全文HTML
--> --> --> 近年来,随着我国工业化进程的不断加快,土壤污染问题越来越严重[1]。钢铁厂、煤气厂和石油化工厂等企业在运营过程中产生大量多环芳烃,使得厂区及周边土壤中多环芳烃的含量极高[2]。多环芳烃具有低水溶性,很难被植物吸收或被微生物降解去除[3];加之污染物与土壤颗粒的长时间接触,对其吸附与老化的作用时间延长,使得这类有机污染物更难被去除[4-5]。因此,土壤中多环芳烃的有效去除成为土壤污染修复的难点之一。目前,基于土壤淋洗技术的化学修复法得到广泛应用[6]。淋洗法具有适用范围广、处理容量大、效果显著等优点,是一种有效的污染土壤修复方法[7]。李爽等[8]以表面活性剂为淋洗剂对炼焦煤气厂污染土壤进行修复,提出复配表面活性剂TX-100/SDS对多环芳烃有显著的增溶效果。王晓光等[9]采用生物柴油作为淋洗剂对污染土壤中的高浓度多环芳烃进行淋洗去除。还有研究[2]对比了非食用性植物油、生物柴油、表面活性剂及其乳化合成的微乳液作为淋洗剂的增溶效果,结果表明乳化合成的微乳液对原污染土壤中多环芳烃具有更显著的洗脱作用。
微乳液是由两种不相溶的液体在表面活性剂界面膜的作用下形成透明且热力学稳定的均相分散体系,通常由油相、水相、表面活性剂和助表面活性剂(简称助剂)构成[10-11],具有稳定、节能高效、界面张力低和增溶能力强等特点[12]。现阶段,微乳液已应用于萃取、纳米材料和药物载体制备,在石油工业和食品等领域也有应用[13]。但是,在土壤淋洗方面应用较少。如何利用微乳液的性质制备高效的土壤淋洗剂还有待进一步的研究。本研究以表面活性剂及助表面活性剂、生物柴油、去离子水制备的微乳液作为洗脱去除污染土壤中多环芳烃的新型淋洗剂,以期在尽可能降低成本的前提下达到理想的去除效果,为污染土壤中多环芳烃的去除提供新方法,也为其他污染物的去除提供新思路。
1.1. 微乳液的制备
采用滴定法制备微乳液淋洗剂,并绘制拟三元相图。固定拟三元相图的3个顶点分别为生物柴油(O)、混合表面活性剂(S)、水(W),将表面活性剂和助剂按一定质量比配成混合表面活性剂溶液备用。再将此溶液与生物柴油按照不同比例混合(质量比为1∶9、2∶8、3∶7、4∶6、5∶5、6∶4、7∶3、8∶2、9∶1),分别置于100 mL试剂瓶中,边搅拌边滴加水,记录溶液从澄清到混浊的边界点用量,绘制出拟三元相图。连接相图中微乳液的形成或破坏的边界点,微乳液区以L表示,乳状液区以E表示,如图1所示。1.2. 不同因素对微乳液体系影响的实验设计
