全文HTML
--> --> --> 污泥是污水生物处理过程中不可避免的危害副产物,含有难降解有机物、病原菌、重金属等污染物[1-2]。目前,我国污泥年产量已超过4.5×107 t(含水率80%),成为全球污泥产量最大的国家,然而50%的污泥并没有得到妥善处理,严重威胁我国生态环境安全,开展污泥减量化研究是我国重大战略需求之一。蠕虫污泥捕食技术与污水处理系统耦合实现污泥减量已取得了广泛的研究[3-4]。蠕虫捕食污泥减量技术通过在污水处理过程中加入蠕虫等微型动物,定向延长污水处理系统的食物链,利用食物链中能量传递的“十分之一定律”,实现污泥减量。相对于污泥的隐性生长、解偶联等污泥减量技术,生物捕食具有无须投加化学物质、处理成本低、副产物少、污泥减量效率高等技术优势[5],在学术研究与工程应用中均取得了广泛的关注[6-7]。然而,蠕虫捕食对污水处理系统微生物菌群特性的影响研究相对缺乏。污水生物处理过程主要利用不同功能微生物相互间的协同降解作用,实现污水的高效处理,因此,微生物的群落结构直接影响着污水的处理效能[8]。污水处理过程中不同的工艺操作与水质条件的波动均可引起微生物菌群的改变,无法适应环境改变的微生物丰度降低,而其他微生物则可能得到富集[9]。因此,不同的环境条件可促进微生物群落的筛选过程[10]。
本研究基于厌氧-缺氧-好氧-膜生物反应器(A2O-MBR)-蠕虫床耦合系统,利用Illumina高通量16S rRNA测序技术,从微生物种类、丰度特征、功能菌群分布相似性及差异性等方面,对比分析蠕虫捕食的耦合对污水处理系统微生物菌群特性的影响,为蠕虫污泥减量技术的应用提供参考。
1.1. 实验装置
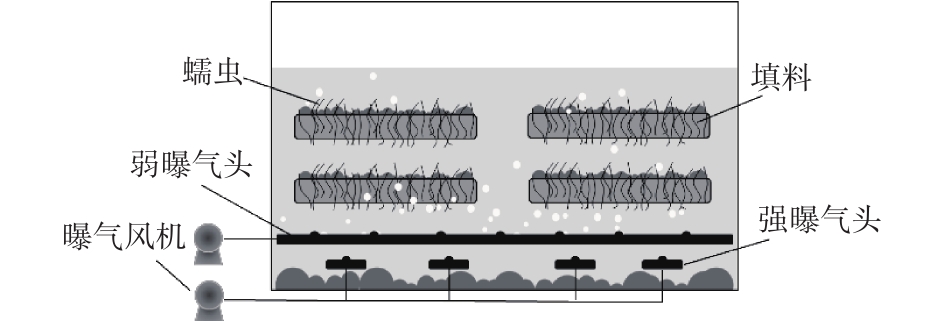
