全文HTML
--> --> --> 胞外聚合物(Extracellular polymeric substance,EPS)是微生物分泌的具有黏性的高分子聚合物,其主要成分为蛋白质、多糖、腐殖酸等物质[1-2]。由于EPS的组成成分中含有大量的羟基、氨基、磷酸基等络合基团,能过通过点中和、络合、离子交换、静电吸引等作用吸附水中重金属[3-5],因此,是一种潜在的重金属吸附剂。近年来,研究人员已逐步开展关于胞外聚合物吸附重金属的研究,并且取得了不错的研究成果。MIAO等[6]提取紧密结合型EPS,对Cu2+进行了吸附实验,研究结果表明,紧密型结合型EPS含量的提高能够促进金属离子的吸附,同时紧密型结合型EPS中羟基、羧基和酰胺对重金属的去除具有重要的作用。SUN等[7]研究了好氧颗粒污泥中松散结合型EPS对Zn2+和Co2+的吸附机制,发现其不仅能起到吸附螯合作用,还能通过絮凝作用强化吸附过程。郑蕾等[8]采用不同组成的活性污泥EPS吸附Cd2+、Zn2+,发现EPS的吸附能力与蛋白质和糖的含量比具有相关性。从已有的研究[8-11]可以看出,关于EPS吸附重金属的研究主要集中在不同结构EPS吸附重金属的特征和机制及不同吸附条件下EPS吸附重金属的吸附效能及模型上,但有关EPS的提取方法对EPS吸附重金属的效能的影响研究较少。如何有效地提取EPS并且保留其有效吸附能力是EPS吸附重金属的研究及其工业化应用的一个重要前提。不同的EPS提取方法对EPS的提取效率和吸附重金属的能力存在一定的影响,从而影响EPS吸附重金属的效能。因此,有必要开展提取方法对EPS吸附重金属效能影响的研究。目前,关于EPS的提取方法的研究有很多,主要通过破坏细胞与EPS之间的结合来实现分离提取EPS的目的[12-13]。常用的提取方法主要有NaOH法[13]、离心法[14]、超声法[15]、加热法[16]及其组合方法[15]等。SUN等[17]对EPS的提取方法进行了评价,结果表明化学法提取效率高于物理法。CAUDAN等[18]采用结合方法提取EPS,结果显示组合方法提取效率要高于单一方法。虽然关于EPS的提取方法的研究已有许多,但是主要集中在EPS提取效率方面,而提取过程中对于EPS吸附重金属的能力影响的相关研究较少。本研究通过考察pH、单一物理提取方法和组合方法对EPS的提取量及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)能力的影响,确定了EPS吸附剂的最优提取方法,为EPS重金属吸附剂的有效提取及工业化应用提参考。
