全文HTML
--> --> --> 油浸泥土主要来源于石油开采过程产生的落地原油和含油矿渣、污泥、垃圾的堆置,以及采油废水滥排、石油泄露事件等[1-2]。石油污染使土壤的通透性降低,影响土壤中植物和微生物的生长。油浸泥土若不妥善处置,将造成污染扩散,影响周边环境和人体健康[3]。油浸泥土内部的轻质油分挥发出来,可进入到大气循环当中,并且随着大气的运动,造成污染扩散。油浸泥土中烃类可渗入地下水,导致地下水水质恶化。因此,油浸泥土已成为巨大的环境隐患,针对其处理处置已引起广泛关注[4-5]。目前,油浸泥土的处置技术主要包括萃取技术、生物处理技术和热脱附技术。热脱附技术是一项利用燃气或者电能等能源对污染土壤加热,并对挥发后的污染物收集和处理的土壤修复技术,热脱附技术对有机污染土壤具有较好的修复效果[6-9]。根据修复方式,热脱附技术分为异位热脱附和原位热脱附技术,异位热脱附技术是将土壤开挖后进行处理,不影响土地的再利用。而原位热脱附技术是一种在污染场地上进行原地修复的技术,具有对土壤扰动小、二次污染可控、处理范围广等优点,尤其是对土壤污染较深、渗透低、黏性强、开挖难度大、不利于异位开挖修复的场地,原位热脱附技术优势更加明显[10-11]。热脱附技术作为一种重要的非燃烧技术,在有机污染土壤修复及含油污泥处置领域具有较好的应用前景。热脱附技术的影响因素较多,如反应条件、反应设备、土壤特性等[1, 12-15]。关于此技术,国外已有较多的研究和应用,但在我国起步较晚,相关研究较少,且机理研究也不够深入。张学良等[16]研究了热脱附技术对苯、氯苯等污染物的处理效果,热脱附对不同有机物的去除率均接近100%,且发现温度、停留时间、含水率、孔隙率等因素均可影响热脱附效果。王锦淮[17]开展了热脱附技术的中试实验,结果表明苯胺、氯苯、1,2-二氯苯和1,4-二氯苯等污染物接近完全去除。BAKER等[18]的研究结果表明,在300 °C的加热温度下,热脱附处理苯、乙苯、萘烯、甲苯效果较好。截至目前,国内外关于热脱附技术的研究及应用主要集中于多环芳烃类及苯系物类污染土壤的处理上,很少应用于油浸泥土的修复,因此,开展针对热脱附技术应用于油浸泥土的影响因素的研究十分必要[19]。
