全文HTML
--> --> --> 近年来,塑料制品的大规模使用造成了严重的环境污染问题,并引起了社会各界的广泛关注[1]。习近平总书记在2019年9月9日召开的“中央全面深化改革委员会第十次会议”上强调:要有力有序有效治理塑料污染。然而,大块塑料经过长期的机械作用、光降解、生物降解、光氧化降解等过程后,逐渐分解成粒径较小的塑料颗粒,当塑料粒径小于5 mm时,称其为微塑料[2-4]。微塑料因具有粒径小、数量多、分布广等特点,容易被动物所吞食[5],产生的危害性更大。COLLIGNON等[6]在卡尔维湾对浮游动物体的内容物进行了检测,在38个样品中,约占74%的样品均含有不同成分的微塑料颗粒。BESSELING等[7]的研究也证明了水体中聚苯乙烯含量越高,海蚯蚓对微塑料颗粒误食也就越多。近年来,国内****对我国渤海湾[8]、长江口[9]、珠江流域和部分内陆湖泊[10]水体和沉积物中的微塑料污染特征进行了初步研究,研究结果均表明,微塑料易随食物链进入生物体内,并最终对人类身体健康产生影响。然而,目前国内外关于微塑料的检测及分析方法还不健全,还未形成统一的标准,特别是微塑料检测中的重要预处理步骤——消解方法尚未统一,对后续的微塑料检测及计数等重要环节产生了不确定性影响。目前,国内外常用的消解方法主要分为4种:酸(HCl、HNO3、HClO4)法[11]、碱(NaOH、KOH)法[11]、氧化剂(H2O2)法[12]和酶法[13]。ROCH等[14]使用1 mg·L?1NaOH和65%浓硝酸进行鱼消化道消解,发现对聚酰胺(PA)产生腐蚀效果。DEHAUT等[15]采用6种不同的消解液进行了研究,发现KOH在24 ℃消解效果最好。DAVIDSON等[16]采用69%~71%HNO3溶液对蛤蜊进行了消解,在90 ℃水浴中加热4 h后发现,组织基本完全消解。MINTENIG等[17]采用酶对样品进行了消解。就常用消解液而言,酸性消解液能较彻底地消解有机物质,但容易破坏微塑料原本的结构[18];碱性消解液与氧化剂均易对微塑料的表面形貌造成影响,但不会对微塑料光学性质、化学特性等产生较大的影响[19-20]。虽然酶对微塑料的影响较小,但因其经济成本较高导致使用率较低。