蠕虫床的结构如图1所示。反应器的有效容积为4 L(长25 cm×宽15 cm×高16 cm),内置4块方形多孔填料,用于蠕虫附着。蠕虫床底部设置双曝气系统,弱曝气系统连续运行,维持蠕虫床中的溶解氧(DO)在0.5~1 mg·L?1;强曝气系统间歇运行,每1 h运行3 min,使污泥均匀混合。蠕虫床的运行温度为23~25 ℃,接种蠕虫量60 g,空白蠕虫床的结构、运行与蠕虫床相同,但不接种蠕虫。为了对比研究蠕虫捕食对污水处理系统微生物菌群结构的影响,本研究采用A2O-MBR(Ⅰ号),A2O-MBR-空白蠕虫床(Ⅱ号)为对照系统,A2O-MBR-蠕虫床(Ⅲ号)为实验组,3组系统的流程如图2所示。
3组系统中A2O-MBR部分完全一样,A2O-MBR有效体积为16.8 L,其中厌氧池、缺氧池、好氧池的体积比为1∶2∶4,污水处理量为32 L·d?1,水力停留时间(HRT)为12.6 h,好氧池污泥浓度维持在6 000~8 000 mg·L?1。膜组件放入A2O的好氧池中,出水泵抽吸比为工作8 min/闲置2 min。每天1.5 L好氧池污泥混合0.5 L出水进入蠕虫床,同时蠕虫床中2 L污泥混合液回流到好氧池中。
1.2. 水质处理效果
实验进水采用小区下水道实际生活污水,进水水质及出水水质如表1所示。采用t-检验对3组系统出水进行统计分析,相对于Ⅰ号系统,Ⅱ号和Ⅲ号系统在出水COD方面没有统计学上的显著性差异(P>0.05);在出水TN和TP方面,Ⅱ号和Ⅲ号系统的出水浓度相对于Ⅰ号系统均显著降低(P<0.01);同时,相对于Ⅱ号系统,Ⅲ号系统的出水TP进一步显著降低(P<0.01)。因此,研究蠕虫床耦合对A2O-MBR系统微生物菌群的影响具有重要意义。1.3. 分析测试方法
为了研究系统长期运行对菌群的影响,在3组系统稳定运行120 d时,对菌群进行取样分析。由于各系统中A2O-MBR的厌氧池、缺氧池和好氧池相互连通,污泥在几个池体中循环,因此,为了充分反映各系统中菌群情况,按照A2O-MBR中厌氧池、缺氧池、好氧池的体积比例,分别取厌氧池、缺氧池、好氧池污泥样品10、20、40 mL,经过滤网过滤,去除大颗粒杂质后,将所取样品分别混合均匀,形成3个污泥样品,于?20 ℃保存,并在1周内送样给北京诺和致源测序公司进行测序分析。