全文HTML
--> --> --> 近些年,我国水污染事故时有发生,威胁到水资源的安全[1-3]。水污染问题不仅影响水生态,还威胁到供水安全,甚至造成社会公共事件。为应对水污染事故,我国构建了相关应急机制,但多针对水污染事故造成的后果以及处理方法。在水污染事故发生后采取的应急及处理方法使得污染物处置难度大,还会增加社会经济成本。如何在事故发生前,建立以风险防控为目标的水源污染突发事件高风险点识别方法,实现有效预警,是当前管理部门所关注的重点之一[4-6]。对事故敏感点进行诊断通常采用事故树分析(fault tree analysis,FTA)方法,亦称为故障树分析法。这种方法是安全系统工程中常用的研究方法,能帮助找出导致事故发生的基本原因事件[7-9]。目前,该方法已经被成功应用于矿山、能源、石化、交通、公共卫生、电力、和经济等多个行业,但在水源污染事故风险点甄别中的应用还很少[10-12]。事故树分析主要将构成事故因素逐级分解成单独事件,采用布尔代数计算各导致事故的最小割集和径集、结构重要度等为研究方法。然而,对于事故概率的估计往往基于经验值,国内同类研究中缺乏关于大量已发生事故案例的定量统计研究[13-15]。
本研究基于世界卫生组织(World Health Organization,WHO)颁发的《饮用水水质准则》和《水安全计划手册——供水企业分步实施的风险管理》,建立水源事故树的基本事故框架。结合我国2000年以来能够查阅到的1 900多起水源污染突发事件案例,统计计算出各个基本风险因素发生概率。采用事故树分析方法和贝叶斯网络定量分析了导致水源污染的各种事件概率,最终通过事故树节点逻辑关系确定水源水质发生污染事故的不同事故节点发生概率。根据我国近20年发生的事故对所有因素进行了导致水源污染的基本事故排序,筛选出水源高风险点,以期为加强水源安全事故风险管控提供技术参考。
1.1. 数据来源
目前,我国尚未建立较大的水源污染突发事件案例数据库,相关部门缺乏详细统计年鉴。根据我国2000—2019年的公开报道资料,本研究收集国内水污染突发事件总计约2 500起。按照污染事件名称、发生时间、发生地点、污染名称、事故原因及水体类别做了统计,选出其中水源(江、河、湖泊、地下水、自备饮用水源)污染事故案例1 900起用于水源地风险甄别研究。1.2. 分析方法
1) 建立水源事故树。水源事故树见图1。参照WHO发的《饮用水水质准则》和水安全计划手册——供水企业分步实施的风险管理方法,结合水源污染事故案例数据,用Visio软件将水源(T)作为顶上事件,突然排污、土地占用、工业区、建筑工事等(A、B、C、D类)作为中间事件,管道事故、企业违规排污、企业安全事故等因素(X类)作为基本事件,根据实际事故之间触发逻辑,建立基本事件造成水源污染的事故树关系图。2) 重要度分析。对水源事故树导出的各类基本因素使用Excel软件整合到水源污染突发事件案例中,应用古典概率模型(式(1))计算基本事件发生的概率。应用基本事件结构重要度(式(2))和基本事件概率重要度(式(3))计算各基本事件的结构重要度和概率重要度并进行排序分析。
3) 风险点甄别。基于1 900起统计数据计算出的各基本事件发生概率,通过事故树逻辑门中的乘(“×”)(式(4))或加(“+”)(式(5))计算顶上事件或者中间事件发生的概率。