1.1. 实验原料
脱水污泥取自佛山禅城某生活污水处理厂的污泥脱水机房(污泥含水率为77%,有机质质量分数为36.78%),该污水处理厂处理工艺采用UNITANK工艺,污泥取回后,立即放置于?18 ℃冰箱,冷冻保存。实验过程中使用的盐酸(HCl)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、氯化钠(NaCl)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)等化学药剂均为分析纯;硝酸(HNO3)、硝酸镉(Cd(NO3)2)为优级纯。
1.2. 实验装置
数显恒温水浴锅(HH-S2,常州万达升实验仪器有限公司);超声波清洗仪(GTSONIC-D20,广东固特超声股份有限公司);冷冻高速离心机(FC-18R,广州市方统生物科技有限公司);台式全温振荡器(ZQTY-70S,上海知楚仪器有限公司);原子吸收分光光度计(200AA,安捷伦科技有限公司);紫外-可见光分光光度计(UV-1800,日本岛津制作所);电子分析天平(AS 220.RS,RADWAG公司);pH计(ST-2100,美国OHAUS公司);恒温磁力搅拌器(HJ-6B,常州朗越仪器制造有限公司)。1.3. 实验方法
在提取脱水污泥前,须对脱水污泥进行清洗,以去除脱水污泥表面的污染物质。按固液比为1∶7的比例加入纯水,充分混匀后,静置去除上清液,重复清洗污泥3遍,清洗后的脱水污泥待用。首先确定不同的提取液pH对EPS提取量及吸附效能的影响。取适量污泥3份,按照固液比为1∶7的比例分别加入0.01 mol·L?1 HCl溶液、0.9% NaCl溶液和0.01 mol·L?1 NaOH溶液,在250 r·min?1转速下,搅拌2 h后,于12 000 r·min?1转速下离心20 min,取其上清液过45 μm滤膜,制备取得EPS。取0.01 g提取后EPS(投加量为100 mg·L?1),投加到100 mL 3.6 mmol·L?1 Cd(Ⅱ)模拟废水中,在165 r·min?1、25 ℃下振荡2 h后,取50 mL吸附溶液,转移进入透析袋(截留分子质量为8 000~12 000 Da)中;在350 r·min?1、25 ℃于500 mL纯水中透析6 h后,取透析袋外的纯水测定水中的Cd(Ⅱ)的浓度。