1)表面活性剂复配种类。实验选择二元表面活性剂复配体系和三元表面活性剂复配体系。准确称取2 g Tween-80和2 g TX-100,用于制备二元表面活性剂复配体系;准确称取2 g Tween-80、2 g Span80和2 g PEG400,用于制备三元表面活性剂复配体系。将复配表面活性剂和助剂按质量比Km=1∶1配成混合表面活性剂溶液,按照1.1节实验方法制备微乳液,并绘制拟三元相图。2)各组分配比对微乳液体系的影响。表面活性剂复配体系依据表面活性剂复配种类的实验结果,实验设定的变化参数包括表面活性剂复配比例(3∶1、2∶1、1∶1、1∶2、1∶3)、助表面活性剂(异丙醇、正丁醇、正戊醇)、表面活性剂与助表面活性剂的比值(1∶2、1∶1、2∶1、4∶1),制备微乳液,并绘制拟三元相图。
3)制备条件对微乳液体系的影响。表面活性剂复配比例、助表面活性剂、表面活性剂与助表面活性剂的比值为实验1.2得出的最佳配比。实验设定的变化参数包括温度(20、25、30、35、40、50 ℃)、pH(5、6、7、8、9、13),制备微乳液,并绘制拟三元相图。
1.3. 污染土壤
供试污染土壤样品采自辽宁某钢铁厂周边区域,多环芳烃总浓度为70.07 mg·kg?1,主要多环芳烃及其浓度见表1。1.4. 土壤多环芳烃的振荡洗脱
1)微乳液与不同类型淋洗剂的洗脱效果对比。称取20 g污染土壤样品。以浓度均为28%的Tween-80、TX-100、Tween-80∶TX-100=1∶1复配表面活性剂、生物柴油(纯物质)、微乳液作为5种不同类型的淋洗剂,固定振荡时间为16 h,淋洗剂与土壤的液固比为8∶1,每个处理3个平行;洗脱后,于恒温振荡器中室温振荡后离心10 min,倒掉上清液,取出5 g淋洗后土壤样品进行前处理,使用高效液相色谱测定进行分析,并比较洗脱前后多环芳烃浓度差异,计算去除率。2)淋洗剂与土壤液固比的影响。称取20 g污染土壤样品。以微乳液为淋洗剂,固定振荡时间,设置淋洗剂与土壤的液固比分别为1∶1、2∶1、4∶1、8∶1,每个处理3个平行;洗脱、振荡后离心10 min,取出5 g土壤样品进行前处理,测定分析并计算去除率。