新疆油田是我国历史久远的大型采油区,石油开采后遗留大量油坑和油浸泥土。本研究在分析新疆某采油区油浸泥土性质的基础上,采用热解炉实验装置,对不同初始含油率(油浸泥土中的石油烃含量)、含水率的油浸泥土进行了热脱附模拟实验,通过测定不同加热温度和加热时间下的固相含油率、能耗等参数,研究了热脱附过程中加热温度、时间、初始含水率、含油率等对热修复效果的影响,为热脱附技术在油浸泥土修复领域的应用提供参考。
1.1. 实验材料与装置
油浸泥土样品采自中国西北新疆某油坑污染场地,采样深度0~30 cm。油浸泥土呈黑色、黏稠、半流质状,称取40 kg油浸泥土,将油浸泥土中的树叶、树枝和石子等异物除去,将油浸泥土充分搅拌、混合均匀,放置于密封箱中保存。原始油浸泥土样品外观见图1。理化性质如下:土壤质地为壤土,pH 7.5,含水率20%,总有机碳0.324 8 g·kg?1,阳离子交换容量23.5 cmol·kg?1。本研究装置为自制热解炉小试装置,热解炉主要由加热系统、冷凝系统、液体收集系统、气体收集系统4个系统组成,见图2。
工艺流程如图3所示。将一定量的供试泥土置于热解炉中,不断通入氮气,使热解炉内保持无氧状态。采用燃气加热的方式对炉内油浸泥土加热,通过温度自动控制系统进行温度调控,使炉内油浸泥土的温度达到实验设定温度。经过一定的停留时间后,将油浸泥土从出料口取出,并进行含油率检测,挥发出的高温混合气体进入冷凝系统,收集到的油水混合物静置分层,分别取上层油相和下层水相用于制备不同含油率和含水率的供试油浸泥土。
1.2. 实验方法
称取500 g(干质量)供试油浸泥土,从进料口加入炉筒中,分别设定不同的加热温度(200、250、300、350、400 °C)和停留时间(0.5、1、2、3、4、5、6 h),待出料冷却后,利用红外分光光度法进行固相含油率检测。每次实验设3组平行样,相对标准偏差控制在5%以内。按照一定比例,将热解炉小试装置回收的水、油添加于上述供试油浸泥土中,制备不同含油率(5%、10%、15%、20%、25%、30%)和含水率(5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%)的供试油浸泥土。在本研究中,设置加热温度300 °C、停留时间4 h的工艺条件,利用不同初始含油率和不同初始含水率的土壤进行热脱附处理,利用红外分光光度法对处理后油浸泥土进行固相含油率检测。每次实验设3组平行样,相对标准偏差控制在5%以内。
为研究加热温度对于油浸泥土热脱附处理效果的影响,将供试油浸泥土(含油率11.3%,含水率20%)置于热解炉中,通过自动调温系统维持炉内油浸泥土温度为200、220、250、300、350、400 °C,停留4 h后卸料。待出料冷却后,测定固相含油率。
