全文HTML
--> --> --> 磷是与能源和水并列的重要资源,具有单向流动和不可再生的特性[1-3]。依据美国地质调查局2010年数据,目前,磷矿资源可持续开采仅能维持50 a左右。一方面,由于磷矿不断受到镉、铀等放射性金属的污染以及富磷矿资源日益稀缺,致使开采难度逐年提高[4];另一方面,随着全球人口的增长以及社会经济的发展,对必须利用磷元素进行生产的产品需求也不断增大。磷矿的稀缺性和不可替代性使上述矛盾不断加剧,解决矛盾的方法之一就是从各种富磷废弃物中进行磷回收。污泥磷回收技术主要是通过物理或化学的方法使污泥产生富磷上清液,通过投加金属盐类形成不溶性磷酸盐沉淀。磷的不同形态及其分布影响着污泥磷回收的效率。从污泥中回收磷的首要条件是污泥中的磷从固相转移到液相中[5]。目前,污泥磷溶出的方法主要有物理法、化学法和生物法等[6]。磷的溶出率基本上与其存在形态相关[7]。对于城市污泥中磷元素的研究,主要集中在污泥综合利用及其资源化利用等方面,包括农田林地应用和建筑材料应用等[8]。城市污泥中总磷含量为30 mg·g?1左右,大部分的磷随污泥进入填埋场所,仅有18.65%的磷被土地利用[9];同时,磷是水体富营养化的主要影响因子,水体中的磷含量增高易造成水华现象。因此,对污泥中磷的溶出过程进行研究十分必要。通过适当的提取方法,了解各形态磷占总磷的比例,对于研究污泥中磷的溶出规律以及污泥的资源化利用具有重要的意义。
自1990年起,化学连续提取法[10]在欧共体标准测量与检测局发起的欧洲标准测试计划框架下逐步发展,是一种标准化的沉积物磷形态分析方法。该方法操作简单,是目前广泛应用的磷形态连续分级提取方法[11],对污泥样品同样具有很好的实际操作性。该方法分3个步骤:第1步实验分离出总磷;第2步分离出无机磷和有机磷;第3步分离出磷灰石无机磷和非磷灰石无机磷。采用盐酸和氢氧化钠进行提取,得到5种磷形态,包括总磷(TP)、无机磷(IP)、有机磷(OP)、非磷灰石无机磷(NAIP)和磷灰石无机磷(AP)[12]。
