全文HTML
--> --> --> 膜处理技术因其具有节省空间和提高出水水质的特点,近年来已经广泛用于污水处理中[1]。然而,膜污染也不容忽视,需要经常维护才能使膜恢复正常运行[2-3];因此,膜污染已成为污水处理的研究热点[1,4]。造成膜污染最关键的原因是形成了不需要的生物滤饼层,该过程主要有以下3个阶段:膜孔被较大的固体堵塞;活性滤饼层(LCL)在膜表面积累;死细胞形成死滤饼层(DCL)并产生细胞外聚合物(EPS)[5-6]。有目的地让生物滤饼生长在多孔网状材料(如无纺布、织物或陶瓷材料)的表面,并自发地形成动态膜(SFDM)[7],以提高筛孔过滤性能,可以达到粗滤的效果(过滤孔径为5~200 μm)[8-11]。这种基于SFDM的粗滤,也被称为动态生物滤网(DMf)[12],现已成为在污水处理中传统微滤(MF,孔径为0.1~1 μm)的替代技术[7,13]。有研究[14]表明,DMf已被用于改善污水AB处理工艺的A阶段(有机物的去除率由40%提高到70%)。
对于DMf来说,快速形成活性滤饼层进行过滤是理想状态,但缓慢累积的死饼层会引起空隙堵塞[5]。大量的研究表明,筛孔大小在以下几个方面起着关键作用:有选择地形成活性滤饼层,以获得较好的出水水质;最大限度地减少EPS积累对膜污染控制的不利影响[15];在反冲洗之后,能快速重新生成有效的生物滤饼层[8,12,16]。
为了系统地分析DMf的形成与污染过程,本研究通过数学模拟和小试实验对DMf进行系统梳理,探讨了动态生物滤网表面密度与EPS浓度之间的关系;在小试规模下研究了筛孔大小对膜形成的影响,分析了动态生物滤网所形成的生物滤饼层中微生物的分布情况,以期为探究EPS对动态生物滤网中滤饼层形成的影响和膜污染进程提供参考。
1.1. 实验装置与方法
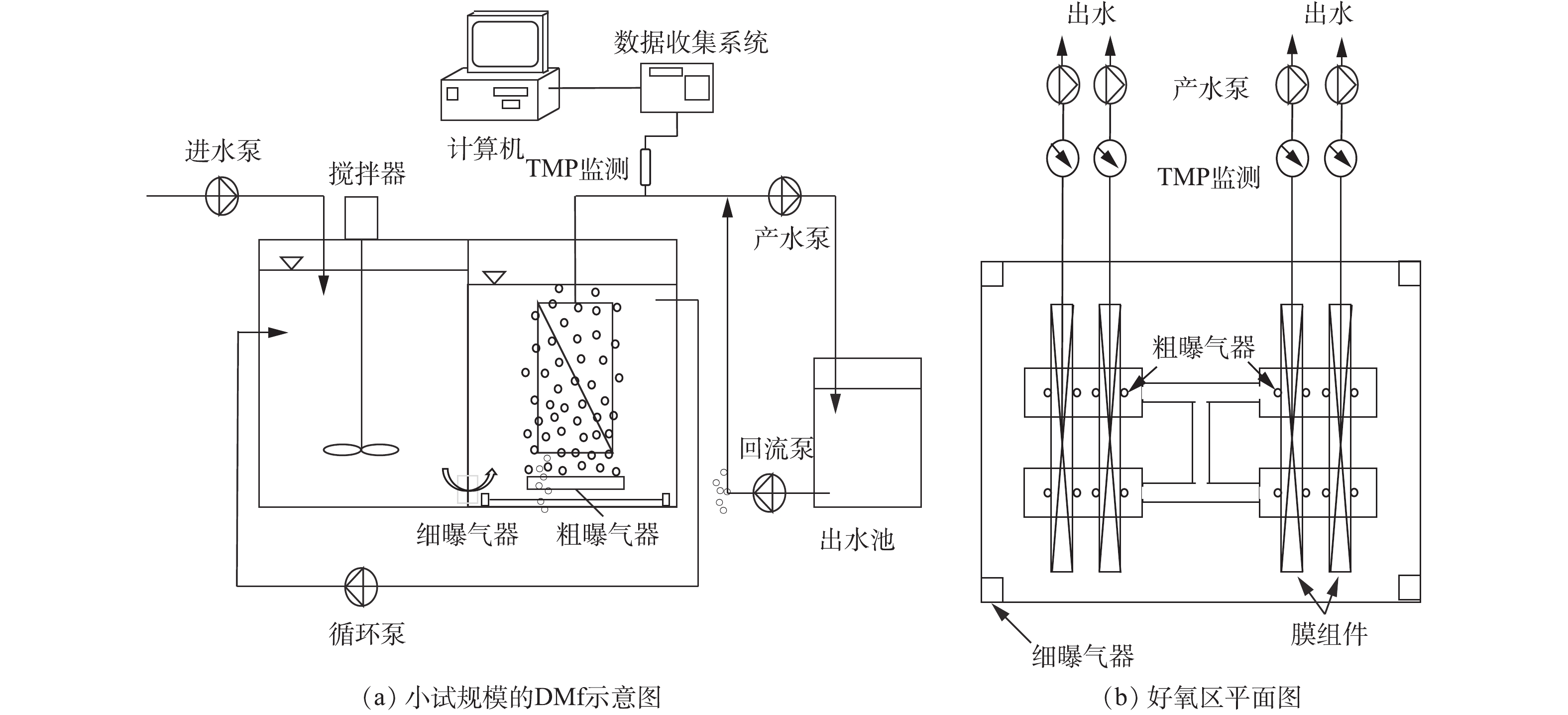