为研究加热时间对于油浸泥土热脱附处理效果的影响,将供试油浸泥土(含油率11.3%,含水率20%)置于热解炉中,通过自动调温系统维持炉内油浸泥土温度为300 °C,分别在停留0.5、1、2、3、4、5、6 h后卸料。待出料冷却后,测定固相含油率。
为研究油浸泥土初始含油率对于热脱附处理效果的影响,分别称取500 g(干质量)含水率为20%,含油率分别为5%、10%、15%、20%、25%、30%的油浸泥土置于热解炉内,通过自动调温系统维持炉内油浸泥土温度为300 °C,热脱附处理4 h后出料。待出料冷却后,测定固相含油率。
为探究油浸泥土初始含水率对于油浸泥土热脱附处理效果和热脱附能耗的影响,分别称取500 g(干质量)含油率均为11.3%,含水率分别为5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%的油浸泥土置于热解炉内,通过自动调温系统维持炉内油浸泥土温度为300 °C,热脱附处理4 h后出料。待出料冷却后,测定固相含油率。
1.3. 油浸泥土含油率的测定和数据处理
油浸泥土含油率的测定采用萃取结合红外测油仪测定的方法[20]。称取10 g(干质量)样品于100 mL具塞磨口锥形瓶中,加入10 g无水硫酸钠,混合均匀,加入25 mL四氯化碳,盖好塞子轻轻摇匀。将锥形瓶置于50~60 °C水浴中,以50~60 r·min?1振荡8 h,然后静置1 h。将上清液倾倒于50 mL 容量瓶中,再向100 mL具塞磨口锥形瓶中加入20 mL四氯化碳,以50~60 r·min?1振荡8 h,然后静置1 h;再次将上清液倾倒于50 mL容量瓶中,定容,利用红外测油仪对上清液进行定量测定分析。采用 Excel 2010 和 Origin7.5软件对实验数据进行处理、数据分析、绘图。
石油烃去除率根据式(1)进行计算。
式中:η为石油烃去除率;C0为油浸泥土初始含油率;Ct为处理后油浸泥土含油率。
2.1. 加热温度对热脱附过程的影响
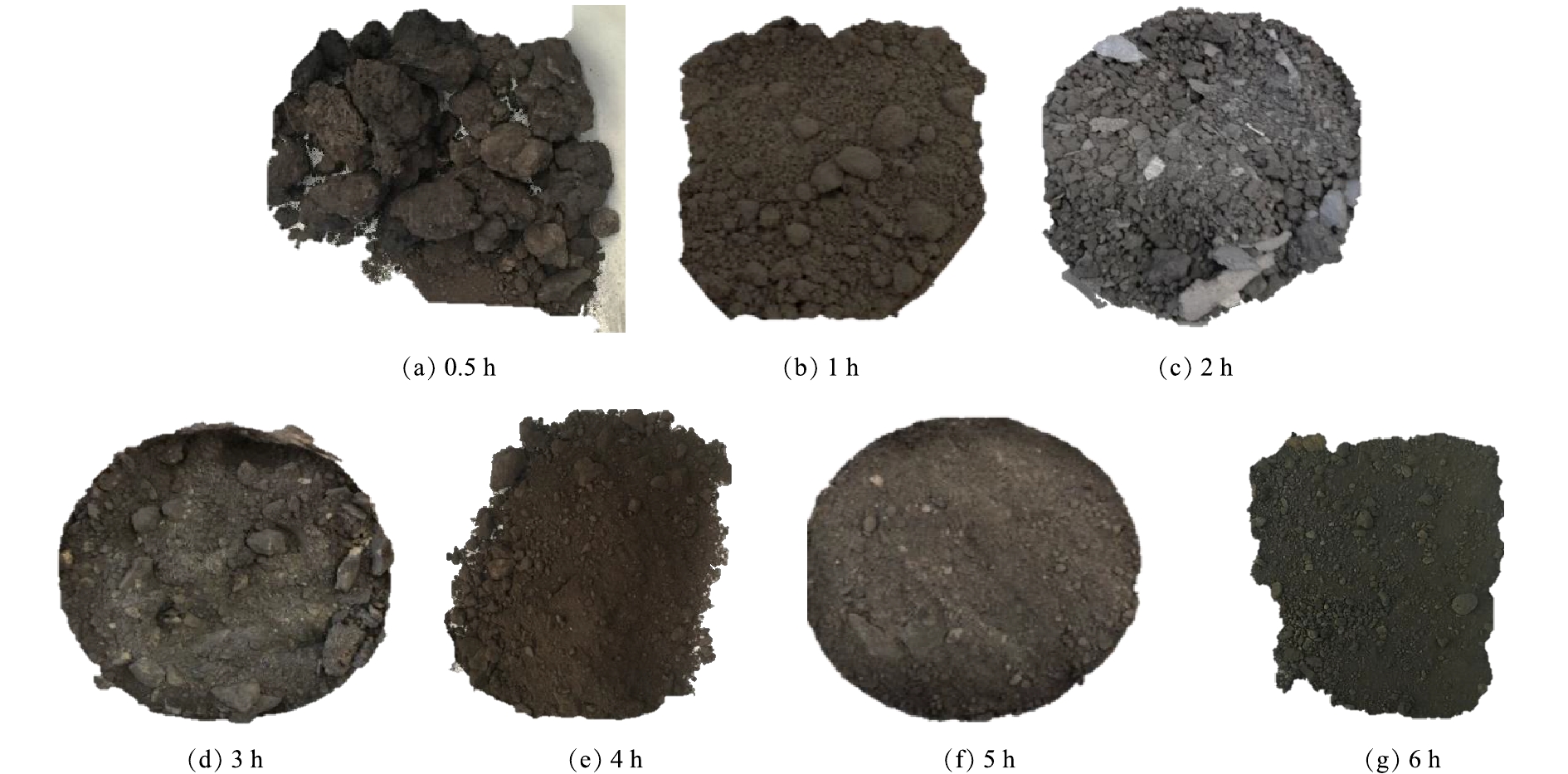
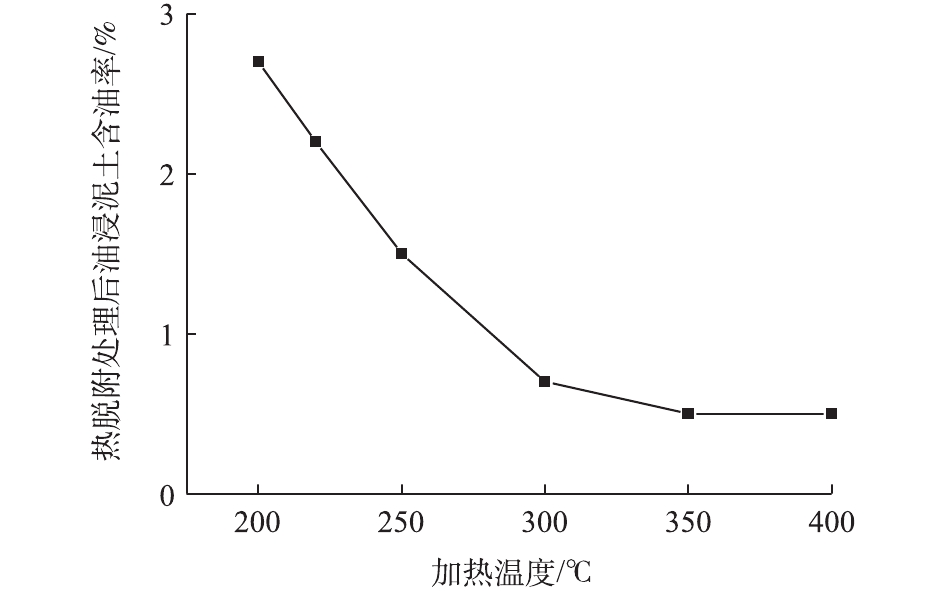