根据提取量和Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量确定提取液pH后,采用单一的物理处理方法和组合的物理处理方法提取EPS,以确定物理处理方法对EPS提取量及吸附效能的影响。
单一物理处理方法:取80 g预处理后污泥各3份,按照固液比为1∶7的比例加入相应的pH提取液,在250 r·min?1 转速搅拌2 h后,在离心(12 000 r·min?1)、超声(40 kHz)和加热(80 ℃)的条件下,处理20 min后,取其上清液过45 μm滤膜,制备取得EPS。
组合物理处理方法:取80 g预处理后污泥各3份,按照固液比为1∶7的比例加入相应的pH提取液,在250 r·min?1 转速搅拌2 h后,在超声(40 kHz,10 min)+离心(12 000 r·min?1,10 min)、超声(40 kHz,10 min)+加热(80 ℃,10 min)和加热(80 ℃,10 min)+离心(12 000 r·min?1,10 min)的组合条件下处理,取其上清液过45 μm滤膜,制备取得EPS。
取0.01 g提取后EPS,投加到100 mL 3.6 mmol·L?1 Cd(II)模拟废水中,在165 r·min?1、 25 ℃下振荡2 h后,取50 mL吸附溶液,转移进入透析袋(截留分子质量8 000~12 000 Da)中,在350 r·min?1、 25 ℃下于500 mL纯水中透析6 h后,取透析袋外的纯水测定水中的Cd(II)的浓度。
1.4. 分析方法
采用Folin-酚法测定提取的EPS中的蛋白质含量;采用蒽酮比色法测定提取的EPS中多糖的含量;采用蛋白质含量和多糖含量总和来表征EPS的总提取量;采用pH计测定pH;采用原子吸收分光光度计测定吸附前后的Cd(Ⅱ)浓度。各实验均进行3次平行实验,取平均值作为最终的实验结果。2.1. pH对EPS提取量及吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的效能影响
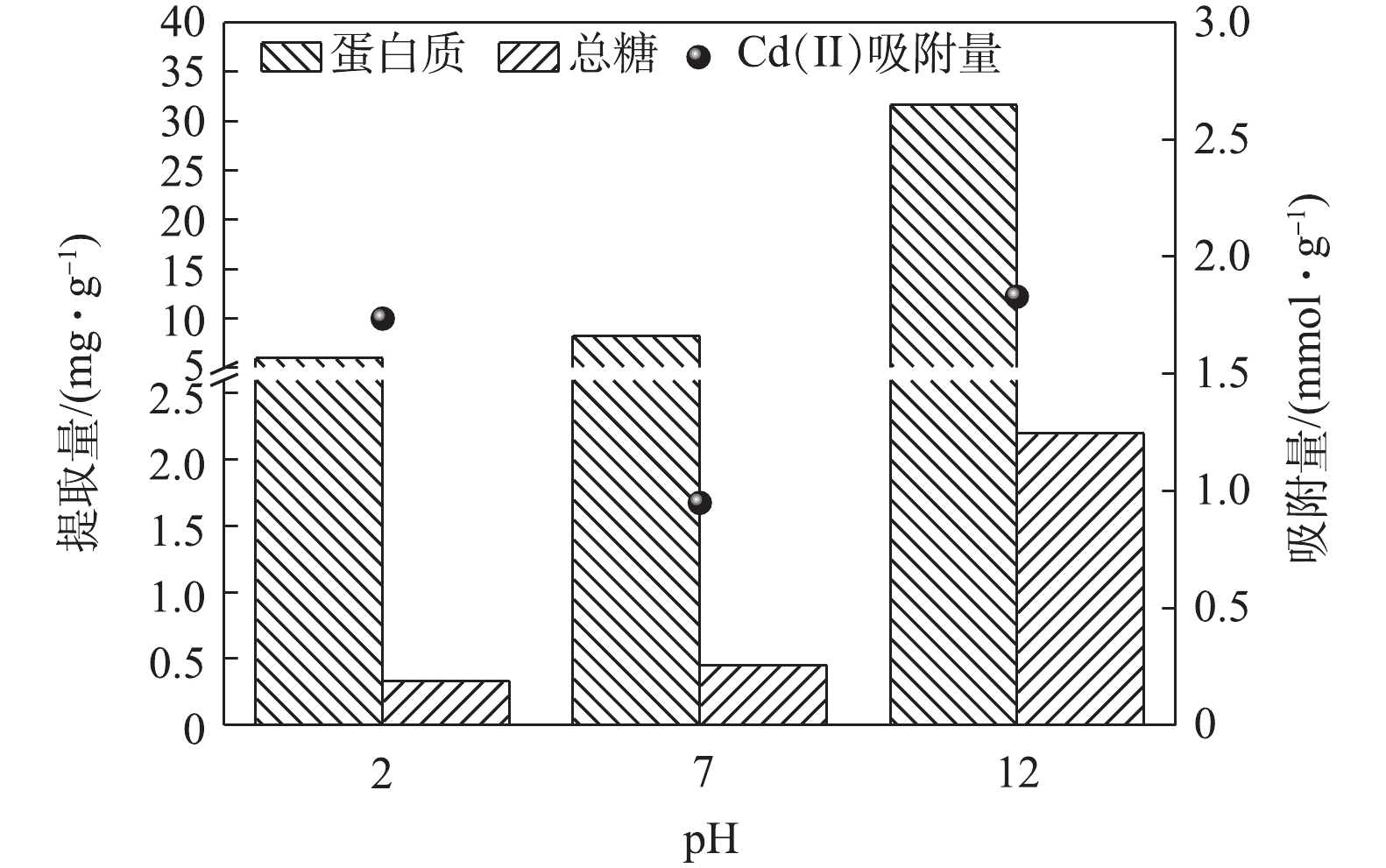