实验装置见图1。DMf反应器由缺氧区(40 L)和好氧区(40 L)组成,用于研究筛孔大小对生物滤饼层形成的影响。系统使用蠕动泵进水,进水采用的人工模拟废水,进水水质如下:382.4 mg·L?1 C6H12O6、40.3 mg·L?1 (NH4)2SO4、4.5 mg·L?1 KH2PO4、220 mg·L?1 NaHCO3 (CaCO3计)、4 mg·L?1 CaCl2·2H2O、36 mg·L?1 KCl、2 mg·L?1 MgSO4·7H2O、20 mg·L?1酵母提取物、0.15 mg·L?1 CoCl2·6H2O、0.03 mg·L?1 CuSO4·5H2O、1.50 mg·L?1 FeCl3·6H2O、0.12 mg·L?1 MnCl2·4H2O、0.06 mg·L?1 Na2MoO4·2H2O、0.12 mg·L?1 ZnSO4·5H2O、0.15 mg·L?1 H3BO3、0.18 mg·L?1 KI。实验所采用的污泥来自香港当地的二级污水处理厂。系统的操作条件如下:水力停留时间为5.5 h、污泥停留时间为30 d、渗透通量为4 m3·(m2·d)?1、污泥浓度为3 000~3 500 mg·L?1、温度为(20±1) oC、好氧区溶解氧为(3.0±0.5) mg·L?1、缺氧区溶解氧为(0.8±0.1) mg·L?1。4个平板尼龙筛网平行安装在好氧区中,所有筛网的配置均相同:框架尺寸为28 cm×17 cm×2 cm;每侧有效过滤面积为0.02 m2(占总表面积的42%),每个模块上覆盖着不同孔径的网格(5、55、100和220 μm),并且覆盖了用于生物滤饼层形成的过滤材料。为确保所有筛网的测试条件相同,渗透通量、MLSS和气水比分别控制在4 m3·(m2·d)?1、(3 000±300) mg·L?1和15 m3·m?3。另一方面,为了独立监测不同筛网情况,实验过程中使用4台排水泵,分别从每个筛网进行产水。利用在线跨膜压力(TMP)监测系统,通过在线数据采集程序和校准装置,将电压信号转换为压力进行TMP监测。