污泥磷溶出有多种方式,其中热解法和酸碱处理法是较为常用且高效的方法。热解法又分为高温预处理(一般温度高于100 ℃)[13]和低温预处理。考虑高温预处理成本较高,且pH对污泥磷溶出的影响一直是****们的研究热点,而添加EDTA可以抑制金属离子在加热过程中对污泥磷溶出的影响。本研究通过SMT法提取污泥中不同形态的磷,分析磷的形态分布规律,并采用低温热解法、酸碱处理法和投加EDTA 3种方式,研究北京市3座污水处理厂污泥中磷的溶出特性,为污泥资源化利用以及污泥磷回收提供参考。
1.1. 实验材料
污泥为经污泥浓缩池处理后的脱水污泥。含水率低,易于储存,且含磷量较高。采自北京市高碑店(传统活性污泥法)、肖家河(A/O工艺)和清河(倒置A/A/O工艺)3座污水处理厂,含水率分别为36.48%、60.40%和74.42%。污泥样品在105 ℃下烘干12 h,经研磨后,过 100 目筛,制成干污泥,存于冰箱备用。1.2. 实验方法
1)污泥中磷的形态分析。以3座污水处理厂污泥中的磷为研究对象,应用SMT法[14]对污泥中各种形态的磷浓度进行检测,逐级提取,采用钼锑抗分光光度法对溶液中的磷进行测定。2)污泥中磷的溶出实验。低温热解实验:分别取3种污泥0. 2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀。将混合液置于恒温水浴锅中,温度分别控制在40、50、60和70 ℃,在中性pH条件下研究,低温热解6 h。投加酸碱实验:分别称取3种污泥0.2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀。分别用浓度为1 mg·L?1的HCl和1 mg·L?1的NaOH调节溶液pH,pH分别控制为4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、8.0、9.0和10.0,在常温条件下研究,反应24 h。