4) 使用贝叶斯网络(Bayes networks, BN)进行验证计算。将事故树中的每个事件映射成贝叶斯网络的节点,事故树中各基本事件发生概率对应到贝叶斯网络中根节点的先验概率,根据事故树中逻辑门的逻辑关系得到贝叶斯网络中对于节点的条件概率[16](见式(6))。
1.3. 模型应用
1) 基本事件发生概率。结合全国1 900起饮用水源突发污染事件案例,用Excel软件对基本污染因素发生频次进行了统计,通过古典模型概率公式(式(1))计算水源基本事件危害的概率。式中:N为样本点总数;K为事件A的样本点个数。
2) 基本事件结构重要度[17]。
式中:
3) 基本事件概率重要度[17]。
式中:
4) 与门结构的顶上事件的发生概率计算公式[18]见式(4)。
或门结构的顶上事件的发生概率计算公式[19]见式(5)。
式中:
5) 贝叶斯网络(BN)是每个节点都带有一张条件概率表的有向无环图。利用联合概率分布得顶事件的发生概率用(式(6))计算。
式中:
2.1. 水源基本事件梳理
根据1 900起事件通过古典概率模型(1)估算近20年导致水污染因素的发生概率,结果见表1。根据实际突发水污染事故案例统计结果,引起我国水源水质风险的基本事件有37类。其中,基本事件风险排序依次主要有:1)工业废水,主要是一些企业违规排放导致的;2)安全事故,主要是针对部分企业设施人为操作不良引发的水质安全事故造成的;3)生活污水、工业废弃物、生活垃圾、藻类、自然灾害,如暴雨、洪水引发的水体污染;4)管道事故,如输油或输送污水管道破裂;5)油类泄漏污染,主要是指交通事故造成的,化工厂占地导致的地下水污染,大型载物船舶航运事故,矿物开采过程中由废水排放和尾矿库渗漏造成的;6)部分植物,如浒苔、水葫芦等蔓延水面生长,造成的水质大面积缺氧状况;7)农药化肥,如河流近地进行农业活动或清洗农药工具;8)小型船只活动、事故车辆、机械渗油、养殖动物浮尸造成的;9)建筑工事坍塌事故、医药废水、氮磷营养物、人为故意破坏,主要是投毒捕鱼事件,水面作业触发的偶然水体污染事故,气候变迁、及清理路面积雪时使用的融雪剂等因素均会对水源水质造成不同程度的影响。
2.2. 概率计算
基于事故树可以定量分析某类事故发生的概率。如基于大量的统计数据可以计算各基本事件发生的概率,通过逻辑门中的加(“+”)或乘(“×”)计算顶上事件发生的概率,与预定的目标进行比较。如果得到的结果超过了允许目标,则采取相应的改进措施,使其降至允许值以下,以达到控制事故率处于设定安全阈值之下的目的[20-21]。根据表1中基本事件的发生概率,按照事故树结构和计算原理,对事故树加以分析。水质污染风险的计算表达式见式(7)。
根据式(7),获得最小割集为38,即造成水质污染的可能路径有38个。由式(2)得基本事件结构重要度计算见式(8),对水源产生污染风险的结果重要度顺序见式(9)。由式(3)得基本事件概率重要度见式(10),对水源产生污染风险的概率重要度顺序见式(11)。
独立性事件发生概率模型,根据事故树节点逻辑关系,由式(4)和式(5)计算出中间事件的概率,结果如表2所示。
