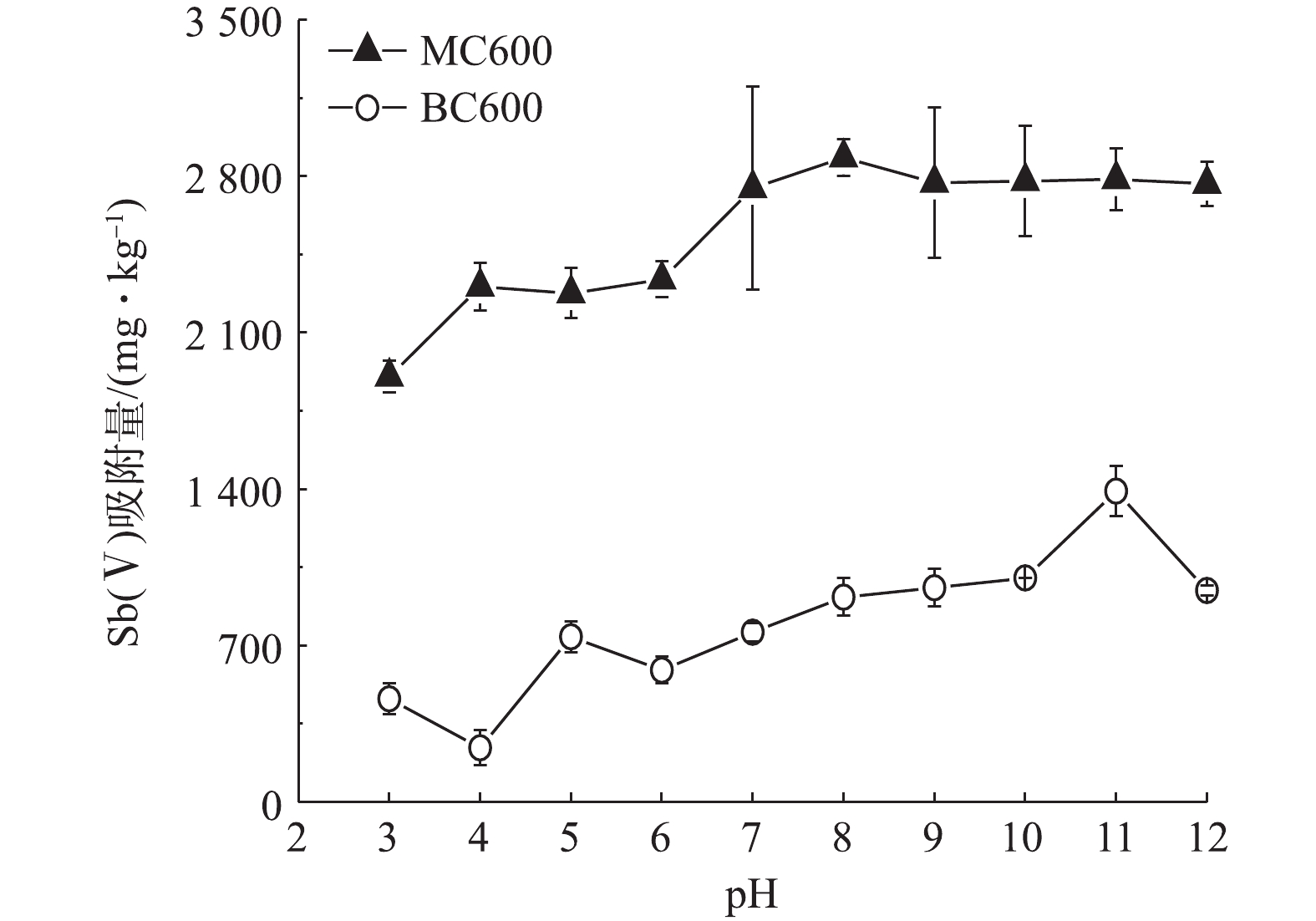
3)最佳pH条件的选择。Sb在环境中的活动性和转化受其环境pH条件的影响明显[31]。图3反应了不同初始pH条件下MC600和BC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量大小变化。由图3可知,在pH=3时,MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量仅为1 903 mg·kg?1,当pH升高至7时吸附量达到2 747 mg·kg?1,之后随着pH的继续升高,吸附量基本趋于稳定;而BC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附效果明显低于MC600,且其吸附量在pH=3~12时均小于1 500 mg·kg?1。根据前期对生物炭的理化性质分析可知,MC600和BC600的零电荷点(PZC)分别为7.74和3.06,在溶液pH>pHPZC时生物炭表面带负电,并且Sb(Ⅴ)在pH>3的氧化水环境中主要以
结合我国西南喀斯特地区锑矿废水的基本特征,受碳酸盐岩地质背景的影响,锑矿废水大多呈现弱碱性[26]。本研究所用到的MC600吸附Sb(Ⅴ)最佳pH条件是中性至碱性区间,因此,为了更真实地模拟野外锑矿废水的pH环境,本研究以pH=7.5来开展MC600去除Sb(Ⅴ)的实验研究。
2.3. 吸附动力学和吸附等温线
1)生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附动力学过程。吸附动力学是描述吸附相中的物质在吸附剂表面的扩散过程,这一过程决定着被吸附物质在固液表面相互作用的时间[33]。由图4可见,在初始浓度为24.36 mg·L?1的条件下,BC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附在8 h时基本达到平衡,吸附量为871 mg·kg?1,且吸附比较稳定,并未出现较明显的解吸现象。而MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附主要分3个阶段;第1阶段,在4 h之前对Sb(Ⅴ)的快速吸附,并在4 h时吸附量达到2 058 mg·kg?1,这说明吸附过程中物理吸附是存在的;第2阶段,随着时间的增加,在24 h处的吸附量逐渐增加至2 869 mg·kg?1;第3阶段,MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量基本趋于稳定。运用4种常规动力学方程对2种生物炭吸附Sb(Ⅴ)的动力学过程进行拟合,拟合参数见表1。2种生物炭吸附Sb(Ⅴ)的拟二级动力学拟合效果(R2≥0.9)高于拟一级动力学,并且其拟合的BC600和MC600平衡吸附量qe(1 029、2 762 mg·kg?1)更接近实验实测值,这表明2种生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)吸附均存在着化学吸附,且其吸附速率受化学吸附控制[34]。Elovich方程用于描述由反应速率和扩散因子综合调控的非均相扩散过程;2种生物炭吸附Sb(Ⅴ)都与Elovich方程有较好的拟合效果,且MC600拟合系数最优(R2=0.993),这说明MC600吸附Sb(Ⅴ)主要为非均质表面吸附[35]。尽管采用模型公式拟合并不能直接证实其吸附的动力学机制,但还是能在一定程度上表明Sb(Ⅴ)在MC600的表面吸附是反应过程和扩散过程等因素共同作用的结果[36]。
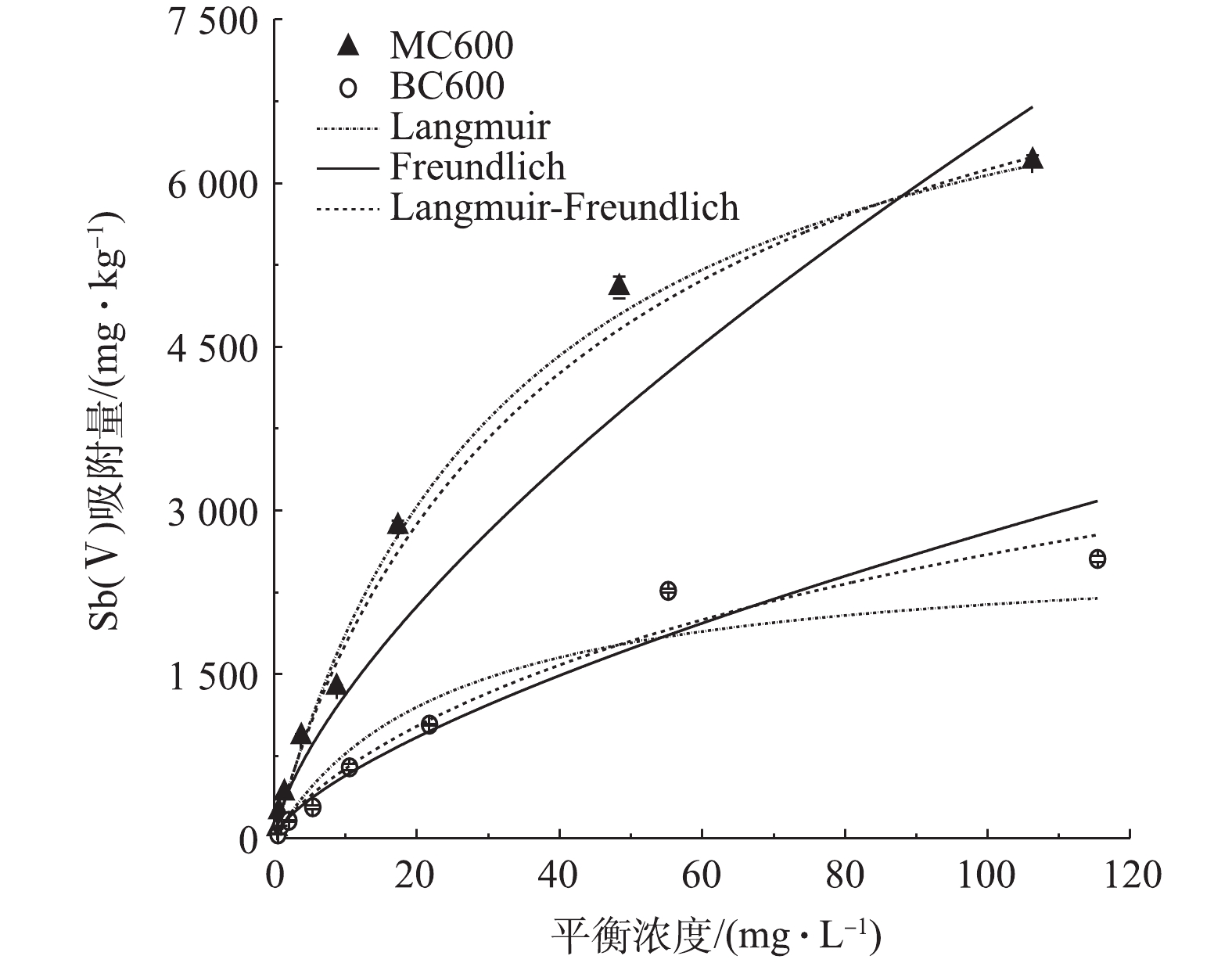
2)生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附等温线研究。吸附等温线常用于描述吸附反应达到平衡状态时吸附质在吸附剂上的分布情况。为了能更好地研究MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)吸附的机理,采用3种经典吸附等温模型对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附过程进行拟合分析。