本研究样品测序以Illumina技术平台为基础,采用双末端测序(Paired-End)方法,采用的引物为515F和907R,引物序列(5′~3′)分别为GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA和CCGTCAATTCCTTTGAGTTT。根据3组污泥样品扩增的结果,根据16S rRNA基因的V4~V5区进行建库,完成建库后,利用HiSeq测序平台测序。
运用软件Microbial-XDF,对产生的测序数据进行数据分析,其中包括数据质控模块Microbial-XDF-QC、操作分类单元(OTU)分析模块Microbial-XDF-OUT、物种注释模块Microbial-XDF-Profiling、样品内微生物多样性评估模块Microbial-XDF-Alpha Diversity、样品间微生物多样性评估模块Microbial-XDF-PCoA和Microbial-XDF-Clustering。
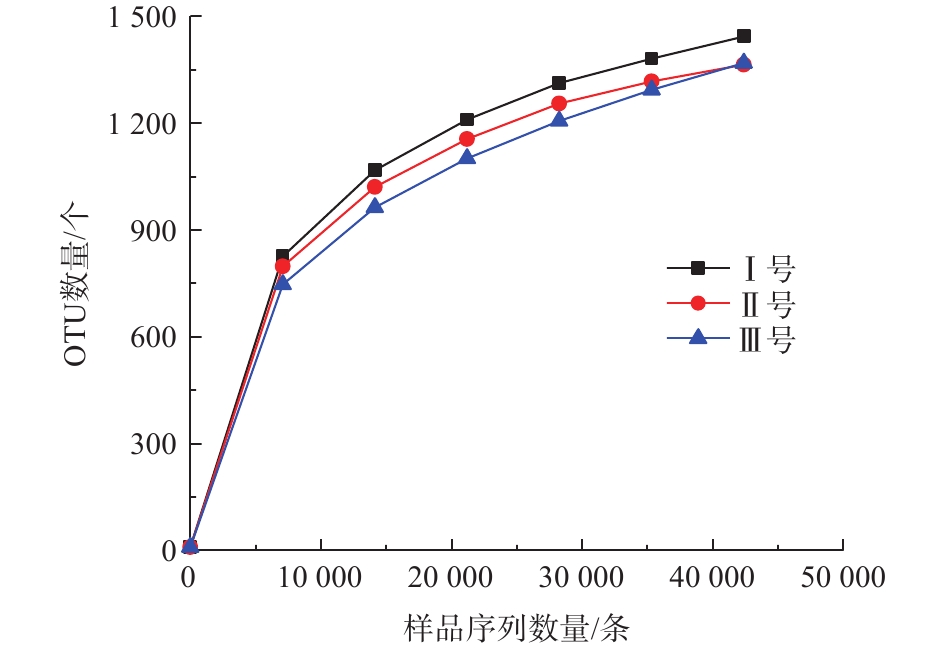
2.1. 微生物种群丰度及多样性分析
根据高通量测序结果,经序列过滤分析后的数据如表2所示。其中3组反应器最终用于分析的优质序列约180 211条,平均长度为372 bp,优质率约85%,能较好反映3组反应器污泥样品的微生物信息。同时,在97%的相似度下,将可用的优质序列聚类为用于物种标记和分类的OTU条段。3组反应器污泥样品OUT数量逐渐趋于平坦(图3),表明取样基本可反映3组污泥样品的微生物种群信息。最终3组样品产生的OTU分别为1 443、1 364、1 368个。然而Ⅲ号的Chao1和ACE指数分别为2 649和1 839,大于Ⅰ号(1 758,1 686)和Ⅱ号(1 459,1 523),表明Ⅲ号微生物群落的丰富性最高[11],且Ⅲ号中存在大量低丰度的物种。Shannon指数和Simpson指数反映的是微生物群落的多样性[12],是衡量物种丰富度与均匀性的综合指标。3组反应器的2种指数排序均为Ⅲ<Ⅰ<Ⅱ,由于Ⅱ号具有最低的物种丰富度,但多样性最大,表明Ⅱ号系统中微生物的均匀性很高。Ⅲ号丰富度最高但多样性最低,表明不同物种的丰度差异较大,即优势菌得到富集,劣势菌丰度不断降低。
