兰州交通大学环境与市政工程学院,兰州 730070
School of Environmental and Municipal Engineering, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou 730070, China
为了解决我国西部农村分散式生活污水污染问题,结合西北地区年平均气温条件特征,基于潜流湿地原理对比研究了混凝土渣、砾石和生物炭脱氮除磷效应,分析其对污染物的降解作用。结果表明:随着水力停留时间(HRT)的延长,污染物含量明显降低,湿地最佳HRT均为2.5 d,3种填料湿地对化学需要量(COD)、氨氮(
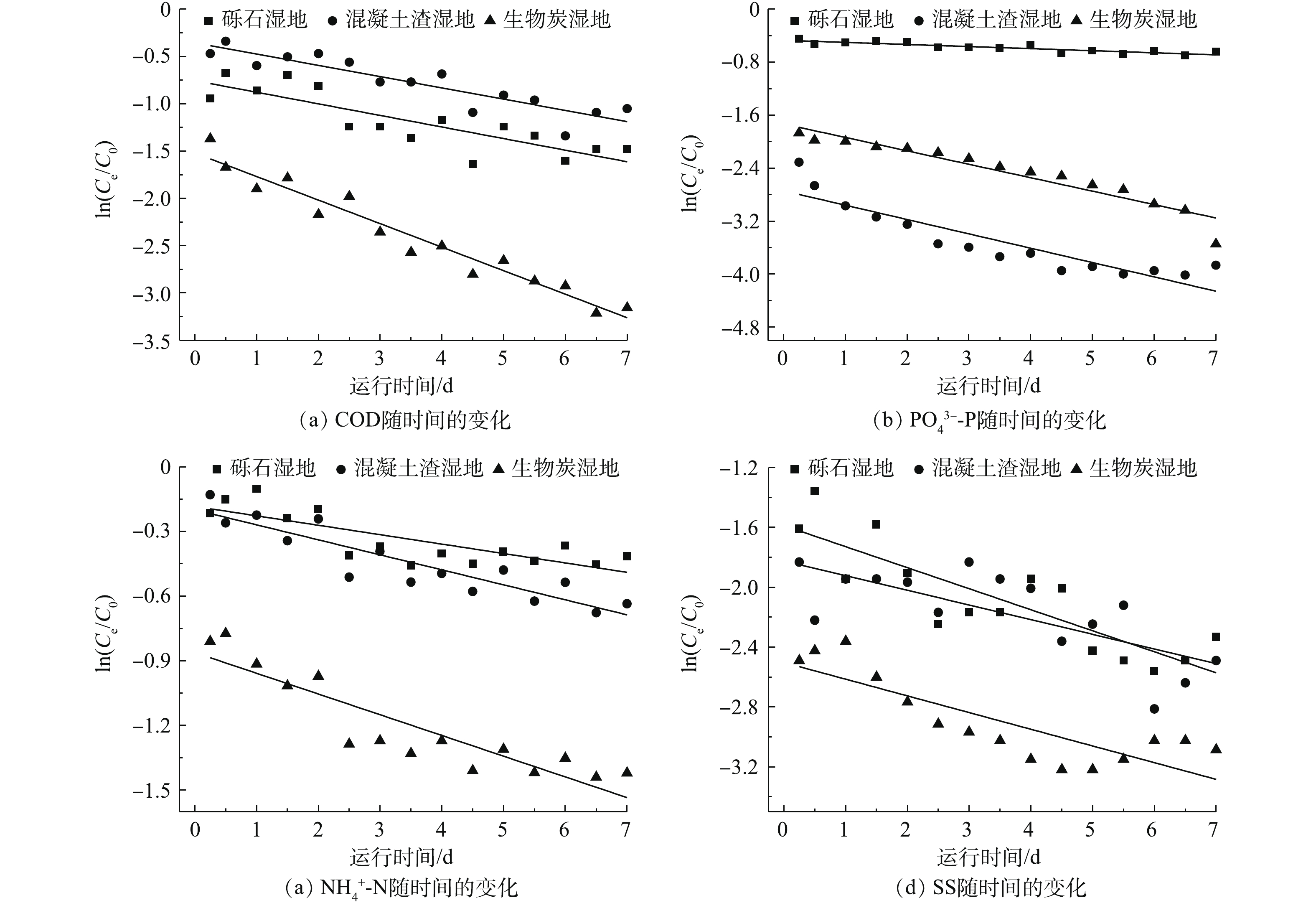
-N、悬浮物(SS)的去除率达到了90.51%、72.38%、94.57%;生物炭作为优选湿地填料还具有较快的污染物降解速率特征,且有机污染物和磷酸盐的生化降解过程符合一级反应动力学模型,
在0.9以上。因此,生物炭作为湿地填料具有良好的应用价值,对解决西北地区农村水污染问题具有重要的意义。
In order to solve the pollution problem of decentralized domestic sewage in the rural area of western China, in combination with the characteristics of annual mean temperature in Northwest China, this study compared the nitrogen and phosphorus removal effects of concrete slag, gravel and biochar based on the principle of subsurface flow wetland(SFW), and the pollutants degradation effect of SFW was also analyzed. The results showed that with the increase of hydraulic retention time (HRT), the pollutant concentration decreased significantly, and the optimum HRT of the wetland was 2.5 d. The differences in the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonia nitrogen (
-P removal from sewage by concrete slag was the highest with the removal rate of 97.11%. Biochar had the strongest comprehensive treatment ability, its removal rates for COD,
-N and suspended matter (SS) were 90.51%, 72.38% and 94.57%, respectively, as the optimal wetland filler, it also showed the fast degradation rate of pollutants, and the corresponding biochemical degradation process of organic contaminant and phosphate accorded with the first-order reaction kinetics model with
