全文HTML
--> --> --> 氡是放射性元素,大气和水体中的氡会对人群健康造成威胁[1-2]。城市地下空间可解决城市发展需求,包含地下储藏室、地下停车场,以及少量地下商业场所[3]。然而,由于建筑材料的氡释放、建筑构造封闭和通风条件差等原因,地下场所空气中氡气浓度较地面建筑偏高。氡气浓度已成为地下建筑室内空气质量的重要指标之一。为更好地管理处于氡暴露下的人口和土地,加拿大、挪威等国绘制了基于土壤氡浓度分布的氡浓度地质危害图[4-5]。我国的广州市[6]、武汉市[7]等在地下建筑辐射环境监测中开展了对地下建筑氡气浓度的测量和氡浓度危害水平的评价工作。吕文亭等[8]对上海地下公共空间环境氡气浓度调查后发现,全天范围内氡气浓度的变化无明显规律;米宇豪等[9]对中国锦屏地下实验室空气氡浓度监测时发现,通风条件会掩盖室内氡气浓度随气温、季节的变化规律。目前,对地下建筑内氡气浓度的研究还主要集中在对氡气的监测及通风性对氡气浓度的影响,尚缺乏对氡气浓度的长期监测及变化规律的分析与研究。地下建筑内氡气浓度变化具有季节性规律,应以年度为周期开展研究,但现有氡气浓度测量周期较短[10-13],尚缺乏完整性。本研究在成都市某地下建筑内开展了连续24个月的氡气浓度监测,拟探索地下建筑内氡气浓度的季节变化规律,分析地下建筑内氡浓度与湿度、温度和气压之间的相关性,进而提出相关的防氡降氡措施,以期为相似结构的地下建筑辐射环境评价提供参考。
1.1. 监测点
选取成都市某地下停车场为监测地点。该地下停车场建筑面积约800 m2,高约2.5 m。地下停车场由混凝土浇筑且粉刷完毕。顶板上覆土绿化,三面临近建筑物,一面临近城市道路。停车场周围无明显污染排放源,仅1个进出口(见图1)。图1中黑点处即监测点位。1.2. 监测仪器
采用中国核工业北京地质研究所研制的FD216型环境氡测量仪开展监测工作。该仪器可测量土壤、空气、水中的氡浓度及氡析出率。仪器体积小,操作简便。FD216测量仪采用硫化锌ZnS(Ag)和光电倍增管组合系统;对空气中氡的测量范围为3~10 000 Bq·m?3;具有较好的稳定性,相对误差≤10%;测量温度?10~+40 ℃,可在相对湿度≤90%的环境中使用。1.3. 监测方法
测量点和测量时间的选择参照《公共场所卫生监测技术规范》(GB/T 17220-1998)来确定。测量点远离通风口,距离墙壁大于50 cm,位于停车场的中心位置。每日取样时间段为09:00—12:00与15:00—18:00,选取时间段是地下停车场营业高峰期。氡气浓度测量方法参照《建筑室内空气中氡检测方法标准》(T/CECS 569-2019),每次测量时间为30 min。同时记录天气状况、温度、湿度和气压等环境参数。以上测量方法满足《民用建筑工程室内环境污染控制规范》(GB 50325-2010)中对民用建筑工程室内空气中氡浓度检测的技术要求。测量时间为2017-08—2019-07,共取得有效测量数据1 208组。2.1. 地下停车场中氡气浓度概况