投加EDTA实验:取3种污泥0.2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀,添加0、5、10和15 mmol·L?1的EDTA,在常温条件下研究,反应24 h。以上实验平行3次,实验数据取平均值。反应结束后均取上清液于2 000 r·min?1离心15 min后,测量磷酸根和总磷的浓度。磷酸根和总磷的测定采用钼锑抗分光光度法。
1.3. 试剂及仪器
试剂包括氢氧化钠、盐酸、磷酸二氢钾、抗坏血酸、钼酸铵、酒石酸锑钾和氯化钠等,均为分析纯。仪器包括恒温振荡器(HY-2B)、紫外可见分光光度计(UV-2102C型)、离心机(TGL-16D)、恒温水浴锅(HH-WO)和台式pH计(Ohaus STARTER 3C)。2.1. 污泥中磷的组成和形态
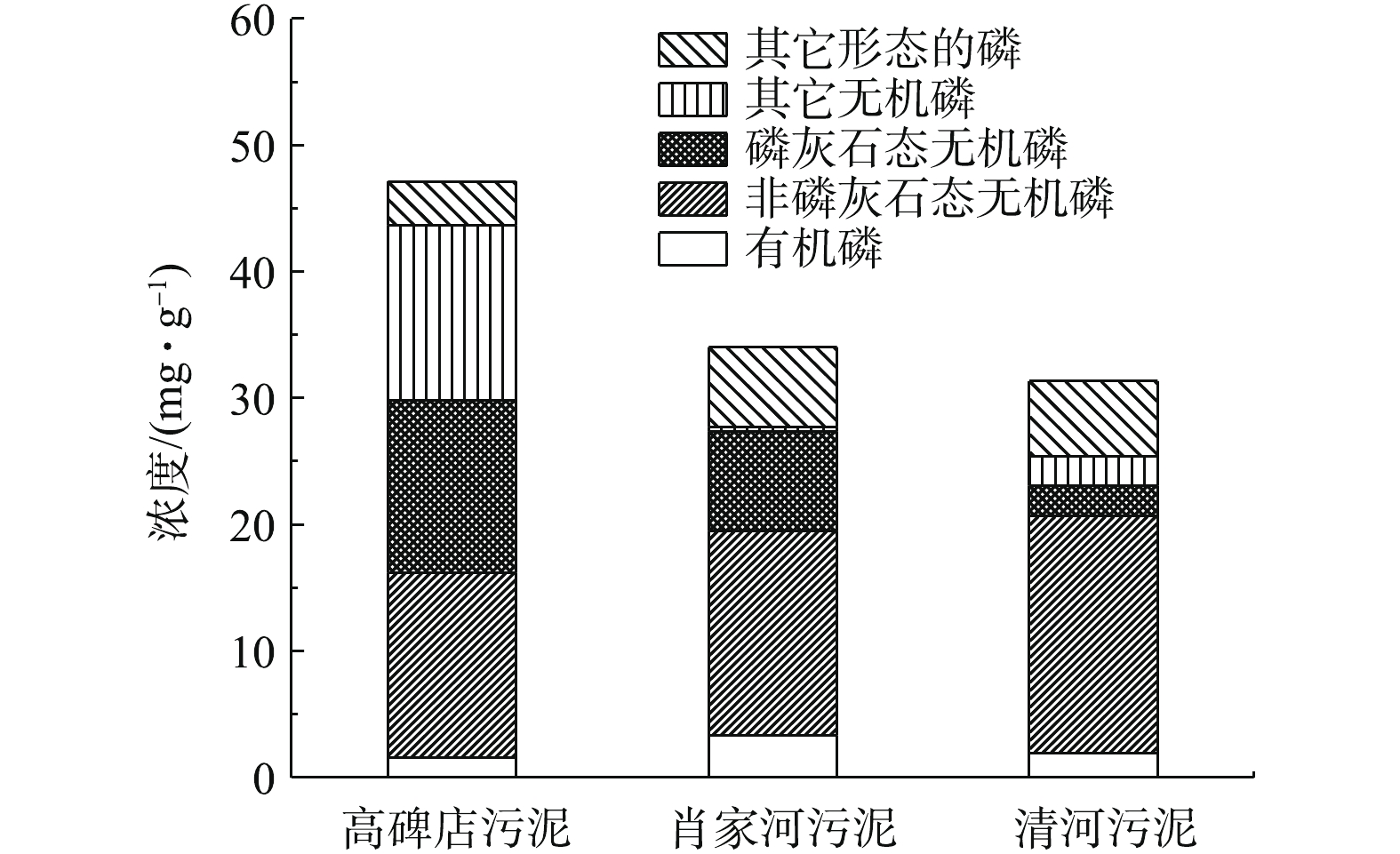
污泥中总磷和各形态磷含量的测定结果如表1所示。各形态磷占总磷的百分比见图1。在SMT分级法中,总磷主要为有机磷和无机磷的总和,无机磷主要为非磷灰石无机磷和磷灰石态无机磷的总和[15]。结果表明,高碑店、肖家河和清河3座污水处理厂污泥的TP浓度分别为47.12、34.03、31.35 mg·g?1,IP依次占TP的89.3%、71.7%、74.7%,这表明污泥中的磷主要以IP的形态存在;而在IP中,NAIP是主要的存在形态;OP含量较低,仅为3%~10%。由图1可知,高碑店和肖家河污水处理厂污泥中的AP占比较高,占TP的30%左右,而清河污水处理厂污泥中的AP含量很低,仅占TP的7.7%,这是因为污水处理厂来水组成不同,致使污泥中各形态磷的占比不同[16]。经调查可知,高碑店和肖家河污水处理厂来水中均含有工业废水,AP是工业废水中磷的主要存在形态,因此,其占比较高;而清河污水处理厂来水为生活污水,因此,其占比相对较低。
2.2. 污泥中磷的溶出实验