3)振荡洗脱时间的影响。称取20 g污染土壤样品。以微乳液为淋洗剂,固定液固比,设置振荡时间分别为2、4、8、16 h,每个处理3个平行;洗脱、振荡后离心10 min,取出5 g土壤样品进行前处理,测定分析并计算去除率。
4)表面活性剂与生物柴油比例对洗脱效果的影响。称取20 g污染土壤样品。由实验1.2得出的最佳组合配制混合表面活性剂溶液,以混合表面活性剂与生物柴油按照3∶7、5∶5、6∶4制备得到的微乳液作为淋洗剂Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ。在由1.4得出的最佳液固比及振荡时间的条件下进行洗脱实验,每个处理3个平行;洗脱、振荡后离心10 min,取出5 g土壤样品进行前处理,测定分析并计算去除率。
1.5. 土壤样品处理
用机械振荡抽提法分析土壤样品中的多环芳烃。准确称取5 g污染土壤样品,置于50 mL玻璃瓶中,加入 20 mL丙酮、15 mL二氯甲烷和10 mL氯化钠溶液,加盖密封后置于摇床,于120 r·min?1、30 ℃的条件下,振荡16 h,取出静置1 h左右,用移液管移出10 mL上层有机相过净化柱,氮气吹干后,用乙腈定容后转入色谱进样瓶,使用高效液相色谱进行测定。1.6. 液相色谱分析方法
高效液相色谱仪(安捷伦1200系列),色谱柱为C-18柱,使用荧光、紫外检测器进行检测。对于钢铁厂土壤的待检测样品,色谱条件为:柱温30 ℃、流动相为乙腈和水、流速为0.8 mL·min?1、进样量10 μL。各种多环芳烃均在其各自的发射/激发波长下进行测定。2.1. 微乳液最佳体系的选择
微乳液体系组分的确定是制备微乳液的关键。由于不同微乳液体系的稳定组成范围不同,因此,微乳液体系在用作淋洗剂前都需对稳定性进行研究,要求其稳定范围宽,对温度、pH变化不敏感[11]。常用的评价微乳液稳定性的指标有微乳区L面积的大小和溶水量等。在一定范围内,形成微乳区面积越大,溶水量越高,微乳液的稳定性越好[13]。