在不同温度条件下,热脱附处理后样品的表观性状如图4所示。原始样品(如图1所示)由于含油率较高而呈黏结状态。油浸泥土的最大污染特征表现为土壤表里的贯通性,石油烃灌满于一定面积、深度土壤中几乎所有孔隙,堵塞绝大多数的土壤气孔;同时由于石油烃的黏稠性,将土壤中原本散状的土壤颗粒胶黏在一起,改变了土壤原有的结构特征。经过4 h热处理后,热脱附温度在250 °C以下的油浸泥土仍呈现黏结块状,从表观上来看仍还有一定量的石油烃。在不同加热温度下,经过热脱附处理后油浸泥土含油率的变化情况如图5所示。设置加热温度为200 °C,经过4 h处理后,油浸泥土含油率降至2.7%;在热脱附温度从200 °C升高至300 °C的过程中,含油率可持续降低至0.7%。在此温度区间内,升高加热温度,石油烃的去除率增大,处置后油浸泥土样品的含油率降低。当加热温度为300 °C时,含油率仅为0.7%,石油烃去除率可达到94%;继续升高温度(>300 °C),油浸泥土的含油率基本保持稳定(含油率保持在0.6%左右)。综合考虑热脱附效果及资源消耗2个因素,该油浸泥土的最佳热脱附处理温度为300 °C。
油浸泥土经过高温加热,土壤中的石油烃会热解吸挥发出来。并且当加热温度提高时,石油烃的C—C键和C—H键易断裂而发生裂解,石油烃链缩短,挥发性增强,从油浸泥土中解吸出来,实现油土分离[17]。本研究结果表明,升高加热温度可以促进油浸泥土中石油烃的去除。这是由于石油烃分子中的化学键在较高温度下更容易断裂,加热温度越高,产生裂解的石油烃种类越多。但当温度在300 °C以上时,油浸泥土含油率无显著变化,这说明在初始含油率保持不变的情况下,加热温度超过一定值时,对热脱附效果的影响有所减弱。王嫣云等[21]研究了不同热解终温对石油烃去除率的影响,结果表明,随着温度升高,热解残渣的含油率逐渐降低,但当热解温度为260 °C时,继续升温,对油浸泥土含油率则无明显影响。 LUNDIN等[22]的研究表明,高温热解有利于垃圾焚烧灰中多氯联苯和多氯联苯并呋喃的去除,热解温度从300 °C升高至500 °C时,热解后固态残渣污染物含量明显降低。热脱附温度的选择与污染物本身的特性有关。对于被苯等挥发性有机物污染的地块,温度上升至100 °C,就有较好的修复效果;而对于多环芳烃、石油烃等半挥发性有机物分子,通常需要升温至300~500 °C,才能达到相同的修复效果[16, 23]。
2.2. 加热时间对热解过程的影响