对1 208组有效测量结果的数值范围进行分析,得到氡气浓度的大小分布(见图2)。该地下停车场上午氡气浓度的分布为8.9~83.1 Bq·m?3,平均值为29.75 Bq·m?3,均方差为11.08 Bq·m?3;下午氡气浓度的分布为8.9~79.9 Bq·m?3,平均值为30.44 Bq·m?3,均方差为11.51 Bq·m?3;测得所有氡气浓度的平均值低于世界平均水平40 Bq·m?3,低于《地下建筑氡及其子体控制标准》(GBZ 116-2002)中地下建筑氡浓度限值[14],与成都市1998—2002年测量的室内平均氡气浓度29.4 Bq·m?3[15]相近。用偏度系数来分析上午和下午氡气浓度分布与正态分布的相似性,其计算公式[16]见式(1)。式中:
该地下停车场上午氡浓度偏度系数为0.865,下午氡浓度偏度系数为0.859。基于以上结果,上午和下午氡气浓度分布形态近似,数据分布偏向高值,且高值集中于夏季。成都属于盆地气候,地下停车场内高温和低温天气较少,温度波动不剧烈,故造成夏季氡气浓度偏高的原因可能是湿度和大气压。频数又称次数,是各观察值所出现的单位数。用频数来代表所测不同值的氡气浓度及各环境因子的个数。由于上午和下午氡气浓度分布形态近似,去除上午的高值后绘制氡气浓度、温度、湿度和大气压的频数分布图(见图3)。由图3可知,去除高值后的氡气浓度、湿度和大气压的分布均近似于正态分布,说明夏季氡气浓度偏高是湿度和大气压的共同作用。夏季大气压较低,使得建材中密度较大的氡气释放迁移至地下停车场空气中,再加上此时地下停车场内空气湿度较大,空气对流相对稳定,气体扩散作用变小,氡气可在空气中不断积累,导致了氡气浓度呈现全年峰值。
2.2. 地下停车场氡气浓度与环境因子相关性分析
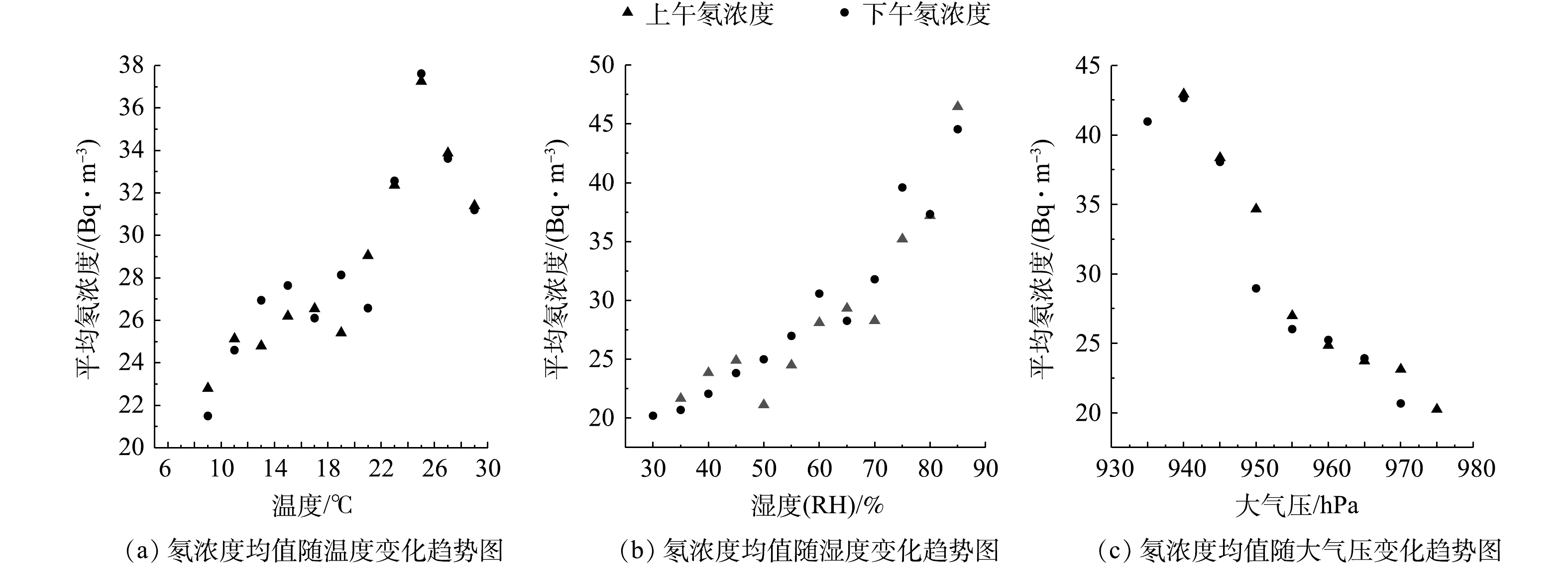
根据1 208组氡气浓度及环境因子间的相关性,将地下停车场氡气浓度分别按温度、湿度和大气压进行分段归类。归类后的均值与温度、湿度、大气压的关系如图4所示。由图4可知,上午和下午的氡气浓度同温度、湿度和大气压之间变化趋势相同。使用SPSS数据统计软件对不同环境因子之间的相关性进行分析,计算其Pearson相关性系数,结果如表1所示。由表1可知,温度与湿度为正相关,温度与大气压为负相关,湿度与大气压为负相关。对不同环境因子与平均氡浓度之间的相关性进行分析(见表2)。氡浓度与温度之间为显著正相关,与湿度之间为显著正相关,与大气压之间为显著负相关。
图4和表2说明氡气浓度与温度之间正相关,这与文献[17]的研究结论一致。在地下停车场中,氡气浓度随温度的变化是由氡析出率和空气对流共同作用。当地下停车场内的温度升高,使得射气介质膨胀,空隙直径和形状发生改变,促进了氡气的析出,氡气浓度增加[18]。地下停车场内外温度差会造成空气对流。当外界空气温度较低时,室外空气通过入口进入地下停车场,对空气中氡浓度产生了稀释效应,降低了氡气浓度;而当外界空气温度较高时,地下停车场内空气相对停滞,氡气在停车场内聚集,此时氡浓度较高[17]。图4和表2说明,氡浓度与湿度之间正相关,这与文献[19]的研究结论一致。由于测点远离通风口,空气对流相对稳定,当空气湿度变大时,气体扩散作用变小,氡在空气中不断积累导致浓度较高[20]。与温度和湿度关系不同,图4和表3说明,氡气浓度与大气压呈负相关,这与参考文献[21]的研究结论一致。当大气压发生改变时,空气和射气介质会因为上下压力的作用,从而造成射气介质内部的压力梯度,大气压力的纵深效应可改变气体的迁移进而造成空气中氡气浓度的变化[22]。当压力变小时,射气介质中一些密度较大部分的氡气会释放至空气中,导致氡气浓度增加。