在离心条件下,不同pH对EPS的组分的提取量及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量如图1所示。由图1可知,随着pH的升高,提取的EPS量呈现逐步增加的趋势,蛋白质的提取量影响最大。EPS提取量在酸性条件下和中性条件下较为接近,随着pH升高至碱性条件,EPS中的蛋白质有明显增加。LIAO等[19]研究表明,EPS表面带有大量的负电荷,可以影响其与其他物质之间的静电作用和氢键的形成,进而影响其提取量。由于pH与静电作用和氢键形成关系密切[20],因此,对EPS的提取以及性质影响也较为明显。强碱性条件能够破坏微生物的细胞壁,同时改变了EPS的水溶性,从而使大量的蛋白质和多糖得到释放[20-21],进而导致提取量剧增。由图1可知,中性条件下提取的EPS对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量最小,而酸性或碱性条件下提取的EPS对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量较中性条件下的高。这说明酸碱的预处理有利于EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的有效成分的提取。在酸性条件下,虽然提取的EPS量较少,但其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力可达到1.73 mmol·g?1。这说明酸性条件下,提取EPS的有效成分或吸附位点较多。SU等[22]和宋小莉[23]的研究表明,蛋白质在强酸的条件下易发生水解,生成氨基酸类化合物,进而增加了EPS中的氨基和巯基等官能团,有利于EPS和重金属发生螯合反应;在碱性条件下,OH?促进了EPS的络合基团去质子化,从而活化EPS的络合基团,最终可增强EPS的络合吸附能力。
根据单位质量EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的量及单位污泥提取EPS的量,计算出酸性、中性和碱性条件下单位污泥提取的EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的总量分别为0.010 9、0.008 2和0.061 8 mmol·g?1。由不同pH的单位污泥提取EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的总量对比可以看出,碱性条件下单位污泥提取EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的总量约为酸性条件下的6倍左右。