在不同加热时间下,油浸泥土热脱附处理后样品的表观性状如图6所示。加热时间(0~1 h)较短时,部分样品仍存在因石油烃的黏稠性而导致的黏结状态;经过4 h热脱附处理后,油浸泥土团聚现象消失,松散程度高,形成均匀细颗粒。对于不同的加热时间,样品含油率检测结果如图7所示。在加热时间为0~0.5 h时,样品中石油烃去除率较明显,含油率从11.3%降至2.6%,这是因为样品中的轻质油挥发速度较快。从0.5 h继续延长加热时间至4 h的过程中,样品含油率从2.6%降低至0.7%;在4~6 h的加热过程中,样品含油率从0.66%降低至0.56%,这表明热脱附处理4 h后,继续延长加热时间,油浸泥土中的含油率基本保持不变,因此,在此时间范围内,加热时间对于样品石油烃的去除效果影响较小。张攀等[11]在进行热脱附处理硝基苯研究时也得到类似的结果,硝基苯的热脱附效率随着热脱附时间的延长而增加,但当加热时间超过30 min时,热脱附效率不再有显著增加。LAM等[24]发现,石油污染土壤含油率会随着加热时间的增加而明显降低,但加热时间超过一定值时,热脱附效果基本不再受加热时间的影响。加热时间对热脱附效果的影响也取决于热脱附温度,较低的热脱附温度需要较长的加热时间才能达到相同的处理效果[25]。综合考虑热脱附效果、资源消耗及运行成本等因素,该油浸泥土的最佳热脱附加热时间为4 h。
2.3. 初始含油率对石油烃去除效果的影响
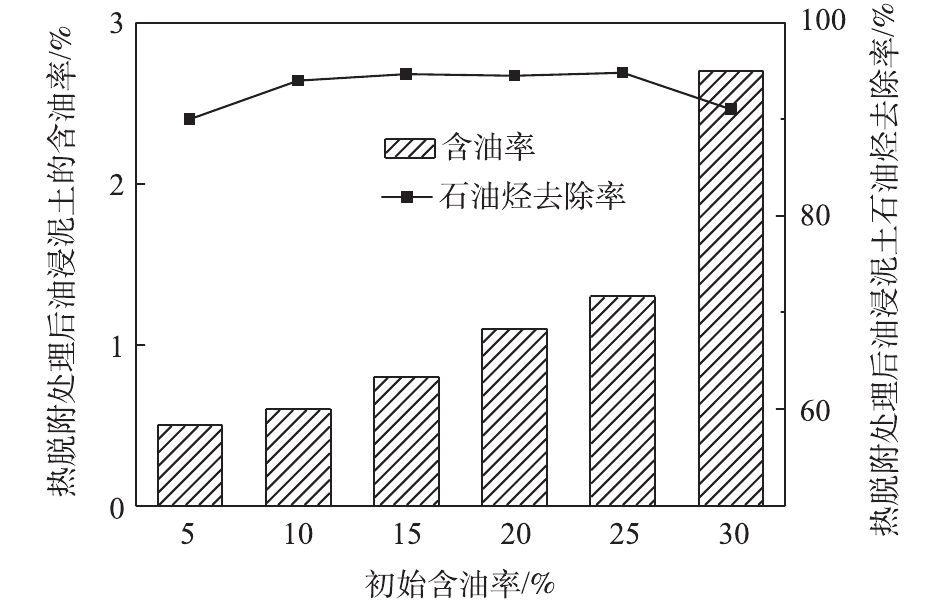
由图8可知,在设置的6个油浸泥土初始含油率浓度梯度(5%、10%、15%、20%、25%、30%)下,随初始含油率的升高,处理后的油浸泥土固相含油率呈现升高趋势,但石油烃去除率基本保持不变。因此,在初始含油率为5%~25%时,热脱附处理后,油浸泥土固相含油率在2%以下;但当初始含油率升高至30%时,石油烃去除率为91%,处理后的样品含油率为2.75%,尚未达到《油气田含油污泥综合利用污染控制要求》(DB 65/T 3998-2017)的修复标准。王嫣云等[21]的研究表明,初始含油率对高温下石油烃去除率影响较小,且去除率于300 °C后保持稳定。这主要是由于初始含油率越高,轻质油含量越高,在较低温度下,有更多组分析出; 含油土壤其他组分在温度升至较高时才逐渐析出,此时饱和去除率已较高,因此,石油烃组分去除率不再随初始含油率变化而变化。王瑛等[26]的研究也表明,土壤中初始DDT含量对DDT的去除率没有显著影响。