经低温热解后,磷逐渐从污泥中溶出到上清液中,其中总磷浓度见图2。在不同温度下,3种污泥中的磷元素均有所溶出。这是由于升温破坏了污泥的表面结构,使污泥絮体分解,污泥中的大量磷得以溶出到上清液中。在50 ℃下,污泥总磷溶出率达到最高,此时高碑店污水处理厂、肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥上清液总磷浓度分别为101.24、99.80、67.02 mg·L?1,总磷溶出率分别为53.7%、73.3%、53.4%。低温热解释放污泥中的磷,其原理是污泥细胞膜中的磷脂双分子层和细胞核中的DNA和RNA含有大量的磷元素,污泥絮体在加热过程中被破坏,可以有效地使其中的磷溶出[17]。因此,当温度从40 ℃升高到50 ℃时,污泥上清液中总磷的浓度升高;当温度从50 ℃升高到70 ℃时,污泥上清液总磷的浓度却呈下降趋势。这是因为温度升高致使污泥系统中的重金属不断释放,并与溶出的磷结合生成沉淀,导致污泥上清液总磷的浓度降低。
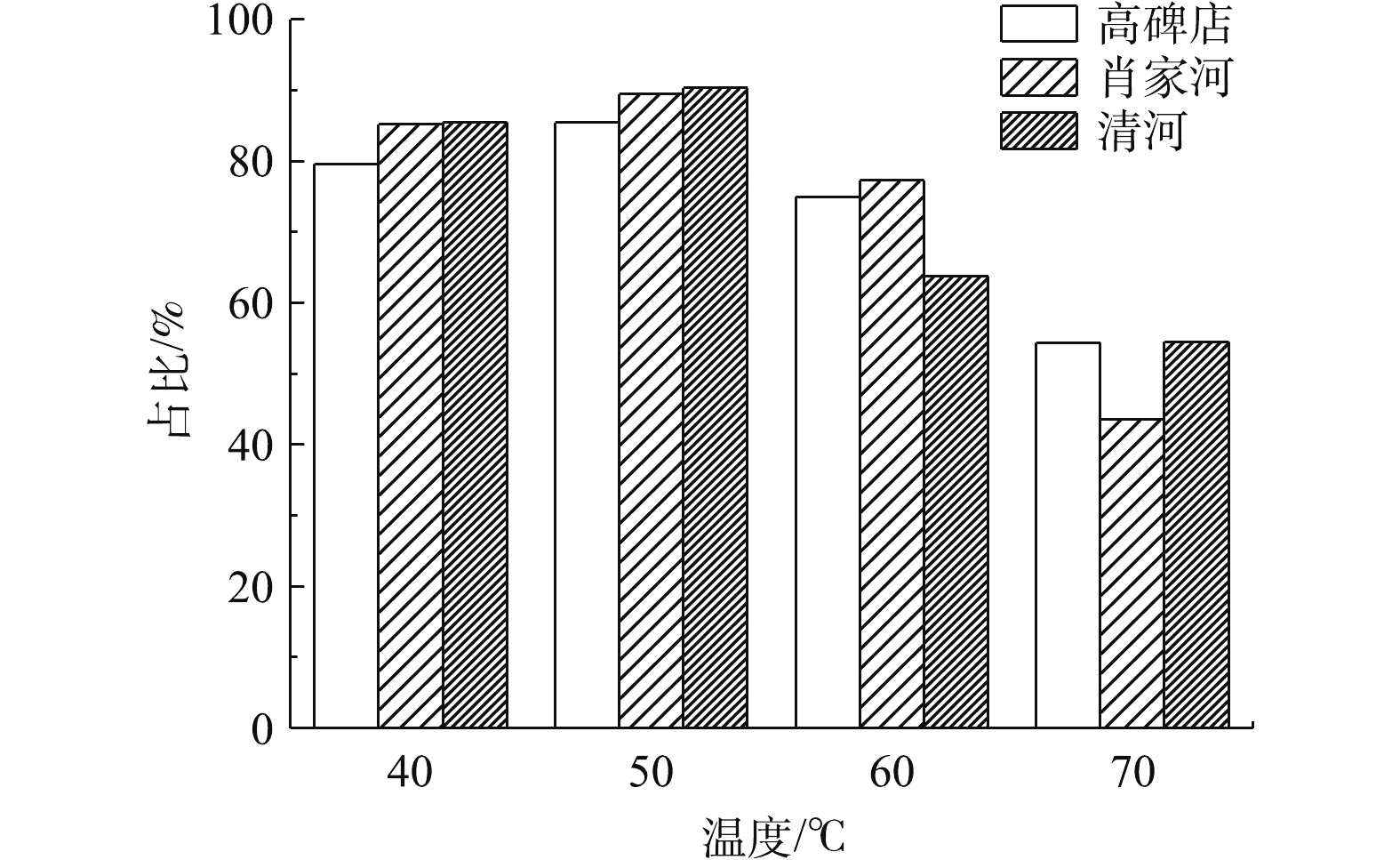
温度是影响污泥磷溶出的重要参数[18],温度过低时,污泥中的磷不能大量溶出;温度过高时,会影响污泥溶出的磷酸根占总磷的比例,而磷酸根的浓度占比越高,越有利于磷的回收[19]。由图3可知,低温热解实验中溶出来的磷以磷酸根为主,在不同温度条件下,3种污泥上清液中磷酸根占总磷的比例均在45%以上;当温度由50 ℃升高到70 ℃时,高碑店污水处理厂、肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥上清液中的磷酸根占总磷的比例均呈现下降的趋势,分别由86%下降到75%,89%下降到44%,90%下降到55%。这是因为污泥上清液中磷酸根占总磷的比例易受污泥中含有的重金属离子的影响,随着温度的升高,污泥中的重金属也不断溶出,从而与上清液中大量的磷酸根离子结合形成不溶性沉淀。