由此可见,虽然酸提和碱提都能够有效地提高EPS对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附效能,但是考虑到单位污泥提取EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)总量差异,确定碱性条件为提取EPS的最佳条件。
2.2. 单一物理提取方法对EPS提取量及吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的效能影响
在碱性提取条件下,不同的物理处理方法对EPS的组分提取量及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的效能影响如图2所示。不同的物理提取方法由于其作用的强度不同,因此,对EPS的提取量及其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的有效组分具有一定的影响。加热法主要通过加热使污泥结构松散,能够有效提高EPS的提取量[23];超声法利用剪切力和空穴形成的压力冲击来使EPS剥离[24];高速离心法主要利用离心力使得EPS脱离。对比3种方法的作用强度,可以看出,加热法最强,离心法最弱。由图2可知,不同的物理处理方法对EPS的提取量有较大的影响,其中加热法的提取量最大,其次为超声法,最低为离心法,这与以往的研究规律相符。虽然提取强度越大,越有利于提取量的增加,但过大的提取强度,容易对EPS中的有效组分造成影响,进而影响其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力。由图2亦可知,虽然加热法的提取量最高,但是其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力却为最低。这主要由于加热过程中,温度过高容易破坏EPS的有效组分[2],导致其吸附能力降低。而超声法通过剪切力等作用,相比加热法较为温和,在有效分离EPS有效组分的同时,又能够避免破坏EPS的有效组分, 其吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力较加热法和离心法要高。