本研究选择微乳区面积和溶水量为评价指标,探究影响微乳液稳定性的主要因素。1)表面活性剂复配体系对微乳液的影响。离子表面活性剂在水体中易与强电解质发生反应,受酸碱环境影响较大,在水体中性质不稳定。相比而言,非离子表面活性剂在水中不发生电离,具有较强的稳定性[14]。因此,本研究选择非离子表面活性剂复配制备微乳液。表面活性剂复配体系对微乳液的影响结果见图2。可以看出,当2种表面活性剂Tween-80∶TX-100=1∶1复配时,无论助剂选择异丙醇、正丁醇还是正戊醇,微乳液微乳区的面积都比3种表面活性剂Tween-80∶Span80∶PEG400=1∶1∶1复配大。因此,二元表面活性剂复配制得的微乳液体系更加稳定。在制备微乳液的过程中,表面活性剂是使油水乳化的重要物质,其种类将直接影响微乳液的结构及稳定性。有研究[15]表明,单一表面活性剂较难满足多组分体系的微乳化要求,而复配表面活性剂的乳化效果要优于单一表面活性剂[16]。这是因为,2种表面活性剂进行复配后产生了协同作用,使得表面活性剂分子间的排斥力降低,有助于微乳液体系的形成[2, 17]。但是,本研究中的2种表面活性剂复配形成微乳液体系的稳定性优于3种表面活性剂。这可能是因为,在3种表面活性剂进行复配的过程中,分子间没有形成稳定的相互作用,因而形成的微乳液体系稳定性不佳。
2)表面活性剂复配比例对微乳液的影响。表面活性剂复配比例对微乳液的影响结果见图3。可以看出,当Tween-80∶TX-100=1∶1时,微乳区面积最大。这是因为,表面活性剂能够改变溶液体系的界面状态,降低油/水界面张力[18]。其用量直接影响增溶生物柴油的量,从而影响了微乳液粒径大小和体系的稳定性。此外,2种表面活性剂Tween-80和TX-100复配且比例为1∶1时,混合胶束间的排斥作用达到最小,从而增强了2种非离子表面活性剂间的吸引力,表面活性剂分子相互靠近的概率增加,并在油水界面达到有效吸附,降低了界面张力,体系的临界胶束浓度(CMC)下降[19],易形成胶束溶液并发生溶胀形成稳定的微乳液体系[20]。
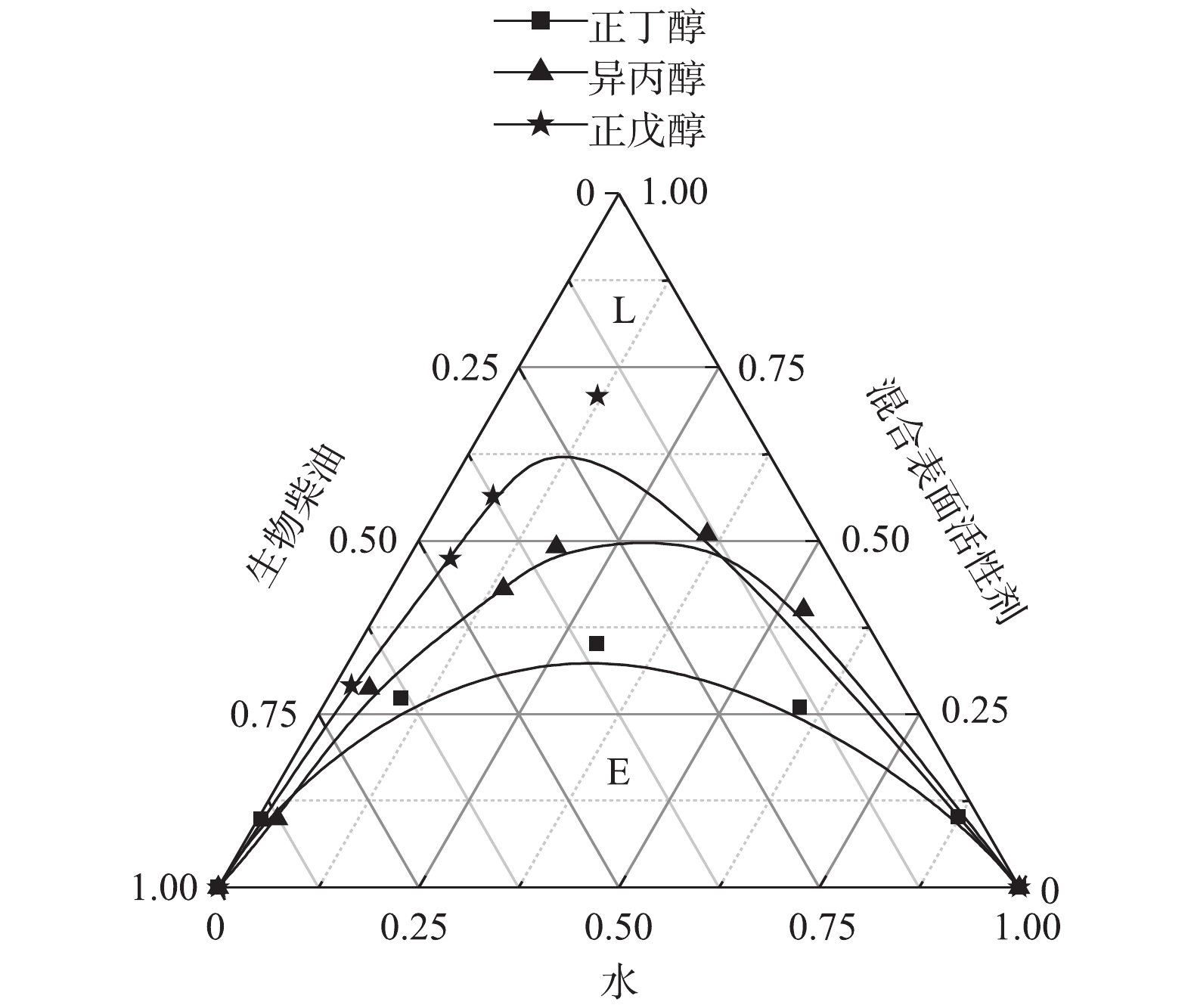