实验选用的实际生活污水具有复杂的营养成分及难降解有机物,可使3组反应器内异养菌种类大幅增长[13]。在Ⅲ号反应器中,微氧-好氧交替环境能富集某些兼性菌;且蠕虫对污泥的捕食作用加速释放污泥中有机物,营造相对的富营养环境,使微生物种群的优势菌群得到富集,同时蠕虫的捕食作用可能进一步影响微生物的菌群结构[14-15]。
2.2. 微生物差异性分析
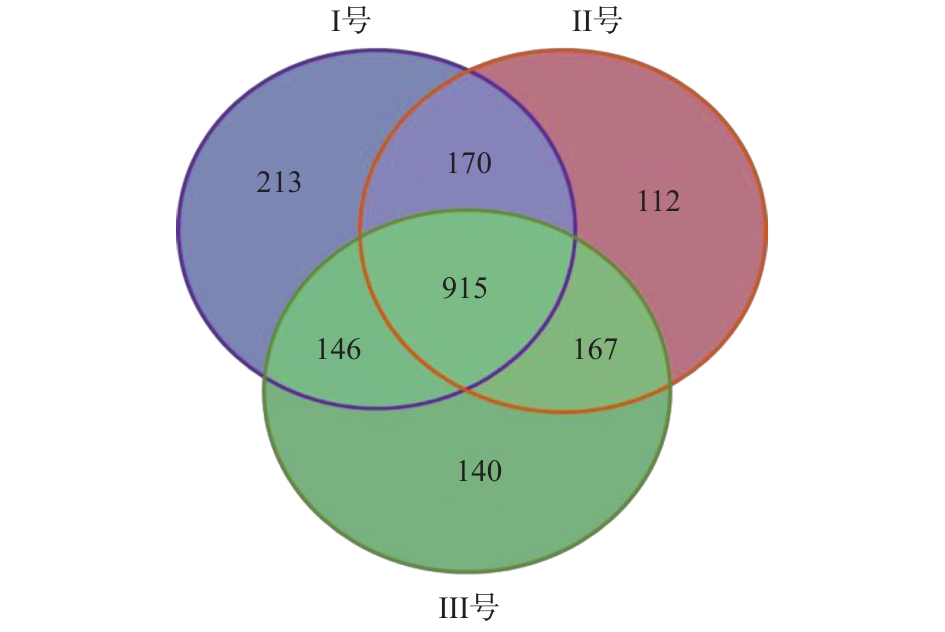
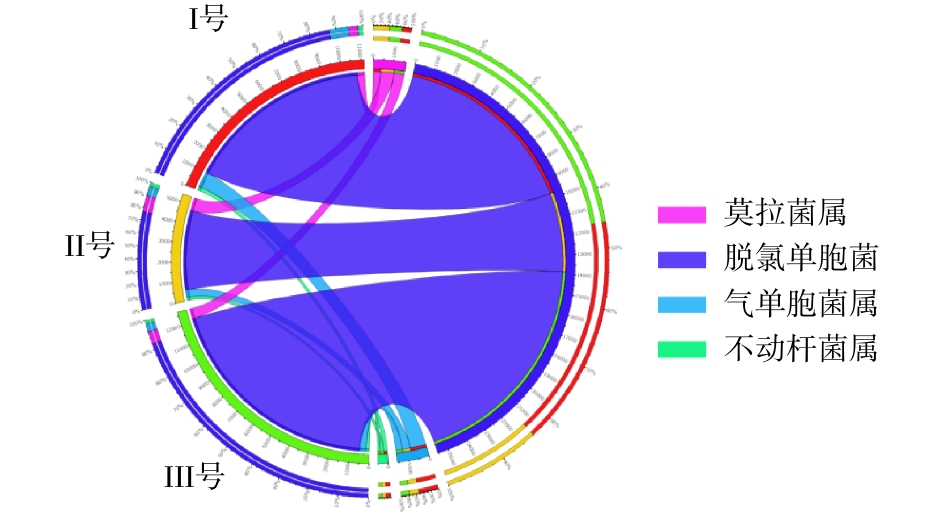
由于3组系统具有不同的运行条件,Ⅱ号和Ⅲ号分别耦合了空白床和蠕虫床,使得系统内微生物种类及丰度得到改变,OTU具有较大差异(图4)。从门、属水平分析3组污泥样品总细菌相对丰度,分布最广微生物依次为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)、浮霉菌门(Planctomycetes)[16],三者丰度之和分别占各组微生物的83%、80%及85%。其中变形菌门包含多种固氮的细菌,3组系统中变形菌门细菌含量分别为63%、52%和64%。拟杆菌门细菌主要存在于人或动物的肠道内,由于进水使用实际的生活污水,因此,污泥样品中含有大量的拟杆菌门细菌[17]。浮霉菌门细菌是一门水生细菌,包含多种专性好氧菌,同时也含有一些关系较远的厌氧氨氧化菌,其含量与系统脱氮能力有关。在属水平的相对丰度分布中,3组样品中可能的脱氮功能菌(亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)、浮霉状菌属(Planctomyces)等)[18]总含量分别为5.2%、4.6%、3.4%。可能的除磷功能菌(脱氯单胞菌(Dechloromonas)、聚磷菌(Candidatus Accumulibacter))[19]总含量分别为16.6%、12.0%、19.2%。