Langmuir模型是一个较理想的吸附方程,适用于吸附剂表面吸附位点上的单分子层吸附;Freundlich模型被认为是一个经验方程,常用于多层异质吸附;Langmuir-Freundlich模型则是介于单分子和双分子层吸附都存在的情况[37-38]。
如图5所示,MC600和BC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量在中低浓度时都随着初始溶液浓度的增加而增加, BC600在平衡浓度为55.2 mg·L?1时接近饱和,之后随着平衡浓度的增加,吸附量并没有明显增加;相比于BC600,磷石膏改性的MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附效果显著提高,在初始浓度分别为24.36、60.9、121.8 mg·L?1的条件下,MC600的吸附量为BC600的吸附量的2.75、2.23、2.43倍。
吸附等温线模型拟合参数如表2所示。Langmuir模型中Q、b分别代表最大吸附量和吸附平衡常数,该模型对BC600和MC600吸附Sb(Ⅴ)过程进行拟合得出最大饱和吸附量分别为2 657 mg·kg?1和8 089 mg·kg?1,由图5可知,MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附效果明显强于BC600。这3种模型对MC600吸附Sb(Ⅴ)都有不错的拟合效果,且拟合系数均在0.930以上。相对来说,Langmuir模型和Langmuir-Freundlich模型对MC600吸附Sb(Ⅴ)的拟合效果最优,说明MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附以单分子层吸附为主,并伴有部分多分子层吸附[39];Freundlich模型的K代表吸附容量,但不是最大吸附量,其值与吸附亲和力有关,K值越大表明吸附速率越快[40],根据该模型对Sb(Ⅴ)吸附的拟合,其MC600的K值为270.9,高于BC600的117.8,表明MC600的吸附速率大于BC600,这与上述实验结果相一致。