在好氧区,安装了2种类型的曝气设备:粗曝气器(5 mm)用于提供足够的剪切应力,来控制生物滤饼的形成和EPS的产生;细曝气器(100~350 μm)使好氧区DO控制在2.5~3.5 mg·L?1[16]。细曝气器安装在好氧区底角,而粗曝气器则均匀安装在平板筛网下方,膜需气量(SADm)为3 m3·(m2·h)?1[16]。筛网会根据TMP的指示进行反冲洗(每次1 min)。当TMP为-20 ~-30 kPa时,通常表示膜污染已经开始[17-18],因此,本研究采用TMP为-20 kPa作为反冲洗的指示压力。渗透液收集在出水池中,用15 L·min?1的流速对膜进行反冲洗。
1.2. 分析与检测方法
在进行生物滤饼形成分析时,本实验研究了4个孔径(5、55、100和220 μm)的尼龙网,以分析孔径对过滤的影响。连续监测了每个模块上生物滤饼的形成和过滤性能,并同时测定了4个膜组件的TMP和渗透悬浮物(SS)浓度。在生物滤饼形成之前,对每个组件进行多个反洗周期实验,然后将所有膜组件从生物滤饼取样系统中取出,分析表面附着的挥发性悬浮固体(VSS)和EPS浓度,并使用激光扫描共聚焦显微镜(CLSM)研究生物滤饼的结构。在进行生物滤饼特征分析时,生物的死亡会导致EPS大量释放,一般来说,可以通过检测多糖的含量来表示。分别从4个测试组件上取1 cm×1 cm的检测样本,重新悬浮在50 mL的消毒水中,然后将混合液用阳离子交换树脂进行多糖提取,以葡萄糖作为标准,采用蒽酮法进行检测。按照标准方法(APHA),分析每种提取物的MLSS和MLVSS,生物滤饼的密度则由检测样本的质量和表面积计算得出。
在进行生物滤饼样本中活/死细胞分布分析时,从前述提到的测试组件样本中切下部分样品(1 cm×1 cm),用细胞渗透性核酸染料和碘化丙啶进行染色,使用细菌活力测试盒,以监测死细胞和活细胞分布。在室温下,在黑暗中培养15 min后,用磷酸盐缓冲液冲洗掉染色液,然后用CLSM进行观察。
临界通量的测定采用流量阶梯法。通量从10 L·(m2·h)?1 依次升高至 90 L·(m2·h)?1,每个通量下运行 10 min,记录 TMP 变化。如果在运行 10 min 内 TMP的值没有明显变化,而在某个通量条件下 TMP 的值有明显上升时,该通量即为临界通量[15]。SS和VSS的测量根据标准方法(APHA)。