由于热解污泥时需要消耗大量能量,因此,从经济性和磷酸根的占总磷比例2个方面进行考虑,在低温热解污泥时,温度并非越高越好。综上所述,确定低温热解温度为50 ℃。薛涛等[20]在处理污泥时,发现最佳的热处理温度为50 ℃,此时释放出来的总磷以磷酸根为主,约占95%。
pH是影响污泥中磷溶出的重要参数,同时改变磷酸盐沉淀的溶解状态,影响磷的溶解特性,从而改变磷的迁移转化过程[21]。污泥随着pH变化的磷溶出情况见图4(柱状图总长表示总磷浓度变化,阴影部分为磷酸根浓度变化)。结果表明,污泥中的磷在酸性、中性和碱性环境均有溶出。当pH小于7时,污泥上清液中磷的浓度均随着pH的增加而减小;当pH大于7时,污泥上清液中的磷浓度均随着pH的增加而增加。经酸碱处理后,污泥中的磷迅速溶出到上清液中,使磷酸根和总磷的浓度提高;在pH为4时,污泥中的磷达到了最大的溶出率。3种污泥上清液中的总磷含量分别为79.91、44.20、45.80 mg·L?1,总磷溶出率分别为42.4%、32.5%、33.6%。
在酸性条件下,由于酸的溶解作用[22],污泥中磷灰石态无机磷中的部分羟基磷灰石和弱吸附态磷迅速溶出,使得上清液中的磷浓度增加。且溶解作用随着酸性的增强而增强;在中性条件下,3种污泥上清液中的总磷含量最低;在碱性条件下,随着pH的升高,3种污泥上清液中的磷酸根浓度均有所下降,这是生成磷沉淀造成的[23]。
由图4可知,在碱性条件下(pH为8~10),清河污水处理厂污泥释放的总磷浓度均大于肖家河污泥,这是因为在pH较高的情况下,污泥中大部分非磷灰石态无机磷会大量溶出[24]。通过对污水处理厂污泥中的磷形态进行分析,清河污水处理厂污泥的AP含量较低,占污泥中TP的7.70%,而NAIP含量高,占污泥中TP的59.70%;肖家河污水处理厂污泥中AP含量高,占污泥中TP的33.20%,NAIP含量低,占污泥中TP的16.17%。NAIP主要是指铁结合态磷或铝结合态磷,是潜在的活性磷,不稳定,在碱性条件下易释放到水中[25]。AP主要是以钙的磷酸盐形式存在,常见于自然生长的磷灰石或湖泊沉积物中。其含量与陆源排放、沉积类型、沉积环境及间隙水中磷酸根含量等其他因素有关,钙结合态磷难溶于水,稳定性较高,只有在pH降低时,有一小部分溶解[26]。因此,肖家河污水处理厂污泥在碱性条件下磷的溶出浓度要低于清河污水处理厂的污泥。