吸附剂材料及其对污染物的最佳去除条件、最大吸附量通常是反应该吸附剂吸附性能的重要因素。对比其他有关水中Sb(Ⅴ)去除的吸附研究发现,在与本研究相似pH的实验条件下,合成锰氧化物[41]与合成Fe-Zr复合金属氧化物[23]对Sb(Ⅴ)的理论最大吸附量分别为86 564 mg·kg?1和51 000 mg·kg?1;含纳米零价铁的聚乙烯醇颗粒吸附剂[42]的理论最大吸附量仅为1 650 mg·kg?1,而氧化锆-碳纳米纤维材料的理论最大吸附量可达57 170 mg·kg?1[43];掺杂镧的磁性生物炭[44]对Sb(Ⅴ)的理论饱和吸附量为18 920 mg·kg?1。尽管本研究的改性生物炭MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)最大理论吸附量在这类吸附材料中不是最高的,为8 089 mg·kg?1,但MC600的原料均为工厂废弃物,制作成本低廉,吸附剂本身对周围环境污染小等优势,可有效削减锑矿废水Sb(Ⅴ)的污染负荷。由此可见,本研究的MC600作为碳酸盐岩地质背景锑矿区含锑废水中Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附剂是具有潜在的应用价值。
2.4. 生物炭吸附稳定性
在实际应用工程中,吸附剂处理污染废水需要满足吸附速率快、吸附容量大、吸附稳定等特点。生物炭对含锑废水进行吸附后,其吸附的稳定性是判断吸附剂综合性能的一个重要依据。为了对比考察生物炭吸附Sb(Ⅴ)的稳定性,本研究选用吸附Sb(Ⅴ)初始浓度相对最大的2个生物炭样品,即分别吸附60.9 mg·L?1和121.8 mg·L?1 Sb(Ⅴ)溶液的MC600样品进行解吸实验,2样品可代表吸附Sb(Ⅴ)近饱和的生物炭样品。结果如表3所示,2种样品对Sb(Ⅴ)的解吸量在第1次时相对最大,但是解吸率均≤20%;随着解吸次数的增加,解吸率迅速降低;第3次的解吸率均小于3%。