2.1. 生物滤饼层中EPS的产量预测
由已有研究[16]可以看出,膜污染的自加速过程分为3个阶段:空隙堵塞后生物滤饼逐渐形成、EPS积累、TMP跃升,表征污染已经发生[18]。为了缓解膜污染问题,理想的DMf应该能够快速形成生物滤饼层(阶段1),可减缓EPS在饼层中的积累(阶段2),以减轻污染(阶段3),这可以通过选择适当孔径的过滤材料(本研究中的尼龙网)[19]来完成。值得注意的是,筛孔尺寸越小,生物滤饼层的形成速度越快,同时也加速了生物滤饼层中EPS的积累,从而导致膜污染。生物滤饼层中EPS的产生是影响膜性能和造成污染的关键因素[1,5]。然而,在系统运行过程中很难获得这个参数。数学模拟方法可以定量表征生物滤饼层中筛孔大小对EPS浓度的影响,从而预测动态生物滤网的形成过程。在本研究中,建立了一个简化模型,将平面密度与EPS产量联系起来,以预测后者。该模型根据FREDERICK等[20]提出的方法(式(1))进行计算,以描述膜生物反应器中EPS的产生。
式中:E为生物滤饼层中EPS浓度,g·g?1;
在实验操作条件下,经式(1)预测的EPS产率和测量的EPS浓度关系如图2(a)所示,测量的EPS浓度与生物滤饼层的面密度关系如图2(b)所示。由图2(a)可以看出,经式(1)预测的EPS产率、生物滤饼层的面密度与实测的EPS浓度之间均具有显著的正相关性,这也证实了所提出的模型可用于预测具有不同孔径的网筛上形成的生物饼中的EPS产生量。
由图2可知,随着网孔尺寸的增加,生物滤饼面密度和EPS浓度均有所降低。不同网孔尺寸对面密度和EPS浓度的影响可以通过式(2)和式(3)进行回归定量评估。
式中:Bb为生物滤饼层面密度,g·m?2;CEPS为生物滤饼层中EPS浓度,mg·g?1;p为筛网孔径,μm。
EPS浓度和网孔尺寸之间的关系结果表明,EPS可能由较厚的饼层产生,因为更大的面密度会释放更多的EPS[21]。EPS浓度和面密度之间的相关性也验证了FANE等[22]的预测结果,即MBR阻力随生物量的增加而增加。