通过计算发现,水源污染风险依次为突然排放、累计污染、交通事故造成的污染。突然排放中,主要以工业废水为主;累计污染中长期对土地占用带来的风险相对较大,其次是其他排污;交通事故造成的污染主要是油类、化学品泄漏水体排放带来的风险。
2.3. 结合贝叶斯网络进行验证计算
为提高事故的预测可靠性,采用贝叶斯网络对事故树进行验证计算。考虑到贝叶斯网络和事故树有很大的相似性,而贝叶斯网络还具有描述事件多态性和事故逻辑关系非确定性的能力,因此,将运用事故树结合贝叶斯网络对水源污染风险进行分析。首先做水源污染事故树到贝叶斯网络的映射,基本事件对应于BN中的根节点,中间事件对应于中间节点,顶事件对应于叶节点,并运用式(6)计算各节点的污染概率,如图2所示。做事故树和贝叶斯网络的事件发生概率结果比较,可以发现计算结果相近,说明计算结果(表3)合理。
3.1. 突发性污染
突发性水污染事件往往没有任何预兆,如管道泄漏、爆炸等都有可能造成水污染事件的爆发[22-24]。根据事故案例统计,我国2000—2019年工业废水造成的污染事件达880多起。引起我国水源水突发性事故污染的直接原因有:企业直接排放工业废水、废水管道事故和企业安全事故、自然灾害等引发的间接工业废水排放。水源上游工业企业数即危险源的数量,与突发水污染事件频数呈正相关[25-27]。结合案例分析可知,工业废水对水源的污染最大,主要原因有:一方面,我国近几年工业发展较快,企业数量增长和产生的工业废水增加,为事故的发生创造了条件;另一方面,近几年我国致力于经济的发展的同时也带来了一定环境方面的问题。大部分生产企业建在河流附近[28-30],案例显示,很多化工企业趁着雨季或暴雨将大量未经处理的废水排入水体的事件时有发生,使水质受到严重污染。因此,雨季往往是高风险时间段。3.2. 累积性污染
1)土地污染。土地的累积性污染主要来自工业区和农业类污染。工业区主要有工业废弃物造成的污染,矿物开采、化工厂以及部分建筑物坍塌事故造成的土地污染;农业活动污染主要是畜牧养殖和农业废弃物等。如遇到暴雨天气,上述累积的污染物极易被大范围释放。2)水生态污染变化。引发水生态效应的基本因素主要有氮磷营养物、藻类及自然因素如光照等。氮肥和磷肥的施用是作物生产必需的措施。农药、化肥的过量使用使得农田养分超出负荷,氮磷等营养物质在雨水等因素的作用下流入水体,最终造成地表水出现营养物累积[31-32],导致藻类爆发。
3)其他排污。主要指垃圾填埋场和生活污水造成的排污。垃圾填埋场对地下水环境的影响主要来自防渗层出现故障,下渗的渗滤液会导致地下水的水质出现变化[9];生活污水的排放和垃圾倾倒,从而威胁河流水体水质[20-21]。
3.3. 交通事故污染
案例统计发现,2003—2019年交通事故引起的水体污染达200起,这必然会对水体产生直接的影响[10]。尤其是船舶交通事故,对航道及附近水体的污染危害较大。交通事故污染中,公路交通事故造成的水体污染,以化学品泄漏排放为主;水上交通以航运事故污染及柴油泄漏排放为重要源。参考文献


 下载:
下载: 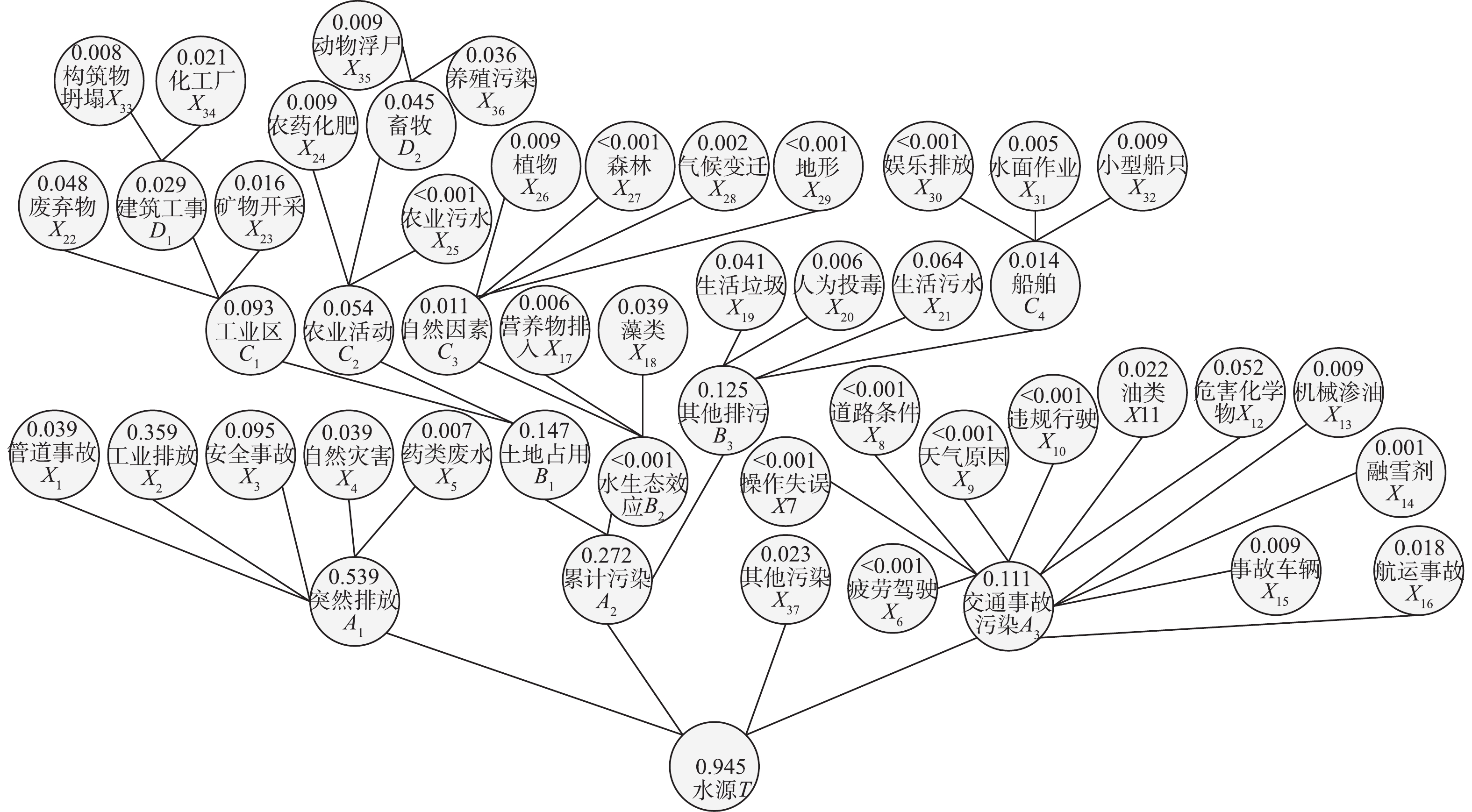
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图