2.4. 初始含水率对石油烃去除效果的影响
在加热温度为300 °C,加热时间为4 h的工艺条件下,初始含水率对供试油浸泥土(含油率11.3%)热脱附效果和天然气用量的影响结果如图9所示。在初始含水率为10%~50%时,随着含水率的升高,石油烃去除率降低,经处理后,油浸泥土固相含油率有所升高。在油浸泥土初始含水率超过40%时,处理后含油率不能达到修复标准。由此可见,油浸泥土初始含水率过高或过低,均会影响热脱附处理效果。高含水率不利于热脱附处理,高含水率的油浸泥土中的水分会以水膜形式存在于油浸泥土表层,在热脱附过程中水脱离会吸收部分热能,这使石油烃得到的能量降低,导致石油烃热脱附效率降低。此外,含水率过高会造成油浸泥土黏结使其通透性降低,堵塞石油烃扩散的通道,影响石油烃的热脱附效果[27]。油浸泥土含水率较低也不利于热脱附处理,油浸泥土中水分子作为极性分子相较于石油烃更容易与土壤上位点结合,占据更多的结合位点,含水率过低时,石油烃分子大量吸附于油浸泥土上,故导致热脱附处理效果较差[28]。如图9所示,天然气用量与油浸泥土初始含水率呈现反比关系,油浸泥土含水率影响热脱附能耗。初始含水率为50%时,天然气使用量为72 m3·h?1(标准状况);当初始含水率降至5%时,天然气使用量降低至20 m3·h?1 (标准状况),高含水率的油浸泥土热脱附过程的耗能是低含水率油浸泥土的3倍之多。虽然过高含水率的油浸泥土热容量高,热损失较慢,但较高的含水率不利于其中污染物的脱附,且易消耗大量的能源,工程成本较高。因此,油浸泥土初始含水率是热脱附技术应用的重点考虑因素之一[29]。
2) 利用本研究热解炉小试装置,对于初始含油率为11.3%、含水率为20%的油浸泥土,综合考虑样品热脱附处理效果、资源消耗及运行成本,加热温度300 °C、加热时间4 h为最佳工艺处理条件。在此最佳条件下,处理后的油浸泥土含油率仅为0.7%,符合油泥处置标准。
3) 油浸泥土初始含水率和含油率是决定是否采用热脱附技术的关键因素。在一定温度和时间范围内,处理后油浸泥土的固相含油率随着初始含油率的升高而升高,不达标的风险增大。适中的初始含水率(10%~20%)有利于热脱附处理,当初始含水率超过40%时,热脱附效果较差且能耗较高。
参考文献


 下载:
下载: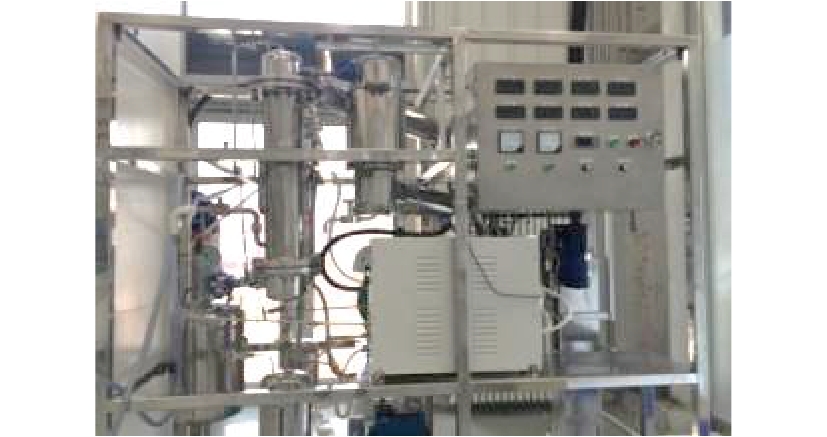 





 点击查看大图
点击查看大图