2.2. 滤饼层的形成与膜污染
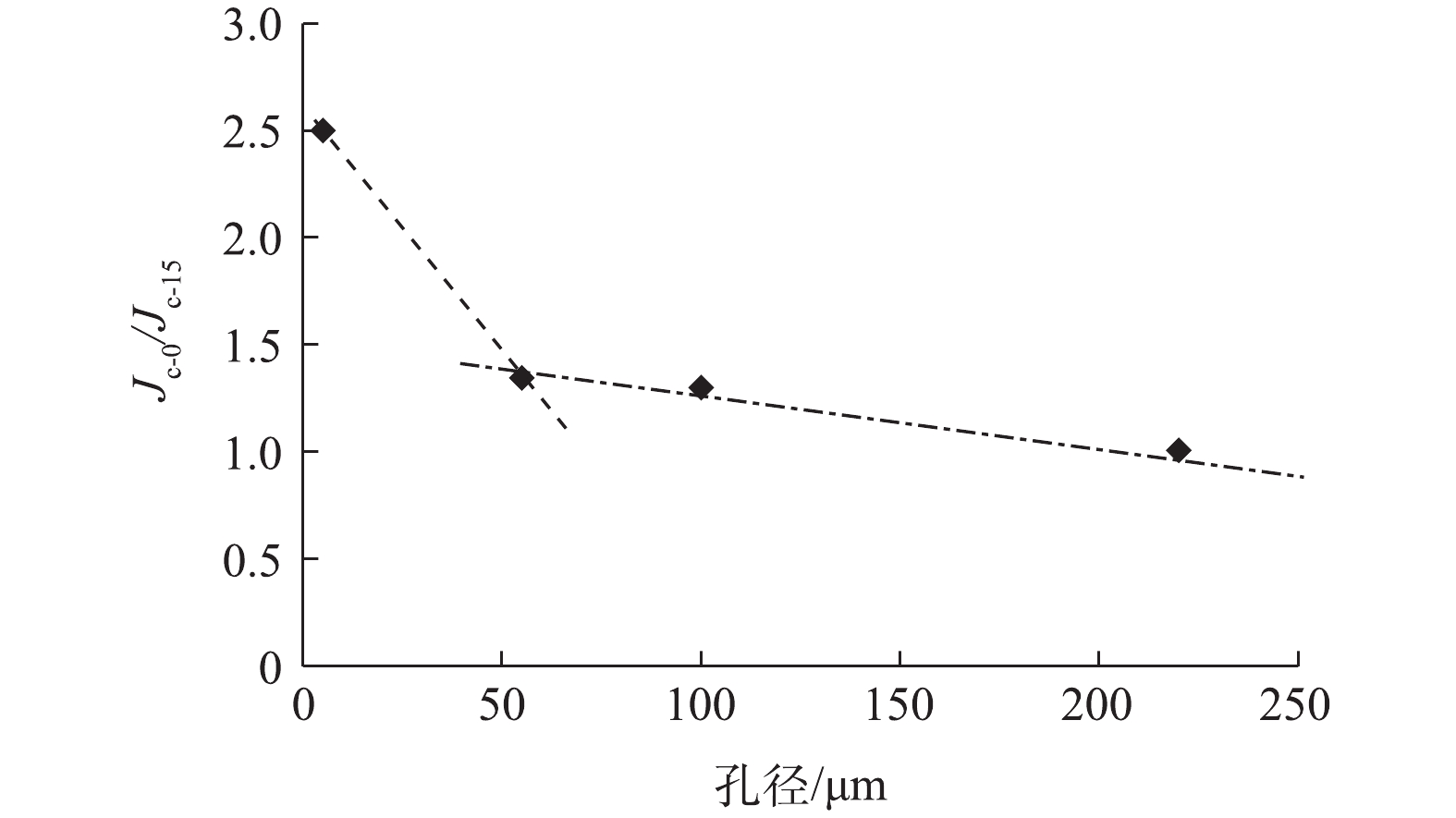
通过监测过滤出水的SS和TMP的变化,研究了生物滤饼的形成和宏观过滤能力,并对DMf的运行情况进行了分析。用在线数据采集程序记录每个膜组件的TMP,然后将电压信号转换为压力信号。随着生物滤饼层的逐渐形成,渗透液中的SS浓度也随之降低,实验结果如图3所示。小孔径膜由于其生物滤饼层形成较快而容易受到膜污染[23]。模块A(5 μm)的TMP比其他模块急剧增加,而模块B(55 μm)、C(100 μm)和D(220 μm)的TMP增长依次逐渐变得缓慢。这也说明可以通过膜孔径来控制生物滤饼层的形成速度。孔径为5、55、100和220 μm的膜的反冲洗时间(定义为2次反冲洗之间的操作周期)分别为6、48、48和72 h,这说明筛孔尺寸为5 μm的反冲洗时间非常短,难以增大;筛孔孔径为55 μm和100 μm的反冲洗循环时间适中,运行成本低,出水质量高,具有较高的实际应用潜力;220 μm筛网具有很长的反冲洗周期,但产生的水质情况较差,不适合实际应用。本研究选择了范围较宽(5~220 μm)的网孔尺寸,以研究网孔尺寸对生物滤饼形成的影响。在实验中,对每个模块进行15次反冲洗循环实验,第1次循环的临界通量与第15次循环的临界通量之比(Jc-0/Jc-15)可以表征长期运行时的膜过滤性能。该数值随着网孔尺寸由5 μm增加至55 μm(模块A和B)而急剧下降,而对于网孔孔径为100 μm的模块C和220 μm的模块D,其值几乎保持稳定(图4)。这说明较厚的生物滤饼所含的EPS的增加会加剧DMf中的膜污染。
2.3. 生物滤饼层中微生物的分布
将生物滤饼层通过CLSM进行观察,LCL显示为绿色,DCL显示为红色,结果如图5所示。由图5可见,生物滤饼层中死细胞的比例及其厚度与网孔尺寸密切相关。在高通量条件下,随着网孔孔径减小,生物量积累速率增加,导致面密度增加。具有较小孔径的网格诱导形成较厚的生物滤饼层,其含有大部分的DCL。