above 0.9. Therefore, biochar has good application value when it is taken as the wetland filler, and is of great significance to solve rural water pollution questions in Northwest China.
.
Baffled wetland structure
Changes of pollutants concentration in baffle wetlands with time
Changes of pollutants with time and difference analysis
First-order kinetics of pollutant removal in a baffle wetland
| [1] | LI H, CHI Z, YAN B, et al. Nitrogen removal in wood chip combined substrate baffled subsurface-flow constructed wetlands: Impact of matrix arrangement and intermittent aeration[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(5): 5032-5038. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-8227-3 |
| [2] | LU S, GAO X, WU P, et al. Assessment of the treatment of domestic sewage by a vertical-flow artificial wetland at different operating water levels[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 208: 649-655. |
| [3] | LIU J, XIE X, ZHANG Y, et al. Experimental study on treatment of rural domestic sewage by four substrates anaerobic baffled reactor-vertical flow wetlands(ABR-VFW)[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(8): 1758-1766. |
| [4] | DING X, XUE Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Effects of different covering systems and carbon nitrogen ratios on nitrogen removal in surface flow constructed wetlands[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 172: 541-551. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.170 |
| [5] | HU Y, HE F, MA L, et al. Microbial nitrogen removal pathways in integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland systems[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 207: 339-345. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.106 |
| [6] | RUBIO I B, MOLLE P, LUIS E, et al. Basic oxygen furnace steel slag aggregates for phosphorus treatment. evaluation of its potential use as a substrate in constructed wetlands[J]. Water Research, 2015, 89: 355-365. |
| [7] | TIAN J, YU C, LIU J, et al. Performance of an ultraviolet mutagenetic polyphosphate-accumulating bacterium PZ2 and its application for wastewater treatment in a newly designed constructed wetland[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2017, 181(2): 735-747. doi: 10.1007/s12010-016-2245-y |
| [8] | YE C, LI L, ZHANG J, et al. Study on ABR stage-constructed wetland integrated system in treatment of rural sewage[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2012, 12: 687-692. |
| [9] | SUN Y F, QI S Y, ZHENG F P, et al. Organics removal nitrogen removal and N2O emission in subsurface wastewater infiltration systems amended with/without biochar and sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 249: 57-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.004 |
| [10] | ZHOU X, LIANG C L, JIA L X, et al. An innovative biochar amended substrate vertical flow constructed wetland for low C/N wastewater treatment: impact of influent strengths[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 844-850. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.044 |