目前,关于消解方法对微塑料识别的影响研究[21]较少,因此,探求一种合适的微塑料消解方法,对提高微塑料检测的可靠性具有重要意义。本研究采用7种常见的消解液对10种不同类型的微塑料颗粒进行了消解,探究了每种消解液对微塑料颗粒质量和表面形态等的影响,进而筛选出对微塑料影响最小的消解方法,可为后续微塑料的计数、识别等提供重要的数据支撑。
1.1. 实验材料
实验选取聚乙烯(PE)、聚苯烯(PP)、可发性聚苯乙烯(ePS)、线性低密度聚乙烯(LLDPE)、低密度聚乙烯(LDPE)、高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)、聚氯乙烯(PVC)、聚苯烯(PS)、尼龙(PA-12)和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)10种常见的微塑料作为实验材料,微塑料粒径为0.1~0.25 mm,选取HNO3、KOH、H2O2、K2S2O8等4种常用的消解液,按照消解液浓度比例,共设置7种消解方案,每种方案设置3组重复实验,消解方法参数如表1所示。1.2. 实验方法
实验前对所有微塑料颗粒进行20 min超声清洗以降低实验误差,而后各取0.5 g微塑料颗粒置于250 mL的具塞锥形瓶中,加入100 mL不同的消解液。将锥形瓶放入恒温培养振荡仪中进行消解,消解条件见表1。消解后,用0.45 μm玻璃纤维膜进行过滤,将过滤后附有微塑料的滤膜在烘箱中50 ℃烘2 h。在加速电压20 kV时,通过SEM-EDS扫描电镜(QUANTA400,美国)对干燥后的微塑料颗粒进行表面形态的鉴定(放大1 000倍),扫描前对微塑料进行镀金处理;在分辨率为4 cm?1,检测波数为400~4 000 cm?1,信噪比为45 000∶1条件下,通过ATR-FT-IR红外光谱仪(RXI,美国)对微塑料颗粒进行成分的识别。