3)助表面活性剂对微乳液的影响。不同助表面活性剂对微乳液影响的结果如图4所示。可以看出,以正丁醇为助剂制备微乳液,微乳区面积明显较大。这是因为,在微乳液的制备过程中,助剂可以协助表面活性剂降低油/水界面张力,增加界面膜的流动性,以减少微乳液形成时的界面弯曲能[21]。碳原子数较小的助剂醇,其分子体积相对较小,因此可以插入胶束中间,起到增溶作用。随着碳原子数增加,可以增溶的接触面积增加。而当碳原子数继续增加,根据胶束增溶机理,醇很难插入到亲水基团之间,扩大增溶面积,效果反而变差[22-24]。此外,随着碳链的增长,醇在水中的溶解度降低,而在生物柴油中的溶解度升高。由于异丙醇在水中的溶解度较大,而正戊醇在生物柴油中的溶解度较大,导致他们在界面层上的吸附量较少,因此增溶水量较小。正丁醇在水和生物柴油中溶解度都相对较小,因而在界面层中的吸附量最多,增溶水量最大,微乳液微乳区面积也最大,体系最稳定[13]。
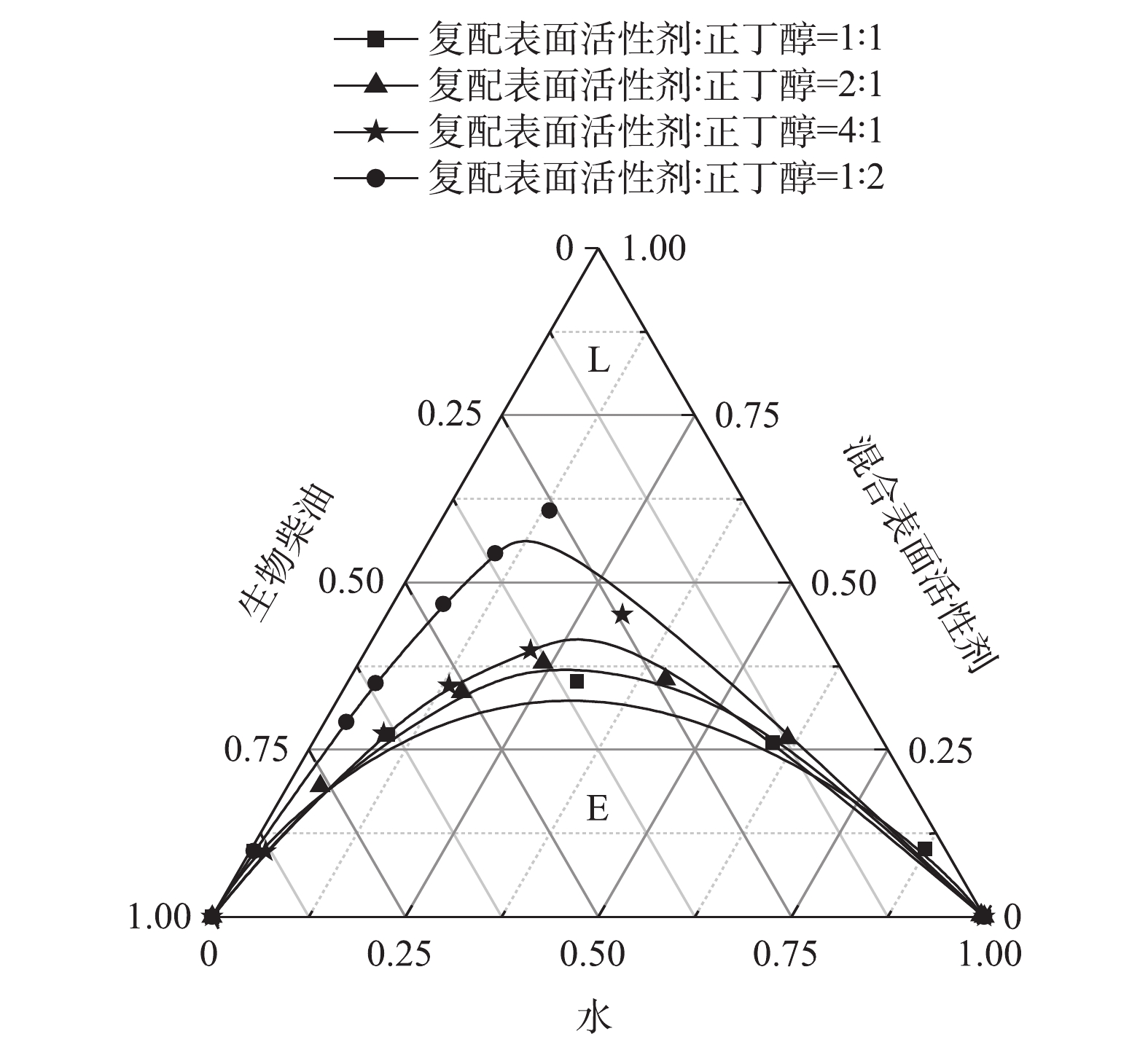
4)复配表面活性剂与助表面活性剂比值对微乳液的影响。复配表面活性剂与助表面活性剂比值对微乳液的影响结果如图5所示。2种表面活性剂进行复配,与正丁醇制备混合表面活性剂,改变Km的值时,微乳液微乳区面积也发生改变。随着Km值减小,微乳区L面积先逐渐增大,当Km值为1(即两者的比例为1∶1)时,微乳区L的面积达到最大;随后,又随Km值的减小而减小。其原因可能是,随着正丁醇含量的增加,醇分子逐渐渗透至表面活性剂界面膜中,增加了界面膜的弯曲弹性,促进了微乳液的形成。正丁醇含量的继续增加,使得微乳区域减小。这可能是因为表面活性剂相对含量减少,导致其在油/水界面的密度下降,不足以维持较低的油/水界面张力,引起相界面稳定性下降,微乳结构破坏[25]。
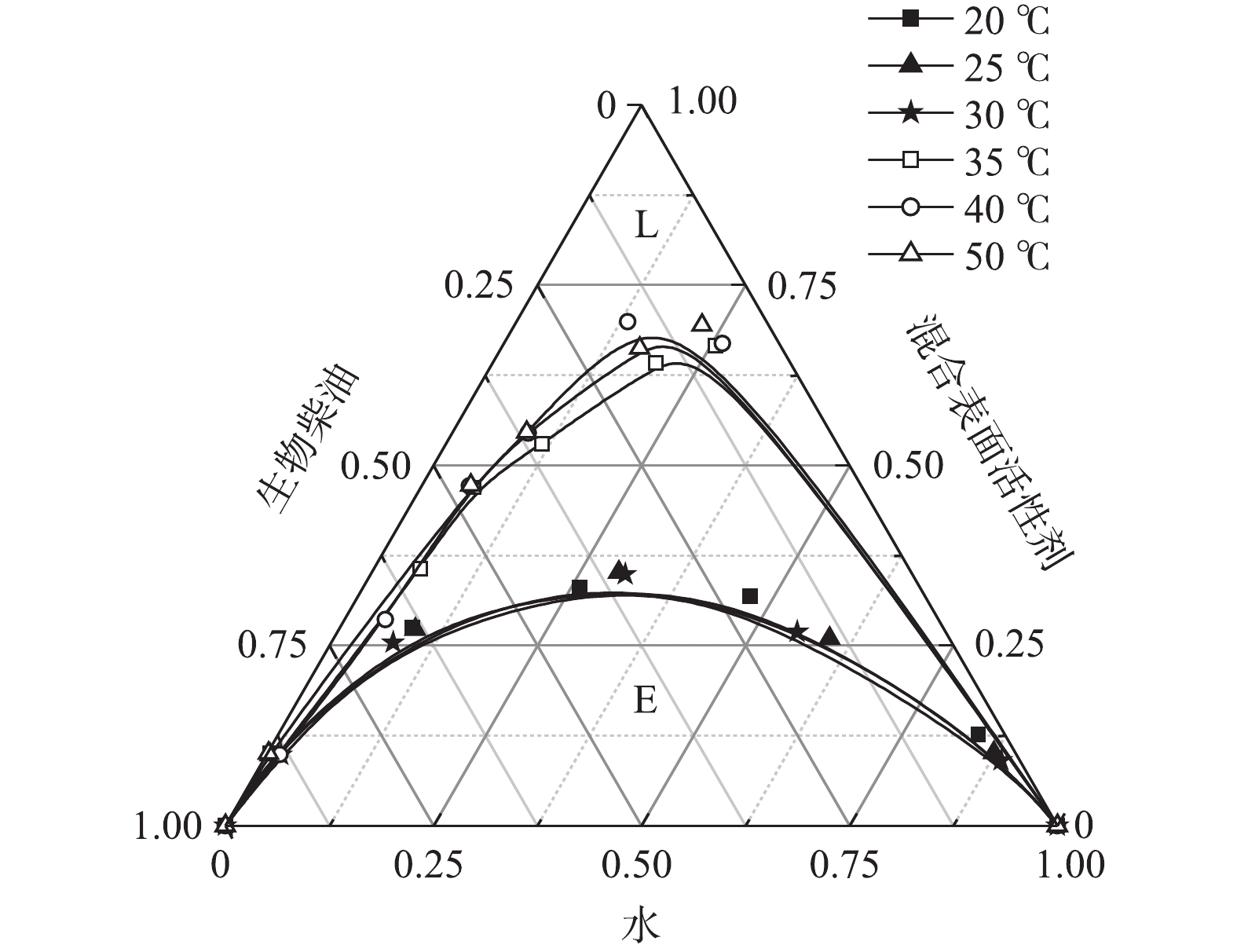
5)温度对微乳液的影响。温度对微乳液的影响如图6所示。高温时,微乳液微乳区L面积较小。这是因为,温度改变了表面活性剂与助表面活性剂分子在油/水界面上的几何排列,从而影响了微乳液液滴的形成[12]。当温度较高时,微乳液形成过程中的原料分子比较容易团聚,使得液滴的粒径增大,体系变得不稳定;常温时,温度与原料的熔点相近,更容易形成均一稳定的微乳液体系。