Ⅲ号污泥中属水平含量超过5%的细菌分别为脱氯单胞菌(11.7%)、聚磷菌(7.5%)、聚糖菌(Candidatus Competibacter)(7.1%)。其中脱氯单胞菌、聚磷菌等脱氮除磷功能菌[20-21]含量为3组反应器中最高,可有效提高污水除磷效能。
2.3. 脱氮功能菌分析
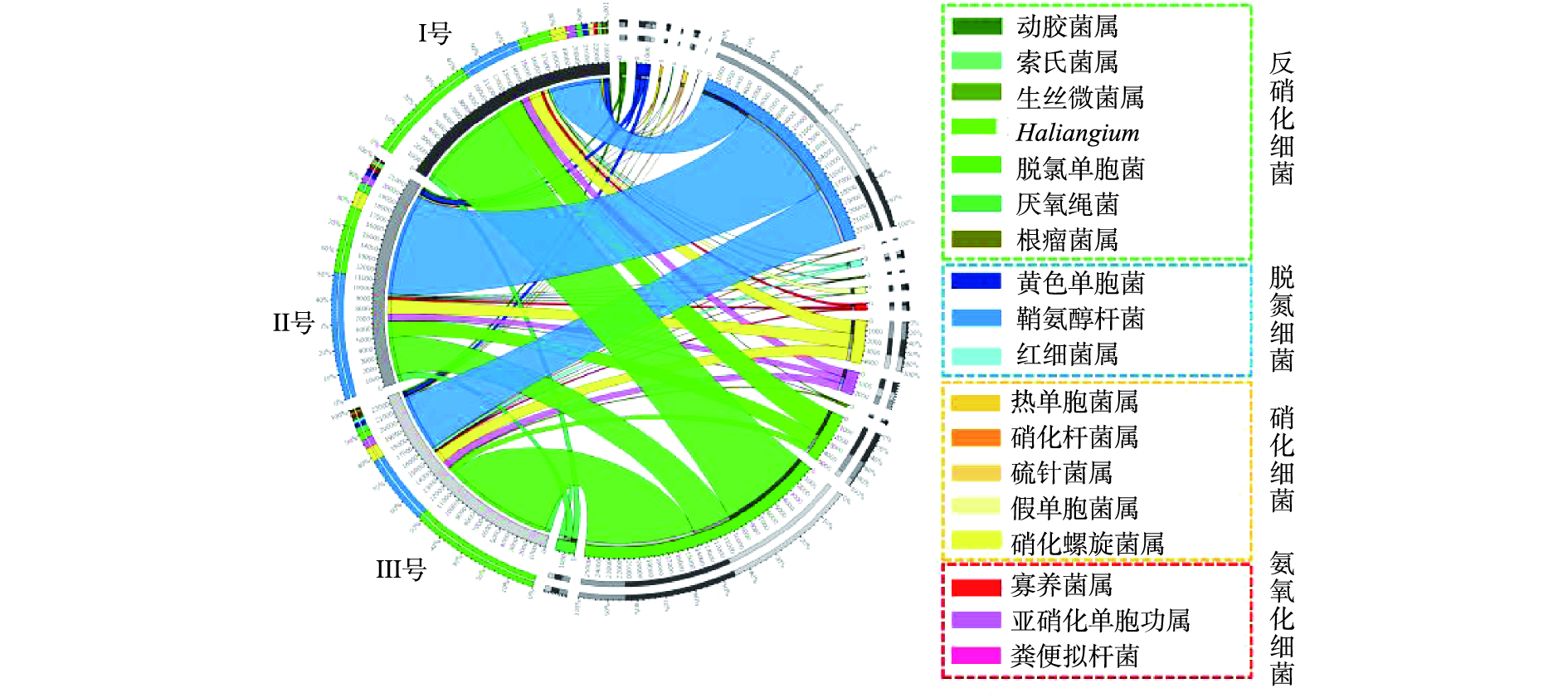
进一步分析3组系统中脱氮功能菌的分布情况(图5)。系统中厌氧氨氧化细菌(AOB)与硝化细菌(NOB)种类较多,说明3组系统中脱氮菌群落结构较为丰富[22]。亚硝化单胞菌属是典型的氨氧化细菌[23],主要发生氨氧化作用,在3组样品中比例分别为0.84%、0.71%和0.79%,硝化细菌在3组样品中分别占2.24%、1.97%和1.60%,由于含量差别不大,3组系统表现出相似的氨氮去除效能。同时一些以硫杆菌属(Thiobacillus)、副球菌属(Paracoccus)为代表的菌属还可以发生自养反硝化作用[24],但此类微生物含量在3组样品中均低于1×10?5,表明反应器中自养反硝化细菌的种类和数量都较少,反硝化细菌以异养型为主[25]。3组系统中反硝化细菌的含量分别约为13.07%、7.03%和13.35%,Ⅲ号可能具有最强的反硝化能力[26]。脱氮功能菌在3组样品中总含量分别为6.19%、11.80%和6.80%,其中红杆菌属(Rhodobacter)、生丝微菌属(Hyphomicrobium)为典型的好氧细菌[27],同时又具备反硝化能力[28],在3组样品中比例分别为0.29%、0.21%和0.45%,说明Ⅲ号反应器好氧池中更可能发生短程硝化反硝化。
2.4. 除磷功能菌分析
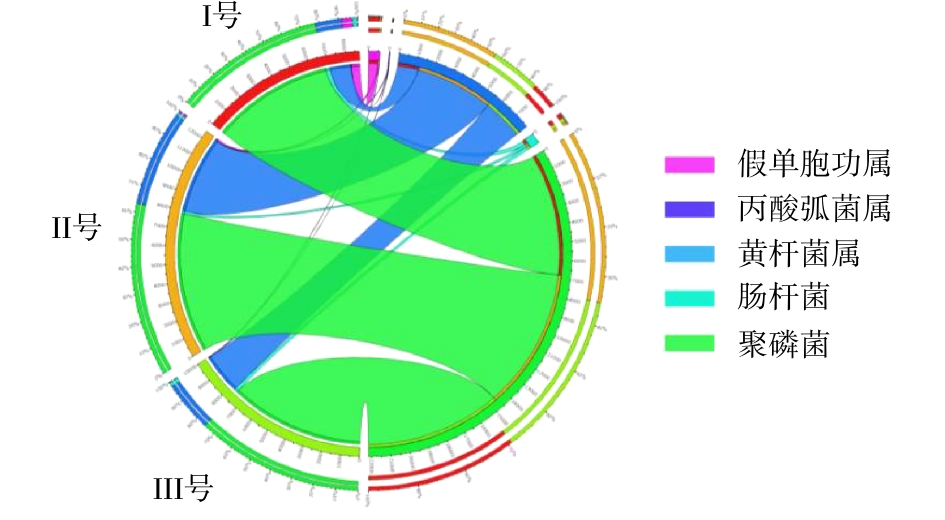