测定前使用ZKKJ粉末压片机(FW-4,天津)对微塑料进行制片处理,使其处于扁平状态;通过荧光分光光度计(F-4600,Hitachi,日本)测定微塑料颗粒的荧光强度。1.3. 数据处理
使用软件Orgin8.0进行数据处理;使用SPSS 20.0进行数据分析与比较,采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)探查各影响因素之间的差异是否显著(取P<0.05)。2.1. 不同消解方法对微塑料质量的影响
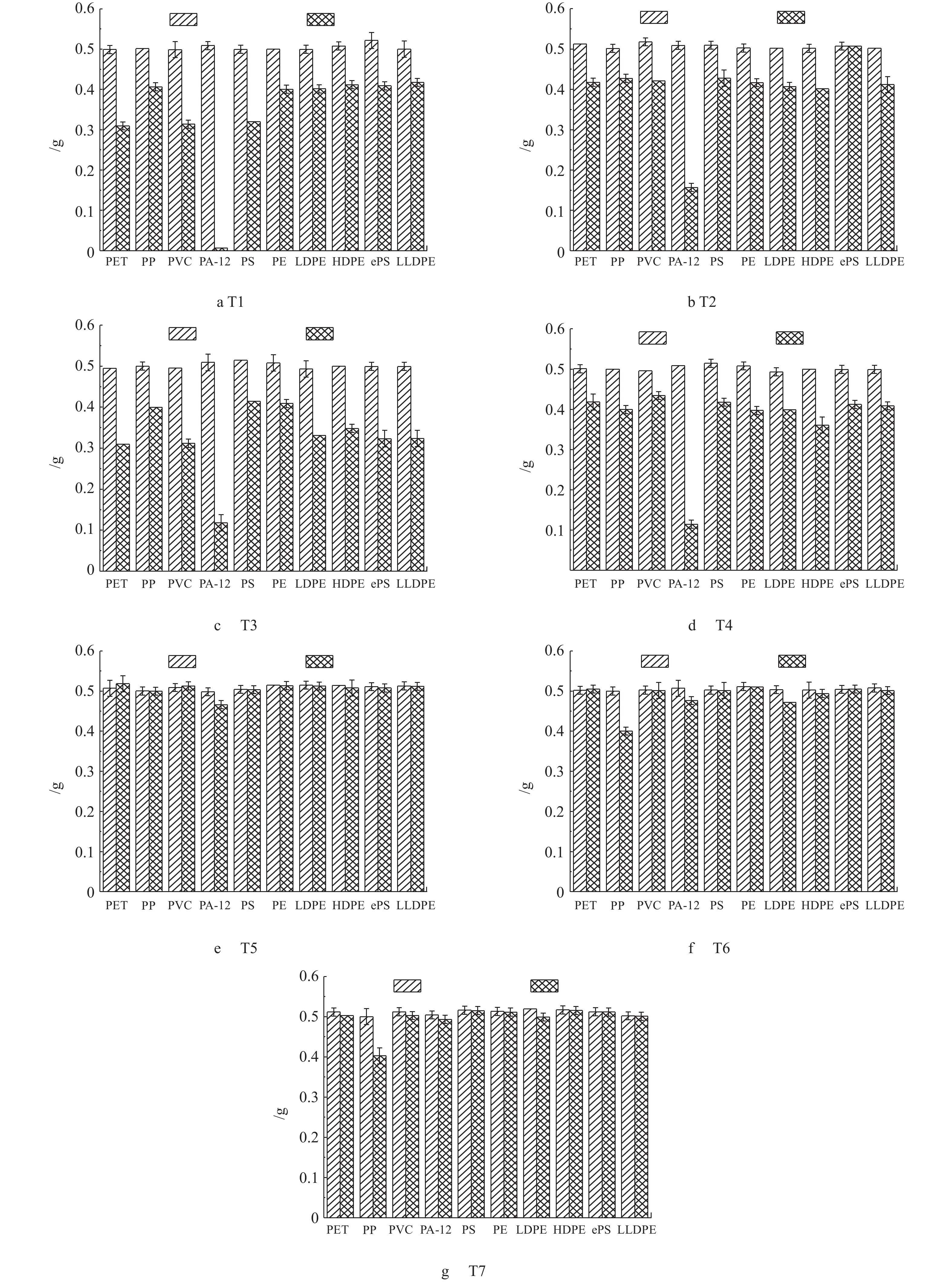
分别称量消解前、后微塑料颗粒质量,结果如图1所示。可以看出,与消解前相比,经T1、T2、T3、T4方案消解后的10种微塑料质量均有显著降低(P<0.05),其中经T1方案消解后,受消解液腐蚀、熔化等因素影响,PA-12质量减少最为严重,较消解前降低了(97±2)%,其他类型的微塑料颗粒质量则平均降低了(38±3)%;同时,经T3、T4方案消解后,PA-12质量减小程度((67±4)%)较其他类型的微塑料((15±3)%)也更大。综上可知,T1、T2、T3、T4消解方案对微塑料质量影响较大,故不宜作为微塑料的消解方案。CLAESSENS等[28]使用HNO3与H2O2混合进行消解发现,产生了大量气泡,且对微塑料颗粒影响较大,这与本研究的结果一致。然而他们的研究[28]也发现,将PS微塑料放入HNO3消解液中会使微塑料产生明显的融合现象,这与本研究的实验结果不同,可能是由于聚苯乙烯的结构属线型结构,且碳原子上连有连续间隔的庞大苯基基团,这种结构决定了PS对一定浓度的无机酸、有机酸、盐类溶液及碱类、醇类、植物油类等均有较好的抵抗性。