总体上,2种样品3次总解吸率均低于30%,说明解吸部分的Sb(Ⅴ)是以物理吸附形式附着在MC600表面,而余下超过70%的Sb(Ⅴ)则已经以化学吸附形式固定在MC600上。一方面,该结果与前述的吸附实验研究结果一致,即本研究所用生物炭对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附以化学吸附为主;另一方面,结果表明本研究使用的MC600吸附Sb(Ⅴ)后绝大部分状态稳定,不易解吸,基本能够满足工程应用要求。2)运用吸附动力学经典方程对BC600和MC600吸附Sb(Ⅴ)的过程进行拟合,发现Elovich方程对MC600的拟合效果最优(R2=0.993),说明本研究的MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附属于非均质表面吸附,该吸附受反应过程和扩散过程等因素共同作用。
3)吸附等温实验表明,MC600的吸附速率明显大于BC600。Langmuir模型和Langmuir-Freundlich模型对MC600吸附Sb(Ⅴ)有较好的拟合效果,拟合系数分别为0.981和0.980,表明MC600对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附以单分子层吸附为主,并伴有部分多分子层吸附。
4)对吸附初始浓度为60.9 mg·L?1和121.8 mg·L?1 Sb(Ⅴ)溶液的MC600样品进行解吸发现,2种样品的3次总解吸率均低于30%,因此,本研究的MC600吸附较高浓度的Sb(Ⅴ)后性能稳定,不易出现解吸,对去除较高浓度的Sb(Ⅴ) 废水具有潜在的应用价值。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 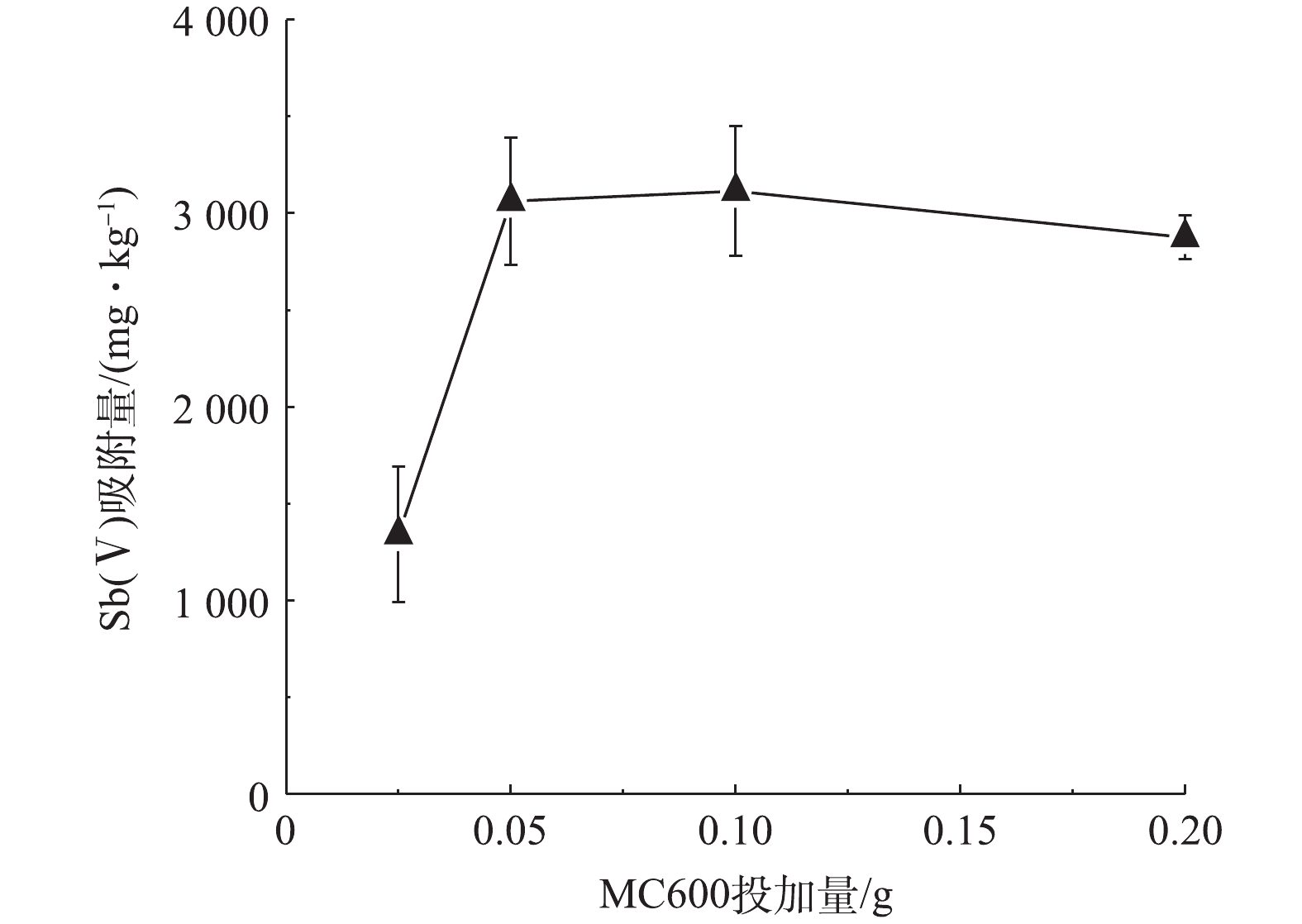

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图