除磷功能菌主要包括好氧除磷菌(PAOs)和反硝化除磷菌(DNPAOs)[29-30]。本研究将可能具有除磷功能的菌属按PAOs和DNPAOs进行分类分析。PAOs在3组样品中的总含量分别为8.74%、12.43%和10.04%(图6),表明Ⅱ号和Ⅲ号系统中好氧除磷功能均得到了强化,且Ⅱ号系统具有最强的好氧除磷潜能。3组反应器中DNPAOs的总量分别为11.16%、5.39%和12.71%(图7)。由于蠕虫床的筛选作用,使得Ⅲ号污泥中含有较丰富的DNPAOs,表现出较强的缺氧反硝化吸磷能力。3组样品中PAOs与DNPAOs的总含量分别为19.90%、17.82%与22.75%。Ⅰ号和Ⅲ号系统中DNPAOs相对PAOs具有丰度优势,且Ⅲ号系统中,PAOs和DNPAOs均得到了富集。Ⅱ号系统中DNPAOs总量的下降与Ⅱ号系统污泥在空白蠕虫床的停留有关,DNPAOs菌的存在至少须满足存在硝态氮、磷酸盐和缺氧环境等条件。在蠕虫床中,由于蠕虫捕食导致污泥中营养物释放的原因,硝态氮和磷酸盐浓度高于空白蠕虫床[31],且蠕虫床间歇曝气的控制方式提供了缺氧环境,使得反硝化除磷作用在蠕虫床中得到强化,因此,DNPAOs菌在Ⅲ号系统中得到了强化。而空白蠕虫床不能提供反硝化除磷的必要条件,同时污泥在空白蠕虫床这个微好氧与间歇好氧环境中的停留能强化传统除磷菌,导致Ⅱ号系统中PAOs菌群得到强化而DNPAOs菌群减少,使得PAOs菌占除磷主导作用。因此,Ⅲ号系统除磷功能菌的强化不仅来自污泥在蠕虫床微氧-好氧交替环境中的停留,更与蠕虫捕食作用及捕食后导致的蠕虫床环境的改变有关。
2)A2O-MBR-蠕虫床耦合系统中好氧反硝化菌得到强化,丰富了脱氮途径,耦合系统中反硝化菌丰度增加,提高脱氮能力。
3)A2O-MBR-蠕虫床耦合系统中好氧除磷菌和反硝化除磷菌均得到了富集,且反硝化除磷菌的丰度达到了12.71%,有效提高了系统除磷效能。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 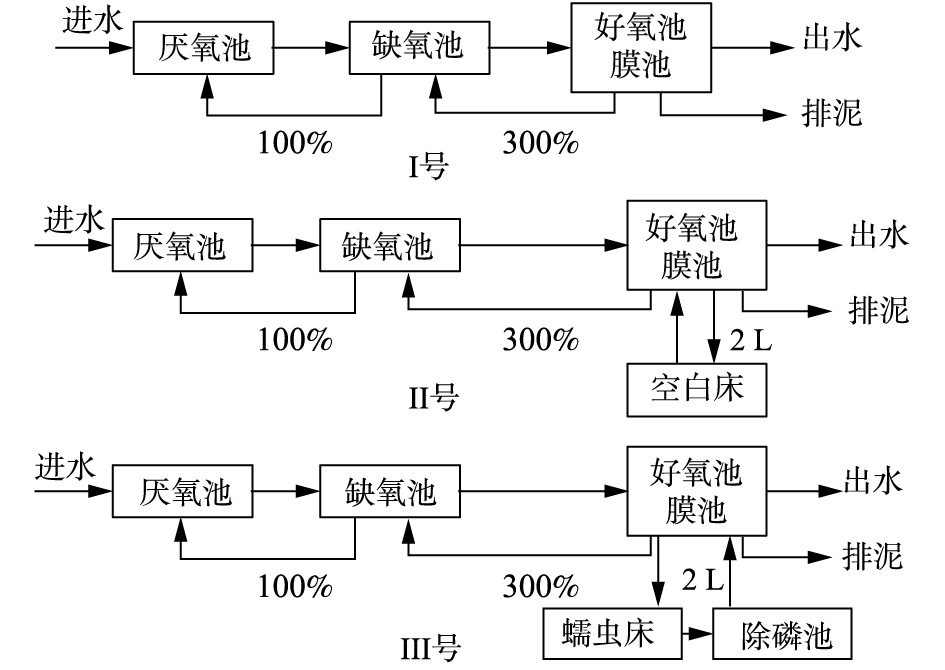
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图