| [11] | 袁敏, 刘晓冰, 唐美珍, 等. 生物炭固定菌强化人工湿地对低温污水中氮素去除的模拟研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2018, 34(5): 463-468. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.05.011 |
| [12] | 张修稳, 李锋民, 卢伦, 等. 10种人工湿地填料对磷的吸附特性比较[J]. 水处理技术, 2014, 40(3): 49-52. |
| [13] | 方伟成, 王静, 周新萍. 3种填料吸附磷的特性及其影响因素[J]. 湿地科学, 2018, 16(3): 341-356. |
| [14] | 王功, 魏东洋, 方晓航, 等. 3种湿地填料对水体中氮磷的吸附特性研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2012, 34(11): 9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2012.11.003 |
| [15] | 卢少勇, 万正芬, 李锋民, 等. 29种湿地填料对氨氮的吸附解吸性能比较[J]. 环境科学研究, 2016, 29(8): 1187-1194. |
| [16] | 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. |
| [17] | SAEED T, SUN G. Kinetic modelling of nitrogen and organics removal in vertical and horizontal flow wetlands[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(10): 3152. |
| [18] | ZHANG S, YANG X L, LI H, et al. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole in bioelectrochemical system with power supplied by constructed wetland-coupled microbial fuel cells[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 244(1): 345-352. |
| [19] | 唐美珍, 汪文飞, 李如如, 等. 生物炭对Pseudomonas flava WD-3的固定化及其强化人工湿地污水处理研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(9): 3442-3448. |
| [20] | DING W, XIAN Y, TAO L, et al. A research on purification effect of the substrate of constructed wetlands with FS-G-CD-S-SS model on phosphorus pollution[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2011, 10: 2645-2653. |