与中性pH条件下相比,投加酸或碱的污泥磷溶出效果均得到提高,且投加酸时的污泥磷释放效果优于投加碱时。综上所述,确定最佳pH为4。
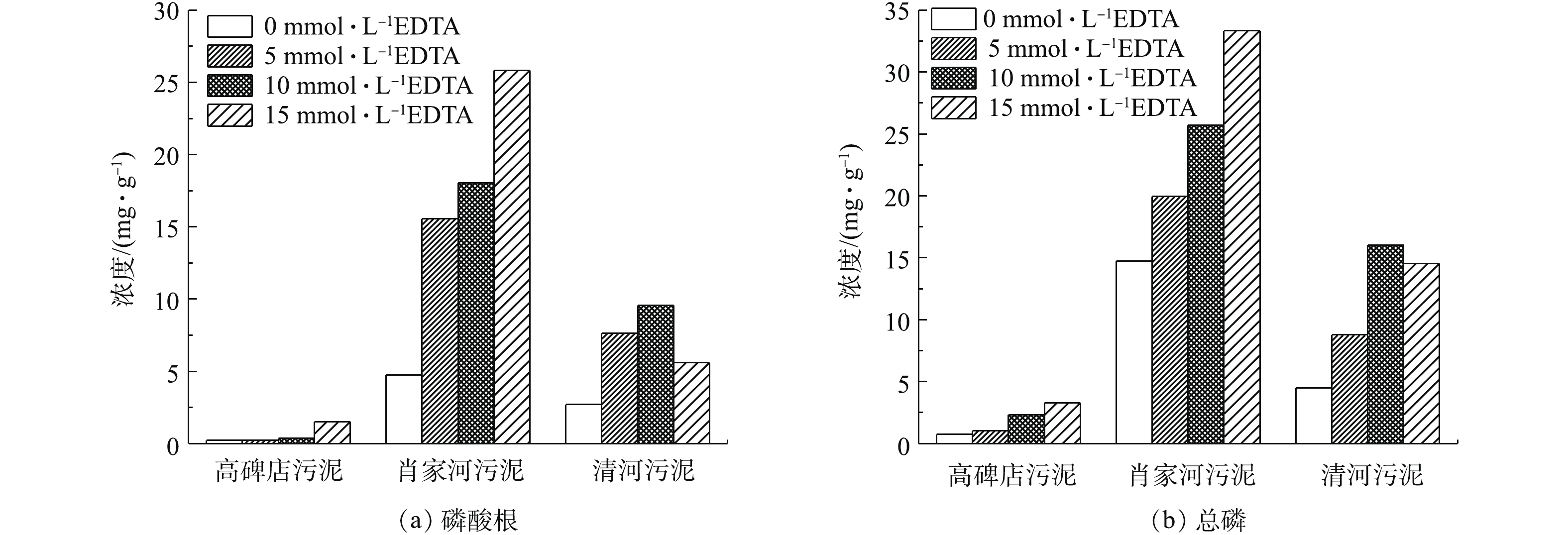
EDTA是一种重要的络合剂,易溶于水,可以与溶液中的金属离子络合形成稳定的水溶性化合物[27],因此,本研究通过添加EDTA来抑制金属离子对污泥磷溶出的影响。添加不同浓度的EDTA,反应24 h后,污泥中磷的溶出情况如图5所示。不添加EDTA时,有一部分总磷从污泥中释放出来,3种污泥总磷的溶出率分别为1.6%、43.3%、14.3%。EDTA均促进了污泥中磷的溶出,但对肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥磷的溶出效果明显[28],当EDTA的浓度达15 mmol·L?1时,肖家河污水处理厂污泥中的磷几乎全部溶出到液相中,总磷溶出率可达97.9%。这是由于当EDTA的添加量达到一定程度时,破坏了污泥的稳定结构,从而使污泥中的生物细胞的表面结构暴露出来。此时细胞壁和细胞膜表面上与脂多糖和蛋白质结合的Ca2+和Mg2+会被EDTA所络合,导致污泥细胞内的磷释放出来[29]。
添加EDTA后,高碑店水厂污泥磷的溶出量并没有明显提高。这是因为其采用了生物除磷法的同时,也投加了大量的铁、铝等金属盐类,使废水中的磷转化为不溶性磷酸盐沉淀,使用的除磷药剂主要为液态硫酸铝[30]。EDTA致使污泥分解,细胞内的磷元素释放出来,同时,污泥上清液中聚集了大量的游离Al3+离子,Al3+与水中的OH?易形成Al(OH)3絮状胶体[31],胶体具有巨大的比表面积,能强烈地吸附磷酸盐。也有研究发现,铁与磷的比值越大,磷的释放量越小[32]。HOLDREN等[33]的研究表明,如果铁、磷的原子数量比大于1.8,那么磷酸盐能够由铁离子的氧化物所固定。上述2点原因阻碍了高碑店污泥中磷的溶出,使污泥上清液中磷酸根的浓度偏低。