2.3. 地下停车场氡气浓度的变化趋势
2017年8月—2019年7月期间,地下停车场氡气浓度随时间变化如图5所示。其中,2018年2月—3月因仪器故障无数据,为确保数据的准确性与可靠性,在2018年8月—2019年7月这段时间采用2台FD216测量仪同时工作以进行数据的补充。由图5可知,地下停车场氡气浓度呈季节性变化,连续2年的监测结果表明,年度变化规律相同。每年8月后,氡气浓度逐渐降低,到冬季处于一个平稳期;秋冬季节,氡气浓度处于15~30 Bq·m?3,地下停车场氡气浓度波动较小,方差为6.4 Bq·m?3;而春夏季氡浓度逐渐升高,氡气浓度多数分布于16.5~67.9 Bq·m?3,这个季节地下停车场氡气浓度波动较大,方差为10.5 Bq·m?3。为进一步摸清氡气浓度的季节性变化规律,将测量数据按月求平均,结果如图6所示。图6显示,相同季节上午和下午的氡气浓度平均值相差不大,但季节性差异明显。氡气浓度在秋冬季节较低,春季开始回升,夏季最高。夏季平均氡气浓度为秋冬季平均氡浓度的1.72倍。有研究表明,地下坑道内的氡气浓度四季变化相差不大[23],而室内氡浓度呈现秋冬季节高于春夏季节的季节性变化[15],这与本研究的监测结果差异较大。造成这种差异的原因可能与建筑内通风条件、建筑结构以及地区气候特征等有关。李晓燕等[17]开展的研究表明,地下停车场季节性内外温差引起空气对流,这与本研究结果一致。
2.4. 有效剂量估算
地下停车场空气中的氡衰变后,氡及其子体所产生的人均年有效剂量式中:
本研究中监测所得地下停车场平均氡浓度为29.75 Bq·m?3,计算得到该地下停车场工作人员吸入室内氡气及其子体所致年均有效剂量为0.643 mSv,低于全球年平均照射剂量(2000年)1.2 mSv[26],也低于我国推荐的室内氡气浓度控制标准[27]。
2.5. 防氡降氡措施及建议
本研究为地下建筑氡污染防治提供了有效的现场数据。基于结果分析,可为今后的地下建筑氡污染防治工作提供参考。普通地下建筑多数采用混凝土浇筑,而普通的混凝土并不具备防氡效果[28]。虽然现阶段地下建筑内氡辐射并未超标,但随着建筑的老化,地面、墙壁、管道出现裂缝,会导致大量的氡逃逸至建筑内部,造成氡浓度的升高。这时在地下建筑内进行氡污染防治是必要的。本研究的结果表明,氡浓度在春夏季偏高,因此,可考虑在地下建筑墙壁表面涂上高性能防氡涂料;同时在高温的夏季及雨季时建立通风、抽气系统,用排水孔管抽气、地板下抽气通风、砌块墙通风等通风方式,并采用机械通风和自然通风相结合的模式达到防氡降氡的效果。此外,为节约能源、确保人群健康,建议建立氡污染信息系统和预警管理系统:在夏季时,可通过该系统对地下建筑内的氡气浓度实施连续监测,根据氡气浓度来调节通风设备功率;在秋冬季节,选择日常工作时间对地下建筑内的氡气浓度进行定时监测,若发现氡气浓度异常则对地下建筑材料与结构进行检查,对未达到要求的地方进行修补与完善。2)开展地下建筑氡污染治理时,应充分考虑氡气浓度的季节性变化,并在地下建筑内建立通风抽气系统和氡污染预警管理系统,优化氡气监测方式,以达到节能目的。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: 



 点击查看大图
点击查看大图