| [21] | PARK J H, WANG J J, KIM S H, et al. Phosphate removal in constructed wetland with rapid cooled basic oxygen furnace slag[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 327: 713-724. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.155 |
| [22] | LI J, HU Z, LI F, et al. Effect of oxygen supply strategy on nitrogen removal of biochar-based vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland: Intermittent aeration and tidal flow[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 223: 366-374. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.082 |
| [23] | TANG J H, LUO W Z, YANG B, et al. Optimization of planting concrete materials with nitrogen and phosphorus removal characteristic[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 382: 022100. |
| [24] | 王宁, 黄磊, 罗星, 等. 生物炭添加对曝气人工湿地脱氮及氧化亚氮释放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10): 115-121. |
| [25] | MAO X, CAO Z, YIN Y, et al. Direct synthesis of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped hierarchical porous carbon networks with biological materials as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(22): 10341-10350. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.04.100 |
| [26] | TANG X Y, YANG Y, MURRAY B, et al. Removal of chlorpyrifos in recirculating vertical flow constructed wetlands with fifive wetland plant species[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 216: 195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.150 |









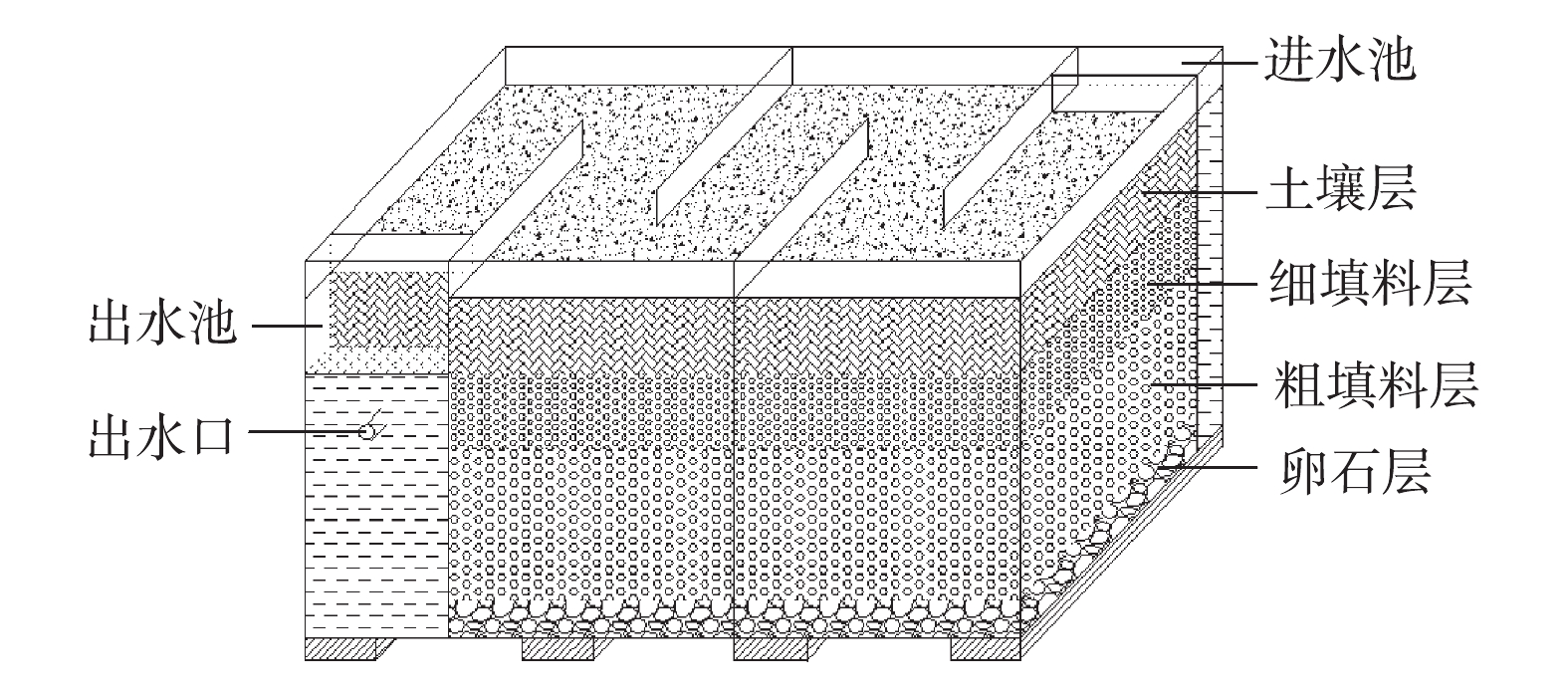
 下载:
下载: 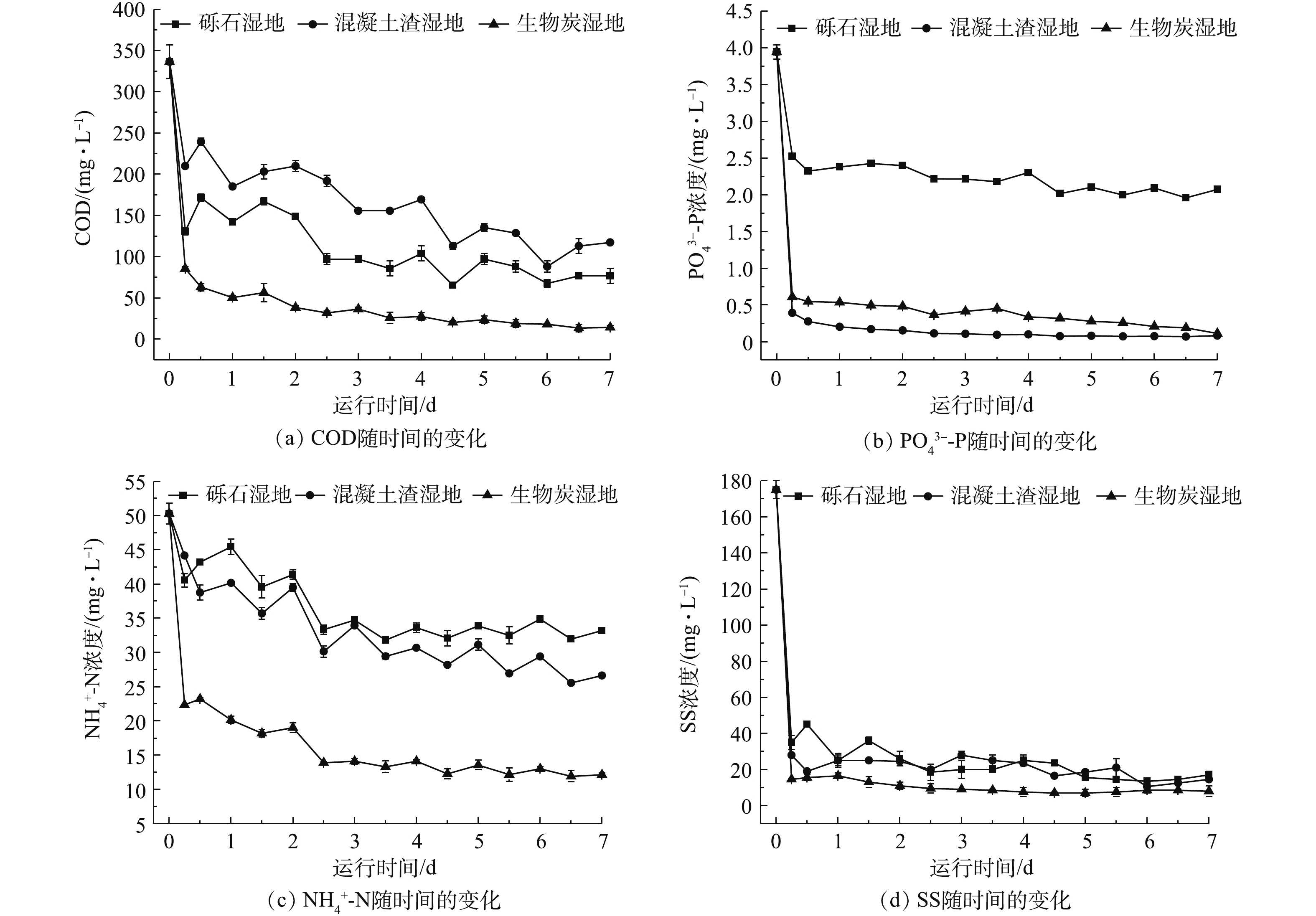
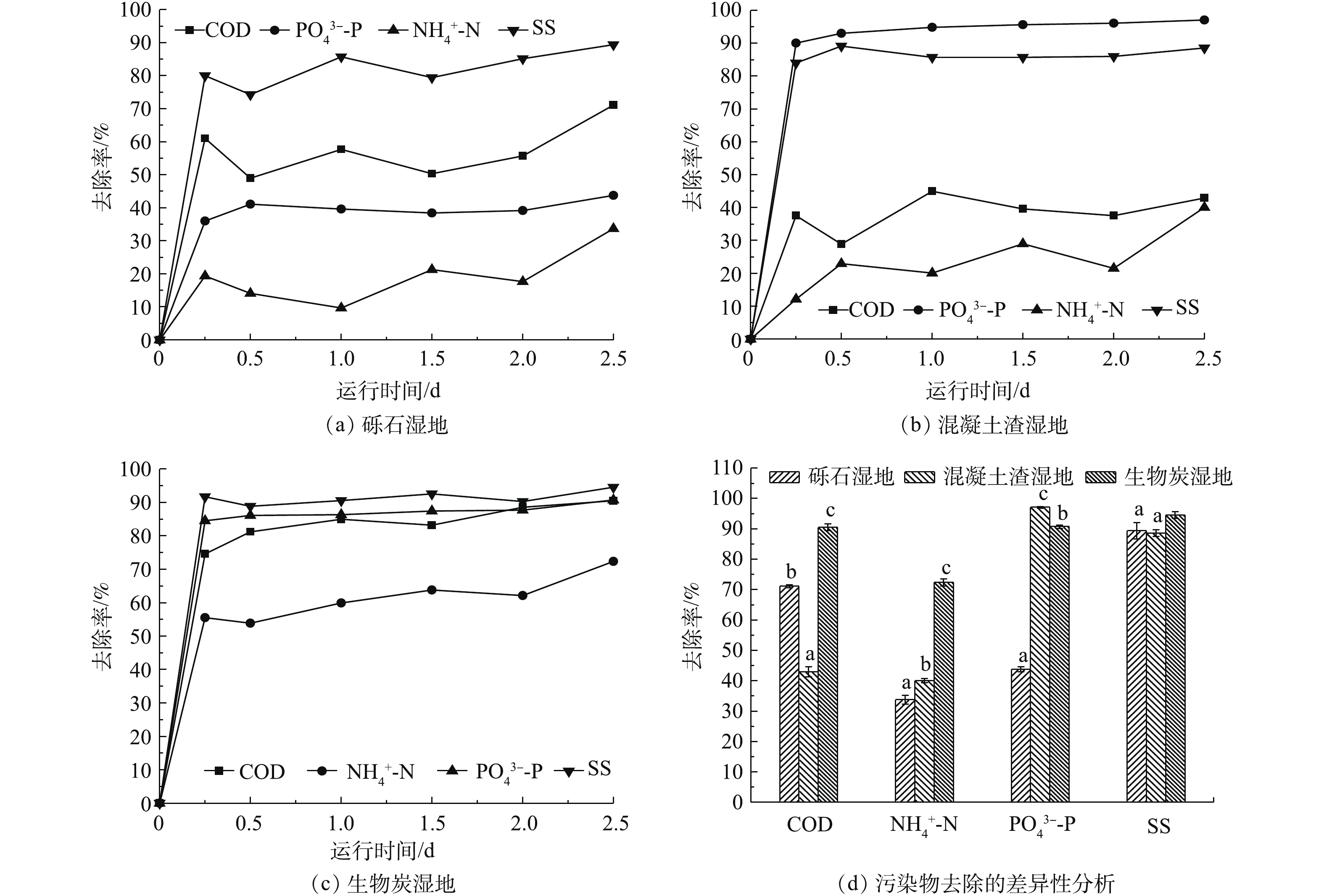












 点击查看大图
点击查看大图