因此,必须控制好提取作用强度,才能有效地提高EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的效能。2.3. 组合物理处理方法对EPS提取量及吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的效能影响
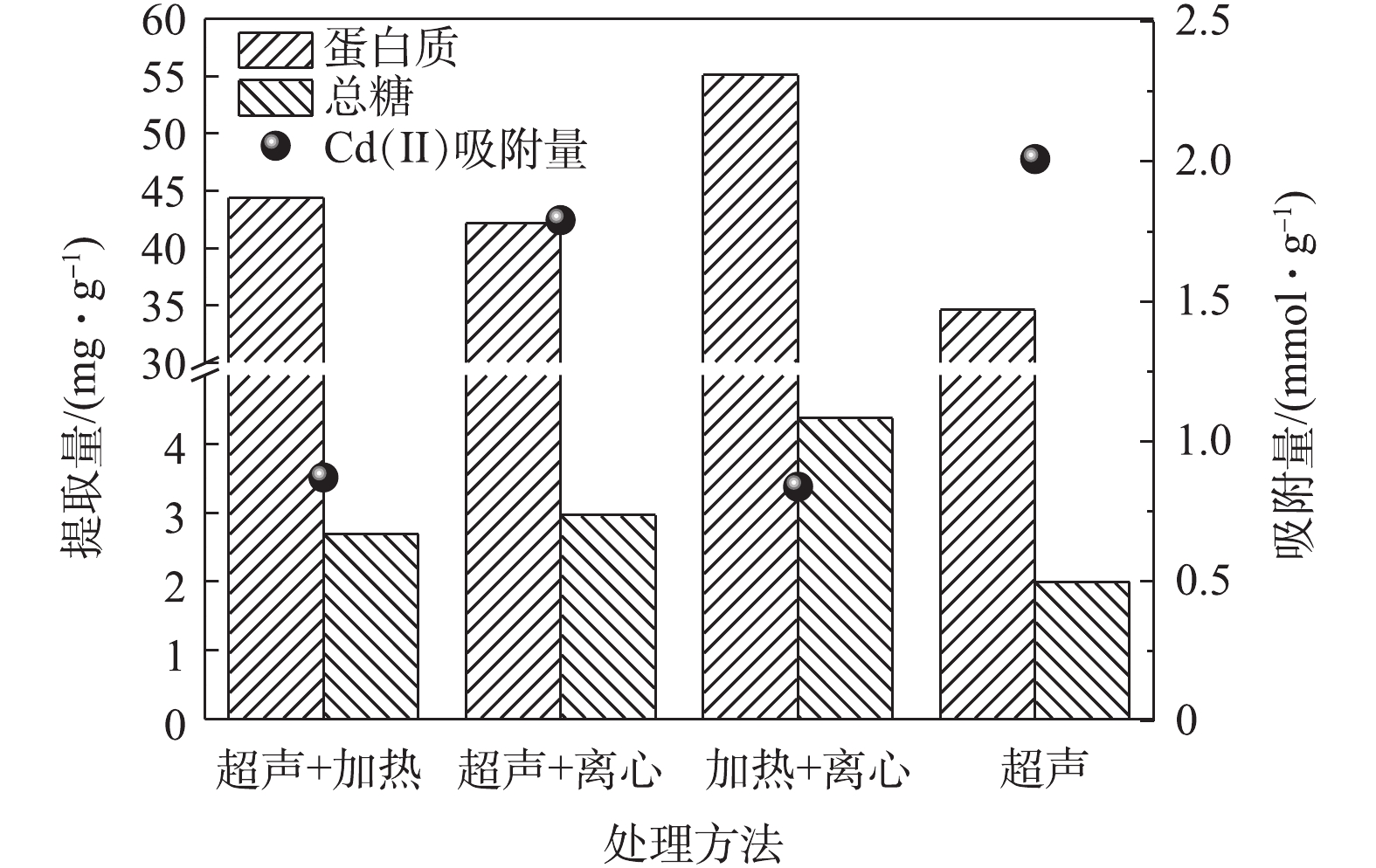
CAUDAN等[18]和MIAO等[25]研究表明,组合物理方法有利于提高EPS的提取量。由图3可知,组合物理处理方法提取的EPS总量均大于单一物理提取方法的EPS提取总量。其中,加热+离心组合预处理提取的EPS量最高,其次为超声+加热,而超声+离心组合处理提取EPS量最小。这主要是由于加热能让EPS大量释出,辅助高速离心,能够更大程度地将EPS分离出来,使得加热+离心的组合方法提取EPS效果最好。超声+离心提供的提取强度较其他的提取方法较弱,导致提取量最低。由不同组合方法吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量对比可以看出,虽然加热+离心的提取量最大,但是其吸附能力最差。原因可能是:由于提取强度的增加,虽然有利于EPS的提取,但是同时也可能破坏了EPS中的有效成分或官能基团,导致其吸附能力下降;同时,通过图3可以看出,单一处理方法提取的EPS的吸附能力均大于组合方法提取的EPS的吸附能力,综合考虑经济性和实用性,超声的预处理方法更有利于EPS吸附剂的提取。2)提取强度与EPS的提取量具有正相关性,其排序为加热>超声>离心;EPS吸附Cd((Ⅱ)的能力与提取强度不具正相关性,提取强度过大,不利于EPS有效吸附组分的保留。在碱性条件下,利用超声处理方法提取的EPS对Cd(II)的吸附能力最强,吸附量达到2.01 mmol·g?1。
3)组合物理提取方法有利于EPS的提取,但其提取的EPS吸附Cd(Ⅱ)的能力较单一物理提取方法提升不高,因此,EPS最佳提取方法为在碱性条件下进行超声提取。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 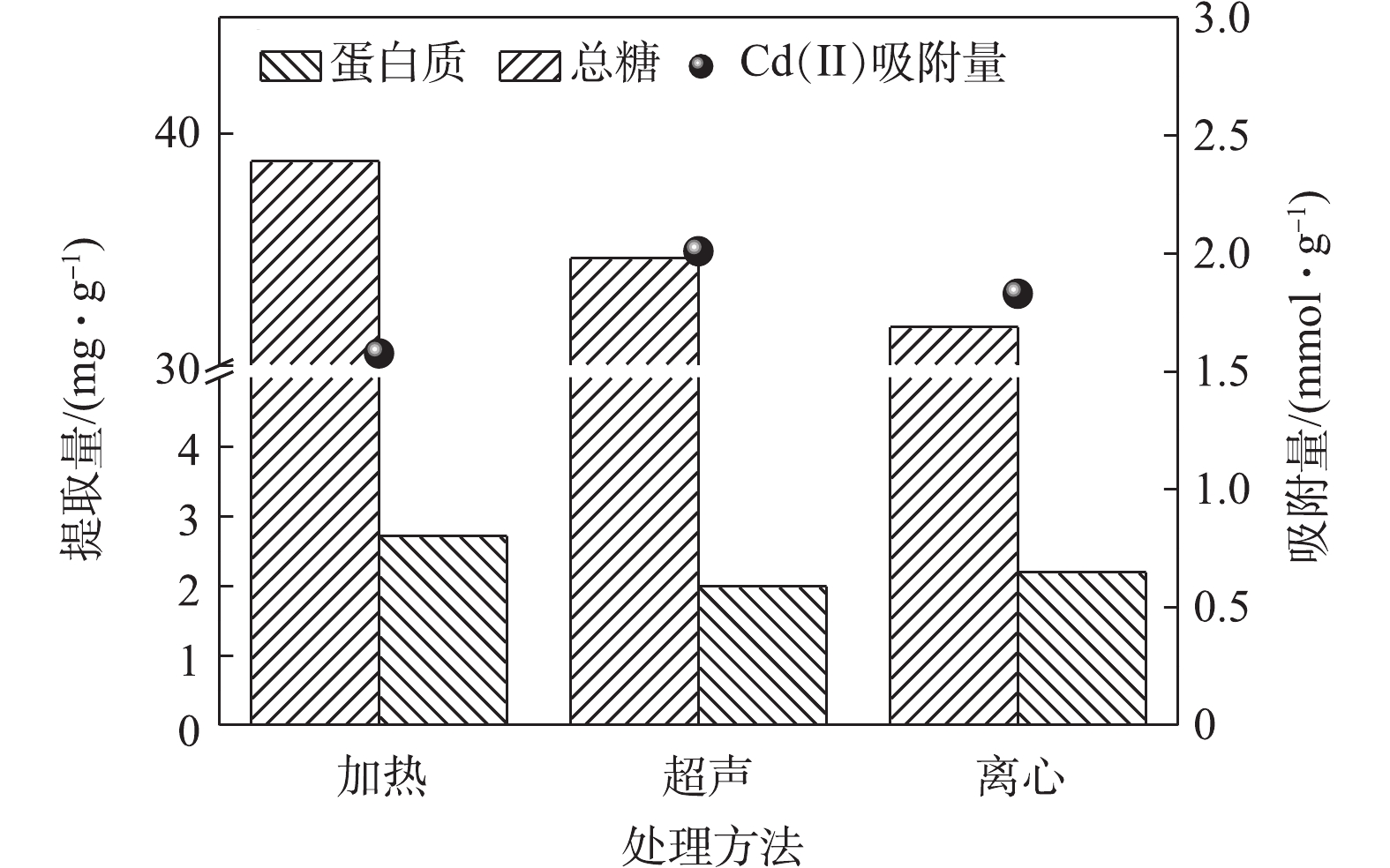
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图