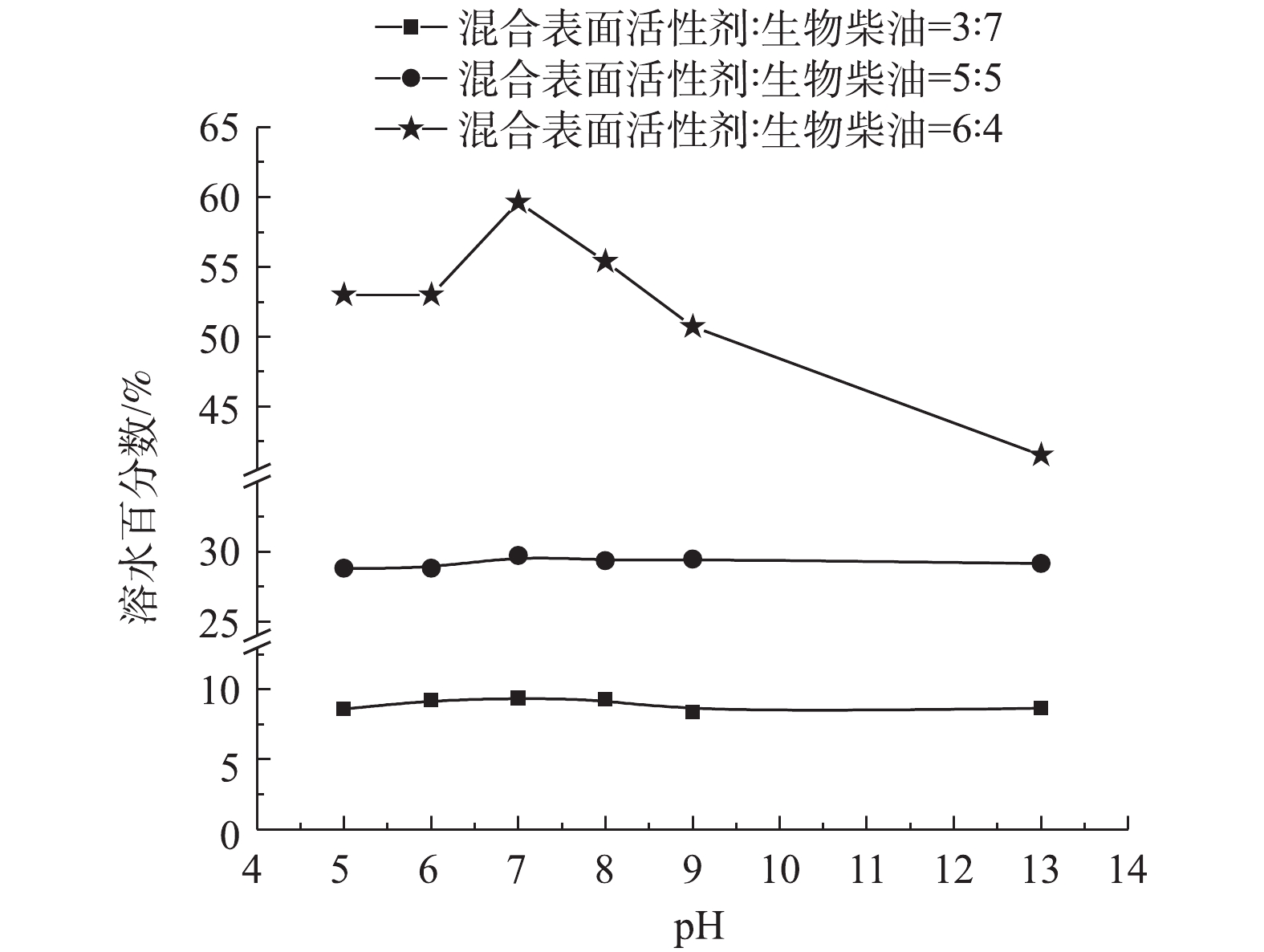
6) pH对微乳液的影响。pH对微乳液的影响结果如图7所示。观察不同的混合表面活性剂与生物柴油的比例均可知,当去离子水的pH为7时,制备得到的微乳液体系溶水百分数最大,效果最好。而且,混合表面活性剂与生物柴油的比为6∶4时,微乳液体系的溶水百分数整体效果比5∶5、3∶7的好。这说明,在一定范围内,微乳液体系制备的过程中混合表面活性剂的比例越大越好。
综合稳定性和经济性因素考虑得出:在室温时,两种表面活性剂Tween-80∶TX-100=1∶1进行复配,正丁醇为助剂,复配表面活性剂与助剂的质量比Km=1∶1制备混合表面活性剂,混合表面活性剂与生物柴油比例在6∶4 (即7.7% Tween-80、7.7% TX-100、15.4%正丁醇、20.5%生物柴油),去离子水的pH=7时制备的微乳液为本研究的最优新型淋洗剂。此时微乳液微乳区L面积最大,体系最稳定,溶水百分数最高,效果最好。
2.2. 微乳液洗脱效果评价与分析
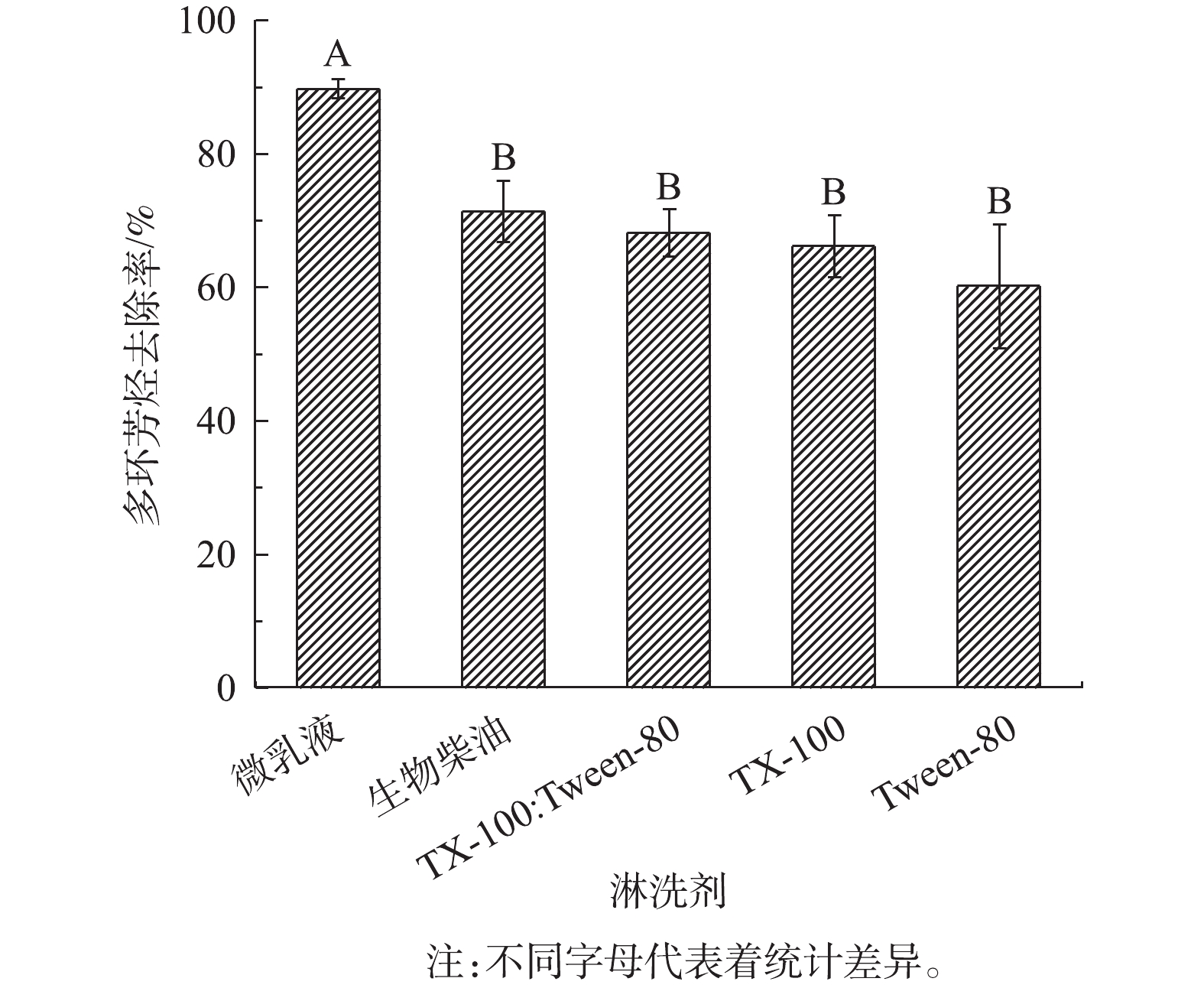
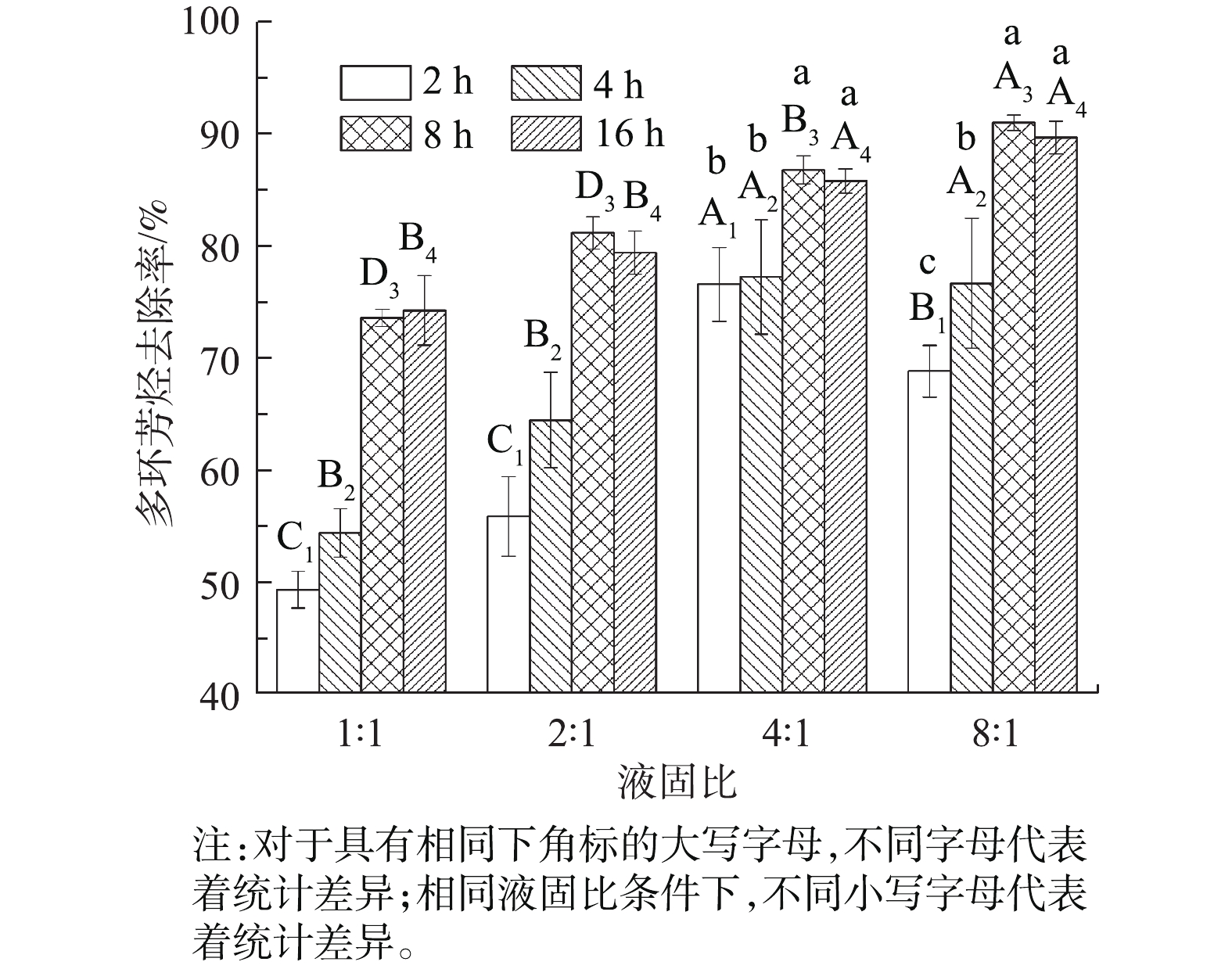
1)微乳液与不同类型淋洗剂的洗脱效果对比。选取相同质量浓度的5种不同类型的淋洗剂(Tween-80、TX-100、TX-100∶Tween-80=1∶1、生物柴油、微乳液)淋洗钢铁厂多环芳烃污染土壤,结果如图8所示。微乳液对多环芳烃的洗脱效果最好,对钢铁厂污染土壤中多环芳烃的去除率高达89.7%,显著高于其他淋洗剂(P<0.05,n=3)。相较于微乳液,非离子表面活性剂Tween-80、TX-100对污染土壤中的多环芳烃去除率不高。两者按照比例为1∶1复配后,多环芳烃去除率虽比两者单独使用时高,但效果提升不明显。由此可见,由表面活性剂、生物柴油和去离子水乳化合成的微乳液,可以更有效地洗脱去除污染土壤中的多环芳烃。王卓然等[26]研究了复配表面活性剂洗脱处理多环芳烃污染土壤,结果表明,鼠李糖脂和Tween-80复配时,洗脱效果较使用单一表面活性剂有优势,这与本研究结果一致。