与酸性消解液相比,T5、T6和T7消解方案对微塑料的质量影响较小,经T5方案消解后的微塑料质量出现少量增加现象,增加幅度为(2±3)%~(3±3)%,这可能是由于在消解过程中微塑料吸附了其他离子等原因产生的;T6、T7方案则对微塑料的质量影响最小,特别是在以30% H2O2作为消解液的T6方案中,消解前、后的微塑料质量变化幅度最小,仅为(0.5±1)%~(3±1)%。已有研究[25]表明,碱性消解液(NaOH、KOH)会对微塑料造成轻微的损害。COLE等[25]发现,使用NaOH消解会导致尼龙纤维部分损伤,且造成PS的降解,这可能是由于NaOH的强腐蚀性所致。另外,PA-12在10种常见微塑料类型中,对消解液的类型选择最为敏感,这可能是由于其自身不耐强酸的特点所决定,且在实验中可以明显观察到PA-12因失去挠性和脆化等原因而出现降解、黄化等现象。综上可知,在7种消解方案中,30% H2O2对微塑料的质量影响最小,根据消解前、后微塑料质量变化情况,故其宜作为最佳的消解方案。这也与KARLSSON等[29]使用H2O2对HDPE、PA、PET、PE等微塑料聚合物消解后,微塑料颗粒仍保持原有的形状、颜色、质量的结论相吻合。
2.2. 不同消解方法对微塑料识别的影响
研究选取对微塑料消解前后质量无显著影响的T5、T6、T7方案消解后的微塑料颗粒作为研究对象,以未经消解处理的微塑料颗粒(T0)作为对照,对10种常见微塑料颗粒进行ATR-FT-IR红外光谱扫描,结果如图2所示。由图2可知,与未经消解处理的微塑料颗粒(T0)相比,经消解处理后的微塑料颗粒光谱强度均在一定程度上发生了变化。经T5、T6、T7方案消解处理后,PA-12微塑料颗粒在1 300~1 700 cm?1处峰强度变大,与T0相比,相应的特征峰更加明显;虽然PE、LDPE、LLDPE、HDPE等4种类型的微塑料颗粒在2 700~3 000 cm?1处特征峰仍然存在,但峰的强度也在不同程度上有所减弱;同时,PET微塑料颗粒在消解后峰强度也有所减弱,PS微塑料颗粒消解后则在700~800 cm?1处峰强度增强,ePS、PP和PVC等3种类型的微塑料颗粒消解前后的光谱特征几乎未发生变化,可见不同消解方法对上述3种类型的微塑料颗粒的红外光谱峰的变化影响最小。