对比肖家河和清河2个污水处理厂,发现肖家河污水处理厂污泥上清液总磷的浓度要明显大于清河污水处理厂对应的总磷浓度,分析其原因是由于肖家河污水处理厂污泥AP含量较高,而清河污水处理厂污泥AP含量较低,在EDTA浓度相同的情况下,AP的溶出率大于NAIP[34]。EDTA对不同污水处理厂污泥中磷的溶出率差异可能和不同磷酸盐化合物中金属离子的结合能大小有关。综合考察药剂投加的成本等因素,确定最佳EDTA浓度为10 mmol·L?1。
2)在50 ℃条件下,3座污水处理厂污泥总磷溶出率达到最高。在从40 ℃升高到70 ℃的过程中,污泥上清液总磷的浓度先升高再下降。低温使磷大量溶出,温度过高,则会导致溶出的磷酸根占总磷的比例下降,影响后续磷回收。
3)污泥磷在酸或碱条件下的溶出效果均优于中性条件,且酸性条件最优。在碱性条件下,清河污水处理厂污泥溶出的总磷含量均大于肖家河污泥。原因之一是清河污水处理厂非磷灰石态无机磷占比大,污泥中大部分非磷灰石态无机磷会大量溶出。
4) EDTA的添加能够明显促进肖家河水厂污泥磷的溶出。在EDTA浓度相同的情况下,磷灰石态无机磷的溶出率大于非磷灰石态无机磷。
5)磷的形态影响着污泥磷的溶出,不同形态的磷在相同实验条件下溶出规律不同,结合磷形态找出合理的释磷条件,有利于提高溶出效率及后续的磷回收。考虑后期磷回收的可行性以及药剂投加成本等因素,确定处理污泥的最佳条件:温度为50 ℃,pH为4,EDTA为10 mmol·L?1。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 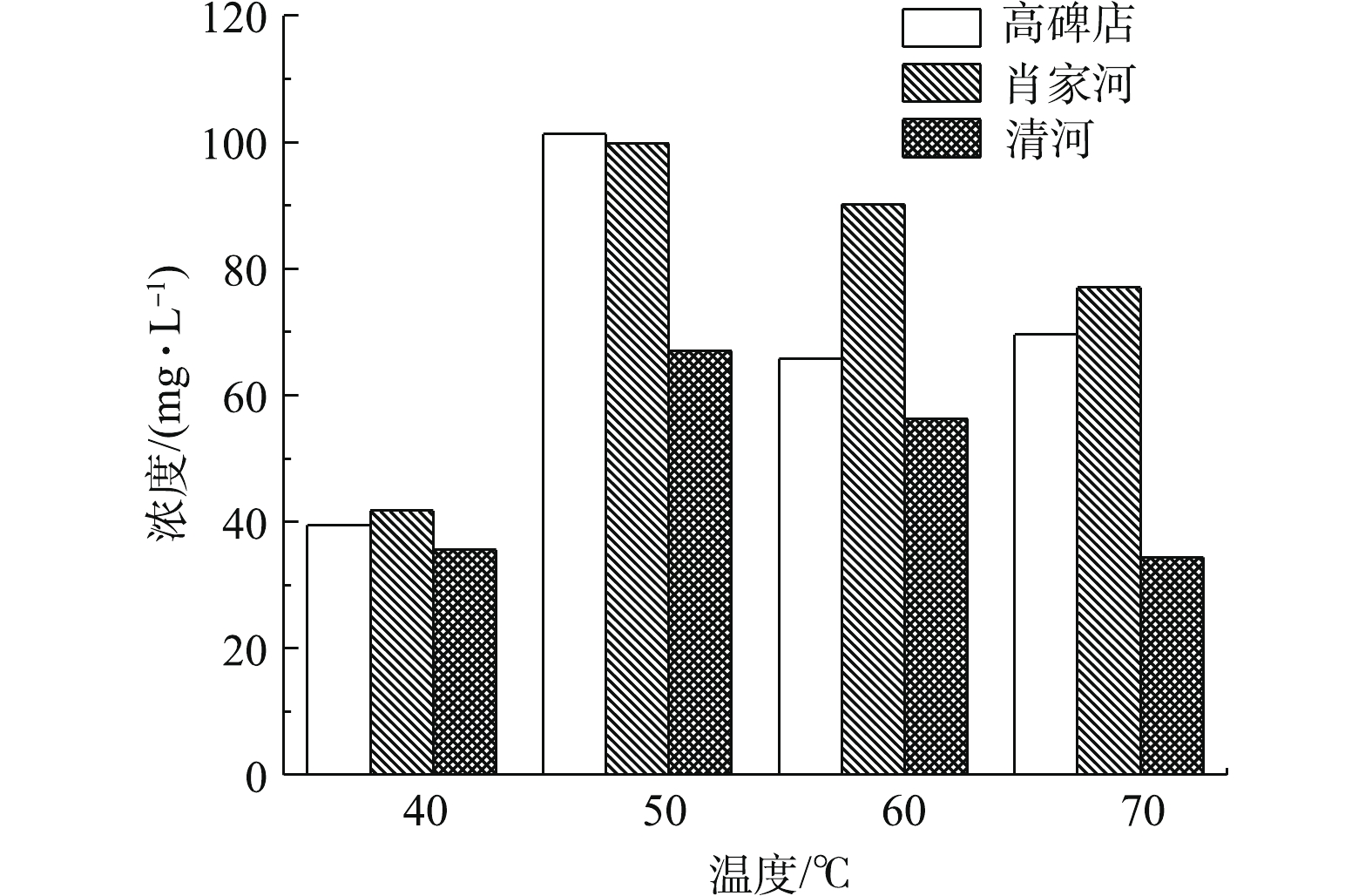

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图