王晓光等[9]选用脂肪酸甲酯(生物柴油的主要成分)作为淋洗剂,修复煤气厂多环芳烃污染土壤,结果表明,脂肪酸甲酯可以有效去除污染土壤中高浓度的多环芳烃。由本研究结果可知,微乳液洗脱多环芳烃的效果最好,这可能是表面活性剂与生物柴油间产生协同作用的结果。表面活性剂同时具有亲水基和亲油基,这种独特的双亲结构一方面可降低土壤颗粒对生物柴油的吸附,提高生物柴油的有效浓度;另一方面还可以提高多环芳烃的表观溶解度[2]。两者结合形成的微乳液可降低水土系统的自由能及表面张力,由此提高多环芳烃的去除率。2)液固比及振荡时间对洗脱效果的影响。改变淋洗剂与原污染土壤的液固比,分别为1∶1、2∶1、4∶1、8∶1;改变淋洗剂的振荡时间,分别为2、4、8、16 h,考察液固比和振荡时间对钢铁厂污染土壤中多环芳烃洗脱效果的影响,结果如图9所示。在液固比为4∶1和8∶1时,洗脱效果显著高于液固比为1∶1和2∶1 (P<0.05,n=3)。这是因为,随着液固比值的增大,液相体积、增溶容积都不断增大,使污染物与表面活性剂能够充分接触,从而提高洗脱效率。从经济角度考虑,可以采用液固比为4∶1的比例。
另外,总体上随着振荡时间的增长,多环芳烃去除率也呈现随之增大的趋势,在振荡8 h时多环芳烃去除率最高,显著高于2和4 h (P<0.05,n=3)。这是因为,土壤颗粒中的多环芳烃克服界面张力,溶解于微乳液油相的过程需要一定时间,随着振荡时间的增加,多环芳烃污染物溶解于淋洗剂中的量也越大。但是,达到足够的时间后,如果不及时分离淋洗剂和土壤颗粒,溶解于微乳液油相中的多环芳烃则又会冲破界面膜的作用力回到土壤固相中,从而导致去除效率略有降低[27]。
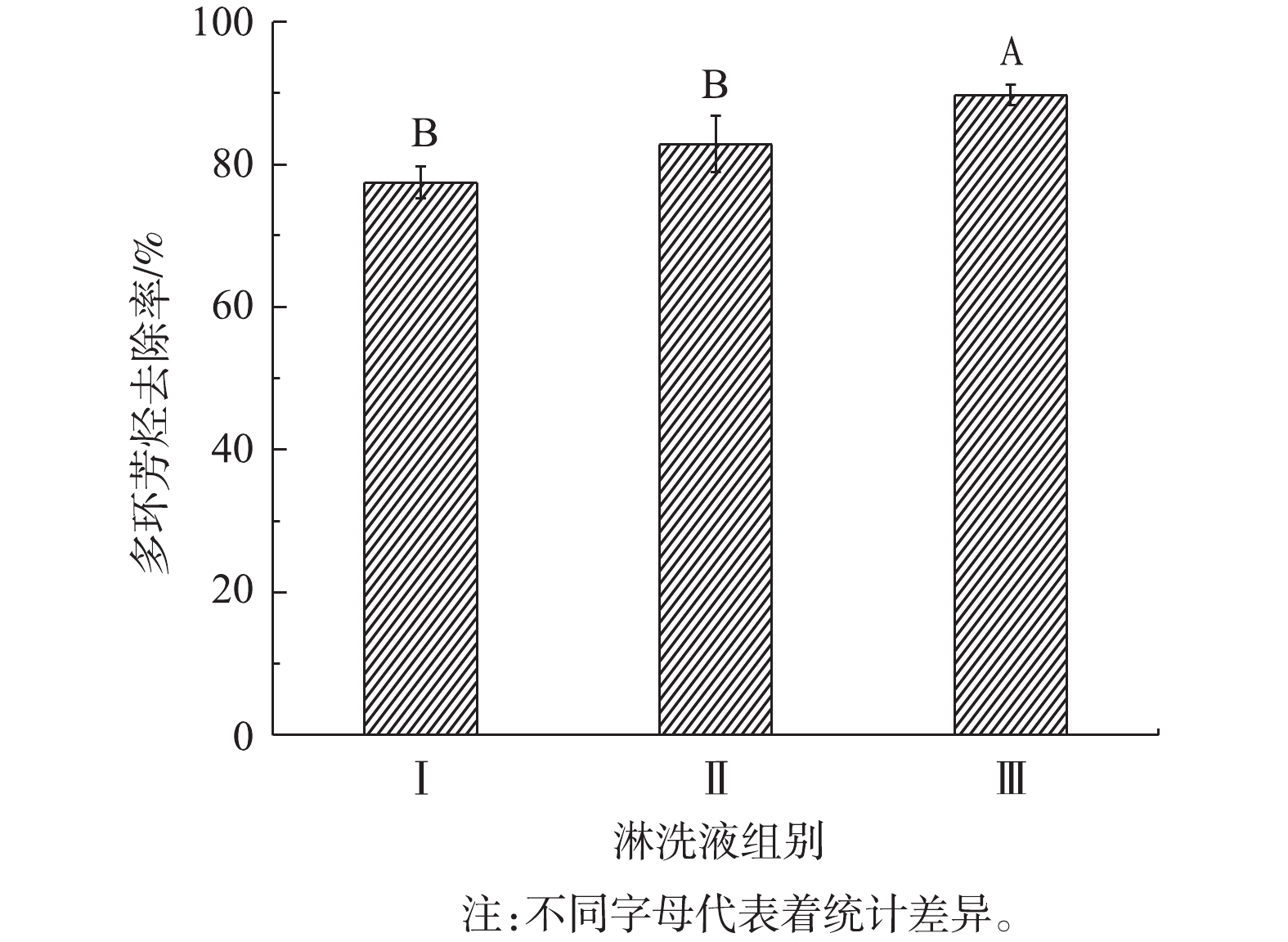
3)表面活性剂与生物柴油比例对洗脱效果的影响。微乳液组分、结构及性质等因素对污染土壤中多环芳烃的去除率均能产生影响。采用混合表面活性剂与生物柴油比例分别为3∶7、5∶5、6∶4的淋洗剂Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ进行实验,探究表面活性剂与生物柴油比例对钢铁厂污染土壤洗脱多环芳烃效果的影响,结果如图10所示。