较高的面密度限制了生物滤饼或生物膜中底物和氧的扩散[24],导致生物滤饼底部的细胞死亡区域增厚并增加了EPS的释放。值得注意的是,在4个网格上形成的生物滤饼层厚度依次约为80、80、60、20 μm,而且LCL的厚度均约为20 μm,但DCL的厚度则由60 μm (5 μm孔网格)到0 μm (220 μm孔网格)不等。稳定的活细胞层厚度也意味着氧气可以渗透到生物滤饼大约20 μm的深度,这与下水道生物膜中的氧渗透结果[24]一致。基于以上结果,确认最佳孔径为55~100 μm,而平均活性污泥粒径为78 μm。孔径为5 μm的膜通过阻断DMf中的几乎所有颗粒(LCL在非常短的时间内形成),能够快速形成生物滤饼,但是在短时间内(约6 h)就会导致膜污染(短时间内DCL形成)。孔径为55~100 μm的膜可以阻挡DMf中的大多数颗粒,但允许小颗粒穿透滤饼层,确保有效形成具有缓慢EPS积累的生物滤饼(LCL形成时间较短,但DCL形成时间较长)。此外,孔径超过100 μm的膜不能保留大部分颗粒,因此,滤饼层不能产生高质量的渗透物(图3)。合适的孔径虽然可以延长DCL的形成,但是当网孔尺寸在55~100 μm时,由于EPS的积累,并不能避免膜污染。
2)孔径为55~100 μm的筛网上形成的动态生物滤网可以阻挡泥水混合液中的大多数颗粒,但有部分细小颗粒仍可穿过滤网表层,并在滤网底层积累,从而产生EPS,最终造成膜污染。
3) CLSM分析结果表明,DMf中死细胞的比例及其厚度与网孔尺寸显著相关。在较厚的DMf中细胞死亡加速。同时发现,在所有实验形成的DMf中,活细胞(绿色)层的厚度均约为20 μm。这表明有效的氧气渗透仅发生在DMf的薄层内,过厚的生物层会阻止氧气的渗透,导致微生物死亡而释放更多的EPS,最终加剧膜污染。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 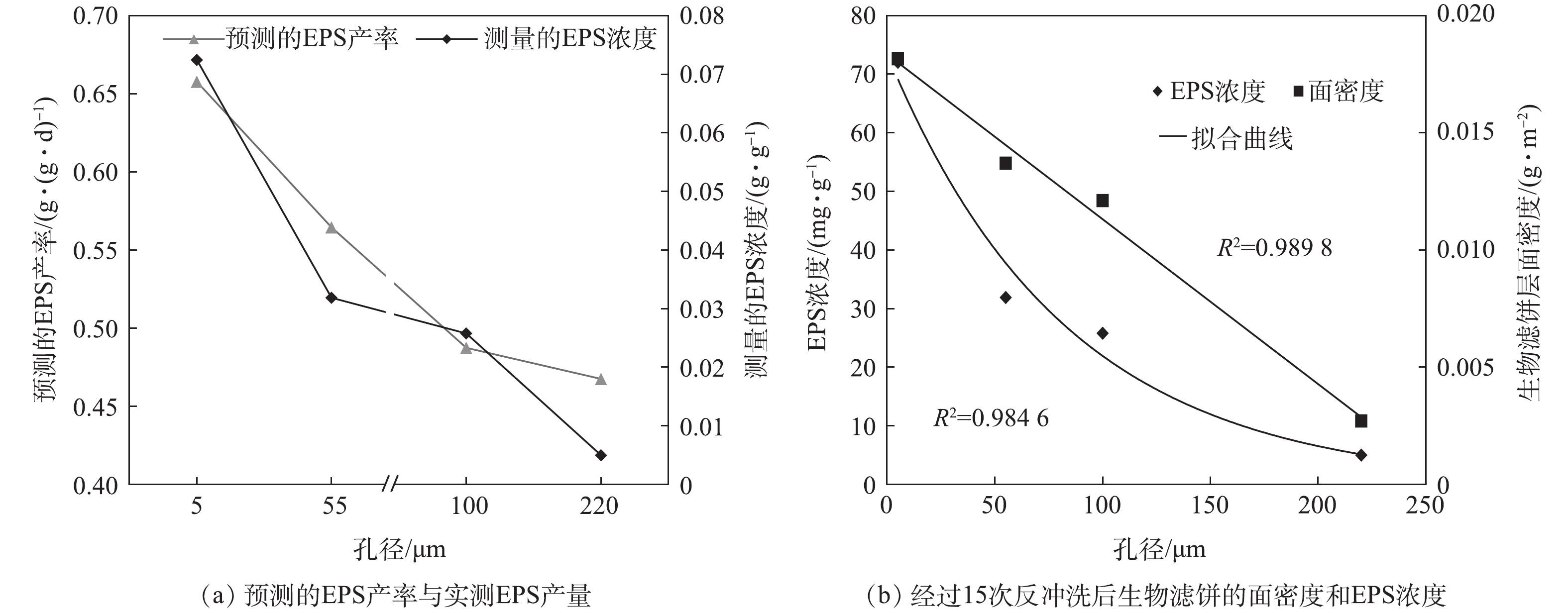


 点击查看大图
点击查看大图