本研究采用ATR-FT-IR红外光谱对消解前后的微塑料颗粒光谱强度进行了比较鉴定。结果显示,消解前、后微塑料光谱强度均发生了改变,红外光谱强度的变化可能是由于激光的冲击点在聚合物表面的位置发生变化而引起的,也可能是由于化学处理后聚合物分子结构的改变而导致的[30-31]。作为新型合成有机物,本研究中消解前、后微塑料的红外图谱均发生改变,还可能是由于微塑料颗粒中含有填料、颜料和染料等添加剂产生的。尽管消解前、后微塑料的红外光谱强度发生了改变,但由图2可知,各波段峰值的变化均不明显,并未改变各类型微塑料原有红外光谱的分布特征,故T5、T6、T7消解方案对微塑料颗粒的识别无显著影响。
2.3. 不同消解方法对塑料荧光强度的影响
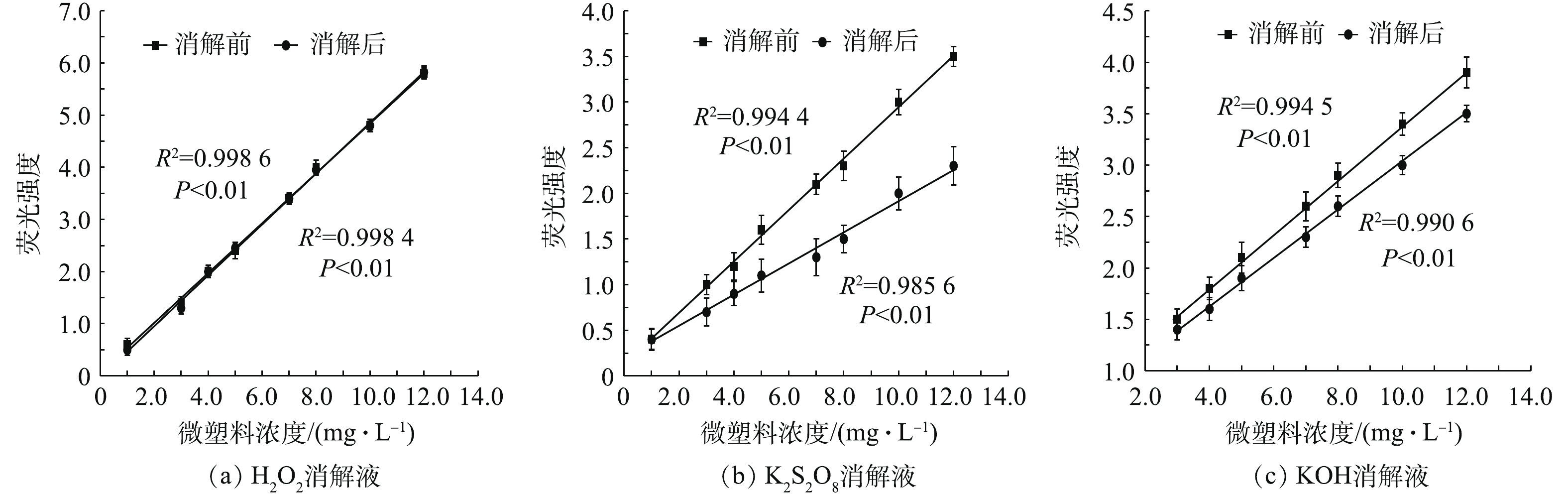
在上述研究的基础上,选取对消解液类型最为敏感的PA-12微塑料颗粒作为研究对象,通过T5、T6、T7消解后,对其荧光强度的影响进行研究,结果如图3所示。H2O2处理后的PA-12在浓度低于5 mg·L?1时,消解后的微塑料颗粒与消解前的微塑料颗粒相比,荧光强度十分相近,变化幅度低于(1±0.01)%;当H2O2浓度较高时,荧光强度也未产生显著的变化。由图3(b)可知,碱性K2S2O8消解后的微塑料颗粒荧光强度与消解液浓度成正比关系,即随浓度的增大,微塑料颗粒荧光强度增大,但随着K2S2O8浓度的升高,消解后微塑料颗粒的荧光强度较消解前有明显降低,平均降低了(10±2)%~(35±2)%;这主要是因为当温度超过60 ℃后,K2S2O8会水解形成2.4. 消解对微塑料颗粒表面形态的影响
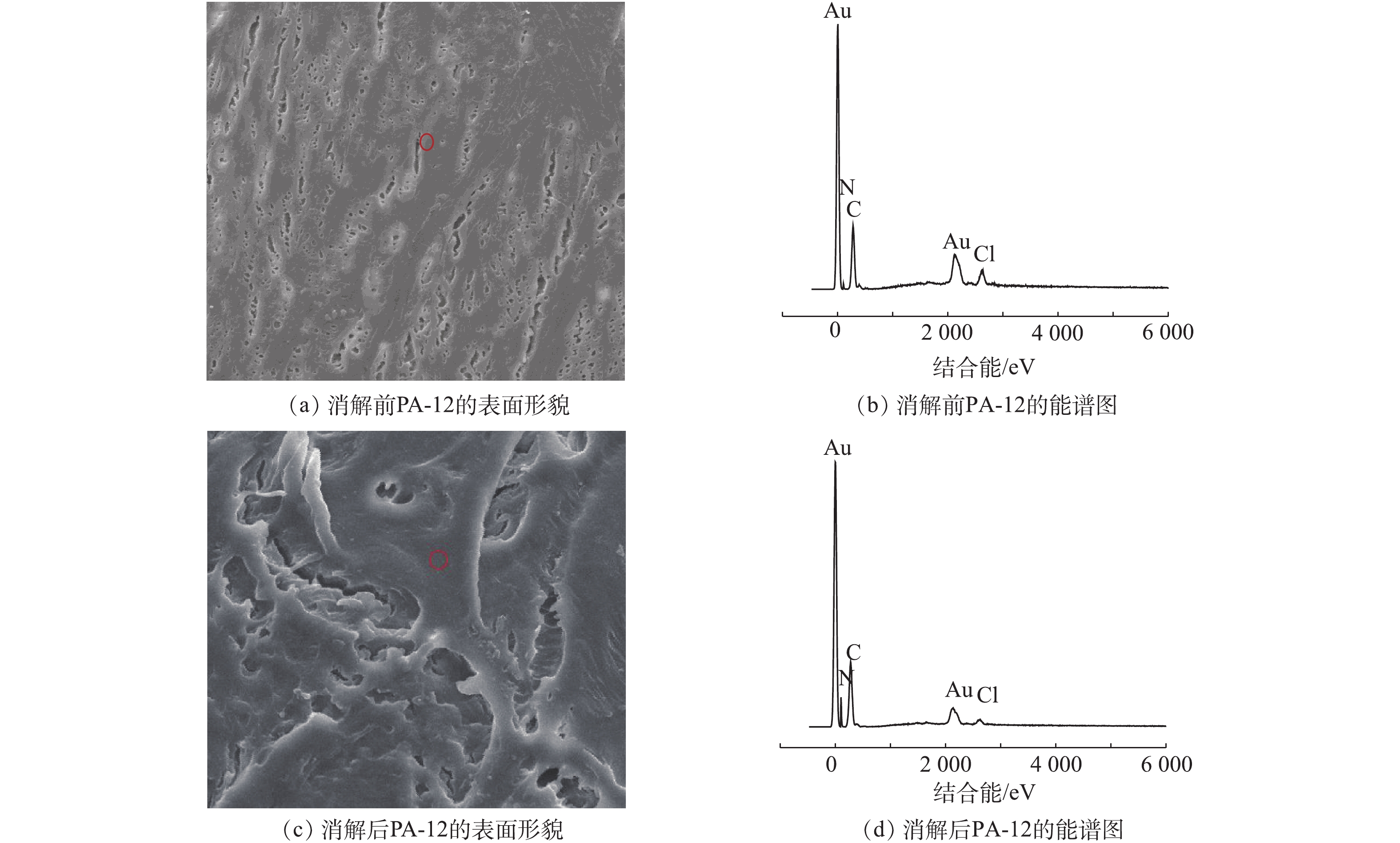