由此可知,淋洗剂Ⅲ对多环芳烃洗脱效果最好,对土壤中多环芳烃的去除率高达89.7%,显著高于其他2种淋洗剂(P<0.05,n=3)。这是因为,洗脱效果和淋洗剂的稳定性有关,淋洗剂体系越稳定,则体系内的表面张力越小;土壤中多环芳烃脱离土壤颗粒进入淋洗剂,溶解于生物柴油基微乳液的油相,需要克服的界面膜作用力越小,淋洗污染土壤效果越好。
孙翼飞等[2]采用2.5%的Tween-80分别与4 mL的非食用性植物油和4 mL的生物柴油制备微乳液,淋洗修复焦化厂多环芳烃污染土壤,去除率分别为25%和30%。相较于其他淋洗剂,应用表面活性剂和生物柴油制备的微乳液对污染土壤多环芳烃的去除效率最高。但GONG等[28]指出,该浓度的Tween-80和生物柴油制备的微乳液对多环芳烃的去除效率仍不够理想,效果不如生物柴油(20 mL的生物柴油,去除率为43.3%)。为了进一步提高多环芳烃的去除率,GONG等[28]采用微乳液与微生物联合修复法,虽将去除率提高至92.6%,但也相应提高了修复的成本。而本研究综合考虑了配制的组分、温度和pH等因素对微乳液制备的影响,确定了微乳液制备的最佳体系,对污染土壤多环芳烃的去除率高达90%左右,在节约成本的情况下极大地提高了多环芳烃的洗脱效率,具有较强的应用潜力。
2)比较不同类型淋洗剂的效果,微乳液对多环芳烃的去除效率显著高于生物柴油、复配表面活性剂、单一表面活性剂。这表明,生物柴油基微乳液对污染土壤中多环芳烃具有明显的增溶效果。其原因为,表面活性剂降低了土壤颗粒对生物柴油的吸附,从而增加有效淋洗剂的浓度,提高污染土壤中多环芳烃的洗脱效率。
3)土壤洗脱实验证明,土壤中多环芳烃的洗脱效率与淋洗剂和土壤的液固比、淋洗振荡时间、微乳液组分质量比等有关;液固比为4∶1,洗脱振荡时间为8 h,混合表面活性剂与生物柴油的比为6∶4制备的微乳液,洗脱效果最好。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: 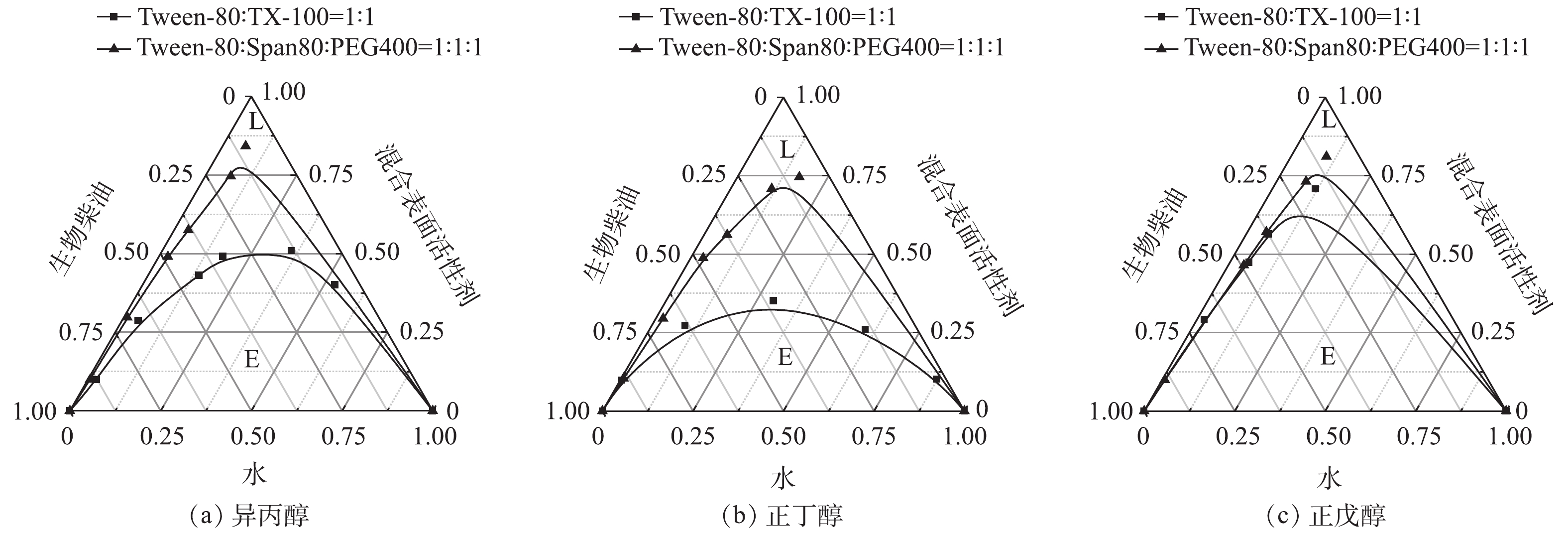

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图