以PA-12微塑料颗粒作为研究对象,通过扫描电镜(SEM)和能谱仪(EDS)对H2O2消解前、后微塑料的表面形态和元素组成进行了分析,如图4所示。由图4(a)可知,未经消解处理的PA-12微塑料颗粒表面比较平整,光滑度较高,孔隙度较小,不利于吸附;经过消解处理后的微塑料颗粒(图4(c))表面则出现了不同程度的破坏,包括微塑料表面裂纹的增加(长度大约120 μm),纵向深度变得较为复杂,粗糙且凹凸不平等现象。图4(b)和图4(d)为消解前后PA-12微塑料颗粒的能谱图,PA-12微塑料颗粒的分子主链上含有酰胺基团—NHCO,故C、N含量较高;而消解前、后的能谱图中均出现Au元素,这是由于PA-12微塑料颗粒为电气绝缘体,在进行扫描电镜前需对其进行镀金处理,使其具有导电性,以便于更加清晰地观察微塑料表面形貌。本研究中采用了周倩等[8]使用的超声清洗的方法,即使用2 mol·L?1的HCl进行超声清洗,由于微塑料的多孔表面,使其镶嵌或附着一些环境物质(如金属离子、有机物),故在EDS中检测到较多的氯离子。2)红外光谱分析表明,H2O2、KOH、K2S2O8消解并未改变各类型微塑料原有的红外光谱特征,消解后微塑料颗粒的特征峰仍然存在,对微塑料颗粒的识别无显著影响。
3)通过对消解前、后微塑料进行荧光、SEM-EDS分析发现,与其他类型消解液相比,经H2O2消解处理后,微塑料的荧光强度发生轻微减弱,且对微塑料表面形态和其对应的元素组成影响较小,故推荐H2O2作为最佳的微塑料消解方案。
4)本研究以新制备的微塑料作为研究对象,没有考虑微塑料与环境中有机污染物的聚集效应,故在后续研究中应考虑微塑料受到老化等因素的影响及其对聚集效应的影响研究。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 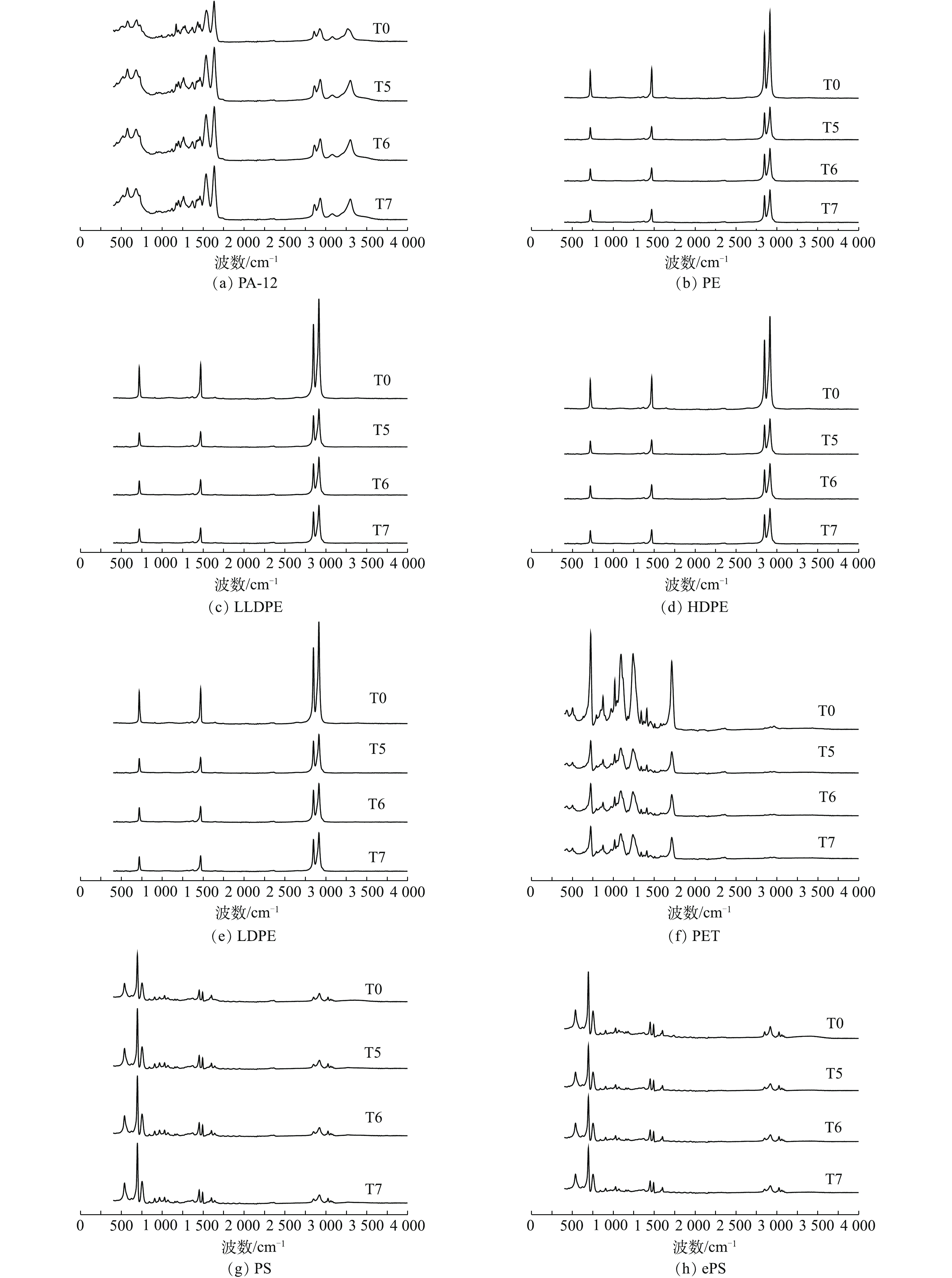
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图